- DL manuals
- D-Link
- Gateway
- DG-102SH
- Manual
D-Link DG-102SH Manual - Using The Boot Menu
Summary of DG-102SH
Page 1
Manual building networks for people d-link dg-102sh voip station gateway version 1.10
Page 2: Contents
2 contents package contents ................................................................................3 introduction............................................................................................4 features and benefits .................................................................
Page 3: Package Contents
3 package contents system requirements: internet explorer version 6.0 or netscape navigator version 6.0 and above computers with windows, macintosh, or linux-based operating systems with an installed ethernet adapter contents of package: d-link dg-102sh voip station gateway ethernet cable (straight-...
Page 4: Introduction
4 introduction the d-link dg-102sh voip station gateway links traditional telephony networks to ip networks with conventional telephony devices such as analog phones or fax machines. The dg-102sh includes two loop start foreign exchange subscriber (fxs) that interfaces with normal rj-11 telephone co...
Page 5: Features and Benefits
5 features and benefits designed for versatility and performance, the dg-102sh voip gateway provides the following features: ** one 10/100 fast ethernet wan port for connecting to a call agent one analog pots interface for pstn life line two analog loop-start fxs interfaces using female rj-11 connec...
Page 6: Getting Started
6 getting started id entifying external components front panel understanding indicators before configuring your voip gateway, take a few minutes to look over this section and familiarize yourself with the front panel led indicators depicted below. Power: this led is lit when the device is receiving ...
Page 7: Getting Started
7 getting started identifying external components 10/100m: this indicator remains unlit when there is no connection, or the port is operating at 10mbps through a connection to a 10base-t device. It is lit when the port is operating at 100mbps through a con- nection to a dual-speed or 100base-tx fast...
Page 8: Getting Started
8 getting started identifying external components fast ethernet lan: a 10/100 dual-speed ethernet port fitted with an rj- 45 connector used to connect the voip gateway to a lan device (hub, switch, pc, etc.). This port accepts category 5 or higher utp cabling with an rj-45 connector. Line: rj-11 pho...
Page 9: Connecting The Network Cable
9 connecting the network cable category 3, 4 or 5 utp cable can be used to make the ethernet connection to your router. The maximum cable length between the dg-102sh and the supporting call agent is 100 meters. The cable must be straight-through (not a crossover cable) with rj-45 connectors at each ...
Page 10: Configuration
10 configuration configuring the voip gateway using a web browser on a computer connected to the device via the wan or lan ethernet connections. In the discussion below, the computer running the browser is referred to as the management station. Using a terminal or computer running terminal emulation...
Page 11: Using Web-Based Management
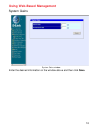
11 the categories listed on the left-side of the web-based management module include: using web-based management the dg-102sh voip gateway offers an embedded web-based (hypertext) in- terface allowing users to manage the device from anywhere on the network through a standard browser such as netscape...
Page 12: Using Web-Based Management
12 using web-based management management configure device ip address the items on this window are described below: restart settings get ip from: select the method the voip gateway will use to obtain its ip settings once it is rebooted. Choices include: manual: when manual is selected, the voip gatew...
Page 13: Using Web-Based Management
13 bootp: when bootp is selected, the voip will attempt to obtain its ip settings from a bootp server located on your lan. Dhcp: when dhcp is selected, the voip will attempt to obtain its ip settings from a dchp server located on your lan. Ip address: enter an ip address for the voip gateway. Subnet...
Page 14: Using Web-Based Management
14 device information device information window using web-based management configure h.323 the items on this window are described below: gatekeeper information mode: choose the gatekeeper mode (default is auto). Gatekeeper ip address: this ip address is necessary if you chose the manual mode defined...
Page 15: Using Web-Based Management
15 using web-based management device information click on the save button at the bottom right of the window to save the settings. Device type: this displays the model name of this device. Mac address: this displays the mac address of this device. Serial number: this displays the serial number of thi...
