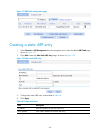
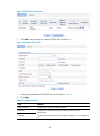
- DL manuals
- H3C
- Wireless Access Point
- WA2610E-AGN
- Web-based Configuration Manual
H3C WA2610E-AGN Web-based Configuration Manual
Summary of WA2610E-AGN
Page 1
H3c wa series access points web-based configuration guide hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Http://www.H3c.Com document version: 6w106-20130802.
Page 2
Copyright © 2003-2013, hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. And its licensors all rights reserved no part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Trademarks h3c, , h3cs, h3cie, h3cne, aolynk, , h ...
Page 3
Preface the h3c wa series access points web-based configuration guide describes the web functions of the wa series, such as quick start, web overview, wireless service configuration, security and authentication related configurations, qos configuration, and advanced settings. Note: • the grayed out ...
Page 4
Symbols convention description warning an alert that calls attention to important information that if not understood or followed can result in personal injury. Caution an alert that calls attention to important information that if not understood or followed can result in data loss, data corruption, ...
Page 5
Category documents purposes your ap. Configuration guides describe software features and configuration procedures. Command references provide a quick reference to all available commands. Operations and maintenance release notes provide information about the product release, including the version his...
Page 6
I contents about the wa series access points web-based configuration guide ····································································· 1 applicable models and software versions ·················································································································...
Page 7
Ii log management configuration ································································································································ 43 displaying syslog ······················································································································...
Page 8
Iii vlan configuration ··················································································································································· 94 overview ·····················································································································...
Page 9
Iv adding a domain name suffix ···································································································································· 136 clearing dynamic dns cache ·········································································································...
Page 10
V recommended configuration procedure ··········································································································· 194 configuring an isp domain ····························································································································...
Page 11
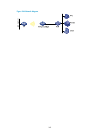
Vi workgroup bridge mode overview ··························································································································· 264 configuring wireless service ·············································································································...
Page 12
Vii configuration procedure ···································································································································· 365 configuring a qos policy ··············································································································...
Page 13
Viii configuring band navigation ····························································································································· 417 configuring multicast optimization ······································································································...
Page 14
1 about the wa series access points web-based configuration guide the h3c wa series access points web-based configuration guide describes the software features for the h3c wa series access points and guide you through the software configuration procedures. These configuration guides also provide con...
Page 15
2 table 2 feature matrix module feature wa2600 series wa3600 series device optical ethernet interface supported on the wa2620x-agnp not supported. Device maintenance the "file type" and "if a file with the same name already exists, overwrite it without any prompt" options in software upgrade are sup...
Page 16
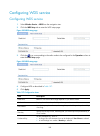
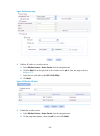
3 quick start the quick start wizard leads you through basic configuration procedures to quickly make your device available for use. Quick start wizard home page from the navigation tree, select quick start to enter the home page of the quick start wizard. Figure 1 home page of the quick start wizar...
Page 17
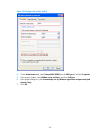
4 figure 2 basic configuration page 2. Configure the parameters as described in table 3 . Table 3 configuration items item description system name specify the name of the current device. By default, the system name of the device is the device model. Country/region code select the code of the country...
Page 18
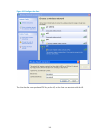
5 figure 3 admin configuration page 2. Configure the parameters as described in table 4 . Table 4 configuration items item description password specify the password for user admin to use to log into the device, in cipher text. Confirm password enter the password again to confirm the password. Passwo...
Page 19
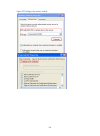
6 figure 4 ip configuration page 2. Configure the parameters as described in table 5 . Table 5 configuration items item description ip address specify the ip address of vlan-interface 1. This ip address is used for logging in to the device. By default, the ip address of vlan-interface 1 is 192.168.0...
Page 20
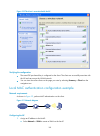
7 figure 5 wireless configuration page 2. Configure the parameters as described in table 6 . Table 6 configuration items item description primary service authentication type select the authentication type for the wireless service, which can be: • none—performs no authentication. • user authenticatio...
Page 21
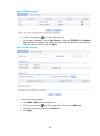
8 figure 6 radius configuration page 4. Configure the parameters as described in table 7 . Table 7 configuration items item description service type select the type of the radius server. Two types are available: standard and enhanced: • extended—specifies extended radius server, which is usually an ...
Page 22
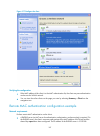
9 encryption configuration select the encrypt box on the wireless configuration page to enter the encryption configuration page shown in figure 7 . Figure 7 encryption configuration page table 8 configuration items item description provide key automatically specify whether to use wep keys provided a...
Page 23
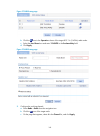
10 item description key id select the wep key index, which can be 1, 2, 3, or 4. Each number represents one of the four static keys of wep. The selected key index is used for frame encryption and decryption. Important: if you enable provide key automatically, the available key id ranges from 1 to 3....
Page 24
11 item description preshared key type • pass-phrase—enter a psk in the form of a character string. You should enter a string that can be displayed and is of 8 to 63 characters. • raw-key—enter a psk in the form of a hexadecimal number. You must enter a valid 64-bit hexadecimal number. Preshared key...
Page 25
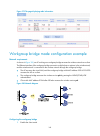
12 configuration summary 1. On the radio configuration page, click next. The configuration summary page appears, displaying all configurations you have made. 2. Click finish to complete your configurations. Figure 10 configuration summary page quick start configuration examples the wireless access m...
Page 26
13 • the ap provides a plain-text wireless service with ssid service. • 802.11n (2.4 ghz) is adopted to inter-work with the existing 802.11g network and meet the high bandwidth requirement. Figure 11 network diagram configuring the ap 1. Perform basic configurations: a. From the navigation tree, sel...
Page 27
14 figure 13 radio configuration page 3. Check and apply the configurations: click next to enter the configuration summary page. If you want to modify certain configurations, click back to return to the previous pages; if the configurations are correct, click finish to apply the configurations. Veri...
Page 28
15 figure 14 network diagram configuring the ap 1. Perform basic configurations: from the navigation tree, select quick start to enter the home page of the quick start wizard. Configure time parameters, login password, and login ip address as needed. 2. Configure wireless service: a. On the ip confi...
Page 29
16 figure 16 encryption configuration page e. Click next to enter the radio configuration page. F. To perform radio configuration: select the 802.11n(2.4ghz) box, and bind wireless service wep to the 802.11n (2.4 ghz) radio. Use default settings for other parameters. G. Click next. Figure 17 radio c...
Page 30
17 click next to enter the configuration summary page. If you want to modify certain configurations, click back to return to the previous pages; if the configurations are correct, click finish to apply the configurations. Verifying the configuration • launch the wireless client, and refresh the netw...
Page 31
18 figure 19 wireless configuration page c. Click next to enter the encryption configuration page. D. To perform encryption configuration: select aes-ccmp for encryption mode. Select wpa2 for security ie. Select pass-phrase from the preshared key type list. Enter the preshared key 12345678. Figure 2...
Page 32
19 use default settings for other parameters. G. Click next. Figure 21 radio configuration page 3. Check and apply the configurations: click next to enter the configuration summary page. If you want to modify certain configurations, click back to return to the previous pages; if the configurations a...
