- DL manuals
- FE
- Inverter
- FRENIC-Multi series
- Instruction Manual
FE FRENIC-Multi series Instruction Manual
Instruction Manual
High Performance Compact Inverter
Thank you for purchasing our FRENIC-Multi series of inverters.
• This product is designed to drive a three-phase induction motor. Read through this instruction
manual and be familiar with the handling procedure for correct use.
• Improper handling might result in incorrect operation, a short life, or even a failure of this
product as well as the motor.
• Deliver this manual to the end user of this product. Keep this manual in a safe place until this
product is discarded.
• For how to use an optional device, refer to the instruction and installation manuals for that
optional device.
Fuji Electric FA Components & Systems Co., Ltd.
INR-SI47-1094-E
Summary of FRENIC-Multi series
Page 1
Instruction manual high performance compact inverter thank you for purchasing our frenic-multi series of inverters. • this product is designed to drive a three-phase induction motor. Read through this instruction manual and be familiar with the handling procedure for correct use. • improper handling...
Page 2
Copyright © 2006 fuji electric fa components & systems co., ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or copied without prior written permission from fuji electric fa components & systems co., ltd. All products and company names mentioned in this manual are trademarks o...
Page 3: Preface
I preface thank you for purchasing our frenic-multi series of inverters. This product is designed to drive a three-phase induction motor for fan and pump applications. Read through this instruction manual and be familiar with proper handling and operation of this product. Improper handling might res...
Page 4
Ii installation • install the inverter on a nonflammable material such as metal. Otherwise fire could occur. • do not place flammable object nearby. Doing so could cause fire. • do not support the inverter by its terminal block cover during transportation. Doing so could cause a drop of the inverter...
Page 5
Iii • ensure that the number of input phases and the rated voltage of the product match the number of phases and the voltage of the ac power supply to which the product is to be connected. Otherwise fire or an accident could occur. • do not connect the power supply wires to output terminals (u, v, a...
Page 6
Iv • the key on the keypad is effective only when the keypad operation is enabled with function code f02 (= 0, 2 or 3). When the keypad operation is disabled, prepare an emergency stop switch separately for safe operations. Switching the run command source from keypad (local) to external equipment (...
Page 7
V maintenance and inspection, and parts replacement • turn the power off and wait for at least five minutes before starting inspection. Further, check that the led monitor is unlit and that the dc link bus voltage between the p (+) and n (-) terminals is lower than 25 vdc. Otherwise, electric shock ...
Page 8
Vi precautions for use driving a 400 v general-purpose motor when driving a 400v general-purpose motor with an inverter using extremely long wires, damage to the insulation of the motor may occur. Use an output circuit filter (ofl) if necessary after checking with the motor manufacturer. Fuji motors...
Page 9
Vii synchronous motors it is necessary to take special measures suitable for this motor type. Contact your fuji electric representative for details. In running special motors single-phase motors single-phase motors are not suitable for inverter-driven variable speed operation. Use three-phase motors...
Page 10
Viii discontinuance of power capacitor for power factor correction do not mount power capacitors for power factor correction in the inverter’s primary circuit. (use the dc reactor to correct the inverter power factor.) do not use power capacitors for power factor correction in the inverter’s output ...
Page 11
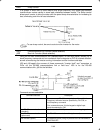
Ix how this manual is organized this manual is made up of chapters 1 through 9. Chapter 1 before using the inverter this chapter describes acceptance inspection and precautions for transportation and storage of the inverter. Chapter 2 mounting and wiring of the inverter this chapter provides operati...
Page 12
X table of content preface ............................................................I safety precautions..................................................I precautions for use .............................................. Vi how this manual is organized .................................. Ix chap...
Page 13
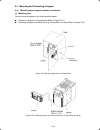
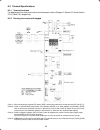
1-1 chapter 1 before using the inverter 1.1 acceptance inspection unpack the package and check the following: (1) an inverter and accessories below are contained in the package. • cooling fan fixing screws (for inverters of 5.5 to 15 kw) • keypad rear cover (with fixing screws) • instruction manual ...
Page 14
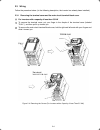
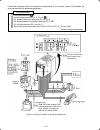
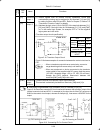
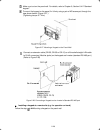
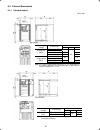
1-2 1.2 external view and terminal blocks (1) outside and inside views figure 1.2 outside and inside views of inverters (frn15e1s-2 ) (2) warning plates and label figure 1.3 warning plate and sub nameplate (3) terminal block location (a) frn0.75e1s-2 (b) frn15e1s-2 figure 1.4 terminal blocks note: ...
Page 15
1-3 1.3 transportation • when carrying an inverter, always support its bottom at the right and left sides with both hands. Do not hold covers or individual parts only. • avoid applying excessively strong force to the terminal block covers as they are made of plastic and are easily broken. 1.4 storag...
Page 16
2-1 chapter 2 mounting and wiring of the inverter 2.1 operating environment install the inverter in an environment that satisfies the requirements listed in table 2.1. Table 2.1 environmental requirements item specifications site location indoors ambient temperature -10 to +50 °c (note 1) relative h...
Page 17
2-2 when mounting two or more inverters horizontal layout is recommended when two or more inverters are to be installed in the same unit or panel. If it is necessary to mount the inverters vertically, install a partition plate or the like between the inverters so that any heat radiating from an in...
Page 18
2-3 (3) mounting direction mount the inverter vertically to the mounting surface and fix it securely with four screws or bolts so that the logo "frenic-multi" can be seen from the front. Do not mount the inverter upside down or horizontally. Doing so will reduce the heat dissipation efficiency of th...
Page 19
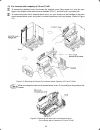
2-4 2.3 wiring follow the procedure below. (in the following description, the inverter has already been installed.) 2.3.1 removing the terminal cover and the main circuit terminal block cover (1) for inverters with a capacity of less than 5.5 kw to remove the terminal cover, put your finger in the d...
Page 20
2-5 (2) for inverters with a capacity of 5.5 and 7.5 kw to remove the terminal cover, first loosen the terminal cover fixing screw on it, and put your finger in the dimple of the terminal cover (labeled "pull"), and then pull it up toward you. To remove the main circuit terminal block cover, put you...
Page 21
2-6 (3) for inverters with a capacity of 11 and 15 kw to remove the terminal cover, first loosen the terminal cover fixing screw on it, and put your finger in the dimple of the terminal cover (labeled "pull"), and then pull it up toward you. To remove the main circuit terminal block cover, hold the ...
Page 22
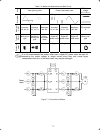
2-7 2.3.2 terminal arrangement diagram and screw specifications the table below shows the main circuit screw sizes, tightening torque and terminal arrangements. Note that the terminal arrangements differ according to the inverter types. Two terminals designed for grounding shown as the symbol, g in ...
