- DL manuals
- H3C
- Network Router
- S3600V2 SERIES
- Layer 2-lan Switching Configuration Manual
H3C S3600V2 SERIES Layer 2-lan Switching Configuration Manual
Summary of S3600V2 SERIES
Page 1
H3c s3600v2 switch series layer 2 — lan switching configuration guide hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Http://www.H3c.Com software version: release 2108 document version: 6w100-20131130
Page 2
Copyright © 2013, hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. And its licensors all rights reserved no part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Trademarks h3c, , h3cs, h3cie, h3cne, aolynk, , h 3 car...
Page 3
Preface the h3c s3600v2 documentation set includes 10 configuration guides, which describe the software features for the h3c s3600v2 switch series release 2108, and guide you through the software configuration procedures. These configuration guides also provide configuration examples to help you app...
Page 4
Configuration guide added and modified features address • enabling mac address migration log notifying mac information n/a ethernet link aggregation new feature: configuring the maximum number of selected ports allowed in an aggregation group port isolation n/a spanning tree n/a bpdu tunneling n/a v...
Page 6
About the h3c s3600v2 documentation set the h3c s3600v2 documentation set includes: category documents purposes product description and specifications marketing brochure describe product specifications and benefits. Technology white papers provide an in-depth description of software features and tec...
Page 7
[products & solutions] – provides information about products and technologies, as well as solutions. [technical support & documents > software download] – provides the documentation released with the software version. Technical support service@h3c.Com http://www.H3c.Com documentation feedback you ca...
Page 8
I contents configuring ethernet interfaces ··································································································································· 1 ethernet interface naming conventions ·····················································································...
Page 9
Ii disabling mac entry aging timer refresh based on destination mac address ····················································· 25 application example ············································································································································· 26 co...
Page 10
Iii port isolation configuration example···························································································································· 60 configuring spanning tree protocols ································································································...
Page 11
Iv performing mcheck ························································································································································ 92 performing mcheck globally ································································································...
Page 12
V port-based vlan configuration example ·········································································································· 126 configuring mac-based vlans ·························································································································...
Page 13
Vi dynamically advertising server-assigned vlans through lldp ··············································································· 165 overview ·················································································································································...
Page 14
Vii configuration prerequisites ································································································································ 207 configuring an uplink policy ··········································································································...
Page 15
Viii service loopback group configuration example ······································································································· 245 network requirements ·························································································································...
Page 16
1 configuring ethernet interfaces ethernet interface naming conventions the ethernet interfaces on the s3600v2 switches are named in the format of interface-type a/b/c, where the following definitions apply: • a—represents the id of the switch in an irf fabric. If the switch is not assigned to any i...
Page 18
3 step command remarks 6. Restore the default settings for the interface. Default optional. Note: make sure that the fiber port speed matches the speed requirement of the inserted transceiver module. For example, after you insert a 1000-mbps transceiver module into a fiber port, configure the port s...
Page 19
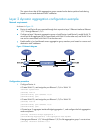
4 figure 1 flow control on ports configure flow control in txrx mode on port b and flow control in rx mode on port a: • when congestion occurs on port c, switch b buffers frames. When the amount of buffered frames exceeds a certain value, switch b sends a common pause frame out of port b to ask port...
Page 20
5 the physical link is still down when the timer expires, the interface reports the link-down event to the upper layers. Link-up event suppression enables an interface to suppress link-up events and start a delay timer each time the physical link goes up. During this delay, the interface does not re...
Page 21
6 • during loopback testing, the ethernet interface operates in full duplex mode. When you disable loopback testing, the port returns to its duplex setting. • loopback testing is a one-time operation, and is not recorded in the configuration file. Configuration procedure to enable loopback testing o...
Page 22
7 • if you execute the command in port group view, the configuration takes effect on all ports in the port group. To configure jumbo frame support in interface view or port group view: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter ethernet interface view. Interface interface-ty...
Page 23
8 task remarks setting speed options for auto negotiation on an ethernet interface optional applicable to layer 2 ethernet interfaces configuring storm suppression optional applicable to layer 2 ethernet interfaces setting the statistics polling interval optional applicable to layer 2 ethernet inter...
Page 24
9 step command remarks 4. Configure jumbo frame support. Jumboframe enable [ value ] by default, the switch allows jumbo frames within 10000 bytes to pass through ethernet interfaces. If you set the value argument multiple times, the latest configuration takes effect. 5. Enable auto power-down. Port...
Page 25
10 note: • this function is available only for layer 2 copper ports that support speed auto negotiation, and is unavailable for combo interfaces. • the speed and speed auto commands supersede each other, and whichever is configured last takes effect. Configuring storm suppression in interface or por...
Page 26
11 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter ethernet interface view. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 3. Set the statistics polling interval on the ethernet interface. Flow-interval interval optional. The default interface statistics polling interval is 300 se...
Page 27
12 when a loop is detected, for example, to shut down the interface. Depending on whether a protective action is configured, the switch takes the actions in table 1 to alleviate the impact of the loop condition. Table 1 actions to take upon detection of a loop condition port type actions no protecti...
Page 28
13 step command remarks 5. Enter ethernet interface view or port group view. • enter ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name use either command. To configure loopback detection on one interface, enter ethernet inte...
Page 29
14 • in auto mode, the interface negotiates pin roles with its peer. To enable the interface to communicate with its peer, make sure that its transmit pins are connected to the remote receive pins. If the interface can detect the connection cable type, set the interface in auto mdi mode. If not, set...
Page 30
15 you can test the cable connection of an ethernet interface for a short or open circuit. The switch displays cable test results within five seconds. If any fault is detected, the test results include the length of the faulty cable segment. To test the cable connection of an ethernet interface: ste...
Page 31
16 step command remarks 2. Set the traffic polling interval of the storm control module. Storm-constrain interval seconds optional. 10 seconds by default. 3. Enter ethernet interface view. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 4. Enable storm control, and set the lower and upper thresholds f...
Page 33
18 configuring loopback and null interfaces configuring a loopback interface introduction to the loopback interface a loopback interface is a software-only virtual interface. It delivers the following benefits: • the physical layer state and link-layer protocols of a loopback interface are always up...
Page 34
19 step command remarks 4. Shut down the loopback interface. Shutdown optional by default, a loopback interface is up. 5. Restore the default settings for the loopback interface. Default optional note: you can configure settings such as ip addresses and ip routes on loopback interfaces. For more inf...
Page 36
21 bulk configuring interfaces you can enter interface range view to bulk configure multiple interfaces with the same feature instead of configuring them one by one. For example, you can perform the shutdown command in interface range view to shut down a range of interfaces. Failure of applying a co...
Page 37
22 configuring the mac address table this feature covers only the unicast mac address table. For information about configuring static multicast mac address table entries for igmp snooping and mld snooping, see ip multicast configuration guide. The mac address table can contain only layer 2 ethernet ...
Page 38
23 manually configuring mac address entries with dynamic mac address learning, a device does not distinguish between illegitimate and legitimate frames, which can invite security hazards. For example, when a hacker sends frames with a forged source mac address to a port different from the one to whi...
Page 40
25 you can disable mac address learning on a per-vlan basis. To disable mac address learning on a vlan: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter vlan view. Vlan vlan-id n/a 3. Disable mac address learning on the vlan. Mac-address mac-learning disable enabled by default. Co...
Page 41
26 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Disable mac entry aging timer refresh based on destination mac address. Mac-address destination-hit disable by default, mac entry aging timer refresh based on destination mac address is enabled. Application example microsoft network lo...
Page 42
27 step command remarks 2. Enter interface view or port group view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name use either command. Settings in layer 2 ethernet interface view take effect on the interfa...
Page 43
28 figure 7 mac address tables of devices when client a roams to ap d to enable mac address roaming: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enable mac address roaming. Mac-address mac-roaming enable disabled by default. Enabling mac address migration log notifying this feature...
Page 44
29 step command remarks 2. Enable mac address migration log notifying. Mac-flapping notification enable by default, mac address migration log notifying is disabled. The mac address migration logs of the last one minute are displayed once every one minute. Displaying and maintaining mac address table...
Page 45
30 figure 8 network diagram configuration procedure # add a static mac address entry. System-view [sysname] mac-address static 000f-e235-dc71 interface ethernet 1/0/1 vlan 1 # add a blackhole mac address entry. [sysname] mac-address blackhole 000f-e235-abcd vlan 1 # set the aging timer for dynamic m...