Page 33
20 summary device information you can view the following information on the device info menu: • device information • system resource state • device interface information • recent system logs (at most five) after logging in to the web interface, you enter the summary > device page. Figure 22 device i...
Page 34
21 select a refresh mode in the refresh period list. • if you select a specific refresh period (for example, 1 minute), the system periodically refreshes the device info page according to the selected refresh period; • if you select manual, click refresh to refresh the page. Device info table 11 con...
Page 35
22 item description status display interface status. • —the interface is up and is connected. • —the interface is up, but not connected. • —the interface is down. To know more information about device interfaces, click the more hyperlink under the device interface information area to enter the devic...
Page 36
23 figure 23 displaying detailed information about wlan service (clear type) table 15 field description field description service template number service template number. Ssid service set identifier (ssid) for the ess. Service template type service template type. Authentication method type of authen...
Page 37
24 figure 24 displaying detailed information about wlan service (crypto type) table 16 field description field description service template number service template number. Ssid ssid provided by the ap. Service template type service template type. Security ie security ie: wpa or wpa2 (rsn) authentica...
Page 38
25 field description maximum clients per bss maximum number of associated clients per bss. Displaying statistics of wlan service figure 25 displaying wlan service statistics displaying connection history information of wlan service figure 26 displaying the connection history information of wlan serv...
Page 39
26 displaying radio displaying wlan services bound to a radio select summary > radio from the navigation tree, click the specified radio unit, and select the wireless service tab to view the wlan services bound to the radio. Figure 27 displaying wlan services bound to the radio the noise floor item ...
Page 40
27 figure 28 displaying detailed radio information table 17 field description field description wlan-radio1/0/1 current state link state of wlan-radio1/0/1. Ip packet frame type output frame encapsulation type. Hardware address mac address of the radio interface. Radio-type interface radio type, whi...
Page 41
28 field description ht protection mode 802.11n protection modes: • no protection mode(0)—the clients associated with the ap, and the wireless devices within the coverage of the ap operate in 802.11n mode, and all the clients associated with the ap operate in either 40 mhz or 20 mhz mode. • non-memb...
Page 42
29 field description output: 3436 packets, 492500 bytes : 3016 unicasts, 424408 bytes : 320 multicasts/broadcasts, 42994 bytes : 100 others, 25098 bytes : 0 fragmented : 948 discarded, 100690 bytes : 0 failed rts, 1331 failed ack : 4394 transmit retries, 1107 multiple transmit retries output packet ...
Page 43
30 field description signal quality —if the signal strength indicator is represented by no signal bar, it indicates that rssi=0. —if the signal strength indicator is represented by one signal bar at the leftmost, it indicates that 0 —if the signal strength indicator is represented by two signal bars...
Page 44
31 table 19 field description field description mac address mac address of the client. Aid association id of the client. User name username of the client: • the field is displayed as -na- if the client adopts plain-text authentication or cipher-text authentication with no username. • the field is ir...
Page 45
32 field description client type client type such as wpa2 (rsn), wpa, or pre-rsn. Authentication method authentication method such as open system or shared key. Akm method akm suite used such as dot1x or psk. 4-way handshake state display the 4-way handshake state: • idle—displayed in initial state....
Page 46
33 figure 31 displaying client statistics note: to view the ip address of the client, enable the arp snooping function in system view through command lines. By default, the arp snooping function is disabled, and na is displayed in the ip address column. Table 21 field description field description a...
Page 47
34 displaying rf ping information radio frequency ping (rf ping) is a ping function performed on wireless links. This function enables you to get the connection information between the ap and its associated clients, such as signal strength, packet re-transmission attempts, and round trip time (rtt)....
Page 48
35 device basic information configuration the device basic information feature provides you the following functions: • set the system name of the device. The configured system name will be displayed on the top of the navigation bar. • set the idle timeout period for a logged-in user. The system logs...
Page 49
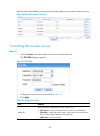
36 figure 34 configuring web idle timeout period 3. Set the web idle timeout period for a logged-in user. 4. Click apply..
Page 50
37 device maintenance configuration software upgrade a boot file, also known as the system software or device software, is an application file used to boot the device. Software upgrade allows you to obtain a target application file from the local host and set the file as the boot file to be used at ...
Page 51
38 item description file type specify the type of the boot file for the next boot: • main—boots the device. • backup—boots the device when the main boot file is unavailable. Important: support for this option depends on your device model. For more information, see "feature matrix." if a file with th...
Page 52
39 if you have selected the box before "check configuration with next startup configuration file", the system checks the configuration before rebooting the device. If the check succeeds, the system reboots the device; if the check fails, the system displays a dialog box to inform you that the curren...
Page 53
40 note: • the generation of the diagnostic file will take a period of time. During this process, do not perform any operation on the web page. • to view this file after the diagnostic file is generated successfully, select device > file management, or download this file to the local host. For more ...
Page 54
41 system time configuration you must configure a correct system time so that the device can work with other devices properly. The device supports setting system time through manual configuration and automatic synchronization of ntp server time. An administrator cannot keep time synchronized among a...
Page 55
42 configuring the system time 1. Select device > system time from the navigation tree. The calendar page appears. Figure 40 calendar page 2. Configure the system time as described in table 24 . 3. Click apply. Table 24 configuration items item description automatic synchronizat ion ntp server 1. En...
Page 56
43 log management configuration system logs contain a large amount of network and device information, including running status and configuration changes. System logs are an important way for administrators to know network and device status. With system log information, administrators can take corres...
Page 57
44 tip: • you can click reset to clear all system logs saved in the log buffer on the web interface. • you can click refresh to manually refresh the page, or you can set the refresh interval on the log setup page to enable the system to automatically refresh the page periodically. For more informati...
Page 58
45 figure 42 set loghost 3. Configure the log host as described in table 26 . 4. Click apply. Table 26 configuration item item description loghost ip/domain set the ipv4 address, domain name or ipv6 address of the loghost. You can specify up to four loghosts. Setting buffer capacity and refresh inte...
Page 59
46 figure 43 syslog configuration page 3. Configure buffer capacity and refresh interval as described in table 27 . 4. Click apply. Table 27 configuration items item description buffer capacity set the number of logs that can be stored in the log buffer. Refresh interval set the refresh period on th...
Page 60
47 configuration management backing up configuration note: when backing up a configuration file, back up the configuration file with the extension .Xml. Otherwise some configuration information may not be restored in some cases (for example, when the configuration is removed). Configuration backup p...
Page 61
48 the page for restoring configuration appears. Figure 45 configuration restore page 3. Click the upper browse button. The file upload dialog box appears. You can select the .Cfg file to be uploaded. 4. After you click the lower browse button. The file upload dialog box appears. You can select the ...
Page 62
49 figure 46 save configuration confirmation common 1. Select device > configuration from the navigation tree. 2. Click the save tab. The page in figure 46 appears. 3. Click save current settings to save the current configuration to the configuration file. Initializing configuration this operation r...
Page 63
50 file management configuration the device saves useful files (such as host software, configuration file) into the storage device, and the system provides the file management function for the users to manage those files conveniently and effectively. Displaying file list 1. Select device > file mana...