Page 23
2-8 (2) the control circuit terminals (common to all models) screw size: m3 tightening torque: 0.5 to 0.6 (n·m) table 2.5 control circuit terminals screwdriver type allowable wire size wire strip length dimension of openings in the control circuit terminals for ferrule (for europe type terminal bloc...
Page 24
2-9 2.3.3 recommended wire sizes table 2.7 lists the recommended wire sizes. The recommended wire sizes for the main circuits are examples of using hiv single wire (for 75 °c) at an ambient temperature of 50°c. Table 2.7 recommended wire sizes recommended wire size (mm 2 )* 1 main circuits main circ...
Page 25
2-10 2.3.4 wiring precautions follow the rules below when performing wiring for the inverter. (1) make sure that the power supply voltage is within the rated voltage range specified on the nameplate. (2) be sure to connect the three-phase power wires to the main circuit power input terminals l1/r, l...
Page 26
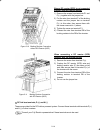
2-11 follow the procedure below for wiring and configuration of the inverter. Figure 2.9 illustrates the wiring procedure with peripheral equipment. Grounding terminals ( g) inverter output terminals (u, v, w, and g) dc reactor connection terminals (p1 and p(+))* dc braking resistor connection termi...
Page 27
2-12 grounding terminals ( g) be sure to ground either of the two grounding terminals for safety and noise reduction. The inverter is designed to use with a safety grounding to avoid electric shock, fire and other disasters. Grounding terminals should be grounded as follows: 1) ground the inverter i...
Page 28
2-13 driving 400 v class series motor • if a thermal relay is installed in the path between the inverter and the motor to protect the motor from overheating, the thermal relay may malfunction even with a wiring length shorter than 50 m. In this situation, add an output circuit filter (option) or low...
Page 29
2-14 figure 2.10 braking resistor connection without dc reactor (dcr) when a dc reactor (dcr) is not connected together with the braking resistor 1) remove the screws from terminals p1 and p(+), together with the jumper bar. 2) put the wire from terminal p of the braking resistor and the jumper bar ...
Page 30
2-15 main circuit power input terminals, l1/r, l2/s, and l3/t (three-phase input), or l1/l and l2/n (single-phase input) 1) for safety, make sure that the molded case circuit breaker (mccb) or magnetic contactor (mc) is turned off before wiring the main circuit power input terminals. 2) connect the ...
Page 31
2-16 table 2.9 symbols, names and functions of the control circuit terminals classifi- cation symbol name functions [13] power supply for the potentio- meter power supply (+10 vdc) for frequency command potentiometer (potentiometer: 1 to 5k Ω) the potentiometer of 1/2 w rating or more should be conn...
Page 32
2-17 table 2.9 continued classifi- cation symbol name functions - since low level analog signals are handled, these signals are especially susceptible to the external noise effects. Route the wiring as short as possible (within 20 m) and use shielded wires. In principle, ground the shielded sheath o...
Page 33
2-18 table 2.9 continued classifi- cation symbol name functions [plc] plc signal power connects to plc output signal power supply. (rated voltage: +24 vdc (maximum 50 ma dc): allowable range: +22 to +27 vdc) this terminal also supplies a power to the circuitry connected to the transistor output term...
Page 34
2-19 table 2.9 continued classifi- cation sym bol name functions analog output analog monitor (fma function) the monitor signal for analog dc voltage (0 to +10 v) is output. You can select fma function with slide switch sw6 on the interface pcb, and change the data of the function code f29. You can ...
Page 35
2-20 table 2.9 continued classifi- cation sym bol name functions [y1] transistor output 1 (1) various signals such as inverter running, speed/freq. Arrival and overload early warning can be assigned to any terminals, [y1] and [y2] by setting function code e20 and e21. Refer to chapter 5, section 5.2...
Page 36
2-21 table 2.9 continued classifi- cation symbol name functions relay ou tput [30a/b/ c] alarm relay output (for any error) (1) outputs a contact signal (spdt) when a protective function has been activated to stop the motor. Contact rating: 250 vac, 0.3a, cos φ = 0.3, 48 vdc, 0.5a (2) any one of out...
Page 37
2-22 2.3.7 setting up the slide switches before changing the switches, turn off the power and wait more than five minutes. Make sure that the led monitor is turned off. Further, make sure, using a multimeter or a similar instrument, that the dc link bus voltage between the terminals p (+) and n (-) ...
Page 38
2-23 figure 2.22 shows the location of slide switches for the input/output terminal configuration. Switching example sw3 off on factory default sw6 sw7 sw8 sw1 factory default fma c1 off sink - fmp v2 on source figure 2.22 location of the slide switches.
Page 39
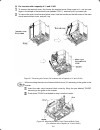
2-24 2.4 mounting and connecting a keypad 2.4.1 mounting style and parts needed for connection (1) mounting style you can mount a keypad in any style described below. Mounting a keypad on the panel wall (refer to figure 2.23.) installing a keypad at a remote site (e.G. For operation on hand) (refer ...
Page 40
2-25 (2) parts needed for connection to mount/install a keypad on a place other than an inverter, parts listed below are needed. Parts name model remarks extension cable (note) cb-5s, cb-3s and cb-1s 3 cables available in length of 5m, 3m, and 1m. Fixing screw m3 × 16 accessories keypad rear cover a...
Page 41
2-26 make a cut-out on the panel wall. For details, refer to chapter 8, section 8.4.2 "standard keypad." to mount the keypad on the panel, fix it firmly using a pair of m3 screws put through the taps shown below. (figure 2.27.) (tightening torque: 0.7 n m) figure 2.27 mounting a keypad on the panel...
Page 42
2-27 2.5 cautions relating to harmonic component, noise, and leakage current (1) harmonic component input current to an inverter includes a harmonic component, which may affect other loads and power factor correcting capacitors that are connected to the same power supply as the inverter. If the harm...
Page 43
3-1 chapter 3 operation using the keypad 3.1 led monitor, keys and led indicators on the keypad as shown at the right, the keypad consists of a four-digit led monitor, six keys, and five led indicators. The keypad allows you to run and stop the motor, monitor running status, and switch to the menu m...
Page 44
3-2 table 3.1 continued item led monitor, keys, and led indicators functions run led lights when any run command to the inverter is active. Lights when the inverter is ready to run with a run command entered by the key (f02 = 0, 2, or 3). In programming and alarm modes, you cannot run the inverter e...
Page 45
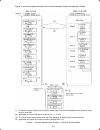
3-3 figure 3.1 shows the status transition of the inverter between these three operation modes. (*1) the speed monitor allows you to select the desired one from the seven speed monitor items by using function code e48. (*2) applicable only when pid control is active (j01 = 1, 2 or 3). (*3) the timer...
Page 46
3-4 3.3 running mode when the inverter is turned on, it automatically enters running mode in which you can: (1) monitor the running status (e.G., output frequency and output current), (2) configure the reference frequency and other settings, (3) run/stop the motor, and (4) jog (inch) the motor. 3.3....
