- DL manuals
- FastVision
- Webcam
- FC13
- User And Reference Manual
FastVision FC13 User And Reference Manual
Summary of FC13
Page 1
1 fastcamera usb user’s and reference manual fvm-00398.
Page 2
2 copyright notice copyright ? 2005 by fastvision llc. All rights reserved. This document, in whole or in part, may not be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated, or reduced to any other electronic medium or machine-readable form without the express written consent of fastvision llc. Fastvision...
Page 3
3 fastvision llc. 131 daniel webster highway, #529 nashua, nh 03060 usa telephone: 603-891-4317 fax: 603-891-1881 web site: http://www.Fast-vision.Com email: sales@fast-vision.Com, or support@fast-vision.Com.
Page 4
4 table of contents copyright notice_____________________________________________ 2 usb2.0 user’s guide to fc13 and fc40 __________________________ 5 the usb 2.0 versions of fast camera 13 and 40___________________________________________5 computer system requirements _______________________________...
Page 5
5 usb2.0 user’s guide to fc13 and fc40 t he usb 2.0 v ersions of f ast c amera 13 and 40 the usb 2.0 versions of fast cameras fv-13 and fv-40 make use of the widely used usb 2.0 computer interface that can carry up to 40 mb/s of data. This interface is a standard part of all recently manufactured de...
Page 6: Software Has Been Installed.
6 h ardware and s oftware i nstallation installation of the camera hardware is very simple and has only one hard rule: c ables and c onnectors operating the usb-connected fastcamera fv13 or fv40 require the use of only two cables: standard usb 2.0 ab cable and the camera specific power cable that ca...
Page 7
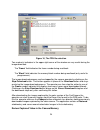
7 figure 2. The usb 2.0 a-b cable connect the standard usb 2.0 ab computer cable to your computer but do not connect it to the camera until after the fastcamera application software is installed. D irect x i nstallation proper operation of the fastcamera usb requires presence of the up-to-date direc...
Page 8
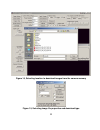
8 figure 3. Fast viewer-usb main screen and camera controls. F ast c amera usb o perating m odes and s tates operation of the fastcamera usb is presumed to alternate between three main and one optional state: 1. Continuous capture is the mode when all incoming video data are stored into the circular...
Page 9
9 capture state. Continuous capture mode is expected to be used as a main maintenance mode to adjust camera parameters, target and focus the camera on the object. You can end this mode only by asserting the internal or external trigger and shifting into the capture completion mode. The software vers...
Page 10
10 figure 4, fastcamera operating modes and transitions..
Page 11
11 f ast c amera -usb a pplication c ontrols the figure 3 shows grouping of camera controls responsible for operation of each camera mode. Continuous capture and preview mode this is the main operating mode of the fastcamera. It is central to its operation and it has the largest set of camera contro...
Page 12
12 the ‘reset’ button sends a reset command to the camera that restores its internal state from the camera internal flash memory. This is the state you find the camera in every time you power it up. You may want to force it if you find the camera is not operating after your parameter changes as you ...
Page 13
13 figure 5, color24 adjustment controls for the video preview display. In some cases when the visual preview image is too dark or too bright to observe you can do a quick image adjustment using the display-digital gain control. The display-digital gain only affects the preview window images. If it ...
Page 14
14 ? The type and relative position of the trigger in the captured video sequence. I mage size and position by default the fastcamera is set to capture video with the full resolution of the image sensor in the camera. For various reasons that include increased capture speed and number of image frame...
Page 15
15 the frame period you have selected, after you press 'apply-(changes)' button. You will be given a choice between a smaller roi height and a lower frame rate. Applying your choice the application will make the smallest possible change. Figure 7, changing roi of the video capture any changes you ma...
Page 16
16 figure 8, adjusting exposure to the frame rate the more intuitive method of setting and adjusting exposure is based on observation of the histogram or the preview video. The histogram window insert is brought about by clicking on the histogram button above the preview window. It displays the freq...
Page 17
17 figure 9, using image histogram to adjust exposure t rigger p osition in the c apture b uffer the 'trigger-settings' button brings up the trigger settings dialog which allows you to choose and set the trigger mode of the camera. See figure 10 below figure 10, trigger settings dialog..
Page 18
18 the trigger settings dialog box controls the settings of the trigger in the camera. Normally the camera should be in free-running mode, with p2 ttl enable checked as in the picture above. That configuration will support both, external and internal trigger modes. The camera link group box enables ...
