- DL manuals
- H3C
- Network Router
- H3C SR6600
- Configuration Manual
H3C H3C SR6600 Configuration Manual - Qos Techniques Overview
2-2
The IntServ model demands high storage and processing capabilities, because it requires that all nodes
along the transmission path maintain resource state information for each flow. The model is suitable for
small-sized or edge networks, but not large-sized networks, for example, the core layer of the Internet,
where billions of flows are present.
For more information about RSVP, see MPLS TE in the MPLS Configuration Guide.
DiffServ Model
The differentiated services (DiffServ) model is a multiple-service model that can satisfy diverse QoS
requirements. Unlike IntServ, DiffServ does not require an application to signal the network to reserve
resources before sending data. DiffServ is easy to implement and extend.
All QoS techniques in this document are based on the Diff-Serv model.
QoS Techniques Overview
The QoS techniques fall into traffic classification, traffic policing, traffic shaping, line rate, congestion
management, and congestion avoidance. The following part briefly introduces these QoS techniques.
Applying QoS Techniques in a Network
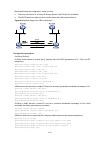
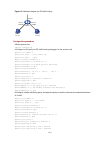
Figure 2-1
Position of the QoS techniques in a network
As shown in
, traffic classification, traffic shaping, traffic policing, congestion management,
and congestion avoidance mainly implement the following functions:
z
Traffic classification uses certain match criteria to assign packets with the same characteristics to a
class. Based on classes, you can provide differentiated services.
Summary of H3C SR6600
Page 1
H3c sr6600 routers acl and qos configuration guide hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Http://www.H3c.Com document version: 20100930-c-1.08 product version: sr6600-cmw520-r2420
Page 2
Copyright © 2007-2010, hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. And its licensors all rights reserved no part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Trademarks h3c, , aolynk, , h 3 care, , top g, , i...
Page 3: Preface
Preface the h3c sr6600 documentation set includes 13 configuration guides, which describe the software features for the h3c sr6600 routers and guide you through the software configuration procedures. These configuration guides also provide configuration examples to help you apply software features t...
Page 4
Convention description # a line that starts with a pound (#) sign is comments. Gui conventions convention description boldface window names, button names, field names, and menu items are in boldface. For example, the new user window appears; click ok. > multi-level menus are separated by angle brack...
Page 5: Obtaining Documentation
Category documents purposes installation guide provides a complete guide to hardware installation and hardware specifications. Card manuals provide the hardware specifications of cards. H3c n68 cabinet installation and remodel introduction guides you through installing and remodeling h3c n68 cabinet...
Page 6: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 acl configuration·····································································································································1-1 acl overview ···············································································································...
Page 7
Ii 4 priority mapping configuration················································································································4-1 priority mapping overview ······················································································································4-1 i...
Page 8
Iii cq configuration example············································································································6-12 configuring wfq ··································································································································6-13 configur...
Page 9
Iv 10 priority marking configuration·············································································································10-1 priority marking overview ·····················································································································10-1 co...
Page 10
V configuring mpls qos·························································································································16-2 configuring mpls car·················································································································16-2 configuring mp...
Page 11: Acl Configuration
1-1 1 acl configuration this chapter includes these sections: z acl overview z acl configuration task list z configuring an acl z creating a time range z configuring a basic acl z configuring an ipv4 basic acl z configuring an advanced acl z configuring an ethernet frame header acl z copying an acl ...
Page 12
1-2 table 1-1 acl categories category acl number ip version match criteria ipv4 source ipv4 address basic acls 2000 to 2999 ipv6 source ipv6 address ipv4 source/destination ipv4 address, protocols over ipv4, and other layer 3 and layer 4 header fields advanced acls 3000 to 3999 ipv6 source/destinati...
Page 13
1-3 acl category depth-first rule sorting procedures ipv4 advanced acl 1) the rule configured with a vpn instance takes precedence. 2) the rule configured with a specific protocol is prior to a rule with the protocol type set to ip. Ip represents any protocol over ip. 3) the rule with more 0s in the...
Page 14: Acl Configuration Task List
1-4 automatic rule numbering and re-numbering the id automatically assigned to an acl rule takes the nearest higher multiple of the numbering step to the current highest rule id, starting with 0. For example, if the numbering step is 5 (the default), and there are five acl rules numbered 0, 5, 9, 10...
Page 15: Configuring An Acl
1-5 task remarks copying an ipv4 acl optional enabling acl acceleration for an ipv4 acl optional ipv6 acl configuration task list perform the following tasks to configure an ipv6 acl: task remarks creating a time range optional configuring an ipv6 basic acl configuring an ipv6 advanced acl required ...
