- DL manuals
- D-Link
- Switch
- DES-2108
- User Manual
D-Link DES-2108 User Manual
Summary of DES-2108
Page 1
Des-2108 8-port 10/100 fast ethernet switch user’s guide.
Page 2: Fcc Warning
Fcc warning this equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class a digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This ...
Page 3: Able of
I t able of c ontents about this guide ................................................................................ 1 terms ........................................................................................... 1 overview of this user’s guide ...................................................
Page 4
Ii 10/100m fast ethernet ports status leds ................................ 12 introduction to switch management ................................................ 15 management options ................................................................. 15 web management utility............................
Page 5
Iii static mac ........................................................................ 40 igmp snooping setting..................................................... 42 storm control..................................................................... 43 device status ..................................
Page 6
Iv spanning tree commands ................................................. 84 snmp commands ............................................................. 90 igmp snooping commands .............................................. 97 static mac commands ....................................................
Page 7: Bout
1 a bout t his g uide this user’s guide tells you how to install your des-2108, how to connect it to your network. Terms for simplicity, this documentation uses the terms “switch” (first letter upper case) to refer to the des-2108, and “switch” (first letter lower case) to refer to all ethernet swit...
Page 8: Ntroduction
2 i ntroduction this section describes the features of the des-2108, as well as giving some background information about fast ethernet and switching technology. Fast ethernet technology the growing importance of lans and the increasing complexity of desktop computing applications are fueling the nee...
Page 9: Switch Description
3 that needs to go from one segment to another (from one port to another) is automatically forwarded by the switch, without interfering with any other segments (ports). This allows the total network capacity to be multiplied, while still maintaining the same network cabling and adapter cards. For fa...
Page 10: Features
4 applications without creating bottlenecks. The built-in light- management engine can be configure the switch's settings for priority queuing, vlans, and port monitoring, and port speed. Features the des-2108 was designed for easy installation and high performance in an environment where traffic on...
Page 11: Ports
5 supports a packet buffer of up to 256 kbytes. Igmp snooping support. Snmp support. Port mirror support. Mib support for: rfc1213 mib ii. Private mib. Provides parallel led display for port status such as link/act, speed, etc. Ports eight (8) 10/100mbps 100base-tx (auto mdi-x/mdi-ii) ports for conn...
Page 12: Npacking And
6 u npacking and s etup this chapter provides unpacking and setup information for the switch. Unpacking open the shipping carton of the switch and carefully unpack its contents. The carton should contain the following items: one des-2108 fast ethernet switch four rubber feet with adhesive backing on...
Page 13
Install the switch in a fairly cool and dry place for the acceptable temperature and humidity operating ranges. Install the switch in a site free from strong electromagnetic field generators (such as motors), vibration, dust, and direct exposure to sunlight. When installing the switch on a level sur...
Page 14
Installing the switch on a rack the switch can be mounted in a standard 19" rack. Use the following diagrams to guide you. Figure 2. Fasten mounting brackets to switch fasten the mounting brackets to the switch using the screws provided. With the brackets attached securely, you can mount the switch ...
Page 15: Power On
9 power on the des-2108 can be used with ac power sources 100 - 240 vac, 50 - 60 hz. The switch’s power supply will adjust to the local power source automatically. Plug one end of the ac power cord into the power connector of the switch and the other end into the local power source outlet. After the...
Page 16: Dentifying
I dentifying e xternal c omponents this chapter describes the front panel, rear panel and led indicators of the switch front panel components the front panel of the switch consists of eight (8) 10/100mbps fast ethernet ports, led indicators and reset button. Figure 4. Front panel view rj-45: eight 1...
Page 17: Rear Panel
Rear panel the rear panel of the switch contains an ac power connector. Figure 5. Rear panel view the ac power connector is a standard three-pronged connector that supports the power cord. Plug-in the female connector of the provided power cord into this socket, and the male side of the cord into a ...
Page 18: Power and Cpu Leds
12 power and cpu leds power on : this led will light green after the switch is powered on to indicate the ready state of the device. Off : when the switch powered off or the power cord has improper connection. Cpu blinking : when the cpu is working, the cpu led is blinking. On/off : the cpu is not w...
