- DL manuals
- Echelon
- Network Router
- 14315R
- User Manual
Echelon 14315R User Manual
Summary of 14315R
Page 1
L on w orks ® router user’s guide 078-0018-01e.
Page 2
Echelon, lonmaker, l on m ark , lontalk, l on w orks , neuron, nodebuilder, 3120, 3150, and the echelon logo are trademarks of echelon corporation registered in the united states and other countries. Lonscanner and 3170 are trademarks of the echelon corporation. Other brand and product names are tra...
Page 3: Welcome
Welcome a l on w orks ® router connects two communications channels within a l on w orks network, and routes lontalk ® messages between them. Using a l on w orks router supports the installation of small or large networks, with dozens to thousands of nodes. This document describes how to design and ...
Page 4: Getting Support
Iv • lonmark ® application layer interoperability guidelines. This manual describes design guidelines for developing applications for open interoperable l on w orks devices, and is available from the lonmark web site, www.Lonmark.Org . • lonworks ftt-10a free topology transceiver user's guide (078-0...
Page 5: Fcc Notice
Fcc notice the rtr-10 router core module is designed to comply with the limits for a class b digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. The router 5000 chip is designed to comply with fcc part 15 subpart b and en 55022 level b. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection ag...
Page 7: Table Of Contents
Table of contents welcome ......................................................................................................... Iii audience ........................................................................................................ Iii related documentation ...........................
Page 8
Viii chapter 3. Lonworks router mechanical interfaces............................. 39 rtr-10 mechanical description ................................................................. 40 router 5000 mechanical description .......................................................... 42 chapter 4. Develop...
Page 9
Appendix a. Communications parameters for lonworks routers .... 81 communications parameters ...................................................................... 82.
Page 11
Lonworks router user’s guide 1 1 introduction to lonworks routers this chapter describes the router theory of operation, including router types, lontalk protocol support for routers, and router use of message buffers..
Page 12: Introduction
2 introduction to lonworks routers introduction in general terms, a router is a device that forwards data packets between communications networks. The router connects to the data lines from each network, and reads address information in each data packet to determine the packet’s destination. A l on ...
Page 13: Lonworks Router Products
Lonworks router user’s guide 3 network where the devices are subject to frequent physical relocation, or if cable installation is difficult. For each of these cases, you use a router to connect the dissimilar l on w orks channels. • enhance the reliability of the l on w orks network. The two channel...
Page 14
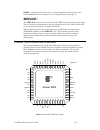
4 introduction to lonworks routers • rtr-10 router core module (model: 61000r) a compact module used by oems to build l on w orks routers. The rtr- 10 consists of the core electronics and firmware needed to implement a router. • router 5000 (model: 14315r) a semiconductor product used by oems to bui...
Page 15
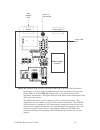
Lonworks router user’s guide 5 figure 2. Block diagram of a lonworks router based on the rtr-10 as the figure shows, an rtr-10 router and two transceiver modules (one to handle each of two channels connected by the router) can be mounted on a motherboard, along with a single power supply and two net...
Page 16
6 introduction to lonworks routers any pair of channel types can be connected by a router by selecting the appropriate pair of transceivers. The rtr-10 router is compatible with all l on w orks transceivers, including standard transceivers for free topology, link power, twisted pair, and power line....
Page 17
Lonworks router user’s guide 7 these external transceivers can run at interface bit rates from 9.8 kbps to 1.25 mbps. A complete router, using the router 5000, consists of two router 5000 half routers, two transceivers, and a motherboard to connect the two half routers, as shown in figure 3. Figure ...
Page 18: Router Types
8 introduction to lonworks routers router types a l on w orks router can use one of four routing algorithms: configured router, learning router, bridge, and repeater. This selection allows you to trade system performance for ease of installation. The configured router and learning router algorithms ...
Page 19
Lonworks router user’s guide 9 a forwarding table is used for each domain on each side of the router. Each forwarding table contains a forwarding flag for each of the 255 subnets and 255 groups in a domain. As shown in figure 4 and figure 5, these flags determine whether or not a message should be f...