Page 19
19 frame flashing is a sign that the exposure and frame rate are incompatible. Typically you should set this to 160 and do not change. Saving and restoring camera settings the internal flash memory of the fastcamera allows you to define the eight sets of the camera parameters that can be saved and r...
Page 20
20 the download button initiates the process of getting the images sequence from the camera memory to the host computer memory. It only works after the camera is triggered and video capture to camera memory is stopped (see preceding explanation of camera states). The images from the camera’s interna...
Page 21
21 figure 13, video sequence list stored as tiff files the first step in this mode inquires operator about location to store camera images and attributes of the tiff files, as in the figures 14 and 15 below..
Page 22
22 figure 14, selecting location to download images from the camera memory figure 15, selecting image file properties and download type.
Page 23
23 the image files can be recorded as the 8-bit or 16 bit tiff files (8 or 16 bits per pixel) and the pixel shift can be helpful in adjusting gain for the 8-bit files. The 16-bit tiff files can not be properly handled by many image viewer programs (notably the one that is shipped by microsoft with w...
Page 24
24 figure 16, the fpn file selection two read-only indicators in the upper right corner of the window are very useful during the image download: the 'frame' field indicates the frame number being read back. The 'block' field indicates the memory block number being read back (only useful to programme...
Page 25
25 the review captured video mode is only useable when the video sequence capture is finished and the mark on the write checkbox is off. When the review camera button is pressed the fastviewer-usb application inquires the camera about the start of each image in the camera memory. The preview display...
Page 26
26 the number of post trigger frames to a large number the trigger frame may not be in memory, and this button will not do anything except display a warning. Remember: review captured video mode can not be stopped until all header information is collected from the camera memory. If you have a camera...
Page 27
27 the optional version of the fastcamera power supply and trigger cable assembly has a db-9f connector which allows user connection of a ttl trigger input to the camera via the camera's 12-pin hirose round power connector. The connections are as follows: pin function 1 ground. 2 expose output. This...
Page 28
28 the input and outputs are 5v tolerant. Outputs have weak drive above 3.3v but may be pulled up to 5v with an external 470 ohm resistor. The trigger input is filtered in the camera to remove glitches shorter that about 75 nanoseconds, however it is advisable to provide a 1 microsecond minimum puls...
Page 29
29 monochrome sensor color sensor master test master test co-planarity test co-planarity test darkfield darkfield graywedge-16 graywedge-16 grayfield white balance gretag macbeth dc.
Page 30
30 smpte 130 fps 130 fps 450 fps 450 fps 500 fps 500 fps figure 20, fast camera test suite.
Page 31
31 reference for the fc13 and fc40 cameras the fc13 and fc40 cameras are based on a three fpga design, a control fpga which controls the timing of the sensor, a data fpga which handles specialized data processing functions and communication of results via usb or camera link, and a ddr fpga which con...
Page 32
32 in free-running mode the minimum frame period depends on the roi height and the line period. When either the frame period or exposure time setting exceeds the minimum period, extra clocks are inserted between frames. A 32-bit frame time counter allows frame periods from the minimum up to 64 secon...
Page 33
33 when viewing high-speed motion, the mv40 works best if the lines are read out at the maximum possible rate while additional time for exposure or frame period is inserted between frames. This maximizes the overlap in the line exposure times. Unfortunately in the non-memory readout modes with reduc...
Page 34
34 width. For the mv40, limitations of the rolling shutter limit the exposure timing resolution to the line readout rate unless the exposure time exceeds the readout time. Subsequent exposures can overlap readout of the current frame in this mode. This can place further restrictions on the exposure ...
Page 35
35 comparators in the control fpga check for changes in the dac settings and re-load the dac's whenever the values are changed. This can happen as a result of the host command to set camera state, or the host command to restore state from flash. C alibration both the mv13 and mv40 sensors have autom...
Page 36
36 camera state is read from one of the 8 pages as selected by the pointer in the header. If the pointer is not valid (1 - 8) or the selected page is uninitialized, the embedded micro skips to step 10. Reference dac's are reprogrammed with the updated values from flash. Camera state is forwarded to ...