Page 19: Ntroduction
15 i ntroduction t o s witch m anagement management options web management utility web-based management interface command line interface (cli) snmp-based management managing management options this system may be managed in-band using tcp/ip telnet protocol and web-based management, accessible throug...
Page 20: Command Line Interface (Cli)
16 command line interface (cli) the switch supports a command line interface (cli) that allows the user to connect to the switch’s management agent using the tcp/ip telnet protocol. Snmp-based management you can manage the switch with an snmp-compatible console program. The switch supports snmp vers...
Page 21: Onfiguration
17 c onfiguration t he s witch through the web browser, telnet and snmp you can configure the switch such as port setting, vlan, qos, snmp, spanning tree… etc. Web management utility with the attached web management utility, you can easily discover all the web management switch, assign the ip addres...
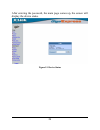
Page 22
Figure 7. Web management utility the web management utility was divided into four parts, discovery list, monitor list, device setting and toolbar function, for details instruction, follow the below section. 18.
Page 23: Discovery List
Discovery list this is the list where you can discover all the web management devices in the entire network. By pressing the “discovery” button, you can list all the web management devices in the discovery list. Double click or press the “add to monitor list” button to select a device from the disco...
Page 24: View Trap:
System name: shows the appointed device system name. Location: shows where the device is located. Trap ip: shows the ip where the trap to be sent. Subnet mask: shows the subnet mask set of the device. Gateway: shows the gateway set of the device. View trap: the trap function can receive the events t...
Page 25: Add Item:
Note: in order to receive trap information, switch has to be configured with trap ip and trap events in web browser, which are available in the trap setting menu (see page 47 for detail). Add item: to add a device to the monitor list manually, enter the ip address of the device that you want to moni...
Page 26: Password Change:
Figure 10. Configuration setting password change: you can use this password change when you need to change the password, fill in the password needed in the dialog box and press “set” button to precede the password change immediately. Figure 11. Password change firmware upgrade: when the device has a...
Page 27: Toolbar
23 toolbar the toolbar in the web management utility have four main tabs, file, view, options and help. File tab: in the “file tab”, there are monitor save, monitor save as, monitor load and exit: monitor save: to record the setting of the monitor list to the default, when you open the web managemen...
Page 28
24 configuring the switch using web browser all software functions of the des-2108 can be managed, configured and monitored via the embedded web-based (html) interface. The switch can be managed from remote stations anywhere on the network through a standard browser such as netscape navigator or mic...
Page 29: Login to Web Manager
Login to web manager before you configure this device, note that when the web smart switch is configured through an ethernet connection, make sure the manager pc must be set on same the ip network. For example, when the default ip address of the web smart switch is 192.168.0.1, then the manager pc s...
Page 30
After entering the password, the main page comes up, the screen will display the device status. Figure 15. Device status 26.
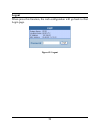
Page 31: Setup Menu
Setup menu when the main page appears, find the setup menu in the left side of the screen (figure 16). Click on the setup item that you want to configure. There are fifteen options: port settings, vlan settings, mirror setting, spanning tree settings, snmp settings, static mac settings, igmp snoopin...
Page 32: Configuring Setup Setting
Configuring setup setting find that there are four items, including port settings, vlan settings, mirror settings, spanning tree, snmp, static mac and igmp snooping in setup menu. Port settings in port settings menu (figure 17), this page will show each port’s status, press the id parameter to set e...
Page 33: Speed:
29 speed: this setting has six modes -- 100m full, 100m half, 10m full, 10m half, auto and disable for speed or port disable selections. Flow control: this setting determines whether or not the switch will be handling flow control. Set flow controlto enable for avoiding data transfer overflow. Or it...
Page 34: Port-Based Vlan:
Port-based vlan: to add a vlan group, press “add group” button, the new vlan configuration window will pop out, you can fill in the description in order to describe this vlan group, check on the port to be a member to this vlan group, and press “apply” button to execute the setting. Figure 19. Vlan ...
Page 35: Ieee 802.1Q Vlan:
Ieee 802.1q vlan: vid table setting: select the vid group that you set. When you select vid table setting, press “add new vid” to create new vid group, from port 01 ~ port 48, select untag port, tag port or not member for each port. To save the vid group, press “apply” button. To remove the selected...
