- DL manuals
- Fagor
- Other
- 8040 TC CNC
- Manual
Fagor 8040 TC CNC Manual
Summary of 8040 TC CNC
Page 1
R ef . 0307 (s oft t: 8. Xx ) (s oft t: 8.1 x ) 8040 cnc n ew f eatures.
Page 2: 40 Cnc
Page 2 of 2 80 40 cnc n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) (s oft t: 8.1 x ).
Page 3: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures page i of ii 80 40 cnc i ndex version 8.01 1 detected errors ..................................................................................................................1 2 the meaningless zeros will not be displayed .................................................................
Page 4: 40 Cnc
Page ii of ii 80 40 cnc n ew f eatures version 8.11 1 detected errors ................................................................................................................39 2 new validation codes ...............................................................................................
Page 5: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 1 of 46 80 40 cnc detected errors v ersion 8.01 1 detected errors nbtool variable the installation and programming manuals indicate that this variable is read-only from the cnc, plc and dnc. Actually, it is read-only from the cnc and dnc and it can only be used ...
Page 6: 40 Cnc
Page 2 of 46 80 40 cnc the meaningless zeros will not be displayed n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) 2 the meaningless zeros will not be displayed from this version on, the data displayed on the screen (positions, feedrates, etc.) will not display the meaningless zeros to the left of the value. Examp...
Page 7: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 3 of 46 80 40 cnc windnc improvements • when done updating it, remove the "memory card" that contains the software version and insert the "memkey card" back. 7 windnc improvements from this cnc version on and having windnc version v2.0 and the following, it is p...
Page 8: 40 Cnc
Page 4 of 46 80 40 cnc telediagnosis n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) 8 telediagnosis it may be used to govern and monitor the cnc status remotely through the rs232 serial line or using a modem through a telephone line. The remote pc must have the windnc application version 2.00 or later installed i...
Page 9: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 5 of 46 80 40 cnc improvements to the profile editor • the pc will display the same information (screens) as the cnc. • it is possible to access the different cnc modes, modify tables and parameters when knowing the password, simulate programs, etc. • for safety...
Page 10: 40 Cnc
Page 6 of 46 80 40 cnc new variables n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) mpgn mp(x-c)n mpsn mpssn mpasn mplcn these variables, related to machine parameters, that until now were read-only, from this version on, can be read and written from the cnc in the following cases: • when they are executed inside...
Page 11: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 7 of 46 80 40 cnc new variables spindle related variables drpos position indicated by the sercos drive of the spindle. Is read-only from the cnc, dnc and plc. Sdrpos position indicated by the sercos drive of the second spindle. Is read- only from the cnc, dnc an...
Page 12: 40 Cnc
Page 8 of 46 80 40 cnc new range of oem subroutines. N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) sasins "a" signal of the cnc sinusoidal feedback for the second spindle. Is read-only from the cnc, dnc and plc. Sbsins "b" signal of the cnc sinusoidal feedback for the second spindle. Is read-only from the cnc, d...
Page 13: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 9 of 46 80 40 cnc improved non- random tool magazine management warning: 14 improved non-random tool magazine management when the tool changer is configured as non-random, the tools must be placed in the tool magazine table in the pre-established order (p1 t1, p...
Page 14: 40 Cnc
Page 10 of 46 80 40 cnc exponential type of leadscrew backlash peak n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) on the tc and tco models, when using oem parameters in the configuration programs, these programs must have the [o] attribute. If they don't, an error will be issued when editing a user cycle that re...
Page 15: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 11 of 46 80 40 cnc functions associated to machine safety by default, all bits are set to "0". 18 functions associated to machine safety 18.1 limit the feedrate of the axes and the spindle speed it is possible to limit the feedrate of the axes and the spindle tu...
Page 16: 40 Cnc
Page 12 of 46 80 40 cnc functions associated to machine safety n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) this variable is also updated with the programmed s value, in the following cases: • when programming "g92 s" in mdi mode • when programming "g92 s" in iso code in tc mode. • in tc mode, when a new speed ...
Page 17: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 13 of 46 80 40 cnc axes (2) controlled by a drive 19 axes (2) controlled by a drive until this version, when having 2 axes controlled by a single drive, the polarity of the analog output (command sign) always corresponded to that of the main axis. From this vers...
Page 18: 40 Cnc
Page 14 of 46 80 40 cnc synchronize a plc axis with a cnc axis n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) plc as long as a block or a part-program is not being executed or simulated. This way, it is possible to resume the tool change from the plc and redefine the tool table according to their positions using ...
Page 19: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 15 of 46 80 40 cnc minimum step "l" in cycles g83, g60 and g61 • general input "inhibit" of the plc axis is ignored, thus not being possible to prevent it from moving. • the execution of the movement of the synchronized slave axis cannot be aborted even by activ...
Page 20: 40 Cnc
Page 16 of 46 80 40 cnc path jog mode n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) caxgain (p163) this g.M.P. Lets the oem decide whether these gains are to be canceled or not. With “caxgain (p163) =1” and high values of ffgain and dergain the machine could be jerky depending on the type of part being machined....
Page 21: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 17 of 46 80 40 cnc tool inspection operation when pressing one of the associated keys, z+ and z-, the cnc acts as follows: the rest of the keys always operate the same way regardless of whether the "path jog" function is on or off. It only moves the selected axi...
Page 22: 40 Cnc
Page 18 of 46 80 40 cnc new instructions in the configuration language n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) warning 29 new instructions in the configuration language the new token "unmodified" of the configuration language indicates that the associated element must not take the editing focus. ;(unmodifi...
Page 23: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 19 of 46 80 40 cnc oscilloscope function capture data and then analyze it. Once data capture has ended, or has been interrupted, it is possible to analyze the signals and modify the parameters that have been previously selected, in order to improve the machining...
Page 24: 40 Cnc
Page 20 of 46 80 40 cnc oscilloscope function n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) 30.1 configuration to define the variables to be analyzed, the trigger conditions and the machine parameters of the cnc or the drive to be modified. It offers 2 screens, one to set the parameters and the other one to defi...
Page 25: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 21 of 46 80 40 cnc oscilloscope function the name field blank. If all 4 channels are deactivated (without associated variable) no capture is possible. The "hidden" channels are not shown graphically (they are not shown on the screen after the data capture). It i...
Page 26: 40 Cnc
Page 22 of 46 80 40 cnc oscilloscope function n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) if selected, specify the trigger condition using the flank, level and position data. Flank it is taken into account when trigger has been selected. It may be an up flank or a down flank. With an up flank, the data capture...
Page 27: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 23 of 46 80 40 cnc oscilloscope function if this option is selected all the signals appear superimposed, with a single graphic zero located at the center of the screen. During the analysis of the signals, it is possible to change modes by pressing the [m] key. C...
Page 28: 40 Cnc
Page 24 of 46 80 40 cnc oscilloscope function n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) drive machine parameters that may be modified when defining the drive machine parameters, that could be changed to adjust the machine, use the following nomenclature: indicate the axis and the parameter number and the gea...
Page 29: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 25 of 46 80 40 cnc oscilloscope function keys or [page up] [page down] to move the signal or press one of these keys: when auto-scaling a channel, the system sets the right vertical scale and offset so the signal shows as big as possible within its graphic strip...
Page 30: 40 Cnc
Page 26 of 46 80 40 cnc oscilloscope function n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) the machine parameters of the axis or the spindle are updated according to the criteria defined in the previous tables, the rest of the parameters are updated according to the general criteria: if the password to the mach...
Page 31: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 27 of 46 80 40 cnc tc model. Execute a part-program 31 tc model. Execute a part-program after accessing the list of stored part-programs and selecting the program to be executed from the left column, it is possible to: 1. Execute the whole part-program. Position...
Page 32: 40 Cnc
Page 28 of 46 80 40 cnc tc model. Modifications in the turning cycle n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) program in execution or interrupted. When editing the active tool, it is possible: to modify the i and k data. Select another tool (t xx recall) and modify its i and k data. When not editing the act...
Page 33: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 29 of 46 80 40 cnc tc model. Modifications in the facing cycle new level this second definition level offers the possibility to select the type of machining for each corner. To modify the type of machining, place the cursor over this icon and press the (a) key. ...
Page 34: 40 Cnc
Page 30 of 46 80 40 cnc tc model. Modifications in the tapping cycle n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) 38 tc model. Modifications in the tapping cycle standard threads on all the levels except in face threading, it is possible to enter the diameter so the cnc calculates the corresponding pitch and de...