Page 20
10 introduction to lonworks routers forwarding is disabled) in the subnet forwarding table. The forwarding flag for the destination address is then checked to determine whether the message should be forwarded or dropped. The forwarding flags are all cleared whenever the router is reset, so the learn...
Page 21: Loop Topology
Lonworks router user’s guide 11 figure 5. Configured and learning router forwarding rules, part 2 as with configured routers, learning routers sometimes modify source addresses for service-pin messages to help prevent message loops. Learning routers, in general, are less efficient in using channel b...
Page 22: Power Line Routers
12 introduction to lonworks routers by router 1 to channel b, then the same message could be forwarded by router 2 back to channel a, starting an endless loop of forwarded messages. Figure 6. Looping topology the lontalk protocol does not support topologies where loops can occur. However, looping to...
Page 23: Message Buffers
Lonworks router user’s guide 13 figure 7. A looping topology with one router routers can be used between power line channels only if the two channels are fully isolated. Such isolation is generally not the case between two phases on the same circuit, but can be the case between phases on different d...
Page 24
14 introduction to lonworks routers forwarded to the transmitting side of the router, priority messages have their own outgoing buffer queue. Thus, priority processing of these outgoing messages is assured because the transmitting side will send messages from the priority output buffer queue before ...
Page 25
Lonworks router user’s guide 15 must be increased, and the count of nonpriority buffers decreased. See chapter 8 of the neuron c programmer’s guide to understand how the network buffer sizes are calculated. See chapter 7, network management messages, on page 71, for a description of how to change th...
Page 26: Router Performance
16 introduction to lonworks routers message. See configuring a router 5000 half-router on page 53 and the example neuron c code in example neuron c source on page 56, for a description of how to change the size and count of buffers. You can also use the nodeutil node utility, which you can download ...
Page 27: Lonworks Router Electrical
Lonworks router user’s guide 17 2 lonworks router electrical interfaces this chapter provides an overview of the electrical interfaces for the rtr-10 router core module and the router 5000 chip..
Page 28: Overview
18 lonworks router electrical interfaces overview this chapter describes the electrical interface and power requirements for a l on w orks router. Electrical interface the following sections describe the electrical interface for a l on w orks router, including detailed descriptions of each of the rt...
Page 29
Lonworks router user’s guide 19 pin name pin description pin number asvc~ a-side service output 12 axid0 a-side transceiver id 0 (lsb) 20 axid1 a-side transceiver id 1 18 axid2 a-side transceiver id 2 17 axid3 a-side transceiver id 3 16 axid4 a-side transceiver id 4 (msb) 15 bclk1 b-side input clock...
Page 30: Aclk2, Bclk1, And Bclk2
20 lonworks router electrical interfaces aclk2, bclk1, and bclk2 a 10 mhz crystal is provided for side a of the rtr-10 router, which can run at only 10 mhz. This clock rate allows side a to be used with transceivers running at interface bit rates from 9.8 kbps to 1.25 mbps. The 10 mhz clock is outpu...
Page 31
Lonworks router user’s guide 21 reinitialization allows a network services tool to change parameters, such as the number of priority slots, without the new values’ being overwritten by the rtr- 10 firmware. Table 5. Rtr-10 router transceiver ids id name media bit rate (bps) input clock 01 (0x01) tp/...
Page 32: Pkt
22 lonworks router electrical interfaces see appendix a, communications parameters for lonworks routers, on page 81, for a listing of the communications parameters for each transceiver type. Pkt the pkt output can be used as a network activity indicator. When packets are passed between the router si...
Page 33: Service~
Lonworks router user’s guide 23 reset~ signal must be driven low by a low voltage protection circuit on the router motherboard as described in low voltage protection on page 37. Service~ the service~ input drives both sides of the rtr-10 router from a single input. You can connect a pushbutton to th...
Page 34
24 lonworks router electrical interfaces table 6 lists the pin assignments for the router 5000 chip. All digital inputs are low-voltage transistor-transistor logic (lvttl) compatible, 5 v tolerant, with low leakage. All digital outputs are slew-rate limited to reduce electromagnetic interference (em...
