- DL manuals
- H3C
- Switch
- H3C S7500E-X
- Configuration Manual
H3C H3C S7500E-X Configuration Manual - Preface
Preface
This configuration guide describes LAN switching fundamentals and configuration. It describes how
to isolate uses in the same VLAN, eliminate Layer 2 loops, divide VLANs, transmit customer network
packets through the public network, and modify VLAN tags for packets.
This preface includes the following topics about the documentation:
•
•
.
•
About the H3C S7500E-X documentation set
.
•
•
•
.
Audience
This documentation is intended for:
•
Network planners.
•
Field technical support and servicing engineers.
•
Network administrators working with the S7500E-X switch series.
Conventions
This section describes the conventions used in the documentation.
Port numbering in examples
The port numbers in the documentation are for illustration only and might be unavailable on your
device.
Command conventions
Convention Description
Boldface Bold text represents commands and keywords that you enter literally as shown.
Italic
Italic text represents arguments that you replace with actual values.
[ ]
Square brackets enclose syntax choices (keywords or arguments) that are optional.
{ x | y | ... }
Braces enclose a set of required syntax choices separated by vertical bars, from which
you select one.
[ x | y | ... ]
Square brackets enclose a set of optional syntax choices separated by vertical bars,
from which you select one or none.
{ x | y | ... } *
Asterisk marked braces enclose a set of required syntax choices separated by vertical
bars, from which you select at least one.
[ x | y | ... ] *
Asterisk marked square brackets enclose optional syntax choices separated by vertical
bars, from which you select one choice, multiple choices, or none.
&<1-n>
The argument or keyword and argument combination before the ampersand (&) sign
can be entered 1 to n times.
#
A line that starts with a pound (#) sign is comments.
Summary of H3C S7500E-X
Page 1
H3c s7500e-x switch series layer 2 - lan switching configuration guide hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Http://www.H3c.Com software version: s7500ex-cmw710-r7178 document version: 6w100-20160118.
Page 2
Copyright © 2016, hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. And its licensors all rights reserved no part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Trademarks h3c, , h3cs, h3cie, h3cne, aolynk, , h 3 car...
Page 3: Preface
Preface this configuration guide describes lan switching fundamentals and configuration. It describes how to isolate uses in the same vlan, eliminate layer 2 loops, divide vlans, transmit customer network packets through the public network, and modify vlan tags for packets. This preface includes the...
Page 4
Gui conventions convention description boldface window names, button names, field names, and menu items are in boldface. For example, the new user window appears; click ok. > multi-level menus are separated by angle brackets. For example, file > create > folder. Symbols convention description warnin...
Page 5
Convention description represents a security card, such as a firewall, load balancing, netstream, ssl vpn, ips, or acg card. About the h3c s7500e-x documentation set the h3c s7500e-x documentation set includes the following categories of documents: category documents purposes hardware specifications...
Page 6
[technical documents] —provides hardware installation, software upgrading, and software feature configuration and maintenance documentation. [products & solutions] —provides information about products and technologies, as well as solutions. [software download] —provides the documentation released wi...
Page 7
I contents configuring the mac address table ································································ 1 overview ···························································································································································· 1 how a mac address en...
Page 8
Ii ethernet link aggregation configuration task list ······························································································ 27 configuring an aggregation group ··················································································································· ...
Page 9
Iii configuring the current device as the root bridge of a specific spanning tree ········································· 76 configuring the current device as a secondary root bridge of a specific spanning tree ··························· 77 configuring the device priority ························...
Page 10
Iv enabling loop detection globally············································································································· 109 enabling loop detection on a port··········································································································· 109 settin...
Page 11
V configuring voice vlans ············································································ 158 overview ························································································································································ 158 methods of identifying ip p...
Page 12
Vi configuring the cvlan tpid ················································································································· 192 configuring the svlan tpid ················································································································· 193 setting...
Page 13
Vii configuring service loopback groups ·························································· 251 overview ························································································································································ 251 configuration restrictions and ...
Page 14
1 configuring the mac address table overview an ethernet device uses a mac address table to forward frames. A mac address entry includes a destination mac address, an outgoing interface, and a vlan id. When the device receives a frame, it uses the destination mac address of the frame to look for a m...
Page 15
2 • static entries —a static entry is manually added to forward frames with a specific destination mac address out of the associated interface, and it never ages out. A static entry has higher priority than a dynamically learned one. • dynamic entries —a dynamic entry can be manually configured or d...
Page 16
3 configuring mac address entries configuration guidelines • you cannot add a dynamic mac address entry if a learned entry already exists with a different outgoing interface for the mac address. • the manually configured static, blackhole, and multiport unicast mac address entries cannot survive a r...
Page 17
4 step command remarks 2. Enter interface view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number • enter s-channel interface view: interface s-channel interface-number.Channel-id...
Page 18
5 step command remarks 2. Add or modify a multiport unicast mac address entry. Mac -address multiport mac -address interface interface-list vlan vlan-id by default, no multiport unicast mac address entry is configured globally. Make sure you have created the vlan and assigned the interface to the vl...
Page 19
6 disabling mac address learning on interfaces when global mac address learning is enabled, you can disable mac address learning on a single interface. To disable mac address learning on an interface: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter interface view. • enter layer 2...
Page 20
7 expires, the device deletes the entry. This aging mechanism ensures that the mac address table can promptly update to accommodate latest network topology changes. A stable network requires a longer aging interval, and an unstable network requires a shorter aging interval. An aging interval that is...
Page 21
8 to configure the device to forward unknown frames received on the interface after the mac learning limit on the interface is reached: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter interface view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view. Interface interface-type interface-numb...
Page 22
9 step command remarks 2. Enter interface view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number • enter s-channel interface view: interface s-channel interface-number.Channel-id...
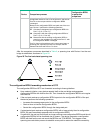
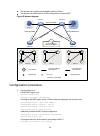
Page 23
10 figure 1 mac address tables of devices when client a accesses ap c when client a roams to ap d, device b learns a mac address entry for client a. Device b advertises it to device a to ensure service continuity for client a, as shown in figure 2 . Figure 2 mac address tables of devices when client...
Page 24
11 configuring mac address move notifications and suppression the outgoing interface for a mac address entry learned on interface a is changed to interface b when the following conditions exist: • interface b receives a packet with the mac address as the source mac address. • interface b belongs to ...
Page 25
12 step command remarks 2. (optional.) set a suppression interval for mac address moves. Mac-address notification mac-move suppression interval interval-value the default setting is 30 seconds. 3. (optional.) set a suppression threshold for mac address moves. Mac-address notification mac-move suppre...
Page 26
13 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enable arp fast update for mac address moves. Mac-address mac-move fast-update by default, arp fast update for mac address moves is disabled. Disabling static source check by default, the static source check feature is enabled on an in...
Page 27
14 step command remarks 2. Enable snmp notifications for the mac address table. Snmp-agent trap enable mac-address [ mac-move ] by default, snmp notifications are enabled for the mac address table. When snmp notifications are disabled for the mac address table, syslog messages are sent to notify imp...
Page 28
15 configuration procedure # add a static mac address entry for mac address 000f-e235-dc71 on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 that belongs to vlan 1. System-view [device] mac-address static 000f-e235-dc71 interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 vlan 1 # add a blackhole mac address entry for mac address 000f-e235-abcd...
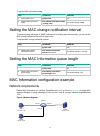
Page 29: Configuring Mac Information
16 configuring mac information the mac information feature can generate syslog messages or snmp notifications when mac address entries are learned or deleted. You can use these messages to monitor user's leaving or joining the network and analyze network traffic. The mac information feature buffers ...
Page 31
18 configuration restrictions and guidelines when you edit the file /etc/syslog.Conf, follow these restrictions and guidelines: • comments must be on a separate line and must begin with a pound sign (#). • no redundant spaces are allowed after the file name. • the logging facility name and the sever...
Page 32
19 3. Enable mac information on device: # enable mac information globally. [device] mac-address information enable # configure the mac information mode as syslog. [device] mac-address information mode syslog # enable mac information on interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to enable gigabitethernet 1/0/1 ...
Page 33
20 configuring ethernet link aggregation ethernet link aggregation bundles multiple physical ethernet links into one logical link, called an aggregate link. Link aggregation has the following benefits: • increased bandwidth beyond the limits of any single link. In an aggregate link, traffic is distr...
Page 34
21 { the port has not received lacpdus from its peer port. Operational key when aggregating ports, the system automatically assigns each port an operational key based on port information, such as port rate and duplex mode. Any change to this information triggers a recalculation of the operational ke...
Page 35
22 link aggregation modes an aggregation group operates in one of the following modes: • static—static aggregation is stable. An aggregation group in static mode is called a static aggregation group. The aggregation states of the member ports in a static aggregation group are not affected by the pee...
Page 36
23 figure 6 setting the aggregation state of a member port in a static aggregation group after the limit on selected ports is reached in a static aggregation group, new member ports in the group are placed in the unselected state. This mechanism prevents traffic interruption on the existing selected...
Page 37
24 lacp functions lacp offers basic lacp functions and extended lacp functions, as described in table 2 . Table 2 basic and extended lacp functions category description basic lacp functions implemented through the basic lacpdu fields, including the system lacp priority, system mac address, port prio...