Page 20
1-10 to do… use the command… remarks configure or edit a rule description rule rule-id comment text optional by default, an ethernet frame header acl rule has no rule description. Copying an acl you can create an acl by copying an existing acl. The new acl has the same properties and content as the ...
Page 21
1-11 follow these steps to enable acl acceleration for an ipv4 acl: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable acl acceleration for an ipv4 acl acl accelerate number acl-number required disabled by default. The acl must exist. Only ipv4 basic acls and advanced acls suppor...
Page 22: Acl Configuration Examples
1-12 acl configuration examples ipv4 acl configuration examples network requirements a company interconnects its departments through device. Configure an acl to deny access from all departments except for the president’s office to the salary server during working hours (from 8:00 to 18:00) on workin...
Page 23
1-13 rule 5 deny ip destination 192.168.0.100 0 time-range work (inactive) ipv6 acl configuration example network requirements a company interconnects its departments through device. Configure an acl to deny access from all departments but the president’s office to the salary server during working h...
Page 24: Qos Overview
2-1 2 qos overview this chapter includes these sections: z introduction to qos z qos service models z qos techniques overview introduction to qos in data communications, quality of service (qos) is the ability of a network to provide differentiated service guarantees for diverse traffic in terms of ...
Page 25: Qos Techniques Overview
2-2 the intserv model demands high storage and processing capabilities, because it requires that all nodes along the transmission path maintain resource state information for each flow. The model is suitable for small-sized or edge networks, but not large-sized networks, for example, the core layer ...
Page 26
2-3 z traffic policing polices flows entering or leaving a router, and imposes penalties on traffic flows that exceed the pre-set threshold to prevent aggressive use of network resources. You can apply traffic policing to both incoming and outgoing traffic of a port. Z traffic shaping proactively ad...
Page 27: Qos Configuration Approaches
3-1 3 qos configuration approaches this chapter includes these sections: z qos configuration approach overview z configuring a qos policy qos configuration approach overview two approaches are available for configuring qos: non-policy approach and policy approach . Some features support both approac...
Page 28
3-2 figure 3-1 qos policy configuration procedure define a class define a behavior define a policy apply the policy to an interface or pvc to a vlan to online users defining a class to define a class, specify its name and then configure the match criteria in class view. Follow these steps to define ...
Page 29
3-3 to do… use the command… remarks configure actions in the traffic behavior see the following chapters based on the purpose of the traffic behavior: traffic policing, traffic filtering, traffic redirecting, priority marking, traffic accounting, and so on. Defining a policy configuring a parent pol...
Page 30
3-4 to do… use the command… remarks nest the child qos policy traffic-policy policy-name required the qos policy specified for the policy-name argument must already exist. Quit traffic behavior view quit –– create the parent policy and enter parent policy view qos policy policy-name — associate the ...
Page 31
3-5 to do… use the command… remarks enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter port group view port-group manual port-group-name interface atm interface-number enter interface view, port group view, or pvc view enter pvc view pvc vpi/vci use one of the approaches settings i...
Page 32
3-6 z you cannot modify or remove the qos policy used by an active user profile. However, you can edit any acl referenced by the qos policy when the user profile has no online users. Z the qos policy applied to a user profile supports only the remark, car, and filter actions. Z do not apply a null p...
Page 34: Priority Mapping Overview
4-1 4 priority mapping configuration the features in this chapter are available only on routers that have a sap interface card. This chapter includes these sections: z priority mapping overview z priority mapping configuration tasks z configuring priority mapping z displaying and maintaining priorit...
Page 35: Configuring Priority Mapping
4-2 priority mapping tables the router provides various types of priority mapping tables, or rather, priority mappings. By looking up a priority mapping table, the router decides which priority value is to assign to a packet for subsequent packet processing. The default priority mapping tables (as s...
Page 37
4-4 follow these steps to change the port priority of an interface: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter interface view or port group view enter port group view port-group manual port-group-name use eithe...
Page 38
4-5 figure 4-1 network diagram for priority trust mode configuration configuration procedure 1) approach 1: configure device to trust packet priority # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 to use dscp values in incoming packets for priority mapping. System-view [device] interfac...
Page 39
4-6 configure port priority, 802.1p-to-local priority mapping table, and priority marking to implement the plan as described in table 4-1 . Table 4-1 configuration plan queuing plan traffic destination traffic priority order traffic source output queue queue priority r&d department 6 high management...
