- DL manuals
- D-Link
- Switch
- xStack DGS-3610 Series
- Configuration Manual
D-Link xStack DGS-3610 Series Configuration Manual
Summary of xStack DGS-3610 Series
Page 1
Xstack dgs-3610 series configuration guide version 10.2.
Page 2
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide revision no.: version 10.2 date: copyright statement d-link corporation. ©2008 all rights reserved. Without our written permission, this document may not be excerpted, reproduced, transmitted, or otherwise in all or in part by any party in any means..
Page 3: Preface
Preface version description this manual matches the firmware version v10.2. Target readers this manual is intended for the following readers: network engineers technical salespersons network administrators conventions in this document 1. Universal format convention arial: arial with the point size 1...
Page 4
3. Signs various striking identifiers are adopted in this manual to indicate the matters that special attention should be paid in the operation, as detailed below: caution warning, danger or alert in the operation. Note description, prompt, tip or any other necessary supplement or explanation for th...
Page 5: Contents
I contents 1 command line interface configuration .............................................................................................. 2-1 1.1 command mode ........................................................................................................................ 2-1 1.2 obtai...
Page 6
Ii 2.5.3 specifying the system to restart after a period of time ............................... 2-9 2.5.4 immediate restart .......................................................................................... 2-9 2.5.5 deleting the configured reload scheme .......................................
Page 7
Iii 4.2.1 transferring files by using the tftp protocol .............................................. 4-1 4.2.2 transferring files by using the xmodem protocol ...................................... 4-2 4.2.3 upgrade the system ..........................................................................
Page 8
Iv 8.1.2 supported vlan ............................................................................................ 8-2 8.1.3 vlan member type ....................................................................................... 8-2 8.2 configuring vlan ..............................................
Page 9
V 11.2.4 mapping layer 3 interfaces of secondary vlan and primary vlan.......... 11-4 11.2.5 configuring layer 2 interface as host port of private vlan ....................... 11-4 11.2.6 configuring layer 2 interface as promiscuous port of private vlan ......... 11-5 11.3 private vlan showing.........
Page 10
Vi 14.1.6 relationship between dhcp snooping and arp detectation.....................14-4 14.1.7 other precautions on dhcp snooping configuration .................................14-4 14.2 dhcp snooping configuration ......................................................................................
Page 11
Vii 15.2.13 configuring fast-leave ..............................................................................15-16 15.2.14 configuring igmp snooping suppression .................................................15-17 15.2.15 configuring static members of igmp snooping ...............................
Page 12
Viii 17.3.5 configuring port priority .............................................................................17-21 17.3.6 configuring path cost of the port ..............................................................17-22 17.3.7 configuring default calculation method of path cost (path cost ...
Page 13
Ix 19 ip address and service configuration .............................................................................................. 19-1 19.1 ip addressing configuration ....................................................................................................19-1 19.1.1 ip address o...
Page 14
X 20.7.1 address pool configuration example ........................................................20-12 20.7.2 manual binding configuration ....................................................................20-13 20.7.3 dhcp client configuration ......................................................
Page 15
Xi 23.2.3 configuring global trusted key id for the ntp ...........................................23-3 23.2.4 configuring ntp server ...............................................................................23-3 23.2.5 disabling receiving ntp packets on the interface .............................
Page 16
Xii 25.3.2 checking mib objects supported by current snmp agent ...................... 25-11 25.3.3 viewing snmp user ...................................................................................25-13 25.3.4 viewing snmp view and group .............................................................
Page 17
Xiii 28 ospf routing protocol configuration .............................................................................................. 28-1 28.1 ospf overview .......................................................................................................................28-1 28.2 ospf con...
Page 18
Xiv 29.7 configuring interaction between bgp and igp ..................................................................... 29-11 29.8 configuration timer of bgp ................................................................................................... 29-11 29.9 configuring path attribute f...
Page 19
Xv 30.3.1 selecting hash keyword ............................................................................ 30-11 30.3.2 selecting the hash algorithm .....................................................................30-12 30.3.3 configuration commands ..............................................
Page 20
Xvi 34.1.2 interface configuration .................................................................................34-3 34.1.3 router id configuration ...............................................................................34-3 34.1.4 authentication mechanism setting ...........................
Page 21
Xvii 35.6.12 enabling igmp ssm-map .........................................................................35-19 35.6.13 configuring igmp ssm-map static .......................................................35-19 35.6.14 clearingup dynamic group membership in igmp cache from response message 35-20...
Page 22
Xviii 37.2.2 precautions for configuring 802.1x .............................................................37-9 37.2.3 configuring the communication between the device and radius server 37-10 37.2.4 setting the 802.1x authentication switch .................................................. 37-11 3...
Page 23
Xix 37.5.3 disabling aaa ..............................................................................................37-4 37.5.4 subsequent configuration steps .................................................................37-4 37.6 configuring authentication .......................................
Page 24
Xx 39.4.4 disabling ssh server ..............................................................................39-2 39.4.5 configuring ssh server support version ....................................................39-3 39.4.6 configuring ssh user authentication timeout duration ..........................
Page 25
Xxi 42.7.3 configuring the minimum interval for tranmission of security events ........42-3 42.7.4 configuring the address binding switch supported by the port..................42-3 42.8 gsn configuration display ..........................................................................................
Page 26
Xxii 44.3.2 configuring mac extended access list ....................................................44-10 44.3.3 configuration of showing mac extended access lists............................. 44-11 44.3.4 mac extended access list example ......................................................... 44...
Page 27
Xxiii 45.3.2 showing policy-map ...................................................................................45-15 45.3.3 showing mls qos interface .........................................................................45-15 45.3.4 showing mls qos queueing ......................................
Page 28
Xxiv 47.2.3 configuring port rldp ................................................................................47-5 47.2.4 configuring detection vlan ...........................................................................47-6 47.2.5 configuring rldp detection interval ...........................
Page 29
Xxv 50.2.4 enabling switches in log system ................................................................50-4 50.2.5 enabling log statistics .................................................................................50-4 50.2.6 enabling the sequential number switch of log information ..........
Page 31: Command Line Interface
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 1 command line interface configuration 2-1 1 command line interface configuration this chapter describes how to use the command line interface. You can also manage the equipment using the command line interface. This chapter covers the following: command m...
Page 32
Chapter 1 command line interface configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 2-2 to enter any of the configuration modes, first enter global configuration mode. From global configuration mode, you can access any of the configuration sub-modes like interface configuration mode. The following ta...
Page 33
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 1 command line interface configuration 2-3 command mode access method prompt exit or access next mode about this mode interface configuration (interface configuration mode) input the interface command to enter to this mode in the global configuration mode:...
Page 34
Chapter 1 command line interface configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 2-4 command description command keyword ? Lists the next variable associated with the keyword. Example: dgs-3610(config)# snmp-server community ? Word snmp community string 1.3 abbreviating commands to abbreviate a co...
Page 35
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 1 command line interface configuration 2-5 error message meaning how to obtain help % ambiguous command: "show c" if you input insufficient characters, the network equipment can not identify the only command. Re-input the command and a question mark immedi...
Page 36
Chapter 1 command line interface configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 2-6 1.7.1 edit shortcut keys the following table lists the edit shortcut keys. Function shortcut key description move cursor in editing line left direction key or ctrl-b move the cursor left by one character. Right di...
Page 37
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 1 command line interface configuration 2-7 left by 20 characters, and the hidden beginning part is replaced by "$" on the screen. The line moves left by 20 characters every time the cursor reaches the right border. Mac-address-table static 00d0.F800.0c0c v...
Page 39
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 1 command line interface configuration 2-9 the alias must begin with the first character from the command line entered, and there should not be blank before it. As above example, it will not indicate the legal alias if the blank is entered before the comma...
Page 41: Management
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management 2-1 2 configuration of switch basic management 2.1 overview this chapter describes how to manage our switches: access control by command authorization logon authentication control system time configuration schedul...
Page 42
Chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management dgs-3610 series configuration guide 2-2 password is encrypted before stored into the configuration file, and the clear text password is changed to the encrypted text password. The enable secret command uses a private encryption algorithm. 2.2.2 defa...
Page 43
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management 2-3 each mode. By configuring passwords for different levels, you can allow different authorized levels to use different commands aggregate. When no password is set for the privileged user level, no password is ve...
Page 44
Chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management dgs-3610 series configuration guide 2-4 dgs-3610(config)# enable secret level 1 0 test dgs-3610(config)# end enter the level 1, you can see the command and its subcommand: dgs-3610# disable 1 dgs-3610> reload ? At reload at a specific time/date canc...
Page 45
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management 2-5 command purpose dgs-3610(config-line)# lockable enable the function for locking the line terminal dgs-3610# lock lock the current line terminal 2.3 logon authentication control 2.3.1 overview in the previous s...
Page 46
Chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management dgs-3610 series configuration guide 2-6 2.3.3 configuring line logon authentication to establish the line logon identity authentication, run the following specific commands in the line configuration mode: command function dgs-3610(config-line)# logi...
Page 47
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management 2-7 command function dgs-3610# clock set hh:mm:ss month day year setting the time and date of the system for example to change the system time to 2003-6-20, 10:10:12- dgs-3610# clock set 10:10:12 6 20 2003 //set t...
Page 48
Chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management dgs-3610 series configuration guide 2-8 will fail because the default date will be in the january in this year when the year is not specified. The usage of string is just like above. For example, if the current system time is 14:31 on january 10, 20...
Page 49
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management 2-9 2.5.3 specifying the system to restart after a period of time in the privileged mode, you can configure the system reload in the specified time with the following commands: command function dgs-3610# reload in...
Page 50
Chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management dgs-3610 series configuration guide 2-10 be the default command prompt (if the system name exceeded to more than 32 characters, the first 32 characters will be intercepted and taked as the system prompt). The prompt will be changed with the system n...
Page 51
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management 2-11 banner: a message-of-the-day (motd) and a login banner. The motd is used for all users who connect to the network devices. When users log in the network devices, the notification message will be displayed in ...
Page 52
Chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management dgs-3610 series configuration guide 2-12 command function dgs-3610(config)# banner login c message c set the text of login banner. C denotes for the delimiter, it can be any characters of your choice (for example, a pound sign ‗&‘ etc.). After input...
Page 53
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management 2-13 2.8.2 viewing system information and version system information consists of system description, system power-on time, hardware version of the system , software version of the system , the software version of ...
Page 54
Chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management dgs-3610 series configuration guide 2-14 command function dgs-3610(config-line)# speed speed set the console transmission rate, in bps. For the serial interface, you can only set the transmission rate as one of 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600 and 115200. ...
Page 55
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management 2-15 figure 2-1 2.10.2 using telnet client you can log in to a remote devices by using the telnet command on the network device: command function dgs-3610# telnet host-ip-address by using this command telnet to lo...
Page 56
Chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management dgs-3610 series configuration guide 2-16 the timeout setting in the line can be cancelled by using the no exec-timeout command in the line configuration mode. Dgs-3610# configure terminal //enter the global configuration mode. Dgs-3610# line vty 0 /...
Page 57
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 2 configuration of switch basic management 2-17 running result: dgs-3610# execute flash:line_rcms_script.Text executing script file line_rcms_script.Text ...... Executing done dgs-3610# configure terminal enter configuration commands, one per line. End wit...
Page 59: Line Mode Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 3 line mode configuration 3-1 3 line mode configuration 3.1 overview this chapter describes some operations on line: enter the line mode increase/decrease line vty quantity configure the allowed communication protocol in line 3.2 line mode configuration 3....
Page 60
Chapter 3 line mode configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 3-2 3.2.3 configure the allowed communication protocol in line to limit the allowed communication protocol type in the line, this command can be used for the configuration. By default, the vty type allows the communication of all ...
Page 61: Configuration Of System
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 4 configuration of system upgrade and maintenance 4-1 4 configuration of system upgrade and maintenance 4.1 overview the upgrade and maintenance of the system are the process to upgrade or upload/download files via the main program or ctrl program on the c...
Page 62
Chapter 4 configuration of system upgrade and maintenance dgs-3610 series configuration guide 4-2 before uploading, firstly start the tftp server software at the local host. Then, select the destination directory for the file to upload at the host. Finally, upload the files by using the following co...
Page 63
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 4 configuration of system upgrade and maintenance 4-3 figure 4-2 command function dgs-3610# copy xmodem flash:filename download a file from the host to the device and name it filename. In the cli command mode, upload the files by performing the following s...
Page 64
Chapter 4 configuration of system upgrade and maintenance dgs-3610 series configuration guide 4-4 figure 4-4 command function dgs-3610# copy flash:filename xmodem upload the file filename from the device to the host. 4.2.3 upgrade the system whatever the box device or chassis device, you can use abo...
Page 65
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 4 configuration of system upgrade and maintenance 4-5 caution whenever you upgrade the master management board, the slave one (if any) is upgraded at the same time to keep the version consistent. The upgrade of a line card will upgrade all the line cards i...
Page 66
Chapter 4 configuration of system upgrade and maintenance dgs-3610 series configuration guide 4-6 system restarting, for reason 'upgrade product !'. 8) the whole system of the management boards will finish the upgrade after the system restarted. Then the upgrade file of single board for loading the ...
Page 67
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 4 configuration of system upgrade and maintenance 4-7 caution during the process of upgrading or automatically upgrading, the prompt will be displayed for not allowing the system to reset. Once the same prompt appears, please do not power off or reset the ...
Page 69: Network Communication
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 5 network communication detection tools 5-1 5 network communication detection tools 5.1 ping connectivity test for the connectivity test of networks, many network devices support the echo protocol. The protocol involves sending a special packet to a specif...
Page 70
Chapter 5 network communication detection tools dgs-3610 series configuration guide 5-2 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (100/100), round-trip min/avg/max = 2/2/3 ms dgs-3610# 5.2 traceroute connectivity...
Page 71
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 5 network communication detection tools 5-3 source address. At the same time, we know the time it takes the network packet to reach the gateway. This is very useful for network analysis. 2. Traceroute example where some gateways in a network are not connec...
Page 73: Configuring Interfaces
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 6 configuring interfaces 6-1 6 configuring interfaces 6.1 overview of interface types this chapter provides the classification of interfaces used in dgs-3610 series as well as a precise definition of each type. Interfaces on dgs-3610 series are classified ...
Page 74
Chapter 6 configuring interfaces dgs-3610 series configuration guide 6-2 tagged frame with vid 0 untagged frame access port receives frames without tags, and adds a default vlan as the tag to the frames without tags. The added tag will be removed before the frames are sent. Tagged frame the access p...
Page 75
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 6 configuring interfaces 6-3 when the trunk port receives a frame with a tag where the vid is different from the native vlan of this trunk port, but vid is the vlan id that the port allows, the frame is accepted. The tag is kept unchanged when the frame is...
Page 76
Chapter 6 configuring interfaces dgs-3610 series configuration guide 6-4 6.1.2.1 svi (switch virtual interface) svi, short for switch virtual interface, is used to implement the logical interface for layer 3 switching. Svi can work as the management interface of the local computer. This interface al...
Page 77
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 6 configuring interfaces 6-5 caution however, when a port is a member port of an l2 aggregate port, the switchport/ no switchport commands will not be used for swiching between the layers.. 6.1.2.3 l3 aggregate ports just like l2 aggregate port, the l3 agg...
Page 78
Chapter 6 configuring interfaces dgs-3610 series configuration guide 6-6 6.2.2 using interface configuration commands you may use the interface command to enter interface configuration mode in global configuration mode. Command function dgs-3610(config)# interface interface id input interface to ent...
Page 79
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 6 configuring interfaces 6-7 gigabitethernet slot/{the first port} - { the last port}; tengigabitethernet slot/{the first port} - { the last port}; aggregate port aggregate port number , - aggregate port number in the range of 1~max;. Interfaces contained ...
Page 80
Chapter 6 configuring interfaces dgs-3610 series configuration guide 6-8 – vlan vlan-id - vlan-id, with vlan id in the range of 1~4094; – fastethernet slot/{the first port} - { the last port}; – gigabitethernet slot/{the first port} - { the last port}; – aggregate port aggregate port number, with ag...
Page 81
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 6 configuring interfaces 6-9 the ports configured as the member of aggregate port must have the same media type. Otherwise, they cannot be added to the ap. The port type of aggregate port member ports cannot be changed. Command function dgs-3610(config-if)...
Page 82
Chapter 6 configuring interfaces dgs-3610 series configuration guide 6-10 dgs-3610# configure terminal dgs-3610(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/2 dgs-3610(config-if)# shutdown dgs-3610(config-if)# end 6.2.6 setting speed, duplexing, and flow control for interfaces the section describes how to s...
Page 83
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 6 configuring interfaces 6-11 mtu refers to the length of a valid data segment in a frame, excluding the overhead of ethernet encapsulation. The mtu of a port is checked during input but not output. The mtu will not be checked at output. If the frame recei...
Page 84
Chapter 6 configuring interfaces dgs-3610 series configuration guide 6-12 attribute default configuration aggregate port none storm control off port protection off port security off 6.2.8.1 configuring switch port 6.2.8.1.1 configuring access/trunk port this section is described to the operation mod...
Page 85
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 6 configuring interfaces 6-13 the following example shows how to set the native vlan of the trunk port gigabitethernet 2/1 to 10. Dgs-3610# configure terminal enter configuration commands, one per line. End with cntl/z. Dgs-3610(config)# interface gigabite...
Page 88
Chapter 6 configuring interfaces dgs-3610 series configuration guide 6-16 you may create a routed port by using no switchport after you have entered an interface in interface mode. Create one routed port and assign an ip address to the routed port: command function dgs-3610(config-if)# no switchport...
Page 89
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 6 configuring interfaces 6-17 dgs-3610(config-if)# no shutdown dgs-3610(config-if)# end 6.3 showing interface configuration and status this section covers the showing content and the showing instances of the interface. You may view the interface status by ...
Page 90
Chapter 6 configuring interfaces dgs-3610 series configuration guide 6-18 vlan : v5 description : svi 5 adminstatus : up operstatus : down primary internet address : 192.168.65.230/24 broadcast address : 192.168.65.255 physaddress : 00d0.F800.0001 lastchange : 0:0h:0m:5s the following is an example ...