Page 46
31 configuring mac information overview introduction to mac information to monitor a network, you must monitor users who are joining and leaving the network. Because a mac address uniquely identifies a network user, you can monitor users who are joining and leaving a network by monitoring their mac ...
Page 48
33 step command remarks 2. Configure the mac information queue length. Mac-address information queue-length value optional 50 by default. Mac information configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 9 , enable mac information on ethernet 1/0/1 on device to send mac address changes i...
Page 49
34 configuring ethernet link aggregation overview ethernet link aggregation, or simply link aggregation, combines multiple physical ethernet ports into one logical link, called an "aggregate link." link aggregation delivers the following benefits: • increases bandwidth beyond the limits of any singl...
Page 50
35 • unselected: an unselected port cannot forward user traffic. Operational key when aggregating ports, the system automatically assigns each port an operational key based on port information such as port rate and duplex mode. Any change to this information triggers a recalculation of the operation...
Page 51
36 the ieee 802.3ad lacp offers basic lacp functions and extended lacp functions, as described in table 3 . Table 3 basic and extended lacp functions category description basic lacp functions implemented through the basic lacpdu fields, including the system lacp priority, system mac address, port ag...
Page 52
37 table 5 a comparison between static and dynamic aggregation modes aggregation mode lacp status on member ports pros cons static disabled aggregation is stable. Peers do not affect the aggregation state of the member ports. The member ports do not adjust the aggregation state according to that of ...
Page 53
38 figure 11 setting the aggregation state of a member port in a static aggregation group aggregating links in dynamic mode lacp is automatically enabled on all member ports in a dynamic aggregation group. The protocol automatically maintains the aggregation state of ports. The dynamic link aggregat...
Page 54
39 figure 12 setting the state of a member port in a dynamic aggregation group meanwhile, the system with the higher system id, which has identified the aggregation state changes on the remote system, sets the aggregation state of local member ports as the same as their peer ports. A dynamic link ag...
Page 55
40 you can choose one of the following criteria or any combination for load sharing: • source/destination mac addresses • source/destination service port numbers • ingress ports • source/destination ip addresses alternatively, you can let the system automatically choose link-aggregation load-sharing...
Page 56
41 configuration guidelines • you cannot assign a port to a layer 2 aggregation group if any of the features listed in table 6 is configured on the port. Table 6 features incompatible with layer 2 aggregation groups feature reference rrpp rrppin high availability configuration guide mac authenticati...
Page 57
42 step command remarks 4. Assign an ethernet interface to the aggregation group. A. Enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number b. Assign the ethernet interface to the aggregation group: port link-aggregation group number repeat these two sub-steps to assign mor...
Page 58
43 configuring a layer 2 dynamic aggregation group step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Set the system lacp priority. Lacp system-priority system-priority optional. By default, the system lacp priority is 32768. Changing the system lacp priority might affect the aggregation ...
Page 59
44 step command remarks 2. Set the system lacp priority. Lacp system-priority system-priority optional. By default, the system lacp priority is 32768. Changing the system lacp priority might affect the aggregation state of the ports in the dynamic aggregation group. 3. Create a layer 3 aggregate int...
Page 60
45 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter aggregate interface view. • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number • enter layer 3 aggregate interface view: interface route-aggregation interface-number use either command. 3. Confi...
Page 61
46 step command remarks 3. Enter aggregate interface view. • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number • enter layer 3 aggregate interface view: interface route-aggregation interface-number use either command. 4. Enable link state traps for the aggregate i...
Page 62
47 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter aggregate interface view. • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number • enter layer 3 aggregate interface view: interface route-aggregation interface-number use either command. 3. Set t...
Page 63
48 step command remarks 2. Enter aggregate interface view. • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number • enter layer 3 aggregate interface view: interface route-aggregation interface-number use either command. 3. Restore the default settings for the aggreg...
Page 64
49 • destination ip address • source mac address • destination mac address • source ip address and destination ip address • source ip address and source port • destination ip address and destination port • source ip address, source port, destination ip address, and destination port • any combination...
Page 65
50 figure 13 load sharing process for cross-switch link aggregation in an irf fabric to enable local-first load sharing for link aggregation: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enable local-first load-sharing for link aggregation. Link-aggregation load-sharing mode local-f...
Page 66
51 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enable link-aggregation traffic redirection. Link-aggregation lacp traffic-redirect-notification enable optional. Disabled by default. Caution: • to prevent traffic interruption, enable link-aggregation traffic redirection on devices a...
Page 67
52 ethernet link aggregation configuration examples in an aggregation group, only ports that have the same port attributes and class-two configurations (see " configuration classes ") as the reference port (see " reference port ") can operate as selected ports. Make sure that all member ports have t...
Page 68
53 [devicea] interface bridge-aggregation 1 [devicea-bridge-aggregation1] quit # assign ports ethernet 1/0/1 through ethernet 1/0/3 to link aggregation group 1. [devicea] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-ethernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1 [devicea-ethernet1/0/1] quit [devicea] interface e...
Page 69
54 the output shows that all link aggregation groups created on the device perform load sharing based on source and destination mac addresses. Layer 2 dynamic aggregation configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 15 : • device a and device b are connected through their respective...
Page 70
55 [devicea-ethernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1 [devicea-ethernet1/0/1] quit [devicea] interface ethernet 1/0/2 [devicea-ethernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 1 [devicea-ethernet1/0/2] quit [devicea] interface ethernet 1/0/3 [devicea-ethernet1/0/3] port link-aggregation group 1 [device...
Page 71
56 layer 3 static aggregation configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 16 : • device a and device b are connected by their layer 3 ethernet interfaces ethernet 1/0/1 through ethernet 1/0/3. • configure a layer 3 static aggregation group on both device a and device b. Configure i...
Page 72
57 aggregation mode: s -- static, d -- dynamic loadsharing type: shar -- loadsharing, nons -- non-loadsharing actor system id: 0x8000, 000f-e2ff-0001 agg agg partner id select unselect share interface mode ports ports type -----------------------------------------------------------------------------...
Page 73
58 [devicea-ethernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1 [devicea-ethernet1/0/1] quit [devicea] interface ethernet 1/0/2 [devicea-ethernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 1 [devicea-ethernet1/0/2] quit [devicea] interface ethernet 1/0/3 [devicea-ethernet1/0/3] port link-aggregation group 1 [device...
Page 74
59 configuring port isolation port isolation enables isolating layer 2 traffic for data privacy and security without using vlans. You can also use this feature to isolate the hosts in a vlan from one another. To use the feature, assign ports to a port isolation group. Ports in an isolation group are...
Page 75
60 port isolation configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 18 , host a, host b, and host c are connected to ethernet 1/0/1, ethernet 1/0/2, and ethernet 1/0/3 of device, and device is connected to the internet through ethernet 1/0/4. All these ports are in the same vlan. Configu...
Page 76
61 configuring spanning tree protocols as a layer 2 management protocol, the spanning tree protocol (stp) eliminates layer 2 loops by selectively blocking redundant links in a network, putting them in a standby state, which still also allows for link redundancy. The recent versions of stp include th...
Page 77
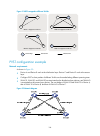
62 basic concepts in stp root bridge a tree network must have a root bridge. The entire network contains only one root bridge. The other bridges in the network are called "leaf nodes." the root bridge is not permanent, but can change with changes of the network topology. Upon initialization of a net...
Page 78
63 calculation process of the stp algorithm the spanning tree calculation process described in the following sections is a simplified process for example only. The stp algorithm uses the following calculation process: 1. Initialize the state. Upon initialization of a device, each port generates a bp...
Page 79
64 table 10 selection of the optimum configuration bpdu step actions 1 upon receiving a configuration bpdu on a port, the device compares the priority of the received configuration bpdu with that of the configuration bpdu generated by the port, and: • if the former priority is lower, the device disc...
Page 80
65 device port name configuration bpdu on the port port a2 {0, 0, 0, port a2} device b port b1 {1, 0, 1, port b1} port b2 {1, 0, 1, port b2} device c port c1 {2, 0, 2, port c1} port c2 {2, 0, 2, port c2} note: in table 11 , each configuration bpdu contains the following fields: root bridge id, root ...