Page 35: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 31 of 46 80 40 cnc tc model. Modifications in the tapping cycle depth in inside threads = 0.5413 x pitch depth in outside threads = 0.6134 x pitch fine pitch metric thread: m (s.I.F.) depth in inside threads = 0.5413 x pitch depth in outside threads = 0.6134 x p...
Page 36: 40 Cnc
Page 32 of 46 80 40 cnc tc model. Modifications in the tapping cycle n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) regular pitch whitworth thread: bsw (w.) the threads must be defined in mm or inches. For example, to define a 1/16 pitch whitworth thread, enter the value of 1.5875 mm or 0.0625 inches. The cnc cal...
Page 37: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 33 of 46 80 40 cnc tc model. Modifications in the tapping cycle the threads must be defined in mm or inches. For example, to define a 3/16 pitch whitworth thread, enter the value of 4.7625 mm or 0.1875 inches. The cnc calculates the pitch and the depth according...
Page 38: 40 Cnc
Page 34 of 46 80 40 cnc tc model. Modifications in the tapping cycle n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) the threads must be defined in mm or inches. For example, to define a 1/4 pitch american thread, enter the value of 6.3500 mm or 0.2500 inches. The cnc calculates the pitch and the depth according t...
Page 39: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 35 of 46 80 40 cnc tc model. Modifications to the grooving cycle threads with different entries the threading range is completed with a new level (5) for multi-entry threads. Available when setting s.M.P. “m19type (p43)=1” the following must be defined: the coor...
Page 40: 40 Cnc
Page 36 of 46 80 40 cnc tc model. Modifications in the profile cycle n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) 40 tc model. Modifications in the profile cycle minimize the machining time in xc and zc profile cycles until this version, after each roughing pass, the tool withdrew to the safety position. From t...
Page 41: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 37 of 46 80 40 cnc tc model. Cycle selection cocyf5 rounding 1 rounding 2 cocyf6 threading 1 threading 2 threading 3 threading 4 threading 5 cocyf7 grooving 1 grooving 2 grooving 3 grooving 4 cut-off cocyz drilling 1 drilling 2 drilling 3 drilling 4 drilling 5 c...
Page 42: 40 Cnc
User notes: n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8. Xx ) page 38 of 46 80 40 cnc.
Page 43: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8.1 x ) page 39 of 46 80 40 cnc detected errors v ersion 8.11 1 detected errors a.M.P. Dformat (p1) the installation manual shows wrong work units. The right work units are: connector x4. To connect the analog spindle the installation manual shows the wrong function associat...
Page 44: 40 Cnc
Page 40 of 46 80 40 cnc detected errors n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8.1 x ) 46 connector x1. Rs232 serial line (8055i model) from this version on, pin 9 no longer supplies 5v. Variables pos(x-c) and tpos(x-c) the values of variables pos(x-c) and tpos(x-c) are in the following units. • they are read fro...
Page 45: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8.1 x ) page 41 of 46 80 40 cnc new validation codes 2 new validation codes due to new software options, the validation code changes from 16 to 24 characters. The new codes are also valid for the memory cards with software versions older than v7.11 3 smooth stop in probing m...
Page 46: 40 Cnc
Page 42 of 46 80 40 cnc new management of the distance- coded reference mark (i0) n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8.1 x ) 46 5 new management of the distance-coded reference mark (i0) from this version on, the distance-coded i0 via sercos may be managed using the input of the drive's second feedback. • the...
Page 47: 40 Cnc
N ew f eatures (s oft t: 8.1 x ) page 43 of 46 80 40 cnc parameters accessible from the oscilloscope or oem subroutine 8 parameters accessible from the oscilloscope or oem subroutine 8.1 axis parameters that may be modified from the oscilloscope the following axis machine parameters may be modified....
Page 48: 40 Cnc
Page 44 of 46 80 40 cnc sampling period n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8.1 x ) 46 9 sampling period from this version on, on the 8055/c and 8055i/c models that do not have the cpu turbo, it is possible to set a sampling period of 2 milliseconds g.M.P. “looptime (p72)”. The following values may be allocate...
Page 49: 40 Cnc
User notes: n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8.1 x ) page 45 of 46 80 40 cnc.
Page 50: 40 Cnc
User notes: n ew f eatures (s oft t: 8.1 x ) page 46 of 46 80 40 cnc.
Page 51: Operating Manual
Operating manual (tc option) ref. 0204-ing.
Page 52
Iii the information described in this manual may be subject to variations due to technical modifications. Fagor automation, s.Coop. Ltda. Reserves the right to modify the contents of the manual without prior notice..
Page 53: Index
V index 1. General concepts 1.1 keyboard .................................................................................................................. 1 1.2 general ...................................................................................................................... 2 1.2.1 man...
Page 54
Vi 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.1. Operation edit mode .................................................................................................. 2 3.1.1 definition of spindle conditions ................................................................................ 3 3.1.2 defi...
Page 55
Vii 4. Program storage 4.1 list of stored programs ............................................................................................. 2 4.2 see content of a program ........................................................................................... 3 4.2.1 seeing the operations in...
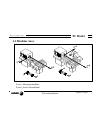
Page 56: 1. General Concepts
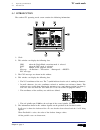
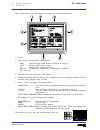
Chapter 1 - page 1 tc work mode 1. General concepts 1.1 keyboard 1. General concepts 1.1 keyboard alphanumeric keys and command keys. Selects character x selects character a selects character r specific keys for the tc model enable selection and definition of machining operations governing external ...
Page 57
Chapter 1 - page 2 tc work mode 1. General concepts 1.2 general 1.2 general it has all the performance features of the t model plus the specific features of the tc mode. For example, the setting of the numerical control must be done in "t" mode. In the tc operating mode the programs p900000 to p9999...
Page 58
Chapter 1 - page 3 tc work mode 1. General concepts 1.2 general some of the programs reserved for the cnc itself have the following meaning: p999998 this is a routines program used by the cnc for interpreting the programs edited in tc format and executing these afterwards. Warning no modifications o...
Page 59
Chapter 1 - page 4 tc work mode 1.2.1 management of text program p999997 on power-up, the cnc copies the texts of program p999997 into the system memory. It checks if program p999997 is in the user memory. If it is not, it looks in "card a", if it is not there either, it assumes the ones provided by...
Page 60
Chapter 1 - page 5 tc work mode 1.3 power-up both on cnc power-up and after the keystroke sequence: the cnc acts as follows: shows «page 0» if it has been defined by the manufacturer. To access this operating mode, press any key. If there is no «page 0», the cnc will display the standard screen for ...
Page 61
Chapter 1 - page 6 tc work mode 1. General concepts 1.4 operating in t mode with tc keyboard 1.5 video off 1.4 operating in t mode with tc keyboard the tc keyboard has been designed to also operate in t mode. The alphanumeric keyboard must be used for the keys replacing softkeys f1 to f7. Alphanumer...
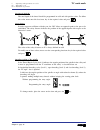
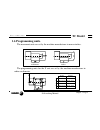
Page 62: 2. Operating In Jog Mode
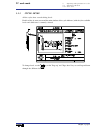
Chapter 2 - page 1 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2. Operating in jog mode the standard tc operating mode screen is: if one presses key the cnc displays the special tc operating mode screen..
Page 63
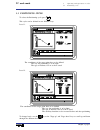
Chapter 2 - page 2 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.1 introduction 2.1 introduction the standard tc operating mode screen contains the following information: 1.- clock 2.- this window can display the following data: sbk when the single block execution mode is selected. Dnc when the dnc mode i...
Page 64
Chapter 2 - page 3 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.1 introduction 6.- this window displays, in large characters, the tool number «t» selected. The graphic representation corresponding to the location code associated with the tool. The offset number «d» associated with the tool. If the tool n...
Page 65
Chapter 2 - page 4 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.1 introduction the special screen for tc operating mode contains the following information: 1.- clock 2.- this window can display the following data: sbk when the single block mode of execution is selected. Dnc when the dnc mode is active. P...
Page 66
Chapter 2 - page 5 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.1 introduction 6.- this window shows the state of the «g» functions and the auxiliary functions «m» that are activated. It also displays the value of variables. Partc states the number of consecutive parts that have been executed with the sa...
Page 67
Chapter 2 - page 6 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.2 axis control 2.2 axis control 2.2.1 work units whenever the tc work mode is accessed, the cnc assumes the work units, «mm or inches», «radii or diameters», «millimeters/minute or millimeters/revolution», etc., that are selected by machine ...