Page 40
4-7 [device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [device-gigabitethernet1/0/2] qos priority 4 [device-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # set the port priority of gigabitethernet 1/0/3 to 5. [device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [device-gigabitethernet1/0/3] qos priority 5 [device-gigabitethernet1/0/3] quit...
Page 41
5-1 5 traffic policing and traffic shaping configuration when configuring traffic policing and traffic shaping, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z traffic policing and traffic shaping overview z traffic policing, traffic shaping, and line rate configuration z displaying an...
Page 42
5-2 complicated evaluation you can set two token buckets (referred to as the c bucket and e bucket respectively) in order to evaluate more complicated conditions and implement more flexible regulation policies. For example, traffic policing uses four parameters: z cir: rate at which tokens are put i...
Page 43
5-3 figure 5-2 schematic diagram for traffic policing token bucket packets dropped packet classification packets to be sent through this interface packets sent tokens are put into the bucket at the set rate queue traffic policing is widely used for policing traffic entering the networks of internet ...
Page 44
5-4 figure 5-3 diagram for traffic shaping token bucket packets dropped packet classification packets to be sent through this interface packets sent tokens are put into the bucket at the set rate queue for example, in figure 5-4 , router a sends packets to router b. Router b performs traffic policin...
Page 45
5-5 figure 5-5 line rate implementation with a token bucket used for traffic control, when there are tokens in the token bucket, the bursty packets can be transmitted; if no tokens are available, packets cannot be transmitted until new tokens are generated in the token bucket. In this way, the traff...
Page 46
5-6 if both a policy referencing car and the qos car command are configured on an interface or pvc, only the policy referencing car takes effect. Configuring traffic policing in policy approach follow these steps to configure traffic policing in policy approach: to do… use the command… remarks enter...
Page 47
5-7 configuring traffic policing in non-policy approach configuring car-list-based traffic policing follow these steps to configure car-list-based traffic policing: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system -view — configure a committed access rate (car) list qos carl carl-index { pre...
Page 48
5-8 configuring traffic shaping z gts for software forwarding does not support ipv6. Z do not configure gts on a main interface and its subinterfaces at the same time. Configuring gts in policy approach follow these steps to configure gts in policy approach: to do… use the command… remarks enter sys...
Page 49
5-9 configuring acl-based gts follow these steps to configure acl-based gts: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — define an acl see acl in the acl and qos configuration guide required enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number — configure acl-based gts ...
Page 50
5-10 displaying and maintaining traffic policing, gts and line rate to do... Use the command... Remarks display car list information display qos carl [ carl-index ] available in any view display the car information on the specified interface display qos car interface [ interface-type interface-numbe...
Page 51
5-11 figure 5-6 network diagram for traffic policing and gts configuration procedure 1) configure router a # configure gts on gigabitethernet 1/0/3 of router a, shaping the packets when the sending rate exceeds 500 kbps to decrease the packet loss ratio of gigabitethernet 1/0/1 of router b. System-v...
Page 52
5-12 ip rate limiting configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 5-7 , limit the rate of packets entering gigabitethernet 1/0/2 of the router as follows: perform per-ip-address rate limiting for traffic sourced from host a through host z, which are on the network segment 2.1.1.1 t...
Page 53
6-1 6 congestion management configuration when configuring congestion management, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z congestion management overview z configuring fifo z configuring pq z configuring cq z configuring wfq z configuring cbq z configuring rtp priority queuing z...
Page 54
6-2 congestion management policies queuing is a common congestion management technique. It classifies traffic into queues and picks out packets from each queue by using a certain algorithm. There are various queuing algorithms, each addressing a particular network traffic problem. Your choice of alg...
Page 55
6-3 priority queuing figure 6-3 priority queuing (pq) packets to be sent through this interface classify schedule high queue middle queue normal queue bottom queue packets sent sending queue interface priority queuing is designed for mission-critical applications. The key feature of mission-critical...
Page 56
6-4 custom queuing figure 6-4 custom queuing (cq) cq organizes packets into 16 classes (corresponding to 16 queues) by certain rules. A certain class of packets enters the corresponding custom queue according to fifo queuing. By default, packets are assigned to queue 1. Queues 1 through 16 are custo...
Page 57
6-5 weighted fair queuing figure 6-5 weighted fair queuing (wfq) wfq is derived from fair queuing (fq), which is designed for fairly sharing network resources, reducing the delay and jitter of all traffic. Fq fully consider the interests of all queues to ensure that: z different queues have fair dis...