Page 81
66 device comparison process configuration bpdu on ports after comparison device c • port c1 receives the configuration bpdu of port a2 {0, 0, 0, port a2}, finds that the received configuration bpdu is superior to its existing configuration bpdu {2, 0, 2, port c1}, and updates its configuration bpdu...
Page 82
67 figure 21 the final calculated spanning tree the configuration bpdu forwarding mechanism of stp the configuration bpdus of stp are forwarded following these guidelines: • upon network initiation, every device regards itself as the root bridge, generates configuration bpdus with itself as the root...
Page 83
68 the device uses the max age to determine whether a stored configuration bpdu has expired and discards it if the max age is exceeded. Rstp rstp achieves rapid network convergence by allowing a newly elected root port or designated port to enter the forwarding state much faster than stp. A newly el...
Page 84
69 mstp provides the following features: • mstp divides a switched network into multiple regions, each of which contains multiple spanning trees that are independent of one another. • mstp supports mapping vlans to spanning tree instances by means of a vlan-to-instance mapping table. Mstp can reduce...
Page 85
70 figure 23 network diagram and topology of mst region 3 mst region a multiple spanning tree region (mst region) consists of multiple devices in a switched network and the network segments among them. All these devices have the following characteristics: • a spanning tree protocol enabled • same re...
Page 86
71 ist an internal spanning tree (ist) is a spanning tree that runs in an mst region. It is also called msti 0, a special msti to which all vlans are mapped by default. In figure 22 , msti 0 is the ist in mst region 3. Cist the common and internal spanning tree (cist) is a single spanning tree that ...
Page 87
72 mstp calculation involves the following port roles: • root port—forwards data for a non-root bridge to the root bridge. The root bridge does not have any root port. • designated port—forwards data to the downstream network segment or device. • alternate port—the backup port for a root port or mas...
Page 88
73 how mstp works mstp divides an entire layer 2 network into multiple mst regions, which are connected by a calculated cst. Inside an mst region, multiple spanning trees are calculated. Each spanning tree is an msti. Among these mstis, msti 0 is the ist. Like stp, mstp uses configuration bpdus to c...
Page 89
74 spanning tree configuration task list before configuring a spanning tree, you must determine the spanning tree protocol to be used (stp, rstp, pvst, or mstp) and plan the device roles (the root bridge or leaf node). Configuration restrictions and guidelines • if gvrp and a spanning tree protocol ...
Page 90
75 task remarks configuring the leaf nodes setting the spanning tree mode required configure the device to operate in stp mode. Configuring the device priority optional configuring the timeout factor optional configuring the maximum port rate optional configuring path costs of ports optional configu...
Page 91
76 task remarks configuring the maximum port rate optional configuring edge ports optional configuring path costs of ports optional configuring the port priority optional configuring the port link type optional configuring the mode a port uses to recognize/send mstp packets optional enabling outputt...
Page 92
77 task remarks configuring edge ports optional configuring path costs of ports optional configuring the port priority optional configuring the port link type optional enabling outputting port state transition information optional enabling the spanning tree feature required performing mcheck optiona...
Page 93
78 task remarks configuring path costs of ports optional configuring the port priority optional configuring the port link type optional configuring the mode a port uses to recognize/send mstp packets optional enabling outputting port state transition information optional enabling the spanning tree f...
Page 96
81 configuring the current device as a secondary root bridge of a specific spanning tree to configure the current device as a secondary root bridge of a specific spanning tree: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Configure the current device as a secondary root bridge. • in...
Page 97
82 device that received it. This prevents devices beyond the reach of the maximum hop from participate in spanning tree calculation, so the size of the mst region is limited. Make this configuration on the root bridge only. All other devices in the mst region use the maximum hop value set for the ro...
Page 98
83 the device detects whether a link failure has occurred with the hello time interval. The spanning tree sends a configuration bpdu every hello time interval. If the device receives no configuration bpdus within the hello time interval, it recalculates the spanning tree. • max age in the cist of an...
Page 99
84 step command remarks 3. Configure the hello timer. • in stp/rstp/mstp mode: stp timer hello time • in pvst mode: stp vlan vlan-list timer hello time optional. Use one of the commands. The default setting is 2 seconds. 4. Configure the max age timer. • in stp/rstp/mstp mode: stp timer max-age time...
Page 100
85 step command remarks 2. Enter interface view or port group view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name use one of the commands. 3. Configure the maximum rate...
Page 101
86 you can have the device automatically calculate the default path cost, or you can configure the path cost for ports. Specifying a standard for the device to use when it calculates the default path cost caution: if you change the standard that the device uses to calculate the default path costs, y...
Page 102
87 link speed port type path cost ieee 802.1d-1998 ieee 802.1t private standard 10 gbps single port 2 2000 2 aggregate interface containing 2 selected ports 1000 1 aggregate interface containing 3 selected ports 666 1 aggregate interface containing 4 selected ports 500 1 configuration restrictions a...
Page 103
88 step command remarks 3. Configure the path cost of the ports. • in stp/rstp mode: stp cost cost • in pvst mode: stp vlan vlan-list cost cost • in mstp mode: stp [ instance instance-id ] cost cost use one of the commands. By default, the system automatically calculates the path cost of each port. ...
Page 104
89 step command remarks 3. Configure the port priority. • in stp/rstp mode: stp port priority priority • in pvst mode: stp vlan vlan-list port priority priority • in mstp mode: stp [ instance instance-id ] port priority priority use one of the commands. The default setting is 128. Configuring the po...
Page 105
90 • legacy—compatible format by default, the packet format recognition mode of a port is auto. The port automatically distinguishes the two mstp packet formats, and determines the format of packets that it will send based on the recognized format. You can configure the mstp packet format on a port....
Page 106
91 enabling the spanning tree feature you must enable the spanning tree feature for the device before any other spanning tree related configurations can take effect. Configuration restrictions and guidelines • you can disable the spanning tree feature for certain ports with the undo stp enable comma...
Page 107
92 step command remarks 3. Enable the spanning tree feature on specific vlans. Stp vlan vlan-list enable by default, the spanning tree feature is enabled on vlans. 4. Enter interface view or port group view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface inter...
Page 108
93 step command 3. Perform mcheck. Stp mcheck note: an mcheck operation takes effect on a device that operates in mstp, rstp, or pvst mode. Configuring digest snooping as defined in ieee 802.1s, connected devices are in the same region only when their mst region-related configurations (region name, ...
Page 109
94 step command remarks 2. Enter interface view or port group view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name use either command. 3. Enable digest snooping on the i...
Page 110
95 [devicea] stp config-digest-snooping # enable digest snooping on ethernet 1/0/1 of device b and enable global digest snooping on device b. System-view [deviceb] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [deviceb-ethernet1/0/1] stp config-digest-snooping [deviceb-ethernet1/0/1] quit [deviceb] stp config-digest-sno...
Page 111
96 figure 27 rapid state transition of an rstp designated port if the upstream device is a third-party device, the rapid state transition implementation might be limited. For example, when the upstream device uses a rapid transition mechanism similar to that of rstp, and the downstream device adopts...
Page 112
97 no agreement check configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 28 : • device a connects to a third-party device that has a different spanning tree implementation. Both devices are in the same region. • the third-party device (device b) is the regional root bridge, and device a i...
Page 113
98 in the network, the irf fabric transparently transmits the received bpdus and does not participate in spanning tree calculations. When a topology change occurs to the irf fabric or user networks, the irf fabric may need a long time to learn the correct mac address table entries and arp entries, r...
Page 114
99 receive configuration bpdus, the system automatically sets the ports as non-edge ports and starts a new spanning tree calculation process. This causes a change of network topology. Under normal conditions, these ports should not receive configuration bpdus. However, if someone forges configuratio...
Page 115
100 step command remarks 2. Enter interface view or port group view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name use either command. 3. Enable the root guard function...
Page 116
101 enabling tc-bpdu guard when a switch receives topology change (tc) bpdus (the bpdus that notify devices of topology changes), the switch flushes its forwarding address entries. If someone forges tc-bpdus to attack the switch, the switch will receive a large number of tc-bpdus within a short time...
Page 118
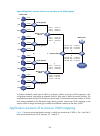
103 figure 30 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure vlans and vlan member ports (details not shown): { create vlan 10, vlan 20, and vlan 30 on device a and device b. { create vlan 10, vlan 20, and vlan 40 on device c. { create vlan 20, vlan 30, and vlan 40 on device d. { configure the...