Page 64
51 the file download dialog box appears. You can select to open the file or to save the file to a specified path. Uploading a file note: uploading a file takes some time. H3c recommends you to not perform any operation on the web interface during the upgrading procedure. 1. Select device > file mana...
Page 65
52 interface management configuration note: support for interface types varies with device models. An interface is the point of interaction or communication used for exchanging data between entities. There are two types of interfaces: physical and logical. A physical interface refers to an interface...
Page 66
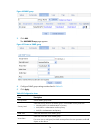
53 figure 49 interface management page 2. Click an interface name in the name column to display the statistics of that interface. The page for displaying interface statistics appears. Figure 50 statistics on an interface.
Page 67
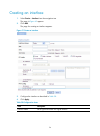
54 creating an interface 1. Select device > interface from the navigation tree the page in figure 49 appears. 2. Click add. The page for creating an interface appears. Figure 51 create an interface 3. Configure the interface as described in table 28 . 4. Click apply. Table 28 configuration items ite...
Page 68
55 item description vid this parameter is available only for layer 3 ethernet subinterfaces. If you are creating a layer 3 ethernet subinterface, set the vlans associated with the subinterface. Important: this configuration item is not configurable because the device does not support layer 3 etherne...
Page 69
56 item description ipv6 config set the way for the interface to obtain an ipv6 link-local address, including: • none: select this option if you do not want to assign an ipv6 link-local address to the interface. • auto: select this option for the system to automatically assign an ipv6 link-local add...
Page 70
57 table 29 configuration items item description port state enables or disables the interface. In some cases, modification to the interface parameters does not take effect immediately. You need to shut down and then bring up the interface to make the modification work. Speed set the transmission rat...
Page 71
58 item description mdi set the medium dependent interface (mdi) mode for the interface. Two types of ethernet cables can be used to connect ethernet devices: crossover cable and straight-through cable. To accommodate these two types of cables, an ethernet interface on the device can operate in one ...
Page 72
59 item description multicast suppression set multicast suppression. You can suppress multicast traffic by percentage or by pps as follows: • ratio: sets the maximum percentage of multicast traffic to the total transmission capability of an ethernet interface. When this option is selected, you need ...
Page 73
60 figure 53 modify a layer 3 physical interface 3. Modify the information about the layer 3 interface. The configuration items of modifying the layer 3 interface are similar to those of creating an interface. Table 31 describes configuration items proper to modifying a layer 3 interface. 4. Click a...
Page 74
61 item description interface status display and set the interface status. • the display of connected indicates that the current status of the interface is up and connected. You can click disable to shut down the interface. • the display of not connected indicates that the current status of the inte...
Page 75
62 figure 55 create vlan-interface 100 c. Select vlan-interface from the interface name list, enter the interface id 100, select the static address option in the ip config area, enter the ip address 10.1.1.2, and select 24 (255.255.255.0) from the mask list. D. Click apply..
Page 76
63 tr-069 configuration tr-069 is a technology specification initiated and developed by the digital subscriber's line (dsl) forum. It defines the general frame, message format, management method, and data model for the management and configuration of home network devices in the next-generation netwo...
Page 77
64 1. Select device > tr-069 from the navigation tree. The tr-069 configuration page appears. Figure 57 tr-069 configuration page 2. Configure tr-069 parameters described in table 32 . 3. Click apply. Table 32 configuration items item description tr-069 enable or disable tr-069. Tr-069 configuration...
Page 78
65 configuration guidelines when you configure tr-069, follow these guidelines: • tr-069 configuration through acs is of higher priority than that through the web interface. You cannot use a configuration mode to modify parameters configured through a configuration mode with a higher priority. • to ...
Page 79
66 user management configuration in the user management part, you can perform the following configuration: • create a local user, and set the password, access level, and service type for the user. • set the super password for switching the current web user level to the management level. • switch the...
Page 80
67 item description access level set the access level for a user. Users of different levels can perform different operations. Web user levels, from low to high, are visitor, monitor, configure, and management. • visitor: users of visitor level can perform the ping and traceroute operations, but they...
Page 81
68 table 34 configuration items item description create/remove set the operation type: • create: configure or modify the super password. • remove: remove the current super password. Password set the password for a user to switch to the management level. Confirm password enter the same password again...
Page 82
69 snmp configuration snmp overview simple network management protocol (snmp) offers the communication rules between a management device and the managed devices on the network; it defines a series of messages, methods and syntaxes to implement the access and management from the management device to ...
Page 83
70 table 35 snmpv1 or snmpv2c configuration task list task remarks enabling snmp required the snmp agent function is disabled by default. Important: if snmp is disabled, all snmp-related configurations are removed. Configuring an snmp view optional after creating snmp views, you can specify an snmp ...
Page 84
71 enabling snmp 1. Select device > snmp from the navigation tree. The snmp configuration page appears. Figure 61 setup page 2. Configure snmp settings on the upper part of the page as described in table 37 . 3. Click apply..
Page 85
72 table 37 configuration items item description snmp enable or disable snmp agent. Local engine id configure the local engine id. The validity of a user after it is created depends on the engine id of the snmp agent. If the engine id when the user is created is not identical to the current engine i...
Page 86
73 figure 63 create an snmp view (1) 4. Enter the view name. 5. Click apply. The page in figure 64 appears. Figure 64 create an snmp view (2) 6. Configure the parameters as described in table 38 . 7. Click add. 8. Repeat steps 6 and 7 to add more rules for the snmp view. 9. Click apply. To cancel th...
Page 87
74 adding rules to an snmp view 1. Select device > snmp from the navigation tree. 2. Click the view tab. The page in figure 62 appears. 3. Click the icon of the target view. The add rule for the view viewdefault window appears. Figure 65 add rules to an snmp view 4. Configure the parameters as descr...
Page 88
75 figure 67 create an snmp community 4. Configure snmp community settings as described in table 39 . 5. Click apply. Table 39 configuration items item description community name set the snmp community name. Access right configure snmp nms access right. • read only: the nms can perform read-only ope...
Page 89
76 figure 68 snmp group 3. Click add. The add snmp group page appears. Figure 69 create an snmp group 4. Configure snmp group settings as described in table 40 . 5. Click apply. Table 40 configuration items item description group name set the snmp group name. Security level select the security level...
Page 90
77 item description notify view select the notify view of the snmp group, that is, the view that can send trap messages. If no notify view is configured, the agent does not send traps to the nms. Acl associate a basic acl with the group to restrict the source ip address of snmp packets, that is, you...
Page 91
78 figure 71 create an snmp user 4. Configure snmp user settings as described in table 41 . 5. Click apply. Table 41 configuration items item description user name set the snmp user name. Security level select the security level for the snmp group. The available security levels are: • noauth/nopriv:...
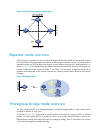
Page 92
79 item description authentication password set the authentication password when the security level is auth/nopriv or auth/priv. The confirm authentication password must be the same with the authentication password.. Confirm authentication password privacy mode select a privacy mode (including des56...
Page 93
80 figure 73 add a target host of snmp traps 6. Configure the settings for the target host as described in table 42 . 7. Click apply. Table 42 configuration items item description destination ip address set the destination ip address or domain name. Select the ip address type: ipv4/domain or ipv6, a...