Page 68
Chapter 2 - page 7 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.3 home search 2.3 home search (machine reference zero ) home search can be done in 2 ways: - home search on all the axes. - home search on a single axis. Home search on all the axes to carry out a search for machine reference zero for all ax...
Page 69
Chapter 2 - page 8 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.4 jogging the axes 2.4.1 continuous jog 2.4 jogging the axes the axes of the machine can be moved in the following ways: - [x] [target position] or [z] [target position] - continuous jog - incremental jog - jogging with an electronic handwhe...
Page 70
Chapter 2 - page 9 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.4 jogging the axes 2.4.2 incremental jog 2.4.2 incremental jog place the left-hand switch in one of the positions incremental movement must be done axis to axis. To do this press the jog key for the direction of the axis to be moved. Each ti...
Page 71
Chapter 2 - page 10 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.4 jogging the axes 2.4.3 jogging with an electronic handwheel 2.4.3 jogging with an electronic handwheel the various handwheel configurations are: general handwheel it can be used to jog any axis one by one. Select the axis and turn the han...
Page 72
Chapter 2 - page 11 tc work mode 2.4.3.1 standard handwheel mode with the general handwheel proceed as follows: 1.- select the axis to be jogged. Press one of the jog keys of the axis to be jogged. The selected axis will be highlighted. When using a fagor handwheel with an axis selector button, the ...
Page 73
Chapter 2 - page 12 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.4 jogging the axes 2.4.3 jogging with an electronic handwheel 2.4.3.2 path handwheel mode with this feature, it is possible to jog two axes at the same time along a linear path (chamfer) or circular path (rounding) with a single handwheel. ...
Page 74
Chapter 2 - page 13 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.4 jogging the axes 2.4.5 master handwheel 2.4.3.3 feed handwheel mode usually, when making a part for the first time, the machine feedrate is controlled by means of the feedrate override switch. From this version on, it is also possible to ...
Page 75
Chapter 2 - page 14 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.5 tool control 2.5 tool control the standard screen for tc operating mode displays the following information about the tool. This window displays the following information: > in large characters, the number "t" of the selected tool and a gr...
Page 76
Chapter 2 - page 15 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.5 tool control 2.5.1 tool change 2.5.1 tool change depending on the type of tool changer, one can have: machine with automatic tool changer machine with manual tool changer in both cases the cnc: executes the routine associated with the too...
Page 77
Chapter 2 - page 16 tc work mode 2.5.1.1 variable tool change point if the manufacturer wishes the user can be allowed to define the tool change point at all times. This feature logically depends on the type of machine and type of changer. This feature allows the tool change to be made beside the pa...
Page 78
Chapter 2 - page 17 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.5 tool control 2.5.2 tool calibration 2.5.2 tool calibration to access tool calibration mode press key the cnc displays the following information: 1.- indicator of the operating mode selected: «tool calibration». 2.- help graphics for tool ...
Page 79
Chapter 2 - page 18 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.5 tool control 2.5.2 tool calibration to calibrate a tool, proceed as follows: 1.- select a tool and access the tool calibration mode. 2.- use a part of known dimensions place that part in in the chuck. Define the part dimensions: (value) (...
Page 80
Chapter 2 - page 19 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.5 tool control 2.5.2 tool calibration location codes available for the type location codes available for the type location codes available for the type 4.- tool calibration. There are two methods: when using a tool presetting table, define ...
Page 81
Chapter 2 - page 20 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.5 tool control 2.5.2 tool calibration 5.- define the values for the tool geometry. The window on the right contains the tool geometry values and the window on the left contains a help diagram. To define one of these values, select the corre...
Page 82
Chapter 2 - page 21 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.5 tool control 2.5.3 live tool 2.5.3 live tool when a live tool is selected, the standard screen of the tc operating mode shows the following information: to select the rpm "s" of the live tool, take these steps: 1. Press to select the "t" ...
Page 83
Chapter 2 - page 22 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.5 tool control 2.5.3 live tool custom and (dfu b7r561 or dfd m2) = cncex1 (m45 s0, m1) if while the tc operating mode is selected (custom=1) ... ... The "stop live tool" key is pressed (dfu b7r561) or the live tool is de-selected (dfd m2) ....
Page 84
Chapter 2 - page 23 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.6 spindle control 2.6 spindle control the standard tc working mode screen has a window for displaying information about the spindle. Since the cnc allows operating with the spindle in rpm, at constant surface speed or in the spindle orienta...
Page 85
Chapter 2 - page 24 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.6 spindle control 2.6.1 spindle in rpm. 2.6.1 spindle in rpm the cnc displays the following information: 1.- actual spindle speed in rpm. 2.- theoretical spindle speed in rpm. To select any other speed press . The cnc will frame the present...
Page 86
Chapter 2 - page 25 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.6 spindle control 2.6.2 constant surface speed 2.6.2 constant surface speed in constant surface speed mode the user sets the tangential speed that there must be at all times between the tool tip and the part. The spindle revolutions therefo...
Page 87
Chapter 2 - page 26 tc work mode 2. Operating in jog mode 2.6 spindle control 2.6.2.1operating at constant surface speed 2.6.2.1 operating at constant surface speed (css) when constant surface speed operating mode is selected (css), the cnc assumes the spindle range selected at present. In this oper...
Page 88
Chapter 2 - page 27 tc work mode 2. Operation in jog mode 2.6 spindle control 2.6.3 spindle orientation 2.6.3 spindle orientation when having spindle orientation (general machine parameter refeed1 (p34) other than 0) the cnc shows the following information: 1.- actual spindle speed in rpm. 2.- angul...
Page 89
Chapter 2 - page 28 tc work mode 2. Operation in jog mode 2.6 spindle control 2.6.3 spindle orientation 2.6.3.1 operation with spindle orientation when having spindle orientation, the cnc uses the same screen as when operating in rpm mode. Rpm mode. To select this mode, press one of these three keys...
Page 90
Chapter 2 - page 29 tc work mode 2.7 control of external devices the cnc allows up to 6 external devices to be activated and deactivated from the keyboard. One of these is the cooling fluid. The activation and deactivation of the devices must be carried out by the machine manufacturer by means of th...
Page 91
Chapter 2 - page 30 tc work mode 2. Operation in jog mode 2.8 handling iso code 2.8 handling iso code with the iso key, it is possible to access the mdi mode or the iso work mode. To access the mdi mode, put the cnc in jog mode and then press the cnc displays a window at the bottom of the standard (...
Page 92
Chapter 3 - page 1 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles the following cnc keys should be used to select the machining operations or cycles: when pressing the cnc shows all the user cycles already defined by the machine manufacturer by means of the application program: wgdraw. The user...
Page 93
Chapter 3 - page 2 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.1 operation edit mode 3.1. Operation edit mode after selecting the cycle edition mode the cnc displays a screen looking like this: 1.- denomination of the operation or work cycle selected. 2.- help graphics. 3.- spindle conditi...
Page 94
Chapter 3 - page 3 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.1 operation edit mode 3.1.1 definition of spindle conditions 3.1.1 definition of spindle conditions work mode (rpm) or (css) move over the "rpm" or "css" icon. This can be done: a) by using the keys b) by pressing . The cnc sel...
Page 95
Chapter 3 - page 4 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.1 operation edit mode 3.1.2 definition of machining conditions 3.1.2 definition of machining conditions some cycles maintain the same machining conditions during the whole execution process (positioning cycle, drilling cycle .....
Page 96
Chapter 3 - page 5 tc work mode 3.1.3 cycle level all the cycles have several editing levels. Each level has its own screen and the main window of the cycle indicates (with tabs) the available levels and which one is currently selected. To change levels, use the key or the "page up" and "page down" ...
Page 97
Chapter 3 - page 6 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.2 simulating and executing the operation 3.2 simulating and executing the cycle there are ways to work with operations or cycles: editing mode and execution mode. Editing mode execution mode to switch from editing mode to execu...
Page 98
Chapter 3 - page 7 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.3 positioning cycle coordinate (xi, zi) 3.3 positioning cycle to select the positioning cycle press this cycle can be defined in two different ways level 1. The coordinates of the target point have to be defined the way the pos...
Page 99
Chapter 3 - page 8 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.3 positioning cycle 3.3.1 definition of data 3.3.1 definition of data type of positioning to select the type of positioning move onto this icon and press the icon changes and the help graphics are updated. Type of feedrate feed...
Page 100
Chapter 3 - page 9 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.4 turning cycle 3.4.1 definition of geometry 3.4 turning cycle to select the turning cycle press 3.4.1 definition of geometry type of turning: internal or external external turning internal turning to modify the type of turning...