Page 119
104 [deviceb] stp region-configuration [deviceb-mst-region] region-name example [deviceb-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 10 [deviceb-mst-region] instance 3 vlan 30 [deviceb-mst-region] instance 4 vlan 40 [deviceb-mst-region] revision-level 0 # activate mst region configuration. [deviceb-mst-region] acti...
Page 120
105 [deviced] stp enable 6. Verify the configurations: in this example, suppose that device b has the lowest root bridge id. As a result, device b is elected as the root bridge in msti 0. You can use the display stp brief command to display brief spanning tree information on each device after the ne...
Page 121
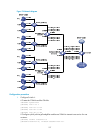
106 figure 31 mstis mapped to different vlans pvst configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 32 : • device a and device b work at the distribution layer. Device c and device d work at the access layer. • configure pvst so that packets of different vlans are forwarded along differ...
Page 122
107 configuration procedure 1. Configure vlans and vlan member ports (details not shown): { create vlan 10, vlan 20, and vlan 30 on device a and device b. { create vlan 10, vlan 20, and vlan 40 on device c. { create vlan 20, vlan 30, and vlan 40 on device d. { configure the ports on these devices as...
Page 123
108 # display brief spanning tree information on device a. [devicea] display stp brief vlan port role stp state protection 10 ethernet1/0/1 desi discarding none 10 ethernet1/0/3 desi forwarding none 20 ethernet1/0/1 desi forwarding none 20 ethernet1/0/2 desi forwarding none 20 ethernet1/0/3 desi for...
Page 124
109 figure 33 spanning trees mapped to different vlans.
Page 125
110 configuring bpdu tunneling overview as a layer 2 tunneling technology, bpdu tunneling enables layer 2 protocol packets from geographically dispersed customer networks to be transparently transmitted over specific tunnels across a service provider network. Background dedicated lines are used in a...
Page 126
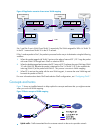
111 • ethernet operation, administration and maintenance (eoam) • garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp) • hw group management protocol (hgmp) • link aggregation control protocol (lacp) • link layer discovery protocol (lldp) • port aggregation protocol (pagp) • per vlan spanning tree (pvst) • spanni...
Page 127
112 figure 35 bpdu tunneling implementation the upper section of figure 35 represents the service provider network (isp network). The lower section, including user a network 1 and user a network 2, represents the customer networks. Enabling bpdu tunneling on edge devices (pe 1 and pe 2) in the servi...
Page 128
113 configuration restrictions and guidelines • settings made in layer 2 ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view take effect only on the current port. Settings made in port group view take effect on all ports in the port group. • before you enable bpdu tunneling for dldp, eoam, g...
Page 129
114 to configure destination multicast mac address for bpdus: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Configure the destination multicast mac address for bpdus. Bpdu-tunnel tunnel-dmac mac-address optional. 0x010f-e200-0003 by default. Note: for bpdus to be recognized, the dest...
Page 130
115 # create vlan 2 and assign ethernet 1/0/1 to vlan 2. [pe1] vlan 2 [pe1-vlan2] quit [pe1] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [pe1-ethernet1/0/1] port access vlan 2 # disable stp on ethernet 1/0/1, and then enable bpdu tunneling for stp on it. [pe1-ethernet1/0/1] undo stp enable [pe1-ethernet1/0/1] bpdu-tun...
Page 131
116 configuration procedure 1. Configure pe 1: # configure the destination multicast mac address for bpdus as 0x0100-0ccd-cdd0. System-view [pe1] bpdu-tunnel tunnel-dmac 0100-0ccd-cdd0 # configure ethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port and assign it to all vlans. [pe1] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [pe1-ethernet...
Page 132
117 configuring vlans overview ethernet is a network technology based on the csma/cd mechanism. Because the medium is shared, collisions and excessive broadcasts are common on ethernet networks. To address the issue, virtual lan (vlan) was introduced to break a lan down into separate vlans. Vlans ar...
Page 133
118 the ethernet ii encapsulation format is used here. Besides the ethernet ii encapsulation format, ethernet also supports other encapsulation formats, including 802.2 llc, 802.2 snap, and 802.3 raw. The vlan tag fields are added to frames encapsulated in these formats for vlan identification. In t...
Page 134
119 • ip subnet • policy • other criteria this chapter covers port-based vlan, mac-based vlan, protocol-based vlan, and ip subnet-based vlan. The port-based vlan implementation is the basis of all other vlan implementations. To use any other vlan implementations, you must configure port-based vlan s...
Page 135
120 configuring basic settings of a vlan interface you can use vlan interfaces to provide layer 3 communication between hosts of different vlans. Vlan interfaces are virtual interfaces used for layer 3 communication between different vlans. They do not exist as physical entities on devices. For each...
Page 136
121 step command remarks 7. Cancel the action of manually shutting down the vlan interface. Undo shutdown optional. By default, a vlan interface is not manually shut down. The vlan interface is up if one or more ports in the vlan is up, and goes down if all ports in the vlan go down. A vlan interfac...
Page 137
122 [switcha] interface vlan-interface 5 [switcha-vlan-interface5] ip address 192.168.0.10 24 [switcha-vlan-interface5] quit # create vlan-interface 10 and configure its ip address as 192.168.1.20/24. [switcha] interface vlan-interface 10 [switcha-vlan-interface10] ip address 192.168.1.20 24 [switch...
Page 138
123 • you can use a nonexistent vlan as the pvid for a hybrid or trunk port but not for an access port. After you use the undo vlan command to remove the vlan that an access port resides in, the pvid of the port changes to vlan 1. The removal of the vlan specified as the pvid of a trunk or hybrid po...
Page 139
124 step command remarks 3. Assign one or a group of access ports to the vlan. Port interface-list by default, all ports belong to vlan 1. To assign an access port (in interface view) or multiple access ports (in port group view) to a vlan: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a ...
Page 140
125 step command remarks 2. Enter interface view or port group view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name u...
Page 141
126 step command remarks 2. Enter interface view or port group view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name u...
Page 142
127 figure 42 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure device a: # create vlan 100, and assign port ethernet 1/0/1 to vlan 100. System-view [devicea] vlan 100 [devicea-vlan100] port ethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-vlan100] quit # create vlan 200, and assign port ethernet 1/0/2 to vlan 200. [devi...
Page 143
128 [devicea-ethernet1/0/3] display vlan 200 vlan id: 200 vlan type: static route interface: not configured description: vlan 0200 name: vlan 0200 tagged ports: ethernet1/0/3 untagged ports: ethernet1/0/2 configuring mac-based vlans introduction to mac-based vlan the mac-based vlan feature assigns h...
Page 144
129 multiple mac address-to-vlan entries, and enable the mac-based vlan feature and dynamic mac-based vlan assignment on the port. Dynamic mac-based vlan assignment uses the following workflows. 1. When the port receives a frame, the port first determines whether the frame is tagged. • if yes, the p...
Page 145
130 • when a port is assigned to the corresponding vlan in a mac address-to-vlan entry, but has not been assigned to the vlan by using the port hybrid vlan command, the port sends packets from the vlan with vlan tags removed. • if you configure both static and dynamic mac-based vlan assignment on th...
Page 146
131 the port trusts the 802.1p priority of incoming packets and your configuration takes effect. For more information about the qos trust dot1p command, see acl and qos command reference. Configuration procedure to configure static mac-based vlan assignment: step command remarks 1. Enter system view...
Page 147
132 step command remarks 6. Enable dynamic mac-based vlan assignment. Mac-vlan trigger enable by default, dynamic mac-based vlan assignment is disabled. When you use the mac-vlan trigger enable command to enable dynamic mac-based vlan assignment, h3c recommends that you configure the vlan precedence...
Page 148
133 mac-based vlan configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 44 : • ethernet 1/0/1 of device a and device c are each connected to a meeting room. Laptop 1 and laptop 2 are used for meetings and might be used in either of the two meeting rooms. • different departments own laptop 1...
Page 149
134 [devicea-vlan100] quit [devicea] vlan 200 [devicea-vlan200] quit # associate the mac address of laptop 1 with vlan 100, and associate the mac address of laptop 2 with vlan 200. [devicea] mac-vlan mac-address 000d-88f8-4e71 vlan 100 [devicea] mac-vlan mac-address 0014-222c-aa69 vlan 200 # configu...
