- DL manuals
- Garmin
- Marine GPS System
- Forerunner 225
- Owner's Manual & Reference
Garmin Forerunner 225 Owner's Manual & Reference
Summary of Forerunner 225
Page 1
Gpsmap tm 215/225 owner’s manual & reference ® 215225manb.Qxd 4/27/00 9:22 am page 1.
Page 2
215225manb.Qxd 4/27/00 9:22 am page 2.
Page 3
Software version 2.12 or above internal database version 3.00 © 1998-2000 garmin corporation g-chart™ cartridge data is copyrighted and may not be copied or used for any other purpose without permission. Garmin corporation, 1200 e. 151 st street, olathe, ks 66062 usa tel: 913.397.8200 fax: 913.397.8...
Page 4
Ii caution: the global positioning system (gps) is operated by the government of the united states, which is solely responsible for its accuracy and maintenance. The sys- tem is subject to changes which could affect the accuracy and performance of all gps equipment. Although the gpsmap is a precisio...
Page 5
Iii garmin corporation warrants this product to be free from defects in materials and manufacture for one year from the date of purchase. Garmin will, at its sole option, repair or replace any components that fail in normal use. Such repairs or replacement will be made at no charge to the customer f...
Page 6
The following optional accessories are available for your gpsmap system: • g-chart electronic chart cartridges • 110/220 volt ac adapter • flush mounting kit • cigarette lighter adapter • mapsource™ pc software • pc interface cable • ga23 h-field dgps antenna • gbr 21/23 dgps receivers • antenna ext...
Page 7
V part one: introduction foreword.......................................................................................................I cautions.......................................................................................................Ii limited warranty & registration....................
Page 8
Section 5: waypoints .........................................................................28-33 creating, editing and using waypoints; using the waypts softkey section 6: mark key ..............................................................................34 marking present position and target...
Page 9
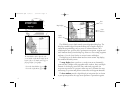
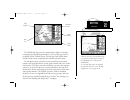
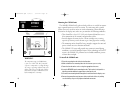
Designed for detailed electronic charting and simple operation, the garmin gpsmap system is a powerful navigation device that can help guide you in waterways around the world: precision performance • 16-color active-matrix tft screen (gpsmap 225) • 3-gray ftn lcd screen (gpsmap 215) • phasetrac12 tm...
Page 10
The gpsmap system uses a set of on-screen ‘softkeys’ m to perform route, waypoint and setup functions. These softkeys allow you to perform many navigation functions and custom setups right from the map display. Viii l the zoom key changes the map display scale to one of 16 avail- able settings, or t...
Page 11
The gpsmap system is designed as an aid to navigation, and is not intended to replace the use of government-approved charts and tradi- tional navigation practices. Make sure you read and understand the mariner’s acknowl- edgement before using the unit. 1 the garmin gpsmap is a powerful electronic ch...
Page 12
I the gpsmap system does not actively track satellites in the simulator mode. Never use the simulator mode for actual navigation. Any waypoints, routes and track logs you create while simulating navigation will be saved in memory, and are available for use when using the unit in normal operating mod...
Page 13
Use the k keypad to choose letters, numbers, spaces and symbols in a data field. Only the appropriate characters will be available for a particular data entry window. 3 now that you are back at the satellite status page, let’s enter a starting posi- tion for our tour. Entering names and numbers in t...
Page 14
The data window (at the right side of the screen) and the softkey menu display (at the bottom of the screen) may be turned off for a full page display of cartography: • to turn the data window off, press b . • to turn the softkey menu off, press g . 4 the gpsmap system is built around a powerful gra...
Page 15
The destination field, located at the top of the data window, shows your bearing (brg) and distance (dis) to a destination waypoint or to the cursor. It also displays your crosstrack error (xtk) and turn (trn) heading to an active destination. The xtk value is the distance you are off a desired cour...
Page 16
As you move the cursor, the distance and bearing from your present position to the cursor will be displayed in the destination field (at the top right of the screen). The cursor’s position coordinates will be dis- played in the position field (below the speed and course field). While in cursor mode,...
Page 17
The gpsmap system stores over 1900 alphanumeric waypoints, with selectable graphic icons and a user-defined comment field. If you mark a navaid position that appears on a g-chart electronic cartridge, the default comment will automatically select the navaid text associated with the marker. 7 to cont...