Page 36: Mirror Setting
Figure 24. Mirror setting port mirroring is a method of monitoring network traffic that forwards a copy of each incoming and/or outgoing packet from one port of a network switch to another port where the packet can be studied. It enables the manager to keep close track of switch performance and alte...
Page 37: Spanning Tree Setting
Figure 25. Mirror setting spanning tree setting this switch supports the 802.1d spanning tree protocol. Every segment will have a single path to the root bridge. All bridges listen for bpdu packets. However, bpdu packets are sent more frequently - with every hello packet. Bpdu packets are sent even ...
Page 38
34 stp function: to selecting enable or disable stp function on the switch. Bridge priority: this value between 0 and 65535 to specify the priority for forwarding packets. The lower the value, the higher the priority. The default is 32768. Bridge max age: this value may be set to ensure that old inf...
Page 39: Snmp Setting
35 snmp setting simple network management protocol (snmp) is an osi layer 7 (application layer) designed specifically for managing and monitoring network devices. Snmp enables network management stations to read and modify the settings of gateways, routers, switches, and other network devices. Use s...
Page 40: Traps
Traps traps are messages that alert network personnel of events that occur on the switch. The events can be as serious as a reboot (someone accidentally turned off the switch), or less serious like a port status change. The switch generates traps and sends them to the trap recipient (or network mana...
Page 41
Add group: to add a snmp community group, press “add group” button, the add snmp community configuration window will pop out; fill in the community name and assign the community enable read_only or read_write. Press “apply” button to execute the setting. Figure 28. Add snmp community group delete gr...
Page 42: Configure Snmp Trap:
Modify group: to modify previously defined snmp community group, click on the id parameter to enter to the selected snmp community group to configure its community name and community enable. Press “apply” to save change of the snmp community group. Figure 30. Modify snmp community group configure sn...
Page 43
Add trap: to create a recipient of snmp traps generated by the switch’s snmp agent, press “add trap” button, and the snmp trap set window will pop out; you can fill in the community name and trap ip address of the remote management station that will serve as the snmp host for the switch and checked ...
Page 44: Static Mac
Modify trap: to modify previously defined snmp trap, click on the id parameter to enter to the selected snmp trap to configure its community name, ip address and events. Press “apply” to save change of the snmp trap. Figure 34. Modify snmp trap static mac the static mac function allows you to enable...
Page 45
Disable auto learning excluding uplink port: when enable the static mac function, the switch’s auto learning function will be disable, check the dialog box of the “disable auto learning excluding uplink port” and then check the dialog box of port numbers to enable the auto learning function of the p...
Page 46: Igmp Snooping Setting
Figure 37. Delete static mac igmp snooping setting igmp snooping allows the switch to read the multicast group ip address and the corresponding mac address from igmp packets that pass through the switch. The number of igmp reports that were snooped is displayed in the reports field. Figure 38. Igmp ...
Page 47: Storm Control
Host timeout (1-16711450): specifies the maximum amount of time a host can be a member of a multicast group without the switch receiving a host membership report. The default is 260 seconds. Router timeout (1-16711450): specifies the maximum amount of time a route can be a member of a multicast grou...
Page 48: Device Status
Device status click on the “status” to present the device status on this screen, it will show the system status, port status, vlan setting, mirror setting, spanning tree status, snmp setting and igmp setting. Figure 40. Device status. Press “refresh” when you need to renew the posted information. 44.
Page 49: Statistic
Statistic the statistic menu screen will show the status of each port packet count. Figure 41. Device statistics for detail packet information, click on the id parameter as figure 42. Figure 42. Port statistics 45.
Page 50: System Setting
System setting the system setting includes the system name, location name, login timeout, ip address, subnet mask and gateway. Through the web management utility, you can easily recognize the device by using the system name and the location name. The login timeout is to set the idle time-out for sec...
Page 51: Trap Setting
Trap setting the trap setting enables the device to monitor the trap through the web management utility, set the trap ip address of the manager where the trap to be sent. Figure 44. Trap setting system events: monitoring the system’s trap. Device bootup: a trap when booting up the system. Illegal lo...
Page 52: Set Password
Set password password is the invaluable tool for the manager to secure web management switch, use this function to change the password. If you forget the password, press the “reset” button in the rear panel of the switch, the current setting includes vlan, port setting… etc. Will be lost and the swi...