Page 150
135 2. On device a and device c, you can see that vlan 100 is associated with the mac address of laptop 1, and vlan 200 is associated with the mac address of laptop 2. [devicea] display mac-vlan all the following mac vlan addresses exist: s:static d:dynamic mac addr mask vlan id prio state ---------...
Page 151
136 • when you use the mode keyword to configure a user-defined protocol template, do not set etype-id in ethernetii etype etype-id to 0x0800, 0x8137, 0x809b, or 0x86dd. Otherwise, the encapsulation format of the matching packets will be the same as that of the ipv4, ipx, appletalk, and ipv6 packets...
Page 152
137 protocol-based vlan configuration example network requirements in a lab environment, as shown in figure 45 , most hosts run the ipv4 protocol, and the rest of the hosts run the ipv6 protocol for teaching purposes. To avoid interference, isolate ipv4 traffic and ipv6 traffic at layer 2. Figure 45...
Page 153
138 [device] vlan 100 [device-vlan100] protocol-vlan 1 ipv4 [device-vlan100] quit # configure port ethernet 1/0/1 as a hybrid port that forwards packets of vlans 100 and 200 untagged. [device] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [device-ethernet1/0/1] port link-type hybrid [device-ethernet1/0/1] port hybrid vl...
Page 154
139 vlan id protocol index protocol type ====================================================== 100 1 ipv4 200 1 ipv6 interface: ethernet 1/0/2 vlan id protocol index protocol type ====================================================== 100 1 ipv4 200 1 ipv6 configuration guidelines protocol-based vl...
Page 155
140 step command remarks 5. Enter interface view or port group view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name u...
Page 156
141 configuration consideration • create vlans 100 and 200. • associate ip subnets with the vlans. • assign ports to the vlans. Configuration procedure # associate ip subnet 192.168.5.0/24 with vlan 100. System-view [devicec] vlan 100 [devicec-vlan100] ip-subnet-vlan ip 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 [de...
Page 157
142 please wait... Done. [devicec-ethernet1/0/12] quit # associate interface ethernet 1/0/1 with ip subnet-based vlans 100 and 200. [devicec] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [devicec-ethernet1/0/1] port link-type hybrid [devicec-ethernet1/0/1] port hybrid vlan 100 200 untagged please wait... Done. [devicec...
Page 159
144 configuring a super vlan overview super vlan, also called vlan aggregation, was introduced to save ip address space. A super vlan is associated with multiple sub-vlans. You can create a vlan interface for a super vlan and assign an ip address for the vlan interface. However, you cannot create a ...
Page 160
145 configuring a super vlan step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter vlan view. Vlan vlan-id if the specified vlan does not exist, this command creates the vlan first, and then enters vlan view. 3. Configure the vlan as a super vlan. Supervlan not configured by default. 4...
Page 162
147 [sysname-vlan3] port ethernet 1/0/3 ethernet 1/0/4 [sysname-vlan3] quit # create vlan 5, and assign ethernet 1/0/5 and ethernet 1/0/6 to it. [sysname] vlan 5 [sysname-vlan5] port ethernet 1/0/5 ethernet 1/0/6 [sysname-vlan5] quit # configure vlan 10 as the super vlan, and configure vlan 2, vlan ...
Page 163
148 ipv4 subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 description: vlan 0003 name: vlan 0003 tagged ports: none untagged ports: ethernet1/0/3 ethernet1/0/4 vlan id: 5 vlan type: static it is a sub vlan. Route interface: configured ipv4 address: 10.0.0.1 ipv4 subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 description: vlan 0005 name: vla...
Page 164
149 configuring an isolate-user-vlan overview an isolate-user-vlan uses a two-tier vlan structure. In this approach, the following types of vlans, isolate-user-vlan and secondary vlan, are configured on the same device. The following are the characteristics of the isolate-user-vlan implementation: •...
Page 165
150 { configure the downlink ports, for example, the ports connecting device b to hosts in figure 48 , to operate in host mode, so that the downlink ports can be added to the isolate-user-vlan associated with the secondary vlan automatically. For more information about the promiscuous and host mode ...
Page 166
151 step command remarks 9. Configure the uplink port for the isolate-user-vlan. A. Enter layer 2 ethernet or aggregate interface view: interface interface-type interface-number or interface bridge-aggregation interface-number b. Configure the port to operate in promiscuous mode in a specific vlan: ...
Page 167
152 isolate-user-vlan configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 49 : • connect device a to downstream devices device b and device c. • configure vlan 5 on device b as an isolate-user-vlan, assign the uplink port ethernet 1/0/5 to vlan 5, and associate vlan 5 with secondary vlans ...
Page 168
153 # assign downlink ports ethernet 1/0/1 and ethernet 1/0/2 to vlan 3 and vlan 2, respectively, and configure the ports to operate in host mode. [deviceb] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [deviceb-ethernet1/0/1] port access vlan 3 [deviceb-ethernet1/0/1] port isolate-user-vlan host [deviceb-ethernet1/0/1]...
Page 169
154 name: vlan 0005 tagged ports: none untagged ports: ethernet1/0/1 ethernet1/0/2 ethernet1/0/5 vlan id: 2 vlan type: static isolate-user-vlan type : secondary route interface: not configured description: vlan 0002 name: vlan 0002 tagged ports: none untagged ports: ethernet1/0/2 ethernet1/0/5 vlan ...
Page 170
155 configuring a voice vlan overview a voice vlan is configured for voice traffic. After assigning the ports that connect to voice devices to a voice vlan, the system automatically configures quality of service (qos) parameters for voice traffic, to improve the transmission priority of voice traffi...
Page 171
156 automatically identifying ip phones through lldp when you use oui addresses to identify ip phones, the number of oui addresses that can be configured is limited. Additionally, when there are plenty of ip phones in the network, you must configure many oui addresses. If your ip phones support lldp...
Page 172
157 ip phone access methods connecting the host and the ip phone in series as shown in figure 51 , the host is connected to the ip phone, and the ip phone is connected to the device. When the host and the ip phone are connected in series, the host and the ip phone must be assigned to different vlans...
Page 173
158 receiving port to the voice vlan, issues acl rules, and configures the packet precedence. You can configure a voice vlan aging time on the device. The system will remove a port from the voice vlan if no packet is received from the port during the aging time. The system automatically assigns port...
Page 174
159 port link type voice vlan assignment mode support for untagged voice traffic configuration requirements manual yes configure the pvid of the port as the voice vlan and assign the port to the voice vlan. Hybrid automatic no n/a manual yes configure the pvid of the port as the voice vlan and confi...
Page 175
160 table 18 how a voice vlan-enabled port processes packets in security and normal mode voice vlan mode packet type packet processing mode security mode untagged packets if the source mac address of a packet matches an oui address configured for the device, it is forwarded in the voice vlan; otherw...
Page 176
161 step command remarks 2. Enter layer 2 ethernet interface view. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 3. Configure the interface to trust the qos priority settings in incoming voice traffic, but not to modify the cos and dscp values marked for incoming traffic of the voice vlan. Voice vla...
Page 177
162 step command remarks 3. Enable the voice vlan security mode. Voice vlan security enable optional. By default, the voice vlan security mode is enabled. 4. Add a recognizable oui address. Voice vlan mac-address oui mask oui-mask [ description text ] optional. By default, each voice vlan has defaul...
Page 178
163 step command remarks 3. Add a recognizable oui address. Voice vlan mac-address oui mask oui-mask [ description text ] optional. By default, each voice vlan has default oui addresses configured. For the default oui addresses of different vendors, see table 15 . 4. Enter interface view. Interface ...
Page 179
164 configuration procedure to enable lldp to automatically discover ip phones: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enable lldp to automatically discover ip phones. Voice vlan track lldp disabled by default. Important: • when the switch is enabled to automatically discover ...
Page 180
165 to identify the voice vlan advertised by lldp, execute the display lldp local-information command, and examine the med information fields in the command output. The lldp packets that the device send to ip phones carry the priority information, but the cdp packets that the device send to ip phone...
Page 181
166 connected to the ip phone is added to the vlan assigned to the ip phone as an tagged member and added to the vlan assigned to the host as a untagged member. Also, the lldp-med tlvs that the device sends to the ip phone carry information about the vlan assigned to the ip phone, so that the voice ...
Page 182
167 figure 55 network diagram configuration procedure # create vlan 2 and vlan 3. System-view [devicea] vlan 2 to 3 please wait... Done. # set the voice vlan aging time to 30 minutes. [devicea] voice vlan aging 30 # since ethernet 1/0/1 might receive both voice traffic and data traffic at the same t...