Page 38
25 how dynamic link aggregation works choosing a reference port the system chooses a reference port from the member ports that are in up state and have the same attribute configurations as the aggregate interface. A selected port must have the same operational key and attribute configurations as the...
Page 39
26 figure 7 setting the state of a member port in a dynamic aggregation group meanwhile, the system with the higher system id is aware of the aggregation state changes on the peer system. The system sets the aggregation state of local member ports the same as their peer ports. When you aggregate int...
Page 40
27 • when the aggregation state of a local port changes in a dynamic aggregation group, the aggregation state of the peer port also changes. • after the selected port limit has been reached, a port joining the aggregation group is placed in the selected state if it is more eligible than a current se...
Page 41
28 tasks at a glance (optional.) configuring an aggregate interface: • setting the description for an aggregate interface • specifying ignored vlans for a layer 2 aggregate interface • reserving a vlan interface resource for a layer 2 aggregate interface • setting the mtu for a layer 3 aggregate int...
Page 42
29 { ac-vsi association (see mpls configuration guide). • you cannot assign a port to a layer 3 aggregation group if any of the following features are configured on the port: { association between ac and cross connection (see mpls configuration guide). { ac-vsi association (see mpls configuration gu...
Page 43
30 step command remarks 2. Create a layer 3 aggregate interface and enter layer 3 aggregate interface view. Interface route-aggregation interface-number when you create a layer 3 aggregate interface, the system automatically creates a layer 3 static aggregation group numbered the same. 3. Exit to sy...
Page 44
31 step command remarks 6. Assign an interface to the specified layer 2 aggregation group. A. Enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number b. Assign the interface to the specified layer 2 aggregation group: port link-aggregation group number repeat these two subst...
Page 45
32 step command remarks 6. Assign an interface to the specified layer 3 aggregation group. A. Enter layer 3 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number b. Assign the interface to the specified layer 3 aggregation group: port link-aggregation group number repeat these two subst...
Page 46
33 step command remarks 3. Set the description for the aggregate interface. Description text by default, the description of an interface is interface-name interface . Specifying ignored vlans for a layer 2 aggregate interface by default, to become selected ports, the member ports must have the same ...
Page 47
34 setting the mtu for a layer 3 aggregate interface the mtu of an interface affects ip packets fragmentation and reassembly on the interface. To set the mtu for a layer 3 aggregate interface: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter layer 3 aggregate interface view. Inter...
Page 48
35 step command remarks 2. Enter aggregate interface view. • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number • enter layer 3 aggregate interface view: interface route-aggregation interface-number n/a 3. Set the minimum number of selected ports for the aggregatio...
Page 49
36 step command remarks 2. Enter aggregate interface view. • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number • enter layer 3 aggregate interface view: interface route-aggregation interface-number n/a 3. Configure the aggregate interface as an edge aggregate inte...
Page 50
37 step command 1. Enter system view. System-view 2. Enter aggregate interface view. • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number • enter layer 3 aggregate interface view: interface route-aggregation interface-number 3. Restore the default settings for the ...
Page 51
38 setting the group-specific load sharing mode in layer 2 aggregate interface view, the switch supports the following load sharing modes and combinations: • source ip address. • destination ip address. • source mac address. • destination mac address. • layer 1 mpls label. • destination ip address a...
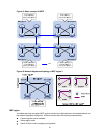
Page 52
39 figure 8 load sharing for multidevice link aggregation in an irf fabric to enable local-first load sharing for link aggregation: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enable local-first load sharing for link aggregation. Link-aggregation load-sharing mode local-first by de...
Page 53
40 • to avoid traffic interruption on layer 2 dynamic aggregate links after link-aggregation traffic redirection is enabled, make sure the corresponding aggregate interfaces do not have static mac address entries. For information about mac address entries, see layer 2—lan switching configuration gui...
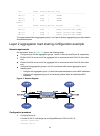
Page 54
41 • configure a layer 2 static aggregation group on both device a and device b. • enable vlan 10 at one end of the aggregate link to communicate with vlan 10 at the other end. • enable vlan 20 at one end of the aggregate link to communicate with vlan 20 at the other end. Figure 9 network diagram co...
Page 55
42 [devicea-bridge-aggregation1] port trunk permit vlan 10 20 [devicea-bridge-aggregation1] quit 2. Configure device b in the same way device a is configured. (details not shown.) verifying the configuration # display detailed information about all aggregation groups on device a. [devicea] display l...
Page 56
43 configuration procedure 1. Configure device a: # create vlan 10, and assign the port gigabitethernet 1/0/4 to vlan 10. System-view [devicea] vlan 10 [devicea-vlan10] port gigabitethernet 1/0/4 [devicea-vlan10] quit # create vlan 20, and assign the port gigabitethernet 1/0/5 to vlan 20. [devicea] ...
Page 57
44 port status priority oper-key flag -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ge1/0/1 s 32768 1 {acdef} ge1/0/2 s 32768 1 {acdef} ge1/0/3 s 32768 1 {acdef} remote: actor partner priority oper-key systemid flag -------------------------------------------------...
Page 58
45 [devicea-vlan10] port gigabitethernet 1/0/5 [devicea-vlan10] quit # create vlan 20, and assign the port gigabitethernet 1/0/6 to vlan 20. [devicea] vlan 20 [devicea-vlan20] port gigabitethernet 1/0/6 [devicea-vlan20] quit # create layer 2 aggregate interface bridge-aggregation 1. [devicea] interf...
Page 59
46 loadsharing type: shar -- loadsharing, nons -- non-loadsharing port status: s -- selected, u -- unselected, i -- individual flags: a -- lacp_activity, b -- lacp_timeout, c -- aggregation, d -- synchronization, e -- collecting, f -- distributing, g -- defaulted, h -- expired aggregate interface: b...
Page 60
47 figure 12 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure the device: # create layer 2 aggregate interface bridge-aggregation 1, and set the link aggregation mode to dynamic. System-view [device] interface bridge-aggregation 1 [device-bridge-aggregation1] link-aggregation mode dynamic # conf...
Page 61
48 ge1/0/2 0 32768 0 0x8000, 0000-0000-0000 {def} the output shows that gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 are in individual state when they have not received lacpdus from the server. Both gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 can forward packets, which ensures zero packet los...
Page 62
49 aggregation mode: static loadsharing type: shar port status priority oper-key -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ge1/0/1 s 32768 1 ge1/0/2 s 32768 1 ge1/0/3 s 32768 1 the output shows that link aggregation group 1 is a layer 3 static aggregation group...
Page 63
50 [devicea] display link-aggregation verbose loadsharing type: shar -- loadsharing, nons -- non-loadsharing port status: s -- selected, u -- unselected, i -- individual flags: a -- lacp_activity, b -- lacp_timeout, c -- aggregation, d -- synchronization, e -- collecting, f -- distributing, g -- def...
Page 64
51 # configure layer 3 aggregation group 1 to load share packets based on source ip addresses. [devicea-route-aggregation1] link-aggregation load-sharing mode source-ip # configure an ip address and subnet mask for layer 3 aggregate interface route-aggregation 1. [devicea-route-aggregation1] ip addr...
Page 65
52 aggregate interface: route-aggregation2 aggregation mode: static loadsharing type: shar port status priority oper-key -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ge1/0/3 s 32768 2 ge1/0/4 s 32768 2 the output shows that: • link aggregation groups 1 and 2 are b...
Page 66
53 [device-route-aggregation1] lacp edge-port [device-route-aggregation1] quit # assign layer 3 ethernet interfaces gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 to aggregation group 1. [device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [device-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1 [device-gig...
Page 67: Configuring Port Isolation
54 configuring port isolation the port isolation feature isolates layer 2 traffic for data privacy and security without using vlans. Ports in an isolation group cannot communicate with each other. However, they can communicate with ports outside the isolation group. Assigning a port to an isolation ...
Page 68
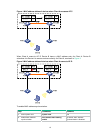
55 displaying and maintaining port isolation execute display commands in any view. Task command display isolation group information. Display port-isolate group [ group-number ] port isolation configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 17 : • lan users host a, host b, and host c ar...
Page 69
56 [device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [device-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port-isolate enable group 2 [device-gigabitethernet1/0/3] quit verifying the configuration # display information about isolation group 2. [device] display port-isolate group 2 port isolation group information: group id: 2 grou...
Page 70
57.
Page 71
58 configuring spanning tree protocols spanning tree protocols eliminate loops in a physical link-redundant network by selectively blocking redundant links and putting them in a standby state. The recent versions of stp include the rapid spanning tree protocol (rstp), the per-vlan spanning tree (pvs...
Page 72
59 upon initialization of a network, each device generates and periodically sends configuration bpdus, with itself as the root bridge. After network convergence, only the root bridge generates and periodically sends configuration bpdus. The other devices only forward the bpdus. Root port on a non-ro...
Page 73
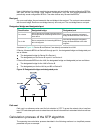
60 calculation process the stp algorithm uses the following calculation process: 1. Network initialization. Upon initialization of a device, each port generates a bpdu with the following contents: { the port as the designated port. { the device as the root bridge. { 0 as the root path cost. { the de...
Page 74
61 step actions configuration bpdu. The following are the principles of configuration bpdu comparison: a. The configuration bpdu with the lowest root bridge id has the highest priority. B. If configuration bpdus have the same root bridge id, their root path costs are compared. For example, the root ...