Page 35
Lonworks router user’s guide 25 name pin number type description rst~ 28 digital i/o reset (active low) vin3v3 29 power 3.3 v power input vdd3v3 30 power 3.3 v power avdd3v3 31 power 3.3 v power cp0 32 comm cp0: receive serial data agnd 33 ground ground cp1 34 comm cp1: transmit serial data nc 35 n/...
Page 36
26 lonworks router electrical interfaces multipliers greater than one, the chip uses a phase-locked loop (pll) to drive and manage the internal on-chip system clock frequency. A router 5000 chip requires a 10.0 mhz external clock signal for operation. An example part that meets the requirements for ...
Page 37: Cp[4..0]
Lonworks router user’s guide 27 important: because the router 5000 a side xout pin drives an input buffer, the values of the external capacitors are not equal. The value for a side xout is specified as 30 pf based on an internal input capacitance of 4.5 pf of the xin/xout pins and internal input cap...
Page 38: Io[11..0]
28 lonworks router electrical interfaces the communications port for the router 5000 is configured to operate in single- ended mode. Table 7 lists the pin assignments for the communications port pins. Table 7. Communications port pin assignments pin drive current single-ended mode (3.3 v) connect to...
Page 39: Trst~)
Lonworks router user’s guide 29 figure 14. Digital io pin connections important: when routing the io[11..0] signals between the two router halves of your router 5000 device, keep the traces as short as possible. See the series 5000 chip data book for more information about the digital i/o pins for a...
Page 40: Scl, And Sda_Cs1~)
30 lonworks router electrical interfaces memory interface (cs0~, miso, mosi, sck, scl, and sda_cs1~) the interface for accessing off-chip non-volatile memory (nvm) is a serial interface that follows either of the following protocols: serial inter-integrated circuit (i 2 c) or serial peripheral inter...
Page 41
Lonworks router user’s guide 31 • traps in some cases it is desirable to use the input capability of the rst~ pin to allow other devices to reset the router 5000. Examples of external devices that can be used for this purpose include push button switches, microcontrollers, and external low-voltage d...
Page 42: Svc~
32 lonworks router electrical interfaces figure 15. Reset circuit – router 5000 for both halves typical applications do not require debounce conditioning of a momentary pushbutton attached to the rst~ pin. The software response time associated with this input is long enough to effectively provide a ...
Page 43
Lonworks router user’s guide 33 to transmit a network management message containing its unique 48-bit neuron id and the application’s program id. This information can then be used by a network management tool to install and configure the router. Table 8 on page 34 lists the state of the service led ...
Page 44: Network Activity Indicator
34 lonworks router electrical interfaces table 8. Service led behavior during different states device state state code service led applicationless and unconfigured 3 on unconfigured (but with an application) 2 flashing configured, hard offline 6 off configured 4 off defective external memory — on th...
Page 45: Power Requirements
Lonworks router user’s guide 35 figure 17. Rx and tx network activity indicator circuits when packets are transmitted, the tx network activity led is active for the duration of the entire data transmission. When packets are received, the rx network activity led is active for each bit received, and i...
Page 46
36 lonworks router electrical interfaces the supply current requirements for the router 5000 chip are outlined in table 9, including typical requirements for the different operating states of the router 5000 at various system clock rates. Important: although general series 5000 chips support 80 mhz ...
Page 47: Low Voltage Protection
Lonworks router user’s guide 37 low voltage protection for a rtr-10 design, it is necessary to include a low voltage protection circuit on the router motherboard to drive the reset~ line of the rtr-10 router. See section 9.4 of the neuron chip data book. Failure to include such protection may cause ...
Page 49: Lonworks Router Mechanical
Lonworks router user’s guide 39 3 lonworks router mechanical interfaces this chapter provides an overview of the mechanical interfaces for the rtr-10 router core module and the router 5000 chip..
Page 50
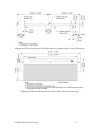
40 lonworks router mechanical interfaces rtr-10 mechanical description the rtr-10 router core module consists of a 67 mm by 23 mm by 7 mm (2.65 in by 0.9 in by 0.3 in) module with the core electronics and firmware required to implement a router. The rtr-10 is attached to a motherboard, using a 40- p...