Page 101
Chapter 3 - page 10 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.4 turning cycle 3.4.2 basic operation safety distance in order to prevent collisions with the part, the cnc allows a part approach point to be set. The safety distance indicates the approach point coordinate with respect to th...
Page 102
Chapter 3 - page 11 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.4 turning cycle 3.4.2 basic operation 5.- finishing operation if the finishing operation was programmed with another tool, the cnc will make a tool change, moving to the change point if the machine requires this. The part fini...
Page 103
Chapter 3 - page 12 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.5 facing cycle 3.5.1 definition of geometry 3.5 facing cycle to select the facing cycle press 3.5.1 definition of geometry coordinates of the starting point (xi, zi) and coordinates of the end point (xf, zf) the coordinates ar...
Page 104
Chapter 3 - page 13 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.5 facing cycle 3.5.2 basic operation 3.5.2 basic operation the machining steps in this cycle are as follows: 1.- if the roughing operation was programmed with another tool the cnc makes a tool change, moving to the change poin...
Page 105
Chapter 3 - page 14 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.5 facing cycle 3.5.2 basic operation 6.- once the operation or cycle has ended, the tool will return to the position it occupied when the cycle was called upon, that is, the point where was pressed. Obviously, when executing a...
Page 106
Chapter 3 - page 15 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.6 taper cycle 3.6 taper cycle to select the taper cycle press this cycle can be defined in two different ways: level 1. A definition is needed for the coordinates of the theoretical corner. The taper angle and final diameter. ...
Page 107
Chapter 3 - page 16 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.6 taper cycle 3.6.1 definition of geometry 3.6.1 definition of geometry type of taper: internal or external external taper internal taper to modify the type of taper move over this icon and press whenever the type of taper is ...
Page 108
Chapter 3 - page 17 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.6 taper cycle 3.6.1 definition of geometry coordinates of the theoretical corner or starting point (xi, zi) and coordinates of the end point (xf, zf) the coordinates are defined one by one. After moving over the coordinates of...
Page 109
Chapter 3 - page 18 tc work mode finishing stocks in x-z it is possible to define a single finishing stock that will be applied depending on the cutter edge or 2 finishing stocks, one per axis (x, z). Use the icon of the finishing area to select the type of finishing stock. The figure on the left ap...
Page 110
Chapter 3 - page 19 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.6 taper cycle 3.6.2 basic operation 3.6.2 basic operation the machining stages in this cycle are as follows: 1.- if the roughing operation was programmed with another tool the cnc will make a tool change, moving to the change ...
Page 111
Chapter 3 - page 20 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.6 taper cycle 3.6.2 basic operation 6.- once the operation or cycle has ended, the tool will return to the position it occupied when the cycle was called upon, that is, the point where was pressed. Obviously, when executing a ...
Page 112
Chapter 3 - page 21 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.7 rounding cycle 3.7 rounding cycle to select the rounding cycle press this cycle can be defined in two different ways: level 1. A definition is needed for the coordinates of the theoretical corner the rounding radius level 2....
Page 113
Chapter 3 - page 22 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.7 rounding cycle 3.7.1 definition of geometry 3.7.1 definition of geometry type of rounding: internal or external external rounding internal rounding. To modify the type of rounding move onto this icon and press whenever the t...
Page 114
Chapter 3 - page 23 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.7 rounding cycle 3.7.1 definition of geometry coordinates of the theoretical corner or the starting point (xi, zi) and coordinates of the end point (xf, zf) the coordinates are defined one by one. After moving onto the coordin...
Page 115
Chapter 3 - page 24 tc work mode finishing stocks in x-z it is possible to define a single finishing stock that will be applied depending on the cutter edge or 2 finishing stocks, one per axis (x, z). Use the icon of the finishing area to select the type of finishing stock. The figure on the left ap...
Page 116
Chapter 3 - page 25 tc work mode 3.7.2 basic operation the machining stages in this cycle are as follows: 1.- if the roughing operation was programmed with another tool the cnc makes the tool change, moving to the change point if this is required by the machine. 2.- the spindle starts at the speed s...
Page 117
Chapter 3 - page 26 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.7 rounding cycle 3.7.2 basic operation 6.-once the operation or cycle has ended, the tool will return to the position it occupied when the cycle was called upon, that is, the point where was pressed. Obviously, when executing ...
Page 118
Chapter 3 - page 27 tc work mode 3.8 threading cycle to select the positioning cycle press this cycle can be defined in four different ways: level 1. Longitudinal threading a definition is needed for: the coordinates of the starting point the z coordinate of the end point the thread pitch the distan...
Page 119
Chapter 3 - page 28 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.8 threading cycle level 3. Face threading a definition is needed for: the coordinates of the starting point the coordinates of the end point the thread pitch the distance to the end of thread the total depth the spindle angula...
Page 120
Chapter 3 - page 29 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.8 threading cycle 3.8.1 definition of geometry 3.8.1 definition of geometry type of threading: internal or external external threading internal threading. To modify the type of threading move onto this icon and press whenever ...
Page 121
Chapter 3 - page 30 tc work mode total thread depth (h) the total depth of the thread should be programmed in radii and with positive value. To define this value, move onto this data item, key in the required value and press safety distance in order to prevent collisions with the part, the cnc allow...
Page 122
Chapter 3 - page 31 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.8 threading cycle 3.8.2 definition of the type of machining 3.8.2 definition of the type of machining threading levels 2 and 3 enable selection by means of the icons located in the lower left-hand window of the way the threadi...
Page 123
Chapter 3 - page 32 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.8 threading cycle 3.8.3 longitudinal threading. Basic operation. 3.8.3 longitudinal threading. Basic operation. The machining passes in this cycle are as follows: 1.- if the operation was programmed with another tool the cnc w...
Page 124
Chapter 3 - page 33 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.8 threading cycle 3.8.4 taper threading. Basic operation. 3.8.4 taper threading. Basic operation. The machining passes in this cycle are as follows: 1.- if the operation was programmed with another tool the cnc will make a too...
Page 125
Chapter 3 - page 34 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.8 threading cycle 3.8.5 face threading. Basic operation 3.8.5 face threading. Basic operation the machining passes in this cycle are as follows: 1.- if the operation was programmed with another tool the cnc will make a tool ch...
Page 126
Chapter 3 - page 35 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.8 threading cycle 3.8.6 thread repair. Basic operation. 3.8.6 thread repair. Basic operation cycle definition: define the dimensions of the thread like at the rest of the levels and the coordinates of one of the roots. To defi...
Page 127
Chapter 3 - page 36 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.9 grooving cycle 3.9 grooving cycle to select grooving cycle press cylindrical grooves and frontal grooves can be made with vertical and incline walls: level 1. Longitudinal grooving one must define: the coordinates of the sta...
Page 128
Chapter 3 - page 37 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.9 grooving cycle level 3. Longitudinal grooving with incline walls. One must define: the coordinates of the starting and end points the final diameter the inclination angles of the incline walls the number of grooves and offse...
Page 129
Chapter 3 - page 38 tc work mode 3.9.1 calibration of the grooving tool when calibrating the grooving tool proper indication should be made of the location codes for the corner that has been calibrated. One same tool can thus be calibrated in three different ways, as shown below: the left-hand corne...
Page 130
Chapter 3 - page 39 tc work mode 3.9.2 definition of geometry type of grooving: internal or external external grooving internal grooving to modify the type of grooving move onto this icon and press whenever the type of threading is changed the cnc modifies the icon and shows the corresponding geomet...
Page 131
Chapter 3 - page 40 tc work mode type of machining to be carried out on each corner. This data must be defined for grooving with incline walls. The type of machining must be defined for all four corners of the groove. A square corner. Radius blend. A chamfer. To change the type of machining, positio...
Page 132
Chapter 3 - page 41 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.9 grooving cycle 3.9.2 definition of geometry groove repetition with the «number of grooves» and «offset» data, the same groove may be repeated along the z axis on longitudinal grooving or along the x axis on face grooving. If...
Page 133
Chapter 3 - page 42 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.9 grooving cycle 3.9.3 basic operation 3.9.3 basic operation the machining passes in this cycle are as follows: 1.- if the operation was programmed with another tool the cnc will make a tool change, moving to the change point ...
Page 134
Chapter 3 - page 43 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.9 grooving cycle 3.9.3 basic operation 7.- the cnc will stop the spindle but keep the machining conditions set for finishing selected; tool (t), axis feed (f) and spindle speed (s). Some points to consider: if t0 is selected a...