Page 53: Be Erased.
Note: when restoring a recorded file, the current password will not be erased. Reset setting the factory reset button helps you to reset the device back to the default setting from the factory. Be aware that the entire configuration will be reset, the ip address of the device will be get from dhcp s...
Page 54: Logout
Logout when press this function, the web configuration will go back to first login page. Figure 49. Logout 50
Page 55: Ip Address of The Switch
Configuring the switch using the cli the switch can be managed through the tcp/ip telnet protocol. The command line interface (cli) can be used to configure and manage the switch via tcp/ip telnet protocol. This section provides a reference for all of the commands contained in the cli. Ip address of...
Page 56: Telnet Ip-Address
Using the cli via telnet interface to configure the switch through the tcp/ip telnet protocol, using an ordinary telnet client program. On many systems to invoke a telnet client is: telnet ip-address where ip-address is the ip address you have assigned to the switch. When you telnet to the switch, i...
Page 57: Command Syntax
53 command syntax the following symbols are used to describe how command entries are made and values and arguments are specified in this manual. The online help contained in the cli and available through console interface uses the same syntax. Note: all commands are case sensitive. Be sure to disabl...
Page 59: Basic Switch Commands
55 basic switch commands the basic switch commands in the command line interface (cli) are listed (along with the appropriate parameters) in the following table. Command parameters show switch config snmp system_contact config snmp system_name config snmp system_location config snmp aging_time reset...
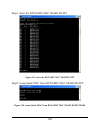
Page 60: Config Snmp System_Contact
Example usage: to display the switch’s information: figure 53. Show switch command config snmp system_contact purpose used to enter the name of a contact person who is responsible for the switch. Syntax config snmp system_contact description the config snmp system_contact command is used to enter th...
Page 61: Config Snmp System_Name
Example usage: to configure the switch contact to “eddy_chou”: figure 54. Config snmp system_contact command config snmp system_name purpose used to configure the name for the switch. Syntax config snmp system_name description the config snmp system_name command configures the name of the switch. Pa...
Page 62: Config Snmp System_Location
Config snmp system_location purpose used to enter a description of location of the switch. Syntax config snmp system_location description the command is used to enter a description of the location of the switch. Parameters - a maximum of 20 character can be used, space character is not allowed. Exam...
Page 63: Config Snmp Aging_Time
59 config snmp aging_time purpose used to set the aging time of the forwarding database. Syntax config snmp system aging_time 1048575 sec> description the aging time affects the learning process of the switch. Dynamic forwarding table entries, which are made up of the source mac addresses and their ...
Page 64: Reset
Example usage: to set the aging time: figure 57. Config snmp aging_time command reset purpose used to reset the switch to the factory default setting syntax reset description the command is used to restore the switch’s configuration to the default setting assigned from the factory. Parameters config...
Page 65: Logout
Logout purpose used to log out a user from the switch’s console. Syntax logout description this command terminates the current session on the switch’s console. Parameters none. Example usage: to terminate the current telnet console session: figure 59. Logout command save purpose used to save changes...
Page 66: Basic Ip Commands
Example usage: to save the switch’s current configuration to non-volatile ram: figure 60. Save command basic ip commands the basic ip commands in the command line interface (cli) are listed (along with the appropriate parameters) in the following table. Command parameters config ipif [ipaddress {gw ...
Page 68: Show Ipif
Show ipif purpose used to display the configuration of an ip interface on the switch. Syntax show ipif description this command will display the configuration of an ip interface of the switch. Parameters none. Example usage: to display ip interface settings: figure 62. Show ipif command switch port ...
Page 70: Show Ports
Example usage: to configure the speed of port 1-3 to be 100 mbps, half duplex, disable of port 4-5, qos of port 3, 4, 6 to be high priority and disable flow control of port 1, 2, 4, 6: figure 63. Config ports command show ports purpose used to display current configuration of a range of ports. Synta...
Page 75
Example usage: to add port 1, 3, 5, 6 to the “sales” vlan group: figure 69. Config vlan command, add vlan group members (port_based vlan) to delete 4 through 6 ports from the “sales” vlan group: figure 70. Config vlan command, delete vlan group members (port_based vlan) to add 1 through 3 as tagged ...