Page 94
81 displaying snmp packet statistics select device > snmp from the navigation tree. The page for displaying snmp packet statistics appears. Figure 74 snmp packet statistics snmp configuration example network requirements the nms connects to the agent, an ap, through an ethernet. The ip address of th...
Page 95
82 a. Select device > snmp from the navigation tree. The setup page appears. Figure 76 enable snmp b. Select the enable option. C. Select the v3 box. D. Click apply. 2. Configure an snmp view. A. Click the view tab. B. Click add. The page for creating an snmp view appears. Figure 77 create an snmp v...
Page 96
83 figure 78 create an snmp view (2) e. Select the included radio box, enter the mib subtree oid interfaces, and click add. F. Click apply. A configuration progress dialog box appears. Figure 79 configuration progress dialog box g. Click close after the configuration process is complete. 3. Configur...
Page 97
84 figure 80 create an snmp group c. Enter group1 in the field of group name, select view1 from the read view box, and select view1 from the write view box. D. Click apply. 4. Configure an snmp user a. Click the user tab. B. Click add. The page in figure 81 appears. C. Enter user1 in the field of us...
Page 98
85 figure 81 create an snmp user 5. Enable the agent to send snmp traps. A. Click the trap tab the page in figure 82 appears. B. Select the enable snmp trap box. C. Click apply. Figure 82 enable the agent to send snmp traps 6. Add target hosts of snmp traps. A. Click add on the trap tab.
Page 99
86 the page in figure 83 appears. B. Select the destination ip address type as ipv4/domain, enter the destination address 1.1.1.2, enter the user name user1, and select v3 from the security model list. C. Click apply. Figure 83 add target hosts of snmp traps configuring the nms caution: the nms must...
Page 100
87 loopback configuration you can check whether an ethernet port works normally by performing the ethernet port loopback test, during which the port cannot forward data packets normally. Ethernet port loopback test can be an internal loopback test or an external loopback test. • in an internal loopb...
Page 101
88 table 43 configuration items item description testing type external. Sets the loopback test type, which can be selected between external and internal. Internal. 3. Click test to start the loopback test. The result box displays the test results. Figure 85 loopback test result configuration guideli...
Page 102
89 mac address configuration note: • mac address configurations related to interfaces apply only to layer 2 ethernet interfaces. • this chapter covers only the management of static and dynamic mac address entries, not multicast mac address entries. A device maintains a mac address table for frame fo...
Page 103
90 figure 86 mac address table of the device configuring a mac address entry 1. Select network > mac from the navigation tree. The system automatically displays the mac tab, which shows all the mac address entries on the device, as shown in figure 87 . Figure 87 the mac tab 2. Click add in the botto...
Page 104
91 figure 88 create a mac address entry 3. Configure the mac address entry as described in table 44 . 4. Click apply. Table 44 configuration items item description mac set the mac address to be added. Type set the type of the mac address entry: • static: static mac address entries that never age out...
Page 105
92 figure 89 set the aging time for mac address entries 3. Set the aging time as described in table 45 . 4. Click apply. Table 45 configuration items item description no-aging specify that the mac address entry never ages out. Aging time set the aging time for the mac address entry. Mac address conf...
Page 106
93 figure 90 create a static mac address entry.
Page 107
94 vlan configuration overview ethernet is a network technology based on the carrier sense multiple access/collision detect (csma/cd) mechanism. As the medium is shared, collisions and excessive broadcasts are common on an ethernet. To address the issue, virtual lan (vlan) was introduced to break a ...
Page 108
95 creating a vlan 1. Select network > vlan from the navigation tree. The system automatically selects the vlan tab and enters the page as shown in figure 92 . Figure 92 vlan configuration page tip: to easily configure a specific range of vlans within a large number of vlans, enter a vlan range in t...
Page 109
96 figure 94 modify a vlan 3. Configure the description and port members for the vlan as described in table 46 . 4. Click apply. Table 46 configuration items item description id display the id of the vlan to be modified. Description set the description string of the vlan. By default, the description...
Page 110
97 3. Click the icon for the port to be modified to enter the page as shown in figure 96 . Figure 96 modify a port 4. Configure the port as described in table 47 . 5. Click apply. Table 47 configuration items item description port display the port to be modified. Untagged member display the vlan(s) ...
Page 111
98 vlan configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 97 : • gigabitethernet 1/0/1 on both devices are hybrid ports with vlan 1 as their default vlan. • configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to allow packets of vlan 1, vlan 2, vlan 6 through vlan 50, and vlan 100 to pass through and allow ...
Page 112
99 figure 99 configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a tagged member of vlan 2 and vlans 6 through 50 d. Click apply. A dialog box appears asking you to confirm the operation. E. Click ok in the dialog box. 3. Configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as an untagged member of vlan 100: a. Click the icon of gigabit...
Page 113
100 • vlan 1 is the default vlan, which cannot be manually created or removed. • some vlans are reserved for special purposes. You cannot manually create or remove them. • dynamic vlans cannot be manually removed..
Page 114
101 arp configuration overview introduction to arp the address resolution protocol (arp) is used to resolve an ip address into an ethernet mac address (or physical address). In an ethernet lan, a device uses arp to resolve the ip address of the next hop to the corresponding mac address. Note: for mo...
Page 115
102 figure 101 arp table configuration page creating a static arp entry 1. Select network > arp management from the navigation tree to enter the default arp table page shown in figure 101 . 2. Click add to enter the new static arp entry page, as shown in figure 102 . Figure 102 add a static arp entr...
Page 116
103 item description advanced options vlan id. Enter a vlan id and specify a port for the static arp entry. Important: the vlan id must be the id of the vlan that has already been created, and the port must belong to the vlan. The corresponding vlan interface must have been created. Port. Removing a...
Page 117
104 static arp configuration example network requirements to enhance communication security between the ap and the router, configure static arp entries on the ap. Figure 104 network diagram configuration procedure note: before performing the following configuration, configure interface vlan-interfac...
Page 118
105 igmp snooping configuration internet group management protocol (igmp) snooping is a multicast constraining mechanism that runs on layer 2 devices to manage and control multicast groups. By analyzing received igmp messages, a layer 2 device that is running igmp snooping establishes mappings betwe...
Page 119
106 recommended configuration procedure step remarks 1. Enabling igmp snooping globally required by default, igmp snooping is disabled. 2. Configuring igmp snooping on a vlan required enable igmp snooping in the vlan and configure the igmp snooping version and querier feature. By default, igmp snoop...
Page 120
107 figure 107 basic igmp snooping configurations configuring igmp snooping on a vlan 1. Select network > igmp snooping from the navigation tree to enter the basic configuration page shown in figure 107 . 2. Click the icon corresponding to the vlan to enter the page you can configure igmp snooping i...
Page 121
108 4. Click apply. Table 50 configuration items item description vlan id this field displays the id of the vlan to be configured. Igmp snooping enable or disable igmp snooping on the vlan. You can proceed with the subsequent configurations only if enable is selected here. Version by configuring an ...