Page 18
Whenever the cursor comes in close proximity to an on-screen waypoint or navaid, it will ‘snap’ to and highlight its on-screen icon. Once an on-screen marker has been high- lighted, destination and position information will be displayed in the data window. This feature makes it easy to review waypoi...
Page 19
9 now add the final waypoint to the route: 1. Use the k keypad to move the arrow cursor as close as possible to the following coordinates: n24º21.777’, w077º51.424. 2. Press the c key to save the waypoint position. 3. Press c to confirm the default waypoint name, symbol and comment. We now have a th...
Page 20
The simulator sog/cog window lets you specify the speed and course for the simulator mode. By leaving the cog field value at the default setting, the gpsmap system will automatically set a course directly to your destination. If you choose to enter your own course over ground, highlight the cog fiel...
Page 21
11 you are now underway toward the first waypoint in your route. Whenever there is an active route in use for navigation, the gpsmap will display route waypoint and leg information on the active route page. To view the active route page from the highway page: 1. Press the i key. The active route pag...
Page 22
12 as you approach a destination waypoint, an audible alert and on-screen message will indicate when you are one minute from your destination. To acknowledge the message: 1. Press the c key. Whenever you’re finished navigating a route with the gpsmap system, you’ll need to clear the active route to ...
Page 23
13 the gpsmap will now provide you with steering guidance to your new waypoint. To stop navigation to a goto destination, clear the active goto: 1. Press the d key. 2. Press the clr goto softkey. (note that in simulator mode, navigation will continue along the previously defined course over ground.)...
Page 24
Reference section 1 – satellite status page 2 – map page 3 – highway page 4 – active route page 5 – waypoints 6 – mark key 7 – goto/mob 8 – routes 9 – auxiliary menu 10 – g-chart cartridges 14 215225manb.Qxd 4/27/00 9:22 am page 14.
Page 25
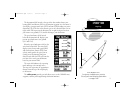
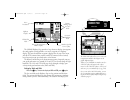
In this example, satellites 5, 21, 23, 25 and 29 are currently being tracked, with the corresponding signal strength bars indicating the relative strength of the signals. Satellites 3, 9, 15, 30 and 31 (shown with numbers highlighted) are visible, but are not currently being tracked. Satellite 8 is ...
Page 26
Whenever your gpsmap is operating with a dgps beacon receiver, the position window will be replaced by a beacon receiver status window. This window will display the beacon receiver status, the signal-to-noise ratio (snr), and the distance from your beacon receiver to the dgps transmitter.( if availa...
Page 27
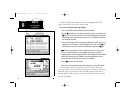
The gpsmap map page provides a comprehensive display of electronic cartography, plotting and navigational data. It is the primary page used for navigating with the gpsmap system. The map page can be broken down into three main sections: map display, data window and softkey menu. The map display show...
Page 28
18 the map display uses the cursor keypad and a set of hard keys to control most map display functions. The l , a , c and e keys, combined with the k keypad lets you select zoom ranges, move the cursor and display chart outlines. Two basic map operating modes determine what cartography is shown on t...
Page 29
19 the cursor allows you to pan away from your present position and scroll to other map areas around the world (even outside of your current g-chart tm coverage). As you pan past the edge of the current map display, the screen will actively scroll forward to provide continuous map coverage wherever ...
Page 30
20 the map display has 16 available range scales from 1/8th to 4096 n.M. (1/4 to 7500km). The map scale is controlled by the l key, with the current scale displayed at the bottom of the data window. To select a map scale: 1. Press the arrow icon on the right or left side of the l key to zoom in or o...
Page 31
21 the second section of the map page is the data window, located at the right side of the screen display. The data window provides a digital display of navigation data in relation to your present position, the cursor position or a particular waypoint. The top area of the data window includes the de...
Page 32
The last section of the map page is the softkey menu, which is displayed across the bottom of the screen. The first two softkeys provide quick access to route and waypoint functions from any gpsmap page. The aux softkey provides instant access to the auxiliary menu. For instructions on using these s...
Page 33
23 the garmin gpsmap system features a graphic map display with 16 zoom scales from 1/8th to 4096 n.M. (1/4 to 7500km). By using g-chart tm inland and offshore chart cartridges, the map display can show a wide variety of chart details such as depth contours, shorelines, marinas and navigation aids. ...