Page 16: Using Web-Based Management
16 using web-based management system gains enter the desired information on the window above and then click save. System gains window.
Page 17: Using Web-Based Management
17 using web-based management prefer codec table first prefer codec table window this window allows you to view the prefer codec table settings. Click the number of tcid column on the window above to access the second prefer codec table window:.
Page 18: Using Web-Based Management
18 using web-based management prefer codec table second prefer codec table window the items on this window are described below: tcid: this displays the port number of this device. (0: port1, 1: port2, 2: port3, 3: port4) prefer codec type: this is a user-defined prefer codec type for the port shown ...
Page 19: Using Web-Based Management
19 using web-based management first analog port phone no. Table window analog port (ingress calls and dialing rule settings for the gateway’s voice ports) this window allows you to view the analog port telephone no. Table settings. Click the number of tcid column on the window above to access the se...
Page 20: Using Web-Based Management
20 using web-based management the items on this window are described below: analog port second analog port telephone no. Table window tcid: this displays the port number of this device. (0: port1, 1: port2, 2: port3, 3: port4) telephone no.:this is a user-defined caller id number for the port shown ...
Page 21: Using Web-Based Management
21 process type: this is a user-defined which situation will activate call forward function. The entry is used only if the call forward is set to enable. Using web-based management analog port click on the save button at the bottom right of the screen to save the settings. Data port (egress calls an...
Page 22: Using Web-Based Management
22 using web-based management data port second data port telephone no. Table window the items on this window are described below: enter the desired information on the window above and then click save. Prefix strip telephone no.: this is a user-defined prefix strip number for outgoing calls to anothe...
Page 23: Using Web-Based Management
23 using web-based management atpm (address translation and parsing module) wizard atpm mode window the items on this window are described below: choose the analog or data mode then click next. Analog: this mode allow user to setup advanced ingress calls and dialing rule settings for the gateway’s v...
Page 24: Using Web-Based Management
24 using web-based management atpm destination table window the items on this window are described below: enter the desired information on the window above and then click next. Destination id.: this is a user-defined destination id for the port shown below. The id cannot be duplicated. Tcid: this is...
Page 25: Using Web-Based Management
25 using web-based management analog mode atpm hunt group table window the items on this window are described below: enter the desired information on the window above and then click next. Hunt group.: this is a user-defined hunt group number for the destination id shown below. Destination id.: this ...
Page 26: Using Web-Based Management
26 using web-based management analog mode atpm address table window the items on this window are described below: dial no.: this is a user-defined prefix dial number used when the user makes a call. Hg id: this displays the hunt group id set in the previous page. Min digits: this is a user-defined m...
Page 27: Using Web-Based Management
27 using web-based management atpm address table first atpm address table window this window allows you to view the atpm address table settings. Click the add or delete icon on the window above to access the second atpm address table window:.
Page 28: Using Web-Based Management
28 using web-based management atpm address table second atpm address table window enter the desired information on the window above and then click save..
Page 29: Using Web-Based Management
29 using web-based management atpm hunt group table first atpm hunt group table window this window allows you to view the atpm hunt group table settings. Click the add or delete icon on the window above to access the second atpm hunt group table window:.
Page 30: Using Web-Based Management
30 using web-based management atpm hunt group table second atpm hunt group table window enter the desired information on the window above and then click save..
Page 31: Using Web-Based Management
31 using web-based management atpm destination table first atpm destination table window this window allows you to view the atpm destination table settings. Click the add or delete icon on the window above to access the second atpm destination table window:.
Page 32: Using Web-Based Management
32 using web-based management atpm destination table second atpm destination table window enter the desired information on the window above and then click save..
Page 33: Using Web-Based Management
33 using web-based management dynamic ip assignment window enter the desired information on the window above and then click save. Dynamic ip assignment.
Page 34: Using Web-Based Management
34 using web-based management static ip assignment first static ip assignment window click on one of the four pointer icons to access and edit the second static ip assignment window:.