Page 122
109 figure 109 advanced configuration 3. Configure igmp snooping on a port as described in table 51 . 4. Click apply. Table 51 configuration items item description port select the port on which advanced igmp snooping features are to be configured. After a port is selected, advanced features configur...
Page 123
110 displaying igmp snooping multicast entry information 1. Select network > igmp snooping from the navigation tree to enter the basic configuration page shown in figure 107 . 2. Click the plus sign (+) in front of show entries to display igmp snooping multicast entries, as shown in figure 110 . Fig...
Page 124
111 igmp snooping configuration example network requirements • as shown in figure 112 , router a connects to a multicast source (source) through ethernet 1/2, and to the ap through ethernet 1/1. • the multicast source sends multicast data to group 224.1.1.1. Host a is a receiver of the multicast gro...
Page 125
112 2. Enable igmp snooping and the function of dropping unknown multicast data on vlan 1 (where gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and wlan-bss 1 reside by default): a. Click the icon corresponding to vlan 1. B. To enable igmp snooping and the function of dropping unknown multicast data on vlan 1: select the en...
Page 126
113 figure 116 information about an igmp snooping multicast entry.
Page 127
114 ipv4 and ipv6 routing configuration note: the term router in this document refers to routers and aps with the routing functions. Overview upon receiving a packet, a router determines the optimal route based on the destination address and forwards the packet to the next router in the path. When t...
Page 128
115 figure 117 ipv4 active route table table 53 field description field description destination ip address destination ip address and subnet mask of the ipv4 route. Mask protocol protocol that discovered the ipv4 route. Preference preference value for the ipv4 route. The smaller the number, the high...
Page 129
116 figure 118 create an ipv4 static route 3. Specify relevant information as described in table 54 . 4. Click apply. Table 54 configuration items item description destination ip address enter the destination host or network ip address, in dotted decimal notation. Mask enter the mask of the destinat...
Page 130
117 item description interface select the outgoing interface. You can select any available layer 3 interface, for example, a virtual interface, of the device. If you select null 0, the destination ip address is unreachable. If you select this option, do not enter any ip address in the next hop field...
Page 131
118 creating an ipv6 static route 1. Select network > ipv6 routing from the navigation tree. 2. Click the create tab to enter the ipv6 static route configuration page, as shown in figure 120 . Figure 120 create an ipv6 static route 3. Specify relevant information as described in table 56 . 4. Click ...
Page 132
119 item description interface select the outgoing interface. You can select any available layer 3 interface, for example, a virtual interface, of the device. If you select null 0, the destination ipv6 address is unreachable. Ipv4 static route configuration example network requirements the ip addres...
Page 133
120 figure 122 configure a default route verifying the configuration 1. Display the route table: enter the ipv4 route page of switch a, switch b, and ap respectively to verify that the newly configured static routes are displayed as active routes on the page. 2. Ping host b from host a (assuming bot...
Page 134
121 ipv6 static route configuration example network requirements the ip addresses of devices are shown in figure 123 . Ipv6 static routes must be configured on switch a, switch b and ap for host a and host b to communicate with each other. Figure 123 network diagram configuration outlines 1. On swit...
Page 135
122 figure 124 configure a default route verifying the configuration 1. Display the route table: enter the ipv6 route page of switch a, switch b, and ap respectively to verify that the newly configured static routes are displayed as active routes on the page. 2. Ping host b from switch a: system-vie...
Page 136
123 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 62/62/63 ms configuration guidelines when you configure a static route, follow these guidelines: 1. If you do not specify the preference when you configure a static route, the default preference is used. Reconfiguration of the default preference applies...
Page 137
124 dhcp overview note: after the dhcp client is enabled on an interface, the interface can dynamically obtain an ip address and other configuration parameters from the dhcp server. This facilitates configuration and centralized management. For more information about the dhcp client configuration, s...
Page 138
125 step remarks 3. Enabling the dhcp server on an interface optional with the dhcp server enabled on an interface, upon receiving a client's request, the dhcp server assigns an ip address from its address pool to the dhcp client. With dhcp enabled, interfaces work in the dhcp server mode. Important...
Page 139
126 2. Select the static option in the address pool field to view all static address pools. 3. Click add to enter the page shown in figure 127 . Figure 127 create a static address pool 4. Configure the static address pool as described in table 57 . 5. Click apply. Table 57 configuration items item d...
Page 140
127 item description gateway address enter the gateway addresses for the client. A dhcp client that wants to access an external host needs to send requests to a gateway. You can specify gateways in each address pool and the dhcp server will assign gateway addresses while assigning an ip address to t...
Page 141
128 figure 128 create a dynamic address pool 4. Configure the dynamic address pool as described in table 58 . 5. Click apply. Table 58 configuration items item description ip pool name enter the name of a dynamic address pool. Ip address enter an ip address segment for dynamic allocation. To avoid a...
Page 142
129 item description gateway address enter the gateway addresses for the client. Dhcp clients that want to access hosts outside the local subnet request gateways to forward data. You can specify gateways in each address pool for clients and the dhcp server assigns gateway addresses while assigning a...
Page 143
130 table 59 field description item description ip address assigned ip address. Client mac address/client id client mac address or client id bound to the ip address. Pool name name of the dhcp address pool where the ip address belongs. Lease expiration lease time of the ip address. Dhcp server confi...
Page 144
131 figure 131 enable dhcp 2. Enable the dhcp server on vlan-interface 1: (this operation can be omitted because the dhcp server is enabled on the interface by default.) a. Click the icon of vlan-interface 1 in the interface configuration field. B. Select the enable option for dhcp server as shown i...
Page 145
132 − enter 10.1.1.2 for gateway address. C. Click apply. Figure 133 configure a dynamic address pool for the dhcp server.
Page 146
133 dns configuration overview domain name system (dns) is a distributed database used by tcp/ip applications to translate domain names into corresponding ip addresses. With dns, you can use easy-to-remember domain names in some applications and let the dns server translate them into correct ip addr...
Page 147
134 configuring dynamic domain name resolution step remarks 1. Configuring dynamic domain name resolution required enable dynamic domain name resolution. This function is disabled by default. 2. Adding a dns server address required not configured by default. 3. Adding a domain name suffix optional n...
Page 148
135 table 60 configuration items item description host name configure the mapping between a host name and an ip address in the static domain mane table. Each host name corresponds to only one ip address. If you configure multiple ip addresses for a host name, the last configured one takes effect.. H...
Page 149
136 figure 137 add a dns server address adding a domain name suffix 1. Select network > dns from the navigation tree 2. Click the dynamic tab to enter the page shown in figure 136 . 3. Click add suffix to enter the page shown in figure 138 . 4. Enter a dns suffix in the dns domain name suffix field....
Page 150
137 dynamic domain name resolution. The ip address of the dns server is 2.1.1.2/16 and the dns server has a com domain, which stores the mapping between domain name host and ip address 3.1.1.1/16. Configure dynamic domain name resolution and the domain name suffix com on the ap that serves as a dns ...
Page 151
138 a. In figure 141 , right click zone com, and then select new host. Figure 141 add a host b. In the dialog box as shown in figure 142 , enter host name host and ip address 3.1.1.1. C. Click add host. Figure 142 add a mapping between domain name and ip address.