Page 34
Note that geographic names and navaid text can’t be displayed simultane- ously at range scales greater than 2 n.M. (4 km) and that navaid text is always available in the review window by highlighting the navaid with the cursor. Waypoint names and lat/lon labels cannot be displayed unless the waypoin...
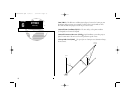
Page 35
25 the gpsmap highway page provides a large character display of navigation data and graphic steering guidance to an active waypoint via a highway display. The active destination waypoint is displayed at the top of the screen, with the ete (estimated time enroute) and eta (estimated time of arrival)...
Page 36
Current date and time as calculated from gps satellites. The date and time for- mats may be changed through the system setup softkey (see section 9), and the time may be set to display either utc (greenwich mean time) time or the local time, based on a local offset entered in the system setup menu. ...
Page 37
27 the last page in the main sequence is the active route page. The active route page shows each waypoint of the active route (in order), with the waypoint name, desired track, cumulative distance and ete or eta for each waypoint from the present position. Your current destination waypoint, the ‘act...
Page 38
28 the garmin gpsmap system stores over 1900 alphanumeric waypoints with a user-defined icon and comment available for each waypoint. Waypoints can be created, reviewed, moved or deleted right from the map page using the target cursor to select positions and waypoints, and are managed through the wa...
Page 39
29 other graphic waypoint functions include reviewing and modifying on-screen waypoints. By moving the cursor close to an on-screen waypoint, you can “snap” to a specific waypoint. Once the target cursor snaps to a waypoint, the waypoint will be highlighted with a white circle, and the gpsmap will d...
Page 40
30 the last two graphic waypoint functions allow you to move a highlighted on-screen waypoint or delete it from system memory using the map display. To move an on-screen waypoint: 1. Use the k keypad to ‘snap to’ the on-screen waypoint. 2. Press the move softkey. 3. Use the k keypad to move the arro...
Page 41
31 to scroll through and review the waypoint list: 1. Press the waypts softkey (if you are not currently in the waypoints submenu). 2. Press the list softkey. 3. Use the k keypad to scroll through the list in either direction. 4. Press the c key to review the highlighted waypoint. 5. Highlight the o...
Page 42
32 the create softkey lets you create new waypoints by entering a name and position, or by entering the distance and bearing from an existing (reference) waypoint. To create a new waypoint from the list submenu: 1. If the waypoints list isn’t currently displayed, select it by pressing the waypts sof...
Page 43
33 to create a new waypoint using a reference waypoint: 1. Follow steps 1-5 (on page 32) for creating a new waypoint. 2. Highlight the reference waypoint field and press the scan softkey. 3. Use the k keypad to scan the waypoint list and find the desired reference waypoint. Press c to confirm the re...
Page 44
The garmin gpsmap system features a f key that lets you quickly capture your present position or a target cursor position and create a new waypoint right from the map display. The f key will capture your present position when the cursor is not in use, or will give you the option of marking your pres...
Page 45
35 the gpsmap’s goto command lets you select any stored waypoint or target cursor position as a destination and quickly set a course from your present position. Once a goto has been activated, the highway page will provide steering guidance to your destination. A goto may be activated on the map dis...
Page 46
36 once a goto has been activated, the gpsmap will keep the waypoint as your active destination and provide steering guidance until you stop the active goto. To stop navigating to an active goto position: 1. Press the d key. 2. Press the clr goto softkey. The gpsmap’s man overboard function (mob) le...
Page 47
Routes are broken down and navigated in smaller segments called ‘legs’. The waypoint you are going to in a leg is called the ‘active to’ waypoint, and the waypoint immediately behind you is called the ‘active from’ waypoint. The line connecting the ‘active to’ and ‘active from’ waypoint is referred ...
Page 48
38 all of the gpsmap route functions are accessed through the routes softkey, located at the far left of the softkey menu. To create a route from the map display: 1. Press the routes softkey to display the route list window. 2. Use the k keypad to select an empty storage route (routes 1-19) and pres...
Page 49
39 when the review mode is in use, the cursor may be used to highlight indi- vidual route legs. When a route leg is highlighted, the ‘active from’ and ‘active to’ waypoints will be displayed at the bottom of the data window, with the desired track (dtk) and distance (dis) for the leg indicated below...