Page 75
62 device port name configuration bpdu on the port port b2 {1, 0, 1, port b2} device c port c1 {2, 0, 2, port c1} port c2 {2, 0, 2, port c2} 2. Configuration bpdus comparison on each device. In table 6 , each configuration bpdu contains the following fields: root bridge id, root path cost, designate...
Page 76
63 device comparison process configuration bpdu on ports after comparison port, device b calculates a designated port configuration bpdu for port b2 {0, 5, 1, port b2}. Device b compares it with the existing configuration bpdu of port b2 {1, 0, 1, port b2}. Device b determines that the calculated on...
Page 77
64 device comparison process configuration bpdu on ports after comparison plus path cost of port c2 (4). Device c determines that the configuration bpdu of port c2 is the optimum, and selects port c2 as the root port with the configuration bpdu unchanged. Based on the configuration bpdu and path cos...
Page 78
65 however, the newly calculated configuration bpdu cannot be propagated throughout the network immediately. As a result, the old root ports and designated ports that have not detected the topology change continue forwarding data along the old path. If the new root ports and designated ports begin t...
Page 79
66 a port's link type determines the type of bpdus the port sends. • an access port sends stp bpdus. • a trunk or hybrid port sends stp bpdus in vlan 1 and sends pvst bpdus in other vlans. Mstp mstp overcomes the following stp, rstp, and pvst limitations: • stp limitations —stp does not support rapi...
Page 80
67 figure 21 basic concepts in mstp figure 22 network diagram and topology of mst region 3 mst region a multiple spanning tree region (mst region) consists of multiple devices in a switched network and the network segments among them. All these devices have the following characteristics: • a spannin...
Page 81
68 • same mstp revision level • physically linked together multiple mst regions can exist in a switched network. You can assign multiple devices to the same mst region, as shown in figure 21 . • the switched network contains four mst regions, mst region 1 through mst region 4. • all devices in each ...
Page 82
69 port roles a port can play different roles in different mstis. As shown in figure 23 , an mst region contains device a, device b, device c, and device d. Port a1 and port a2 of device a connect to the common root bridge. Port b2 and port b3 of device b form a loop. Port c3 and port c4 of device c...
Page 83
70 • learning—the port receives and sends bpdus, learns mac addresses, but does not forward user traffic. Learning is an intermediate port state. • discarding—the port receives and sends bpdus, but does not learn mac addresses or forward user traffic. Note: when in different mstis, a port can be in ...
Page 84
71 in addition to basic mstp features, the following features are provided for ease of management: • root bridge hold • root bridge backup • root guard • bpdu guard • loop guard • tc-bpdu guard • port role restriction • tc-bpdu transmission restriction • support for hot swapping of interface cards a...
Page 85
72 • the member ports of an aggregation group do not participate in spanning tree calculation. However, the ports still reserve their spanning tree configurations for participating in spanning tree calculation after leaving the aggregation group. Spanning tree configuration task lists before configu...
Page 86
73 tasks at a glance • (optional.) configuring edge ports • (optional.) configuring the port link type • (optional.) enabling outputting port state transition information • (required.) enabling the spanning tree feature configuring the leaf nodes: • (required.) setting the spanning tree mode • (opti...
Page 87
74 tasks at a glance (optional.) performing mcheck (optional.) configuring protection features (optional.) enabling snmp notifications for new-root election and topology change events mstp configuration task list tasks at a glance configuring the root bridge: • (required.) setting the spanning tree ...
Page 88
75 setting the spanning tree mode the spanning tree modes include: • stp mode —all ports of the device send stp bpdus. Select this mode when the peer device of a port supports only stp. • rstp mode —all ports of the device send rstp bpdus. A port in this mode automatically transits to the stp mode w...
Page 89
76 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter mst region view. Stp region-configuration n/a 3. Configure the mst region name. Region-name name the default setting is the mac address. 4. Configure the vlan-to-instance mapping table. • instance instance-id vlan vlan-id-list • ...
Page 90
77 step command remarks device as the root bridge. Stp root primary • in pvst mode: stp vlan vlan-id-list root primary • in mstp mode: stp [ instance instance-list ] root primary function as the root bridge. Configuring the current device as a secondary root bridge of a specific spanning tree step c...
Page 91
78 configuration bpdus sent by the regional root bridge always have a hop count set to the maximum value. When a device receives this configuration bpdu, it decrements the hop count by one, and uses the new hop count in the bpdus that it propagates. When the hop count of a bpdu reaches zero, it is d...
Page 92
79 its state after a forward delay timer to make sure the state transition of the local port stays synchronized with the peer. • hello time —interval at which the device sends configuration bpdus to detect link failures. If the device receives no configuration bpdus within the timeout period, it rec...
Page 93
80 step command remarks stp vlan vlan-id-list timer hello time 4. Set the max age timer. • in stp/rstp/mstp mode: stp timer max-age time • in pvst mode: stp vlan vlan-id-list timer max-age time the default setting is 20 seconds. Setting the timeout factor the timeout factor is a parameter used to de...
Page 94
81 step command remarks rate of the ports. Configuring edge ports if a port directly connects to a user terminal rather than another device or a shared lan segment, this port is regarded as an edge port. When network topology change occurs, an edge port will not cause a temporary loop. Because a dev...
Page 95
82 you can specify a standard for the device to use in automatic calculation for the default path cost. The device supports the following standards: • dot1d-1998—the device calculates the default path cost for ports based on ieee 802.1d-1998. • dot1t—the device calculates the default path cost for p...
Page 96
83 link speed port type path cost ieee 802.1d-1998 ieee 802.1t private standard ports aggregate interface containing four selected ports 50000 140 1000 mbps single port 4 20000 20 aggregate interface containing two selected ports 10000 18 aggregate interface containing three selected ports 6666 16 a...
Page 97
84 link speed port type path cost ieee 802.1d-1998 ieee 802.1t private standard containing two selected ports aggregate interface containing three selected ports 66 1 aggregate interface containing four selected ports 50 1 configuring path costs of ports when the path cost of a port changes, the sys...
Page 98
85 cost of every port will be reset and automatically re-calculated after you change the current pathcost standard. Continue?[y/n]:y cost of every port has been re-calculated [sysname] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/3] stp vlan 20 to 30 cost 2000 configuring the port pri...
Page 101
88 performing mcheck the mcheck feature enables user intervention in the port status transition process. When a port on an mstp, rstp, or pvst device connects to an stp device and receives stp bpdus, the port automatically transits to the stp mode. However, the port cannot automatically transit back...
Page 102
89 • region name. • revision level. • vlan-to-instance mappings. A spanning tree device identifies devices in the same mst region by determining the configuration id in bpdu packets. The configuration id includes the region name, revision level, and configuration digest. It is 16-byte long and is th...
Page 103
90 digest snooping configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 24 , device a and device b connect to device c, which is a third-party device. All these devices are in the same region. Enable digest snooping on the ports of device a and device b that connect to device c, so that the...
Page 104
91 both rstp and mstp devices can perform rapid transition on a designated port only when the port receives an agreement packet from the downstream device. Rstp and mstp devices have the following differences: • for mstp, the root port of the downstream device sends an agreement packet only after it...
Page 105
92 configuration prerequisites before you configure the no agreement check feature, complete the following tasks: • connect a device to a third-party upstream device that supports spanning tree protocols through a point-to-point link. • configure the same region name, revision level, and vlan-to-ins...
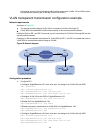
Page 106
93 • the spanning tree feature is disabled on device a and device b and enabled on all devices in user network 1 and user network 2. • the irf fabric transparently transmits bpdus for both user networks and is not involved in the calculation of spanning trees. When the network topology changes, it t...
Page 107
94 configuring protection features a spanning tree device supports the following protection features: • bpdu guard • root guard • loop guard • port role restriction • tc-bpdu transmission restriction • tc-bpdu guard • bpdu drop configuring bpdu guard for access layer devices, the access ports can di...
Page 109
96 the initial state of a loop guard-enabled port is discarding in every msti. When the port receives bpdus, it transits its state. Otherwise, it stays in the discarding state to prevent temporary loops. Do not enable loop guard on a port that connects user terminals. Otherwise, the port stays in th...
Page 110
97 make this configuration on the port that connects to the user access network. To configure tc-bpdu transmission restriction: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter layer 2 ethernet or aggregate interface view. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 3. Enable tc...
Page 111
98 step command remarks 2. Enter layer 2 ethernet interface view. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 3. Enable bpdu drop on the current interface. Bpdu-drop any by default, bpdu drop is disabled. Enabling snmp notifications for new-root election and topology change events this feature ena...
Page 112
99 task command display information about ports blocked by spanning tree protection features. Display stp abnormal-port display bpdu statistics on ports. Display stp bpdu-statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number [ instance instance-list ] ] display information about ports shut down by ...
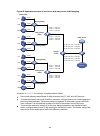
Page 113
100 figure 29 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure vlans and vlan member ports. (details not shown.) { create vlan 10, vlan 20, and vlan 30 on both device a and device b. { create vlan 10, vlan 20, and vlan 40 on device c. { create vlan 20, vlan 30, and vlan 40 on device d. { configu...