Page 51
Lonworks router user’s guide 41 figure 19. Rtr-10 recommended pcb hole pattern (component side, vertical mounting) figure 20. Rtr-10 pcb footprint (component side, horizontal mounting).
Page 52
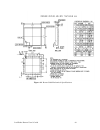
42 lonworks router mechanical interfaces figure 21. Rtr-10 recommended pcb hole pattern (component side, horizontal mounting) decisions about component placement on the motherboard must consider electromagnetic interference (emi) and electrostatic discharge (esd) issues; see chapter 5, lonworks rout...
Page 53
Lonworks router user’s guide 43 figure 22. Router 5000 mechanical specifications.
Page 55: Developing A Lonworks Router
Lonworks router user’s guide 45 4 developing a lonworks router this chapter describes the process of developing a router based on the rtr-10 router core module or the router 5000 chip..
Page 56
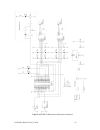
46 developing a lonworks router developing a router with the rtr-10 to create a l on w orks router with the rtr-10, perform the following steps: 1. Build a router motherboard according to the specifications described in chapter 2, lonworks router electrical interfaces, on page 17, and the guidelines...
Page 57
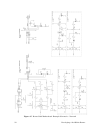
Lonworks router user’s guide 47 figure 23. Rtr-10 motherboard example schematic.
Page 58
48 developing a lonworks router using predefined transceivers the rtr-10 router includes built-in transceiver parameters for the transceivers listed in table 5 on page 21. When using any of these transceivers, the communications parameters are automatically programmed, as described in chapter 2, lon...
Page 59
Lonworks router user’s guide 49 installation procedures for the lonmaker integration tool are described in chapter 6, installing a lonworks router, on page 65. The preceding four steps complete the configuration when a single custom transceiver is used. Proceed with the following steps if two custom...
Page 60
50 developing a lonworks router 4. Install the router on a network as described in chapter 6, installing a lonworks router, on page 65. The network could be a development network for initial testing, a manufacturing network for configuration during manufacture, or a production network for field inst...
Page 61
Lonworks router user’s guide 51 figure 26. Router 5000 motherboard example schematic – core.
Page 62
52 developing a lonworks router figure 27. Router 5000 motherboard example schematic – network.
Page 63
Lonworks router user’s guide 53 configuring a router 5000 half-router before programming, a router 5000 uses its default communications parameters, which define a simplified single-ended mode 78 kbps channel. The default communications parameters allow you to load an application image over a 78 kbps...
Page 64
54 developing a lonworks router • platform: custom • transceiver type: (depends on router type) • neuron chip model: neuron 5000 • clock multiplier: 2 (recommended) important: if the other router-half uses a series 3100 chip, do not specify a value higher clock multiplier value than 2. You can speci...
Page 65: Buffer Configurations
Lonworks router user’s guide 55 figure 29. Example nodebuilder device template for the router 5000 you can also use this template to export a specific domain configuration (limited to domain 0) along with a receive transaction timer (typically, 768 ms) and a location string. Buffer configurations th...
Page 66: Example Neuron C Source
56 developing a lonworks router example neuron c source this section shows an example neuron c file for router 5000 development. This file primarily controls the router’s buffering, but it also contains important declarations to set up the parallel io configuration and explicit addressing. // // cop...
Page 67
Lonworks router user’s guide 57 // the transceiver id is declared here to allocate // space for it in the link. Eeprom unsigned int mip_eevars[2] = { 0x00, // m/s designation. 0x00 // txid, always last (not used). }; #pragma ignore_notused code_pad #pragma ignore_notused pios1 #pragma ignore_notused...
Page 69
Lonworks router user’s guide 59 5 lonworks router design issues this chapter examines a number of design issues, including a discussion of pcb layout, electromagnetic interference (emi), and electrostatic discharge (esd), for l on w orks routers..
Page 70: Pcb Layout Guidelines
60 lonworks router design issues pcb layout guidelines printed circuit board (pcb) layout for a router 5000 is similar to layout for a neuron 5000 processor, and should include the following general features: • star-ground configuration: arrange the various blocks of the device that directly interfa...