Page 76: Config Management _Vlan
To delete port 3 from the vlan tag 10: figure 72. Config vlan command, delete vlan group members (802.1q_based vlan) config management _vlan purpose used to change the management vlan in 802.1q_based vlan type on the switch. Syntax config management _vlan description this command allows you to chang...
Page 77: Enable Port_Based Vlan
73 enable port_based vlan purpose used to change the vlan type to port_based vlan type on the switch. Syntax enable port_based vlan description this command allows you to change the vlan type to port_based vlan on the switch. Parameters none. Example usage: to switched the vlan type to port_based vl...
Page 78: Enable 802.1Q_Based Vlan
74 enable 802.1q_based vlan purpose used to change the vlan type to 802.1q_based vlan on the switch. Syntax enable 802.1q_based vlan description this command allows you to change the vlan type to 802.1q_based vlan on the switch. Parameters none. Example usage: to switched the vlan type to 802.1q_bas...
Page 79: Config Pvid
Config pvid purpose used to configure the 802.1q port vlan id and priority. Syntax config pvid priority description this command allows you to configure the 802.1q port vlan id and priority. Parameters - a port or range of ports to configure to the specified pvid. - to configure the 802.1q vlan id t...
Page 81: Show Mirror
Example usage: to enable and configure the port mirror function of the switch: figure 79. Config mirror port command to disable port mirror function of the switch: figure 80. Config mirror port command, disable port mirror function show mirror purpose used to show the current mirroring configuration...
Page 82: Trap Commands
Example usage: to display port mirroring configuration: figure 81. Show mirror command trap commands the trap mirroring commands in the command line interface (cli) are listed (along with the appropriate parameters) in the following table. Command parameters config discovery trap_ip ipaddress {vid }...
Page 83: Config Discovery Trap_Ip
Each command is listed, in detail, in the following sections. Config discovery trap_ip purpose used to configure an ip address of the trap recipient of web management utility to the switch. Syntax config discovery trap_ip ipaddress {vid } description the command is configure an ip address of the tra...
Page 85
Example usage: to configure the events type of the switch: figure 83. Config discovery trap_event command 81.
Page 87: Show Discovery Trap
83 show discovery trap purpose used to show the configuration of the discovery trap on the switch. Syntax show discovery trap description the command is display the configuration of the discovery trap on the switch.. Parameters none. Example usage: to display discovery trap configuration: figure 85....
Page 89: Disable Stp
85 disable stp purpose used to disable stp on the switch. Syntax disable stp description this command allows the spanning tree protocol to be disabled on the switch. Parameters none. Example usage: to disable stp on the switch: figure 87. Disable stp command.
Page 92: Show Stp
Example usage: to configure stp with path cost 10, priority of 100 for ports 1-5: figure 89. Config stp ports command show stp purpose used to display the switch’s current stp configuration. Syntax show stp description this command displays the switch’s current stp configuration. Parameters none. Ex...
Page 93: Show Stp Ports
89 show stp ports purpose used to display the switch’s current stp group of ports configuration on the switch. Syntax show stp ports {portlist} description this command displays the stp group of configuration on the switch. Parameters - specifies a port or range of ports to be viewed. Example usage:...
Page 95: Create Snmp Community
91 each command is listed, in detail, in the following sections. Create snmp community purpose used to create an snmp community string to define the relationship between the snmp manager and an agent. The community string acts like a password to permit access to the agent on the switch. One or more ...
Page 97: Show Snmp Community
Example usage: to delete the snmp community string “admin”: figure 93. Delete snmp community command show snmp community purpose used to display snmp community strings configured on the switch. Syntax show snmp community description this command is used to display snmp community strings that are con...
Page 98: Create Snmp Host
94 create snmp host purpose used to create a recipient of snmp traps generated by the switch’s snmp agent. Syntax create snmp host {vid } trap_community description this command creates a recipient of snmp traps generated by the switch’s snmp agent parameters - the ip address of the remote managemen...
Page 99: Enable Snmp Traps
Purpose used to display the recipient of snmp traps generated by the switch’s snmp agent. Syntax show snmp host description this command is used to display the ip addresses and configuration information of remote snmp managers that are designated as recipients of snmp traps that are generated by the...