Page 35: Using Web-Based Management
35 using web-based management static ip assignment second static ip assignment window enter the desired information on the window above and then click save..
Page 36: Using Web-Based Management
36 using web-based management nat configuration nat configuration window after entering the desired information into the window above, enable or disable the nat function and then click save..
Page 37: Using Web-Based Management
37 using web-based management first local server configuration window this window allows you to view the current local server configuration settings. Click the edit icon on the window above to access the second local server configuration window. Local server configuration.
Page 38: Using Web-Based Management
38 using web-based management local server configuration second local server configuration window after completing the local server configuration settings on the window above, select enabled or disabled in the drop-down menu under state and then click save..
Page 39: Using Web-Based Management
39 using web-based management snmp trap configuration snmp trap configuration window the items on this window are described below: click on the save button at the bottom right of the window to save the settings. Trap manager ip address: the ip address of the trap receiving station. Community name: a...
Page 40: Using Web-Based Management
40 using web-based management administration management window to add or change a user account, fill in the appropriate information in the user name, old password (if applicable), new password, and confirm new password fields. Click on the save button to keep the settings. Administration management.
Page 41: Using Web-Based Management
41 using web-based management ethernet statistics ethernet statistics window the items on this window are described below: rx packets: the total number of packets received by the device. Rx bytes: the total number of bytes contained in packets received by the device. Rx non ucast packets: the number...
Page 42: Using Web-Based Management
42 rx collision errors: the number of collision errors. Rx short frames: the number of packets smaller than the 64-octet minimum. Rx crc errors: the number of packets received that failed the crc checksum test. Rx overrun packets: the number of packets received that exceed the 1518 octet maximum len...
Page 43: Using Web-Based Management
43 using web-based management dsp statistics dsp statistics window this window displays a variety of dsp statistics..
Page 44: Using Web-Based Management
44 using web-based management tcid configuration tcid configuration window this read-only window displays a variety of tcid configuration settings..
Page 45: Using Web-Based Management
45 using web-based management coding profile coding profile window this read-only window displays various coding profile settings..
Page 46: Using Web-Based Management
46 using web-based management firmware and configuration update firmware and configuration update window the items on this window are described below: software update mode: this specifies downloading the image file through a wan link or lan link. Tftp server address: the ip address of the tftp serve...
Page 47: Using Web-Based Management
47 using web-based management save changes window after the settings have been saved to nv-ram, they will become the default settings for the device, and they will be used every time it is powered on, reset or rebooted. The only exception to this is a factory reset, which will clear all settings and...
Page 48: Using Web-Based Management
48 using web-based management factory reset factory reset to default value window before performing a factory reset, be absolutely certain that this is what you want to do. Once the reset is complete, all of the device’s settings stored in nv- ram will be erased and restored to the values present wh...
Page 49: Using Web-Based Management
49 using web-based management restart system restart system window to perform a reboot of the device, which resets the system, click the restart button..
Page 50: Setting Up A Console
50 8 data bits (sometimes called a “word length” of 8 bits) 1 stop bit (sometimes referred to as a 1-bit stop interval) no flow control arrow keys enabled configuration using a console setting up a console first-time configuration can be carried out through a “console,” that is, either (a) a vt100-t...
Page 51: Setting Up A Console
51 configuration using a console setting up a console a typical console connection is illustrated below: example of a console connection configuring the voip gateway using telnet once you have set an ip address for your device, you can use a telnet pro- gram (in a vt-100 compatible terminal mode) to...
Page 52: Console Usage Conventions
52 the up and down arrow keys, the left and right arrow keys, the tab key, and the backspace key can be used to move between selected items. It is recommended that you use the tab key and backspace key for moving around the console. Items in uppercase are commands. Moving the selection to a com- man...
Page 53: Configuration Settings
53 configuration using a console configuration settings in order for the voip to function, you must provide the device with the following information: define where the device receives its ip settings from. Ip settings – ip address, subnet mask, and default gateway all of these settings are found in ...
