- DL manuals
- Fantom Drives
- Storage
- MGT-08SC08A
- Installation Reference Manual
Fantom Drives MGT-08SC08A Installation Reference Manual
Summary of MGT-08SC08A
Page 1
Raid scsi to s-ata installation reference guide revision 1.0 p/n: pw0020000000315.
Page 2: Copyright
Copyright no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written consent. Trademarks all products and trade names used in this document are tradem...
Page 3: Fcc Compliance Statement
Fcc compliance statement this equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class b digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in residential installations. This equipment generat...
Page 4: About This Manual
About this manual welcome to your r edundant a rray of i ndependent d isks system user’s guide. This manual covers everything you need to know in learning how to install or configure your raid system. This manual also assumes that you know the basic concepts of raid technology. It includes the follo...
Page 5: Table of Contents
Table of contents chapter 1 introduction 1.1 key features.......................................................................................................... 1.2 raid concepts................................................................................................. 1.3 scsi concepts.......
Page 6
3.6.7 delete hot spare......................................................................................... 3.6.8 rescue raid set.......................................................................................... 3.7 volume set function........................................................
Page 7: Chapter 1
Introduction 1-1 chapter 1 introduction the raid subsystem is a ultra 320 lvd scsi-to-serial ata ii raid (redundant arrays of independent disks) disk array subsystem. It consists of a raid disk array controller and eight (8) disk trays. The subsystem is a “host independent” raid subsystem supporting...
Page 8: 1.1 Key Features
Introduction 1-2 1.1 key features subsystem features: features an intel 80321 64 bit risc i/o processor build-in 128mb cache memory, expandable up to 1024mb ultra 320 lvd host port supports up to eight (8) 1" hot-swappable serial ata ii hard drives high quality advanced cooling fans local audible ev...
Page 9: 1.2 Raid Concepts
Introduction 1-3 1.2 raid concepts raid fundamentals the basic idea of raid (redundant array of independent disks) is to combine multiple inexpensive disk drives into an array of disk drives to obtain performance, capacity and reliability that exceeds that of a single large drive. The array of drive...
Page 10: Definition of Raid Levels
Introduction 1-4 by striping the drives in the array with stripes large enough so that each record falls entirely within one stripe, most records can be evenly distributed across all drives. This keeps all drives in the array busy during heavy load situations. This situation allows all drives to wor...
Page 11: Raid 1
Introduction 1-5 raid 1 , also known as disk mirroring, is simply a pair of disk drives that store duplicate data but appear to the computer as a single drive. Although striping is not used within a single mirrored drive pair, multiple raid 1 arrays can be striped together to create a single large a...
Page 12: Raid 3
Introduction 1-6 raid 3 sector-stripes data across groups of drives, but one drive in the group is dedicated to storing parity information. Raid 3 relies on the embedded ecc in each sector for error detection. In the case of drive failure, data recovery is accomplished by calculating the exclusive o...
Page 13: Raid 6
Introduction 1-7 raid 6 is similar to raid 5 in that data protection is achieved by writing parity information to the physical drives in the array. With raid 6, however, two sets of parity data are used. These two sets are different, and each set occupies a capacity equivalent to that of one of the ...
Page 14: Dual-Level Raid
Introduction 1-8 dual-level raid achieves a balance between the increased data availability inherent in raid 1 and raid 5 and the increased read performance inherent in disk striping (raid 0). These arrays are sometimes referred to as raid 0+1 or raid 10 and raid 0+5 or raid 50. In summary: raid 0 i...
Page 15: Raid Management
Introduction 1-9 raid management the subsystem can implement several different levels of raid technology. Raid levels supported by the subsystem are shown below. Raid level description min drives 0 1 3 5 6 0 + 1 block striping is provide, which yields higher performance than with individual drives. ...
Page 16: 1.3 Scsi Concepts
Introduction 1-10 1.3 scsi concepts before configuring the subsystem, you must first understand some basic scsi concepts so that the subsystem and scsi devices will function properly. 1.3.1 multiple scsi format support the subsystem support the scsi interface standards listed below. Note that the da...
Page 17: 1.3.3 Terminators
Introduction 1-11 1.3.3 terminators based on scsi specifications, the scsi bus must be terminated at both ends, meaning the devices that are connected to the ends of the scsi bus must have their bus terminators enabled. Devices connected in the middle of the scsi bus must have their terminators disa...