Page 91
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 6 configuring interfaces 6-19 outucastpkts : 17284 outmulticastpkts : 249 outbroadcastpkts : 336 undersize packets : 0 oversize packets : 0 collisions : 0 fragments : 0 jabbers : 0 crc alignment errors : 0 alignmenterrors : 0 fcserrors : 0 dropped packet e...
Page 93
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 7 aggregate port configuration 7-1 7 aggregate port configuration this chapter explains how to configure an aggregate port on dgs-3610 series. 7.1 overview 7.1.1 understanding aggregate port multiple physical connections can be bound together and to form a...
Page 94
Chapter 7 aggregate port configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 7-2 mac address + destination mac address, source ip address, destination ip address and source ip address + destination ip address packets. The aggregateport load-balance command can be used to set the traffic distribution s...
Page 95
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 7 aggregate port configuration 7-3 figure 7-2 ap traffic balancing source mac based traffic distribution destination mac based traffic distribution aggregate link 7.2 configuring aggregate port 7.2.1 default configurations of aggregate port the default con...
Page 96
Chapter 7 aggregate port configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 7-4 once a port is added to an ap, the attributes of the port will be replaced by those of the ap. Once a port is removed from an ap, the attributes of the port will be restored as those before it is added to the ap. Note whe...
Page 97
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 7 aggregate port configuration 7-5 7.2.5 configuring traffic balancing of aggregate port in the configuration mode, configure the traffic balancing for the ap by performing the following steps: command function dgs-3610(config)# aggregateport load-balance ...
Page 99: Vlan Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 8 vlan configuration 8-1 8 vlan configuration this chapter describes how to configure ieee802.1q vlan. 8.1 overview virtual local area network (vlan) is a logical network divided on a physical network. Vlan corresponds to the l2 network in the iso model. T...
Page 100
Chapter 8 vlan configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 8-2 device must be used for communication between vlans. Dgs-3610 series can perform ip routing between vlans through the svi (switch virtual interfaces). For the configuration about the svi, please see interface management configurati...
Page 101
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 8 vlan configuration 8-3 8.2.2 default vlan configuration parameter default value range vlan id 1 1-4094 vlan name vlan xxxx, where xxxx is the vlan id no range vlan state active active, inactive 8.2.3 creating/modifying a vlan in the privileged mode, you ...
Page 102
Chapter 8 vlan configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 8-4 command function dgs-3610(config-if)# switchport mode access define the vlan member type of the interface (l2 access port) dgs-3610(config-if)# switchport access vlan vlan-id assign the port to one vlan. The following example add e...
Page 103
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 8 vlan configuration 8-5 figure 8-2 switch dgs-3610 switch switch switch you can set one common ethernet port or one aggregate port to a trunk port (for the details of aggregate port, see configuring aggregate port). To switch an interface between the acce...
Page 104
Chapter 8 vlan configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 8-6 8.3.2 configuring a trunk port 8.3.2.1 trunk port basic configuration in the privileged mode, an interface can be configured to a trunk port. Command function dgs-3610(config-if)# switchport mode trunk define the interface type as ...
Page 105
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 8 vlan configuration 8-7 dgs-3610# show interfaces fastethernet 1/15 switchport switchport is enabled mode is trunk port acsess vlan is 1,native vlan is 1 protected is disabled vlan lists is 1,3-4094 8.3.4 configure native vlan. One trunk port can receive/...
Page 106
Chapter 8 vlan configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 8-8 gigabitethernet 3/7 gigabitethernet 3/8 gigabitethernet 3/9 gigabitethernet 3/10 gigabitethernet 3/11 gigabitethernet 3/12 vlan[6] "vlan0006" gigabitethernet 3/1 dgs-3610#show vlan id 1 vlan[1] "vlan0001" gigabitethernet 3/1 gigabi...
Page 107: Super Vlan Configuration
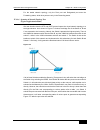
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 9 super vlan configuration 9-1 9 super vlan configuration this chapter describes the super vlan configuration of dgs-3610 series. 9.1 overview super vlan is a method for vlan division. Super vlan, also called vlan aggregate, is a management technology for ...
Page 108
Chapter 9 super vlan configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 9-2 the process of communication between two aggregated sub vlans when the vlan is aggregated is described below. See the above diagram: sub vlan2 and sub vlan4 are aggregated to super vlan3. An ip sub-net is assigned to super vl...
Page 109
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 9 super vlan configuration 9-3 9.3 configuring sub vlan of super vlan supervlan is meaningful only when subvlan is configured for it. To make vlan belong to the sub vlan of super vlan, use the following comands. Note: sub vlan configuration may fail due to...
Page 110
Chapter 9 super vlan configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 9-4 caution users can delete the previous configurations by executing no subvlan-address-range . 9.5 setting virtual interface for super vlan when a user in sub vlan needs to perform layer 3 communication, a virtual layer 3 inter...
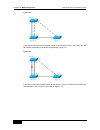
Page 111
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 9 super vlan configuration 9-5 9.7 showing super vlan setting show the super vlan setting using the following command. Command function dgs-3610# show supervlan show supervlan setting 9.8 configuration example figure 9-2 supervlan 3 svi 3: 192.168.1.1/24 s...
Page 112
Chapter 9 super vlan configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 9-6 # add a member port for subvlan2 switchport access vlan 2 ! Interface gigabitethernet 0/25 # add a member port for subvlan4 switchport access vlan 4 ! # create a virtual layer 3 interface that corresponds to super vlan interf...
Page 113
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 10 protocol vlan configuration 10-1 10 protocol vlan configuration 10.1 protocol vlan technology every packet that the device port receives should be classified based on vlan, so that the packet belongs to a unique vlan. There are three possibilities: 1. I...
Page 114
Chapter 10 protocol vlan configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 10-2 address-based and packet type and ethernet type-based vlan classifications, and the input packet matches them both, the ip address-based vlan classification takes effect. It‘s better to configure the protocol vlan after ...
Page 115
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 10 protocol vlan configuration 10-3 10.2.3 configuring the profile of packet type and ethernet type configure the packet type and ethernet type using the following commands: command description configure terminal enter configuration mode protocol-vlan prof...
Page 116
Chapter 10 protocol vlan configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 10-4 command description no protocol-vlan profile id clear certain profile on this port end exit the interface mode the following example applies profile 1 and profile 2 to the ge port 1 of slot 3. The vlan is classfied to vl...
Page 117: Private Vlan Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 11 private vlan configuration 11-1 11 private vlan configuration 11.1 private vlan technology if the service provider offers a vlan to each subscriber, the service provider supports a limited number of subscribers because one device supports 4096 vlans at ...
Page 118
Chapter 11 private vlan configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 11-2 11.2 private vlan configuration 11.2.1 default private vlan setting no private vlan is configured by default. 11.2.2 configuring vlan as a private vlan configure through using the following commands: command description c...
Page 119
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 11 private vlan configuration 11-3 vlan type status routed interface associated vlans --- ---- -------- ------ --------- ------------------ 303 comm inactive disabled no association 404 isol inactive disabled no association 11.2.3 associating secondary vla...
Page 120
Chapter 11 private vlan configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 11-4 11.2.4 mapping layer 3 interfaces of secondary vlan and primary vlan you can perform the following configuration to complete the command: command description configure terminal enter configuration mode interface vlan p_vi...
Page 121
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 11 private vlan configuration 11-5 for example: dgs-3610# configure terminal dgs-3610(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/2 dgs-3610(config-if)# switchport mode private-vlan host dgs-3610(config-if)# switchport private-vlan host-association 202 203 dgs-36...
Page 122
Chapter 11 private vlan configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 11-6 11.3 private vlan showing 11.3.1 showing private vlan you can show the contents of private vlan using the following commands: command description show vlan private-vlan [type] show the contents of private vlan dgs-3610# s...
Page 123: 802.1Q Tunneling
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 12 802.1q tunneling 12-1 12 802.1q tunneling 12.1 understanding 802.1q tunneling the commercial users of the network service providers usually have special requirements for the supported vlan and vlan ids. There may be superposition in the range of the vla...
Page 124
Chapter 12 802.1q tunneling dgs-3610 series configuration guide 12-2 the frames from the user end trunk port to the tunnel port of the network edge device of the vendor are usually carrying ieee 802.1q tag with one vlan id. After the frames enter the tunnel port, they will be added with another 802....
Page 125
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 12 802.1q tunneling 12-3 12.2 configuring 802.1q tunneling this chapter includes: default configurations of the 802.1q tunneling 802.1q tunneling configuration guide restriction of 802.1q tunneling configuration configuring an 802.1q tunneling port configu...
Page 126
Chapter 12 802.1q tunneling dgs-3610 series configuration guide 12-4 12.2.3 restriction of 802.1q tunneling configuration the following restrictions apply to configuration of 802.1q tunneling: the routing ports cannot be configured as tunnel ports. The ap port can be configured as a tunnel port. The...
Page 127
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 12 802.1q tunneling 12-5 12.2.5 configuring an uplink port in the global configuration mode, using the interface command to enter the interface configuration mode. Follow these steps to configure the tunnel port: command description configure terminal ente...
Page 128
Chapter 12 802.1q tunneling dgs-3610 series configuration guide 12-6 12.2.7 configuring priority duplication of user tag in the global configuration mode, using interface command to enter the interface configuration mode. Follow these steps to perform configuration: command description configure ter...
Page 129: Mac Address Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 13 mac address configuration 13-1 13 mac address configuration 13.1 managing the mac address table 13.1.1 overview the mac address table contains address information used for forwarding packets between ports. The mac address table includes three types of a...
Page 130
Chapter 13 mac address configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 13-2 13.1.1.2 static address a static address is a mac address manually configured. Static address is the same as the dynamic address in function, but oppositely, static address canl only be added and deleted manually (instead ...
Page 132
Chapter 13 mac address configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 13-4 command function dgs-3610(config)# mac-address-table static mac-add vlan vlan-id interface interface-id mac-addr: specify the destination mac address that the entry corresponds to. Vlan-id: specify the vlan to which this a...
Page 133
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 13 mac address configuration 13-5 13.1.3 viewing mac addresses information view information of the mac address table in the device: command function dgs-3610# show mac-address-table show all types of mac addresses information (including dynamic address, st...
Page 134
Chapter 13 mac address configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 13-6 caution the total address space of the mac address table available on the dgs-3610 series devices is 16384. Show the setting of address aging time: dgs-3610# show mac-address-table aging-time aging time : 300 13.2 the chan...
Page 135
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 13 mac address configuration 13-7 caution mac address notifications are generated only for dynamic addresses, and notifications are not generated for static addresses. 13.2.2 configuring mac address changing notification function by default, the global swi...
Page 136
Chapter 13 mac address configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 13-8 this example shows how to enable the mac address notification function and send the trap of mac address change notification to the nms with the ip address 192.168.12.54 with the authentication name public. The interval of ...
Page 137
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 13 mac address configuration 13-9 dgs-3610# show mac-address-table notification history history index:1 entry timestamp: 15091 mac changed message : operation vlan mac address interface ---------- ---- -------------- -------------------- added 1 00d0.F808....
Page 138
Chapter 13 mac address configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 13-10 dgs-3610# show address-bind ip address binding mac addr ---------- ----------------------- 3.3.3.3 00d0.F811.1112 3.3.3.4 00d0.F811.1117 13.3.4 configuring the exceptional ports for address binding if you wish the address...
Page 139: Dhcp Snooping Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 14 dhcp snooping configuration 14-1 14 dhcp snooping configuration 14.1 dhcp snooping overview 14.1.1 understanding dhcp the dhcp is widely used to dynamically allocate the reusable network resources, for example, ip address. A typical ip acquisition proce...
Page 140
Chapter 14 dhcp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 14-2 14.1.2 understanding dhcp snooping dhcp snooping monitors users by snooping the packets between the client and the server. Dhcp snooping can also be used to filter dhcp packets. It can be configured properly to filter il...
Page 141
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 14 dhcp snooping configuration 14-3 option82 can obtain more user information, so as to assign the ip to users more accurately. The format of option82 that uploaded by dhcp snooping is shown as follows: figure 14-2 agent circuit id figure 14-3 agent remote...
Page 142
Chapter 14 dhcp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 14-4 caution when the address binding is used, the switch can only support the limited dhcp users for the limit of the hardware list item, if the users are too much on the switch, it may cause that the legal user can not add ...
Page 143
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 14 dhcp snooping configuration 14-5 14.2 dhcp snooping configuration 14.2.1 configuration of enabling and disabling dhcp snooping the dhcp snooping function of the device is disabled by default. It can be enabled by using the ip dhcp snooping command to st...
Page 144
Chapter 14 dhcp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 14-6 command description dgs-3610# configure terminal enter configuration mode dgs-3610(config)# [no] ip dhcp snooping bindingbinding mac-addrees vlan vlan_id ip ip-addressaddress interface interface-id set a dhcp static user...
Page 145
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 14 dhcp snooping configuration 14-7 command function dgs-3610# configure terminal enter the configuration mode. Dgs-3610(config)# interface interface enter the interface configuration mode. Dgs-3610(config-if)# [no] ip dhcp snooping address-bind enable/dis...
Page 146
Chapter 14 dhcp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 14-8 14.2.7 writing dhcp snooping database information to flash manually in order to prevent loss of dhcp user information in the device due to restart of device following electricity failure, you can write information in the...
Page 147
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 14 dhcp snooping configuration 14-9 command description dgs-3610# clear ip dhcp snooping binding clear information from the current database the following example shows how to clear information from the current database manually: dgs-3610# clear ip dhcp sn...
Page 149
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration 15-1 15 igmp snooping configuration 15.1 overview 15.1.1 understanding igmp before understanding the igmp, let us first describe the concept and function of ip multicast. On the internet, the multimedia services such as video...
Page 150
Chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 15-2 figure 15-1 point to multiple-point propagation mode unicast: multiple copies are needed. Broadcast: host not wanting it also receives it multicast provides a good solution to this problem multicast provides a good solut...
Page 151
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration 15-3 group connected. Currently, there are three versions of igmp: igmpv1 is described in rfc 1112, igmpv2 is described in rfc 2236, and igmpv3 is described in rfc 3376. We describe respectively, as below, how the host joins ...
Page 152
Chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 15-4 group-specific query: used to query the members of the specified group under the interface: group-and-source-specific query: this type is the new one in the igmpv3, used to query whether any member under the interface ne...
Page 153
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration 15-5 figure 15-2 router interface host interface other equipment or direct connection the messages sent from the host, such as igmp report, and igmp leave will be forwarded from this port to the router. Only the igmp query me...
Page 154
Chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 15-6 figure 15-4 multicast server multicast router multicast receiver igmp snooping the switch that supports igmp snooping not only has to forward the multicast data the multicast flow receiver, but also has to forward the mu...
Page 155
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration 15-7 15.1.4 understanding operation modes of igmp snooping disable mode: in this mode, igmp snooping is not effective, that is, the switch does not ―snoop‖ the igmp message between the host and the router or multicast frame w...
Page 156
Chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 15-8 the ivgl mode and svgl mode of igmp snooping provided by dgs-3610 strengthens the network application flexibility, enabling it to adapt to different network environment. 15.1.5 understanding source port check dgs-3610 se...
Page 157
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration 15-9 figure 15-6 router interface equipment requirement: the switch supports igmp snooping. Required setup: 1. Enable igmp snooping function. 2. Set upper link as router interface. Characteristics: 1. Simple configuration; 2....
Page 158
Chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 15-10 15.2.1 igmp snooping default igmp snooping status disable status router interface all interfaces are not router interface, and do not conduct dynamic learning. Source port check off igmp profile entry is null, and the d...
Page 161
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration 15-13 you can delete the association with the profile by using no ip igmp snooping vlan vlan-id mrouter interface interface-id profile . This example configures the range of multicast frame forwarded by the router interface: ...
Page 162
Chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 15-14 command function dgs-3610(config)# ip igmp snooping ivgl enable igmp snooping and set it to the ivgl mode. Dgs-3610(config)# end return to the privileged mode. Following example shows to enables igmp snooping and sets i...
Page 163
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration 15-15 15.2.9 configuring disable mode in the configuration mode, set igmp snooping to the disable mode by performing the following steps: command function dgs-3610(config)# no ip igmp snooping disable igmp snooping dgs-3610(c...
Page 164
Chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 15-16 15.2.12 configuring source ip check in the configuration mode, you can set igmp snooping source ip check by performing the following steps: command function dgs-3610(config)# ip igmp snooping source-check default-server...
Page 165
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration 15-17 15.2.14 configuring igmp snooping suppression in the configuration mode, set igmp snooping suppression by performing the following steps: command function dgs-3610(config)# ip igmp snooping suppression enable enable the...
Page 166
Chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 15-18 dgs-3610(config)# show ip igmp snooping gda abbr: m - mrouter d - dynamic s - static vlan address member ports ---- -------------- ----------------------------- 1 224.1.1.1 gigabitethernet 0/7(s) 15.2.16 configuration i...
Page 167
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration 15-19 15.3.1 viewing current mode in the privileged mode, use the following command to view the current working mode and global configuration of igmp snooping: command function dgs-3610# show ip igmp snooping view the current...
Page 168
Chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 15-20 command function dgs-3610# show ip igmp snooping mrouter view the route connection port information of igmp snooping the following example shows to use the show ip igmp snooping command to view the igmp snooping router ...
Page 169
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration 15-21 15.3.6 viewing igmp profile in the privileged mode, view the igmp profile information by using the following command: command function dgs-3610# show ip igmp profile profile-number view the igmp profile information. 15....
Page 170
Chapter 15 igmp snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 15-22 function (deleting all address bindings) or delete the ace of acl occupying multiple masks, and the source port check can be enabled normally. When the igmp snooping or setting router interface is enabled, if the source...
Page 171: Pim Snooping Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 16 pim snooping configuration 16-1 16 pim snooping configuration this chapter will describe how to configure the protocol independent multicast snooping on the dgs-3610 series. It will cover the content below: understand the pim snooping principle. Configu...
Page 172
Chapter 16 pim snooping configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 16-2 in the figure 16-2, the multicast data only flows into the ports that connect to the multicast router b and c, but not flows into the router d. Figure 16-2 multicast flow after pim snooping is enabled multicast source rec...