Page 47
3-5 table 3.3 continued monitor items display sample on the led monitor *1 led indicator : on, : off unit meaning of displayed value function code e43 pid command *3, *4 1*0* hz a kw - 10 pid feedback amount *3, *5 )0* hz a kw - pid command/feedback amount transformed to that of virtual phys...
Page 48
3-6 3.3.2 setting up frequency and pid commands you can set up the desired frequency and pid commands by using and keys on the keypad. It is also possible to set up the frequency command as load shaft speed, motor speed etc. By setting function code e48. setting up a frequency command using and ke...
Page 49
3-7 settings under pid process control to enable the pid process control, you need to set function code j01 to "1" or "2." under the pid control, the items that can be specified or checked with and keys are different from those under regular frequency control, depending upon the current led monito...
Page 50
3-8 setting up the frequency command with and keys under pid process control when function code f01 is set to "0" ( / keys on keypad) and frequency command 1 is selected as a manual speed command (when disabling the frequency setting command via communications link or multi-frequency command), switc...
Page 51
3-9 settings under pid dancer control to enable the pid dancer control, you need to set function code j01 to "3." under the pid control, the items that can be specified or checked with and keys are different from those under the regular frequency control, depending upon the current led monitor set...
Page 52
3-10 setting up the primary frequency command with and keys under pid dancer control when function code f01 is set to "0" ( / keys on keypad) and frequency command 1 is selected as a primary frequency command (when disabling the frequency setting command via communications link and multi-frequency c...
Page 53
3-11 3.3.3 running/stopping the motor by factory default, pressing the key starts running the motor in the forward direction and pressing the key decelerates the motor to stop. The key is enabled only in running mode. The motor rotational direction can be selected by changing the setting of function...
Page 54
3-12 table 3.9 menus available in programming mode menu # menu led monitor shows: main functions refer to: 0 "quick setup" *fn: displays only basic function codes to customize the inverter operation. Section 3.4.1 !F__ f codes (fundamental functions) !E__ e codes (extension terminal functions) !C__ ...
Page 55
3-13 3.4.1 set g up basic function codes quickly -- menu #0 "quick setup" -- tin menu #0 "quick setup" in programming mode allows you to quickly display and set up a basic set of function codes specified in chapter 5, section 5.1, "function code tables." to use menu #0 "quick setup," you need to set...
Page 56
3-14 figure 3.2 shows the menu transition in menu #0 "quick setup." figure 3.2 menu transition in menu #0 "quick setup" basic key operation this section gives a description of the basic key operation, following the example of the function code data changing procedure shown in figure 3.3. This exampl...
Page 57
3-15 (5) change the function code data using the and keys. (in this example, press t e h key two times to change data 0 to 2 .) (6) press the key to establish the function code data. The saue appears and the data will be saved in the memory inside the inverter. The display will return to the functio...
Page 58
3-16 3.4.3 checking changed function codes -- menu #2 "data checking" -- menu #2 "data checking" in programming mode allows you to check function codes that have been changed. Only the function codes whose data has been changed from the factory defaults are displayed on the led monitor. You can refe...
Page 59
3-17 basic key operation to monitor the running status on the drive monitor, set function code e52 to "2" (full-menu mode) beforehand. (1) turn the inverter on. It automatically enters running mode. In that mode, press the key to switch to programming mode. The function selection menu appears. (2) u...
Page 60
3-18 displaying running status to display the running status in hexadecimal format, each state has been assigned to bits 0 to 15 as listed in table 3.13. Table 3.14 shows the relationship between each of the status assignments and the led monitor display. Table 3.15 gives the conversion table from...
Page 61
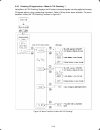
3-19 3.4.5 checking i/o signal status -- menu #4 "i/o checking" -- using menu #4 "i/o checking" displays the i/o status of external signals including digital and analog i/o signals without using a measuring instrument. Table 3.16 lists check items available. The menu transition in menu #4 "i/o check...
Page 62
3-20 basic key operation to check the status of the i/o signals, set function code e52 to "2" (full-menu mode) beforehand. (1) turn the inverter on. It automatically enters running mode. In that mode, press the key to switch to programming mode. The function selection menu appears. (2) use the and k...
Page 63
3-21 displaying control i/o signal terminals the status of control i/o signal terminal may be displayed with on/off of the led segment or in hexadecimal display. • display i/o signal status with on/off of each led segment as shown in table 3.17 and the figure below, each of segments "a" to "g" on le...
Page 64
3-22 table 3.18 segment display for i/o signal status in hexadecimal format led no. Led4 led3 led2 led1 bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 input terminal (rst)* (xr)* (xf)* - - - - - - x5 x4 x3 x2 x1 rev fwd output terminal - - - - - - - 30 a/b/c - - - - - - y2 y1 binary 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0...
Page 65
3-23 3.4.6 reading maintenance information -- menu #5 "maintenance information" -- menu #5 "maintenance information" contains information necessary for performing maintenance on the inverter. The menu transition in menu #5 "maintenance information" is as same as its of in menu #3 "drive monitoring."...
Page 66
3-24 table 3.20 continued led monitor shows: item description 5_08 number of startups shows the content of the cumulative counter of times the inverter is started up (i.E., the number of run commands issued). 1.000 indicates 1000 times. When any number from 0.001 to 9.999 is displayed, the counter i...
Page 67
3-25 3.4.7 reading alarm information -- menu #6 "alarm information" -- menu #6 "alarm information" shows the causes of the past 4 alarms in alarm code. Further, it is also possible to display alarm information that indicates the status of the inverter when the alarm occurred. Figure 3.6 shows the me...
Page 68
3-26 basic key operation to view the alarm information, set function code e52 to "2" (full-menu mode) beforehand. (1) turn the inverter on. It automatically enters running mode. In that mode, press the key to switch to programming mode. The function selection menu appears. (2) use the and keys to di...
Page 69
3-27 table 3.21 continued led monitor shows: (item no.) item displayed description 6_11 max. Temperature of heat sink shows the temperature of the heat sink. Unit: ºc 6_12 (displayed ith the on/off of led segments) terminal i/o signal status w 6_13 us (in hexadecimal format) terminal input signal st...
Page 70
3-28 displaying the status of inverter a code is displayed, you may check various running status information (output fre nd output y pressing the t the time of alarm when the alarm quency a current, etc.) b key. The and data for each ru n will be displayed alternately. Further ti using the item nu...
Page 71
4-1 chapter 4 running the motor 4.1 running the motor for a test 4.1.1 inspection and preparation prior to powering on check the following prior to powering on. (1) check if connection is correct. Especially check if the power wires are connected to the inverter input terminals l1/r, l2/s and l3/t o...
Page 72
4-2 4.1.3 preparation before running the motor for a test--setting function code data before running the motor, set function code data specified in table 4.1 to the motor ratings and your system design values. For the motor, check the rated values printed on the nameplate of the motor. For our syste...
Page 73
4-3 2) selection of tuning process check the situation of the machine system and choose between "tuning while the motor is stopped (p04 or a18 = 1)" and "tuning while the motor is running (p04 or a18 = 2)." in the case of "tuning while the motor is running (p04 or a18 = 2)," also adjust the accelera...
