- DL manuals
- Farymann Diesel
- Engine
- 15B Series
- Workshop Manual
Farymann Diesel 15B Series Workshop Manual
3
CONTENTS
I
General Information
I.1.
Introduction
5
I.2.
Farymann Diesel engines
7
I.3.
Engine identification
7-8
I.4.
Cross reference old - new engine type
8
II
Technical Data
II.1.
General engine data
9
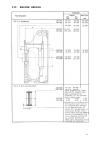
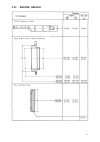
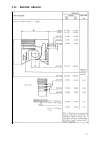
II.2.
Picture of model 15/18
10
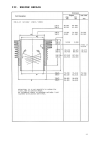
II.3.
Sectional view of model 15/18
11
II.4.
Special tools
12-14
III
Engine Repair
III.1.
Engine disassembly
15-27
III.2.
Wear and tear measurements
28-41
III.3.
Engine reassembly
42-58
III.4.
Lubrication system
59
III.5.
Function and repair of fuel system
60-65
III.6.
Governor
66-70
III.7.
Resurfacing of valve seats
70
III.8.
Setting datas for fuel timing
71-72
III.9.
Tightening torques
73
IV
Trouble Shooting
74-78
Summary of 15B Series
Page 1
3 contents i general information i.1. Introduction 5 i.2. Farymann diesel engines 7 i.3. Engine identification 7-8 i.4. Cross reference old - new engine type 8 ii technical data ii.1. General engine data 9 ii.2. Picture of model 15/18 10 ii.3. Sectional view of model 15/18 11 ii.4. Special tools 12-...
Page 2: Preface
4 preface this manual is for workshop use only and intended for use by experienced mechanics. Only the standard type of engine models 15b/d 18b/d 29c/32a are illustrated and dealt with. Because there are, however, many different type variants which can differ to a greater or lesser degree from the s...
Page 3: Gasoline
5 i.1. Introduction to diesel engines nowadays diesel engines are well known and quite common in all kinds of machinery and equipement as an alternative to the well established gasoline engine. Most people who are fully familiar with gasoline engines are reluctant to deal with a diesel. This is with...
Page 4: I. General Information
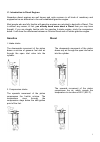
I. General information 6 iii. Power stroke a spark created by a spark plug ignites the fuel. The resulting expansion of the combustion gases forces the piston down. Fuel in a fine mist is sprayed into the cylinder and self ignites in the hot air. The resulting expansion of the combustion gases force...
Page 5: I. General Information
I. General information 7 i.2. Farymann diesel engine all farymann diesel engines are 4 stroke, direct injection diesel engines. They are built as single cylinder engines in vertical and horizontal cylinder configuration.The direct injection guarantees an outstanding efficiency with low fuel consumpt...
Page 6: I. General Information
I. General information 8 i.3. Engine identification an engine name plate is affixed to every engine. In addition to the name plate the engine order number and, effective july 1985, the running engine number are also stamped on the crankcase. The complete engine code must be quoted when ordering spar...
Page 7: II. Technical Data
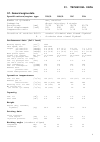
Ii. Technical data 9 ii.1. General engine data specifications/engine type 15b/d 18b/d 29c 32a ______________________________________________________________________ number of cylinders one, vertical combustion direct injection, 4 stroke bore/stroke [mm] 75/55 82/55 90/74 95/74 total displacement [cm...
Page 8: III.1. Disassembly
Iii.1. Disassembly 10
Page 9: II. Technical Data
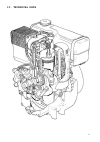
Ii. Technical data 11.
Page 10: II. Technical Data
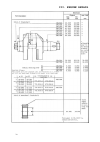
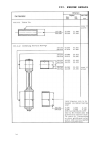
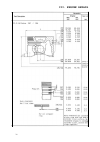
Ii. Technical data 12 ii.4. Special tool list it is assumes that authorized farymann diesel dealers have all of the common tools needed to service diesel engines i.E. Metric open end and ring spanners, sockets, torque wrench, mtric caliper and depth gauge as well as piston ring pliers, piston ring c...
Page 11: II. Technical Data
Ii. Technical data 15 13 748.132.6 cranksh. Race puller use with puller to remove crankshaft roller bearing race 748.137.2 crankshaft gear puller use with puller to remove crankshaft gear wheel 748.136.2 puller for parts 148.132.6 and 748.137.2 748.122.6 flywheel puller to remove flywheel from crank...