Page 50
The next softkey in the route review mode allows you to modify a route by moving, inserting or removing route waypoints on screen or editing a route through a text review window. To modify the on-screen route: 1. Select the route review mode for the desired route, as described on page 38. 2. Press t...
Page 51
41 the insert softkey allows you to add a waypoint before the first route waypoint or after the last route waypoint; or add a new route waypoint to an existing route leg. To insert a new starting or ending route waypoint: 1. Use the k keypad to snap to and highlight the first or last route waypoint....
Page 52
To remove a route waypoint: 1. Use the k keypad to snap to and highlight the waypoint you want to remove. 2. Press the remove softkey. The ent text softkey will display a text editing window where you may add a route comment, insert or delete waypoints or review any waypoint of the on-screen route. ...
Page 53
The edit route window will also let you scroll through the list of route waypoints, review each waypoint, and change waypoint information. To review a route waypoint: 1. Select the edit route window using either method described on page 42. 2. Use the k keypad to scroll through and select the waypoi...
Page 54
The select route waypoint window also lets you rename a route waypoint, or delete a waypoint from system memory (‘active to’ waypoints cannot be deleted). To rename a route waypoint: 1. Press the rename softkey. 2. Use the k keypad to enter the new name. 3. Press the ok softkey to accept the new way...
Page 55
45 in addition to the graphic on-screen creation of routes, the gpsmap system also provides a data entry window for creating new routes. To create a route through data entry: 1. Press the routes softkey to display the route list window. 2. Use the k keypad to select an empty route and press the c ke...
Page 56
46 the gpsmap’s aux softkey provides access to the various system, naviga- tion and interface setup menus used to customize your unit’s operation. Once you have pressed the aux softkey, you’ll see a complete list of available options listed by category. Each category on the list has its own submenu ...
Page 57
47 when an auxiliary menu option is selected and displayed, you’ll see a complete listing of available functions, with the current setting for each option indicated. Once you’ve entered a submenu, you’ll use one of two data entry formats to enter most of your setup preferences: the option window pro...
Page 58
Operational mode lets you select between normal operation and simulator mode. The gpsmap system does not track satellites in simulator mode, and should not be used for actual navigation. Waypoints and routes created in simulator mode are saved in memory and are available for use in normal mode. Whil...
Page 59
Position format lets you select the coordinate system used to display position. You can select latitude/longitude in three display formats: degrees only (e.G., n37.25818º), degrees and minutes (e.G., n37º15.490) or degrees, minutes and seconds (e.G., n37º15’29.4”). Options are also available for utm...
Page 60
The navigation setup submenu is also used to select map datums and adjust the built-in position and velocity filters. The gpsmap system’s default map datum is wgs 84, a worldwide map datum that’s suitable for use with most government charts. You should only change the map datum if the legend on the ...
Page 61
Count down timer controls an alarm to sound when an entered interval (up to 99:59:59) has expired. Enter a time interval in the time field and use the control field to the immediate right to run, stop or reset the timer. Elapsed timer provides a running clock to 99:59:59. To run, stop or reset the e...
Page 62
The gpsmap interface setup submenu provides interface settings for con- necting external nmea electronic devices, a pc and/or a differential gps (dgps) beacon receiver. The settings, listed at the top of the interface setup window, control a bi-directional i/o port with six (built in dgps) or nine (...
Page 63
53 the interface setup submenu also controls the built-in beacon receiver (if so equipped) or allows you to connect to an external beacon receiver (if purchased without the built-in beacon receiver). When using an external beacon receiver, three additional formats are provided to accept rtcm input c...
Page 64
When equipped with a built-in beacon receiver or external dgps receiver, the gpsmap system can automatically scan for the dgps beacon signal or you may manually enter a frequency and bit rate. Dgps status will be displayed on the satellite status page (only when the unit is in 2d or 3d nav mode), al...
Page 65
The “bcn rcvr” field on the status page will show one of the following: • tuning— unit is attempting to tune to the specified frequency and bit rate. • scanning— unit is automatically scanning through the frequencies and bit rates. • receiving— unit is receiving dgps signal and ready for operation. ...