Page 74
4-4 errors during tuning improper tuning would negatively affect the operation performance and, in the worst case, could even cause hunting or deteriorate precision. Therefore, if the inverter finds any abnormality in the results of the tuning or any error in the process of the tuning, it will dis...
Page 75
4-5 ------------------------------------------------ procedure for test run ------------------------------------------------- (1) turn the power on and check that the led monitor blinks while indicating the *00 hz frequency. (2) set the frequency to a low frequency such as 5 hz, using / keys. (check...
Page 76
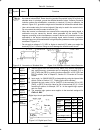
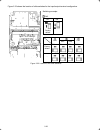
5-1 chapter 5 function codes 5.1 function code tables the following tables list the function codes available for the frenic-multi series of inverters. F codes: fundamental functions code incre- ment unit change when running data copying default setting refer to page: f00 0: - - y y 0 1: 2: 3: f01 0:...
Page 77
5-2 (f codes continued) code incre- ment unit change when running data copying default setting refer to page: f29 analog output [fm] 0: output in voltage (0 to 10 vdc) ( fma ) - - y y 0 5-30 (mode selection) 2: output in pulse (0 to 6000 p/s) ( fmp ) f30 (voltage adjustment) 0 to 300 (fma ) 1 % y* f...
Page 78
5-3 e codes: extension terminal functions code incre- ment unit change when running data copying default setting refer to page: e01 t erminal [x1] function - - n y 0 5-35 e02 t erminal [x2] function 0 (1000): select multi-frequency ( ss1 ) - - n y 1 e03 t erminal [x3] function 1 (1001): select multi...
Page 79
5-4 (e code continued) code incre- ment unit change when running data copying default setting refer to page: e29 frequency arrival delay t ime 0.01 to 10.00 0.01 s y y 0.10 5-47 e30 0.0 to 10.0 0.1 hz y y 2.5 e31 0.0 to 400.0 0.1 hz y y t able a *4 - e32 (hysteresis width) 0.0 to 400.0 0.1 hz y y 1....
Page 80
5-5 (e code continued) code incre- ment unit change when running data copying default setting refer to page: e98 terminal [fwd] function - - n y 98 e99 terminal [rev] function 0 (1000): select multi-frequency ( ss1 ) - - n y 99 1 (1001): select multi-frequency ( ss2 ) 2 (1002): select multi-frequenc...
Page 81
5-6 (c code continued) code incre- ment unit change when running data copying default setting refer to page: c31 -5.0 to 5.0 0.1 % y* y 0.0 5-50 c32 (gain) 0.00 to 200.00 *1 0.01 % y* y 100.0 5-27 c33 (filter time constant) 0.00 to 5.00 0.01 s y y 0.05 5-50 c34 (gain base point) 0.00 to 100.00 *1 0....
Page 82
5-7 h codes: high performance functions code incre- ment unit change when running data copying default setting refer to page: h03 data initialization 0: disable initialization - - n n 0 5-53 1: 2: initialize motor 1 parameters 3: initialize motor 2 parameters h04 auto-reset (t imes) 1 times y y 0 h0...
Page 83
5-8 (h code continued) code incre- ment unit change when running data copying default setting refer to page: h68 slip compensation 1 0: - - n y 0 5-32 (operating conditions) 1: 2: 3: h69 automatic deceleration 0: disable - - y y 0 5-62 (mode selection) 2: 4: h70 overload prevention control 0.01 hz/s...
Page 84
5-9 (a code continued) code incre- ment unit change when running data copying default setting refer to page: a14 control mode selection 2 0: - - n y 0 - 1: dynamic torque vector operation 2: 3: 4: a15 motor 2 (no. Of poles) 2 to 22 2 poles n y1 y2 4 a16 (rated capacity) 0.01 0.01 kw hp n y1 y2 rated...
Page 85
5-10 j codes: application functions code incre- ment unit change when running data copying default setting refer to page: j01 0: disable - - n y 0 - 1: enable (process control, normal operation) 2: enable (process control, inverse operation) 3: enable (dancer control) j02 (remote command sv) 0: up/d...
Page 86
5-11 y codes: link functions code incre- ment unit change when running data copying default setting refer to page: y01 rs-485 communication (standard) 1 to 255 - (station address) 1 - n y 1 y02 (communications error processing) 0: immediately trip with alarm er8 - - y y 0 1: 3: continue to run y03 (...
Page 87
5-12 changing, val and saving fu tion code data when e inverter is r ng idating, nc th unni function codes are indicated by the following based on whether they can be changed or not when the inverter is running: notation change when running validating and saving function code data and y* possible if...
Page 88
5-13 5.2 overview of function codes this section provides an overview of the function codes frequently used for the frenic-multi series of inverter. Et function codes g ot given below, er to the frenic-mult codes" and t -485 c tion f00 data protecti for d ails about the iven below and other function...
Page 89
5-14 data for f01, c30 function 2 enable the current input to terminal [c1] (c1 function) (+4 to +20 ma dc, maximum frequency obtained at +20 ma dc). 3 enable the sum of voltage (0 to +10 vdc) and current inputs (+4 to +20 ma dc) given to terminals [12] and [c1] (c1 function), respectively. See the ...
Page 90
5-15 f02 eration method op f02 sel e source that specifies a run command for running the motor. Data f 2 ects th or f0 run command source description keypad (rotation direction specified by terminal command) enables the / keys to run and stop the motor. The rotation direction of the motor is specifi...
Page 91
5-16 f04 f05 f06 h50 h52, h5 -li quency and voltage) cy and voltage) rated voltage at base frequency 1 maximum output voltage 1 base frequency 1 , h51 3 non non-linear near v/f pattern 1 (fre v/f pattern 2 (frequen these function base essentially requi tor h50 through h5 s ttern by specifying increa...
Page 92
5-17 examples: (linear) v/f pattern normal v/f pattern with two non-linear points f07 f08 e10 e11 deceleration time 1 acceleration time 1 acceleration time 2 deceleration time 2 f07 spec the maxi decreases f ifies the acceleration time, the length of time the frequency increases from 0 hz to mum...
Page 93
5-18 • if you choose s-curve acceleration/deceleration or curvilinear acceleration/ deceleration in a acceleration/decele cceleration/deceleration pattern (h07), the actual ration times are longer than the specified times. Refer to the description of h07 for details. • specifying an improperly short...
Page 94
5-19 when the variable torque v/f pattern is selected (f37 = 0 or 3), the output voltage ay be low and insufficient voltage output may result in less output torque of the otor at a low frequency zone, depending on some characteristics of the motor itsel m m f an mmended to increase the output voltag...
Page 95
5-20 • auto t this fun r light loa over-exc the moto orque boost tion automatically optimizes the output voltage to fit the motor with its load. Unde d, auto torque boost decreases the output voltage to prevent the motor from itation. Under heavy load, it increases the output voltage to increase out...