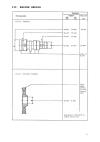
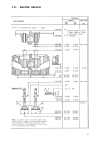
Page 12: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 14 748.129.4 bearing driver to remove and install regulation shaft bushing 748.123.4 bearing driver handle treated handle for various bearing drives 748.125.4 valve guide driver to remove and install valve gides 748.131.5 valve sring compr. To remove and install valves 748.135.2 r...
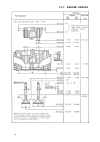
Page 13: II. Technical Data
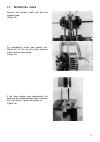
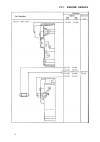
Ii. Technical data 15 iii.1. Engine disassembly prior to dismantling the engine clean off engine exterior thoroughly.Dismantling will be greatlyfacilitated by location withgood lighting and freedom ofmovement, away from dirt andmetal chips.The work to be carried out isdescribed and illustrated step ...
Page 14: III. Engine Repair
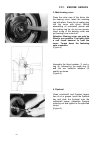
Iii. Engine repair 16 1. Drain lubrication oil place suitable container under the drain hole. Remove oval flange of oil drain, remove oilfilter. Wait until oil has fully trained, if necessary, tip over engine. (figures 1 and 1a) 2.Air cleaner remove the two aircleaner selflocking nuts. Pull off the ...
Page 16: III.1. Disassembly
Iii.1. Disassembly 17 5. Fuel tank support brackets pull off the fuel tank upport brackets as well as the intake and the exhaust manifold gaskets. Figure 4) 6. Air deflectors remove the two screws and lockwashers holding the air deflector shields on top of the crankcase. (figure 5) 7. Valve cover re...
Page 17: III. Engine Repair
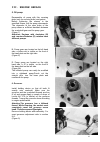
Iii. Engine repair 18 loosen the high pressure line at the injector in the same way. (figure 8) 9. Fuel injector remove the two hex nuts and their lockwashers from thr injector clamp. And pull out the injector. If the injector sticks in the hand, use a soft faced hammer and tap slightly on the injec...
Page 18: II. Technical Data
Ii. Technical data 19 remove the cylinder head nuts and the cylinder head. (figure 12) for dismantling valves use special tool. Watch out for the two thin steel washers under the inlet valve spring. (figure 13) if the valve guides need replacement (for wear and tear measurements refer to section iii...
Page 19: III. Engine Repair
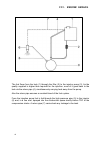
Iii. Engine repair 20 shout the valve seat be damaged to the point that grinding of valves is not sufficient, the seat can be resurfaced with tool (for wear and tear limits and detailed instructions for use of tool refer to section iii.2. Resp. Iii.7.) (figure 15) 11. Cylinder shields remove the bol...
Page 20: II. Technical Data
Ii. Technical data 21 compression release after removing its screws, pull the compression release out of the gearcase. (figure 18) 13. Cylinder rotate the flywheel until the piston reaches the bottom of its stroke. Carefully slide the cylinder up off the studs. Attention: if the repair does not requ...
Page 21: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 22 with a drift pin gently hammer piston pin out of the piston from flywheel side. Attention: if piston pin sticks in piston, remove piston compete with connecting rod (step 15 and hammer out piston pin after the assembly has been removed from engine. (figure 25) 15. Connecting ro...
Page 22: II. Technical Data
Ii. Technical data 23 17. Gear cover remove the six allen screws and pull off the gear cover. If nenecessary, tap at the gear cover with a soft faced hammer to loosen it.If, when removing, the cover should catch on the governor beneath, turning the flywheel slightly will free it. (figure 25) do not ...
Page 23: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 24 17.2. Cramshaft remove the snap ring holding the cramshaft in the gear cover. Press out the cramshaft using the driver. (figure 28) to pull off the camshaft gear wheel, use puller or press out the camshaft. (figure 29) after the camshaft is removed, the roller bearing can be pr...
Page 24: II. Technical Data
Ii. Technical data 25 17.3. Speed regulation assembly lay the gear cover down on the work bench. Remove the retaining ring from the regulation shaft with a pliers.Pull the shaft outwards till the ratchet plate is free from the pin.Unhook the outer torsion spring from the boss(use a pliers and watch ...
Page 25: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 26 20. Flywheel using socket on stricker and a hammer, loosen the flywheel nut by two turns. Attention:if the flywheel has to be removed from an engine without dismantling the governor/regulation linkage, it is necessary to place the acceleration lever at full load position. Other...
Page 26: II. Technical Data
Ii. Technical data 27 22. Crankshaft remove the crankshaft from the crankcase, being careful not to drag the crankshaft gear on the main bearing bushing. To pull off the crankshaft gear wheel,use puller. (figure 38) 22.1. In case the roller bearing needs replacement, replace also the inner race,whic...