Page 114
101 [deviceb-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 10 [deviceb-mst-region] instance 3 vlan 30 [deviceb-mst-region] instance 4 vlan 40 # configure the revision level of the mst region as 0. [deviceb-mst-region] revision-level 0 # activate mst region configuration. [deviceb-mst-region] active region-configurati...
Page 115
102 verifying the configuration in this example, device b has the lowest root bridge id. As a result, device b is elected as the root bridge in msti 0. When the network is stable, you can use the display stp brief command to display brief spanning tree information on each device. # display brief spa...
Page 116
103 figure 30 mstis mapped to different vlans pvst configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 31 , device a and device b work at the distribution layer, and device c and device d work at the access layer. Configure pvst to meet the following requirements: • packets of a vlan are f...
Page 117
104 figure 31 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure vlans and vlan member ports. (details not shown.) { create vlan 10, vlan 20, and vlan 30 on both device a and device b. { create vlan 10, vlan 20, and vlan 40 on device c. { create vlan 20, vlan 30, and vlan 40 on device d. { configu...
Page 118
105 [devicec] stp vlan 10 20 40 enable 5. Configure device d: # set the spanning tree mode to pvst. System-view [deviced] stp mode pvst # enable the spanning tree feature globally and in vlan 20, vlan 30, and vlan 40. [deviced] stp global enable [deviced] stp vlan 20 30 40 enable verifying the confi...
Page 119
106 30 gigabitethernet1/0/2 alte discarding none 40 gigabitethernet1/0/3 root forwarding none based on the output, you can draw a topology for each vlan spanning tree, as shown in figure 32 . Figure 32 vlan spanning tree topologies.
Page 120: Configuring Loop Detection
107 configuring loop detection overview incorrect network connections or configurations can create layer 2 loops, which results in repeated transmission of broadcasts, multicasts, or unknown unicasts. The repeated transmissions can waste network resources and can paralyze networks. The loop detectio...
Page 121
108 • code—protocol sub-type, which is 0x0001, indicating the loop detection protocol. • version—protocol version, which is always 0x0000. • length—length of the frame. The value includes the inner header, but excludes the ethernet header. • reserved—this field is reserved. Frames for loop detection...
Page 122
109 note: incorrect recovery can occur when loop detection frames are discarded to reduce the load. To avoid this, use the shutdown action, or manually remove the loop. Loop detection configuration task list tasks at a glance (required.) enabling loop detection (optional.) setting the loop protectio...
Page 123
110 setting the global loop protection action step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Configure the global loop protection action. Loopback-detection global action shutdown by default, the device generates a log but performs no action on the port on which a loop is detected. Se...
Page 124
111 displaying and maintaining loop detection execute display commands in any view. Task command display the loop detection configuration and status. Display loopback-detection loop detection configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 35 , configure loop detection on device a to m...
Page 125
112 [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 100 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # configure the global loop protection action as shutdown. [devicea] loopback-detection global action shutdo...
Page 126
113 %feb 24 15:04:44:243 2013 devicea lpdt/5/lpdt recovered: loopback on gigabitethernet1/0/1 recovered. %feb 24 15:04:44:248 2013 devicea lpdt/5/lpdt recovered: loopback on gigabitethernet1/0/2 recovered. The output shows the following information: • device a detected loops on ports gigabitethernet...
Page 127: Configuring Vlans
114 configuring vlans overview ethernet is a family of shared-media lan technologies based on the csma/cd mechanism. An ethernet lan is both a collision domain and a broadcast domain. Because the medium is shared, collisions and broadcasts are common in an ethernet lan. Typically, bridges and layer ...
Page 128
115 to a different value. For compatibility with a neighbor device, configure the tpid value on the device to be the same as the neighbor device. • priority—3-bit long, identifies the 802.1p priority of the frame. For more information, see acl and qos configuration guide . • cfi—1-bit long canonical...
Page 129
116 note: • as the system default vlan, vlan 1 cannot be created or deleted. • before you delete a dynamic vlan or a vlan locked by an application, you must first remove the configuration from the vlan. Configuring basic settings of a vlan interface for hosts of different vlans to communicate at lay...
Page 130
117 step command remarks 8. (optional.) bring up the vlan interface. Undo shutdown by default, a vlan interface is not manually shut down. The following guidelines apply to the vlan interface that is in default state: • the vlan interface is down if all ports in the vlan are down. • the vlan interfa...
Page 131
118 how ports of different link types handle frames actions access trunk hybrid in the inbound direction for an untagged frame tags the frame with the pvid tag. • if the pvid is permitted on the port, tags the frame with the pvid tag. • if not, drops the frame. In the inbound direction for a tagged ...
Page 132
119 step command remarks 2. Enter interface view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter s-channel interface view: interface s-channel interface-number.Channel- id • enter s-channel aggregate interface view: inte...
Page 133
120 step command remarks 5. (optional.) configure the pvid of the trunk port. Port trunk pvid vlan vlan-id the default setting is vlan 1. Rpr logical interfaces do not support this command. Assigning a hybrid port to a vlan a hybrid port supports multiple vlans. You can assign it to the specified vl...
Page 134
121 configuring mac-based vlans introduction this feature is available only on hybrid ports. The mac-based vlan feature assigns hosts to a vlan based on their mac addresses. This feature is also called user-based vlan because vlan configuration remains the same regardless of a user's physical locati...
Page 135
122 { if the frame is tagged, the port gets the source mac address of the frame. { if the frame is untagged, the port selects a vlan for the frame by using the following matching order: − mac-based vlan (fuzzy and exact mac address match). − ip subnet-based vlan. − protocol-based vlan. − port-based ...
Page 136
123 when you configure dynamic mac-based vlan assignment, follow these guidelines: • when a port joins a vlan specified in the mac-to-vlan entry, one of the following events occurs depending on the port configuration: { if the port has not been configured to allow packets from the vlan to pass throu...
Page 138
125 step command remarks 5. Enable the mac-based vlan feature. Mac-vlan enable by default, mac-based vlan is disabled. 6. Enable dynamic mac-based vlan assignment. Mac-vlan trigger enable by default, dynamic mac-based vlan assignment is disabled. The vlan assignment for a port is triggered only when...
Page 139
126 use this feature when untagged packets from an ip subnet or ip address must be transmitted in a vlan. This feature is available only on hybrid ports, and it processes only untagged packets. An ip subnet-based vlan has one or multiple subnets to match inbound packets. Each subnet has a unique ind...
Page 140
127 • assign the port to the protocol-based vlans. • associate the port with the protocol templates of the protocol-based vlans. When an untagged packet arrives at the port, the port processes the packet as follows: • if the protocol type and encapsulation format in the packet match a protocol templ...
Page 141
128 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Create a vlan group and enter vlan group view. Vlan-group group-name by default, no vlan group exists. 3. Add vlans to the vlan group. Vlan-list vlan-id-list by default, no vlan exists in a vlan group. Displaying and maintaining vlans...
Page 142
129 figure 39 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure device a: # create vlan 100, and assign gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to vlan 100. System-view [devicea] vlan 100 [devicea-vlan100] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-vlan100] quit # create vlan 200, and assign gigabitethernet 1/0/2 to vlan...
Page 143
130 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/3] display vlan 200 vlan id: 200 vlan type: static route interface: not configured description: vlan 0200 name: vlan 0200 tagged ports: gigabitethernet1/0/3 untagged ports: gigabitethernet1/0/2 mac-based vlan configuration example network requirements as shown in figu...
Page 144
131 [devicea] vlan 200 [devicea-vlan200] quit # associate the mac addresses of laptop 1 and laptop 2 with vlans 100 and 200, respectively. [devicea] mac-vlan mac-address 000d-88f8-4e71 vlan 100 [devicea] mac-vlan mac-address 0014-222c-aa69 vlan 200 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a hybrid port,...
Page 145
132 state: s - static, d – dynamic mac address mask vlan id dot1q state 000d-88f8-4e71 ffff-ffff-ffff 100 0 s 0014-222c-aa69 ffff-ffff-ffff 200 0 s total mac vlan entries count: 2 ip subnet-based vlan configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 41 , the hosts in the office belong t...
Page 146
133 [devicec-vlan200] quit # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/11 as a hybrid port, and assign it to vlan 100 as a tagged vlan member. [devicec] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/11 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/11] port link-type hybrid [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/11] port hybrid vlan 100 tagged [devicec-gig...
Page 147
134 to isolate ipv4 and ipv6 traffic at layer 2, configure protocol-based vlans to associate the ipv4 and arp protocols with vlan 100, and associate the ipv6 protocol with vlan 200. Figure 42 network diagram configuration procedure in this example, l2 switch a and l2 switch b use the factory configu...
Page 148
135 [device-vlan100] quit # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a hybrid port, and assign it to vlans 100 and 200 as an untagged vlan member. [device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [device-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type hybrid [device-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port hybrid vlan 100 200 untagged # ...
Page 149
136 vlan id protocol index protocol type status 100 1 ipv4 active 100 2 ethernet ii etype 0x0806 active 200 1 ipv6 active interface: gigabitethernet 1/0/2 vlan id protocol index protocol type status 100 1 ipv4 active 100 2 ethernet ii etype 0x0806 active 200 1 ipv6 active.