Page 96
5-21 the figure below shows operating characteristics of the electronic thermal overload protection when f10 = 1. The characteristic factors α 1 through α 3 as well as their corresponding switching frequencies f 2 and f 3 vary with the characteristics of the motor. The tables below list the factors ...
Page 97
5-22 thermal time constant (f12) f12 specifies the thermal time constant of the motor. If the current of 150% of the overload detection level specified by f11 flows for the time specified by f12, the electronic thermal overload protection becomes activated to detect the motor overload. The thermal...
Page 98
5-23 f14 h13 h14 h16 tantaneous power failure restart mode after ins restart mode after momentary power failure, restart time restart mode after momentary power failure, frequency fall rate restart mode after momentary power failure, allowable momentary power failure time ifies the action to be take...
Page 99
5-24 restar ) the inver tion that dc link bus volta load of th short, the voltag ot be great enough for a momentary power failure to be recognized, estart mode (after a er is restored, the in hrough a charging stage and enters -run state. When a mome y pow s, the p sequen circuit as t situation, the...
Page 100
5-25 during a momentary power failure, the motor slows down. After pow restarts at the frequency just before the momentary power failure. T er is restored, the inverter hen, the current limiting function works and the output frequency of the inverter automatically decreases. When the output frequenc...
Page 101
5-26 restart after momentary power failure (frequency fall rate) (h14) during restart after a momentary power failure, if the inverter output frequency and the idling motor speed cannot be harmonized with each other, an overcurrent will flow, activating the overcurrent limiter. If it happens, the ...
Page 102
5-27 f18 c50 c32 c37 c42 bias (frequency command 1) , c34 , c39 , c44 bias (for frequency 1) (bias base point) analog input adjustment for [12] (gain, gain base point) analog input adjustment [c1] (gain, gain base point) analog input adjustment [v2] (gain, gain base point) when any analog input for ...
Page 103
5-28 (p to = 0). Sin base poi (point b) oint a) set the nput being at 1 v, set the bias to 0% (f18 c (full scale), set the bias n reference frequency to 0 hz for an analog i e 1 v is the bias base point and it is equal to 10% of 10 v t to 10% (c50 = 10). To make the maximum frequency equal to the re...
Page 104
5-29 in general, specify data of function code f20 at a value close to the rated slip frequency of motor. If you set it at an extremely high value, control may become unstable and an overvoltage alarm may result in some cases. The dc brake function of the inverter does not provide any holding mechan...
Page 105
5-30 spec larg ifying a too low carrier frequency will cause the output current waveform to have a amount of ripples. As a result, the motor loss increases, causing the moto e r tem to cause a current limiting alarm. When the carrier frequency is set to 1 khz or below, therefore, reduce the load so ...
Page 106
5-31 f f unction (f31) specifies what is output to analog output terminal [fm]. Ata for f31 [fm] output function (monitor the following) meter scale (full scale at 100%) 31 d 0 (before slip compensation) (equivalent to the motor synchronous speed) maximum frequency (f03/a01) output frequency outpu...
Page 107
5-32 ue limiter and current limiter are very similar activated concurrently, they may conflict each oth the torq function each other. If both are er and cause a hunting in the st oncurrent ters. F42 h68 tion sy em. Avoid c activation of these limi control mode sele slip compensa ction 1 1 (operating...
Page 108
5-33 in the slip compensation and dynamic torque vector control, the inverter uses the motor parameters to control its speed. Therefore, the following conditions should be satisfied; if not, the inverter may not get the proper performance from the mo . • a single motor should be controlled. (it is d...
Page 109
5-34 the table below these values external bra standard mode lists the discharging capability and allowable average loss of the braking resistor. Epend upon the inverter and braking resistor models. D king resistors ls r relay mounted on the the overhe termina braking to prot resisto the dis rmal se...
Page 110
5-35 10% ed models continuou braking resistor s braking (100% braking torque) intermittent braking (period: less than 100s) power supply inverter type voltage type qty. (kws) time (s) average loss (kw) (%ed) resistance ( Ω) discharging capacity braking allowable duty frn0.1e1s-2 1000 100 frn0.2e1s...
Page 111
5-36 function code data active on active terminal com off mands assigned symbol 0 1000 ss1 1 1001 ss2 2 1002 ss4 3 1003 ele lti-fre y ( ss s ct mu quenc 0 to 15 steps) 8 4 100 acc/de e rt1 4 select c tim 6 1006 enable 3-wire operation hld 7 1007 coast to a stop bx 8 10 set alarm rst 08 re 1009 9 abl...
Page 112
5-37 term ent and data setting inal function assignm ti-f to 15 steps) (function code 0, 1, 2, and 3) the combination of /off ss2, ss4 and ss cts one of different fr cy c ction codes c0 19 (multi- uency 0 with this, the inverter can drive the motor at 16 differe set freque es. The table below list f...
Page 113
5-38 enable 3-wire operation -- hld (function code data = 6) rse rev run command iss eration. Turning this terminal command on self-holds the forward fwd or reve ued with it, to enable 3-wire inverter op short-circuiting the terminals between hld and [cm] (i.E., when hld is on) self-holds the firs...
Page 114
5-39 ready for jogging -- jog (function code data = 10) this terminal command is used to jog or inch the motor for positioning a work piece. Turning this command on makes the inverter ready for jogging. Simultaneous keying + keys on the keypad is functionally equivalent to this command; however, i...
Page 115
5-40 select motor 2 / motor 1 -- m2/m1 (function code data = 12) ossible , the digital terminal output swm2 ( fault. M2/m1 swm2 status after completion of switching turning this terminal command on switches from motor 1 to motor 2. Switching is p only when the inverter is stopped. Upon completion ...
Page 116
5-41 motor 2 imposes functional restrictions on the following function codes. Confirm the settings of those function codes before use. Functions restrictions related function codes non-linear v/f pattern disabled. Linear v/f pattern only h50 to h53 starting frequency starting frequency holding time ...
Page 117
5-42 the up/down control is available in two modes--one mode (h61 = 0) in which the initial value of the reference frequency is fixed to "0.00" at the start of the up/down control and the other mode (h61 = 1) in which the reference frequency applied in the pr control ap initial value. W rence f s up...
Page 118
5-43 enable communications link via rs-485 or field bus (option) -- le (function code data = 24) turning this terminal command on assigns priorities to frequency commands or run commands received via the rs-485 communications link (h30) or the field bus option (y98). No le assignment is functional...
Page 119
5-44 the table below lists functions that can be assigned to terminals [y1], [y make the explanations simp 2], and [30a/b/c]. To ler, the examples shown below are all written for the normal logic (active on). Function code data active on active off functions assigned symbol 0 1000 inverter running r...
Page 120
5-45 undervoltage detected -- lu (function code data = 3) this output signal comes on when the dc link bus voltage of the inverter drops below the specified undervoltage level, and it goes off when the voltage exceeds the level. This si n the undervoltage pr activated so that tor is i .G., tripped...