Page 27: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 28 iii. 2. Dimension table - wearing parts.
Page 28: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 29.
Page 29: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 30
Page 30: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 31.
Page 31: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 32.
Page 32: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 33.
Page 33: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 34.
Page 34: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 35.
Page 35: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 36.
Page 36: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 37.
Page 37: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 38.
Page 38: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 39.
Page 39: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 40
Page 40: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 41.
Page 41: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 42 iii. 3. Engine reassembly.
Page 42: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 43 1. Crankcase press the bearing bush with driver. Take care that the joining line of the bearing bush is located as shown and that the oil holes in the bushing and the crankcase are properly lined up. (figure 1) 2. Crankshaft to install the crankshaft gear wheel and the inner ra...
Page 43: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 44 3. Main bearing cover press the outer race of the driver into the bearing cover. Insert the retaining ring with pliers. Press the oil sealing ring into the cover with driver. Before assembling oil crankshaft journal and the sealing ring lip, do not use grease. Insert o-ring in ...
Page 44: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 45 5. Oil pump reassemble oil pump with thin covering plate (only for securing bolts) and gasket. Before tightening the screws to the specified torque, pull the pump downwards. The clearance in the srew holes of the pump allows a sufficient backlash between the crankshaft gear and...
Page 45: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 46 7. Connecting rod to install new bearing shells, take a shell half and lay it to approx. ¾ into the cap. Now press with your thumb the bearing in a sliding movement onto ist seat. The bearing lip must fit into the grove in the cap. The connection rod side shell half is installe...
Page 46: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 47 using a driver press the camshaft bearing into the gear cover. (figure 14) now press the camshaft with driver into the bearing using a driver as a counter pressure piece for the bearing. Make sure that the bearing seats fully against the bearing seat flange. Insert the retainin...
Page 47: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 48 slide the eccentric shaft through the bearing bush in the housing and into the control lever. Turn the acceleration lever downwards („stop“-position) until spring leg of the return spring can be managed to get into the notch of the eccentric shaft. (figure 16c) use a wire loop ...
Page 48: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 49 oil the ring and piston skirts. Check that piston ring gaps are 120 degrees offset. Compress rings with ring compressor. Lay the cylinder down on the bench with the bottom facing up. Install the piston into the cylinder from the bottom. Never tap on the piston crown. Attention:...
Page 49: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 50 grind in the valves. The rotocap and the conical shaped spring belong to the exhaust valve. The two thin steel washers must be under the cylindrical spring of the inlet valve. Fit new sealing cap onto the inlet valve guide. Before fitting the rotocap check for proper function: ...
Page 50: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 51 insert the governor pin into the bore in the governor. Use grease to keep the pin in place. Line up the timing mark on the camshaftgear with the mark on the gear cover. (marks „a“ and „b“). Install the gear cover (remember to place the gaskets) onto the crankcase being careful ...
Page 51: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 52 - install the cover. Align the camshaft gear and gear cover timing marks. Now check the flywheel and crankcase timing marks. The timing is acceptable, if they are within ± 2 mm ( ± 0.0787) of each other. When installing the gear cover screws, note that the top two and bottom le...
Page 52: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 53 when a new decompression device is installed the correct function must be checked. To do so install the decompression device with the 0.4 mm (0.0157“) thick gasket, continue with step 14, 15 and 16. Turn the piston approx. 1/8 revolution before tdc and measure with a depth gaug...
Page 53: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 54 15. Rocker arms place piston to tdc position. Line up rocker arms and push rods and oil the rocker arm bolt before installing it into the support. Attention: to prevent damage of push rods while torquing the cylinder head nuts, ensure sufficient clearence between setting screw ...
Page 54: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 55 18. Cylinder shields and air guides install both halves of cylinder shields and the clamping bolt. Do not overtighten the bolt. It is sufficient when the bold protrudes about 1-2 mm (0.0394“-0.0787“) out of the locknut. Install the two air guides on top of the crankcase. (figur...
Page 55: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 56 21. High pressure fuel pipe install the high pressure fuel pipe and tighten the union nuts on injector and pump. While tightening nut on pump and injector maintain counter parts with a 14 mm wrench. (figure 39) 22. Valve cover install the valve cover gasket and the valve cover,...
Page 56: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 57 24. Fuel tank place the fuel tank on the tank brackets. Slide both tank straps over the tank and brackets. Do not forget to reinstall the two tank seam protectors. Tighten the straps. (figure 42) 25. Fuel leak-off and supply line install banjo bolts on the fuel leak- off/supply...
Page 57: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 58 27. Test run the engine is now completely reassembled. Install engine on a test bench and carry out a test run. The engine does not require a long time running-in program. After a short run according to below specifications the engine is ready for normal operation. Also the use...