Page 18: 1.4 Array Definition
Introduction 1-12 1.4 array definition 1.4.1 raid set a raid set is a group of disks containing one or more volume sets. It is impossible to have multiple raid sets on the same disks. A volume set must be created either on an existing raid set or on a group of available individual disks (disks that ...
Page 19: 1.4.3 Easy of Use Features
Introduction 1-13 1.4.3 easy of use features 1.4.3.1 instant availability/background initialization raid 0 and raid 1 volume set can be used immediately after the creation. But the raid 3, 5 and 6 volume sets must be initialized to generate the parity. In the normal initialization, the initializatio...
Page 20
Introduction 1-14 1.4.3.3 online capacity expansion online capacity expansion makes it possible to add one or more physical drive to a volume set, while the server is in operation, eliminating the need to store and restore after reconfiguring the raid set. When disks are added to a raid set, unused ...
Page 21: 1.4.4 High Availability
Introduction 1-15 1.4.3.4 online raid level and stripe size migration user can migrate both the raid level and stripe size of an existing volume set, while the server is online and the volume set is in use. Online raid level/ stripe size migration can prove helpful during performance tuning activiti...
Page 22
Introduction 1-16 1.4.4.2 hot-swap disk drive support the raid subsystem has built the protection circuit to support the replace- ment of udma hard disk drives without having to shut down or reboot the system. The removable hard drive tray can deliver “hot swappable,” fault- tolerant raid solutions ...
Page 23: Chapter 2
Getting started 2-1 chapter 2 getting started getting started with the subsystem consists of the following steps: unpack the storage subsystem. Identifying parts of the subsystem. Connecting to host. Scsi termination. Power on the subsystem. Install hard drives. 2.1 unpacking the subsystem before co...
Page 24
Getting started 2-2 move the components; contact the dealer where the subsystem was purchased for further instructions. The package contains the following items: • raid subsystem unit • one power cord • two external scsi cables • one external null modem cable • one rj-45 ethernet cable • installatio...
Page 25: 2.2.1 Front View
Getting started 2-3 2.2 identifying parts of the subsystem the illustrations below identify the various features of the subsystem. Get yourself familiar with these terms as it will help you when you read further in the following sections. 2.2.1 front view 2 3 1 s l o t s l o t s l o t s l o t s l o ...
Page 26
Getting started 2-4 3. Environment status function if temperature irregularity in these systems occurs (hdd slot tem- perature over 60 o c) or disk fault, this led will turn red and an alarm will sound. Green led indicates power is on. Blue blinking led indicates data is being accessed. Parts disk f...
Page 27: 2.2.2 Rear View
Getting started 2-5 2.2.2 rear view 1. Host channel a & b the subsystem is equipped with 2 host channels (host channel a and host channel b). The host channel with two 68-pin scsi connectors at the rear of the subsystem for scsi in and out. 2. R-link port : remote link through rj-45 ethernet for rem...
Page 28: 2.3 Connecting to Host
Getting started 2-6 2.3 connecting to host the subsystem supports the ultra 320 scsi lvd interface which provides fast 320mb/s data transfer rates using a 16-bit scsi bus. Installation of the disk array is very similar to the installation of a standard scsi drive. The scsi connector accepts the stan...
Page 29
Getting started 2-7 ! Note: 1. When one or more scsi devices are connected, the total length of all cables (internal or external) must not exceed 3 meters (9.8 ft.) to ensure reliable operation. 2. For safety reasons, make sure the disk array and host computer are turned off when you plug-in the scs...
Page 30: 2.4 Scsi Termination
Getting started 2-8 2.4 scsi termination two 68-pin wide scsi connectors are provided on the back of the enclosure for connecting the array to the system. These connectors are used in one of two ways: if the disk array is the only external scsi device, or is the last external device in a daisy-chain...
Page 31
Getting started 2-9 note: if you are connecting another external device after the subsystem, make sure to disable the terminator at the subsystem’s host channel a & b out connector. The default host channel’s terminator is disabled. ! Correct scsi termination procedures require that the last devices...