Page 54: Configure Ip
54 configuration using a console configure ip bootp: use the key to select the method that the voip gate- way will use to obtain its ip settings once it is rebooted. Choices include: manual: when manual is selected, the voip gateway will obtain its ip settings from the fields located just below. Boo...
Page 55
55 the voip gateway comes with a default ip address of 10.1.10.4. You must make sure your computer is in the same subnet as the voip gateway. You can do this by changing the ip address of the computer using the screen shown below. Configuration using a console configuring the voip gateway using a we...
Page 56
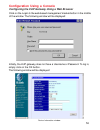
56 click on the login to the web-based management module button in the middle of the window. The following window will be displayed: configuration using a console configuring the voip gateway using a web browser initially, the voip gateway does not have a username or password. To log in, simply clic...
Page 57
57 configuration using a console configuring the voip gateway using a web browser to begin configuring the device, click on the config ip & h.323 folder on the left-hand side of the window (shown below). Next, click on config device ip address. The following window will appear: configure device ip a...
Page 58: Restart Settings
58 configuration using a console configuring the voip gateway using a web browser the items on this window are described below: restart settings get ip from: select the method the voip gateway will use to obtain its ip settings once it is rebooted. Choices include: manual: when manual is selected, t...
Page 59: Gatekeeper Information
59 configuration using a console configuring the voip gateway using a web browser the items on this window are described below: configure h.323 window gatekeeper information mode: choose the gatekeeper mode (default is auto). Gatekeeper ip address: this ip address is necessary if you chose the manua...
Page 60: Using The Boot Menu
60 using the boot menu to access the boot menu, you must first make sure the console is connected to the diagnostics port (an rs-232 port with a 9-socket d-shell connector and dce-type wiring) and the appropriate cabling for the connection is being used. Please see the previous section, “configurati...
Page 61: Using The Boot Menu
61 using the boot menu each item on the ip configuration screen is described below: boot menu—ip configuration screen configuring the ip gatekeeper mode: use the key to select the gatekeeper mode once the device is rebooted (restarted). Choices include: no gatekeeper: when no gatekeeper is selected,...
Page 62: Using The Boot Menu
62 using the boot menu after you have finished, press to save changes to ram. Next, press the key to return to the boot menu. Position the cursor over the save changes item and press . This will save the settings to nv-ram so they will still be present after powering off or restarting the device. Po...
Page 63: Using The Boot Menu
63 using the boot menu device information this screen displays various types of information about the dg-102sh as well as allowing you to enter information pertaining to name, location, and how to reach the person responsible for maintaining the device. Use the key to highlight the second menu item ...
Page 64: Using The Boot Menu
64 using the boot menu device information update firmware and configuration files new software can be downloaded from a tftp server. Use the key to highlight the third menu item on the boot menu, update firmware and configuration files, and press . The update boot and application screen will be disp...
Page 65: Using The Boot Menu
65 using the boot menu update boot and application each item on the update boot and application screen is described below: software update mode: this specifies downloading the image file through a wan link. Tftp server address: the ip address of the tftp server where the runtime or configuration fil...
Page 66: Using The Boot Menu
66 using the boot menu save changes boot menu—saving settings screen after the settings have been saved to nv-ram, they will become the default settings for the device, and they will be used every time it is powered on, reset, or rebooted. The only exception to this is a factory reset, which will cl...
Page 67: Using The Boot Menu
67 using the boot menu factory reset boot menu—factory reset screen restart system to perform a system reset, use the keys to highlight the last menu item on the boot menu, restart system, and press . The following reboot device screen will be briefly displayed: boot menu—restart system screen.
Page 68: Command Line Interface
68 command line interface the dg-102sh voip gateway offers a line-at-a-time prompt and response scheme to execute various configuration instructions. The interface displays a single prompt character ggdbg> when it is ready to accept a command (ex. Ggdbg>set or ggdbg>show). Typing a question mark aft...