Page 58
6-6 necessary to perform the congestion avoidance mechanism (tail drop or wred) and bandwidth restriction check before packets are enqueued. When dequeued, packets are scheduled by wfq. Cbq provides an emergency queue to enqueue emergent packets. The emergency queue is a fifo queue without bandwidth...
Page 59
6-7 congestion management technology comparison breaking through the single congestion management policy of fifo for traditional ip routers, the current router provides all the congestion management technologies above mentioned to offer powerful qos capabilities, meeting different qos requirements o...
Page 60: Configuring Fifo
6-8 type number of queues advantages disadvantages cbq configurable (0 to 64) z flexibly classify traffic based on various rules and provide different queue scheduling mechanisms for expedited forwarding (ef), assured forwarding (af) and best-effort (be) services. Z provide a highly precise bandwidt...
Page 61: Configuring Pq
6-9 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number interface atm interface-number enter interface view or pvc view enter pvc view pvc vpi/vci enter either view as needed. Configurations made in interface view take ef...
Page 62
6-10 pq configuration procedure apply a pq list to an interface. For an interface, a newly applied pq list overwrites the previous one. Follow these steps to configure pq: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — configure a pq list qos pql pql-index protocol ip [ queue-ke...
Page 63: Configuring Cq
6-11 figure 6-7 network diagram for pq configuration procedure configure router a # configure acls to match the packets from server and host a respectively. [routera] acl number 2001 [routera-acl-basic-2001] rule permit source 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 [routera] acl number 2002 [routera-acl-basic-2002] rule p...
Page 64
6-12 configuration procedure follow these steps to configure cq: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — configure a cq list qos cql cql-index protocolip [ queue-key key-value ]queue queue-number optional use a command as needed. Specify the default queue qos cql cql-inde...
Page 65: Configuring Wfq
6-13 # configure cq list 1. [sysname] qos cql 1 protocol ip acl 2001 [sysname] qos cql 1 queue 1 serving 2000 # apply cq list 1 to serial 2/0/1. [sysname] interface serial 2/0/1 [sysname-serial 2/0/1] qos cq cql 1 configuring wfq configuration procedure on an interface with wfq not configured, the q...
Page 66: Configuring Cbq
6-14 [sysname-serial2/0/1] qos wfq queue-length 100 queue-number 512 configuring cbq follow these steps to configured cbq: 1) define a class 2) define a traffic behavior 3) define a policy 4) apply the qos policy in the interface/pvc view the system pre-defines some classes, traffic behaviors and po...
Page 68
6-16 z you cannot configure the queue ef command together with any of the commands queue af, queue-length , and wred in a traffic behavior. Z the default class cannot be associated with a traffic behavior including ef. Z to reference both the queue ef command and the queue af command in a policy, yo...
Page 69
6-17 check that the queue af or queue wfq command has been configured, before you configure the queue-length command. Executing the undo queue af command or the undo queue wfq command cancels also the queue-length command. Using wred drop follow these steps to use wred drop: to do… use the command… ...
Page 70
6-18 to do… use the command… remarks configure the exponent for wred to calculate the average queue size wred weighting-constant exponent required the default exponent is 9. Before configuring the wred weighting-constant command, make sure the queue af command or the queue wfq command has been confi...
Page 71
6-19 follow these steps to configure the lower limit, upper limit, and drop probability denominator for an ip precedence value in wred: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — create a traffic behavior and enter traffic behavior view traffic behavior behavior-name required th...
Page 72
6-20 to do… use the command… remarks enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number interface atm interface-number enter interface view or pvc view enter pvc view pvc vpi/vci use either command settings in interface view take effect on the current interface. Settings in pvc view take...
Page 73
6-21 z if the interface is a virtual interface (a tunnel interface, layer 3 aggregate interface, hdlc link bundle interface, or rpr logical interface, for example), 0 kbps applies. Z you are recommended to configure the maximum available interface bandwidth to be smaller than the actual available ba...
Page 74
6-22 setting the maximum reserved bandwidth as a percentage of available bandwidth the maximum reserved bandwidth is set on a per-interface basis. It decides the maximum bandwidth assignable for the qos queues on an interface. It is typically set no greater than 80% of available bandwidth, consideri...
Page 75
6-23 before performing the configuration, make sure that: z the route from router c to router d through router a and router b is reachable. Z the dscp fields have been set for the traffic before the traffic enters router a. Figure 6-8 network diagram for cbq configuration configuration procedure con...