Page 71
Lonworks router user’s guide 61 power supply circuitry power supply connector center of star ground esd keepout area network connector tpt/xf-1250 pcb figure 30. Example pcb layout for a router 5000 with a tpt/xf-1250 transceiver in the figure, the area marked core represents the essential circuitry...
Page 72: Emi Design Issues
62 lonworks router design issues emi design issues the high-speed digital signals associated with microcontroller designs can generate unintentional electromagnetic interference (emi). High-speed voltage changes generate rf currents that can cause radiation from a product with a length of wire or pi...
Page 73
Lonworks router user’s guide 63 • most of the rf noise originates in the cpu portion of the rtr-10 router—which effectively means the entire board. Most of the rf noise originates with the router 5000 chip. • most of the emi will be radiated by the network cable and the power cable. • filtering is g...
Page 74
64 lonworks router design issues when esd hits to circuitry cannot be avoided through creepage, clearance, and ground guarding techniques (that is, at external connector pins), explicit clamping of the exposed lines is required to shunt the esd current. In general, exposed lines require diode clamps...
Page 75
Lonworks router user’s guide 65 6 installing a lonworks router this chapter describes how to install a l on w orks router..
Page 76: Introduction
66 installing a lonworks router introduction to install a l on w orks router, perform the following steps: 1. Define a network topology. 2. Physically attach the router to a l on w orks network. 3. Connect power to the router. 4. Logically install the router on the network. 5. Test the router instal...
Page 77: Connecting Power
Lonworks router user’s guide 67 proper electrical termination is essential for each twisted-pair channel. Failure to terminate the network can degrade performance, and in some cases, eliminate a device’s ability to communicate with other devices. For tp/xf and tp/rs485 channels, use the terminator c...
Page 78
68 installing a lonworks router installing the router on a network after a router is physically attached to a network, and powered-up, it must be logically installed on the network. You can install a router using a network management tool, such as the lonmaker integration tool. Alternatively, you ca...
Page 79
Lonworks router user’s guide 69 4. For configured routers, load the group and subnet routing tables on both sides of the router using the group or subnet table download network management message. There are 255 forwarding flags for subnets and 255 forwarding flags for groups on each side for each do...
Page 81: Network Management Messages
Lonworks router user’s guide 71 7 network management messages this chapter describes network management messages for l on w orks routers. These messages are used for router installation, as described in chapter 6, installing a lonworks router, on page 65..
Page 82: Introduction
72 network management messages introduction as described in chapter 6, routers are installed using network management messages. These messages are sent as explicit messages by a network management tool, such as the lonmaker integration tool. Routers respond to many of the same messages as any l on w...
Page 83: Router-Specific Messages
Lonworks router user’s guide 73 network management message request code success response failed response update domain 0x63 0x23 0x03 leave domain 0x64 0x24 0x04 update key 0x65 0x25 0x05 query domain 0x6a 0x2a 0x0a set node mode 0x6c 0x2c 0x0c read memory 0x6d 0x2d 0x0d write memory 0x6e 0x2e 0x0e ...
Page 84: Set Router Mode
74 network management messages table 13. Router-specific network management messages network management message request code success response failed response set router mode 0x74 0x34 0x14 group or subnet table clear 0x75 0x35 0x15 group or subnet table download 0x76 0x36 0x16 group forward 0x77 0x3...
Page 85: Group Forward
Lonworks router user’s guide 75 typedef enum { normal = 0, // not a temporary bridge. Init_rtr_table = 1, // copy forwarding tables from eeprom // for configured routers. // initialize forwarding tables for // learning routers. Temp_bridge = 2 // temporarily a bridge until next reset // or normal ro...
Page 86: Subnet Forward
76 network management messages eeprom flags are set, otherwise only the ram flag is set, allowing temporary forwarding for a given group. This message uses the request-response protocol. The configuration checksum in eeprom is updated if eeprom is changed. Typedef struct { unsigned unused1 : 1; unsi...