Page 152
139 configuring the ap 1. Enable dynamic dns: a. Select network > dns from the navigation tree. B. Click the dynamic tab to enter the page shown in figure 143 . C. Select the enable option for dynamic dns. D. Click apply. Figure 143 enable dynamic dns 2. Configure the ip address of the dns server: a...
Page 153
140 c. Click apply. Figure 145 add a domain name suffix verifying the configuration use the ping host command on the ap to verify that the communication between the ap and the host is normal and that the corresponding destination ip address is 3.1.1.1. 1. Select diagnostic tools > ping from the navi...
Page 154
141 pppoe overview point-to-point protocol over ethernet (pppoe) uses the client/server model. It establishes point-to-point links over ethernet, and encapsulates ppp packets in ethernet frames. Aps configured as pppoe clients can be connected to the internet through a remote access device, and acce...
Page 155
142 figure 148 pppoe client information 2. Click add to enter the page for creating a pppoe client, as shown in 2 . Figure 149 create a pppoe client 3. Configure the parameters for the pppoe client as described in table 61 . 4. Click apply. Table 61 configuration items task remarks dialer interface ...
Page 156
143 task remarks ip config configure the way the dialer interface obtains its ip address: • none: not configure ip address • static address: statically configure an ip address and subnet mask for the interface • ppp negotiate: obtain an ip address through ppp negotiation • unnumbered: borrow the ip ...
Page 157
144 figure 150 statistic information table 62 field description field description interface ethernet interface where the pppoe session belongs. This field is null when the pppoe session is bundled with a vlan interface. Session number pppoe session id. Received packets number of received packets in ...
Page 158
145 figure 151 summary information table 63 field description field description session number pppoe session id. Dialer interface number number of the dialer interface corresponding to the pppoe session. Interface ethernet interface where the pppoe session belongs. This field is null when the pppoe ...
Page 159
146 configuring the pppoe client 1. Create a pppoe client: a. Select network > pppoe from the navigation tree. The system automatically enters the client page. B. Click add to enter the page shown in figure 153 . C. To create a pppoe client: enter 1 as the dialer interface name. Enter user1 as the u...
Page 160
147 1. Select network > pppoe from the navigation tree of the ap and click the session tab. 2. Select summary information from the information type list. Figure 154 shows that ppp negotiation is completed. Figure 154 display the summary information of pppoe sessions configuration guidelines the dial...
Page 161
148 service management overview the service management module provides the following types of services: telnet, ssh, sftp, http and https. You can enable or disable the services as needed. In this way, the performance and security of the system can be enhanced, thus secure management of the device c...
Page 162
149 configuring service management 1. Select network > service from the navigation tree to enter the service management configuration page, as shown in figure 155 . Figure 155 service management 2. Enable or disable various services on the page as described in table 64 . 3. Click apply. Table 64 con...
Page 163
150 item description https enable https service. Specifies whether to enable the https service. The https service is disabled by default. Port number. Sets the port number for https service. You can view this configuration item by clicking the expanding button in front of https. Important: when you ...
Page 164
151 diagnostic tools overview ping you can use the ping function to check whether a device with a specified address is reachable, and to examine network connectivity. A successful execution of the ping command involves the following steps: 1. The source device sends an icmp echo request (echo-reques...
Page 165
152 ping operation ipv4 ping operation 1. Select diagnostic tools > ping from the navigation tree to enter the ipv4 ping configuration page. 2. Click the expansion button before advanced setup to display the configurations of the advanced parameters of ipv4 ping operation, as shown in figure 156 . F...
Page 166
153 figure 157 ipv4 ping operation results ipv6 ping operation 1. Select diagnostic tools > ping from the navigation tree. 2. Enter the ipv6 ping configuration page (default setting). 3. Expand advanced setup to display the configurations of the advanced parameters of ipv6 ping operation, as shown i...
Page 167
154 figure 158 ipv6 ping 4. Enter the ipv6 address or host name of the destination device in the destination ip address or host name field. 5. Set the advanced parameters for the ipv6 ping operation. 6. Click start to execute the ping command. 7. View the result in the summary field, as shown in fig...
Page 168
155 figure 159 ipv6 ping operation results trace route operation note: • the web interface does not support trace route on ipv6 addresses. • before performing the trace route operations, execute the ip ttl-expires enable command on the intermediate device to enable the sending of icmp timeout packet...
Page 169
156 figure 160 trace route configuration page 3. Enter the destination ip address or host name. 4. Click start to execute the trace route command. 5. View the result in the summary field, as shown in figure 161 . Figure 161 trace route operation results.
Page 170
157 web overview the device provides web-based configuration interfaces for visual device management and maintenance. Figure 162 web-based network management operating environment logging in to the web interface you can use the following default settings to log in to the web interface: • username—ad...
Page 171
158 note: • the pc where you configure the device is not necessarily the web-based network management terminal. A web-based network management terminal is a pc (or another terminal) used to log in to the web interface and is required to be reachable to the device. • after logging in to the web inter...
Page 172
159 • title area—on the left, displays the path of the current configuration interface in the navigation area; on the right, provides the save button to quickly save the current configuration, the help button to display the web related help information, and the logout button to log out of the web in...
Page 173
160 function menu description user level set idle timeout display and configure the idle timeout period for a logged-in user. Configure device maintena nce software upgrade upload the file to be upgraded from the local host to upgrade the system software. Management reboot reboot the device. Managem...
Page 174
161 function menu description user level configure snmp. Configure loopback test perform the loopback test on ethernet interfaces. Configure network mac mac display mac address information. Monitor create or remove mac addresses. Configure setup display and configure mac address aging time. Configur...
Page 175
162 function menu description user level dns static domain name resolution display, create, modify, or delete a static host name-to-ip address mapping. Configure dynamic domain name resolution display and configure related parameters for dynamic domain name resolution. Display, create, or delete an ...
Page 176
163 function menu description user level parameter setting display radio parameters. Monitor configure radio parameters. Configure channel scan display channel scanning, including scanning mode, scanning type and scanning interval. View the ap operating mode (normal, monitor, and hybrid). Monitor co...
Page 177
164 function menu description user level guest display guest users' configuration information. Monitor add, modify, and remove guest users. Management generate a key pair, destroy a key pair, retrieve a certificate, request a certificate, and delete a certificate. Configure certificat e manage ment ...
Page 178
165 function menu description user level acl ipv4 display display ipv4 acl configuration information. Monitor add add an ipv4 acl. Configure basic setup configure a rule for a basic ipv4 acl. Configure advanced setup configure a rule for an advanced ipv4 acl. Configure link setup create a rule for a...
Page 179
166 function menu description user level add add a class. Configure setup configure the classification rules for a class. Configure delete delete a class or its classification rules. Configure behavior display display traffic behavior configuration information. Monitor add add a traffic behavior. Co...
Page 180
167 common web interface elements common buttons and icons table 66 common buttons and icons button and icon description bring the configuration on the current page into effect. Cancel the configuration on the current page, and go to the corresponding display page or device information page. Refresh...
Page 181
168 figure 165 content display by pages searching function the web interface provides you with the basic and advanced searching functions to display only the entries that match specific searching criteria. • basic search: as shown in figure 165 , enter the keyword in the field above the list, select...