Page 76
6-24 # apply the qos policy in the outbound direction of router a. [routera] interface serial 1/0/1 [routera-serial1/0/1] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [routera-serial1/0/1] qos apply policy dscp outbound with the above configurations complete, ef traffic is forwarded preferentially when congesti...
Page 77: Qos Token Configuration
6-25 # configure rtp priority queuing on serial 1/0/1: the start port number is 16384, the end port number is 32767, and 64 kbps of bandwidth is reserved for rtp packets. When congestion occurs to the outgoing interface, rtp packets are assigned to the rtp priority queue. [sysname-serial1/0/1] qos r...
Page 78
6-26 configuring packet information pre-extraction configuration procedure the packets that a tunnel interface passes to a physical interface are encapsulated in a tunnel (gre or ipsec). Thus, the ip data (including layer 3 and layer-4 information) that the qos module obtains from the physical inter...
Page 79
7-1 7 hardware congestion management configuration the features in this chapter are available only on routers that have a sap interface card. This chapter includes these sections: z hardware congestion management overview z hardware congestion management configuration approach z per-queue hardware c...
Page 80
7-2 the key to congestion management is how to define a dispatching policy for resources to decide the order of forwarding packets when congestion occurs. Congestion management techniques congestion management uses queuing and scheduling algorithms to classify and sort traffic leaving a port. Each q...
Page 81
7-3 z sp mode 0: in this mode, basic sp queuing is used. Z sp mode 1: in this mode, when the remaining external memory space is sufficient, basic sp queuing is used; when the remaining external memory space is 0, the scheduling algorithm can preferentially forward lower priority packets stored in th...
Page 82
7-4 z wrr queuing with the maximum delay: assures that packets in the highest-priority queue are transmitted within the specified maximum delay, which makes it different from basic wrr queuing. Wfq queuing figure 7-4 schematic diagram for wfq queuing the only difference between wfq and wrr is that: ...
Page 83
7-5 task remarks configuring sp queuing optional configure wrr queuing optional per-queue hardware congestion management configuring wfq queuing optional per-queue hardware congestion management configuring sp queuing sp queuing comprises basic sp queuing and multi-mode sp queuing. Support for sp qu...
Page 84
7-6 with a wrr queue configured on an interface, wrr queuing is enabled on the interface, and other queues on the interface use the default wrr scheduling value and are assigned to the default wrr priority group. Configuration procedure 1) configuring basic wrr queuing follow these steps to configur...
Page 85
7-7 configuration example 1) network requirements z enable wrr queuing on the interface. Z assign queue 0 and queue 1 to the sp group. Z assign queue 2, queue 3, and queue 4 to wrr group 1, with the weight of 1, 5, and 10 respectively. 2) configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # co...
Page 86
7-8 configure wfq queues on an interface and assign the scheduling weight 1, 5, 10, 20, and 10 to queue 1, queue 3, queue 4, queue 5, and queue 6 respectively. 2) configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # configure wfq queues on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. [sysname] interface gigabitethe...
Page 87: Congestion Avoidance
8-1 8 congestion avoidance when configuring congestion avoidance, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z congestion avoidance overview z introduction to wred configuration z configuring wred on an interface z displaying and maintaining wred z wred configuration example congest...
Page 88
8-2 z when the queue size is between the lower threshold and the upper threshold, the received packets are dropped at random. The longer a queue is, the higher the drop probability is. However, a maximum drop probability exists. Different from red, wred determines differentiated drop policies for pa...
Page 89
8-3 introduction to wred configuration on the sr6600 routers, wred is configured and enabled directly on interfaces. Before configuring wred on an interface, determine the following parameters: z the upper threshold and lower threshold: when the average queue size is smaller than the lower threshold...
Page 90: Wred Configuration Example
8-4 z set the following parameters for packets with ip precedence 3: lower threshold 20, upper threshold 40, and drop probability denominator 15. Z set the exponential factor for the average queue size calculation to 6. Configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # enter interface view....
Page 91
8-5 figure 8-2 network diagram for wred configuration configuration procedure # configure acls to match the packets from server, telephone, host a, and host b respectively. System-view [router] acl number 2001 [router-acl-basic-2001] rule 1 permit source 10.1.1.1 0 [router-acl-basic-2001] quit [rout...
Page 92
8-6 [router] traffic behavior behavior4 [router-behavior-behavior4] remark ip-precedence 2 [router-behavior-behavior4] quit [router] qos policy aa [router-qospolicy-aa] classifier class1 behavior behavior1 [router-qospolicy-aa] classifier class2 behavior behavior2 [router-qospolicy-aa] classifier cl...