Page 173
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 16 pim snooping configuration 16-3 16.4.1 enable pim snooping globally to enable the pim snooping globally, execute the following tasks: command function dgs-3610(config)# ip pim snooping dgs-3610(config)# no ip pim snooping enable the pim snooping. Disabl...
Page 175: Mstp Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-1 17 mstp configuration 17.1 mstp overview 17.1.1 stp and rstp 17.1.1.1 stp and rstp overview this device can support both the stp protocol and the rstp protocol and comply with the ieee 802.1d and ieee 802.1w standards. The stp pr...
Page 176
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-2 17.1.1.2 bridge protocol data units (bpdu): to span a stable tree-type topology, it should depend on the elements below: the unique bridge id of each bridge consists of the bridge priority and the mac address. The bridge to root ...
Page 177
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-3 17.1.1.3 bridge id in accordance with the prescription of the ieee 802.1w standard, each bridge should present unique bridge id, which will be taken as the standard to select the root bridge in the algorithm of the spanning tree....
Page 178
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-4 r = root port d = designated port a = alternate port b = backup port unless otherwise stated, the priority of the port will be lowered from left to right. Figure 17-1 figure 17-2 s h a r e d m e d i u m b d figure 17-3 b d shared...
Page 179
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-5 for the stable network topology, only the root port and designated port enter the forwarding status, while other ports are only in the discarding status. 17.1.1.6 spanning of network topology tree (typical application solution) w...
Page 180
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-6 figure 17-5 if the failure of the active path between switch a and switch b occurs, the backup link will take action immediately to generate corresponding figure 17-6. Figure 17-6 if the failure of the path between switch b and s...
Page 181
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-7 figure 17-7 17.1.1.7 quick convergence of rstp we now introduce the special function of rstp, which enables the ―quick‖ forwarding of the port. The stp protocol will carry out the forwarding after 30s since the port role is selec...
Page 182
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-8 figure 17-8 caution certain conditions must be met before the above "handshaking" process can take place, namely ―point -to-point connect‖ must be used between ports. In order to maximize the power of you device, do not use non-p...
Page 183
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-9 figure 17-9 b d shared medium root bridge r a figure 17-10 shared medium root bridge in addition, the following figure is a ―point-to-point‖ connection and should be differentiated by users carefully. Figure 17-11 shared medium r...
Page 184
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-10 17.1.1.8 compatibility of rstp and stp the rstp protocol is completely compatible with the stp protocol, and will automatically judge whether the bridge connected with supports the stp protocol or the rstp protocol by the versio...
Page 185
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-11 for traditional spanning-tree protocol is not related to the vlan, it will cause the following problem under specified network topology: as shown in figure 17-4, devices a and b are located in vlan1, and devices c and d in vlan2...
Page 186
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-12 figure 17-16 in this way, it prevents the form of loop and has no effect on the communication among the same vlans. 17.1.2.2 how to partition mstp region according to above description, the mstp region should be partitioned rati...
Page 187
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-13 to this port is of the same mst region as itself. Otherwise, it is considered to come from another region. We recommend you configure the corresponding table of the instance-vlan in the stp-closed mode, and then enable the mstp ...
Page 188
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-14 figure 17-18 as is shown in figure 17-19, switch c with the highest priority is selected as the region root in the msti 2 (instance 2). Then, the link between switch a and b is discarding according to other parameters. Hence, fo...
Page 189
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-15 in region 2, since root path cost from device b to cst root is the lowest one, device b is selected as the cist regional root in this region. Similarly, device c is chosen as the cist regional root in region 3. Figure 17-20 cist...
Page 190
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-16 17.1.2.6 compatibility with mstp, rstp and stp protocol for the stp protocol, the mstp will send the stp bpdu to be compatible with it like the rstp. For detailed information, refer to the "compatibility of rstp and stp‖ section...
Page 191
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-17 17.2.2 understanding bpdu guard the bpdu guard may be global enabled or execute enabled for single interface. There are some slightly difference between these two ways. You can use the spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default co...
Page 192
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-18 17.2.5 understanding tc guard the tc-protection function can ensure to reduce the dynamic mac address and remove the arp when the network produces a large number of tc packets. However, it will still produce much deletion operat...
Page 193
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-19 caution when the automatic identification function of the edge port conflicts with the manual port fast, it will take the manual configuration as the standard. This function will take action when the specified port and the downs...
Page 194
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-20 17.3.2 enable and disable spanning tree protocol once the spanning-tree protocol is enabled, the device starts to run the spanning-tree protocol. By default, this device runs mstp. The spanning-tree protocol is disabled on the d...
Page 195
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-21 command function dgs-3610# copy running-config startup-config save the configuration. If you want to restore the default mode of the spanning tree protocol, use the global configuration command no spanning-tree mode to set. 17.3...
Page 196
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-22 with smaller port number will enter the forwarding status. You can assign different port priorities for different instances on one port, by which each instance can run separate spanning tree protocol. Same as the device priority...
Page 197
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-23 command function dgs-3610# configure terminal enter the global configuration mode. Dgs-3610(config)# interface interface-id enter the configuration mode of this interface, the legal interface contains the physical port and the a...
Page 198
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-24 port rate interface ieee 802.1d (short) ieee 802.1t (long) 1000m common port 4 20000 aggregate link 3 19000 in the privileged mode, perform these steps to configure the default calculation method of the port path cost: command f...
Page 199
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-25 in the privilege mode, perform these steps to configure the forward-delay time: command function dgs-3610# configure terminal enter the global configuration mode. Dgs-3610(config)# spanning-tree forward-time seconds configure th...
Page 200
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-26 command function dgs-3610# configure terminal enter the global configuration mode. Dgs-3610(config)# spanning-tree tx-hold-count numbers configure the maximum count of the bpdu sent per second, whose value range is 1-10, 3 by de...
Page 201
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-27 17.3.13 configuring protocol migration processing this setting is to enable this port to execute the version check forcibly. For related description, refer to the compatibility of rstp and stp. Command function dgs-3610# clear s...
Page 202
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-28 command function transferred to the instance 0 automatically. Dgs-3610(config-mst)# name name specify the mst configuration name, this string can present up to 32 bytes. Dgs-3610(config-mst)# revision version specify the mst rev...
Page 203
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-29 command function dgs-3610# show running-config check the configuration entries. Dgs-3610# copy running-config startup-config save the configuration. If you want to restore to the default value, use the global configuration comma...
Page 204
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-30 17.4.3 enabling bpdu guard if the bpdu is received from this port, the enabled bpdu guard will enter the error-disabled status. In the privileged mode, perform these steps to configure the bpdu guard: command function dgs-3610# ...
Page 205
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-31 command function dgs-3610(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast enable the portfast of this interface. Dgs-3610(config-if)# end return to the privileged exec mode. Dgs-3610# show running-config check the configuration entries. Dgs-...
Page 206
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-32 command function dgs-3610# show running-config check the configuration entities. Dgs-3610# copy running-config startup-config save the configuration. It will enter the privilege mode and configure the tc guard on the port accord...
Page 207
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 17 mstp configuration 17-33 command function dgs-3610# copy running-config startup -config save the configuration. To disable the bpdu source mac check, run no bpdu src-mac-check in the interface mode. 17.4.8 disabling the automatic identification of edge ...
Page 208
Chapter 17 mstp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 17-34 command meaning dgs-3610# show spanning-tree summary show the each instance information and the forwarding status information of this port of mstp dgs-3610# show spanning-tree mst configuration show the configuration information...
Page 209: Span Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 18 span configuration 18-1 18 span configuration 18.1 overview 18.1.1 understanding span you can copy the packets from one port to another port connected with a network analysis device or rmon analyzer by using the span to analyze the communication on the ...
Page 210
Chapter 18 span configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 18-2 couldn‘t be mirrored to the mirroring destination port (that is to say that the tx direction is not effective configured on the mirroring source port). For dgs-3610 series, span supports the enabled mirroring destination port and...
Page 211
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 18 span configuration 18-3 18.2.3 source port the source port (also known as the monitored interface) is a switched port, routed port or ap. This port is monitored for network analysis. In the single span session, you can monitor input, output and bi-direc...
Page 212
Chapter 18 span configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 18-4 18.2.8 span configuration guide please follow the rules below when configure the span. The network analyzer should be connected to the monitoring interface. The destination port can not be source port, and the source port can not...
Page 213
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 18 span configuration 18-5 to delete the span session, use the no monitor session session_number global configuration command. To delete the span session, use the no monitor session all global configuration command. You can use the no monitor session sessi...
Page 214
Chapter 18 span configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 18-6 18.3 showing the span status the show monitor privileged command allows you to show the current span status. The following example illustrates how to show the current status of span session 1 by using the show monitor privileged ...
Page 215: Ip Address And Service
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 19 ip address and service configuration 19-1 19 ip address and service configuration 19.1 ip addressing configuration 19.1.1 ip address overview ip address is made up of 32 binary bits and expressed in dotted decimal format for the convenience of writing a...
Page 216
Chapter 19 ip address and service configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 19-2 for category d, the four highest-order bits are set to ―1110‖, other bits are used as multicast addresses. 8 16 24 32 d type network 1 1 1 0 multicast address note no addresses are allowed with the four highest-...
Page 217
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 19 ip address and service configuration 19-3 class ip address range network numbers category a network 10.0.0.0~10.255.255.255 1 category a networks category b network 172.16.0.0~172.31.255.255 16 category b networks category c network 192.168.0.0~192.168....
Page 218
Chapter 19 ip address and service configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 19-4 note theoretically, bits of subnet masks can be any bits of the host addresses. Our product only supports continuous subnet masks from left to right which is started from network portion. For the feature configu...
Page 219
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 19 ip address and service configuration 19-5 command function dgs-3610(config-if)# no ip address ip-address mask secondary cancel the configuration of the secondary ip addresses on an interface. 19.1.2.2 configuration of address resolution protocol (arp) f...
Page 220
Chapter 19 ip address and service configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 19-6 to configure static arp, execute the following command at global configuration mode: command function dgs-3610(config)# arp ip-address mac-address arp-type define static arp. Where, arp-type can only support the...
Page 221
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 19 ip address and service configuration 19-7 19.1.2.4 broadcast packets processing configuration a broadcast packet is a data packet destined for all hosts on a particular physical network. Our product supports two kinds of broadcast packets: directed broa...
Page 222
Chapter 19 ip address and service configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 19-8 directed broadcasts which arrived at the final destination subnet, while other directed broadcasts packets will be forwarded normally. You can define an access list to control which directed broadcasts are forwa...
Page 224
Chapter 19 ip address and service configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 19-10 figure 19-1 secondary ip address configuration example it is required to configure rip routing protocol, but the version can only be set as ripv1, and display the routes of 172.16.2.0/24 on router c, and displa...
Page 225
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 19 ip address and service configuration 19-11 router rip network 172.16.0.0 network 192.168.12.0 19.2 ip service configuration 19.2.1 ip services configuration task list ip service configuration includes the following tasks which are all optional. You can ...
Page 226
Chapter 19 ip address and service configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 19-12 19.2.2.2 enabling icmp redirect messages routes are sometimes less than optimal it is possible for the device to be forced to resend a packet through the same interface on which it was received. If the router r...
Page 227
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 19 ip address and service configuration 19-13 to set the ip mtu value, use the following command in interface configuration mode: command function dgs-3610(config-if)# ip mtu bytes set the mtu value with the range 68~1500. Dgs-3610(config-if)# no ip mtu re...
Page 229: Dhcp Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 20 dhcp configuration 20-1 20 dhcp configuration 20.1 introduction to dhcp dhcp (dynamic host configuration protocol), detailed in rfc 2131, provides configuration parameters for hosts over the internet. Dhcp is based on client/server working mode. The dhc...
Page 230
Chapter 20 dhcp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 20-2 figure 20-1 server host (broadcast packet) (unicast packet) (unicast packet) (broadcast packet) process of dhcp requesting an ip address: 1. The host sends a dhcpdiscover broadcast packet to locate a dhcp server in the network; 2...
Page 231
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 20 dhcp configuration 20-3 simplify configuration tasks and reduce network construction cost. Dynamic address assignment significantly simplifies equipment configuration, and even reduces deployment cost if devices are deployed in the places where there ar...
Page 232
Chapter 20 dhcp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 20-4 dhcp client configuration of the hdlc encapsulation link (optional) 20.5.1 enabling dhcp server and relay agent to enable the dhcp server and the relay agent, execute the following commands in the global configuration mode: comma...
Page 233
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 20 dhcp configuration 20-5 you can give a meaningful name that can be memorized easily to the dhcp address pool. The name of address pool contains characters and digits. Our producet allows you to define multiple address pools. The ip address of relay agen...
Page 234
Chapter 20 dhcp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 20-6 command function dgs-3610(dhcp-config)# bootfile filename configure the name of the client boot file 20.5.6 configuring default gateway for client the configured default gateway for the client will be used as the default gateway ...
Page 235
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 20 dhcp configuration 20-7 20.5.9 configuring domain name server a dns server should be specified for domain name resolution when the client accesses the network resources using a host name. To configure a domain name server available to the dhcp client, e...
Page 236
Chapter 20 dhcp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 20-8 command function dgs-3610(dhcp-config)# netbios-node-type type configure the netbios node type 20.5.12 configuring network number and mask for dhcp address pool to configure dynamic address binding, you must configure the subnet ...
Page 237
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 20 dhcp configuration 20-9 to define manual address binding, you first need to define a host address pool for each manual binding, and then define the ip address and hardware address or client id for the dhcp client. The mac address is the hardware address...
Page 238
Chapter 20 dhcp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 20-10 20.5.15 configuring packet ping timeout by default, this ip address is considered not existent if there is no response within 500 milliseconds following the ping operation by the dhcp server. You can change the time for the serv...
Page 239
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 20 dhcp configuration 20-11 20.5.19 configuring dhcp client on hdlc encapsulated link our product supports the hdlc-encapsulated port to obtain a dynamically assigned ip address using dhcp. To configure the dhcp client, execute the following command in the...
Page 240
Chapter 20 dhcp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 20-12 command function dgs-3610# show ip dhcp binding [address] show dhcp address binding information dgs-3610# show ip dhcp conflict show dhcp address conflict information dgs-3610# show ip dhcp server statistics show dhcp server sta...
Page 241
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 20 dhcp configuration 20-13 ! Ip dhcp pool net172 network 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 172.16.1.254 domain-name rg.Com dns-server 172.16.1.253 netbios-name-server 172.16.1.252 netbios-node-type h-node lease 30 20.7.2 manual binding configuration...
Page 243: Dhcp Relay Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 21 dhcp relay configuration 21-1 21 dhcp relay configuration 21.1 overview 21.1.1 understanding dhcp the dhcp is widely used to dynamically allocate the reusable network resources, for example, ip address. The dhcp client sends the dhcp discover broadcast ...
Page 244
Chapter 21 dhcp relay configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 21-2 figure 21-1 vlan 10 and vlan 20 correspond to the 10.0.0.1/16 and 20.0.0.1/16 networks respectively, while the dhcp server is located on the 30.0.0.1/16 network. To have a dynamic ip management on the 10.0.0.1/16 and 20.0.0...
Page 245
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 21 dhcp relay configuration 21-3 figure 21-2 agent remote id 21.1.4 understanding dhcp relay check server-id function when dhcp is used, generally multiple dhcp servers will be available for each network for the purpose of backup, so that the network will ...
Page 246
Chapter 21 dhcp relay configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 21-4 command function dgs-3610(config)# service dhcp enable the dhcp agent dgs-3610(config)# no service dhcp disable the dhcp agent 21.2.2 configuring the dhcp server ip address after you have configured the ip address of the dh...
Page 247
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 21 dhcp relay configuration 21-5 command function dgs-3610(config)# ip dhcp relay information option dot1x enable the dhcp option dot1x function dgs-3610(config)# no ip dhcp relay information option dot1x disable the dhcp option dot1x function 21.2.4 confi...
Page 248
Chapter 21 dhcp relay configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 21-6 then, apply the command to the global interfaces using the command ip dhcp relay information option dot1x access-group denyaccesseachotherofunauthrize . In the global configuration mode, configure dhcp option dot1x access-g...
Page 249
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 21 dhcp relay configuration 21-7 command function dgs-3610(config)# no ip dhcp relay check server-id disable the dhcp relay check server-id function 21.2.7 configuring dhcp relay suppression after the ip dhcp relay suppression command is configured, the in...
Page 250
Chapter 21 dhcp relay configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 21-8 21.3.1 precautions on dhcp option dot1x configuration 1. This command works only when the configuration related to aaa/802.1x is correct. 2. When this scheme is adopted, the ip authorization of the dhcp mode of 802.1x shoul...
Page 251
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 21 dhcp relay configuration 21-9 password 7 0137 line vty 3 4 login end.
Page 253: Dns Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 22 dns configuration 22-1 22 dns configuration 22.1 dns overview each ip address may present a host name, which consists of one or more strings, and it is separated by the decimal between the strings. For the host name, it is not necessary to remember the ...
Page 254
Chapter 22 dns configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 22-2 22.2.2 enabling dns resolution service this section describes how to enable the dns resolution service. Command function dgs-3610(config)# ip domain-lookup enable the function of dns resolution. The command no ip domain-lookup is ...
Page 255
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 22 dns configuration 22-3 22.2.5 clearing cache table of dynamic host names this section describes how to clear the cache table of dynamic host names. If the command clear host or clear host * is entered, the dynamic cache table will be cleared. Otherwise,...
Page 257: Ntp Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 23 ntp configuration 23-1 23 ntp configuration 23.1 unerstanding ntp network time protocol (ntp) is a protocol for the time synchronization of network devices. It is designed to synchronize the network devices with the server or clock source, to provide hi...
Page 258
Chapter 23 ntp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 23-2 23.2.1 configuring global security authentication mechanism for the ntp the ntp client of dgs-3610 series supports encrypting communication with the server by means of key encryption. There are two steps to configure the ntp clien...
Page 259
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 23 ntp configuration 23-3 command function ntp authentication-key key-id md5 key-string [enc-type] specify a global authentication key for the ntp. Key-id : 1-4294967295 key-string : its length is not limited. Enc-type : there are two types: 0 and 7. No nt...