Page 69: Command Line Interface
69 command line interface general setup commands nwdbg un definition: this command sets the username if there is a username string, or shows the username/password if only nwdbg un is typed. Parameter(s): characters> example: nwdbg un 123456789012 nwdbg pw definition: this command sets the password i...
Page 70: Command Line Interface
70 command line interface general setup commands nwdbg dtmf_relay definition: this command turns the dual tone multiple frequency (dtmf) relay function on or off, or shows the dtmf relay state if only nwdbg dtmf_relay is typed. Parameter(s): example: nwdbg dtmf_relay 0 nwdbg mac definition: this com...
Page 71: Command Line Interface
71 command line interface general setup commands nwdbg ip definition: this command sets the fixed ip address, which is used as the system’s ip address if the software boot mode is manual mode. If only nwdbg ip is typed, this command shows the ip configuration. Parameter(s): example: nwdbg ip 10.1.1....
Page 72: Command Line Interface
72 command line interface general setup commands nwdbg tftp definition: this command sets the software download link to either a wan link or a lan link. If only nwdbg tftp is typed, this command shows the download link. Parameter(s): example: nwdbg tftp 0 nwdbg dns definition: this command sets the ...
Page 73: Nwdbg Config
73 nwdbg config definition: this command shows all the configuration settings made by nwdbg commands. Parameter(s): none. Example: nwdbg config ping definition: this command lets the user ping an ip address from the device. Parameter(s): (type space). -n count: number of echo requests to send. -w ti...
Page 74: Command Line Interface
74 command line interface tftp client setup commands when the user enters tftp, the screen will show all commands about the tftp client: ggdbg>tftp tftp srvip – set the ip address of tftp server tftp get – get the remote image file if is not specified, the image file name in eeprom will be employed....
Page 75: Command Line Interface
75 command line interface tftp client setup commands tftp get filename> definition: gets the image from the tftp server. The is the name of the image on the tftp server. If any error occurs during the image download, the message error will be displayed. When the user enters tftp get, the file name i...
Page 76: Technical Specifications
76 technical specifications call control protocols compliance h.323 voice compression g.711 (a-law and u-law), g.723.1, g.729a analog voice ports type: loop-start fxs interfaces dtmf tone detection/generation v.21/v.25 modem/fax tone detection echo cancellation: g.165/g.168 ethernet ports wan: nway ...
Page 77: Network Management
77 network management snmp management agent base mib ii telnet provisioning manage functions through an intuitive web-based graphical user interface local management console tftp: the built–in trivial file transfer protocol provides firmware upgrade security password authentication protocol/challeng...
Page 78: Number of Ports
78 number of ports one 10/100base-tx fast ethernet port (wan) one 10/100base-tx fast ethernet port (lan) two loop-start fxs rj-11 ports one pstn pots rj-11 port for life line one rs-232c, db-9 console port power supply ac-to-dc power adapter (provided) dc input: 12vdc/1a operating temperature 0 - 50...
Page 79
79 subject to the terms and conditions set forth herein, d-link systems, inc. (“d-link”) provides this limited warranty for its product only to the person or entity that originally purchased the product from: • d-link or its authorized reseller or distributor and • products purchased and delivered w...
Page 80
80 submitting a claim: the customer shall return the product to the original purchase point based on its return policy. In case the return policy period has expired and the product is within warranty, the customer shall submit a claim to d-link as outlined below: • the customer must submit with the ...
Page 81
81 repair, replacement or refund of the defective or non-conforming product. The maximum liability of d-link under this warranty is limited to the purchase price of the product covered by the warranty. The foregoing express written warranties and remedies are exclusive and are in lieu of any other w...
Page 82: Registration
82 register online your d-link product at http://support.Dlink.Com/register/ registration.
Page 83
83 t tt ttechni echni echni echni echnical support cal support cal support cal support cal support you can find software updates and user documentation on the d-link website. D-link provides free technical support for customers within the united states and within canada for the duration of the warra...