Page 32
Getting started 2-10 2.5 powering-on the subsystem when you connect the disk array to the host computer, you should press the on/off power supply switch. It will turn the disk array on and the self-test will be started automatically. 1. Plug in the power cord or power connector located at the rear o...
Page 33: 2.6 Install Hard Drives
Getting started 2-11 2.6 install hard drives this section describes the physical locations of the hard drives supported by the subsystem and gives instructions on installing a hard drive. The subsystem supports hot-swapping allowing you to install or replace a hard drive while the subsystem is runni...
Page 34
Getting started 2-12 4. To install the hard drive into the drive tray, first insert the hard drive as show below. Note: when removing the drive tray module from the enclosure, handle with care to prevent dropping the module. ! 5. Turn the drive tray over. Notice the 4 screws. Tighten these 4 screws ...
Page 35: Chapter 3
Raid configuring 3-1 ! Chapter 3 raid configuring the subsystem has a setup configuration utility built in containing important information about the configuration as well as settings for various optional func- tions in the subsystem. This chapter explains how to use and make changes to the setup ut...
Page 36
Raid configuring 3-2 terminal emulation mode to the monitor port located at the rear of the subsystem. Note: you may connect a terminal while the subsystem’s power is on. 2. Power-on the terminal. 3. Run the vt100 program or an equivalent terminal program..
Page 37
Raid configuring 3-3 4. The default setting of the monitor port is 115200 baud rate, 8 data bit, non-parity, 1 stop bit and no flow control..
Page 38
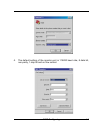
Raid configuring 3-4 5. Click disconnect button. 6. Open the file menu, and then open properties..
Page 39
Raid configuring 3-5 7. Open the settings tab. 8. Open the settings tab. Function, arrow and ctrl keys act as: terminal keys, backspace key sends: crtl+h, emulation: vt100, telnet terminal: vt100, back scroll buffer lines: 500. Click ok..
Page 40
Raid configuring 3-6 keyboard function key definitions “ a “ key - to move to the line above “ z “ key - to move to the next line “ enter “ key - submit selection function “ esc “ key - return to previous screen “ l ” key - line draw “ x ” key - redraw 9. Now, the vt100 is ready to use. After you ha...
Page 41: Main Menu
Raid configuring 3-7 main menu the main menu shows all function that enables the customer to execute actions by clicking on the appropriate link. Note: the password option allows user to set or clear the raid subsystem’s password protection feature. Once the password has been set, the user can only ...
Page 42
Raid configuring 3-8 option quick volume and raid set setup raid set functions volume set functions physical drive functions raid system functions ethernet configuration views system events clear event buffer hardware monitor system information description create a raid configurations which is consi...
Page 43
Raid configuring 3-9 function use the up or down arrow keys to go through the information on the lcd screen. This is also used to move between each menu when you configure the subsystem. This is used to enter the option you have selected. Press this button to return to the previous menu. Parts up or...
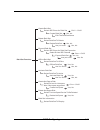
Page 44: 3.3 Menu Diagram
Raid configuring 3-10 raid 0 quick volume / raid setup raid 1 or 0+1 raid 1 or 0+1 +spare raid 3 raid 5 raid 3 + spare raid 5 + spare raid 6 raid 6 + spare selected capacity select stripe size 4k,8k,16k,32k,64k,128k create vol / raid set yes, no selected capacity select stripe size 4k,8k,16k,32k,64k...
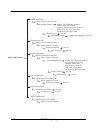
Page 45
Raid configuring 3-11 create raid set raid set function delete raid set expand raid set activate raid set create hot spare disk delete hot spare disk raid set information select ide drives for raid set create raid set edit the raid set name select raid set to delete delete raid set yes, no are you s...
Page 46
Raid configuring 3-12 create volume set volume set function delete volume set check volume set stop volume check display volume info. Create volume from raid set volume creation create volume delete volume from raid set select volume to delete delete volume set yes, no check volume from raid set sel...
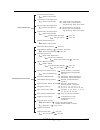
Page 47
Raid configuring 3-13 physical drives create pass through disk delete pass through disk identify selected drive select the drives select the drives select the drives delete pass through are you sure? Yes, no select the drives modify pass through disk view drive information scsi channel, scsi id, scs...