Page 260
Chapter 23 ntp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 23-4 ntp version 3 is the default version of communication with the server. Meantime, the source interface can be configured to send the ntp message, and the ntp message from relevant server can only be received on the sending interfac...
Page 261
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 23 ntp configuration 23-5 23.2.6 enabling/disabling ntp function the function of command no ntp is to disable the ntp synchronization service, stop the time synchronization, and clear relevant information of ntp configuration. The ntp function is disabled ...
Page 262
Chapter 23 ntp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 23-6 23.3 display of ntp information 23.3.1 debugging the ntp if you want to debug the ntp function, this command may be used to output necessary debugging information for troubleshooting. To debug the ntp function, run the following c...
Page 263
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 23 ntp configuration 23-7 that on the ntp server, set this ntp server on the network as the synchronization server, and begin to synchronize the time. Dgs-3610(config)# no ntp dgs-3610(config)# ntp authentication-key 6 md5 wooooop dgs-3610(config)# ntp aut...
Page 265: Udp-Helper Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 24 udp-helper configuration 24-1 24 udp-helper configuration 24.1 udp-helper configuration 24.1.1 udp-helper overview the main function of udp-helper is to implement the relay and forward of udp broadcast message. By configuring the destination server requ...
Page 266
Chapter 24 udp-helper configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 24-2 24.2.2 enable the function of relay and forwarding for udp-helper command function dgs-3610(config)# udp-helper enable the command udp-helper enable is used to enable the function of relay and forward for udp broadcast pack...
Page 267
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 24 udp-helper configuration 24-3 24.2.4 configuring udp port requiring relay and forwarding command function dgs-3610(config)# ip forward-protocol udp id configure the udp port requiring delay and forwarding. If only the udp parameter is specified, the def...
Page 269: Snmp Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 25 snmp configuration 25-1 25 snmp configuration 25.1 snmp related information 25.1.1 overview as the abbreviation of simple network manger protocol, snmp has been a network management standard (rfc1157) since the august, 1988. So far, the snmp is supporte...
Page 270
Chapter 25 snmp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 25-2 figure 25-1 relation diagram between the nms and agent nms operation notification communication agent operation notification the mib (management information base) is a virtual information base for network management. There are la...
Page 271
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 25 snmp configuration 25-3 25.1.2 snmp protocol versions this software supports these snmp versions: snmpv1: the first formal version of the simple network management protocol, which is defined in rfc1157. Snmpv2c: the community-based administrative framew...
Page 272
Chapter 25 snmp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 25-4 figure 25-3 packet types in snmp snmp management process udp port 161 snmp agent process udp port 161 udp port 161 udp port 162 the port 161 of udp is used by the first three operations sent from the nms to the agent and the resp...
Page 273
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 25 snmp configuration 25-5 security model level authentication encryption description snmpv3 noauthnopriv user name none ensures the data validity through user name. Snmpv3 authnopriv md5 or sha none provides an authentication mechanism based on hmac-md5 o...
Page 274
Chapter 25 snmp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 25-6 2: the following 16 bytes are for ipv6 address 3: the following 6 bytes are for mac address 4: texts, assigned by product providers, 27 octets at most 5: hexadecimal number, assigned by product providers, 27 bytes at most 6-127: ...
Page 275
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 25 snmp configuration 25-7 25.2.2 configuring mib views and groups you can decide whether a mib object allowed by a snmp view or not through the access-control model based on snmp view, only the mib objects allowed by the snmp view can be accessed. For acc...
Page 276
Chapter 25 snmp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 25-8 to remove the specified user, the no snmp-server user username groupname command can be used. 25.2.4 configuring snmp host address in special cases, agent may actively send messages to nms. To configure nms host address that the ...
Page 277
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 25 snmp configuration 25-9 25.2.7 shielding snmp agent the snmp agent service is a service provided by the product of our company. It‘s enabled by default. When the agent service is not required, the snmp agent unction and related configuration information...
Page 278
Chapter 25 snmp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 25-10 command function dgs-3610(config-if)# no snmp-server enable traps enable or disable the function to send the link trap for the interface. No link trap will be sent for the interface according to the following configuration. Dgs-...
Page 279
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 25 snmp configuration 25-11 0 set-request pdus 2406 snmp packets output 0 too big errors (maximum packet size 1500) 4 no such name errors 0 bad values errors 0 general errors 2370 get-response pdus 36 snmp trap pdus snmp global trap: disabled snmp logging:...
Page 280
Chapter 25 snmp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 25-12 snmpoutpkts snmpinbadversions snmpinbadcommunitynames snmpinbadcommunityuses snmpinasnparseerrs snmpintoobigs snmpinnosuchnames snmpinbadvalues snmpinreadonlys snmpingenerrs snmpintotalreqvars snmpintotalsetvars snmpingetrequest...
Page 281
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 25 snmp configuration 25-13 25.3.3 viewing snmp user to view the snmp users configured on the current agent, run the command show snmp user in the privileged user mode: dgs-3610# show snmp user user name: test engine id: 8000131103000000000000 storage-type...
Page 282
Chapter 25 snmp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 25-14 respectively. A network management software (taking hp openview as an example) is running on the nms. Figure 25-4 typical networking diagram of snmp wan port: detailed configuration of the network device enable the snmp agent se...
Page 283
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 25 snmp configuration 25-15 figure 25-5 network topology diagram now it is possible to query or set the managed units in the network device. Click the tool->snmp mib brower menu on the hp openview to display the following dialog box. Enter the ip address 1...
Page 284
Chapter 25 snmp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 25-16 hp openview has powerful function for the network management. For example, the traffic statistics of network interface can be expressed in the form of graph. For the other functions of snmp, see the document of network managemen...
Page 285
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 25 snmp configuration 25-17 dgs-3610(config)# snmp-server host 192.168.65.199 traps version 3 priv v3user.
Page 287: Configuration Of Rmon
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 26 configuration of rmon 26-1 26 configuration of rmon 26.1 overview rmon (remote monitoring) is a standard monitoring specification of ietf (internet engineering task force). It can be used to exchange the network monitoring data among various network mon...
Page 288
Chapter 26 configuration of rmon dgs-3610 series configuration guide 26-2 26.1.3 alarm alarm is the third group in rmon. It monitors a specific management information base (mib) object at the specified interval. When the value of this mib object is higher than the predefined upper limit or lower tha...
Page 289
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 26 configuration of rmon 26-3 caution the current version of our product supports only the records of ethernet. The index value should be within 1-65535. At most 10 control entry can be configured. Bucket-number : the control entry specifies the used data ...
Page 290
Chapter 26 configuration of rmon dgs-3610 series configuration guide 26-4 the keyword trap indicates the action is to send the trap message to the nms when the event is triggered. Community : the community name when sending the trap. Description-string : the description of the event. 26.2.4 showing ...
Page 291
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 26 configuration of rmon 26-5 dgs-3610(config)# rmon alarm 10 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.12.6 30 delta rising-threshold 20 1 falling-threshold 10 1 owner zhangsan dgs-3610(config)# rmon event 1 log trap rmon description "ifinnucastpkts is too much " owner zhangsan ...
Page 292
Chapter 26 configuration of rmon dgs-3610 series configuration guide 26-6 pkts : 726 broadcastpkts : 502 multicastpkts : 189 crcalignerrors : 0 undersizepkts : 0 oversizepkts : 0 fragments : 0 jabbers : 0 collisions : 0 utilization : 0 26.3.4.4 show rmon statistics dgs-3610# show rmon statistics sta...
Page 293: Rip Routing Protocol
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration 27-1 27 rip routing protocol configuration 27.1 rip overview the rip (routing information protocol) is a relatively old routing protocol, which is widely used in small or homogeneous networks. The rip uses the distance...
Page 294
Chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 27-2 for other feature applications of the rip, see the ip routing “protocol independent” feature configuration chapter. 27.2 rip configuration task list to configure the rip, perform the following tasks. The first two...
Page 295
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration 27-3 27.2.2 configuration of packet unicast for the rip the rip is usually a broadcast protocol. If the rip routing information needs to be transmitted via the non-broadcast networks, you need to configure the router s...
Page 296
Chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 27-4 command function dgs-3610(config-if)# ip split-horizon enable split horizon the default of all the interface are configured as enabling split horizon. 27.2.4 defining the rip version our product supports rip versi...
Page 297
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration 27-5 27.2.5 disable automatic route summary the automatic route summary of the rip is the process to automatically summarize them into classful network routers when subnet routes pass through classful network borders. ...
Page 298
Chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 27-6 the key chain defines the set of the keys that can be used by the interface. If no key chain is configured, no authentication will be performed even if a key chain is applied to the interface. Oure product support...
Page 299
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration 27-7 27.2.8 configuring the rip route source address validation by default, the rip will validate the source addresses of the incoming route update packets. If the source address of a packet is invalid, the rip will di...
Page 300
Chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 27-8 to forbid or allow some interface to receive the rip packet, execute the following command in the interface configuration mode: command function dgs-3610(config-if)# no ip rip receive enable forbid the interface t...
Page 301
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration 27-9 figure 27-1 example of configuring rip split horizon frame relay sub-address the route should be configured to achieve the following purposes: 1) all routers run the rip routing protocol; 2) routerb and routerc ca...
Page 302
Chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 27-10 configuration of device b: #configuring ethernet port interface fastethernet0/0 ip address 172.16.20.1 255.255.255.0 #configure the wan port interface serial1/0 ip address 192.168.123.2 255.255.255.0 encapsulatio...
Page 303
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration 27-11 configuration of device e: # configuring ethernet port interface fastethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.13.5 255.255.255.0 # configuring rip route protocol router rip version 2 network 192.168.13.0 27.3.2 example of ...
Page 304
Chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 27-12 key-string keyb accept-lifetime 00:00:00 dec 3 2000 infinite send-lifetime 00:00:00 dec 4 2000 infinite # configuring ethernet interface interface fastethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 ip rip auth...
Page 305
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration 27-13 figure 27-3 example of configuring packet unicast for the rip following are to be implemented via the configuration of rip packet unicast: 1. Router a can learn the route of notification from router c. 2. Router ...
Page 306
Chapter 27 rip routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 27-14 interface loopback0 ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 # configuring rip route protocol router rip version 2 network 192.168.12.0 network 192.168.20.0 configuration of device c: # configuring ethernet interfac...
Page 307: Ospf Routing Protocol
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-1 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28.1 ospf overview ospf (open shortest path first) is an internal gateway routing protocol based on link status as developed by ietf ospf work group. Ospf is a routing proto...
Page 308
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-2 if there is no link cost or network change, the ospf will become quiet. If any changes occur on the network, the ospf notifies the changes via the link status, but only the changed ones. The devices involved in t...
Page 309
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-3 caution currently, our product does not support the following functions, but will support them in future versions; ospf line on-demand support, as defined in rfc 1793; function of ospf graceful restart, as define...
Page 310
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-4 the default ospf configuration is shown as below: interface parameters interface cost: none is preset lsa retransmit interval: 5 seconds. Lsa transmit delay: 1 second. Hello packet transmit interval : 10 seconds ...
Page 311
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-5 network area (network area) none device id undefined; the ospf protocol does not run by default route summarization (summary-address) undefined changing lsas group pacing 240 seconds timers shortest path first (s...
Page 312
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-6 dgs-3610(config-router)# end 28.2.2 configuring the ospf interface parameters the ospf allows you to change some particular interface parameters. You can set such parameters as needed. It should be noted that som...
Page 313
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-7 command meaning dgs-3610(config-if)#ip ospf database-filter all out (optional) prevent the interfaces from flooding the lsas packets. By default, ospf floods new lsas over all interfaces in the same area, except ...
Page 314
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-8 commands, you can allow x.25 and frame relay to have the broadcast capability, so that the ospf can see the networks like x.25 and frame relay as the broadcast networks. The point-to-multipoint network interface ...
Page 315
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-9 command function dgs-3610(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-multipoint configure the point-to-multipoint network type for an interface dgs-3610(config-if)# exit exit to the global configuration mode dgs-3610(c...
Page 316
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-10 command function dgs-3610(config-router)# neighbor ip-address [priority number] [poll-interval seconds] specify the neighbor and designate its priority and round robin interval of hello. In a non-broadcast netwo...
Page 317
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-11 message from the designated routers within specified time and it is considered that the router is down. To configure the broadcast network type, execute the following commands in the interface configuration mode...
Page 318
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-12 there is no asbr in stub areas. In other words, the routes outside an autonomous system cannot be transmitted in the area. To configure the ospf area parameters, execute the following commands in the routing pro...
Page 319
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-13 to configure an area as the nssa, execute the following commands in the routing process configuration mode: command function dgs-3610(config-router)# area area-id nssa [no-redistribution] [no-summary] [default-i...
Page 320
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-14 note if route summary is configured, the detailed routes in this area will not be advertised by the abr to other areas. 28.2.7 configuring route summary when routes are injected to the ospf when the routes are r...
Page 321
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-15 these routers, the packets are transparent to them and are simply forwarded as common ip packets), and the abrs exchange route information directly. The route information means the type-3 lsas generated by the a...
Page 322
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-16 note when the stub area is configured, the abr will generate the default route automatically, and notifies it to all routers within the stub area. 28.2.10 using the loopback address as the route id the ospf rout...
Page 323
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-17 command function dgs-3610(config-router)#distance ospf {[inter-area dist1] [inter-area dist2] [external dist3 ]} change the ospf management distance 28.2.12 configuring the route calculation timer when the ospf ...
Page 324
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-18 to restore the default value, use the no timers lsa-group-pacing in the router configuration mode. 28.2.14 configuring route selection ospf calculates the destination based on the cost, where the route with the ...
Page 325
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-19 28.2.15 configuring whether to check the mtu value when the interface receives the database description packets when the ospf receives the database description packet, it will check whether the mtu interface is ...
Page 326
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-20 by default, all interfaces are allowed to receive/send the ospf packets. To re-enable the network interface to send the route information, you can use the no passive-interface interface-id command. To set all ne...
Page 327
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-21 command meaning dgs-3610# show ip ospf [process-id][area-id] database ospf database information can show the information of each type of lsas for specified processes. Area-id: it specifies the area on which the ...
Page 328
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-22 command meaning dgs-3610# show ip ospf [process-id] [area-id] database [asbr-summary] [link-state-id] [self-originate] dgs-3610# show ip ospf [process-id] [area-id] database [external] [link-state-id] dgs-3610# ...
Page 329
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-23 10.10.10.50 1 full/dr 00:00:38 10.10.10.50 eth0/0 ospf process 100: neighbor id pri state dead time address i nterface 10.10.11.50 1 full/backup 00:00:31 10.10.11.50 eth0/1 dgs-3610# show ip ospf 1 neighbor ospf...
Page 330
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-24 number of outgoing current dd exchange neighbors 0/5 number of external lsa 4. Checksum 0x0278e0 number of opaque as lsa 0. Checksum 0x000000 number of non-default external lsa 4 external lsa database is unlimit...
Page 331
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-25 28.4.1 example of configuring the ospf nbma network type configuration requirements: the three devices must be fully connected in a meshed network via frame relay. Each device has only one frame relay line, whic...
Page 332
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-26 configuration of device b: #configure the wan port interface serial 1/0 ip address 192.168.123.2 255.255.255.0 encapsulation frame-relay ip ospf network non-broadcast ip ospf priority 5 #configuring ospf routing...
Page 333
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-27 figure 28-2 example of configuring the ospf point-to-multipoint network type requirements: 1) the point-to-multipoint network should be configured among devices a, b, and c. Concrete configuration of devices if ...
Page 334
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-28 ip address 192.168.123.2 255.255.255.0 encapsulation frame-relay ip ospf network point-to-multipoint #configuring ospf routing protocol router ospf 1 network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 192.168.123.0 0...
Page 335
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-29 figure 28-3 example of configuring ospf authentication concrete configuration of devices the authentication configuration of the ospf involves two parts: 2. Specifying the authentication mode of the area in the ...
Page 336
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-30 the two devices are connected via ethernet. Figure 28-4 shows the ip address allocation and connection of the equipment. Figure 28-4 example of configuring ospf route summary requirements: 1) both devices run th...
Page 337
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-31 #configuring ospf routing protocol router ospf 1 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 28.4.5 ospf abr, asbr configuration examples configuration requirements: four devices form an ospf routing area. Networks 19...
Page 338
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-32 router ospf 1 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 configuration of device b: #configuring ethernet interface interface fastethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0 #configure the wan port interface se...
Page 339
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-33 #configuring rip routing protocol router rip network 200.200.1.0 network 172.200.1.0 on device b, you can see the ospf generates the following routes. Please note that the external route type becomes ―e1‖. O e1 ...
Page 340
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-34 four devices form an ospf routing area. Networks 192.168.12.0/24 and 192.168.23.0/24 belong to area 0, while network 192.168.34.0/24 belongs to area 34. Figure 28-6 shows the ip address allocation and connection...
Page 341
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-35 interface serial1/0 ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0 #configuring ospf routing protocol router ospf 1 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 configuration of device c: #...
Page 342
Chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 28-36 four devices form an ospf routing area. Networks 192.168.12.0/24 belongs to area 0, network 192.168.23.0/24 to area 23, while network 192.168.34.0/24 belongs to area 34. Figure 28-7 shows the ip address allocati...
Page 343
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 28 ospf routing protocol configuration 28-37 #add the loopback ip address and take it as the id of the ospf router. Interface loopback2 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 #configuring ospf route protocol router ospf 1 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 ne...
Page 345: Bgp Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-1 29 bgp configuration the bgp (border gateway protocol) is an egp (exterior gateway protocol) to communicate with the routers of different autonomous systems, whose main function is to switch the network availability information am...
Page 346
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-2 bgp route aggregate supported bgp route dampening supported bgp routing reflector supported as confederation supported bgp soft reset supported 29.1 operating bgp protocol to operate the bgp function, execute the following operati...
Page 347
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-3 tcp md5 authentication used off timer keepalive time 60seconds holdtime 180seconds connectretry time 120seconds advinterval(ibgp) 15seconds advinterval(ebgp) 30seconds path attribute med 0 local_pref 100 route aggregate off routin...