Page 150: Configuring Super Vlans
137 configuring super vlans hosts in a vlan typically use ip addresses in the same subnet. For layer 3 interoperability with other vlans, you can create a vlan interface for the vlan and assign an ip address to it. This requires a large number of ip addresses. The super vlan feature was introduced t...
Page 151
138 to configure a super vlan: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter vlan view. Vlan vlan-id n/a 3. Configure the vlan as a super vlan. Supervlan by default, a vlan is not a super vlan. 4. Associate the super vlan with the sub-vlans. Subvlan vlan-id-list by default, a s...
Page 152
139 task command display information about super vlans and their associated sub-vlans. Display supervlan [ supervlan-id ] super vlan configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 43 : • gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 are in vlan 2. • gigabitethernet 1/0/3 and gigabit...
Page 153
140 # create vlan 3, and assign gigabitethernet 1/0/3 and gigabitethernet 1/0/4 to the vlan. [devicea] vlan 3 [devicea-vlan3] port gigabitethernet 1/0/3 gigabitethernet 1/0/4 [devicea-vlan3] quit # create vlan 5, and assign gigabitethernet 1/0/5 and gigabitethernet 1/0/6 to the vlan. [devicea] vlan ...
Page 154
141 it is a sub vlan. Route interface: configured ipv4 address: 10.1.1.1 ipv4 subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 description: vlan 0003 name: vlan 0003 tagged ports: none untagged ports: gigabitethernet1/0/3 gigabitethernet1/0/4 vlan id: 5 vlan type: static it is a sub vlan. Route interface: configured ipv4...
Page 155: Configuring The Private Vlan
142 configuring the private vlan vlan technology provides a method for isolating traffic from customers. At the access layer of a network, customer traffic must be isolated for security or accounting purposes. If vlans are assigned on a per-user basis, a large number of vlans will be required. The p...
Page 156
143 2. Configure the secondary vlans. 3. Associate the secondary vlans with the primary vlan. 4. Configure the uplink and downlink ports: { configure the uplink port (for example, the port connecting l2 device b to l3 device a in figure 44 ): − when the port allows only one primary vlan, configure t...
Page 158
145 step command remarks 15. Configure the downlink port as a host or trunk secondary port. • configure the downlink port as a host port: port private-vlan host • configure the downlink port as a trunk secondary port of the specified vlans: port private-vlan vlan-id-list trunk secondary by default, ...
Page 159
146 private vlan configuration examples promiscuous port configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 45 , configure the private vlan feature to meet the following requirements: • on device b, vlan 5 is a primary vlan that is associated with secondary vlans 2 and 3. Gigabitethernet ...
Page 160
147 # configure the uplink port gigabitethernet 1/0/5 as a promiscuous port of vlan 5. [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/5] port private-vlan 5 promiscuous [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/5] quit # assign the downlink port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 to vlan 2, and configur...
Page 161
148 secondary vlan id: 2-3 vlan id: 5 vlan type: static private vlan type: primary route interface: not configured description: vlan 0005 name: vlan 0005 tagged ports: none untagged ports: gigabitethernet1/0/2 gigabitethernet1/0/3 gigabitethernet1/0/5 vlan id: 2 vlan type: static private vlan type: ...
Page 162
149 • vlans 5 and 10 are primary vlans on device b. The uplink port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 on device b permits the packets from vlans 5 and 10 to pass through tagged. • on device b, the downlink port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 permits secondary vlan 2. The downlink port gigabitethernet 1/0/3 permits secon...
Page 163
150 [deviceb] vlan 10 [deviceb-vlan10] private-vlan secondary 6 8 [deviceb-vlan10] quit # configure the uplink port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk promiscuous port of vlans 5 and 10. [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port private-vlan 5 10 trunk promiscuous [...
Page 164
151 primary vlan id: 5 secondary vlan id: 2-3 vlan id: 5 vlan type: static private vlan type: primary route interface: not configured description: vlan 0005 name: vlan 0005 tagged ports: gigabitethernet1/0/1 untagged ports: gigabitethernet1/0/2 gigabitethernet1/0/3 vlan id: 2 vlan type: static priva...
Page 165
152 trunk promiscuous and trunk secondary port configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 47 , configure the private vlan feature to meet the following requirements: • vlans 10 and 20 are primary vlans on device a. The uplink port gigabitethernet 1/0/5 on device a permits the pack...
Page 166
153 [devicea-vlan20] private-vlan primary [devicea-vlan20] quit # create vlans 11, 12, 21, and 22. [devicea] vlan 11 to 12 [devicea] vlan 21 to 22 # associate secondary vlans 11 and 12 with primary vlan 10. [devicea] vlan 10 [devicea-vlan10] private-vlan secondary 11 12 [devicea-vlan10] quit # assoc...
Page 167
154 # assign the port gigabitethernet 1/0/3 to vlan 11. [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port access vlan 11 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] quit # assign the port gigabitethernet 1/0/4 to vlan 21. [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4 [deviceb-gigabitether...
Page 168
155 gigabitethernet1/0/5 untagged ports: none vlan id: 12 vlan type: static private-vlan type: secondary route interface: not configured description: vlan 0012 name: vlan 0012 tagged ports: gigabitethernet1/0/5 untagged ports: gigabitethernet1/0/3 the output shows that: • the trunk promiscuous port ...
Page 169
156 system-view [devicea] vlan 10 [devicea-vlan10] private-vlan primary [devicea-vlan10] quit # create vlans 2 and 3. System-view [devicea] vlan 2 to 3 # associate primary vlan 10 with secondary vlans 2 and 3. [devicea] vlan 10 [devicea-vlan10] private-vlan primary [devicea-vlan10] private-vlan seco...
Page 170
157 ipv4 subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 description: vlan 0010 name: vlan 0010 tagged ports: none untagged ports: gigabitethernet1/0/1 gigabitethernet1/0/2 gigabitethernet1/0/3 vlan id: 2 vlan type: static private vlan type: secondary route interface: configured ipv4 address: 192.168.1.1 ipv4 subnet mas...
Page 171: Configuring Voice Vlans
158 configuring voice vlans overview a voice vlan is used for transmitting voice traffic. The device can configure qos parameters for voice packets to ensure higher transmission priority of the voice packets. Common voice devices include ip phones and integrated access devices (iads). This chapter u...
Page 172
159 automatically identifying ip phones through lldp if ip phones support lldp, configure lldp for automatic ip phone discovery on the device. The device can then automatically discover the peer through lldp, and exchange lldp tlvs with the peer. If the lldp system capabilities tlv received on a por...
Page 173
160 figure 50 connecting the host and ip phone in series connecting the ip phone to the device as shown in figure 51 , ip phones are connected to the device without the presence of the host. Use this connection method when ip phones sends out untagged voice packets. In this scenario, you must config...
Page 174
161 when the device reboots, the port is reassigned to the voice vlan to ensure the correct operation of the existing voice connections. The reassignment occurs automatically without being triggered by voice traffic as long as the voice vlan operates correctly. Manual mode use manual mode when only ...
Page 175
162 if an ip phone sends out tagged voice traffic, and its access port is configured with 802.1x authentication, guest vlan, auth-fail vlan, or critical vlan, vlan ids must be different for the following vlans: • voice vlan. • pvid of the access port. • 802.1x guest, auth-fail, or critical vlan. If ...
Page 176
163 voice vlan configuration task list tasks at a glance (required.) configuring the qos priority settings for voice traffic (required.) use one of the following methods: • configuring a port to operate in automatic voice vlan assignment mode • configuring a port to operate in manual voice vlan assi...
Page 177
164 configuring a port to operate in automatic voice vlan assignment mode configuration restrictions and guidelines when you configure a port to operate in automatic voice vlan assignment mode, follow these restrictions and guidelines: • do not configure a vlan as both a voice vlan and a protocol-ba...
Page 178
165 step command remarks 8. Enable the voice vlan feature on the port. Voice-vlan vlan-id enable by default, the voice vlan feature is disabled. Before you configure a voice vlan, you must create a vlan. Configuring a port to operate in manual voice vlan assignment mode configuration restrictions an...
Page 179
166 step command remarks 6. Assign the access, trunk, or hybrid port to the voice vlan. • for the access port, see " assigning an access port to a vlan ." • for the trunk port, see " assigning a trunk port to a vlan ." • for the hybrid port, see " assigning a hybrid port to a vlan ." after you assig...
Page 180
167 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter layer 2 ethernet interface view. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 3. Configure an advertised voice vlan id. Lldp tlv-enable med-tlv network-policy vlan-id by default, no advertised voice vlan id is configured. For m...
Page 181
168 displaying and maintaining voice vlans execute display commands in any view. Task command display the voice vlan state. Display voice-vlan state display oui addresses on a device. Display voice-vlan mac-address voice vlan configuration examples automatic voice vlan assignment mode configuration ...
Page 182
169 [devicea] voice-vlan aging 30 # enable security mode for voice vlans. [devicea] voice-vlan security enable # add mac addresses of ip phones a and b to the device with the mask ffff-ff00-0000. [devicea] voice-vlan mac-address 0011-1100-0001 mask ffff-ff00-0000 description ip phone a [devicea] voi...