Page 48
Raid configuring 3-14 auto speed down ethernet configuration two tb cdb select show system events view system events clear event buffer clear event buffer yes, no the hard monitor information hardware monitor the system information system information inband scsi function inband scsi channel inband s...
Page 49: R-Link Ethernet Port
Raid configuring 3-15 3.4 web browser-based remote raid management via r-link ethernet port configuration of the internal raid subsystem with remote raid management is a web browser-based application, which utilizes the browser installed on your oper- ating system. Web browser-based remote raid mana...
Page 50: Main Menu
Raid configuring 3-16 individual category quick create raid set functions volume set functions physical drive system control information description create a raid configuration, which is consist of the number of physical disk installed; it can modify the volume set capacity, raid level, and stripe s...
Page 51: Configuration Procedures
Raid configuring 3-17 configuration procedures below are a few practical examples of concrete configuration procedures. 3.5 quick create the number of physical drives in the raid subsystem determines the raid levels that can be implemented with the raid set. You can create a raid set associated with...
Page 52
Raid configuring 3-18 greater two tb volume support: no: still keep the volume size with max. 2tb limitation. 64bit lba: the max. Size 512tb, for unix or linux. Due to lsi53c1030t does not support 16byte cdb for 64bit lba, vendor specific 12byte cdb is used for 64bit lba support. The system may dete...
Page 53: 3.6 Raid Set Functions
Raid configuring 3-19 3.6 raid set functions use the raid set function and volume set function if you prefer to customize your system. User manual configuration can full control of the raid set setting, but it will take longer to complete than the quick volume/raid setup configuration. Select the ra...
Page 54: 3.6.2 Delete Raid Set
Raid configuring 3-20 3.6.2 delete raid set to delete a raid set, click on the delete raid set link . A “ select the raid set to delete” screen is displayed showing all raid set existing in the current controller. Click the raid set number you which to delete in the select column to delete screen. T...
Page 55: 3.6.3 Expand Raid Set
Raid configuring 3-21 3.6.3 expand raid set use this option to expand a raid set, when a disk is added to your system. This function is active when at least one drive is available. To expand a raid set, click on the expand raid set link. Select the target raid set, which you want to expand it. Tick ...
Page 56
Raid configuring 3-22 migrating occurs when a disk is added to a raid set. Migration status is dis- played in the raid status area of the raid set information when a disk is added to a raid set. Migrating status is also displayed in the associated volume status area of the volume set information whe...
Page 57: 3.6.4 Offline Raid Set
Raid configuring 3-23 3.6.4 offline raid set if user wants to move the raid set, when the raid subsystem is power on. User can use the offline raid set option to offline the raid set. After user complete the function, the hdd state will change to offline mode. To offline a raid set, click on the off...
Page 58
Raid configuring 3-24.
Page 59
Raid configuring 3-25.
Page 60: 3.6.6 Create Hot Spare
Raid configuring 3-26 when you choose the create hot spare option in the raid set function, all unused physical devices connected to the current controller appear: select the target disk by clicking on the appropriate check box. Tick on the confirm the operation , and click on the submit button in t...
Page 61: 3.6.8 Rescue Raid Set
Raid configuring 3-27 3.6.8 rescue raid set if you try to rescue missing raid set, please contact our engineer for assistance. 3.6.7 delete hot spare select the target hot spare disk to delete by clicking on the appropriate check box. Tick on the confirm the operation , and click on the submit butto...
Page 62: 3.7 Volume Set Function
Raid configuring 3-28 3.7 volume set function a volume set is seen by the host system as a single logical device. It is orga- nized in a raid level with one or more physical disks. Raid level refers to the level of data performance and protection of a volume set. A volume set ca- pacity can consume ...
Page 63
Raid configuring 3-29 volume name: the default volume name will always appear as volume set. #. You can re- name the volume set name providing it does not exceed the 16 characters limit. Raid level: set the raid level for the volume set. Highlight raid level and press enter . The available raid leve...
Page 64
Raid configuring 3-30 to two tera bytes only. A patch driver is needed to enable the system to detect over two tera bytes. Please contact your vendor for supporting. 4k block: the max. Size 16tb , just use with “ basic disk manager “ under os window 2000, 2003 or xp. Noted that can’t be used by with...