Page 93: Traffic Filtering Overview
9-1 9 traffic filtering configuration this chapter includes these sections: z traffic filtering overview z configuring traffic filtering z traffic filtering configuration example traffic filtering overview you can filter in or filter out a class of traffic by associating the class with a traffic fil...
Page 95: Priority Marking Overview
10-1 10 priority marking configuration this chapter includes these sections: z priority marking overview z configuring priority marking z priority marking configuration example priority marking overview priority marking sets the priority fields or flag bits of packets to modify the priority of traff...
Page 96
10-2 to do… use the command… remarks create a policy and enter policy view qos policy policy-name — associate the class with the traffic behavior in the qos policy classifier tcl-name behavior behavior-name — exit policy view quit — to an interface or pvc applying the qos policy to an interface or p...
Page 97
10-3 figure 10-1 network diagram for priority marking configuration internet host a host b device data server 192.168.0.1/24 mail server 192.168.0.2/24 file server 192.168.0.3/24 ge1/0/1 ge1/0/2 configuration procedure # create advanced acl 3000, and configure a rule to match packets with destinatio...
Page 98
10-4 # create a behavior named behavior_mserver, and configure the action of setting the dscp value to 24. [device] traffic behavior behavior_mserver [device-behavior-behavior_mserver] remark dscp 24 [device-behavior-behavior_mserver] quit # create a behavior named behavior_fserver, and configure th...
Page 99: Traffic Redirecting Overview
11-1 11 traffic redirecting configuration the features in this chapter are available only on routers that have a sap interface card. This chapter includes these sections: z traffic redirecting overview z configuring traffic redirecting z traffic redirecting configuration examples traffic redirecting...
Page 100
11-2 to do… use the command… remarks associate the class with the traffic behavior in the qos policy classifier tcl-name behavior behavior-name — exit policy view quit — to an interface or pvc applying the qos policy to an interface or pvc — apply the qos policy to a vlan applying the qos policy to ...
Page 101
11-3 figure 11-1 network diagram for redirecting traffic to an interface configuration procedure # create basic acl 2000, and configure a rule to match packets with source ip address 2.1.1.1. System-view [devicea] acl number 2000 [devicea-acl-basic-2000] rule permit source 2.1.1.1 0 [devicea-acl-bas...
Page 102
11-4 # create a behavior named behavior_2, and configure the action of redirecting traffic to interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3. [devicea] traffic behavior behavior_2 [devicea-behavior-behavior_2] redirect interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [devicea-behavior-behavior_2] quit # create a behavior named beh...
Page 103: Eacl Configuration
12-1 12 eacl configuration the features in this chapter are available only on routers that have a sap interface card. This chapter includes these sections: z eacl overview z eacl configuration task list z configuring bt traffic limiting z eacl configuration example z troubleshooting eacl eacl overvi...
Page 104: Eacl Configuration Example
12-2 to do… use the command… remarks define an acl rule rule [ rule-id ] permit tcp [ rule-string ] required exit acl view quit — enter class view traffic classifier tcl-name — configure an acl based match criterion if-match acl acl-number required match bt packets if-match protocol bittorrent requi...
Page 105
12-3 figure 12-1 network diagram for bt traffic limiting ge1/0/3 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/1 vlan 40 vlan 3 host a host b 2.0.0.1/8 1.0.0.1/8 router configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # configure a qos policy for bt traffic limiting and apply it to the service card. [router] acl number 300...
Page 106: Troubleshooting Eacl
12-4 troubleshooting eacl symptom the eacl feature does not work on the router. Analysis z appropriate rules should be configured. Z a traffic behavior should be specified for the traffic class in the policy. Z the packets on the designated port should be redirected to the service card. Solution z v...
Page 107: Dar Configuration
13-1 13 dar configuration this chapter includes these sections: z dar overview z configuring dar for p2p traffic identification z displaying and maintaining dar z dar configuration examples dar overview the deeper application recognition (dar) feature identifies packets of dynamic protocols like bit...
Page 108
13-2 configuring a p2p protocol group you can configure a p2p protocol group to include multiple p2p protocols. You can reference this p2p protocol group in a traffic class to perform qos actions on them. Follow these steps to configure a p2p protocol group: to do… use the command… remarks enter sys...
Page 109: Dar Configuration Examples
13-3 follow these steps to configure dar packets accounting: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number — enable dar packet accounting dar protocol-statistic [ flow-interval time ] required disabled by default displa...