Page 348
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-4 to inject the network information advertised by the bgp speaker to its bgp speaker by means of the network commands by manual, execute the following operations in the bgp configuration mode: command meaning router(config-router)# ...
Page 349
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-5 29.4 configuring bgp peer (group) and its parameters for the bgp is an external gateway protocol (egp), it is necessary for the bgp speakers to know who is their peer (bgp peer). It is mentioned in the overview of the bgp protocol...
Page 352
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-8 by default, each member of the peer group will inherit all configurations of the peer group. However, each member is allowed to configure the optional configurations which have no effect on the output update independently, to repl...
Page 353
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-9 caution to disable the connection established with specified peer (group) and reserve the configuration information set for this specified peer (group), use the neighbor shutdown command. If such configuration information is not r...
Page 355
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-11 to cancel the synchronization mechanism of bgp speakers, execute the following operations in the bgp configuration mode: command meaning router(config-router)# nosynchronization (optional) cancel the synchronization of bgp and ig...
Page 358
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-14 caution this command is not recommended to use under the full mesh network environment (such as ethernet), for this command will cause the extra hops of the message and increase unnecessary overhead. 29.9.3 multi_exit_disc attrib...
Page 359
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-15 command meaning router(config-router)# bgp deterministic-med (optional) allow to compare with the path of the peers from the same as firstly. By default, they will be compared with by the received sequence, the later received pat...
Page 360
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-16 local-as: indicate this path will not be issued to out of this as. When the confederation is configured, this path will not be issued to other autonomous systems or sub autonomous systems. You can control the receiving, priority ...
Page 361
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-17 29.9.6 other related configuration by default, if two paths with full identical path attributes are received from different ebgp peers during the selection of the optimal path, we will select the optimal path according to the pat...
Page 362
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-18 29.11 configuring route aggregate for bgp for the bgp-4 supports cidr, it allows to create the aggregate table item to reduce the bgp route table. Of course, only when there is valid path within the aggregate scope, the bgp aggre...
Page 363
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-19 the rule to implement the route reflector within the as is shown as follows: configure the route reflector and specify its client, so the route reflector and other clients form a cluster. The route reflector establishes the conne...
Page 364
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-20 in general, it is not necessary to establish the connection relationship between the clients of the route reflector within the cluster, and the route reflector will reflect the route among clients. However, if the full connection...
Page 365
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-21 command meaning router(config-router)# bgp dampening half-life-time reuse suppress max-suppress-time (optional) configure the parameters of the route dampening. Half-life-time(1-45minutes), 15minutes by default. Reuse (1-20000), ...
Page 366
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-22 attribute information of next_hop, med and local_pref retains constant when the information is exchanged. To implement the as confederation, execute the following operations in the bgp configuration mode: command meaning router(c...
Page 367
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-23 caution it is not recommended to change the management distance of the bgp route. If it is necessary to change, please keep it in mind that: 1. The external-distance should be lower than the management distance of other igp route...
Page 368
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-24 29.17 protocol independent configuration 29.17.1 route-map configuration the bgp protocol applies the route-map policy on a large scale. For the configuration of the route-map policy, refer to the protocol independent configurati...
Page 369
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-25 *> 211.21.26.0/24 110.110.110.10 0 1000 300 *> 1.1.1.0/24 192.168.88.250 444 0 606 *> 179.98.0.0 192.168.88.250 444 0 606 *> 192.92.86.0 192.168.88.250 8883 0 606 *> 192.168.88.0 192.168.88.250 444 0 606 *> 200.200.200.0 192.168....
Page 370
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-26 router a router b router c 192.168.4.3 192.168.5.3 192.168.4.2 192.168.5.2 ibgp ebgp in this example, the bgp configuration of various devices is shown as follows: configuration of device a: ! Router bgp 100 neighbor 192.168.4.2 ...
Page 371
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-27 in the schematics, there is a route p in the router a, which is sent to router c by the ibgp neighbor relationship. If the router c is configured with the bgp synchronization, it is necessary for the router c to wait for the igp ...
Page 372
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-28 this configuration indicates that only the route which passes through the as-path access-list 2 tofilter can be advertised to the neighbor 193.1.12.10, and the advertised route from the neighbor 193.1.12.10 can be received only w...
Page 373
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-29 the concrete configuration is shown as follows: router bgp 100 aggregate-address 193.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 configure one aggregate route: router bgp 100 aggregate-address 193.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 as-set the as-path segment of aggregated rou...
Page 374
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-30 the configurations of all the devices in this example are as below: the configuration of router a: ! Router bgp 65530 bgp confederation identifier 100 bgp confederation peers 65531 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 10.0.3.2 remot...
Page 375
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-31 neighbor 10.0.3.2 remote-as 65530 neighbor 10.0.4.4 remote-as 65530 the configuration of router d: ! Router bgp 65530 bgp confederation identifier 100 bgp confederation peers 65531 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 10.0.2.4 remot...
Page 376
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-32 in this example, the router d is a route reflector. The configurations of all the devices in this example are as below: the configuration of router a: ! Router bgp 100 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 192.168.5.3 remote-as 100 n...
Page 377
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-33 ! Router bgp 100 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 192.168.5.12 remote-as 100 neighbor 192.168.5.12 description route-reflector client neighbor 192.168.5.12 route-reflector-client neighbor 192.168.6.5 remote-as 100 neighbor 192.1...
Page 378
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-34 the configuration of router a: ! Router bgp 100 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor ibgp-group peer-group neighbor ibgp-group description peer in the same as neighbor 192.168.6.2 remote-as 100 neighbor 192.168.6.2 peer-group ibgp-g...
Page 379
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-35 29.18.7.2 configuring ebgp peergroup use the neighbor a.B.C.D remote-as num command to configure an ebgp peer, firstly, take the neighbor external peer-group command to create a peergroup with the name external , and then apply t...
Page 380
Chapter 29 bgp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 29-36 the configuration of router a: ! Router bgp 100 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor ebgp-group peer-group neighbor ebgp-group distribute-list 2 in neighbor ebgp-group route-map set-med out neighbor 192.168.1.5 remote-as 200 neighbo...
Page 381
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 29 bgp configuration 29-37 in the following topology, the configurations of md5 on each router are as below: figure 29-8 the relationship between the routers is: the as the router a located is 100, the as the router b and router c is 200, the usage of ip a...
Page 383: Protocol-Independent
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 30 protocol-independent configuration 30-1 30 protocol-independent configuration 30.1 ip route configuration 30.1.1 configuring static routes static routes are manually configured so that the packets to the specified destination network go through the spec...
Page 384
Chapter 30 protocol-independent configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 30-2 route source default management distance ospf route 110 rip route 120 unreachable route 255 the static routes to the ports can be advertised by such dynamic routing protocols as rip and ospf, no matter whether sta...
Page 385
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 30 protocol-independent configuration 30-3 command function dgs-3610(config)# ip default-network network configure the default network dgs-3610(config)# no ip default-network network delete the default network note to generate the default routes by using t...
Page 386
Chapter 30 protocol-independent configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 30-4 routing area , or those in the rip routing area to the ospf routing area. Routes can be redistributed among all the ip routing protocols. In route redistribution, the route maps are often used to enforce condition...
Page 387
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 30 protocol-independent configuration 30-5 command function route(config-route-map)# match ip next-hop access-list-number […access-list-number] match the next-hop address in the access list access-list-number : 1-199, 1300-2699, route(config-route-map)# ma...
Page 388
Chapter 30 protocol-independent configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 30-6 at route redistribution, it is not necessary to convert the metric of one routing protocol into that of another routing protocol, since different routing protocols use distinctively different measurement methods. ...
Page 390
Chapter 30 protocol-independent configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 30-8 30.2.3 configuration examples: 30.2.3.1 example of static route redistribution configuration requirements: one device exchanges route information with other devices via the rip. In addition, there are three static...
Page 391
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 30 protocol-independent configuration 30-9 figure 30-1 example of rip&ospf redistribution the ospf only redistributes the routes in the rip routing area and the route type is type-1. The rip only redistributes the 192.168.10.0/24 route in the ospf routing ...
Page 392
Chapter 30 protocol-independent configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 30-10 dgs-3610(config-if)# ip address 200.168.23.2 255.255.255.0 #configure ospf and set the redistribution route type dgs-3610(config)# router ospf dgs-3610(config-router)# redistribute rip metric 100 metric-type 1 su...
Page 393
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 30 protocol-independent configuration 30-11 ! Dgs-3610(config)# router ospf dgs-3610(config-router)# redistribute rip subnets route-map redrip dgs-3610(config-router)# network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 ! Dgs-3610(config)# access-list 20 permit 200.168....
Page 394
Chapter 30 protocol-independent configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 30-12 sip+dip+tcp/udp port sip+dip+udf sip + tcp/udp port +udf sip + dip+tcp/udp port +udf the default keyword has only sip. 30.3.2 selecting the hash algorithm there are two hash algorithms available: crc32_upper sele...
Page 395
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 30 protocol-independent configuration 30-13 dgs-3610(config)#ip ref ecmp load-balance crc32_lower dip port udf 50
Page 397: Policy-Based Routing
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 31 policy-based routing configuration 31-1 31 policy-based routing configuration policy-based routing is a packet forwarding mechanism more flexible than the routing based on the target network. If policy-based routing is used, the router will determine ho...
Page 398
Chapter 31 policy-based routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 31-2 command function dgs-3610(config-route-map)# match ip address access-list-number match the address in the access list dgs-3610(config-route-map)# match length min max match the length of the packet 3. Define the o...
Page 399
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 31 policy-based routing configuration 31-3 dgs-3610(config-route-map)# match ip address 1 dgs-3610(config-route-map)# set ip next-hop 192.168.5.5 dgs-3610(config-route-map)# int f 0/0 dgs-3610(config-if)# ip policy route-map name to configure the policy-ba...
Page 400
Chapter 31 policy-based routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 31-4 11. Set ip next-hop 12. Set ip default next-hop 13. Set interface 14. Set default interface 15. Set tos 16. Set preference 17. Set dscp restrictions: caution 1. On our products with version 10.2, one interface can...
Page 401: Ipv6 Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 32 ipv6 configuration 32-1 32 ipv6 configuration 32.1 ipv6 related information with the quick growth of internet and the increasing consumption of the ipv4 address space, the limitation of the ipv4 is more obvious. The research and practice of the internet...
Page 402
Chapter 32 ipv6 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 32-2 play. It should be mentioned that the ipv6 supports such address configuration methods as the stateful and the stateless. In the ipv4, the dynamical host configuration protocol (dhcp) implements the automatic setting of the host ...
Page 403
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 32 ipv6 configuration 32-3 icmpv6 redirection address conflict detection ipv6 stateless auto-configuration ipv6 address configuration ipv6 route forwarding, support static route configuration configuration of various parameters for the ipv6 protocol diagno...
Page 404
Chapter 32 ipv6 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 32-4 32.1.2 type of ipv6 address in rfc2373, there are the following three defined types of ipv6 addresses: unicast: identifier of a single interface. The packet to be sent to a unicast address will be transmitted to the interface of ...
Page 405
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 32 ipv6 configuration 32-5 tla id field (top-level aggregation identifier): top-level aggregation identifier, containing toppest address routing information. It refers to the maximum route information in the inter-working. It is 13 bits long and can provid...
Page 408
Chapter 32 ipv6 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 32-8 figure 32-1 prefix ipv6 unicast or anycast address interface id ff02 0 1 ff lower 24 multicast address of the corresponding requested node 24bits 32.1.2.3 anycast addresses the anycast address is similar with the multicast addres...
Page 409
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 32 ipv6 configuration 32-9 32.1.3 ipv6 packet header structure the format of the ipv6 packet header is shown as the figure below: figure 32-3 in the ipv4, all packet headers take 4 bytes as the unit. While in the ipv6, the packet header takes 8 bytes as th...
Page 410
Chapter 32 ipv6 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 32-10 hop limit: the length is 8 bits. When one router forwards the packet for one time, this field will reduce 1. If this field is 0, this packet will be discarded. It is similar to the life span field in the ipv4 packet header. Sour...
Page 411
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 32 ipv6 configuration 32-11 furthermore, when the data packet to be sent is larger than the mtu in the data transmission path, the host will be fragment by itself. This host-fragmented behavior makes it not necessary for the router to process the fragment ...
Page 412
Chapter 32 ipv6 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 32-12 the neighbor solicitation message can also be used to detect the reachability of the neighbor (for the existing neighbor). At this time, the destination address of the neighbor solicitation message is the unicast address of this...
Page 413
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 32 ipv6 configuration 32-13 the router advertisement (ra) is also used to respond to the router solicitation (rs) message sent by the host, and the router solicitation (rs) message allows the host to obtain the auto-configuration information immediately, b...
Page 414
Chapter 32 ipv6 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 32-14 caution once the interface of ipv6 is created and the link of the interface is in the up status, the system will automatically generate link-local addresses for the interface. At present, the ipv6 doesn‘t support the configurati...
Page 415
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 32 ipv6 configuration 32-15 ff02:1::1 ff02:1::2 ff02:1::1:ff00:1 mtu is 1500 bytes icmp error messages limited to one every 10 milliseconds icmp redirects are enabled nd dad is enabled, number of dad attempts: 1 nd reachable time is 30000 milliseconds nd a...
Page 416
Chapter 32 ipv6 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 32-16 use the no ipv6 redirects command to close the redirection function. The following is an example to configure the redirection function: dgs-3610(config)# interface vlan 1 dgs-3610(config-if)# ipv6 redirects dgs-3610(config-if)# ...
Page 417
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 32 ipv6 configuration 32-17 dgs-3610(config)# ipv6 neighbor fec0:0:0:1::100 vlan 1 00d0.F811.1234 dgs-3610(config)# end dgs-3610# show ipv6 neighbors verbose fec0:0:0:1::100 ipv6 address linklayer addr interface fec0:0:0:1::100 00d0.F811.1234 vlan 1 state:...
Page 418
Chapter 32 ipv6 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 32-18 dgs-3610(config)# interface vlan 1 dgs-3610(config-if)# ipv6 nd dad attempts 3 dgs-3610(config-if)# end dgs-3610# show ipv6 interface vlan 1 interface vlan 1 is up, ifindex: 2001 address(es): mac address: 00:d0:f8:00:00:01 inet6...
Page 420
Chapter 32 ipv6 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 32-20 command meaning show ipv6 neighbors [verbose] [interface-id] [ipv6-address] show the neighbor information. Show ipv6 route [static] [local] [connected] show the information of the ipv6 route table. 1. View the ipv6 information i...
Page 421
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 32 ipv6 configuration 32-21 ipv6 address linklayer addr interface fe80::200:ff:fe00:1 0000.0000.0001 vlan 1 state: reach/h age: - asked: 0 fec0:1:1:1::1 0000.0000.0001 vlan 1 state: reach/h age: - asked: 0
Page 423: Ipv6 Tunnel Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration 33-1 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration 33.1 overview the ipv6 is designed to inherit and replace the ipv4. However, the evolution from the ipv4 to the ipv6 is a gradual process. Therefore, before the ipv6 completely replaces the ipv...
Page 424
Chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 33-2 caution the structure formed by connecting isolated ipv6 networks with the ipv6 tunnel technology is not the final network architecture of the ipv6. The technology is only for transition. The model to use the tunnel techno...
Page 425
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration 33-3 be configured on the area border router of an isolated ipv6 network. For each packet, it automatically builds a tunnel connecting the area border router in another ipv6 network. The destination address is the ipv4 address ...
Page 426
Chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 33-4 33.1.4 isatap tunnel intra-site automatic tunnel addressing protocol (isatap) is an ipv6 tunnel technology by which an intra-site ipv6 architecture takes an ipv4 network as one nonbroadcast multi-access (nbma) link layer, ...
Page 427
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration 33-5 for example, the ipv6 prefix is 2001::/64 and the embedded ipv4 address is 192.168.1.1. In the isatap address, the ipv4 address is denoted as the hexadecimal numeral of c0a8:0101. Therefore, its corresponding isatap addres...
Page 429
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration 33-7 command meaning interface tunnel tunnel-num specify a tunnel interface number to create a tunnel interface and enter the interface configuration mode. Tunnel mode ipv6ip 6to4 specify that the type of a tunnel is the 6to4 t...
Page 430
Chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 33-8 the reason is that the last 32 bits of the interface identifier in the ipv6 address are composed of theipv4 address of the interface referenced by the tunnel source address. Refer to the above chapters and sections for mor...
Page 431
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration 33-9 command meaning no ipv6 nd suppress-ra by default, it is disabled to send router advertisement packets on an interface. Enable the function with the command, allowing automatic configuration of the isatap host. End return ...
Page 432
Chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 33-10 command meaning show ipv6 route view the ipv6 router table. 1. View the information of a tunnel interface. Dgs-3610# show interface tunnel 1 tunnel 1 is up, line protocol is up hardware is tunnel, encapsulation tunnel tun...
Page 433
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration 33-11 33.4 ipv6 tunnel configuration instances the following chapters/sections introduce ipv6 tunnel configuration instances. Manual ipv6 tunnel configuration instance 6to4 tunnel configuration instance isatap tunnel configurat...
Page 434
Chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 33-12 interface fastethernet 2/2 no switchport ipv6 address 2001::1/64 no ipv6 nd suppress-ra (optional) #configure manual tunnel interface interface tunnel 1 tunnel mode ipv6ip ipv6 enable tunnel source fastethernet 2/1 tunnel...
Page 435
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration 33-13 33.4.2 6to4 tunnel configuration instance figure 33-5 as shown in the above figure, using a 6to4 tunnel, an ipv6 network (6to4 site) accesses the ipv6 backbone network (6bone) via the 6to4 relay router. With the 6to4 tunn...
Page 436
Chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 33-14 no ipv6 nd suppress-ra # configure the 6to4 tunnel interface interface tunnel 1 tunnel mode ipv6ip 6to4 ipv6 enable tunnel source fastethernet 0/1 # configure the route to the tunnel ipv6 route 2002::/16 tunnel 1 # config...