Page 135
Chapter 3 - page 44 tc work mode 3.10 drilling and tapping cycles to select the drilling cycle and the tapping cycle press depending on the type of machine and how the cnc machine parameters have been set, up to 5 cycles magy be available: drilling cycle. Multiple drilling cycle tapping cycle. Multi...
Page 136
Chapter 3 - page 45 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.10 drilling and tapping cycles level 3. Multiple drilling cycle. Multiple drilling is possible on the side of the part or on its face a definition is needed for: the coordinates of the first point the total depth the dwell at ...
Page 137
Chapter 3 - page 46 tc work mode 3.10.1 definition of geometry machining on the face or side of the part: machinig on the face of the part machining on the side of the part: to change the type of machining, position over this icon and press every time the type of tapping is changed, the cnc modifies...
Page 138
Chapter 3 - page 47 tc work mode number of operations (n) position over this data, key in the desired value and press dimensions of the slot (l, i) "l" indicates the length of the slot and "i" its depth. To define them, position over the corresponding data (l or i), key in the value and press penetr...
Page 139
Chapter 3 - page 48 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.10 drilling and tapping cycles 3.10.2 basic operation, drilling cycle 3.10.2 basic operation. Drilling cycle the machining passes in this cycle are as follows: 1.- if the operation was programmed with another tool the cnc will...
Page 140
Chapter 3 - page 49 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.10 drilling and tapping cycles 3.10.3 basic operation. Tapping cycle 3.10.3 basic operation. Tapping cycle the machining passes in this cycle are as follows: 1.- if the operation was programmed with another tool the cnc will m...
Page 141
Chapter 3 - page 50 tc work mode 3.10.4 basic operation. Multiple drilling cycle the machining steps for this cycle are: 1.- if the spindle is working in open loop (rpm or css mode) the cnc stops the spindle and performs a home search on the spindle (io). 2.- if the operation was programmed with ano...
Page 142
Chapter 3 - page 51 tc work mode 10.- once the operation or cycle has ended, the tool will return to the position it occupied when the cycle was called upon, that is, the point where was pressed. Obviously, when executing a complete part, a combination of operations or cycles, the tool does not retu...
Page 143
Chapter 3 - page 52 tc work mode 3.10.5 basic operation. Multiple tapping cycle the machining steps for this cycle are: 1.- if the spindle is working in open loop (rpm or css mode) the cnc stops the spindle and performs a home search on the spindle (io). 2.- if the operation was programmed with anot...
Page 144
Chapter 3 - page 53 tc work mode 3.10.6 basic operation. Multiple slot milling cycle the machining steps for this cycle are: 1.- if the spindle is working in open loop (rpm or css mode) the cnc stops the spindle and performs a home search on the spindle (io). 2.- if the operation was programmed with...
Page 145
Chapter 3 - page 54 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.11 profile cycle 3.11 profile cycle to select the profile cycle press this cycle can be defined in four ways: level 1. Defining all the points of the profile. Level 2. Using a part-program which contains the profile..
Page 146
Chapter 3 - page 55 tc work mode 3.11.1 level 1. Profile definition this mode allows the profile to be defined by means of the description of its theoretical corners. Up to 12 points can be used for defining said corners. Point p1 is the profile starting point. The remaining points must be correlati...
Page 147
Chapter 3 - page 56 tc work mode 3.11.2 level 2. Profile definition to define the «profile program» move onto the "profile part-program" or "p" window. After selecting this window one can: key in the required «profile program» required. If the "profile program" is already known, key in the number an...
Page 148
Chapter 3 - page 57 tc work mode 3.11.3 level 2. Optimizing of the machining of a profile when defining the desired profile only, the cnc assumes that the rough part is cylindrical and it machines it as indicated on the left diagram. When the part profile is known, it is recommended to define both p...
Page 149
Chapter 3 - page 58 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.11 profile cycle 3.11.4 geometry definition. Levels 1, 2. Zx profile 3.11.4 geometry definition. Levels 1, 2. Zx profile internal or external profile external profile internal profile. To modify the type of profile move onto t...
Page 150
Chapter 3 - page 59 tc work mode coordinates of the starting point (x, z) the coordinates are defined one by one. After moving onto the coordinates for the axis to be defined, one can: a) manually enter the value. Key in the required value and press b) assign the present position of the machine. Mov...
Page 151
Chapter 3 - page 60 tc work mode finishing stocks in x-z it is possible to define a single finishing stock that will be applied depending on the cutter edge or 2 finishing stocks, one per axis (x, z). Use the icon of the finishing area to select the type of finishing stock. The figure on the left ap...
Page 152
Chapter 3 - page 61 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.11 profile cycle 3.11.5 basic operation. Levels 1, 2. Zx profile 3.11.5 basic operation. Levels 1,2. Zx profile the machining steps in these cycles are the following: 1.- if the roughing operation was programmed with another t...
Page 153
Chapter 3 - page 62 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.11 profile cycle 3.11.6 level 1. Example 3.11.6 level 1. Example geometry definition external profile working quadrant type of machining profile definition p1 x 12.0000 p6 x 43.0000 z - 0.0000 z - 37.5000 r 6.0000 p2 x 16.0000...
Page 154
Chapter 3 - page 63 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.11 profile cycle 3.11.7 level 2. Examples 3.11.7 level 2. Examples geometry definition external profile work quadrant type of machining profile definition abscissa and ordinate of the starting point z = 0 x = 0 section 1 ........
Page 155
Chapter 3 - page 64 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.11 profile cycle 3.11.7 level 2. Examples geometry definition external profile work quadrant type of machining profile definition abscissa and ordinate of the starting point z = 80 x = 0 section 1 ................................
Page 156
Chapter 3 - page 65 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.11 profile cycle 3.11.7 level 2. Examples geometry definition external profile work quadrant type of machining profile definition abscissa and ordinate of the starting point. Z = 170 x = 0 section 1.......Counterclockwise circ...
Page 157
Chapter 3 - page 66 tc work mode geometry definition outside profile work quadrant type of machining definition of the desired final profile profile abscissa and ordinate of the starting point z = 170 x = 0 section 1 .. Counterclockwise arc ....... Zc = 140 xc = 0 radius = 30 section 2 .. Counterclo...
Page 158
Chapter 3 - page 67 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.11 profile cycle 3.11.7 level 2. Examples geometry definition external profile work quadrant type of machining profile definition abscissa and ordinate of the starting point z = 180 x = 0 section 1..........Counterclockwise ci...
Page 159
Chapter 3 - page 68 tc work mode 3. Operating with operations or cycles 3.11 profile cycle 3.11.7 level 2. Examples geometry definition external profile work quadrant type of machining profile definition abscissa and ordinate of the starting point...............Z = 128 x = 0 section 1.......Counterc...
Page 160: 4. Program Storage
Chapter 4 - page 1 tc work mode 4. Program storage 4. Program storage this cnc allows the editing, simulating and executing of part-programs. Each of these programs consists of the interlinking of elementary operations or cycles and/or blocks edited in iso code. The form of editing or defining said ...
Page 161
Chapter 4 - page 2 tc work mode 4. Program storage 4.1 list of stored programs 4.1 list of stored programs to access the list of part-programs stored press note: if the «tool calibration» mode is selected you cannot directly access the list of part-programs. This mode must first be left, that is, pr...
Page 162
Chapter 4 - page 3 tc work mode 4.2 see content of a program to see the content of a part-program, select this with the pointer from the left-hand column. To do this use and . The right -hand column will display the cycles which said part consists of: if you press or or the pointergoes on to the rig...
Page 163
Chapter 4 - page 4 tc work mode 4. Program storage 4.3 edit a new part-program 4.3.1 storage of an operation of cycles 4.3 edit a new part-program to edit a new part-program the following steps should be taken: * press to access the list of part-programs stored. * use the pointer to select the optio...
Page 164
Chapter 4 - page 5 tc work mode 4. Program storage 4.4 erasing a part-program 4.5 copy a part-program in another 4.4 erasing a part-program to erase a part-program follow these steps: * press to access the list of part-programs stored. * use the pointer to select from the left-hand column the part-p...
Page 165
Chapter 4 - page 6 tc work mode 4. Program storage 4.6 modifying a part-program 4.6 modifying a part-program to modify a part-program the following steps must be taken: * press to access the list of part-programs stored. * use the pointer to select from the left-hand column the part-program you wish...
Page 166
Chapter 4 - page 7 tc work mode 4. Program storage 4.6 modifying a part-program 4.6.3 adding or inserting a new operation to add or insert an operation take the same steps as to store an operation. * define the desired block or cycle, assigning this the relevant data. * press to access the list of p...