Page 110
13-4 [router-classifier-p2p] if-match protocol-group 1 [router-classifier-p2p] quit # configure a packet filtering behavior. [router] traffic behavior deny [router-behavior-deny] filter deny [router-behavior-deny] quit # create a qos policy and associate the traffic behavior with the class in the po...
Page 111
14-1 14 class-based accounting configuration this chapter includes these sections: z class-based accounting overview z configuring class-based accounting z displaying and maintaining class-based traffic accounting z class-based accounting configuration example class-based accounting overview class-b...
Page 112
14-2 displaying and maintaining class-based traffic accounting to verify the class-based accounting configuration, use the display qos policy command in any view to display the traffic statistics collected after the configuration is complete. Class-based accounting configuration example class-based ...
Page 113
14-3 direction: inbound policy: policy classifier: classifier_1 operator: and rule(s) : if-match acl 2000 behavior: behavior_1 accounting enable: 28529 (packets).
Page 114: Appendix
15-1 15 appendix this chapter includes these sections: z appendix a acronym z appendix b default priority mapping tables z appendix c introduction to packet precedences appendix a acronym table 15-1 appendix a acronym acronym full spelling af assured forwarding be best effort car committed access ra...
Page 115
15-2 acronym full spelling pir peak information rate pq priority queuing qos quality of service red random early detection rsvp resource reservation protocol rtp real time protocol sla service level agreement te traffic engineering tos type of service tp traffic policing ts traffic shaping voip voic...
Page 116
15-3 input priority value dot1p-lp mapping dot1p-dp mapping 7 7 0 table 15-3 the default dscp-dp and dscp-dot1p priority mapping tables input priority value dscp-dp mapping dscp-dot1p mapping dscp drop precedence (dp) 802.1p priority (dot1p) 0 to 7 0 0 8 to 15 0 1 16 to 23 0 2 24 to 31 0 3 32 to 39 ...
Page 117
15-4 appendix c introduction to packet precedences ip precedence and dscp values figure 15-1 tos and ds fields as shown in figure 15-1 , the tos field in the ip header contains eight bits. The first three bits (0 to 2) represent ip precedence from 0 to 7. According to rfc 2474, the tos field is rede...
Page 118
15-5 dscp value (decimal) dscp value (binary) description 30 011110 af33 34 100010 af41 36 100100 af42 38 100110 af43 8 001000 cs1 16 010000 cs2 24 011000 cs3 32 100000 cs4 40 101000 cs5 48 110000 cs6 56 111000 cs7 0 000000 be (default) 802.1p priority 802.1p priority lies in the layer 2 header and ...
Page 119
15-6 table 15-7 description on 802.1p priority 802.1p priority (decimal) 802.1p priority (binary) description 0 000 best-effort 1 001 background 2 010 spare 3 011 excellent-effort 4 100 controlled-load 5 101 video 6 110 voice 7 111 network-management 802.11e priority to provide qos services on wlan,...
Page 120: Mpls Qos Configuration
16-1 16 mpls qos configuration this chapter includes these sections: z mpls qos overview z configuring mpls qos z mpls qos configuration example mpls qos overview z the mpls-related knowledge is necessary for understanding mpls qos. For more information about mpls, see mpls basic in the mpls configu...
Page 121: Configuring Mpls Qos
16-2 the exp field in an mpls label is processed as follows: z any qos-capable router can reset the exp field of the outer label. Z during label encapsulation, the tos field of the ip packet is directly changed into the exp field of the mpls label. Z the exp field remains unchanged when label swappi...
Page 122
16-3 configuring mpls priority marking in an mpls network, you can adjust the priority of an mpls traffic flow by re-marking its exp value. Configuration prerequisites mpls related configurations are completed. Configuration procedure follow these steps to configure the mpls priority marking action ...
Page 124
16-5 for traffic with an exp value of 2; guarantee 30% of the bandwidth for traffic with an exp value of 3; guarantee the delay and 40% of the bandwidth for traffic with an exp value of 4. For more information about the mpls configuration, see mpls l3vpn in the mpls configuration guide . This sectio...
Page 125
16-6 [pe1-behavior-exp1] traffic behavior exp2 [pe1-behavior-exp2] remark mpls-exp 2 [pe1-behavior-exp2] traffic behavior exp3 [pe1-behavior-exp3] remark mpls-exp 3 [pe1-behavior-exp3] traffic behavior exp4 [pe1-behavior-exp4] remark mpls-exp 4 [pe1-behavior-exp4] quit # define a qos policy to assoc...