Page 66
If a proximity alarm circle overlaps with an existing alarm circle, a ‘proximity overlap’ warning will be displayed. As long as the over- lap exists, the overlap warning will be dis- played each time the gpsmap is turned on. If you enter an alarm circle overlap, the gpsmap will only inform you of th...
Page 67
57 the gpsmap system features a route planning window that will calculate and display the desired track and distance to route waypoints, along with the total fuel required and estimated time enroute (ete). To use the route planning mode: 1. Highlight the route trip planning option from the auxiliary...
Page 68
58 the gpsmap’s point-to-point planning feature lets you calculate the desired track, trip distance, fuel usage, ete and eta between any two waypoints or your present position and a stored waypoint. The planning mode will also pro- vide sunrise and sunset data at your destination on the specified ar...
Page 69
Recording status lets you define how track plot memory will be used: off– no track plot will be recorded. (note: selecting ‘off’ will prevent you from using the tracback feature.) fill– a track plot will be recorded until track memory is full. Wrap (default)– a track plot will be continuously record...
Page 70
Section 9 auxiliary menu track recording tracback start tracback allows you to retrace your path using the track plot automatically stored in the receiver’s memory. This eliminates the need to manually store way- points along the way. A track plot is an electronic breadcrumb trail, showing the path ...
Page 71
61 section 9 auxiliary menu on-screen glossary viewing messages the last listing on the auxiliary options menu is the glossary function. The gpsmap’s on-screen glossary contains basic information on general navigation terms and abbreviations, as well as helpful hints on using your unit. To use the o...
Page 72
The garmin gpsmap system uses g-chart™ digital cartography to display nautical charts on-screen. G-chart™ inland and offshore cartridges are installed in the card slot located at the bottom right of the gpsmap unit. G-chart™ car- tridges may be installed or removed at any time, whether the unit is o...
Page 73
63 once a g-chart cartridge has been inserted, the map coverage outlines for the cartridge will automatically appear on screen. Keep in mind that the display will not automatically scroll to the map area or zoom to a level where you can see the coverage outlines. If you do not immediately see the ou...
Page 74
Some g-chart™ cartridges include port services information, which lists available services and facilities for the selected area. When this information is available, a port services ‘information’ icon will appear on the map display (typically at lower scale settings only). To view port services infor...
Page 75
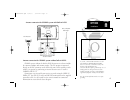
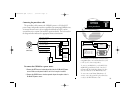
Your gpsmap system includes the following hardware components: gpsmap unit gimbal mount bracket (with knobs) gps antenna with 30’ cable power/data cable 2-amp in-line fuse (included with power/data cable) antenna combiner (for gpsmap purchased with built-in dgps) antenna coupler and whip antenna (fo...
Page 76
To begin installation, you’ll need to select a suitable mounting position for the antenna(s) and the gpsmap unit. Once you’ve identified the best mounting locations for your application, install the antenna(s) and its cable(s) first, then the unit and power/data cable. Mounting the antenna(s) the gp...
Page 77
Antenna connection for gpsmap system with built-in dgps antenna connection for gpsmap system without built-in dgps: gpsmap systems without the built-in dgps beacon receiver do not include the antenna combiner and antenna coupler. The gps antenna is connected directly to the bnc connector on the back...
Page 78
Mounting the gpsmap unit the garmin gpsmap’s fully gasketed and sealed case is suitable for mount- ing in exposed locations or at the nav station. The unit comes with a gimbal bracket that can be used for surface or overhead mounting. When choosing a location for the display unit, make sure you cons...
Page 79
69 connecting the power/data cable the power/data cable connects the gpsmap system to a 10-40 volt dc power source and provides interface capabilities for connecting nmea devices, an external beacon receiver (if not equipped with built-in dgps), and an external alarm (see section 9 for interface ope...
Page 80
Complete information concerning nmea formats and sentences is available for purchase from nmea at: nmea po box 3435 new bern, nc 28564-3435 252-638-2626 252-638-4885 fax. 70 the following interface formats are supported by the gpsmap system for connection to up to three nmea devices (gpsmap units wi...
Page 81
Gpsmap specifications physical case: fully gasketed, high-impact plastic alloy size: 5.8”h x 9”w x 3”d (14.7 x 22.9 x 7.6 cm) weight: less than 3 lbs. (1.4 kg) temperature range: -4º to 158ºf (-20º to 70ºc) performance receiver: differential-ready 12 parallel channel acquisition time: approx. 15 sec...