Page 167
Chapter 5 - page 1 tc work mode 5. Execution and simulation 5. Execution and simulation simulation allows graphic reproduction of a part-program or an operation with the data that has been defined. By means of simulation, one can thus check the part-program or the operation before executing or stori...
Page 168
Chapter 5 - page 2 tc work mode 5. Execution and simulation 5.1 simulating or executing an operation or cycle 5.1 simulating or executing an operation or cycle all the operations or cycles have 2 operating modes: execution mode and edition mode execution mode edition mode simulation the operation or...
Page 169
Chapter 5 - page 3 tc work mode 5.2 simulating or executing a part-program whenever you wish to simulate or execute a part-program do the following: * press to access the list of part-programs stored. * select the program to be simulated or executed from the left-hand column. To simulate the part-pr...
Page 170
Chapter 5 - page 4 tc work mode 5.4 execution mode when you press to execute an operation or part-program, the cnc displays the standard tc operating mode screen. If you press the cnc displays the special tc operating mode screen. After selection, the operation or part can be executed as many times ...
Page 171
Chapter 5 - page 5 tc work mode 5.4.1 tool inspection depending on how the cnc has been set, tool inspection will be available after interrupting the execution without pressing any key or after pressing once tool inspection has been selected, one can: jog the axes up to the tool change position move...
Page 172
Chapter 5 - page 6 tc work mode 5.5 graphic representation when you press the cnc displays the "t" model graphic representation page. To leave the graphic representation mode press or in the operation manual, t-tc models, section «graphics» in the «execution / simulation» chapter, there is an explan...
Page 173
Chapter 5 - page 7 tc work mode graphic parameters simulation speed. In the top right-hand of the screen select the percentage of the simulation speed to be applied. To select the percentage use the keys and for the cnc to assume said value, press colors of the path. This only applies in line graphi...
Page 174: Self-Teaching Manual
Self-teaching manual (tc option) ref. 0112-ing.
Page 175: Index
Index chapter 1 theory on cnc machines 1.1.- machine axes ……………………………………………………………………….3 1.2.- machine reference zero and part zero ……………………...………………………4 1.3.- home search ………………………………………………………………………..5 1.4.- travel limits ……………………………………………………………………….. 6 1.5.- part zero preset …………………………………...…………………...
Page 176
Chapter 4 automatic operations 4.1.- operation keys ………….……..………………………………………………...… 3 4.2.- work modes .……………………..……………………….……………………….. 5 4.3.- example of an automatic operation. Taper turning …….………………..…...…….6 4.3.1.- edit an operation .……………………………………………………………….6 4.3.2.- simulate an operation ………...
Page 177: Theory On Cnc Machines
Chapter 1 theory on cnc machines.
Page 178: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 1 page 2 tc model theory on cnc machines this chapter describes: • how to name the axes of the machine. • what machine reference zero and part zero are. • what “home search” is. • what travel limits are. • how to preset a part zero. • which are the programming units. > m...
Page 179: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 1 page 3 tc model theory on cnc machines 1.1 machine axes. Z axis: along the machine. X axis: across the machine..
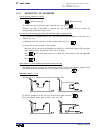
Page 180: Tc Model
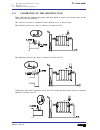
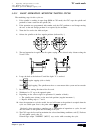
Self-teaching manual chapter 1 page 4 tc model theory on cnc machines 1.2 machine reference zero and part zero. They are the references the machine needs in order to work: – machine ref. Zero (o m ): is set by the manufacturer and it is the origin point for the axes. – part zero (o p ): is set by th...
Page 181: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 1 page 5 tc model theory on cnc machines 1.3 home search. When the cnc is off, the axes may be moved by hand or by accident. In these situations, the cnc no longer keeps track of the real position of the axes. That is why a “home search” should be carried out on power-up...
Page 182: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 1 page 6 tc model theory on cnc machines 1.4 travel limits. Hard limits cnc limits there are two types of limits: – hard limits: mechanical limits set on the machine to prevent the carriage from moving beyond the ways. – cnc limits: set at the cnc by the manufacturer to ...
Page 183: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 1 page 7 tc model theory on cnc machines 1.5 part zero preset. It is easier to program movements from a part zero. The part zero is only set on the z axis. O m : machine ref. Zero. O p : part zero..
Page 184: Tc Model
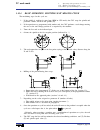
Self-teaching manual chapter 1 page 8 tc model theory on cnc machines 1.6 programming units. The movement units are set by the machine manufacturer in mm or inches. Millimeters inches the programming units for the x axis are set by the machine manufacturer in radius or diameter. Radius diameter a x=...
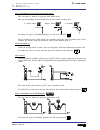
Page 185: Tc Model
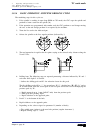
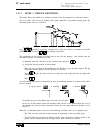
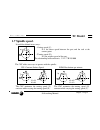
Self-teaching manual chapter 1 page 9 tc model theory on cnc machines 1.7 spindle speed. It could be defined in two ways: css: constant surface speed. N1=n2 v1>v2 v1=v2 n1 rpm: revolutions per minute. The cnc maintains the cutting speed (v) constant while varying the turning speed (n). The cnc maint...
Page 186: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 1 page 10 tc model theory on cnc machines to work at css, two things must be borne in mind: the part zero must be at the part’s turning axis so that the calculated turning speed is the same as the best cutting speed. The maximum turning speed must be programmed because t...
Page 187: Tc Model
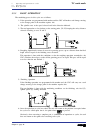
Self-teaching manual chapter 1 page 11 tc model theory on cnc machines 1.8 axis feedrate. The feedrate units are set by the machine manufacturer, being: – mm/rev: the axis feedrate varies depending on the spindle speed. – mm/min: the axis feedrate is independent from the spindle speed . Note it is r...
Page 188: Theory On Tools
Chapter 2 theory on tools.
Page 189: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 2 page 2 tc model theory on tools this chapter describes: • what the tool turret is. • what the tool table is and what information it contains. • what tool presetting is. • defects due to errors in the tool table. > due to wrong tool calibration. > due to wrong tool loca...
Page 190: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 2 page 3 tc model theory on tools 2.1 the tool turret. The tools this cnc can use are placed on the tool turret. This turret may have either a manual or automatic tool changer. When manual, the tool change is carried out like on a conventional machine. When automatic, al...
Page 191: Tc Model
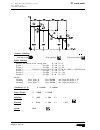
Self-teaching manual chapter 2 page 4 tc model theory on tools 2.2 tool table. The tool table contains tool information such as their position on the turret, dimensions, etc. When changing the tool, the cnc takes this tool information. The information kept in the tool table refers to: t, d, x, z, i,...
Page 192: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 2 page 5 tc model theory on tools r: tool radius. I: tool wear along the x axis. K: tool wear along the z axis. A: cutter angle. B: cutter width. C: cutting angle. X: tool length (in radius) along the x axis z: tool length along the z axis. Tool ref..
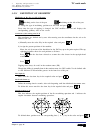
Page 193: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 2 page 6 tc model theory on tools once the tool dimensions are known; the cnc must know which is the calibration point for that tool (location code) to compensate for the shaded area (radius compensation). The location code depends on the orientation of the machine axes....
Page 194: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 2 page 7 tc model theory on tools most common location codes..
Page 195: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 2 page 8 tc model theory on tools.
Page 196: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 2 page 9 tc model theory on tools most common location codes..
Page 197: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 2 page 10 tc model theory on tools.
Page 198: Tc Model
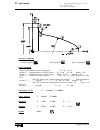
Self-teaching manual chapter 2 page 11 tc model theory on tools 2.3 tool calibration. By calibrating a tool, we indicate to the cnc the tool dimensions. It is essential to carry this operation out properly for obtaining the parts with the right dimensions and for controlling the same point after cha...
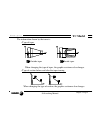
Page 199: Tc Model
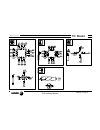
Self-teaching manual chapter 2 page 12 tc model theory on tools x1: real dim. Z1: real dim. X2: wrong dim. X2 right part dimensions wrong part dimensions wrong machining tools calibrated wrong right machining tools calibrated right part to be machined tools defects due to wrong length calibration ri...
Page 200: Tc Model
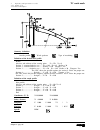
Self-teaching manual chapter 2 page 13 tc model theory on tools defects due to wrong location codes the tool has a real tip and another theoretical tip. Real tool tip theoretical tool tip when working with the theoretical tool tip, there are machining ridges left. To avoid this, the cnc works with t...