Page 183
170 ge1/0/1 2 auto 6 46 ge1/0/2 3 auto 6 46 manual voice vlan assignment mode configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 53 : • device a transmits only voice traffic. • ip phone a send untagged voice traffic. For correct voice traffic transmission, perform the following tasks on d...
Page 184
171 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] voice-vlan 2 enable [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit verifying the configuration # display the oui addresses and their masks and descriptions. [devicea] display voice-vlan mac-address oui address mask description 0001-e300-0000 ffff-ff00-0000 siemens phone 0003-...
Page 185: Configuring Mvrp
172 configuring mvrp multiple registration protocol (mrp) is an attribute registration protocol used to transmit attribute values. Multiple vlan registration protocol (mvrp) is a typical mrp application. It synchronizes vlan information among devices. Mvrp propagates local vlan information to other ...
Page 186
173 join message an mrp participant sends a join message to request the peer participant to register attributes in the join message. When receiving a join message from the peer participant, an mrp participant performs the following tasks: • registers the attributes in the join message. • propagates ...
Page 187
174 leaveall message each mrp participant starts its leaveall timer when starting up. When the timer expires, the mrp participant sends leaveall messages to the peer participant. Upon sending or receiving a leaveall message, the local participant starts the leave timer. The local participant determi...
Page 188
175 • effectively reduces the number of leaveall messages in the network. • prevents the leaveall timer of a particular participant from always expiring first. Mvrp registration modes vlan information propagated by mvrp includes dynamic vlan information from other devices and local static vlan infor...
Page 189
176 receive undesired copies. For more information about port mirroring, see network management and monitoring configuration guide . • mvrp takes effect only on trunk ports. For more information about trunk ports, see " configuring vlans ." • enabling mvrp on a layer 2 aggregate interface takes effe...
Page 191
178 table 14 dependencies of the join, leave, and leaveall timers timer lower limit upper limit join 20 centiseconds half the leave timer leave twice the join timer leaveall timer leaveall leave timer on each port 32760 centiseconds enabling gvrp compatibility enable gvrp compatibility for mvrp when...
Page 192
179 • the devices can register and deregister dynamic vlans. • the devices can keep identical vlan configurations for each msti. Figure 55 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure device a: # enter mst region view. System-view [devicea] stp region-configuration # configure the mst region...
Page 193
180 # globally enable the spanning tree feature. [devicea] stp global enable # globally enable mvrp. [devicea] mvrp global enable # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port, and configure it to permit all vlans. [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port lin...
Page 194
181 [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 20 40 # enable mvrp on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] mvrp enable [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit # configure gigabitethe...
Page 195
182 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as a trunk port, and configure it to permit all vlans. [devicec] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan all # enable mvrp on gi...
Page 196
183 ----[gigabitethernet1/0/1]---- config status : enabled running status : enabled join timer : 20 (centiseconds) leave timer : 60 (centiseconds) periodic timer : 100 (centiseconds) leaveall timer : 1000 (centiseconds) registration type : normal registered vlans : 1(default) declared vlans : 1(defa...
Page 197
184 • gigabitethernet 1/0/2 has declared vlan 1, and registered and propagated no vlans. • gigabitethernet 1/0/3 has registered vlan 20, declared vlan 1 and vlan 10, and propagated vlan 20 through mvrp. # display local vlan information on device b. [deviceb] display mvrp running-status -------[mvrp ...
Page 198
185 1(default), 10 declared vlans : 20 propagated vlans : 10 the output shows that the following events have occurred: • gigabitethernet 1/0/1 has registered vlan 1, declared vlan 1 and vlan 20, and propagated vlan 1 through mvrp. • gigabitethernet 1/0/2 has registered vlan 1 and vlan 10, declared v...
Page 199
186 • gigabitethernet 1/0/1 has registered vlan 1, vlan 10, and vlan 20, declared vlan 1, and propagated vlan 1 and vlan 10 through mvrp. • gigabitethernet 1/0/2 has registered vlan 1 and vlan 20, declared vlan 1 and vlan 10, and propagated vlan 1 and vlan 20 through mvrp. # display local vlan infor...
Page 200
187 [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] mvrp registration fixed [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] quit # display local mvrp vlan information on gigabitethernet 1/0/3. [deviceb] display mvrp running-status interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 -------[mvrp global info]----...
Page 201
188 the output shows that dynamic vlan information on gigabitethernet 1/0/3 is not changed after you set its mvrp registration mode to fixed..
Page 202: Configuring Qinq
189 configuring qinq this document uses the following terms: • cvlan—customer network vlans, also called inner vlans, refer to vlans that a customer uses on the private network. • svlan—service provider network vlans, also called outer vlans, refer to vlans that a service provider uses to transmit v...
Page 203
190 when a tagged ethernet frame from ce 1 arrives at pe 1, the pe tags the frame with svlan 3. The double-tagged ethernet frame travels over the service provider network until it arrives at pe 2. Pe 2 removes the svlan tag of the frame, and then sends the frame to ce 4. Figure 57 typical qinq appli...
Page 204
191 restrictions and guidelines when you configure qinq, follow these restrictions and guidelines: • before you configure qinq on a port, you must remove any vlan mappings on the port. After you enable qinq on the port, you can configure all vlan mapping types except two-to-two vlan mapping on it. I...
Page 205
192 configuring the tpid for vlan tags tpid identifies a frame as an 802.1q tagged frame. The tpid value varies by vendor. On an h3c device, the tpid in the 802.1q tag added on a qinq-enabled port is 0x8100 by default, in compliance with ieee 802.1q. In a multi-vendor network, make sure the tpid set...
Page 206
193 step command remarks 2. Configure the tpid value for cvlan tags. Qinq ethernet-type customer-tag hex-value the default setting is 0x8100 for cvlan tags. Configuring the svlan tpid step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter layer 2 ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggre...
Page 207
194 step command remarks 6. Configure a priority marking action for svlan tags. • replace the priority in the svlan tags of matching frames with the configured priority: remark dot1p dot1p-value • copy the 802.1p priority in the cvlan tag to the svlan tag: remark dot1p customer-dot1p-trust n/a 7. Re...
Page 208
195 qinq configuration examples basic qinq configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 58 : • the service provider assigns vlan 100 to company a's vlans 10 through 70. • the service provider assigns vlan 200 to company b's vlans 30 through 90. • the devices between pe 1 and pe 2 in...
Page 209
196 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as a trunk port, and assign it to vlans 100 and 200. [pe1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [pe1-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [pe1-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 100 200 # set the tpid value in the svlan tags to 0x8200 on gigabitethern...
Page 210
197 # configure all ports on the forwarding path to allow frames from vlans 100 and 200 to pass through without removing the vlan tag. (details not shown.) vlan transparent transmission configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 59 : • the service provider assigns vlan 100 to a co...
Page 211
198 2. Configure pe 2: # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port, and assign it to vlans 100 and 3000. System-view [pe2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 100 3000 # configure vlan 100 as the pvid...
Page 212: Configuring Vlan Mapping
199 configuring vlan mapping overview vlan mapping re-marks vlan tagged traffic with new vlan ids. H3c provides the following types of vlan mapping: • one-to-one vlan mapping —replaces one vlan tag with another. • many-to-one vlan mapping —replaces multiple vlan tags with the same vlan tag. • one-to...
Page 213
200 figure 60 application scenario of one-to-one and many-to-one vlan mapping as shown in figure 60 , the network is implemented as follows: • each home gateway uses different vlans to transmit the pc, vod, and voip services. • to further subclassify each type of traffic by customer, configure one-t...
Page 214
201 application scenario of one-to-two and two-to-two vlan mapping figure 61 shows a typical application scenario of one-to-two and two-to-two vlan mapping. In this scenario, the two remote sites of the same vpn must communicate across two sp networks. Figure 61 application scenario of one-to-two an...
Page 215
202 figure 62 basic vlan mapping terms one-to-one vlan mapping as shown in figure 63 , one-to-one vlan mapping is implemented on the customer-side port and replaces vlan tags as follows: • replaces the cvlan with the svlan for the uplink traffic. • replaces the svlan with the cvlan for the downlink ...
Page 216
203 figure 64 many-to-one vlan mapping implementation one-to-two vlan mapping as shown in figure 65 , one-to-two vlan mapping is implemented on the customer-side port to add the svlan tag for the uplink traffic. For the downlink traffic to be correctly sent to the customer network, make sure the svl...
Page 217
204 figure 66 two-to-two vlan mapping implementation vlan mapping configuration task list when you configure vlan mapping, follow these guidelines: • to add vlan tags to packets, you can configure both vlan mapping and qinq. Vlan mapping takes effect if a configuration conflict occurs. For more info...
Page 218
205 step command remarks 2. Enter layer 2 ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number n/a 3. Set the link type o...
Page 219
206 enabling dhcp snooping step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enable dhcp snooping. Dhcp snooping enable by default, dhcp snooping is disabled. For more information about dhcp snooping configuration commands, see layer 3—ip services command reference . Enabling arp detecti...
Page 220
207 step command remarks 6. Enable dhcp snooping entry recording. Dhcp snooping binding record by default, dhcp snooping entry recording is disabled on an interface. Configuring the network-side port step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter layer 2 ethernet interface view ...
Page 221
208 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter layer 2 ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation inter...