Page 182
169 figure 167 advanced search take the arp table shown in figure 165 as an example. To search for the arp entries with 000f at the beginning of the mac address, and ip address range 192.168.1.50 to 192.168.1.59: 1. Click the advanced search link, specify the search criteria on the advanced search p...
Page 183
170 figure 169 advanced search function example (ii) figure 170 advanced search function example (iii) sorting function the web interface provides you with the basic sorting function to display entries in certain orders. On a list page, you can click the blue heading item of each column to sort the ...
Page 184
171 figure 171 basic sorting function example (based on ip address in the descending order) configuration guidelines • the web-based configuration interface supports the operating systems of windows xp, windows 2000, windows server 2003 enterprise edition, windows server 2003 standard edition, windo...
Page 185
172 troubleshooting web browser failure to access the device through the web interface symptom you can ping the device successfully, and log in to the device through telnet. Http is enabled and the operating system and browser version meet the web interface requirements. However, you cannot access t...
Page 186
173 the dialog box security settings appears. 4. Enable these functions: run activex controls and plug-ins, script activex controls marked safe for scripting and active scripting. Figure 173 internet explorer setting (ii) 5. Click ok in the security settings dialog box. Configuring firefox web brows...
Page 187
174 figure 174 firefox web browser setting.
Page 188
175 radio configuration radio frequency (rf) refers to electrical signals that can be transferred over the space to a long distance. 802.11b/g in the ieee 802.11 standards operates at the 2.4 ghz band, 802.11a operates at the 5 ghz band, and 802.11n operates at both the 2.4 ghz and 5 ghz bands. Radi...
Page 189
176 item description 802.11n important: the option is available only when the ap supports 802.11n and the radio mode is 802.11n. Bandwidth mode 802.11n can bond two adjacent 20-mhz channels together to form a 40-mhz channel. During data forwarding, the two 20-mhz channels can work separately with on...
Page 190
177 4. Expand advanced setup. Figure 176 radio setup (advanced setup) 5. Configure the radio as described in table 68 . 6. Click apply. Table 68 configuration items item description preamble preamble is a pattern of bits at the beginning of a frame so that the receiver can sync up and be ready for t...
Page 191
178 item description fragment threshold specify the maximum length of frames that can be transmitted without fragmentation. When the length of a frame exceeds the specified fragment threshold value, it is fragmented. • in a wireless network where error rate is high, you can decrease the fragment thr...
Page 192
179 item description short retry threshold number of retransmission attempts for unicast frames smaller than the rts/cts threshold if no acknowledgment is received for it. Max receive duration interval for which a frame received by an ap can stay in the buffer memory. Configuring data transmit rates...
Page 193
180 table 69 configuration items item description 802.11a configure rates (in mbps) for 802.11a. By default: • mandatory rates are 6, 12, and 24. • supported rates are 9, 18, 36, 48, and 54. • multicast rate: automatically selected from the mandatory rates. The transmission rate of multicasts in a b...
Page 194
181 mcs index number of spatial streams modulation data rate (mbps) 800ns gi 400ns gi 4 1 16-qam 39.0 43.3 5 1 64-qam 52.0 57.8 6 1 64-qam 58.5 65.0 7 1 64-qam 65.0 72.2 8 2 bpsk 13.0 14.4 9 2 qpsk 26.0 28.9 10 2 qpsk 39.0 43.3 11 2 16-qam 52.0 57.8 12 2 16-qam 78.0 86.7 13 2 64-qam 104.0 115.6 14 2...
Page 195
182 mcs index number of spatial streams modulation data rate (mbps) 800ns gi 400ns gi 11 2 16-qam 108.0 120.0 12 2 16-qam 162.0 180.0 13 2 64-qam 216.0 240.0 14 2 64-qam 243.0 270.0 15 2 64-qam 270.0 300.0 16 3 bpsk 40.5 45.0 17 3 qpsk 81.0 90.0 18 3 qpsk 121.5 135.0 19 3 16-qam 162.0 180.0 20 3 16-...
Page 196
183 item description multicast mcs set the multicast mcs for 802.11n. The multicast mcs is adopted only when all the clients use 802.11n. If a non 802.11n client exists, multicast traffic is transmitted at a mandatory mcs data rate. Select a multicast mcs index from the mcs indexes supported by all ...
Page 197
184 figure 179 setting channel calibration note: when an ap uses the radio whose working channel is auto to establish a wds link, the auto dynamic channel select (dfs) function of the radio automatically takes effect. Auto dfs of the radio is automatically performed at a calibration interval when th...
Page 198
185 figure 180 setting parameters 3. Configure calibration parameters as described in table 74 . 4. Click apply. Table 74 configuration items item description 802.11g protection because 802.11b and 802.11g use different modulation modes, 802.11g protection needs to be enabled for a 802.11g device to...
Page 199
186 item description 802.11g protection mode • rts/cts—use rts/cts mode to implement 802.11g protection. Before sending data to a client, an ap sends an rts packet to the client, ensuring that all the devices within the coverage of the ap do not send data in the specified time after receiving the rt...
Page 200
187 figure 181 setting channel scanning 3. Configure channel scanning as described in table 75 . Table 75 configuration items item description scan 802.11h channel some 802.11h channels, called radar channels, overlap some 802.11a channels. If the device operates on an overlapping channel, its servi...
Page 201
188 item description 5ghz excluded channel/2.4ghz excluded channel to avoid selecting improper channels, you can exclude specific channels from automatic channel selection. The excluded channels will not be available for initial automatic channel selection, dfs, and mesh dfs. This feature does not a...
Page 202
189 • monitor mode as shown in figure 183 , when ap 2 operates in monitor mode, it monitors all devices in the wlan through scanning 802.11 frames and records scan results, but it does not provide wlan services. For the channel detection results, see " displaying detection record ." figure 183 monit...
Page 203
190 figure 185 setting ap operating mode 3. Configure the ap operating mode as described in table 76 . 4. Click apply. Table 76 configuration items item description work mode set the ap operating mode: • normal—the ap only provides wlan data services. • monitor—the ap only scans all 802.11 frames in...
Page 204
191 figure 186 displaying detection record note: at present, aps, wireless bridges, clients, and ad hoc devices can be detected. Configuring the detection record aging time 1. Select radio > channel detection from the navigation tree. 2. Click the history record tab. 3. Configure the detect record a...
Page 205
192 figure 188 displaying history record note: if an entry in the detection record is not refreshed within the aging time, it is deleted from the detection record and added into the history record. Antenna select radio > antenna to select an appropriate antenna for the corresponding radio. Figure 18...
Page 206
193 aaa configuration the web interface supports configuring internet service provider (isp) domains and configuring aaa methods for isp domains. Aaa overview authentication, authorization, and accounting (aaa) provides a uniform framework for implementing network access management. It provides the ...
Page 207
194 configuring aaa configuration prerequisites • to deploy local authentication, configure local users on the access device as described in " user configuration ." • to deploy remote radius authentication, authorization, or accounting, create the radius schemes to be referenced as described in " ra...
Page 208
195 figure 191 domain setup page 2. Configure an isp domain as described in table 77 . 3. Click apply. Table 77 configuration items item description domain name enter the isp domain name, which is for identifying the domain. You can enter a new domain name to create a domain, or specify an existing ...