Page 58: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 59 figure 1 figure 2 a gear pump (2) sucks the oil from the oil sump (1) and pumps it through the oilfilter (3) to the main bearing (5) and to the conrod bearing. Piston, piston pin, cylinder liner and rocker arms are splash lubricated. When oil pressure rise above 4,5 bar (63 psi...
Page 59: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 60 the fuel flows from the tank (1) through the filter (2) to the injector pump (3). As the quality supplied is higher than required for the injection, most of it goes back to the tank via the return pipe (4), simultaneously carrying heat away from the pump. Also the return pipe e...
Page 60: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 61 iii.5.1. Fuel system the fuel filter prevents the entry of dirt into the injection pump. The normal lifespan of the filter is approx. 2000 operation hrs., however, it depends on the purity of the fuel used. Prior to changing fuel filter, clean the fuel pipe from dirt with a rag...
Page 61: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 62 to check the injection pressure, connect the complete injector valve to a nozzle tester. Pump with the hand lever till the nozzle ejects.The fuel must be ejected evently atomized without drippling at the specified pressure. (figure 6) caution: keep hands away from nozzle spray!...
Page 62: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 63 iii.5.3. Excess starting fuel button for ease of starting all engines are fitted with an excess startingfuel pull button. (figure 8) a cone limits the travel of the injector pump fuel rack. When the starting fuel button is pulled down prior to start, the cone allows the fuel ra...
Page 63: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 64 iii.5.4. Adjustment of fuel injection timing the correct setting of the commencement of delivery is a basic requirement for a troublefree function of the engine. As the injection timing is fixed, a check and respectively readjustment is only necessary when the engine speed was ...
Page 64: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 65 use a flexible ruler and measure the distance between tdc marks on the flywheel and housing. (figure 12) compare the measurement with the valves at the table iii.8 observing the correct flywheel diameter and engine speed. If the measured value is out of tolerance, readjust the ...
Page 65: III. Engine Repair
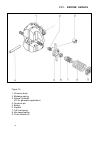
Iii. Engine repair 66 figure 15 1. Governor body 2. Midrange spring 3. Spacer ((instead of 2 for generator application) 4. Governor pin 5. Bridge 6. Support 7. Full load spring 8. Idle speed spring 9. Cross slotted nut.
Page 66: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 67 the purpose of governor is to maintain constantly the specified speed of the engine. Therefore, centrifugal and resilient spring forces are used to monitor the amount of fuel injected by the injection pump. According to the utilization of the engine, there are several types of ...
Page 67: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 68 due to the control lever pivoting on the eccentric regulation shaft the distance between tappet bolt and governor pin increases when the acceleration lever is moved towards full load position. Thus enabling the small tension spring to push the control lever and the connected in...
Page 68: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 69 crank the engine until the governor flyweights stand in a vertical position. Put the acceleration lever in full load position. Open the lock plate and loosen the castle nut. Screw in tappelt bolt completely till tappet rests on control lever. Insert a screwdriver between the fl...
Page 69: III. Engine Repair
Iii. Engine repair 70 iii.6.3. Acceleration lever the acceleration lever is fixed in its position on the excentric shaft with a pin. The rachet plate located behind the lever is not fixed and only kept in place by the m8 nut. As the ratched plate is used as a buffer for the engine shut down, the cor...
Page 70
71 iii.8. Adjustment – injection pump – begin of delivery flywheel- begin of delivery (mm) btdc - toleranz engine type part-no.: dia- +-2mm engine speed (mm -1 ) meter mm 1500 1800 2000 2500 2800 3000 3300 3600 738.146.4 15b/d 738.149.4 738.158.4 15b 738.160.4 738.174.4 15b 738.181.4 15d 738.185.4 2...
Page 71
72 iii.8.1 adjustment – injection pump – begin of delivery flywheel- end of delivery (mm) btdc - toleranz engine type part-no.: dia- +-2mm engine speed (mm -1 ) meter mm 1500 1800 2000 2500 2800 3000 3300 3600 738.146.4 15b/d 738.149.4 738.158.4 15b 738.160.4 738.174.4 15b 738.181.4 15d 738.185.4 25...
Page 72
73 iii.9 torque specifications 15b/15d/18b/18d 29c/32a spanner size tightening tourque (nm) spanner size tightening tourque (nm) (mm) min max (mm) min max cylinder head nuts 13 30 33 17 52 56 connecting road nuts 13 30 33 14 52 56 valve cover nuts 13 8 12 13 8 12 main bearing plate nuts 13 30 33 13 ...
Page 73
74.
Page 74
75.
Page 75
76.
Page 76
77.