Page 121
5-46 heat sink overheat early warning -- oh (function code data = 28) when it drops down to the "overheat trip 0h1 capacitors and cooling fan. If this ction code data = 33) frequency command source is eak connection. This esumed. (refer to the inve this outp the dc bra ion. (timer)) or e38 (curr...
Page 122
5-47 e2 e30 9 frequency arrival delay time (for far2) frequency arrival (hysteresis width for far and far2) the moment the output frequency reaches the zone defined by "reference frequency ± hysteresis width specified by e30," the "frequency arrival signal" far comes on. After the delay time specifi...
Page 123
5-48 e39 e50 coefficient for constant feeding rate tim coefficient for speed indication e e39 and e50 specify coefficients for determining the constant feeding rate time, load shaft speed, and line speed, as well as for displaying the output status monitored. Calculation expression coefficient for s...
Page 124
5-49 e61 e62 e63 (c1 function) terminal [12] extended function terminal [c1] extended function terminal [c1] extended function (v2 function) e61, e62, and e63 define the property of terminals [12], [c1] (c1 function), and [c1] (v2 function), respectively. There is no need to set up these terminals i...
Page 125
5-50 c21 timer operation 1 enab a run command and continues c2 les or disables a timer operation that is triggered by for the timer count previously specified with the / keys. The operating procedure for the timer operation is given below. Data for c21 function 0 disable timer operation 1 enable tim...
Page 126
5-51 p01 motor 1 (no. Of poles) p01 specifies the number of poles of the motor. Enter the value given on the nameplate of the motor. This setting is used to display the motor on the led monitor (refer to e43). The following expression is used for the conversion. Speed 120 motor no. Of poles x freque...
Page 127
5-52 where, r1: primary resistance of the motor ( Ω) v d cable r1: resistance of the output cable ( Ω) v: rated voltage of the motor (v) i: rated current of the moto ) r (a %x (p08): enter the alue calculate by the following expression. (%) = %x 100 × x cable + xm) + (x2 / xm × x2 + x1 x2 reac of ...
Page 128
5-53 for p99, enter the following data ding to the motor type. • p99 = 0 (motor characteristics 0): fuji standard 8-series motors (current standard) • p99 = 3 (motor characteristics 3): fuji standard 6-series motors (conventional standard) • p99 = 4 (other motors): other manufacturer’s or unknown mo...
Page 129
5-54 uji standard 8-series motors (p99 = 0 or a39 = 0) or other motors (p99 = 4 or a39 are as listed in the following tables. 20 j) no-load %r %x (%) rated slip frequency (hz) when f = 4) are selected, the motor parameters 0 v class series (example for frn_ _ _e1 - pacity rated motor ca (kw) curre...
Page 130
5-55 h04, h05 auto-reset (times and reset interval) (tripped inverter w listed be alarm status led monitor displays: alarm status led monitor displays: h04 and h05 specify the auto-reset function that makes the inverter automatically attempt to reset the tripped state and restart without issuing an ...
Page 131
5-56 h06 cooling fan on/off control ise during running, the cooling fan stops a certain level while the inverter stops. However, since fre tchi e co tens its life, the cooling r n it is h06 specifies wheth ep run the coo all the time or to control its o . D 6 an to prolong the life of the cooling fa...
Page 132
5-57 acceleration cy change is 20% or more of the max uency> acce elerat 0/10 rati time) (referen or dece /deceleration /deceleration time maximum frequency> acceleration or deceleration time (s): (2 × 5/100 + 90/100+ 2 × 5/100) × (reference acceleration or deceleration time) = 1.1 × (reference acce...
Page 133
5-58 h09 an able auto search for idling motor speed at starting") d stm terminal command ("en the combination of h09 data and the stm state determines whether to perform the auto search as listed below. Auto search for idling motor speed at starting data for h09 stm for restart after momentary power...
Page 134
5-59 h11 deceleration mode h11 specifies the deceleration mode to be applied when a run command is turned off. Data for h11 function 0 normal deceleration the inverter decelerates and stops the motor according to deceleration commands specified by h07 (acceleration/deceleration pattern), f08 (decele...
Page 135
5-60 h28 droop control in a system in which two or more motors drive single machinery, any speed gap between inverter-driven motors results in some load unbalance between motors. The droop control allows each inverter to drive the motor with the its load, elimina such kind oad unbalan speed droop ch...
Page 136
5-61 comman y h30 (mode selection) d sources specified b data for h30 frequency command run command 0 inverter itself (f01/c30) inverter itself (f02) via rs-485 communications link (sta tself (f02) ndard) inverter i 1 2 inverter itself (f01/c30) via rs-485 communications link (standard) 3 via (st rs...
Page 137
5-62 h45 h97 clear alarm data mock alarm h45 causes the inverter to generate a mock alarm in order to check whether external sequences function correctly at the time of machine setup. Setting the h45 data to "1" displays mock alarm err on the led monitor and issues alarm output alm to the digital ou...
Page 138
5-63 h70 overload prevention control h70 spe ut frequency ue to an o load. T e output freque efore the inverter trips du a hea ad (wit n of 0h1 or 0lu , respec ely). It i r equipment such as pump ase in the output freque leads t and it is nece en when the output fre dat r h70 func c ver ifies the de...
Page 139
5-64 input pha tion ( lin ) (bit 1) se loss protec on dete ve stress inflicted on the apparatus connected to the main circuit up ction of an excessi due to phase loss or line-to-line voltage unbalance in the three-phase power supplied to the inverter, this feature stops the inverter and displays an ...
Page 140
5-65 conversio ) n table (decimal to/from binary binary binary decimal bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0 decimal bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 16 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 17 1 0 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 1 0 18 1 0 0 1 0 3 0 0 0 1 1 19 0 0 1 1 1 4 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 20 1 0 1 5 0 0 1 0 1 21 1 0 1 0 1 6 0 1 0 1 1...
Page 141
5-66 mode selection (j65) j65 specifies operation when the load amount exceeds that of one specified by j64. Data for j65 mode description 0 disable the inverter cancels the overload stop function. 1 decelerate to stop the inverter decelerate-to-stops the motor by the specified deceleration time. 2 ...
Page 142
5-67 releasing the brake the inverter releases the brake (terminal command brks: on) after checking torque generation of the motor, monitoring whether it applies both the output current and frequency to the motor, which are higher than ones specified for the time long enough. Function code name data...
Page 143
6-1 chapter 6 troubleshooting 6.1 before proceeding with troubleshooting if any of the protective functions have been activated, first remove the cause. Then, after checking that the all run commands are set to off, reset the alarm. Note that if the alarm is reset while any run commands are set to o...
Page 144
6-2 6.2 if no alarm code appears on the led monitor 6.2.1 motor is running abnormally [ 1 ] the motor does not rotate. Possible causes what to check and suggested measures (1) no power supplied to the inverter. Check the input voltage, output voltage and interphase voltage unbalance. Î turn on a mol...
Page 145
6-3 possible causes what to check and suggested measures (7) a frequency command with higher priority than the one attempted was active. Check the higher priority run command with menu #2 "data checking" and menu #4 "i/o checking" using the keypad, referring to the block diagram of the drive command...