Page 437
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration 33-15 33.4.3 isatap tunnel configuration instance figure 33-6 ff02 : :1 (the isatap address to be automatically configured) the isatap address to be automatically configured the configuration on the tunneling interface as shown...
Page 438
Chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 33-16 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 # configure the isatap tunnel interface interface tunnel 1 tunnel mode ipv6ip isatap tunnel source fastethernet 0/1 ipv6 address 2005:1::/64 eui-64 no ipv6 nd suppress-ra # connect the...
Page 439
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration 33-17 note in the above figure, it is an instance of composite application of 6to4 tunnel and isatap tunnels. With the 6to4 tunnel technology, various 6to4 sites are interconnected and the 6to4 site accesses the cernet network ...
Page 440
Chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 33-18 interface tunnel 2 tunnel mode ipv6ip 6to4 ipv6 enable tunnel source gigabitethernet 0/1 # configure the route to the 6to4 tunnel ipv6 route 2002::/16 tunnel 2 # configure the routeto the 6to4 relay router rt-d to access ...
Page 441
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration 33-19 interface gigabitethernet 0/1 no switchport ip address 211.162.7.1 255.255.255.0 # connect the interfaces of the ipv4 network inside the site interface fastethernet 0/1 no switchport ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 #...
Page 442
Chapter 33 ipv6 tunnel configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 33-20 tunnel source gigabitethernet 0/1 #configure the route to the 6to4 tunnel ipv6 route 2002::/16 tunnel 1.
Page 443: Ospfv3 Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 34 ospfv3 configuration 34-1 34 ospfv3 configuration ospf v2 (rfc2328, ospfv2) runs under the ipv4. The rfc2740 describes ospf v3 (ospfv3) and its extended ospfv2 protocol and provides support for ipv6 routes. This document briefly describes the ospfv3 pro...
Page 444
Chapter 34 ospfv3 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 34-2 can be generated. Thus, when performing the spf calculation, we must consider all the router-lsas generated by the device. Router-lsas and network-lsas describe the link topology of areas together. Caution through the flag bits...
Page 445
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 34 ospfv3 configuration 34-3 2. Associate router-lsas and record the prefix information about routers in the current area, all loopback interfaces, point-to-point links, point-to-multipoint links, virtual links and stub networks. Other main changes of lsa ...
Page 446
Chapter 34 ospfv3 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 34-4 34.1.4 authentication mechanism setting the ospfv2 itself supports two authentication modes: plain text authentication and key authentication based on md5. The ospfv3 itself does not provide any authentication. It will use the ...
Page 447
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 34 ospfv3 configuration 34-5 router id undefined virtual link virtual link undefined hello packet sending interval 10 seconds dead interval: 4 times of the hello packet interval. Lsa sending delay 1 second lsa retransmit interval. 5 seconds area configurat...
Page 448
Chapter 34 ospfv3 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 34-6 to run the ospfv3, follow these steps in the privileged mode: command function configure terminal enter the global configuration mode. Ipv6 router ospf process-id start the ospfv3 route process and enter the ospfv3 configuratio...
Page 450
Chapter 34 ospfv3 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 34-8 caution you can modify the parameter setting of an interface based on actual needs. However, be sure that the settings of some parameters must be identical to those of neighbors. Otherwise, it is impossible to establish the adj...
Page 451
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 34 ospfv3 configuration 34-9 command function area area-id stub [no-summary] configure a stub area. No-summary:configure the area to a totally stub area, blocking inter-stub-area area border routers to send type 3 information into the stub area. Area area-...
Page 452
Chapter 34 ospfv3 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 34-10 caution 1. It is not allowed to create a virtual connection in the stub area and nssa. 2. A virtual connection can be taken as a special interface, so its configuration is the same to that of a normal interface. You must ensur...
Page 453
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 34 ospfv3 configuration 34-11 for example, if the bandwidth reference value of an interfaces is 100 mbps and the bandwidth of network interfaces is 10mbps, the automatically calculated interface cost value of the network interface is 100/10=10. Currently, ...
Page 454
Chapter 34 ospfv3 configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 34-12 to configure the ospfv3 route redistribution, run the following commands in the ospfv3 configuration mode: command function redistribute protocol [metric metric-value] [metric-type type-value] [route-map map-tag] redistribute ...
Page 455
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 34 ospfv3 configuration 34-13 34.8.1 ospfv3 debug command in the privileged configuration mode, execute the following commands to start the debug commands of the ospfv3 process: command function debug ipv6 ospf event show the ospfv3 event information. Debu...
Page 457: Ip Multicast Routing
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-1 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35.1 overview this chapter describes how to configure multicast routing protocols. For a complete description of the ip multicast routing commands, please refer to other chapt...
Page 458
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-2 igmp is used between the hosts and routers in a lan to track relations between group members.. Pim-dm is a dynamic multicast routing protocol, which is used between routers for multicast forwarding based on multic...
Page 459
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-3 35.1.2.2 igmpv2 in version 2, there are only four packet types: membership query version 1 membership report version 2 membership report leave group the process is basically the same as that of version 1, except t...
Page 460
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-4 35.1.2.3 igmpv3 in the applications of the igmpv1 and v2, there are the following defects: lack of effective measures to control multicast sources difficult to establish the multicast path due to the unknown locat...
Page 461
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-5 if the equipment in the network supports igmp v3, host a wants to receive the traffic from s1 only, it can send the igmpv3 packet of join g include s1. If host b wants to receive the traffic from s2 only, it can s...
Page 462
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-6 the process of igmp version3 is similar to that of the igmp version2. Igmp version3 is downward compatible with igmp version1 and igmp version2. 35.1.3 pim-dm overview the protocol independent multicast (pim) is d...
Page 463
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-7 active to send a prune message to upstream without waiting for timeout of upstream pruning state so as to enable pruning to forwarding state. As long as source s can still send messages to group g, the first hop s...
Page 464
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-8 figure 35-4 join mechanism of pim-sm explicitly sender (s,g) joining to (s,g) registration share tree unicast (*,g) joining to data flow receiver source tree unicast (s,g) registration stopped the pim-sm will forw...
Page 465
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-9 group address. The bsr message is sent hop-by-hop within the whole domain. The device receives and saves these bsr message. If the dr receives the member relationship report of some group from the direct connectio...
Page 466
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-10 multicasts them, and sets the ttl to 1. In this way, the gsr message is received by all devices hop-by-hop. Since the messages contain the ip address of the bsr, the candidate bsr can know which router is the cur...
Page 467
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-11 command purpose ip pim dense-mode enter the interface that needs to run pim-dm and enable pim-dm multicast routing process in the interface configuration mode. It demonstrates how to configure pim-dm on fastether...
Page 468
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-12 command purpose ip multicast ttl-threshold ttl-value configure ttl threshold at the interface. 35.6.1.2 configuring ip multicast boundary execute ip multicast boundary to configure multicast boundary of an interf...
Page 469
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-13 in the global configuration mode, execute the following command to configure multicast static route. Command purpose ip mroute source-address mask {interface-type interface-number} [distance] configure multicast ...
Page 470
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-14 35.6.2.2 adding membership information on routers statically sometimes the subnet connected to an interface has no host that can send igmp member reports, but you still want the switch to forward the multicast pa...
Page 471
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-15 35.6.3 configuring query count of the last member when the packet of leaving group is received, the querier sends the specific membership query to verify whether there is any member in the group. By default the p...
Page 472
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-16 execute the command no ip igmp query-interval to restore the default configuration. 35.6.6 configuring the maximum response interval the membership query packet sent by the querier requires the maximum response i...
Page 473
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-17 when exceeding the limit configured for the interface or globally. Run the following commands in the interface mode: command function dgs-3610(config) # ip igmp limt number configure the igmp status quantity limi...
Page 474
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-18 note when acl is located from 1 to 99, igmp v1/v2/v3 will only match group (g). When acl is 100-199, igmp v1 / v2 will match (source ip of 0.0.0.0, group ip). When acl is located in 100-199, igmp v3 will match (s...
Page 475
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-19 interface will judge the member information maintained itself is connected from the interface with mroute-proxy. Hence, the configuration of proxy-server is equal that this interface only executes the host behavi...
Page 476
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-20 command function dgs-3610(config)# ip igmp ssm-map static 11192.168.2.2 all groups that comply with acl 11 will be mapped into the source address 192.168.2.2. 35.6.14 clearingup dynamic group membership in igmp c...
Page 477
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-21 command function dgs-3610# show ip igmp groups a.B.C.D detail show the details of the specified member in the directly-connected subnets. Dgs-3610# show ip igmp interface interface-type show the information of th...
Page 478
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-22 igmp last member query counter is 7 igmp last member query interval is 255 1/10seconds igmp has 5 different config in this interface igmp nif learnt mem num is 0 igmp nif limit num is 1024 igmp other querier inte...
Page 479
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-23 command function dgs-3610# debug ip igmp fsm turn on igmp debug final-state-machine switch dgs-3610# debug igmp tib turn on igmp debug tree switch. Dgs-3610# debug ip igmp warnning turn on igmp debug warning swit...
Page 480
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-24 to configure the sending interval of hello message, please execute the following commands in the interface mode: command function dgs-3610(config-if)# ip pim query-interval seconds set the sending interval of the...
Page 481
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-25 35.6.21.4 configuring pim neighbor filtering the function of neighbor filtering can be enabled on the interface to enhance the network security. When the neighbor filtering is configured, if a neighbor is refused...
Page 482
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-26 command function no ip pim state-refresh disable enable the processing and forwarding of the pim-dm status update messages the status renew function is enabled by default. Caution disabling the status update mess...
Page 483
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-27 show the status of pim-dm command function show ip pim dense-mode interface [ interface-type interface-number ] [ detail ] show the pim-dm interface information. Show ip pim dense-mode neighbor [interface-type in...
Page 484
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-28 enabling pim-sm (required) configuring the hello message sending interval (optional) configuring pim-sm neighbor filtering (optional) configuring the priority of specified device dr (optional) configuring the can...
Page 485
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-29 caution enabling the pim-sm is effective only when the multicast routing is enabled in the global configuration mode. During the execution of this command, if the prompt "failed to enable pim-sm on , resource tem...
Page 486
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-30 command function no ip pim neighbor-filter access-list disabling the function of pim neighbor filtering in current interface. By default, the neighbor filtering function is disabled in the interface. Note ip pim ...
Page 487
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-31 35.6.22.7 configure the static rp in a small-scale network, you can use the static rp to use the pim-sm, which requires that the static rp configuration of all devices in the pim-sm domain must be consistent to e...
Page 488
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-32 35.6.22.8 configuring candidate rp the configured candidate rp can be sent to the bsr by certain interval and then flooded to all the pim-sm devices in the domain, thus ensuring the uniqueness of rp mapping. Plea...
Page 489
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-33 command function ip pim rp-candidate ifname (priority) (interval) (grouplist) use the candidate rp to configure this device no ip pim rp-candidate cancel the candidate rp configuration 35.6.22.11 configuring the ...
Page 491
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-35 command function ip pim spt-threshold allow the last-hop device to switch from the shared tree to the shortest path tree no ip pim spt-threshold disable this function 35.6.22.17 switching the last-hop device from...
Page 492
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-36 command function show ip pim sparse-mode rp-hash a.B.C.D execute this command to show the rp information selected. Show ip pim sparse-mode rp mapping show the group-rp mapping information and rp settings show ip ...
Page 493
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-37 35.7.1.2 device configuration take the device 1 as an example to show how to configure pim-dm. The steps of device 2 and 3 are similar to device 1. Step 1: enable multicast router dgs-3610# configure terminal dgs...
Page 494
Chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 35-38 ! Route rip network 192.168.21.0 network 192.166.1.0 network 192.166.100.0 version 2 ! Ip pim-sm bsr-candidate loopback0 30 201 ip pim-sm rp-candidate loopback0 ! Router_b: ! Ip multicast-routing ! Interface ethe...
Page 495
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 35 ip multicast routing configuration 35-39 ! Router rip network 192.168.21.0 network 192.168.100.0 ! Ip pim-sm bsr-candidate loopback0 30 201 ! Router_b: ! Ip multicast-routing ! Interface loopback0 ip address 192.168.100.144 255.255.255.0 ip pim-sm ! Int...
Page 497: Port-Based Flow Control
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 36 port-based flow control configuration 36-1 36 port-based flow control configuration 36.1 storm control 36.1.1 overview excessive broadcast, multicast or unicast packets with unknown names in lan will result in slow network speed and considerably increas...
Page 499
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 36 port-based flow control configuration 36-3 gigabitethernet 0/2 disabled disabled disabled none gigabitethernet 0/3 disabled disabled disabled none gigabitethernet 0/4 disabled disabled disabled none gigabitethernet 0/5 disabled disabled disabled none gi...
Page 500
Chapter 36 port-based flow control configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 36-4 36.2.2 configuring protected ports set one port as the protection port: command function dgs-3610(config-if)# switchport protected set this interface as a protected port you can reset a port as unprotected port...
Page 501
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 36 port-based flow control configuration 36-5 you can use the command of show interfaces switchport to view the configuration of protected port. Dgs-3610# show interfaces gigabitethernet 0/3 switchport interface switchport mode access native protected vlan...
Page 502
Chapter 36 port-based flow control configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 36-6 36.3.2 configuring port security 36.3.2.1 default configuration of port security the table below shows the default configuration of port security: item default configuration port security switch the port securi...
Page 503
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 36 port-based flow control configuration 36-7 command function dgs-3610(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum value set the maximum number of security addresses on the interface. The range is between 1 and 1000 and the default value is 128. Dgs-3610...
Page 504
Chapter 36 port-based flow control configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 36-8 command function dgs-3610(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address mac-address [ip-address ip-address] manually configure the security address on the interface. Ip-address (optional): ip address bound u...
Page 505
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 36 port-based flow control configuration 36-9 in the interface configuration mode, execute no switchport port-security aging time to disable the port security aging. Execute the no switchport port-security aging static to apply the aging time only to dynam...
Page 506
Chapter 36 port-based flow control configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 36-10 36.3.3 viewing port security information in the privileged mode, you can view the security information of a port with the following commands. Command function dgs-3610#show port-security interface [interface-i...
Page 507
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 36 port-based flow control configuration 36-11 gi0/1 128 1 restrict gi0/2 128 0 restrict gi0/3 8 1 protect.
Page 509: Configuration Of 802.1X
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-1 37 configuration of 802.1x this chapter describes the contents related to the aaa service configurations. The 802.1x is used to control the authentication over network access of users, and provide authorization and accountin...
Page 510
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-2 before the client passes the authentication, only the eapol (extensible authentication protocol over lan) packets can be transmitted over the network. After successful authentication, normal data flows can be transmitted ove...
Page 511
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-3 authenticator: the authenticator is usually an access device like the switch. The responsibility of the device is to control the status of the connection of a client to the network according to the current authentication sta...
Page 512
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-4 figure 37-2 authorized users unauthorized users work station (client) switch this is a typical authentication process initiated by users (in some special cases, the switch can actively initiate authentication request, whose ...
Page 513
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-5 on an 802.1x-enabled device, all ports are uncontrolled ports by default. We can set a port as a controlled port, to impose authentication over all the users under that port. When a user has passed authentication (the switch...
Page 514
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-6 this solution is described as below: requirements of this solution: 1. The user supports 802.1x. That is, it is installed with the 802.1x client (windows xp carried, star-supplicant or other ieee802.1x-compliant client softw...
Page 515
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-7 b. The 802.1x-enabled device is used as the convergence layer device figure 37-4 backbone layer equipment convergence layer equipment (supporting 802.1x authenticator) access layer equipment (be able to transparently transmi...
Page 516
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-8 characteristics of this solution: 1. The convergence layer device must be of high quality since the network is large and numerous users are connected, since any of its fault may cause the failures of accessing the network. 2...
Page 517
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-9 configuring on-line client probe configuring the option flag for eapol frames to carry tag 37.2.1 default configuration of 802.1x the following table lists some defaults of the 802.1x item default authentication disable acco...
Page 518
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-10 you cannot enable 1x authentication for aggregate port. If the 1x function is enabled on only one port of a switch, all the ports will send the 1x protocol packets to the cpu. 37.2.3 configuring the communication between th...
Page 519
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-11 following example sets the server ip to 192.168.4.12, authentication udp port to 600, and the key to agreed password: dgs-3610# configure terminal dgs-3610(config)# radius-server host 192.168.4.12 dgs-3610(config)# radius-s...
Page 520
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-12 dgs-3610(config)# aaa authentication dot1x authen group radius dgs-3610(config)# dot1x authentication authen dgs-3610(config)# end dgs-3610# show running-config ! Aaa new-model ! Aaa authentication dot1x authen group radius...
Page 521
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-13 command function dot1x port-control auto set the port to be a controlled port (enable interface authentication). You can use the no option of the command to disable the authentication of the interface. End return to the pri...
Page 522
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-14 the following example enables re-authentication and sets the re-authentication interval to 1000 seconds. Dgs-3610# configure terminal dgs-3610(config)# dot1x re-authentication dgs-3610(config)# dot1x timeout re-authperiod 1...
Page 523
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-15 37.2.8 setting the packet retransmission interval after the device sends the eap-request/identity, it resends that message if no response is received from the user within a certain period. By default, this value is 3 second...
Page 524
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-16 dgs-3610#show dot1x you can use the no dot1x max-req command torestore the maximum number of packet re-transmissions to its default. The following example sets the maximum number of packet retransmissions to 5: dgs-3610# co...
Page 525
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-17 command function dot1x timeout server-timeout seconds set the maximum response time of the radius server. You can use the no option of the command to restore it to its default. End return to the privileged mode. Write save ...
Page 526
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-18 command function dot1x auto-req enable automatic authentication. It is disabled by default. End return to the privileged mode. Write save the configuration. Show dot1x show the dot1x configurations. The no option of the com...
Page 527
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-19 it is possible to set to the function of stopping sending the request packets when the user authentication passes. In some applications (only one user under a port, for example), we can stop sending authentication requests ...
Page 528
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-20 authentication of the user and the user‘s logoff or when the device detects user disconnection. After the first successful authentication of the user, the device sends an accounting start request to the server. When the use...