Page 222
209 step command remarks 3. Set the link type of the port. • configure the port as a trunk port: port link-type trunk • configure the port as a hybrid port: port link-type hybrid by default, the link type of a port is access. 4. Assign the port to the original vlans and the translated vlans. • port ...
Page 223
210 service vlans on home gateways vlans on wiring-closet switches (switch a and switch b) vlans on campus switch (switch c) voip vlan 3 vlans 301, 302, 303, 304 vlan 503 figure 67 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure switch a: # create the original vlans. System-view [switcha] vlan ...
Page 224
211 [switcha] vlan 301 to 302 # configure the customer-side port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port. System-view [switcha] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk # assign gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to all original vlans and translated vlans. [switcha-gigabi...
Page 225
212 [switchc-vlan302] arp detection enable [switchc-vlan302] vlan 103 [switchc-vlan103] arp detection enable [switchc-vlan103] vlan 203 [switchc-vlan203] arp detection enable [switchc-vlan203] vlan 303 [switchc-vlan303] arp detection enable [switchc-vlan303] vlan 104 [switchc-vlan104] arp detection ...
Page 226
213 # configure the network-side port gigabitethernet 1/0/3 to use the original vlan tags of the many-to-one mappings to replace the vlan tags of the packets destined for the user network. [switchc] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [switchc-gigabitethernet1/0/3] vlan mapping nni # configure gigabitet...
Page 227
214 303-304 n/a 503 n/a one-to-two and two-to-two vlan mapping configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 68 : • two vpn a branches, site 1 and site 2, are in vlan 5 and vlan 6, respectively. • the two sites use different vpn access services from different service providers, sp 1 ...
Page 228
215 [pe1-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 100 [pe1-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit 2. Configure pe 2: # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port. System-view [pe2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk # assign gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to vlan 100...
Page 229
216 [pe4-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port hybrid vlan 200 untagged # configure a one-to-two vlan mapping on customer-side port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 to add svlan tag 200 to packets from vlan 6. [pe4-gigabitethernet1/0/2] vlan mapping nest single 6 nested-vlan 200 [pe4-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit verifying ...
Page 230: Configuring Lldp
217 configuring lldp overview in a heterogeneous network, a standard configuration exchange platform makes sure different types of network devices from different vendors can discover one another and exchange configuration. The link layer discovery protocol (lldp) is specified in ieee 802.1ab. The pr...
Page 231
218 lldp frame formats lldp sends device information in lldp frames. Lldp frames are encapsulated in ethernet ii or snap frames. • lldp frame encapsulated in ethernet ii figure 70 ethernet ii-encapsulated lldp frame table 17 fields in an ethernet ii-encapsulated lldp frame field description destinat...
Page 232
219 figure 71 snap-encapsulated lldp frame table 18 fields in a snap-encapsulated lldp frame field description destination mac address mac address to which the lldp frame is advertised. It is the same as that for ethernet ii-encapsulated lldp frames. Source mac address mac address of the sending por...
Page 233
220 table 19 basic management tlvs type description remarks chassis id specifies the bridge mac address of the sending device. Mandatory. Port id specifies the id of the sending port: • if the lldpdu carries lldp-med tlvs, the port id tlv carries the mac address of the sending port. • otherwise, the...
Page 234
221 note: • h3c devices support only receiving protocol identity tlvs and vid usage digest tlvs. • layer 3 ethernet ports support only link aggregation tlvs. • ieee 802.3 organizationally specific tlvs table 21 ieee 802.3 organizationally specific tlvs type description mac/phy configuration/status c...
Page 235
222 type description extended power-via-mdi allows a network device or terminal device to advertise power supply capability. This tlv is an extension of the power via mdi tlv. Hardware revision allows a terminal device to advertise its hardware version. Firmware revision allows a terminal device to ...
Page 236
223 the token bucket mechanism to rate limit lldp frames. For more information about the token bucket mechanism, see acl and qos configuration guide. Lldp automatically enables the fast lldp frame transmission mechanism in either of the following cases: • a new lldp frame is received and carries dev...
Page 237
224 performing basic lldp configurations enabling lldp to make lldp take effect on specific ports, you must enable lldp both globally and on these ports. To use lldp together with openflow, you must enable lldp globally on openflow switches. As a best practice to prevent lldp from affecting topology...
Page 238
225 step command remarks 2. Enter layer 2/layer 3 ethernet interface view, management ethernet interface view, or layer 2/layer 3 aggregate interface view. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 3. Set the lldp operating mode. • in layer 2/layer 3 ethernet interface view or management etherne...
Page 239
226 step command remarks 2. Enter layer 2/layer 3 ethernet interface view, management ethernet interface view, or layer 2/layer 3 aggregate interface view. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 3. Enable lldp polling and set the polling interval. • in layer 2/layer 3 ethernet interface view ...
Page 243
230 step command remarks 5. Set the number of lldp frames sent each time fast lldp frame transmission is triggered. Lldp fast-count count the default setting is 4. 6. Set the fast lldp frame transmission interval. Lldp timer fast-interval interval the default setting is 1 second. Setting an encapsul...
Page 244
231 step command remarks 2. Disable lldp pvid inconsistency check. Lldp ignore-pvid-inconsistency by default, lldp pvid inconsistency check is enabled. Configuring cdp compatibility to make your device work with cisco ip phones, you must enable cdp compatibility. If your lldp-enabled device cannot r...
Page 245
232 step command remarks 3. Enter layer 2/layer 3 ethernet interface view, management ethernet interface view, or layer 2/layer 3 aggregate interface view. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 4. Configure cdp-compatible lldp to operate in rx or txrx mode. Lldp compliance admin-status cdp {...
Page 246
233 • in dcbx rev 1.00 and dcbx rev 1.01: { application protocol (app). { enhanced transmission selection (ets). { priority-based flow control (pfc). • in ieee std 802.1qaz-2011: { ets configuration. { ets recommendation. { pfc. { app. H3c devices can send these types of dcbx information to a server...
Page 247
234 setting the dcbx version when you set the dcbx version, follow these restrictions and guidelines: • for dcbx to work correctly, configure the same dcbx version on the local port and peer port. As a best practice, configure the highest version supported on both ends. Ieee std 802.1qaz-2011, dcbx ...
Page 249
236 step command remarks 14. Apply the qos policy. • (method 1) to the outgoing traffic of all ports: qos apply policy policy-name global outbound • (method 2) to the outgoing traffic of a layer 2 ethernet interface: a. Enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number...
Page 250
237 step command remarks 6. Configure the behavior to mark packets with the specified local precedence value. Remark local-precedence local-precedence by default, no local precedence marking action is configured. 7. Return to system view. Quit n/a 8. Create a qos policy and enter qos policy view. Qo...
Page 251
238 configuring pfc parameters to prevent packets with an 802.1p priority value from being dropped, enable pfc for the 802.1p priority value. This feature reduces the sending rate of packets carrying this priority when network congestion occurs. The device uses pfc parameters to negotiate with the s...
Page 252
239 step command remarks 4. Enable lldp-med trapping (in layer 2/layer 3 ethernet interface view or management ethernet interface view). Lldp notification med-topology-change enable by default, lldp-med trapping is disabled. 5. Return to system view. Quit n/a 6. (optional.) set the lldp trap transmi...
Page 253
240 figure 74 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure switch a: # enable lldp globally. System-view [switcha] lldp global enable # enable lldp on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. By default, lldp is enabled on ports. [switcha] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/1] lldp en...
Page 254
241 bridge mode of lldp: customer-bridge the current number of lldp neighbors: 2 the current number of cdp neighbors: 0 lldp neighbor information last changed time: 0 days, 0 hours, 4 minutes, 40 seconds transmit interval : 30s fast transmit interval : 1s transmit credit max : 5 hold multiplier : 4 ...
Page 255
242 number of received unknown tlv : 3 lldp agent nearest-nontpmr: port status of lldp : enable admin status : disable trap flag : no med trap flag : no polling interval : 0s number of lldp neighbors : 0 number of med neighbors : 0 number of cdp neighbors : 0 number of sent optional tlv : 1 number o...
Page 256
243 number of med neighbors : 1 number of cdp neighbors : 0 number of sent optional tlv : 0 number of received unknown tlv : 5 lldp agent nearest-nontpmr: port status of lldp : enable admin status : disable trap flag : no med trap flag : no polling interval : 0s number of lldp neighbors : 0 number o...
Page 257
244 number of lldp neighbors : 0 number of med neighbors : 0 number of cdp neighbors : 0 number of sent optional tlv : 16 number of received unknown tlv : 0 cdp-compatible lldp configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 75 , gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 of switc...
Page 258
245 # configure cdp-compatible lldp to operate in txrx mode on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/1] lldp compliance admin-status cdp txrx [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit # enable lldp on gigabitethernet 1/0/2. By default, lldp is enabled on ports. [switcha] interface gigabitethe...
Page 259
246 figure 76 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Enable lldp and dcbx tlv advertising: # enable lldp globally. System-view [switcha] lldp global enable # enable lldp and dcbx tlv advertising on interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1. [switcha] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [switcha-gigabitetherne...
Page 260
247 4. Configure ets parameters: # configure the 802.1p-to-local priority mapping table to map 802.1p priority value 3 to local precedence 3. (this is the default mapping table. You can modify this configuration as needed.) [switcha] qos map-table outbound dot1p-lp [switcha-maptbl-out-dot1p-lp] impo...