Page 146
6-4 [ 2 ] the motor rotates, but the speed does not increase. Possible causes what to check and suggested measures (1) the maximum frequency currently specified was too low. Check the data of function codes f03 and a01 (maximum frequency). Î readjust the data of f03 and a01. (2) the data of frequenc...
Page 147
6-5 possible causes what to check and suggested measures (9) in the toque control mode, the output frequency does not increase. Check whether data of torque limiter related function codes (f40, f41, e16 and e17) is correctly configured and the torque limit switching signal tl2/tl1 is correct. Î reco...
Page 148
6-6 possible causes what to check and suggested measures (3) frequency switching or multi-frequency command was enabled. Check whether the relay signal for switching the frequency command is chattering. Î if the relay has a contact problem, replace the relay. (4) the connection between the inverter ...
Page 149
6-7 [ 6 ] the motor does not accelerate and decelerate at the set time. Possible causes what to check and suggested measures (1) the inverter ran the motor by s-curve or curvilinear pattern. Check the data of function code h07 (acceleration/deceleration pattern). Î select the linear pattern (h07 = 0...
Page 150
6-8 [ 7 ] even if the power recovers after a momentary power failure, the motor does not restart. Possible causes what to check and suggested measures (1) the data of function code f14 is either "0" or "1." check if an undervoltage trip occurs. Î change the data of function code f14 (restart mode af...
Page 151
6-9 possible causes check and measures check whether the keypad is properly connected to the inverter. Î remove the keypad, put it back, and see whether the problem persists. Î replace the keypad with another one and check whether the problem persists. (3) the keypad was not properly connected to th...
Page 152
6-10 6.3 if an alarm code appears on the led monitor quick reference table of alarm codes alarm code name refer to alarm code name refer to 0c1 0l1 0l2 electronic thermal overload alarm 1 electronic thermal overload alarm 2 6-17 0c2 0lu overload 6-17 0c3 instantaneous overcurrent 6-10 er1 memory e...
Page 153
6-11 possible causes what to check and suggested measures (2) ground faults occurred at the inverter output terminals. Remove the wires connected to the inverter output terminals (u, v, and w) and perform a megger test. Î remove the part that short-circuited (including replacement of the wires, rela...
Page 154
6-12 possible causes what to check and suggested measures (2) a surge current entered the input power supply. If within the same power supply a phase-advancing capacitor is turned on or off or a thyristor converter is activated, a surge (temporary precipitous rise in voltage or current) may be cause...
Page 155
6-13 possible causes what to check and suggested measures (4) peripheral equipment for the power circuit malfunctioned, or the connection was incorrect. Measure the input voltage to find where the peripheral equipment malfunctioned or which connection is incorrect. Î replace any faulty peripheral eq...
Page 156
6-14 [ 5 ] 0pl output phase loss problem output phase loss occurred. Possible causes what to check and suggested measures (1) inverter output wires are broken. Measure the output current. Î replace the output wires. (2) wires for motor winding are broken. Measure the output current. Î replace the mo...
Page 157
6-15 [ 7 ] 0h2 alarm issued by an external device problem external alarm was inputted (thr). (when "enable external alarm trip" thr is assigned to one of digital input terminals [x1] through [x5], [fwd], and [rev]) possible causes what to check and suggested measures (1) an alarm function of the ext...
Page 158
6-16 possible causes what to check and suggested measures (6) the value set for the torque boost (f09 and a05) was too high. Check the data of function codes f09 and a05 and readjust the data so that the motor does not stall even if you set the data to a lower value. Î readjust the data of the funct...
Page 159
6-17 [ 10 ] 0l1 electronic thermal overload alarm 1 0l2 electronic thermal overload alarm 2 problem electronic thermal protection for motor 1 or motor 2 activated. Possible causes what to check and suggested measures (1) the characteristics of electronic thermal did not match those of the motor over...
Page 160
6-18 possible causes what to check and suggested measures check the cumulative running time of cooling fan. Refer to chapter 3, section 3.4.6 "reading maintenance information – "maintenance information"." Î replace the cooling fan. (6) the service life of the cooling fan has expired or the cooling f...
Page 161
6-19 [ 13 ] er2 keypad communications error problem a communications error occurred between the standard keypad or the multi-function keypad and the inverter. Possible causes what to check and suggested measures (1) break in the communications cable or poor contact. Check continuity of the cable, co...
Page 162
6-20 [ 17 ] er6 operation protection problem you incorrectly operated the inverter. Possible causes what to check and suggested measures (1) the key was pressed when h96 = 1 or 3. Although a run command had been inputted from the input terminal or through the communications port, the inverter was fo...
Page 163
6-21 possible causes what to check and suggested measures (4) the rated capacity of the motor was significantly different from that of the inverter. Check whether the rated capacity of the motor is smaller than that of the inverter by three or more orders of class or larger by two or more orders of ...
Page 164
6-22 possible causes what to check and suggested measures (6) a high intensity noise was given to the inverter. Check if appropriate noise control measures have been implemented (e.G., correct grounding and routing of control and main circuit wires). Î improve noise control. Î improve noise reductio...
Page 165
6-23 [ 21 ] erh hardware error problem abnormality on the control pcb or related hardware. Possible causes what to check and suggested measures (1) the interface pcb is wrongly mounted. Remove the interface pcb once and remount it into the card slot until it clicks into place. (2) the capacity is no...
Page 166
6-24 6.4 if an abnormal pattern appears on the led monitor while no alarm code is displayed [ 1 ] – – – – (center bar) appears problem a center bar (– – – –) has appeared on the led monitor. Possible causes what to check and suggested measures (1) any of pid commands and their feedback related funct...
Page 167
7-1 chapter 7 maintenance and inspection perform daily and periodic inspection to avoid trouble and keep reliable operation for a long time. Take care of the following items during work. • before proceeding to the maintenance and inspection, turn off the power and wait more than five minutes. Make s...
Page 168
7-2 table 7.1 continued check part check item how to inspect evaluation criteria keypad 1) check if the display is clear. 2) check if there is missing parts in the characters. 1), 2) visual inspection 1), 2) the display can be read and there is no fault. Structure such as frame and cover 1) abnormal...
Page 169
7-3 table 7.1 continued check part check item how to inspect evaluation criteria control ci rcuit printed circuit board 1) check for loose screws and connectors. 2) check for odor and discoloration. 3) check for cracks, breakage, deformation and remarkable rust. 4) check the capacitors for electroly...
Page 170
7-4 7.3.1 judgment on service life (1) viewing data necessary for judging service life; measurement procedures through menu #5 "maintenance information" in programming mode, you can view on the keypad various data (as a guideline) necessary for judging whether key components such as the dc link bus ...
Page 171
7-5 -2 measuring the capacitance of the dc link bus capacitor (during power-off time under ordinary operating condition) if the measuring method for discharging condition of the dc link bus capacitor during a power-off time under the ordinary operating condition at the end user’s installation is dif...