Page 87: Router Status
Lonworks router user’s guide 77 this message uses the request-response protocol. The configuration checksum in eeprom is updated if eeprom is changed. Typedef struct { unsigned unused1 : 1; unsigned domain_index : 1; unsigned unused2 : 5; unsigned ram_or_eeprom : 1; // 0 => ram, 1 => ram+eeprom unsi...
Page 88: Far Side Escape Code
78 network management messages typedef struct { algorithm type; // configured, learning, bridge, // or repeater rtr_mode mode; // temp_bridge or normal } nm_rtr_status_response; far side escape code when this message code is placed in the message, and is followed by any network management or network...
Page 89
Lonworks router user’s guide 79 mode = read_only_relative (1) offset = 0x0019; count = 1; form = both_cs_recalc (1) data = buffer_sizes; the buffer_sizes value contains two nibble fields that control the size of both the input and output buffers. The output size value also controls the priority outp...
Page 90: Count
80 network management messages typedef enum { count_1 = 0x2; count_2 = 0x3; count_3 = 0x4; count_5 = 0x5; count_7 = 0x6; count_11 = 0x7; count_15 = 0x8; count_23 = 0x9; count_31 = 0xa; count_47 = 0xb; count_63 = 0xc; } queue_count_entry; set input and non-priority buffer queue count the buffer queue...
Page 91: Lonworks Routers
Lonworks router user’s guide 81 a communications parameters for lonworks routers l on w orks routers are initially programmed with communications parameters as listed in this appendix. Parameters for l on m ark approved transceivers correspond to the parameters defined by the l on w orks interoperab...
Page 92: Communications Parameters
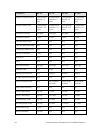
82 communications parameters for lonworks routers communications parameters table 14, table 15 on page 83, table 16 on page 85, and table 17 on page 86 together list the communications parameters for l on w orks routers. Table 14. Communications parameters, part 1 parameter tp/xf-78 tp/xf-1250 tp/ft...
Page 93
Lonworks router user’s guide 83 parameter tp/xf-78 tp/xf-1250 tp/ft-10 tp/rs485-39 alternate rate n/a n/a n/a n/a wakeup pin direction n/a n/a n/a n/a xcvr controls preamble n/a n/a n/a n/a general purpose data n/a n/a n/a n/a allow node override n/a n/a n/a n/a receive start delay 2.9 bits 14.0 bit...
Page 94
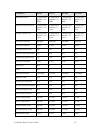
84 communications parameters for lonworks routers parameter rf-10 pl-10 pl-20c pl-20n number of priority slots configurable; default = 4 slots configurable; default = 8 slots configurable; default = 8 slots configurable; default = 8 slots average packet size configurable; default = 15 bytes configur...
Page 95
Lonworks router user’s guide 85 parameter rf-10 pl-10 pl-20c pl-20n preamble length n/a 36.7 bits 33.5 bits 33.5 bits use raw data no no no no table 16. Communications parameters, part 3 parameter pl-30 tp/rs485- 625 tp/rs485- 1250 tp/rs485-78 transceiver id 18 (0x12) 10 (0x0a) 11 (0x0b) 12 (0x0c) m...
Page 96
86 communications parameters for lonworks routers parameter pl-30 tp/rs485- 625 tp/rs485- 1250 tp/rs485-78 network bit rate 1882 bps 625 kbps 1.25 mbps 78 kbps alternate rate n/a n/a n/a n/a wakeup pin direction output n/a n/a n/a xcvr controls preamble yes n/a n/a n/a general purpose data 00 8a 00 ...
Page 97
Lonworks router user’s guide 87 parameter fo-10 dc-78 dc-625 dc-1250 minimum clock configurable; default = 10 mhz configurable; default = 10 mhz configurable; default = 10 mhz configurable; default = 10 mhz number of priority slots configurable; default = 16 slots configurable; default = 0 slots con...
Page 98
88 communications parameters for lonworks routers parameter fo-10 dc-78 dc-625 dc-1250 missed preamble 4.0 bits 0.0 bits 0.0 bits 0.0 bits preamble length n/a n/a n/a n/a use raw data no no no no.
Page 99
Www.Echelon.Com.