Page 37
37 7 1 camera state storage 7 8 1 camera state storage 8 9 1370 fpga bit stream (sized for 2v1000 + 2v250) 1379 2716 available for data fpga initialization and user data 4095 1 reserved table 2 - flash memory layout table 3 shows the layout of the first page in flash memory. This contains enough des...
Page 38
38 16 4 data fpga initialization data length in bytes 20 1 camera state to load at power on (1 to 8) 20 357 reserved for additional header / id info 377 11 part number, ascii "800??-5????" 388 3 part revision, ascii "010" 391 9 serial number, ascii "xxx??????" 400 128 fpga bit stream file header fro...
Page 39
39 10 2 vref2: 23 e0 12 2 vbias1: 30 00 14 2 vref3: 32 e8 16 2 vbias2: 40 00 18 2 vref4: 41 36 20 2 vbias3: 50 00 22 2 vln1: 54 d9 24 2 vbias4: 60 00 26 2 vlp: 64 d9 28 2 vunused1: 70 00 30 2 vclamp3: 70 00 32 2 vunused2: 80 00 34 2 vrstpix: 8d 17 36 2 roi start pixel 38 2 roi end pixel 40 2 roi sta...
Page 40
40 50 4 frame period in pixel clocks 54 4 exposure delay in pixel clocks 58 2 serial link bit period in pixel clocks 60 1 camera link readout mode 61 1 camera link clock frequency 62 1 binning 63 1 memory options 64 1 sensor resolution - 8/10 bit 65 2 trigger mode (2nd byte is data fpga dependent) 6...
Page 41
41 sensor reference voltages are presented to the dac's exactly as they are stored in the state. The order listed above is the recommended order, but other orders may work. The format for these is ms byte first with the most significant nibble indicating the command code to the dac. Pairs of values ...
Page 42
42 the data within a command or response packet may contain 8-bit binary data with escaping as described below. The camera requires only one stop bit for framing and sends one stop bit when responding. Baud rate to comply with the camera link specification, the default baud rate is 9600. The serial ...
Page 43
43 the intent of the protocol is to allow hand typing of commands from a terminal except for long commands like flash page write that would only be done using the fastvision camera control gui. Response protocol each command signals completion by sending the command character g-z (always uppercased)...
Page 44
44 to simplify command processing, commands that are handled in the control fpga are assigned in ascending order starting with "g," and commands for the data fpga are assigned in descending order starting with "z." g et c amera s tate this command takes no arguments. The camera responds with "g" fol...
Page 45
45 are sent indicating the number of bytes remaining when the operation aborted. This is usually zero, unless the fpga re-asserted the init line. S ave c urrent c amera s tate to f lash this command takes one argument. The argument can be 01 to 08 and indicates which of the 8 flash storage areas to ...
Page 46
46 0x50 block erase 0x82 main memory page program through buffer 1 0x85 main memory page program through buffer 2 the following non-write commands are also implemented with write flash: 0x53 main memory page to buffer 1 transfer 0x55 main memory page to buffer 2 transfer 0x60 main memory page to buf...
Page 47
47 the entire array if the continuous array read flash command is used. All arguments are ascii hex. The exact syntax of the read flash command is: 'm' where opcode is one byte (2 hex digits), addr is 3 bytes (6 hex digits), cmd_len is one byte (2 hex digits), and data_len is four bytes (8 hex digit...
Page 48
48 'n' where is 4 hex digits of offset per table 4 and is 2 to 1024 hex digits (always a multiple of 2) of data which will be stored sequentially into the current camera state as shown in table 4. Actual registers affected by the command are updated as the data comes in, except where further synchro...
Page 49
49 this command can take no arguments or it can take a 32-bit (8 hex digits) address. This command is only effective in the memory readout modes. If enabled, the cc2 line will also initiate this command allowing operation without the gui. The data fpga will respond with "y" followed by a carriage-re...
Page 50
50 normally the data sent to the data fpga from the control fpga is limited in bandwidth at the source, either by the host serial baud rate or the flash memory read rate. Response data from the data fpga, which always gets forwarded to the host, must be sent at the host baud rate. To reduce the redu...
Page 51
51 picoblaze reads the data at sub address 0x60 this status bit is cleared. The usb host does not have a similar status bit; however it can be safely assumed that the picoblaze will process characters as fast as they come in, as long as no transmission occurs between the carriage-return that complet...