Page 183
168 [devicea-ethernet1/0/2] voice vlan mode auto [devicea-ethernet1/0/2] voice vlan 3 enable verifying the configurations # display the oui addresses, oui address masks, and description strings. Display voice vlan oui oui address mask description 0001-e300-0000 ffff-ff00-0000 siemens phone 0003-6b00...
Page 184
169 figure 56 network diagram configuration procedure # configure the voice vlan to operate in security mode. A voice vlan operates in security mode by default. (optional) system-view [devicea] voice vlan security enable # add a recognizable oui address 0011-2200-0000. [devicea] voice vlan mac-addre...
Page 185
170 # display the states of voice vlans. Display voice vlan state maximum of voice vlans: 128 current voice vlans: 1 voice vlan security mode: security voice vlan aging time: 1440 minutes voice vlan enabled port and its mode: port vlan mode cos dscp --------------------------------------------------...
Page 186
171 configuring gvrp the generic attribute registration protocol (garp) provides a generic framework for devices in a switched lan, such as end stations and switches, to register and deregister attribute values. The garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp) is a garp application that registers and dere...
Page 187
172 a garp participant sends join messages when it wishes to declare its attribute values or receives join messages from other garp participants. Join messages fall into joinempty and joinin. A garp participant sends joinempty messages to declare attribute values that it has not registered. It sends...
Page 188
173 • on a garp-enabled network, each port maintains its own hold, join, and leave timers, but only one leaveall timer is maintained on each device. This leaveall timer applies to all ports on the device. • the value ranges for the hold, join, leave, and leaveall timers are dependent on one another....
Page 189
174 field description value attribute event event that the attribute describes • 0x00—leaveall event • 0x01—joinempty event • 0x02—joinin event • 0x03—leaveempty event • 0x04—leavein event • 0x05—empty event attribute value attribute value vlan id for gvrp if the value of the attribute event field i...
Page 190
175 • gvrp configuration made in ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view takes effect on the current interface only; gvrp configuration made in port group view takes effect on all the member ports in the group. • gvrp configuration made on a member port in an aggregation group ta...
Page 191
176 step command remarks 4. Configure the link type of the ports as trunk. Port link-type trunk access by default. For more information about the port link-type trunk command, see layer 2—lan switching command reference. 5. Assign the trunk ports to all vlans. Port trunk permit vlan all by default, ...
Page 192
177 • if you want to restore the default settings of the timers, restore the hold timer first, followed by the join, leave, and leaveall timers. Table 20 dependencies of the garp timers timer lower limit upper limit hold 10 centiseconds no greater than half of the join timer join no less than twice ...
Page 193
178 • device a and device b are connected through their ports ethernet 1/0/1. • enable gvrp and configure the normal registration mode on ports to enable the registration and deregistration of dynamic and static vlan information between the two devices. Figure 59 network diagram configuration proced...
Page 194
179 according to the output, information about vlan 1, static vlan information of vlan 2 on the local device, and dynamic vlan information of vlan 3 on device b are all registered through gvrp. # display the local vlan information that gvrp maintains on port ethernet 1/0/1 of device b. [deviceb] dis...
Page 195
180 [deviceb] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [deviceb-ethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [deviceb-ethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan all # enable gvrp on ethernet 1/0/1, and set the gvrp registration mode to fixed on the port. [deviceb-ethernet1/0/1] gvrp [deviceb-ethernet1/0/1] gvrp registration fixe...
Page 196
181 # configure port ethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port, and assign it to all vlans. [devicea] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-ethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [devicea-ethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan all # enable gvrp on ethernet 1/0/1, and set the gvrp registration mode to forbidden on the ...
Page 197
182 configuring qinq throughout this document, customer network vlans (cvlans), also called inner vlans, refer to the vlans that a customer uses on the private network. Service provider network vlans (svlans), also called outer vlans, refer to the vlans that a service provider uses to carry vlan tag...
Page 198
183 figure 62 typical qinq application scenario as shown in figure 62 , customer network a has cvlans 1 through 10, and customer network b has cvlans 1 through 20. The service provider assigns svlan 3 for customer network a, and assigns svlan 4 for customer network b. When a tagged ethernet frame fr...
Page 199
184 figure 63 single-tagged ethernet frame header and double-tagged ethernet frame header the default maximum transmission unit (mtu) of an interface is 1500 bytes. The size of an outer vlan tag is 4 bytes. H3c recommends that you increase the mtu of each interface on the service provider network to...
Page 200
185 • do not configure qinq on a reflector port. For more information about reflector ports, see network management and monitoring configuration guide. • on a port with basic qinq enabled, you must configure the port to allow packets from its pvid to pass through. On a port with selective qinq enabl...
Page 201
186 • for vlans whose packets are to be transparently transmitted through a port, do not configure vlan mapping for them on the port. For more information about vlan mapping, see " configuring vlan mapping ." configuration procedure to configure vlan transparent transmission: step command remarks 1....
Page 204
189 to configure inner vlan id substitution: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Create a class and enter class view. Traffic classifier classifier-name [ operator and ] by default, the operator of a class is and. 3. Configure a match criterion to match the specified inner ...
Page 205
190 0x8200 and 0x9100 as the cvlan tpid and svlan tpid, respectively. Otherwise, the devices cannot correctly identify tagged frames between them. Configuring the cvlan tpid step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Configure the tpid value for cvlan tags. Qinq ethernet-type cust...
Page 206
191 figure 64 network diagram configuration procedure important: make sure that you have configured the switches in the service provider network to allow qinq packets to pass through. 1. Configure pe 1: { configure ethernet 1/0/1: # configure ethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port and assign it to vlan 100....
Page 207
192 { configure ethernet 1/0/3: # configure ethernet 1/0/3 as a trunk port and assign it to vlan 200. [pe1] interface ethernet 1/0/3 [pe1-ethernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk [pe1-ethernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 200 # configure vlan 200 as the pvid for the port. [pe1-ethernet1/0/3] port trunk p...
Page 208
193 vlan transparent transmission configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 65 : • the two branches of a company, site 1 and site 2, are connected through the service provider network and uses vlans 10 through 50. • pe 1 and pe 2 are edge devices on the service provider network a...
Page 209
194 [pe1] interface ethernet 1/0/2 [pe1-ethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [pe1-ethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 10 to 50 # set the tpid value in the outer vlan tag to 0x8200 on the port. [pe1-ethernet1/0/2] qinq ethernet-type service-tag 8200 [pe1-ethernet1/0/2] quit 2. Configure pe 2: { conf...
Page 210
195 figure 66 network diagram configuration procedure important: make sure that you have configured the switches in the service provider network to allow qinq packets to pass through. 1. Configure pe 1: { configure ethernet 1/0/1: # configure ethernet 1/0/1 as a hybrid port to permit frames of vlan ...
Page 211
196 [pe1-behavior-p200] nest top-most vlan-id 200 [pe1-behavior-p200] quit # create a qos policy named qinq, associate traffic class a10 with traffic behavior p100, and associate traffic class a20 with traffic behavior p200. [pe1] qos policy qinq [pe1-qospolicy-qinq] classifier a10 behavior p100 [pe...
Page 212
197 # create a qos policy named qinq, associate traffic class a10 with traffic behavior p100, and associate traffic class a20 with traffic behavior p200. [pe2] qos policy qinq [pe2-qospolicy-qinq] classifier a10 behavior p100 [pe2-qospolicy-qinq] classifier a20 behavior p200 [pe2-qospolicy-qinq] qui...
Page 213
198 figure 67 network diagram configuration procedure important: be sure that you have configured the switches in the service provider network to allow qinq packets to pass through. 1. Configure pe 1: { configure ethernet 1/0/1: # configure ethernet 1/0/1 as a hybrid port to permit frames of vlan 10...
Page 214
199 [pe1-behavior-p200] nest top-most vlan-id 200 [pe1-behavior-p200] quit # create a qos policy named qinq, associate traffic class a10 with traffic behavior p100, and associate traffic class a20 with traffic behavior p200. [pe1] qos policy qinq [pe1-qospolicy-qinq] classifier a10 behavior p100 [pe...