Page 126
16-7 [p-qospolicy-queue] classifier exp4 behavior ef [p-qospolicy-queue] quit # apply the qos policy in the outbound direction of serial 2/0/2 on router p. [p] interface serial 2/0/2 [p-serial2/0/2] qos apply policy queue outbound after the above configuration, when congestion occurs in vpn 1, the b...
Page 127: Fr Qos Configuration
17-1 17 fr qos configuration this chapter includes these sections: z fr qos overview z configuring fr qos z displaying and maintaining fr qos z fr qos configuration examples fr qos overview fr qos on an fr interface, you can use generic quality of service (qos) services to perform traffic policing, ...
Page 128
17-2 z committed burst size (cbs): size of the traffic that the fr network is certain to transmit within the interval of tc. When congestion occurs in the network, the network guarantees transmitting traffic conforming to cbs. Z excess burst size (ebs): maximum size of the traffic that can exceed cb...
Page 129
17-3 figure 17-3 how a token bucket works in the token bucket approach, packets requiring flow control is evaluated by the token bucket before transmission. If the number of tokens in the token bucket is enough for sending these packets, the packets are allowed to pass through, in other words, the p...
Page 130
17-4 for example, to send an 800-byte packet, 6400 bits (800 × 8) of tokens are required. Given the cir of 64000 kbps, it takes 6400/64000=0.1s to put the required tokens into the token bucket, that is, the tc for the packet is 100 ms. The packet is transmitted after 6400 bits of tokens are put into...
Page 131
17-5 fr traffic policing fr traffic policing monitors the traffic entering the network from each pvc, and restricts the traffic within a permitted range. If the traffic on a pvc exceeds the user-defined threshold, the router takes some measures like packet drop to protect the network resources. Figu...
Page 132
17-6 packets at the rate of 128 kbps. In this case, the de flag bits in the packets of the traffic between cbs and cbs + ebs are set to 1, and the packets of the traffic exceeding cbs + ebs are directly dropped. Fr queuing besides fr pvc queues, fr interfaces also have interface queues. With frts di...
Page 133: Configuring Fr Qos
17-7 congestion occurs, packets with the fe flag bits set to 1 are dropped; as for forward packets to be forwarded, the fecn flag bits in the fr packet headers are set to 1; as for backward packets on the same pvc, the becn flag bits in the fr packet headers are set to 1. If no backward packets is t...
Page 134
17-8 z the fr class of the fr interface to which the fr pvc belongs follow these steps to configure and create an fr class: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — create an fr class and enter fr class view fr class class-name required by default, no fr class is created. ...
Page 136
17-10 configuring fr congestion management fr congestion management includes congestion management on the fr interface and congestion management on the fr pvc. You can set the congestion thresholds in fr pvc view or fr interface view for a specific fr class. The router determines whether congestion ...
Page 138
17-12 configuring fr interface queuing universal queuing mechanisms (including fifo, pq, cq, wfq, cbq, and rtpq) are available on fr interfaces. For more information about fifo, pq, cq, wfq, cbq, and rtpq, see qos in the acl and qos configuration guide . Pvc pq is specific to fr interfaces and is av...
Page 139
17-13 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter fr class view fr class class-name — enable fr fragmentation fragment [ fragment-size ] required disabled by default z the configured fr fragmentation function takes effect after you associate the fr pvcs requiring fr fragmentation with the fr class and...
Page 140
17-14 fr qos configuration examples frts configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 17-10 , the router is connected to the fr network through serial 2/0/1. Its average transmit rate is 96 kbps, maximum transmit rate is 128 kbps, and minimum transmit rate is 32 kbps. Configure frts...
Page 141
17-15 system-view [routera] fr class test1 [routera-fr-class-test1] fragment 80 [routera-fr-class-test1] quit # configure serial 2/0/1 as an fr interface and enable frts on serial 2/0/1. [routera] interface serial 2/0/1 [routera-serial2/0/1] link-protocol fr [routera-serial2/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.2...
Page 142: Index
18-1 18 index a acl configuration examples 1-12 acl configuration task list 1-4 acl overview 1-1 appendix a acronym 15-1 appendix b default priority mapping tables 15-2 appendix c introduction to packet precedences 15-4 b c class-based accounting configuration example 14-2 class-based accounting ove...
Page 143
18-2 k l m mpls qos configuration example 16-4 mpls qos overview 16-1 n o p per-queue hardware congestion management 7-5 priority mapping configuration examples 4-4 priority mapping configuration tasks 4-2 priority mapping overview 4-1 priority marking configuration example 10-2 priority marking ove...