Page 52
52 6f8 - 6ff register shadow memory for read back of otherwise write-only bits. 700 - 7ff i2c shared area. P ico b laze r egister m ap all of the following registers can only be accessed when the register access enable signal is set. This is accomplished by making any access to locations 00 through ...
Page 53
53 4 response to a serial trigger command bit 3 reserved. Bit 2 calibrate sensor. This is a pulsed signal that schedules a calibration when this bit is written to 1. Writing this bit to zero has no effect. Actual calibration may happen much later, since the sensor control logic schedules calibration...
Page 54
54 0 x fd uart to / from c amera l ink . Writing this location sends a byte of serial data to the frame grabber. Reading gets a byte of serial data and acknowledges its receipt. See the status bit descriptions below for more information. 0 x fe dac and f lash c ontrol / f lash and uart s tatus . The...
Page 55
55 0 x ff fpga c onfiguration . The bits are: bit 7 read only "fget8" status. This is high when the sequencer is still running from a prior operation. Bit 6 is reserved. Bit 5 fpga loaded on write, fpga done on read. Writing this bit high indicates that the program has finished loading the data fpga...
Page 56
56 obviously be overwritten without affecting the sensor registers if the sensor register write enable bit is off. The layout of these registers intentionally matches the flash state storage. 0 x 24 s tart p ixel , low 8 bits . 0 x 25 s tart p ixel , high 8 bits . This is the leftmost pixel in the r...
Page 57
57 this is the line readout time in pixel clocks - 1. I.E. The actual period is one clock more than this number. 0 x 2e e xposure p eriod , bits 0 x 2f e xposure p eriod , bits 0 x 30 e xposure p eriod , bits 0 x 31 e xposure p eriod , bits this is the desired exposure time in pixel clocks. Actual e...
Page 58
58 bit 6 invert ttl trigger. Setting this bit to 1 indicates the ttl trigger input on p2 is active low level, or falling edge. Bit 5 enable ttl trigger. Set this bit to 1 to enable ttl trigger input on p2. Clear to 0 to disable ttl trigger input. Bit 4 synchronous exposure. This bit only affects fre...
Page 59
59 bit 1 invert cc2. Setting this bit to 1 indicates the cc2 input is active on falling edge. Setting this bit to 0 indicates the cc2 input is active on rising edge. Bit 0 enable camera link cc2. Set this bit to 1 to enable cc2 readout image. When enabled, the active edge of cc2 causes the current m...
Page 60
60 d irect from the s ensor -m emory o ptions [2:0] = 0 sensor data is written continuously to memory with each frame overwriting the previous frame at memory location zero. If preview bit is enabled, readout to the usb runs continuously at the maximum rate of the usb port with no attempt to synchro...
Page 61
61 via the frame valid line. Bits 95:64 are the starting address of the previous frame in memory. This is a block address, not a byte address. Because of treating the ddr data as sdr at 128 bits wide, a “word” is 16 bytes. The block to be read always starts at a 16 word boundary, thus the minimum ad...
Page 62
62 bit 7 this bit is 1 whenever the memory is enabled for writing new frames. This includes any time the memory mode is programmed for direct or fifo, and in circular buffer mode from the time memory is reset (z command) until all post-trigger frames have been written to memory. Use this as the busy...
Page 63
63 bit 4 1=preview the selected frame (y command address). (bit3=0) the read back count determines how many frames are returned by each y command when bits 3 and 4 of the memory mode are zero. Zero and one give you 1 frame for each command, 2 through 255 give you more. When the camera is reading out...
Page 64
64 troubleshooting there are several things you can try before you call fastvision technical support for help: _____ make sure the computer is plugged in. Make sure the power source is on. _____ go back over the hardware installation to make sure that the system is properly installed. _____ go back ...
Page 65
65 _____ also, each product has its serial number and revision number written on either in ink or in bar-code form. _____ the version of the fastviewer software that you are using. _____ the type and version of the host operating system, i.E., windowsxp. _____ note the types and numbers of all your ...
Page 66
66 fastvision llc. 71 spit brook road, suite 200 nashua, nh 03060 usa clearly mark the outside of your package: attention rma #90xxx remember to include your return address and the name and number of the person who should be contacted if we have questions. R eporting b ugs we at fastvision are conti...
Page 67
67 when you are describing a software problem, include revision numbers of all associated software. For documentation errors, photocopy the passages in question, mark on the page the number and title of the manual, and either fax or mail the photocopy to fastvision. Remember to include the name and ...