Page 201: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 2 page 14 tc model theory on tools defects due to wrong radius values rr: real radius. Rf: wrong radius (false). Machining ridges rf rr rf rr there is residual stock due to the radius difference..
Page 202: Hands-On Training
Chapter 3 hands-on training.
Page 203: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 2 tc model hands-on training this chapter describes: • the keyboard and the screen • how to carry out a “home search”. > maintaining the part zero. > without maintaining the part zero. •how to operate with the spindle. > what the speed ranges (gears) are. > how to...
Page 204: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 3 tc model hands-on training 3.1 screen and keyboard description. 3.1.1 power-up. On power-up, the cnc will display the following screen. Screen for the tc mode. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 2 section 2.3 if this screen is not displayed, it is becau...
Page 205: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 4 tc model hands-on training 3.1.2 keyboard description. 1.- keys to define the machining operations. 2.- keys for external devices: live tool and work modes for the spindle (rpm/css). 3.- alphanumeric keyboard and command keys. 4.-operator panel. Note: refer to t...
Page 206: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 5 tc model hands-on training description of the operator panel. 1. Axes jogging keys. 2. Work mode selector. (continuous jog ( ), incremental jog ( ) or with handwheel ( )). 3. Selection of spindle turning direction ( ) and start-up. Spindle speed override percent...
Page 207: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 6 tc model hands-on training 3.1.3 description of the standard screen. 1.- time, single-block/continuous execution, program number, execution status (in position, execution, interrupted or reset) and plc. 2.- cnc messages. 3.- tool position referred to part zero a...
Page 208: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 7 tc model hands-on training 3.1.4 description of the auxiliary screen. 1.- time, single block/continuous execution, program number, execution status (in position, execution, interrupted or reset) and plc. 2.- cnc messages. 3.- lines of the selected program. 4.- a...
Page 209: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 8 tc model hands-on training 3.2 home search. After powering the machine up, carry out the “home search” just in case the axes of the machine have moved while the cnc was off. A “home search” can be carried out in two ways. 3.2.1 maintaining the part zero. The “ho...
Page 210: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 9 tc model hands-on training 3.2.2 without maintaining the part-zero. The “home search” is carried out on one axis at a time. 1st.-the cnc does not know the possition of the carriages. X?, z? Different from the displayed x, z. 2nd.-home search on the x axis. Press...
Page 211: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 10 tc model hands-on training 3.3 spindle. The spindle of a machine can work in two modes: – rpm: at constant turning speed. (section 1.7) – css: at constant surface speed.(section 1.7) press to select the work mode. 3.3.1 speed ranges (gears). With this cnc the m...
Page 212: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 11 tc model hands-on training 3.3.2 work in rpm mode. (revolutions per minute) to select the work speed (in rpm), press: + (turning speed) + the cnc shows the following information: start the spindle clockwise. Stop the spindle. Start the spindle counter-clockwise...
Page 213: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 12 tc model hands-on training 3.3.3 work at constant surface speed. (css) before programming the cutting speed, the working speed range must be selected. The cnc assumes the current range by default. Once the change is completed, enter the css mode and press . To ...
Page 214: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 13 tc model hands-on training start the spindle using the jog keys of the operator panel. Spindle clockwise. Stop the spindle. Spindle counter-clockwise. Increases or decreases the applied override % to the turning speed. Depending on the position of the axes, the...
Page 215: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 14 tc model hands-on training 3.4 axis jog. To select the jog mode, use the selector switch: jog keys each key is used for moving the axis in one direction according to the axes of the machine. (section 1.1) handwheel it can have one or two handwheels. The axes mo...
Page 216: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 15 tc model hands-on training 3.4.1 handwheels. – select the jog mode with the selector switch. ( position) jog table handwheel selector switch s w i t c h p o s i t i o n d i s t a n c e p e r lin e o f t h e h a n d w h e e l d i a l 1 1 m i c r o n . 1 0 1 0 m ...
Page 217: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 16 tc model hands-on training 3.4.2 incremental jog. Every time a jog key is pressed, the axis will move the selected increment at the programmed feedrate. (in rapid, if f=0). – select the distance to move at the selector. ( position) – move the axes with the jog ...
Page 218: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 17 tc model hands-on training 3.4.3 continuous jog. Mm/min. – enter the feedrate value: + 120 + – change the % override of the axes with the selector switch in position. – jog the axes with the jog keys. Jog keys actual displacement: 120 mm/min (100%) actual displ...
Page 219: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 18 tc model hands-on training 3.4.4 continuous jog. Mm/rev. In this mode, the feedrate is a function of the spindle (either stopped or turning). – enter the feedrate value: + 0.1 + – change the % override for the axes feedrate with the selector switch. ( position)...
Page 220: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 19 tc model hands-on training 3.4.5 rapid jog key. – jog the axes with the jog keys and press the rapid jog key ( ). The axes move as fast as possible (set by the machine manufacturer). Jog keys actual displacement: in rapid rapid jog key any position note: refer ...
Page 221: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 20 tc model hands-on training 3.5 tools. 3.5.1 tool selection. Depending on the machine, there are two possibilities: • machine with manual tool changer. The tool change is carried out like on a conventional machine: – change the tool on the machine. Remove the ol...
Page 222: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 21 tc model hands-on training • machine with automatic tool changer. No tool has to be removed. – press – enter the tool number. – press – the cnc rotates the turret until the new tool is in work position. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 3 section 3.5....
Page 223: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 22 tc model hands-on training 3.5.2 tool calibration. – just before calibrating the tools, a “home search” must be carried out on all axes. Homing the x axis. + + homing the z axis. + + home home – to calibrate a tool, a part previously turned and faced is needed....
Page 224: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 23 tc model hands-on training – access the calibration mode. Press . The cnc shows the tool calibration screen. Dimensions of the part used for tool calibration. Calibration tool tip (location code). Actual axes position cutting conditions. Work mode. Help graphic...
Page 225: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 24 tc model hands-on training part dimensions 1.- measure the part. – go to the tool calibration window. – enter the x value. – enter the z value. 2.- start the spindle. 3.- select the tool to be calibrated. + (tool number) + 4.- jog the axes until touching the pa...
Page 226: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 25 tc model hands-on training 3.5.3 how to change any data on the tool table. To change the values (t, d, a, b, c, r, location code, i, k), enter the calibration mode and press: + (tool number) + the cnc shows the data for that tool. – to change the data, place th...
Page 227: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 26 tc model hands-on training 3.5.4 tool change position. The machine manufacturer may allow selecting the tool change position. Tool change position referred to home. Enter the x and z coordinates of the tool change position. • + + (x value) + • + + (z value) + w...
Page 228: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 3 page 27 tc model hands-on training 3.6 checking for proper calibration. – preset the part zero. Approach the tool along z. Press + + withdraw the tool part zero position. Select a tool e.G. Location code 3 – start the spindle and touch the part diameter with several to...
Page 229: Automatic Operations
Chapter 4 automatic operations.
Page 230: Tc Model
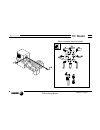
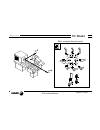
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 2 tc model automatic operations this chapter describes: • which are the keys associated with the automatic operations. • which are the various work modes. • taper turning example. > how to edit the parameters of the operation and what they mean. > how to simulate ...
Page 231: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 3 tc model automatic operations 4.1 operation keys. Layout of the automatic function keys.
Page 232: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 4 tc model automatic operations grooving. Threading. Rounding. Taper turning. Facing. Turning . Positioning. Drilling/tapping. Profile. Operation keys: cycle level selection within an operation..
Page 233: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 5 tc model automatic operations 4.2 work modes. There are 2 work modes: edit mode editing the parameters of the operation or cycle. Simulation of an operation or cycle.( ) execution mode simulation of an operation or cycle. ( ) execution of an operation or cycle. ...
Page 234: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 6 tc model automatic operations 4.3 example of an automatic operation. Taper turning. Help graphics. Spindle status. Actual axes position cutting conditions. Cycle geometry definition. Roughing conditions. Finishing conditions. 4.3.1 edit an operation. – select th...
Page 235: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 7 tc model automatic operations – set the operation data. To select an icon (symbol), data or coordinate: •use the keys to move the cursor. •press or . The cnc selects the first coordinate of the axis. Press it again to select the second coordinate. Press it again...
Page 236: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 8 tc model automatic operations the information shown by the icons is: •type of taper. When changing the type of taper, the graphic assistance also changes. •type of section before and after the taper turning. When changing the type of section, the graphic assista...