Page 82
The gpsmap system uses an on-screen message field to alert you to important information. Whenever a message appears, press the c key to confirm the message. There are two types of messages: temporary messages and condition messages. Temporary messages are cleared from the message page after viewing,...
Page 83
73 memory battery low —the internal lithium battery that maintains waypoint, route and track plot memory (when the unit is off) needs to be replaced. Take your unit to an authorized garmin service center for installation of a new battery. No dgps position —not enough data is being received to comput...
Page 84
74 received invalid waypoint —a waypoint was received during upload transfer that has an invalid identifier. Receiver failed —a failure in receiver hardware has been detected. If this message persists, do not use the unit and take it to an authorized dealer for repair. Route is full —you have attemp...
Page 85
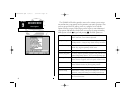
75 the chart below gives an approximate utc(universal time coordinate) time offset for the various longitudinal zones. Check with local charts for more detailed informa- tion. If you are in daylight savings time, add one hour to the offset. Longitudinal zone offset w180.0º to w172.5º -12 w172.5º to ...
Page 86
76 adindan adindan- ethiopia, mali, senegal, sudan afgooye afgooye- somalia ain el abd ‘70 ain el anbd 1970- bahrain island, saudi arabia anna 1 ast ‘65 anna 1 astro ‘65- cocos i. Arc 1950 arc 1950- botswana, lesotho, malawi, swaziland, zaire, zambia, zimbabwe arc 1960 kenya, tanzania ascnsn isld ‘5...
Page 87
77 cape cape- south africa cape canavrl cape canaveral- florida, bahama islands carthage carthage- tunisia ch-1903 ch 1903- switzerland chatham 1971 chatham 1971- chatham island (new zealand) chua astro chua astro- paraguay corrego alegr corrego alegre- brazil djakarta djakarta (batavia)- sumatra is...
Page 88
78 central america (belize, costa rica, el salvador, guatemala, honduras, nicaragua) nad27 conus north am. 1927- mean value (conus) nad27 cuba north american 1927- cuba nad27 grnland north american 1927- greenland (hayes peninsula) nad27 mexico n. American 1927- mexico nad27 san sal north american 1...
Page 89
79 almanac data —satellite constellation information (including location and health of satellites) that is transmitted to your receiver from every gps satellite. Almanac data must be acquired before gps navigation can begin. Bearing —the compass direction from your position to a destination. Course ...
Page 90
Turn (trn)— the difference and direction in degrees between the bearing to your destination and your course over ground. The trn value is used to indicate what direction and how many degrees to turn to get back on course. Universal time coordinated (utc)— the time of day at the prime meridian (0º lo...
Page 91
81 section h appendix loran tds loran td system loran c is a radio navigation aid operated and maintained in the united states by the united states coast guard. The name loran is an acronym for "long range navigation". The loran system covers the entire united states and the u.S. Coastal confluence ...
Page 92
82 section h appendix loran tds information will reflect those changes. Since the gpsmap unit does not rely on the loran signal for navigation, it can reference a different gri chain and/or secondary stations and still navigate to the location stored in memory. The loran position format field is loc...
Page 93
A activating routes........................................39 active route ..................................11, 27, 37 active route page .................................11, 27 active waypoints ...........................25, 27, 37 alarm setup................................................51 ancho...
Page 94
G g-chart cartridges.................................62-64 glossary ..........................................59, 79-80 goto key ...............................Viii, 12, 35-36 grid coordinates ........................................49 ground speed............................................79 h hea...
Page 95
P packing list .................................................Iv page key ..................................................Viii physical specifications ................................71 point-to-point planning ..............................58 port services information ..............................
Page 96
215225manb.Qxd 4/27/00 9:22 am page 86.
Page 97
215225manb.Qxd 4/27/00 9:22 am page 87.
Page 98
® © 1998-2000 garmin corporation 1200 e. 151st street, olathe, ks 66062 u.S.A. Web site address: www.Garmin.Com garmin (europe) ltd., unit 5, the quadrangle, abbey park, romsey, hampshire so51 9aq u.K. Garmin (asia) corp., no. 68, jangshu 2 nd rd., shijr, taipei county, taiwan part number 190-00061-...