Page 65: 3.7.2 Delete Volume Set
Raid configuring 3-31 3.7.2 delete volume set to delete volume from raid set system function, move the cursor bar to the main menu and click on the delete volume set link. The select the volume set to delete screen will show all raid set number. Tick on a raid set number and the confirm the operatio...
Page 66: 3.7.3 Modify Volume Set
Raid configuring 3-32 3.7.3 modify volume set to modify a volume set from a raid set: (1). Click on the modify volume set link. (2). Tick on the volume set from the list that you wish to modify. Click on the submit button. The following screen appears. Use this option to modify volume set configurat...
Page 67
Raid configuring 3-33.
Page 68: 3.7.4
Raid configuring 3-34 3.7.4 volume set migration migrating occurs when a volume set is migrating from one raid level to another, a volume set strip size changes, or when a disk is added to a raid set. Migration status is displayed in the volume status area of the raidset hierarchy screen when one ra...
Page 69: 3.7.5 Check Volume Set
Raid configuring 3-35 3.7.5 check volume set use this function to perform volume set consistency check, which verifies the correctness of redundant data (data blocks and parity blocks) in a volume set. This basically means computing the parity from the data blocks and comparing the results to the co...
Page 70: 3.7.6 Stop Volumeset Check
Raid configuring 3-36 3.7.6 stop volumeset check use this option to stop the check volume set function. Note: when the 2 options are not selected, it will only check for errors. It is recommended to perform check volume set with the 2 options unselected at first. If the result shows error, the two o...
Page 71: 3.8 Physical Drive
Raid configuring 3-37 3.8 physical drive choose this option from the main menu to select a physical disk and to per- form the operations listed below. 3.8.1 create pass-through disk to create pass-through disk, move the mouse cursor to the main menu and click on the create pass-through link. The rel...
Page 72
Raid configuring 3-38 3.8.2 modify pass-through disk use this option to modify the pass-through disk attribute. User can modify the cache mode, tagged command queuing, max scsi speed and scsi channel/id/lun on an existed pass through disk. To modify the pass-through drive attribute from the pass-thr...
Page 73
Raid configuring 3-39 3.8.3 delete pass-through disk to delete pass-through drive from the pass-through drive pool, move the mouse cursor bar to the main menus and click on delete pass through link. After you complete the selection, tick on the confirm the operation and click on the submit button to...
Page 74: 3.9 System Configuration
Raid configuring 3-40 3.9 system configuration 3.9.1 system configuration to set the raid system function, move the cursor bar to the main menu and click on he raid system function link. The raid system function menu will show all items. Select the desired function. System beeper setting: the alert ...
Page 75
Raid configuring 3-41 terminal port configuration: speed setting values are 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200,38400, 57600, and 115200. Stop bits values are 1 bit and 2 bits. Note: parity value is fixed at none. Data bits value is fixed at 8 bits. Jbod/raid configuration the raid subsystem supports jbod...
Page 76
Raid configuring 3-42 ered up altogether at the same time. The power transfer time (lag time) from the last hdd to the next one can be set within the range of 0.4 to 6.0. Spin down idle hdd (minutes): this option is to spin down hard drives after they have been idle for a select- able amount of time...
Page 77
Raid configuring 3-43 3.9.2 u320 scsi target config to set the u320 scsi target function, move the cursor bar to the main menu and click on the u320 scsi target config . Channel 0 / 1 qas: the enabled option supports quick arbitration and selection (qas). Qas re- duces the overhead of control releas...
Page 78: 3.9.3 Ethernet Config
Raid configuring 3-44 3.9.3 ethernet config to set the ethernet function, move the cursor bar to the main menu and click on he ethernet config . The raid system ethernet function menu will show all items. Select the desired function. 3.9.3.1 dhcp host name support if dhcp function is “ enabled ” and...
Page 79: 3.9.4 Alert By Mail Config
Raid configuring 3-45 3.9.4 alert by mail config to set the event notification function, move the cursor bar to the main menu and click on the alert by mail config . The raid system event notification function menu will show all items. Select the desired function. When an abnormal condition occurs, ...
Page 80: 3.9.5 Snmp Configuration
Raid configuring 3-46 3.9.5 snmp configuration the snmp gives users independence from the proprietary network management schemes of some manufacturers and snmp is supported by many wan and lan manufacturers enabling true lan/ wan management integration. To set the snmp function, move the cursor bar ...