Page 529
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-21 the no aaa accounting network command deletes the accounting method list. The no dot1x accounting command restores the default dot1x accounting method. The following example sets the ip address of the accounting server to 1...
Page 530
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-22 dgs-3610# configure terminal dgs-3610(config)# aaa accounting update dgs-3610(config)# end dgs-3610# write memory dgs-3610# show running-config 37.2.14 configuring ip authorization modes the 802.1x implemented on dgs-3610 s...
Page 531
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-23 in this mode, it is required to configure the dhcp relay and the related option82. If the dhcp relay function is enabled and the option82 policy is selected, see the dhcp relay configuration guide and command references for...
Page 532
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-24 dgs-3610(config)# end dgs-3610# show running-config ! Aaa new-model ! Aaa authorization ip-auth-mode radius-server ! Dgs-3610# write memory 37.2.15 releasing advertisement our 802.1x allows you to configure the reply-packet...
Page 533
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-25 command function show running-config show the configuration. Caution if the list of the host is empty, the port allows any host authentication. 37.2.17 authorization to make it easier for operators, our products can provide...
Page 534
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-26 figure 37-8 for the customized header, follow those provided above. The maximum data rate is 10m, that is, 10000kbsp, and makes 0x00002710 in the hex system. You only need to fill in the corresponding field. This function c...
Page 535
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-27 dgs-3610(config)# end dgs-3610# show dot1x 802.1x status: disabled authentication mode: chap authed user number: 0 re-authen enabled: disabled re-authen period: 3600 sec quiet timer period: 10 sec tx timer period: 3 sec sup...
Page 536
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-28 37.2.20 configuring and managing online users dgs-3610 series provides management for authenticated users via snmp. The administrator can view the information of the authorized users via snmp, and forcedly log off a user. T...
Page 537
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-29 command function show dot1x show the configuration. 37.2.24 shielding proxy server and dial-up the two major potential threats to network security are: the user sets its own proxy server and the user makes dial-up to access...
Page 538
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-30 figure 37-10 37.2.25 configuring on-line client probe to ensure accurate charging, an on-line probe mechanism is needed to detect whether a user is on-line within a short period. The re-authentication mechanism specified in...
Page 539
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-31 command function show dot1x show the configuration. 37.2.26 configuring the option flag for eapol frames to carry tag in accordance with ieee 802.1x, the eapol packets cannot be added with vlan tag. However, based on the po...
Page 541
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-33 37.3.1 viewing the radius authentication and accounting configuration run the show radius server command to check the related configuration of the radius sever, and run the show aaa user command to view the user-related inf...
Page 542
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-34 command function configure terminal enter the global configuration mode. Dot1x auth-address-table address mac-addr interface interface set the list of the hosts that can be authenticated. End return to the privileged mode. ...
Page 543
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-35 hello interval: 20 seconds hello alive: 250 seconds dgs-3610# 37.3.6 other precautions for configuring 802.1x 1. When there is no ip authorization mode, each device supports 10,000 authenticated users. 2. Concurrent use of ...
Page 544
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-36 users cannot communicate. For the filtering domain templates in particular, at least one must be available for user authentication in the ip authentication mode..
Page 545
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-1 aaa configuration the access control is used to control specific users who can access the network server and specific services that the users can access on the network. The authentication, authorization and accounting (aaa) ...
Page 546
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-2 password authentication and more. The difference lies in the degree of their network protection, and the aaa provides the security protection of a higher level. The aaa has the following advantages: powerful flexibility and ...
Page 547
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-3 the figure above illustrates a typical aaa network configuration, including two security servers: r1 and r2 are both radius servers. Suppose the system administrator has defined a method list, r1 is used first to capture the...
Page 548
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-4 for complete descriptions of the commands mentioned in this chapter, see the related chapters in the security configuration command reference. 37.5.2 enabling aaa it is required to enable aaa first to use the aaa security fe...
Page 549
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-5 37.6.1 defining aaa authentication method list to configure the aaa authentication, the first step is to define a named list of the authentication method, and then the applications use the defined list for authentication. Th...
Page 550
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-6 command function configure terminal enter the global configuration mode. Aaa new-model turn on the aaa switch. Aaa authentication login test group radius local define a method list named "test" in the global configuration mo...
Page 551
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-7 caution the aaa security features are available for your configuration only after the aaa is enabled through the command aaa new-model in the global configuration mode. For details, see aaa overview. In many cases, the user ...
Page 552
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-8 caution since the keyword none enables any dial-up user to pass the authentication even if the security server has no reply, it is only used as the backup authentication method. We suggest not using the "none" identity authe...
Page 554
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-10 command function end return to the privileged mode. Show aaa method-list confirm the configured method list. Configure terminal enter the global configuration mode. Line vty line-num enter the line configuration mode login ...
Page 555
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-11 37.7 configuring authorization the aaa authorization enables the administrator to control services available to users. After the aaa authorization service is enabled, the network device configures user sessions through user...
Page 557
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x 37-13 37.7.5 none authorization to enable no authorization for the user, you need to execute the aaa authorization command with keyword none. Command function configure terminal enter the global configuration mode. Aaa new-model ...
Page 558
Chapter 37 configuration of 802.1x dgs-3610 series configuration guide 37-14 37.8.2 network accounting the network accounting provides the accounting information about user session, including the packet number, bytes, ip address and username. Note the format of radius accounting information varies w...
Page 561: Radius Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 38 radius configuration 38-1 38 radius configuration 38.1 radius overview the remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) is a distributed client/server system that works with the aaa to perform authentication for the users who are attempting to ma...
Page 562
Chapter 38 radius configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 38-2 figure 38-1 typical radius network configuration wan pc 1 pc 2 nas radius server 38.2 radius configuration tasks to configure radius on the network device, perform the following tasks first: enable aaa. For the details, see aaa...
Page 563
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 38 radius configuration 38-3 command function radius-server host ip-address [auth-port port ] [acct-port port] configure the ip address or hostname of the remote radius security server and specify the authentication port and accounting port. Radius-server ...
Page 564
Chapter 38 radius configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 38-4 id function type 6 net ip 6 7 user name 7 8 password 8 9 file-directory 9 10 file-count 10 11 file-name-0 11 12 file-name-1 12 13 file-name-2 13 14 file-name-3 14 15 file-name-4 15 16 max up-rate 16 17 version to server 17 18 f...
Page 565
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 38 radius configuration 38-5 id function type 15 file-name-4 15 16 max up-rate 75 17 version to server 17 18 flux-max-high32 18 19 flux-max-low32 19 20 proxy-avoid 20 21 dailup-avoid 21 22 ip privilege 22 23 login privilege 42 24 limit to user number 50 no...
Page 566
Chapter 38 radius configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 38-6 redgiant# configure redgiant(config)# radius attribute 24 vendor-type 67 redgiant(config)# show radius vendor-specific id vendor-specific type-value ---- -------------------- ---------- 1 max down-rate 76 2 qos 77 3 user ip 3 4...
Page 567
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 38 radius configuration 38-7 note the radius server can be a component that comes with the windows 2000/2003 server (ias) or the unix system, or the special server software of some manufacturers. Here is an example about how to configure the radius for net...
Page 569: Ssh Terminal Service
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 39 ssh terminal service 39-1 39 ssh terminal service 39.1 about ssh ssh is short for secure shell. The ssh connection functions like a telnet connection, except that all transmissions based on the connection are encrypted. When the user logs on to the devi...
Page 570
Chapter 39 ssh terminal service dgs-3610 series configuration guide 39-2 39.4 ssh configuration 39.4.1 default ssh configurations item default value ssh service end status off ssh version compatible mode (supporting versions 1 and 2) ssh user authentication timeout period 120s ssh user re-authentica...
Page 571
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 39 ssh terminal service 39-3 command description configure terminal enter the configuration mode no enable service ssh-server disable the ssh server. 39.4.5 configuring ssh server support version by default, the ssh server v1 and v2 are compatible. You can...
Page 572
Chapter 39 ssh terminal service dgs-3610 series configuration guide 39-4 command description ip ssh authentication-retries retry times configure ssh re-authentication times (range 0-5) no ip ssh authentication-retries reset the ssh re-authentication times to the default value 3. Note: for details of...
Page 573
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 39 ssh terminal service 39-5 click ok, and the following dialog box appears: figure 39-2 click connect to log into the host just configured, as shown below: figure 39-3 ask the machine that is logging into the host 192.168.5.245 to see whether the key from...
Page 574
Chapter 39 ssh terminal service dgs-3610 series configuration guide 39-6 figure 39-4 enter the telnet login password to enter the ui that is the same as the telnet. See the interface below: figure 39-5.
Page 575: Cpu Protection Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 40 cpu protection configuration 40-1 40 cpu protection configuration 40.1 overview 40.1.1 function of cpu protect malicious attacks often occur in the network environment, and such attacks will create too much load for our switches. Sometimes when the pack...
Page 576
Chapter 40 cpu protection configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 40-2 the switch provides a protection method to control the bandwidth and priority for each type of packets sent to the cpu. You can configure the maximum rate and priority for each type of packet sent to the cpu port in pac...
Page 577
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 40 cpu protection configuration 40-3 type default maximum bandwidth (pps) default priority dhcp_option82 128 0 udp_helper 128 0 through the command no cpu-protected type, the maximum bandwidth and priority setting of the packet can be reset to the default ...
Page 578
Chapter 40 cpu protection configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 40-4 40.3 viewing cpu protect information on the switch, you can view the following information about the cpu protect: viewing the statistics of packets received by the cpu of the management board viewing the statistics of p...
Page 579
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 40 cpu protection configuration 40-5 type pps total drop ------------ --------- --------- --------- arp 200 200 15 bpdu 200 8 0 dhcp 200 0 0 gvrp 200 0 0 ipv6-mc 200 0 0 dvmrp 200 0 0 igmp 200 0 0 ospf 200 0 0 pim 200 0 0 rip 200 0 0 vrrp 200 0 0 unknow-ip...
Page 581: Anti-Attack System Guard
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 41 anti-attack system guard configuration 41-1 41 anti-attack system guard configuration 41.1 overview it is known that many attacks of hackers and invasion of network virus start with scanning the active hosts in the network. The great amount of scanning ...
Page 582
Chapter 41 anti-attack system guard configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 41-2 41.2 anti-attack system guard configuration the anti-attack system guard is completed in the global configuration mode. It is required to enter the global configuration mode first for anti-attack system guard ...
Page 583
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 41 anti-attack system guard configuration 41-3 command meaning configure terminal enter the global configuration mode. Interface interface-id enter the configuration mode of this interface. Legal interfaces include physical interfaces. System-guard isolate...
Page 584
Chapter 41 anti-attack system guard configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 41-4 command meaning show system-guard check the configuration entities. Copy running-config startup-config save the configuration. Caution the smaller the threshold is set, the weaker the accuracy of the judging f...
Page 585
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 41 anti-attack system guard configuration 41-5 if you want to restore the default value of the maximum quantity for monitored hosts, execute the no system-guard detect-maxnum command in the global configuration mode. 41.2.6 setting exceptional ips free fro...
Page 586
Chapter 41 anti-attack system guard configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 41-6 command meaning clear system-guard [interface interface-id [ip-address ip-address]] clear isolated users. Where, clear system-guard indicates clearing all isolated users; clear system-guard interface interface...
Page 587
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 41 anti-attack system guard configuration 41-7 41.2.8.2 viewing the information of isolated ips for system guard command meaning show system-guard isolate-ip [interface interface-id] check the information of isolated ips of the ports for anti-scanning dgs-...
Page 589: Gsn Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 42 gsn configuration 42-1 42 gsn configuration 42.1 overview of gsn security solution the gsn security solution consists of the following four elements: 42.2 security policy management platform 42.3 security agent 42.4 restore system 42.5 security switch 4...
Page 590
Chapter 42 gsn configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 42-2 when the security agent detects that its own security policy does not comply with the security level set by the management platform, the security agent will immediately upload its own security log to the security policy management...
Page 592
Chapter 42 gsn configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 42-4 command description [no] security address-bind enable enable the address binding policy note this function takes effect only when the global gsn support is enabled and the configured port is an authentication port. In addition, wh...
Page 593
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 42 gsn configuration 42-5 gsn, you should not enable any other functions that may consume hardware entries as far as possible when you enable gsn. 42.9.2 functions in conflict with the gsn due to the features of gsn application, the gsn is in conflict with...
Page 595: Dynamic Arp Inspection
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 43 dynamic arp inspection configuration 43-1 43 dynamic arp inspection configuration 43.1 understanding dai dai, an acronym of dynamic arp inspection, refers to validity inspection of received arp packets. Illegal arp packets will be discarded. 43.1.1 unde...
Page 596
Chapter 43 dynamic arp inspection configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 43-2 buffer using ipa and maca, and sends an arp response. Upon receiving this response, device a updates its arp buffer using ipb and macb. With this model, device c can mistake the corresponding relationship of arp...
Page 597
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 43 dynamic arp inspection configuration 43-3 43.1.4 interface trust status and network security arp packets are checked according to the trust status of each port on the device. Dai check is ignored for the packets that are received through trusted ports a...
Page 598
Chapter 43 dynamic arp inspection configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 43-4 43.2.1 enabling global dai function this feature is disabled by default. Dai-related security check will be performed for arp packets only when the global dai function is enabled. If this global switch is enable...
Page 599
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 43 dynamic arp inspection configuration 43-5 to set the trust status of a port, execute the following commands in the interface configuration mode: command function dgs-3610(config-if)# ip arp inspection trust set the port as a trusted port dgs-3610(config...
Page 600
Chapter 43 dynamic arp inspection configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 43-6 43.3 showing dai configuration 43.3.1 showing dai enabling status of vlan to show the enabling status of vlan, execute the following command in the global configuration mode: command function dgs-3610(config)# s...
Page 601
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 44 access control list configuration 44-1 44 access control list configuration 44.1 overview as part of the gsn security solution, dgs-3610 series uses access control lists to provide a powerful data flow filtering function. At present, dgs-3610 series sup...
Page 602
Chapter 44 access control list configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 44-2 44.1.2 why to configure access lists there are many reasons why we need configure access lists, shown as follows: restrict route updating: control the places of sending and receiving the route updating information....
Page 603
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 44 access control list configuration 44-3 access lists are usually configured in the following locations of network devices: devices between the internal network and external network (such as the internet) devices at the borders of two parts in a network d...
Page 604
Chapter 44 access control list configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 44-4 of a packet and the source port field of udp. In this way, these two aces use different filtering domain templates. Rules refer to the values of the ace filtering domain template. For example, one ace is: permit tc...
Page 605
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 44 access control list configuration 44-5 address is not in the ip range of the svi-associated subnet. Suppose the ip address of vlan 1 is 192.168.64.1 255.255.255.0, ace is set to deny udp any 192.168.65.1 0.0.0.255 eq 255 , and an ip extended acl is crea...
Page 606
Chapter 44 access control list configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 44-6 44.2.1.1 implicating “deny any data flow” rule statement the ending part of each access list implicates a ―deny any data flow‖ rule statement. Therefore, if a packet matches no rule, it is denied. As shown in the f...
Page 608
Chapter 44 access control list configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 44-8 44.2.4 ip access list example configuration requirements: there are two devices switch a and switch b, as shown in figure 45-3: figure 44-3 basic access list example unix host pc to implement the following security...
Page 609
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 44 access control list configuration 44-9 dgs-3610(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 any eq telnet time-range check dgs-3610(config)# access-list 101 deny icmp 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 any dgs-3610(config)# access-list 101 deny ip 2....
Page 610
Chapter 44 access control list configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 44-10 the mac extended access list (number 700 – 799) forwards or blocks the packets based on the source and destination mac addresses, and can also match the ethernet protocol type. A single mac access list can use mul...
Page 611
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 44 access control list configuration 44-11 note method 1 only configures the numerical value acl. Method 2 can configure names and numerical value acl and specify the priorities of table entries (supporting priority ace products). 44.3.3 configuration of s...
Page 612
Chapter 44 access control list configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 44-12 44.4 configuring expert extended access list to configure expert extended access lists on a device, you must specify unique names or numbers for the access lists of a protocol to uniquely identifying each access l...
Page 616
Chapter 44 access control list configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 44-16 44.6 configuring access list acl80 the acl80 is also called the user-defined access list, which means matching the first 80 bytes of a packet for filtering. A packet consists of a series of byte flows. The acl80 e...
Page 617
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 44 access control list configuration 44-17 letter meaning offset letter meaning offset d vlan tag field 14 r source ip address 38 e dsap (destination service access point) field 18 s destination ip address 42 f ssap (source service access point) field 19 t...
Page 618
Chapter 44 access control list configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 44-18 deeff ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff 54 configuration of the second ace fails because the 16 bytes are occupied by the first ace. To configure for the second ace, you must delete the first one. 44.7 configuring ...
Page 619
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 44 access control list configuration 44-19 dgs-3610# configure terminal dgs-3610(config)# 3. Enter the acl configuration mode. Dgs-3610(config)# ip access-list extended test-tcp-flag dgs-3610(config-ext-nacl)# 4. Add an acl entry dgs-3610(config-ext-nacl)#...
Page 620
Chapter 44 access control list configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 44-20 the ace numbers are as follows after ip access-list resequence tst_acl 100 3 is run: dgs-3610(config)# ip access-list resequence tst_acl 100 3 ace1: 100 ace2: 103 ace3: 106 when adding ace4 without entering sn-num...
Page 621
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 44 access control list configuration 44-21 command function dgs-3610(config-time-range)# absolute [start time date] end time date set the absolute time range (optional). For details, see the configuration guide of time-range. Dgs-3610(config-time-range)# p...
Page 622
Chapter 44 access control list configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 44-22 44.10 configuration examples 44.10.1 configuring tcp one-way connection the one-way acl function can be enabled through the configuration of tcp flag filtering 44.10.1.1 configuration requirements to ensure the se...
Page 623
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 44 access control list configuration 44-23 # permit other ip packets dgs-3610(config-ext-nacl)# permit ip any any 2) applying the acl to the interface # exit the acl mode. Dgs-3610(config-ext-nacl)# exit # enter the application of the interface g3/2 dgs-36...