Page 215
200 # set the tpid value in the outer tag to 0x8200. [pe1-ethernet1/0/2] qinq ethernet-type service-tag 8200 [pe1-ethernet1/0/2] quit 2. Configure pe 2: { configure ethernet 1/0/1: # configure ethernet 1/0/1 as a hybrid port to permit frames of vlan 100 and vlan 200 to pass through untagged. [pe2] i...
Page 216
201 [pe2-classifier-a100] if-match customer-vlan-id 30 [pe2-classifier-a100] if-match service-vlan-id 100 [pe2-classifier-a100] quit # configure traffic behavior t100 to mark matching packets with cvlan 10. [pe2] traffic behavior t100 [pe2-behavior-t100] remark customer-vlan-id 10 [pe2-behavior-t100...
Page 217
202 configuring vlan mapping overview vlan mapping re-marks vlan tagged traffic with new vlan ids. H3c provides the following types of vlan mapping: • one-to-one vlan mapping—replaces one vlan tag with another. You can use one-to-one vlan mapping to sub-classify traffic from a particular vlan for gr...
Page 218
203 figure 68 application scenario of one-to-one and many-to-one vlan mapping to further sub-classify each type of traffic by customer, perform one-to-one vlan mapping on the wiring-closet switches, and assign a separate vlan for each type of traffic from each customer. The required total number of ...
Page 219
204 figure 69 application scenario of two-to-two vlan mapping site 1 and site 2 are in vlan 2 and vlan 3, respectively. The vlan assigned for vpn a is vlan 10 in the sp 1 network and vlan 20 in the sp 2 network. If site 1 sends a packet to site 2, the packet is processed on the way to its destinatio...
Page 220
205 • downlink traffic—traffic transmitted from the service provider network to the customer network. • network-side port—a port connected to or closer to the service provider network. • customer-side port—a port connected to or closer to the customer network. • uplink policy—a qos policy that defin...
Page 221
206 figure 72 many-to-one vlan mapping implementation each dhcp snooping entry contains information about one dhcp client, including its ip address, mac address, and cvlan. For more information about dhcp snooping, see layer 3—ip services configuration guide. Two-to-two vlan mapping implement two-to...
Page 222
207 configuring one-to-one vlan mapping perform one-to-one vlan mapping on wiring-closet switches (see figure 68 ) to isolate traffic by both user and traffic type. Perform these tasks to configure one-to-one vlan mapping: task description configuring an uplink policy creates cvlan-to-svlan mappings...
Page 224
209 configuring the network-side port step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter interface view or port group view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name • enter layer 2 a...
Page 225
210 task description configuring the network-side port configures vlan and other settings required for many-to-one vlan mapping (required). Configuration prerequisites before configuring many-to-one vlan mapping: • make sure that all home users obtain ip addresses through dhcp. For how to assign ip ...
Page 226
211 step command remarks 4. Return to system view. Quit 5. Create a traffic behavior and enter traffic behavior view. Traffic behavior behavior-name repeat these steps to configure one behavior for each svlan. 6. Configure an svlan marking action. Remark service-vlan-id vlan-id 7. Return to system v...
Page 227
212 configuring the network-side port step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter interface view. • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number n/a 3. ...
Page 228
213 task description configuring an uplink policy for the network-side port replaces foreign cvlans with local cvlans for uplink traffic (required). Configuring a downlink policy for the customer-side port replaces local svlans and cvlans with foreign svlans and cvlans (required). Configuring the cu...
Page 229
214 step command remarks 2. Create a class and enter class view. Traffic classifier tcl-name [ operator and ] repeat these steps to create one class for each local svlan and foreign cvlan pair. 3. Specify a foreign cvlan as a match criterion. If-match customer-vlan-id vlan-id 4. Specify a local svla...
Page 230
215 step command remarks 11. Associate the class with the behavior. Classifier tcl-name behavior behavior-name repeat this step to create other class-behavior associations. Configuring the customer-side port step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter interface view or port g...
Page 231
216 step command remarks 3. Configure the link type of the port. • configure the port as a trunk port: port link-type trunk • configure the port as a hybrid port: port link-type hybrid use one of the commands. The default link type of an ethernet port is access. 4. Assign the port to all svlans. • a...
Page 232
217 figure 74 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure switch a: # create the cvlans and the svlans. System-view [switcha] vlan 2 to 3 [switcha] vlan 101 to 102 [switcha] vlan 201 to 202 [switcha] vlan 301 to 302 # configure uplink policies p1 and p2 to enable one svlan to transmit one s...
Page 233
218 [switcha-classifier-c1] traffic classifier c2 [switcha-classifier-c2] if-match customer-vlan-id 2 [switcha-classifier-c2] traffic classifier c3 [switcha-classifier-c3] if-match customer-vlan-id 3 [switcha-classifier-c3] quit [switcha] traffic behavior b1 [switcha-behavior-b1] remark service-vlan...
Page 234
219 [switcha-behavior-b33] quit [switcha] qos policy p11 [switcha-policy-p11] classifier c11 behavior b11 [switcha-policy-p11] classifier c22 behavior b22 [switcha-policy-p11] classifier c33 behavior b33 [switcha-policy-p11] quit [switcha] qos policy p22 [switcha-policy-p22] classifier c44 behavior ...
Page 235
220 [switchc-vlan301] vlan 102 [switchc-vlan102] arp detection enable [switchc-vlan102] vlan 202 [switchc-vlan202] arp detection enable [switchc-vlan202] vlan 302 [switchc-vlan302] arp detection enable [switchc-vlan302] vlan 103 [switchc-vlan103] arp detection enable [switchc-vlan103] vlan 203 [swit...
Page 236
221 [switchc-policy-p1] classifier c1 behavior b1 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation [switchc-policy-p1] classifier c2 behavior b2 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation [switchc-policy-p1] classifier c3 behavior b3 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation [switchc-policy-p1] quit [switchc] qos policy p2 [switchc-policy-p2] class...
Page 237
222 two-to-two vlan mapping configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 75 , two vpn a branches, site 1 and site 2, are in vlan 10 and vlan 30, respectively. The two site use different vpn access services of different service providers, sp 1 and sp 2. Sp 1 assigns vlan 100 for site...
Page 238
223 3. Configure pe 3: # configure an uplink policy down_uplink for customer-side port ethernet 1/0/1 to substitute svlan id 200 for the svlan id in the incoming traffic tagged with cvlan 10 and svlan 100. System-view [pe3] traffic classifier down_uplink [pe3-classifier-down_uplink] if-match custome...
Page 239
224 # set network-side port ethernet 1/0/2 as a trunk port, assign it to vlan 200, and apply uplink policy up_uplink to the outgoing traffic on the port. [pe3] interface ethernet 1/0/2 [pe3-ethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [pe3-ethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 200 [pe3-ethernet1/0/2] qos app...
Page 240
225 configuring lldp overview background in a heterogeneous network, a standard configuration exchange platform ensures that different types of network devices from different vendors can discover one another and exchange configuration for the sake of interoperability and management. The ietf drafted...
Page 241
226 field description source mac address mac address of the sending port. If the port does not have a mac address, the mac address of the sending bridge is used. Type ethernet type for the upper layer protocol. It is 0x88cc for lldp. Data lldpdu. Fcs frame check sequence, a 32-bit crc value used to ...
Page 242
227 tlvs tlvs are type, length, and value sequences that carry information elements. The type field identifies the type of information, the length field measures the length of the information field in octets, and the value field contains the information itself. Lldpdu tlvs fall into the following ca...
Page 243
228 type description protocol identity indicates protocols supported on the port. An lldpdu can carry multiple different tlvs of this type. Note: • h3c devices support only receiving protocol identity tlvs. • layer 3 ethernet ports do not support ieee 802.1 organizationally specific tlvs. 3. Ieee 80...
Page 244
229 type description extended power-via-mdi allows a network device or terminal device to advertise power supply capability. This tlv is an extension of the power via mdi tlv. Hardware revision allows a terminal device to advertise its hardware version. Firmware revision allows a terminal device to ...
Page 245
230 this is the fast sending mechanism of lldp. With this mechanism, a specific number of lldpdus are sent successively at 1-second intervals, to help lldp neighbors discover the local device as soon as possible. Then, the normal lldpdu transmit interval resumes. Receiving lldpdus an lldp-enabled po...
Page 246
231 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enable lldp globally. Lldp enable by default, lldp is globally enabled. 3. Enter ethernet interface view or port group view. • enter layer 2/layer 3 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter port group...