Page 100: Disable Snmp Traps
Example usage: to enable snmp trap support on the switch: figure 97. Enable snmp traps command disable snmp traps purpose used to disable snmp trap support on the switch. Syntax disable snmp traps description this command is used to disable snmp trap support on the switch. Parameters none. Example u...
Page 102: Enable Igmp Snooping
Example usage: to set up static router ports: figure 99. Config router_ports command (add static router ports) to delete static router ports: figure 100. Config router_ports command (delete static router ports) enable igmp snooping purpose used to enable igmp snooping on the switch. Syntax enable ig...
Page 103: Disable Igmp Snooping
Example usage: to enable igmp snooping on the switch: figure 101. Enable igmp snooping command disable igmp snooping purpose used to disable igmp snooping on the switch. Syntax disable igmp snooping description this command disables igmp snooping on the switch. Parameters none. Example usage: to dis...
Page 104: Show Router_Ports
100 show router_ports purpose used to display the currently configured router ports on the switch. Syntax show router_ports description this command is used to display the currently configured router ports on the switch. Parameters none. Example usage: to display the router ports: figure 103. Show r...
Page 106: Static Mac Commands
Example usage: to configure igmp snooping: figure 105. Config igmp_snooping command static mac commands the layer 2 forwarding database commands in the command line interface (cli) are listed (along with the appropriate parameters) in the following table. Command parameters enable smac disable smac ...
Page 107: Enable Smac
103 enable smac purpose used to enable static mac function on the switch. Syntax enable smac description this command allows you to enable static mac function on the switch. Parameters none. Example usage: figure 106. Enable static mac function disable smac purpose used to disable static mac functio...
Page 109: Show Smac
Show smac purpose used to display the static mac address forwarding database. Syntax show smac description this command allows you to display the static mac address forwarding database. Parameters none. Example usage: figure 110. Show static mac address forwarding database show fdb purpose used to d...
Page 110
Example usage: figure 111. Show dynamic mac address forwarding database create smac (port-based vlan) 106.
Page 112
Step1: show the dynamic mac search list figure 113. Show the dynamic mac search list step2: create static mac from dynamic mac search list: figure 114. Create static mac from dynamic mac search list id 001 108.
Page 114: Echnical
110 t echnical s pecifications general standards: ieee 802.3 10base-t ethernet ieee 802.3u 100base-tx fast ethernet ansi/ieee 802.3 auto-negotiation ieee 802.3x full duplex flow control protocol: csma/cd data transfer rate: ethernet: 10mbps (half-duplex), 20mbps (full-duplex) fast ethernet: 100mbps ...
Page 115: Physical and Environmental
111 physical and environmental ac inputs: 100-240 vac, 50-60 hz power consumption: 9 watts maximum operating temperature: 0 ~ 40 degrees celsius storage temperature: -10 ~ 70 degree celsius humidity: 10% ~ 90% rh, non-condensing dimensions: 280 mm x 180 mm x 44 mm emi: fcc class a, ce mark class a, ...
Page 116: Arranty and
W arranty and r egistration i nformation (all countries and regions excluding usa) wichtige sicherheitshinweise 1. Bitte lesen sie sich diese hinweise sorgfältig durch. 2. Heben sie diese anleitung für den spätern gebrauch auf. 3. Vor jedem reinigen ist das gerät vom stromnetz zu trennen. Vervenden ...
Page 117
13. Durch die lüftungsöffnungen dürfen niemals gegenstände oder flüssigkeiten in das gerät gelangen. Dies könnte einen brand bzw. Elektrischen schlag auslösen. 14. Öffnen sie niemals das gerät. Das gerät darf aus gründen der elektrischen sicherheit nur von authorisiertem servicepersonal geöffnet wer...
Page 118
Warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. D-link neither assumes nor authorizes any other person to assume for it any other liability in connection with the sale, installation maintenance or use of d-link's products. D-link shall not be liable under this warranty if its tes...
Page 119
This warranty applies on the condition that the product registration card is filled out and returned to a d-link office within ninety (90) days of purchase. A list of d-link offices is provided at the back of this manual, together with a copy of the registration card. If the product proves defective...
Page 120
Software: warranty service for software products may be obtained by contacting a d-link office within the applicable warranty period. A list of d-link offices is provided at the back of this manual, together with a copy of the registration card. If a registration card for the product in question has...