Page 172
7-6 cooling fan select menu #5 "maintenance information" and check the accumulated run time of the cooling fan. The inverter accumulates hours for which the cooling fan has run. The display is in units of 1000 hours. The accumulated time should be used just a guide since the actual service life will...
Page 173
7-7 table 7.4 meters for measurement of main circuit item input (primary) side output (secondary) side dc link bus voltage (p (+)-n (-)) w avefor m voltage current voltage current name of meter ammeter a r , a s , a t voltmeter v r , v s , v t wattmeter w r , w t ammeter a u , a v , a w voltmeter v ...
Page 174
7-8 7.5 insulation test because an insulation test is made in the factory before shipment, avoid a megger test. If a megger test is unavoidable, follow the procedure below. Because a wrong test procedure will cause breakage of the inverter, take sufficient care. A dielectric strength test will cause...
Page 175
7-9 7.6 inquiries about product and guarantee (1) when making an inquiry upon breakage of the product, uncertainties, failure or inquiries, inform your fuji electric representative of the following information. 1) inverter type (refer to chapter 1, section 1.1.) 2) ser no. (serial number of equipmen...
Page 176
8-1 chapter 8 specifications 8.1 standard models 8.1.1 three-phase 200 v class series *1 fuji 4-pole standard motor *2 rated capacity is calculated assuming the output rated voltage as 220 v. *3 output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage. *4 use the inverter at the current enclosed with p...
Page 177
8-2 8.1.2 three-phase 400 v class series *1 fuji 4-pole standard motor *2 rated capacity is calculated assuming the output rated voltage as 440 v. *3 output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage. *4 use the inverter at the current enclosed with parentheses ( ) or below when the carrier freq...
Page 178
8-3 8.1.3 single-phase 200 v class series *1 fuji 4-pole standard motor *2 rated capacity is calculated by assuming the output rated voltage as 220 v. *3 output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage. *4 use the inverter at the current enclosed with parentheses ( ) or below when the carrier ...
Page 179
8-4 8.2 specifications of keypad related 8.2.1 general specifications of keypad table 8.1 general specifications items specification remarks protective structure front side: ip40, back (mounting) side: ip20 site to be installed in door ambient temperature -10 to 50 °c ambient humidity 5 to 95% rh, n...
Page 180
8-5 8.3 terminal specifications 8.3.1 terminal functions for details about the main and control circuit terminals, refer to chapter 2, section 2.3.5 and section 2.3.6 (table 2.9), respectively. 8.3.2 running the inverter with keypad (note 1) when connecting an optional dc reactor (dcr), remove the j...
Page 181
8-6 8.3.3 running the inverter by terminal commands (note 1) when connecting an optional dc reactor (dcr), remove the jumper bar from the terminals [p1] and [p (+)]. (note 2) install a recommended molded-case circuit breaker (mccb) or an earth-leakage circuit-breaker (elcb) (with an overcurrent prot...
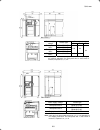
Page 182
8-7 8.4 external dimensions 8.4.1 standard models unit: mm dimensions (mm) power supply voltage inverter type d d1 d2 frn0.1e1s-2 frn0.2e1s-2 92 10 frn0.4e1s-2 107 25 three-phase 200 v frn0.75e1s-2 132 50 frn0.1e1s-7 frn0.2e1s-7 92 10 frn0.4e1s-7 107 82 25 single-phase 200 v frn0.75e1s-7 152...
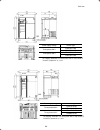
Page 183
8-8 unit: mm dimensions (mm) power supply voltage inverter type d d1 d2 frn1.5e1s-2 three-phase 200 v frn2.2e1s-2 frn1.5e1s-4 three-phase 400 v frn2.2e1s-4 150 86 single-phase 200 v frn1.5e1s-7 160 96 64 note: a box ( ) in the above table replaces a, c, e, j, or k depending on the shipping destin...
Page 184
8-9 unit: mm power supply voltage inverter type frn5.5e1s-2 three-phase 200 v frn7.5e1s-2 frn5.5e1s-4 three-phase 400 v frn7.5e1s-4 note: a box ( ) in the above table replaces a, c, e, j, or k depending on the shipping destination. For three-phase 200 v class series of inverters, it replaces a, c, ...
Page 185
8-10 8.4.2 standard keypad unit: mm for remote operation or panel wall-mounting (the keypad rear cover should be mounted.).
Page 186
8-11 8.5 protective functions name description led monitor displays alarm output [30a/b/c] overcurrent protection stops the inverter output to protect the inverter from an overcurrent resulting from overload. During acceleration 0c1 short-circuit protection stops the inverter output to protect the i...
Page 187
8-12 name description led monitor displays alarm output [30a/b/c] overload protection stops the inverter output if the insulated gate bipolar transistor (igbt) internal temperature calculated from the output current and temperature of inside the inverter is over the preset value. 0lu yes external al...
Page 188
8-13 name description led monitor displays alarm output [30a/b/c] option communications error detection upon detection of an error in the communication between the inverter and an optional card, stops the inverter output. Er4 — option error detection when an option card has detected an error, this f...
Page 189
8-14 name description led monitor displays alarm output [30a/b/c] protection against momentary power failure upon detecting a momentary power failure lasting more than 15 ms, this function stops the inverter output. If restart after momentary power failure is selected, this function invokes a restar...
Page 190
9-1 chapter 9 list of peripheral equipment and options the table below lists the main peripheral equipment and options that are connected to the frenic-multi. Use them in accordance with your system requirements. For details, refer to the frenic-multi user's manual (meh457), chapter 6 "selecting per...
Page 191
9-2 name of peripheral equipment function and application main peri pheral equi pment magnetic contactor (mc) an mc can be used at both the power input (primary) and output (secondary) sides of the inverter. At each side, the mc works as described below. When inserted in the output circuit of the in...
Page 192
9-3 name of option function and application dc reactors (dcrs) a dcr is mainly used for power supply matching and for input power factor correction (for reduction of harmonics). 1) for power supply matching - use a dcr when the capacity of a power supply transformer exceeds 500 kva and is 10 times o...
Page 193
9-4 name of option function and application external potentiometer for frequency commands an external potentiometer may be used to set the drive frequency. Connect the potentiometer to control signal terminals [11] to [13] of the inverter. Multi-function keypad allows you to monitor the status of th...
Page 194: Memo
Memo memo.
Page 195
High performance compact inverter instruction manual first edition, march 2006 fuji electric fa components & systems co., ltd. The purpose of this instruction manual is to provide accurate information in handling, setting up and operating of the frenic-multi series of inverters. Please feel free to ...
Page 196
Fuji electric fa components & systems co., ltd. Mitsui sumitomo bank ningyo-cho bldg., 5-7, nihonbashi, odemma-cho, chuo-ku, tokyo, 103-0011, japan phone: +81 3 5847 8011 fax: +81 3 5847 8172 url http://www.Fujielectric.Co.Jp/fcs/ 2006-03 (c06/c06) 10cm.