Page 247
232 enabling lldp polling with lldp polling enabled, a device periodically searches for local configuration changes. On detecting a configuration change, the device sends lldpdus to inform neighboring devices of the change. To enable lldp polling: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-vi...
Page 248
233 configuring the management address and its encoding format lldp encodes management addresses in numeric or character string format in management address tlvs. By default, management addresses are encoded in numeric format. If a neighbor encoded its management address in character string format, ...
Page 249
234 as the expression shows, the ttl can be up to 65535 seconds. Ttls greater than 65535 will be rounded down to 65535 seconds. Configuration restrictions and guidelines • to make sure that lldp neighbors can receive lldpdus to update information about the current device before it ages out, configur...
Page 250
235 step command remarks 2. Enter ethernet interface view or port group view. • enter layer 2/layer 3 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name use either command. 3. Set the encapsulation format for lldpdus to snap....
Page 251
236 information a bout the display lldp neighbor-information command, see layer 2—lan switching command reference. To make your device work with cisco ip phones, you must enable cdp compatibility. If your lldp-enabled device cannot recognize cdp packets, it does not respond to the requests of cisco ...
Page 252
237 step command remarks 4. Configure cdp-compatible lldp to operate in txrx mode. Lldp compliance admin-status cdp txrx disable mode by default. Configuring lldp trapping lldp trapping notifies the network management system (nms) of events such as newly-detected neighboring devices and link malfunc...
Page 254
239 # enable lldp on ethernet1/0/1. (you can skip this step because lldp is enabled on ports by default.) set the lldp operating mode to tx. [switchb] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [switchb-ethernet1/0/1] lldp enable [switchb-ethernet1/0/1] lldp admin-status tx [switchb-ethernet1/0/1] quit 3. Verify the ...
Page 255
240 [switcha] display lldp status global status of lldp: enable the current number of lldp neighbors: 1 the current number of cdp neighbors: 0 lldp neighbor information last changed time: 0 days,0 hours,5 minutes,20 seconds transmit interval : 30s hold multiplier : 4 reinit delay : 2s transmit delay...
Page 256
241 figure 80 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure a voice vlan on switch a: # create vlan 2. System-view [switcha] vlan 2 [switcha-vlan2] quit # set the link type of ethernet 1/0/1 and ethernet 1/0/2 to trunk and enable voice vlan on them. [switcha] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [switcha...
Page 257
242 platform : cisco ip phone 7960 duplex : full cdp neighbor-information of port 2[ethernet1/0/2]: cdp neighbor index : 2 chassis id : sep00141cbcdbff port id : port 1 sofrware version : p0030301mfg2 platform : cisco ip phone 7960 duplex : full as the sample output shows, switch a has discovered th...
Page 258
243 configuring a service loopback group overview to increase traffic redirecting throughput, you can bundle multiple ethernet ports of a device together to increase bandwidth and implement load sharing. These ports that act as a logical link form a service loopback group. A service loopback group m...
Page 259
244 figure 81 setting the state of each member port in a service loopback group note: every time a new port is assigned to a service loopback group, the system resets the state of the member ports in the service loopback group according to the process described previously. Configuration restrictions...
Page 260
245 step command remarks 4. Assign the ethernet interface to the specified service loopback group. Port service-loopback group number by default, a port does not belong to any service loopback group. You can configure this command on different ports to assign multiple ports to a service loopback gro...
Page 261
246 [devicea-ethernet1/0/3] undo ndp enable [devicea-ethernet1/0/3] port service-loopback group 1 [devicea-ethernet1/0/3] quit # create logical interface tunnel 1 and reference service loopback group 1 on tunnel 1. [devicea] interface tunnel 1 [devicea-tunnel1] service-loopback-group 1.
Page 262
247 configuring mvrp overview multiple registration protocol (mrp) is an attribute registration protocol and transmits attribute messages. Multiple vlan registration protocol (mvrp) is a typical mrp application. Mvrp propagates and learns vlan configuration among devices. Mvrp enables a device to pr...
Page 263
248 mvrp registers and deregisters vlan attributes as follows: • when a port receives the declaration of a vlan attribute, the port registers the vlan and joins the vlan. • when a port receives the withdrawal of a vlan attribute, the port deregisters the vlan and leaves the vlan. Figure 82 shows a s...
Page 264
249 mrp timers the implementation of mrp uses the following timers to control mrp message transmission. • periodic timer on startup, an mrp participant starts its own periodic timer to control mrp message transmission. The mrp participant collects the mrp messages to be sent before the periodic time...
Page 265
250 • fixed an mvrp participant in fixed registration mode disables deregistering dynamic vlans, sends declarations for dynamic vlans and static vlans, and drops received mvrp protocol packets. As a result, an mvrp participant port in fixed registration mode does not deregister or register dynamic v...
Page 266
251 duplicates. For more information about port mirroring, see network management and monitoring configuration guide. • enabling mvrp on a layer 2 aggregate interface enables both the aggregate interface and all selected member ports in the link aggregation group to participate in dynamic vlan regis...
Page 268
253 table 28 dependencies of the join, leave, and leaveall timers timer lower limit upper limit join 20 centiseconds half the leave timer leave twice the join timer leaveall timer leaveall leave timer on each port 32760 centiseconds note: you can restore the periodic timer to the default at any time...
Page 270
255 figure 83 network diagram configuration procedure configuring device a # enter mst region view. System-view [devicea] stp region-configuration # configure the mst region name, vlan-to-instance mappings, and revision level. [devicea-mst-region] region-name example [devicea-mst-region] instance 1 ...
Page 271
256 # globally enable mvrp. [devicea] mvrp global enable # configure port ethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port, and configure it to permit all vlans. [devicea] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-ethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [devicea-ethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan all # enable mvrp on port eth...
Page 272
257 [deviceb] mvrp global enable # configure port ethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port, and configure it to permit vlans 20 and 40. [deviceb] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [deviceb-ethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [deviceb-ethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 20 40 # enable mvrp on port ethernet 1/0/1. [de...
Page 273
258 # configure port ethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port, and configure it to permit all vlans. [devicec] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [devicec-ethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [devicec-ethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan all # enable mvrp on port ethernet 1/0/1. [devicec-ethernet1/0/1] mvrp enable [dev...
Page 274
259 [deviced-ethernet1/0/2] quit verifying the configuration 1. Verify the normal registration mode configuration: use the display mvrp running-status command to display the local mvrp vlan information to verify whether the configuration takes effect. # check the local vlan information on device a. ...
Page 275
260 # check the local vlan information on device b. [deviceb] display mvrp running-status -------[mvrp global info]------- global status : enabled compliance-gvrp : false ----[ethernet1/0/1]---- config status : enabled running status : enabled join timer : 20 (centiseconds) leave timer : 60 (centise...
Page 276
261 ----[ethernet1/0/1]---- config status : enabled running status : enabled join timer : 20 (centiseconds) leave timer : 60 (centiseconds) periodic timer : 100 (centiseconds) leaveall timer : 1000 (centiseconds) registration type : normal local vlans : 1(default), 10, 20, ----[ethernet1/0/2]---- co...
Page 277
262 periodic timer : 100 (centiseconds) leaveall timer : 1000 (centiseconds) registration type : normal local vlans : 1(default), the output shows that: { port ethernet 1/0/1 has learned vlan 1 and dynamic vlan 20 created on device b through mvrp. { port ethernet1/0/2 has learned only vlan 1 through...
Page 278
263 leave timer : 60 (centiseconds) periodic timer : 100 (centiseconds) leaveall timer : 1000 (centiseconds) registration type : fixed local vlans : 1(default), 10, the output shows that the dynamic vlan information on ethernet 1/0/3 is not changed after you set the mvrp registration mode to fixed o...
Page 279
264 index a b c d e g i l m o p q r s v a assigning a port to the isolation group, 59 b bpdu tunneling configuration examples, 114 c configuration example for mvrp in normal registration mode, 254 configuration guidelines, 21 configuration prerequisites, 250 configuring a device to advertise voice v...
Page 280
265 displaying and maintaining ethernet link aggregation, 51 displaying and maintaining gvrp, 177 displaying and maintaining isolate-user-vlan, 151 displaying and maintaining lldp, 237 displaying and maintaining loopback and null interfaces, 19 displaying and maintaining mac address tables, 29 displ...
Page 281
266 vlan mapping configuration examples, 216 vlan mapping configuration tasks, 206 voice vlan configuration examples, 166.