Page 237: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 9 tc model automatic operations •work quadrant indicates the type of corner to be machined. •machining direction. : turning. : facing. When changing the machining direction, the graphic help also changes. Note: when selecting an icon, its meaning appears at the bo...
Page 238: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 10 tc model automatic operations 4.3.2 simulate an operation. It is used for checking the tool path on the screen. – press . The cnc will display the graphics menu. To access the various options, press their corresponding keys: funtion: f1 f2 f3 f4 f5 f6 f7 key: t...
Page 239: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 11 tc model automatic operations •type of graphics. – “x-z” graphics. The tool path is represented by color lines. – “solid x-z” graphics. Starting at the first block, the simulation shows how the tool removes material. When done, it shows the resulting part. Note...
Page 240: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 12 tc model automatic operations •display area. It is possible to define the display area by setting the maximum and minimum axis coordinates. –to set the coordinates, use . –once the data has been set, press . •zoom. It is used for enlarging or reducing the drawi...
Page 241: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 13 tc model automatic operations •graphic parameters. Simulation speed: for selecting the % override of the simulation speed being applied. Tool path colors: for changing the tool path colors on “x-z” graphics. Colors for solid graphics: for changing the colors of...
Page 242: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 14 tc model automatic operations 4.3.3 execute an operation. The operations can be executed from beginning to end or a pass at a time. This choice is made with . To start the execution, enter into “execution mode” and press . Once execution has started: : interrup...
Page 243: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 15 tc model automatic operations tool inspection. With this option, the operation may be interrupted for inspecting and replacing the tool or for modifying the tool wear value. – press . – depending on the machine manufacturer, on some machines will also have to b...
Page 244: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 4 page 16 tc model automatic operations modifying the tool wear value. With this option, the i, k values may be changed. The entered values are incremental and will be added to those stored previously. – press . The cnc shows the table for that tool. – use the keys to po...
Page 245: Summary of Work Cycles
Chapter 5 summary of work cycles.
Page 246: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 5 page 2 tc model summary of work cycles 5.1 positioning cycles. In this cycle level, it is possible to define the auxiliary functions to be executed before and after the movement. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 4 section 4.3.
Page 247: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 5 page 3 tc model summary of work cycles 5.2 turning cycle note: refer to the operation manual chapter 4 section 4.4.
Page 248: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 5 page 4 tc model summary of work cycles 5.3 facing cycle. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 4 section 4.5.
Page 249: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 5 page 5 tc model summary of work cycles 5.4 taper cycles. In this cycle level, one defines the coordinates of the theoretical corner, the taper angle and the final diameter. In this cycle level, one defines the coordinates of the starting point and end point. Note: refe...
Page 250: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 5 page 6 tc model summary of work cycles 5.5 rounding cycles. In this cycle level, one defines the coordinates of the theoretical corner and the rounding radius. In this cycle level, one defines the coordinates of the starting point and end point as well as the rounding ...
Page 251: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 5 page 7 tc model summary of work cycles 5.6 threading cycles. Longitudinal threading. Face threading note: refer to the operation manual chapter 4 section 4.8.
Page 252: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 5 page 8 tc model summary of work cycles note: refer to the operation manual chapter 4 section 4.8 face threading thread repair only when having spindle orientation..
Page 253: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 5 page 9 tc model summary of work cycles 5.7 grooving cycles. Radial grooving. Face (axial) grooving note: refer to the operation manual chapter 4 section 4.9.
Page 254: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 5 page 10 tc model summary of work cycles radial grooving with incline walls. Face grooving with incline walls. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 4 section 4.9.
Page 255: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 5 page 11 tc model summary of work cycles 5.8 drilling and tapping cycles. Drilling cycle. Tapping cycle. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 4 section 4.10 note: when having spindle orientation, the cycles described in appendix i will be displayed..
Page 256: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 5 page 12 tc model summary of work cycles 5.9 profile cycles. In this cycle level, one defines all the points of the profile. This cycle level uses a part-program containing all the profile data. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 4 section 4.11.
Page 257: Conversational Part-Programs
Chapter 6 conversational part-programs.
Page 258: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 2 tc model conversational part-programs this chapter describes: • what a conversational part-program is. • how to edit it. • how to change it. (inserting or deleting operations). • simulate/execute an operation. • simulate/execute starting at a particular operatio...
Page 259: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 3 tc model conversational part-programs 6.1 what is a conversational part-program? It is a set of operations ordered secuentially. Each operation is defined separately and they are then stored one after the other in a program the name of the part-program can be an...
Page 260: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 4 tc model conversational part-programs 6.2 edit a part-program. To edit a part-program, we first choose the operations needed to execute the part. A part may be executed in various ways. Different solutions for the same part profile taper turning rounding turning.
Page 261: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 5 tc model conversational part-programs once the sequence of operations has been chosen (in this case, we will make the previous example), the part-program is built by editing the operations one by one. Dro mode (key in the number) + + (comment) + v.G : + + + note...
Page 262: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 6 tc model conversational part-programs choose the operation and define the parameters repeat these steps with the other operations. In our case, the finished part-program will be: program number.
Page 263: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 7 tc model conversational part-programs 6.3 modify a part-program. The cnc shows the cycle with all its data. Modify the operation parameters like in the editing mode. The cnc requests an option. Choose replace. The new operation replaces the previous one. The ope...
Page 264: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 8 tc model conversational part-programs note: refer to the operation manual chapter 5 section 5.6.3 choose operation new operations can also be inserted into a part-program. Define the parameters and cutting conditions of the operation to be inserted. Press choose...
Page 265: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 9 tc model conversational part-programs the cnc requests confirmation operations can be deleted from a part-program. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 5 section 5.6.1 select, on the right column, the operation to be deleted. Delete an operation.
Page 266: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 10 tc model conversational part-programs the position of an operation can also be changed. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 5 section 5.6.2 select the new position select, on the right column, the operation to be moved. The operation is inserted behind ...
Page 267: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 11 tc model conversational part-programs 6.4 simulate/execute an operation. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 6 section 6.3 more information about the graphics screen in chapter 4.3.2 of this manual. Select, on the right column, the operation to be simul...
Page 268: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 12 tc model conversational part-programs 6.5 simulate/execute starting at a particular operation. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 6 section 6.2.1 graphics screen more information about the graphics screen in chapter 4.3.2 of this manual. Select, on the...
Page 269: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 13 tc model conversational part-programs 6.6 simulate/execute a part-program. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 6 section 6.2 graphics screen more information about the graphics screen in chapter 4.3.2 of this manual. Select, on the left column, the part...
Page 270: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 14 tc model conversational part-programs 6.7 copy a part-program into another one. Select, on the left column, the part-program to be copied: key in the number and comment of the new program. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 5 section 5.5.
Page 271: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual chapter 6 page 15 tc model conversational part-programs 6.8 delete a part-program. Select, on the left column, the part-program to be deleted: note: refer to the operation manual chapter 5 section 5.4 the cnc requests confirmation..
Page 272: Ther Machining Operations
Appendix i o ther machining operations on a lathe.
Page 273: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual appendix i. Page 2 tc model other machinig operations on a lathe i.1 introduction. For this type of machining operations, the machine must have a spindle which can be oriented and a live tool. If the machine has these features, the cnc menu will offer the “multiple drilling” and...
Page 274: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual appendix i. Page 3 tc model other machinig operations on a lathe i.2 spindle orientation. With this feature, the spindle can be oriented to the desired angular position for drilling holes and milling slots both on the face of the part or on its turning surface. The cnc shows the...
Page 275: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual appendix i. Page 4 tc model other machinig operations on a lathe i.3 live tool. When selecting this type of tool, the cnc shows the following information: to enter the live tool turning speed, press to select the tool window. Then press: + (turning speed) + to start the live too...
Page 276: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual appendix i. Page 5 tc model other machinig operations on a lathe i.4 multiple drilling. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 4 section 4.10/4.10.4 multiple drilling on the turning surface. Multiple drilling on the face. +.
Page 277: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual appendix i. Page 6 tc model other machinig operations on a lathe i.5 multiple tapping. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 4 section 4.10/4.10.5 multiple tapping on the turning surface. Multiple trapping on the face. +.
Page 278: Tc Model
Self-teaching manual appendix i. Page 7 tc model other machinig operations on a lathe i.6 slot milling. Note: refer to the operation manual chapter 4 section 4.10/4.10.6 slot milling on the turning surface. Slot milling on the face. +.