Page 625: Qos Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 45 qos configuration 45-1 45 qos configuration 45.1 qos overview the fast development of the internet results in more and more demands for multimedia streams. Generally, people have different service quality requirements for different multimedia, which req...
Page 626
Chapter 45 qos configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 45-2 carried by the first 3 bits in the tag control information of 802.1q frame header, which contains the priority information of one of the 8 categories. These three bits are generally called user priority bits. Carried by the first ...
Page 627
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 45 qos configuration 45-3 note the above criteria take effect only when the qos trust mode of the port is enabled. Enabling the qos trust mode of a port does not mean getting the qos information directly from the packet or the input port of the packet with...
Page 628
Chapter 45 qos configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 45-4 45.1.2.2 policing the policing action happens after the data classifying is completed. It is used to constrain the transmission bandwidth occupied by the classified dataflow. The policing action will check every packet in the clas...
Page 629
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 45 qos configuration 45-5 45.2 configuring qos 45.2.1 default qos configuration make clear the following points of qos before configuration: one interface can be associated with at most one policy-map. One policy-map can have multiple class-maps. One class...
Page 630
Chapter 45 qos configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 45-6 45.2.2 configuring the qos trust mode of the interface by default, the qos trust mode of an interface is disabled. Command description configure terminal enter the configuration mode interface interface enter the interface configu...
Page 631
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 45 qos configuration 45-7 default cos: trust dscp default cos: 6 dgs-3610# 45.2.4 configuring class maps you may create and configure class maps through the following steps: command description configure terminal enter the configuration mode ip access-list...
Page 632
Chapter 45 qos configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 45-8 command description configure terminal enter the configuration mode [no] policy-map policy-map-name create and enter into the policymap configuration mode, where policy-map-name is the name of the policymap to be created. The no o...
Page 635
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 45 qos configuration 45-11 45.2.9 configuring cos-map you may set cos-map to select the queue the output packets enter. The default value of cos-map is provided in the default qos configuration section. Command description configure terminal enter the conf...
Page 636
Chapter 45 qos configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 45-12 45.2.10 configuring cos-to-dscp map cos-to-dscp map is used to map the cos value of a packet to internal dscp value. You may follow these steps to set cos-to-dscp map. The default value of cos-to-dscp is provided in the default q...
Page 637
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 45 qos configuration 45-13 dgs-3610# configure terminal dgs-3610(config)# mls qos map dscp-cos 0 32 56 to 6 dgs-3610(config)# show mls qos maps dscp-cos dscp cos dscp cos dscp cos dscp cos ---- --- ---- --- ---- --- ---- --- 0 6 1 0 2 0 3 0 4 0 5 0 6 0 7 0...
Page 638
Chapter 45 qos configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 45-14 command description configure terminal enter the configuration mode mls qos map ip-prec-dscp dscp1...Dscp8 modify the setting of ip-precedence-to-dscp map, where dscp1...Dscp8 are the dscp values corresponding to ip-precedence va...
Page 639
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 45 qos configuration 45-15 45.3.2 showing policy-map you may show the contents of policy-map through the following steps: command description show policy-map [policy-name [class class-name]] show qos policy map, policy-nam e is the selected name of policy ...
Page 640
Chapter 45 qos configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 45-16 cos-queue map: cos qid --- --- 0 1 1 2 2 1 3 4 4 1 5 1 6 1 7 1 wrr bandwidth weights: qid weights --- ------- 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 45.3.5 showing mls qos scheduler you may show the qos scheduling method through the fol...
Page 641
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 45 qos configuration 45-17 --- ---- 0 0 1 8 2 16 3 24 4 32 5 40 6 48 7 56 dgs-3610# show mls qos maps dscp-cos dscp cos dscp cos dscp cos dscp cos ---- --- ---- --- ---- --- ---- --- 0 6 1 0 2 0 3 0 4 0 5 0 6 0 7 0 8 1 9 1 10 1 11 1 12 1 13 1 14 1 15 1 16 ...
Page 642
Chapter 45 qos configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 45-18 45.3.8 showing policy-map interface you can show the configuratiom of port policymap through following steps command function show policy-map interface interface] showing the configuration of (port) policymap dgs-3610# show polic...
Page 643: Vrrp Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 46 vrrp configuration 46-1 46 vrrp configuration 46.1 overview the virtual router redundancy protocol (vrrp) is designed to work in the active/standby mode to ensure that the function switching can be implemented without affecting internal and external dat...
Page 644
Chapter 46 vrrp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 46-2 than one device within the group becomes master, repeat the preempt process in step 1. In this process, the device with the maximum priority will be selected as the master device to execute the vrrp backup function. Figure 46-1 v...
Page 645
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 46 vrrp configuration 46-3 46.2.1 route redundancy the basic vrrp applications are illustrated in figure 47-2. Figure 46-2 basic vrrp applications as shown in figure 47-2, devices a, b and c are connected with the lan through ethernet interfaces, on which ...
Page 646
Chapter 46 vrrp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 46-4 as shown in figure 47-3, two virtual devices are set. For virtual device 1, device a uses the ip address 192.168.12.1 of ethernet interface fa0/0 as the ip address of the virtual device, and thus device a becomes the master devic...
Page 647
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 46 vrrp configuration 46-5 parameter is not used, the ip address set here will become the master ip address of the virtual router. Note if the virtual ip address (primary or secondary) of the vrrp group is the same as the ip address (primary or secondary) ...
Page 648
Chapter 46 vrrp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 46-6 if the current device becomes the master in the vrrp group, it will notify its vrrp status, priority and more information by sending vrrp advertisements in the set interval. By default, this interval is 1 second. Note when the vr...
Page 649
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 46 vrrp configuration 46-7 matter whether the vrrp group in the preemption mode, the corresponding vrrp group will be in the master status automatically (as long as the corresponding ethernet interface is available). 46.3.7 setting a monitored interface fo...
Page 650
Chapter 46 vrrp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 46-8 note in case the advertisement interval in the vrrp advertisement received by the vrrp backup device is inconsistent with the advertisement interval configured locally, the vrrp backup device discards the vrrp advertisement if th...
Page 651
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 46 vrrp configuration 46-9 command purpose dgs-3610# show vrrp interface type number [brief] show the vrrp status of the specified network interface here are some examples of the command: 1. Show vrrp dgs-3610# show vrrp gigabitethernet 0/1 - group 1 state...
Page 652
Chapter 46 vrrp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 46-10 dgs-3610# show vrrp interface gigabitethernet 0/0 gigabitethernet 0/0 - group 1 state is backup virtual ip address is 192.168.201.1 configured virtual mac address is 0000.5e00.0101 advertisement interval is 3 sec preemption is e...
Page 653
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 46 vrrp configuration 46-11 here are some examples of the command: 1. Debug vrrp command dgs-3610# debug vrrp dgs-3610# vrrp: grp 1 advertisement priority 120, ipaddr 192.168.201.213 vrrp: grp 1 event - advert higher or equal priority %vrrp-6-statechange: ...
Page 654
Chapter 46 vrrp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 46-12 the above displayed information indicates the vrrp advertisement is received from 192.168.201.213 for vrrp group 1, whose priority is 120. 5. Debug vrrp state command dgs-3610# debug vrrp state vrrp state debugging is on dgs-361...
Page 655
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 46 vrrp configuration 46-13 ! ! Hostname "r3" ! ! ! Interface fastethernet 0/0 no switchport ip address 192.168.12.217 255.255.255.0 ! Interface gigabitethernet 1/1 no switchport ip address 60.154.101.5 255.255.255.0 ! Interface gigabitethernet 2/1 no swit...
Page 656
Chapter 46 vrrp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 46-14 vrrp 1 timers advertise 3 vrrp 1 ip 192.168.201.1 ! Interface gigabitethernet 2/1 no switchport ip address 202.101.90.63 255.255.255.0 ! Router ospf network 202.101.90.0 0.0.0.255 area 10 network 192.168.201.0 0.0.0.255 area 10 ...
Page 657
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 46 vrrp configuration 46-15 failure, device r2 takes its place to function as the gateway (which is just the virtual device address 192.168.201.1). Especially, when the wan interface gigabitethernet 2/1 of device r1 is unavailable, device r1 will decrease ...
Page 658
Chapter 46 vrrp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 46-16 network 60.154.101.0 0.0.0.255 area 10 network 192.168.201.0 0.0.0.255 area 10 ! ! End as shown above, devices r1 and r2 are in the same vrrp backup group 1, use the same vrrp backup group authentication mode (no authentication)...
Page 659
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 46 vrrp configuration 46-17 interface gigabitethernet 2/1 no switchport ip address 202.101.90.63 255.255.255.0 ! Router ospf network 202.101.90.0 0.0.0.255 area 10 network 192.168.201.0 0.0.0.255 area 10 ! ! End configurations on device r2: ! ! Hostname "r...
Page 660
Chapter 46 vrrp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 46-18 analysis: ensure that at least one router in the backup group is active. If it is possible to ping the virtual ip address from other network devices, the causes may be the vrrp status changing needs some time (although brief). E...
Page 661: Rldp Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 47 rldp configuration 47-1 47 rldp configuration 47.1 about rldp 47.1.1 understanding rldp the rapid link detection protocol (rldp) is one of d-link's proprietary link protocol designed to detect ethernet link fault quickly. General ethernet link detection...
Page 662
Chapter 47 rldp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 47-2 able to receive the echo packet of the neighbor port as well as the probe packet of the neighbor port. Otherwise, the link is considered abnormal. Note to make use of the one-way detection and two-way detection functions of the r...
Page 663
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 47 rldp configuration 47-3 one-way link detection: figure 47-3 one-way link detection the so-called one-way link detection means the link connected with the port can receive packet only or send packets only (due to misconnection of the optical receiving li...
Page 664
Chapter 47 rldp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 47-4 this means that a fault occurs at the frame transmission/receiving at both ends of the link. As shown above, the port of the device sends the rldp probe packet but has never received the echo packet or the probe packet from the n...
Page 665
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 47 rldp configuration 47-5 47.2.2 configuring global rldp the port rldp works only when the global rldp is enabled. In the global configuration mode, follow these steps to enable rldp: command function dgs-3610(config)# rldp enable turn on the global rldp ...
Page 666
Chapter 47 rldp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 47-6 unidirection detect information: action : shutdown svi state : normal bidirection detect information : action : warnning state : normal loop detect information : action : block state : normal several precautions in configuring po...
Page 667
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 47 rldp configuration 47-7 command function dgs-3610(config)# rldp detect-interval interval configure the detection interval within the range 2-15s, 3s by default. Dgs-3610(config)# end return to the privileged mode. The no option of the command restores d...
Page 668
Chapter 47 rldp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 47-8 note the errdisable recover command can be used in the global configuration mode to restart, instantly or at fixed time, the rldp detection of the port that is set as the violation port by rlp. 47.3 viewing rldp information the f...
Page 669
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 47 rldp configuration 47-9 as shown above, port gigabitethernet 0/1 is configured with unidirection detection. No error is detected now, and the port status is normal. Port gigabitethernet 0/24 is configured with bidirection detection, and bidirection faul...
Page 671: Tpp Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 48 tpp configuration 48-1 48 tpp configuration 48.1 tpp overview the topology protection protocol (tpp) is a topology stability protection protocol. The network topology is rather fragile. Illegal attacks in the network may cause abnormal cpu utilization o...
Page 672
Chapter 48 tpp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 48-2 figure 48-1 as shown in the above dual-core topology, a and b are the l3 convergence devices, and c and d are the l2 access devices. A is the mstp root bridge. The topology protection functions of all the devices are enabled. The ...
Page 673
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 48 tpp configuration 48-3 note the topology protection function is suitable for the point-to-point link network, and adjacent network devices must enable the topology protection function. Besides, during the tpp configuration, you often need to use cpu top...
Page 674
Chapter 48 tpp configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 48-4 command function dgs-3610(config-if)# end exit to the privileged mode. The no tp-guard port enable command disables the topology protection on the port. This command is suitable only on layer-2 switching ports and routing ports.It...
Page 675
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 48 tpp configuration 48-5 the global topology protection function is enabled on a, b, c, d, and e, and the topology protection function is enabled on all the ports.. 48.5 viewing tpp information the following tpp-related information can be viewed: view the...
Page 677: File System Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 49 file system configuration 49-1 49 file system configuration 49.1 overview the file system is an organization for storing and managing the files on the auxiliary storage devices. The switch provides the serial flash as the auxiliary storage device to sto...
Page 678
Chapter 49 file system configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 49-2 49.2.2 changing directories it means the shifts from the current director to the specified directory. In the privileged mode, use this command through the following steps: command function dgs-3610# cd directroy enter the ...
Page 679
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 49 file system configuration 49-3 dgs-3610# dir dgs-3610# dir ../bak 49.2.5 formating the system in the privileged user mode, format the device managed and operated by the file system through the following command: command function dgs-3610# makefs dev dev...
Page 680
Chapter 49 file system configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 49-4 49.2.9 removing files in the privileged user mode, delete a file permanently through the following step: command function dgs-3610# del filename delete the specified file. The following example deletes the temporary file n...
Page 681: Log Configuration
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 50 log configuration 50-1 50 log configuration 50.1 overview during the operation of a device, various state changes occur such as the link status up/down, and various events occur such as receiving abnormal packets and handling exceptions. Our product pro...
Page 682
Chapter 50 log configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 50-2 50.2 log configuration 50.2.1 log switch the log switch is turned on by default. If it is turned off, the device will not print log information in the user window, or send log information to the syslog server, or record the log in...
Page 683
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 50 log configuration 50-3 terminal monitorallows log information to be displayed on the current vty (such as the telnet window). Logging hostspecifies the address of the syslog server that will receive the log information. Our product allows the configurat...
Page 684
Chapter 50 log configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 50-4 50.2.4 enabling switches in log system by default, the system name is not included in the log information. To add or remove the system name in the log information, perform the following commands in the global configuration mode. C...
Page 685
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 50 log configuration 50-5 command function dgs-3610(config)# logging console level set the level of log information allowed to be displayed on the console dgs-3610(config)# logging monitor level set the level of log information allowed to be displayed on t...
Page 686
Chapter 50 log configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 50-6 by default, the level of the log information allowed to be displayed in the vty window is set to 7. By default, the level of the log information to be sent to the syslog server is set to 6. By default, the level of the log informa...
Page 687
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 50 log configuration 50-7 14 log alert 15 clock daemon 16 local use 0 (local0) 17 local use 1 (local1) 18 local use 2 (local2) 19 local use 3 (local3) 20 local use 4 (local4) 21 local use 5 (local5) 22 local use 6 (local6) 23 local use 7 (local7) the defau...
Page 688
Chapter 50 log configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 50-8 50.3 log monitoring to monitor log information, run the following commands in the privileged user mode: command function dgs-3610# show logging view the log packets in memory buffer as well as the statistical information of logs d...
Page 689: Poe Management
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 51 poe management configuration 51-1 51 poe management configuration 51.1 overview poe (power over ethernet) is a mechanism that provides 45v~-57v dc to the remote pd devices (ip phone, wlan ap and network camera) via twisted pair cables. The pse (power so...
Page 690
Chapter 51 poe management configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 51-2 51.2.1 remote power supply configuration the switch supporting poe can automatically detect whether the device connected to a port is a standard pd device and provide supply power to the standard pd device. You can enab...
Page 691
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 51 poe management configuration 51-3 show run verify the configuration of the steps above copy running-config startup-config save the settings into the parameter file. For example, enable/disable the poe of interface 1 on line card 1: dgs-3610# dgs-3610# c...
Page 692
Chapter 51 poe management configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 51-4 51.2.4 setting the maximum allowed voltage of the poe system the ethernet interface of the switch supporting poe can provide the maximum allowed voltage of 57v. You can set the maximum allowed voltage according to the a...
Page 693
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 51 poe management configuration 51-5 in the auto mode, the power is allocated according to the detected port pd type. In the auto mode, the equipment allocates power to classes 1~3 pd devices as follows: class1~4w, class2~7w, lass3~15.4w and class0~15.4w. ...
Page 694
Chapter 51 poe management configuration dgs-3610 series configuration guide 51-6 command description show poe interfaces gigabitethernet [interface-id] show the power supply status of the specified port show poe interfaces show the power supply status of all poe ports (the 24 ports that the poe syst...
Page 695
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 51 poe management configuration 51-7 the remote power supply of s7600p-48gt is pse. The following exmaple shows the power status of the poe system of s7600 products: external power mangement: auto external pse total power: 1200.0 w external pse total power...
Page 697: Stack Management
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 52 stack management 52-1 52 stack management 52.1 understanding stack 52.1.1 overview the stack technology is for centralized management and port expansion. You can connect multiple separate switches into a centralized stack system by using stack ports and...
Page 698
52-2 52.1.3 starting and stopping a stack if no stack module is inserted in the slot of a switch in the start process, the switch works in the standalone mode. If a stack module is inserted, the switch detects whether the stack link is connected. If yes, the switch works in the stack mode. If the sw...
Page 699
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 52 stack management 52-3 attribute default value device description switch 52.2.2 identifying stack member device according to the device number the host in the stack system is selected according to device priorities. The one with the highest priority is s...
Page 700
52-4 caution after configuration is completed, you need to execute the write command to save it. After the stack is reset, the priority takes effect only after a new stack system is established. 52.2.4 configuring device description for easier memory, you can set a description for a stack member. In...
Page 701
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 52 stack management 52-5 command description dgs-3610# show member [member] show the stack information of the member device. Member: 1-max, configuring the specified member device. Note the display information of partial examples in this manual may include...
Page 702
52-6 7 2 1 1 dem-412cx 8 0 48 48 dgs-3610-52_static_module 8 1 1 1 dem-412cx 8 2 1 1 dem-412cx dgs-3610#show version system description : dgs-3610-26 gigabit ethernet switch system start time : 2007-4-23 17:39:11 system hardware version : 1.0 system software version : v10.2.00(2), release(39975) sys...
Page 703
Dgs-3610 series configuration guide chapter 52 stack management 52-7 software version : v10.2.00(2), release(39975) boot version : 10.1.11330 ctrl version : 10.1.11330 serial number : 1234942570007 device-8 hardware version : 1.0 software version : v10.2.00(2), release(39975) boot version : 10.1.113...