Page 261
248 priority group id of priority 6: 6 priority group 0 percentage: 2 priority group 1 percentage: 4 priority group 2 percentage: 6 priority group 3 percentage: 0 priority group 4 percentage: 10 priority group 5 percentage: 18 priority group 6 percentage: 27 priority group 7 percentage: 31 number of...
Page 262
249 dcbx parameter data priority group id of priority 1: 0 priority group id of priority 0: 0 priority group id of priority 3: 1 priority group id of priority 2: 0 priority group id of priority 5: 0 priority group id of priority 4: 0 priority group id of priority 7: 0 priority group id of priority 6...
Page 263
250 parameter type: remote pad byte present: no dcbx parameter valid: yes reserved: 0 dcbx parameter data pfc enabled on priority 0: no pfc enabled on priority 1: no pfc enabled on priority 2: no pfc enabled on priority 3: yes pfc enabled on priority 4: no pfc enabled on priority 5: no pfc enabled o...
Page 264
251 configuring service loopback groups overview a service loopback group contains one or multiple ethernet ports for looping packets sent out by the device back to the device. This feature must work with other features, such as gre. A service loopback group provides one of the following services: •...
Page 266
253 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port service-loopback group 1 all configurations on the interface will be lost. Continue?[y/n]:y [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/3] quit # create the interface tunnel 1 and set it to gre mode...
Page 267: Index
254 index numerics 1\ 1 vlan mappingapplication scenario, 199 1 vlan mappingconfiguration, 204, 209 1 vlan mappingimplementation, 201, 202 2 vlan mappingapplication scenario, 201 2 vlan mappingconfiguration, 207, 214 2 vlan mappingimplementation, 201, 203 2\ 2 vlan mappingapplication scenario, 201 2...
Page 268
255 voice vlan port operation configuration (automatic assignment), 164, 168 b backing up mst backup port, 69 bandwidth ethernet link aggregate interface (expected bandwidth), 35 lldp ets parameters, 236 basic management lldpdu tlv types, 219 blackhole entry mac address table, 1, 4 block action (loo...
Page 269
256 lldp dcbx, 232, 245 lldp ets parameter, 236 lldp group-based wrr queuing, 237 lldp management address, 228 lldp management address encoding format, 228 lldp pfc parameter, 238 lldp trapping, 238 lldp-med trapping, 238 loop detection, 107, 109, 111 mac address move notification, 11, 11 mac addres...
Page 270
257 voice vlan qos priority setting configuration, 163 cost spanning tree port path cost calculation standard, 81 spanning tree port path cost configuration, 81, 84 stp path cost, 59 creating super vlan sub-vlan, 137 cst mst region connection, 68 customer lldp customer bridge mode, 224 cvlan qinq ba...
Page 271
258 ethernet link aggregation edge aggregate interface, 27 ethernet link aggregation group, 30 ethernet link aggregation mode, 22 layer 2 ethernet link aggregation, 42 layer 2 ethernet link aggregation edge aggregate interface, 46 layer 2 ethernet link aggregation group (dynamic), 30 layer 3 etherne...
Page 272
259 aggregate group selected ports min/max, 34 aggregate interface, 20 aggregate interface (description), 32 aggregate interface configuration, 32 aggregate interface default settings, 36 aggregate interface shutdown, 36 aggregation group, 20 aggregation group restrictions, 28 basic concepts, 20 con...
Page 273
260 ethernet link aggregation lacp, 23 ethernet link aggregation load sharing, 37 ethernet link aggregation load sharing mode, 27, 37 ethernet link aggregation member port state, 20 layer 2 ethernet link aggregation group (dynamic), 30 layer 2 ethernet link aggregation group (static), 29 layer 3 eth...
Page 274
261 ethernet link aggregation configuration, 20, 27, 40 ethernet link aggregation display, 40 ethernet link aggregation dynamic mode, 23 ethernet link aggregation edge aggregate interface, 27, 35, 46 ethernet link aggregation group, 28 ethernet link aggregation group (dynamic), 30, 30 ethernet link ...
Page 275
262 voice vlan lldp enable, 166 voice vlan lldp enable restrictions, 166 voice vlan port operation configuration (automatic assignment), 164, 168 voice vlan port operation configuration (manual assignment), 165, 170 voice vlan port operation configuration restrictions (automatic assignment), 164 voi...
Page 276
263 agent, 217 app parameter configuration, 234 basic concepts, 217 basic configuration, 224, 239 bridge mode set, 224 cdp compatibility configuration, 231 cdp-compatible configuration, 244 configuration, 217, 223, 239 dcbx configuration, 232, 245 dcbx version set, 234 disabling pvid inconsistency c...
Page 277
264 m m\ 1 vlan mappingapplication scenario, 199 1 vlan mappingarp detection, 206 1 vlan mappingconfiguration, 205, 209 1 vlan mappingconfiguration restrictions, 205 1 vlan mappingcustomer-side port, 206 1 vlan mappingdhcp snooping, 206 1 vlan mappingimplementation, 201, 202 1 vlan mappingnetwork-si...
Page 278
265 lldp txrx, 222, 224 mac information syslog, 16 mac information trap, 16 mvrp registration, 176 mvrp registration fixed, 175 mvrp registration forbidden, 175 mvrp registration normal, 175 spanning tree mcheck, 88 spanning tree mstp, 75 spanning tree pvst, 75 spanning tree rstp, 75 spanning tree s...
Page 279
266 layer 3 ethernet link aggregation (dynamic), 49 layer 3 ethernet link aggregation (static), 48 layer 3 ethernet link aggregation edge aggregate interface, 52 layer 3 ethernet link aggregation load sharing, 50 lldp basic configuration, 224, 239 lldp configuration (cdp-compatible), 244 lldp dcbx c...
Page 280
267 vlan mapping configuration (1\2), 207, 214 vlan mapping configuration (2\2), 208, 214 vlan mapping configuration (m\1), 205, 209 vlan mapping m\1 customer-side port, 206 vlan mapping m\1 implementation, 202 vlan mapping m\1 network-side port, 207 vlan port-based configuration, 128 voice vlan ass...
Page 281
268 pfc priority (lldp), 238 polling lldp enable, 225 port ethernet aggregate interface, 32 ethernet aggregate interface (description), 32 ethernet link aggregate group selected ports min/max, 34 ethernet link aggregate interface (expected bandwidth), 35 ethernet link aggregate interface default set...
Page 282
269 spanning tree path cost configuration, 81, 84 spanning tree port link type configuration, 85 spanning tree port mode configuration, 86 spanning tree port priority configuration, 85 spanning tree port role restriction, 96 spanning tree port state transition output, 86 spanning tree root guard, 95...
Page 283
270 configuring layer 3 ethernet link aggregation group (dynamic), 31 configuring layer 3 ethernet link aggregation group (static), 29 configuring layer 3 ethernet link aggregation load sharing, 50 configuring lldp, 223, 239 configuring lldp (cdp-compatible), 244 configuring lldp 802.1p-to-local pri...
Page 284
271 configuring super vlan interface, 138 configuring vlan, 128 configuring vlan basic settings, 115 configuring vlan group, 127 configuring vlan interface basics, 116 configuring vlan mapping, 204, 209 configuring vlan mapping (1\1), 204, 209 configuring vlan mapping (1\2), 207, 214 configuring vla...
Page 285
272 setting ethernet link aggregation load sharing mode (global), 37 setting ethernet link aggregation load sharing mode (group-specific), 38 setting layer 3 aggregate interface (mtu), 34 setting lldp bridge mode, 224 setting lldp dcbx version, 234 setting lldp frame encapsulation format, 230 settin...
Page 286
273 region mst, 67 mst region configuration, 75 mst region max hops, 77 mst regional root, 68 registering mvrp registration fixed mode, 175 mvrp registration forbidden mode, 175 mvrp registration mode, 176 mvrp registration normal mode, 175 reinitialization delay (lldp), 225 restoring ethernet link ...
Page 287
274 ethernet link aggregate group selected ports min/max, 34 ethernet link aggregate interface (expected bandwidth), 35 ethernet link aggregation load sharing mode (global), 37 ethernet link aggregation load sharing mode (group-specific), 38 ethernet link aggregation member port state, 22, 25 layer ...
Page 288
275 mac address table entry configuration (global), 3 mac address table entry configuration (on interface), 3 mac-based vlan static assignment, 121, 123 static mac address entry static source check disable, 13 stp algorithm calculation, 59 basic concepts, 58 bpdu forwarding, 64 configuration, 72 des...
Page 289
276 lldp management address encoding format, 228 lldp parameters, 229 lldp+dcbx tlv advertisement, 233 lldpdu basic management types, 219 lldpdu lldp-med types, 219 lldpdu management address tlv, 222 lldpdu organization-specific types, 219 topology stp tcn bpdu protocol packets, 58 traffic ethernet ...
Page 290
277 voice vlan port mode, 162 voice vlan port operation configuration (automatic assignment), 164, 168 voice vlan port operation configuration (manual assignment), 165, 170 voice vlan port operation configuration restrictions (automatic assignment), 164 voice vlan port operation configuration restri...