Page 81: 3.9.6 Ntp Configuration
Raid configuring 3-47 message. This allows user to easily define which raid unit is having problem. Once this setting is done, alert by mail configuration will also work in the same way. Snmp trap notification configurations: select the desired function. After you complete the addition, tick on the ...
Page 82: 3.9.7 View Events
Raid configuring 3-48 3.9.7 view events to view the raid subsystem controller’s information, move the mouse cursor to the main menu and click on the system information link. The raid sub- system events information screen appears. Choose this option to view the system events information: timer, devic...
Page 83: 3.9.8 Generate Test Events
Raid configuring 3-49 3.9.8 generate test events if you want to generate test events, move the cursor bar to the main menu and click on he generate test events . Tick on the confirm the operation , and click on the submit button in the screen to create the hot spares. Then click on the view events/m...
Page 84: 3.9.9 Clear Events Buffer
Raid configuring 3-50 3.9.9 clear events buffer use this feature to clear the entire events buffer information. 3.9.10 modify password to set or change the raid subsystem password, move the mouse cursor to raid system function screen, and click on the change password link. The modify system password...
Page 85: 3.9.11 Upgrade Firmware
Raid configuring 3-51 the password option allows user to set or clear the raid subsystem’s password protection feature. Once the password has been set, the user can only monitor and configure the raid subsystem by providing the correct password. The password is used to protect the internal raid subs...
Page 86: 3.10 Information Menu
Raid configuring 3-52 3.10 information menu 3.10.1 raidset hierarchy use this feature to view the internal raid subsystem current raid set, current volume set and physical disk configuration. 3.10.2 system information to view the raid subsystem controller’s information, move the mouse cursor to the ...
Page 87: 3.10.3 Hardware Monitor
Raid configuring 3-53 3.10.3 hardware monitor to view the raid subsystem controller’s hardware monitor information, move the mouse cursor to the main menu and click the hardware monitor link. The hard- ware information screen appears. The hardware monitor information provides the temperature and vol...
Page 88: Raid
Raid configuring 3-54 3.11 creating a new raid or reconfiguring an existing raid you can configure raid sets and volume sets using quick create or raid set functions/volume set functions configuration method. Each configuration method requires a different level of user input. The general flow of ope...
Page 89
Raid configuring 3-55 3.12 upgrading the firmware upgrading flash firmware programming utility since the raid subsystem controller features flash firmware, it is not neces- sary to change the hardware flash chip in order to upgrade the raid firmware. The user can simply re-program the old firmware t...
Page 90
Raid configuring 3-56 upgrading firmware through ansi/vt-100 terminal emulation get the new version firmware for your raid subsystem controller. For example, download the bin file from your oem’s web site onto the c: 1. From the main menu, scroll down to “raid system function” 2. Choose the “update ...
Page 91
Raid configuring 3-57 4. Select “zmodem modem” under protocol. Zmodem as the file transfer protocol of your terminal emulation software. 5. Click browse. Look in the location where the firmware upgrade software is located. Select the file name: “xxxxxxx.Bin” and click open. 6. Click send. Send the f...
Page 92
Raid configuring 3-58 7. When the firmware completes downloading, the confirmation screen appears. Press “yes” to start program the flash rom. 8. When the flash programming starts, a bar indicator will show “ start updating firmware. Please wait:”..
Page 93
Raid configuring 3-59 9. The firmware upgrade will take approximately thirty seconds to complete. 10. After the firmware upgrade is complete, a bar indicator will show “ firmware has been updated successfully”. Note: the user has to reconfigure all of the settings after the firmware upgrade is compl...
Page 94
Raid configuring 3-60 upgrading firmware through web browser management get the new version firmware for your raid subsystem controller. 1. To upgrade the raid subsystem firmware, move the cursor to upgrade firmware link. The upgrade the raid system firmware screen appears. 2. Click browse. Look in ...
Page 95
Raid configuring 3-61 5. After the firmware upgrade is complete, a bar indicator will show “ firmware has been updated successfully”.
Page 96: Appendix A
Technical specification a-1 appendix a technical specification raid processor raid level cache memory no. Of channels (host+disk) host bus interface data transfer disk interface hot swap disk bays hot swap power supply cooling fan maid support multiple raid selection smtp, snmp support array roaming...