Page 209
196 figure 192 authentication method configuration page 3. Configure authentication methods for different types of users in the domain, as described in table 78 . 4. Click apply. A configuration progress dialog box appears. 5. After the configuration progress is complete, click close. Table 78 confi...
Page 210
197 item description login authn configure the authentication method and secondary authentication method for login users. Options include: • hwtacacs—performs hwtacacs authentication. You must specify the hwtacacs scheme to be used. • local—performs local authentication. • none—does not perform auth...
Page 211
198 table 79 configuration items item description select an isp domain select the isp domain for which you want to specify authentication methods. Default authz configure the default authorization method and secondary authorization method for all types of users. Options include: • hwtacacs—performs ...
Page 212
199 configuring accounting methods for the domain 1. Select authentication > aaa from the navigation tree. 2. Click the accounting tab to enter the accounting method configuration page. Figure 194 accounting method configuration page 3. Configure accounting methods for different types of users in th...
Page 213
200 item description lan-access accounting configure the accounting method and secondary accounting method for lan access users. Options include: • local—performs local accounting. • none—does not perform accounting. • radius—performs radius accounting. You must specify the radius scheme to be used....
Page 214
201 the local user management page appears. B. Click add. C. Enter telnet as the username. D. Enter abcd as the password. E. Enter abcd again to confirm the password. F. Select common user as the user type. G. Select configure as the level. H. Select telnet as the service type. I. Click apply. Figur...
Page 215
202 figure 197 configure isp domain test 3. Configure the isp domain to use local authentication for login users: a. Select authentication > aaa from the navigation tree b. Click the authentication tab. C. Select the domain test. D. Select the login authn box and select the authentication method loc...
Page 216
203 4. Configure the isp domain to use local authorization for login users: a. Select authentication > aaa from the navigation tree. B. Click the authorization tab. C. Select the domain test. D. Select the login authz box and select the authorization method local. E. Click apply. A configuration pro...
Page 217
204 radius configuration radius overview the remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) protocol is the most commonly used protocol for implementing authentication, authorization, and accounting (aaa). Radius uses the client/server model. It can protect networks against unauthorized access ...
Page 218
205 figure 201 radius scheme configuration page 3. Enter a scheme name. 4. Select a server type and a username format. Table 81 configuration items item description server type select the type of the radius servers supported by the device, which can be: • standard—specifies the standard radius serve...
Page 219
206 figure 202 common configuration area 6. Configure the advanced parameters..
Page 220
207 table 82 configuration items item description authentication key set the shared key for radius authentication packets and that for radius accounting packets. The radius client and the radius authentication/accounting server use md5 to encrypt radius packets, and they verify the validity of packe...
Page 221
208 item description realtime accounting interval set the interval for sending real-time accounting information. The interval must be a multiple of 3. To implement real-time accounting, the device must send real-time accounting packets to the accounting server for online users periodically. Differen...
Page 222
209 item description send accounting-on packets enable or disable the accounting-on feature. The accounting-on feature enables a device to send accounting-on packets to radius servers after it reboots, making the servers forcedly log out users who logged in through the device before the reboot. Impo...
Page 223
210 item description key specify the shared key for communication with the radius server. If no shared key is specified here, the shared key specified in the common configuration part is used. Confirm key radius configuration examples network requirements as shown in figure 204 , a radius server run...
Page 224
211 h. Select the ap from the device list or manually add the ap (with the ip address 10.1.1.2). Note: the ip address of the added access device must be the same as the source ip address of the radius packets sent from the ap. By default, it is the ip address of the radius packets' outbound interfac...
Page 225
212 figure 206 device management user configuration page configuring the ap 1. Configure the radius scheme system: a. Select authentication > radius from the navigation tree. B. Click add. C. Enter the scheme name system, select the server type extended, and select the username format without domain...
Page 226
213 figure 207 radius authentication server configuration page f. In the radius server configuration area, click add to enter the radius server configuration page again. G. Select primary accounting as the server type, enter 10.1.1.1 as the ip address of the primary accounting server, enter the port...
Page 227
214 figure 209 radius scheme configuration 2. Create the isp domain bbb: a. From the navigation tree, select authentication > aaa. The domain setup page appears, as shown in figure 210 . B. Enter the domain name test. C. Click apply..
Page 228
215 figure 210 create an isp domain 3. Configure an authentication method for the isp domain: a. Click the authentication tab. B. Select the domain name bbb. C. Select the default authn box and then select the authentication mode radius. D. Select the radius scheme system from the name list to use i...
Page 229
216 4. Configure an authorization method for the isp domain: a. Click the authorization tab. B. Select the domain name bbb. C. Select the default authz box and select the authorization mode radius. D. Select the radius scheme system from the name list to use it as the authorization scheme. E. Click ...
Page 230
217 figure 213 configure an accounting method for the isp domain 6. Enable the telnet service: a. From the navigation tree, select network > services. B. Select the enable telnet service box. C. Click apply. Figure 214 enable the telnet service 7. Log in to the cli and configure the ap to use aaa fo...
Page 231
218 • if you remove the accounting server used for online users, the device cannot send real-time accounting requests and stop-accounting messages for the users to the server, and the stop-accounting messages are not buffered locally. • the status of radius servers (blocked or active) determines whi...
Page 232
219 hwtacacs configuration hwtacacs overview hw terminal access controller access control system (hwtacacs) is an enhanced security protocol based on tacacs (rfc 1492). Similar to radius, it uses a client/server (c/s) model for information exchange between network access server (nas) and hwtacacs se...
Page 233
220 step remarks 3. Configuring hwtacacs parameters optional. This section describes how to configure the parameters that are necessary for information exchange between the device and hwtacacs server. Creating hwtacacs scheme system 1. If the hwtacacs scheme system does not exist, select authenticat...
Page 234
221 table 85 configuration items configuration item description server type select the type of the server to be configured, which can be authentication server, authorization server and accounting sever. Primary server ip enter the ip address of the primary server. When no primary server is specified...
Page 235
222 figure 217 hwtacacs parameter configuration 3. Configure hwtacacs parameters as described in table 86 . 4. Click apply. Table 86 configuration items item description nas-ip source ip address for the device to use in hwtacacs packets to be sent to the hwtacacs server. Use a loopback interface add...
Page 236
223 item description stop-accounting buffer enable or disable buffering stop-accounting requests without responses in the device. Since stop-accounting requests affect the charge to users, a nas must make its best effort to send every stop-accounting request to the hwtacacs accounting servers. For e...
Page 237
224 item description unit of packets specify the unit for data packets sent to the hwtacacs server for traffic accounting. Options include: • packet. • kilo-packet. • mega-packet. • giga-packet. If you leave the box blank, the default unit is used. Hwtacacs configuration example network requirements...
Page 238
225 figure 219 create an hwtacacs scheme 2. Configure the hwtacacs authentication server: a. Select authentication server as the server type. B. Enter 10.1.1.1 as the ip address of the primary server. C. Enter 49 as the authentication port number of the primary server. D. Select the shared key box, ...
Page 239
226 b. Click the parameter configuration tab. C. Select the username format without-domain. D. Click apply. Figure 221 configure the parameters for communication 6. Configure isp domain test: a. From the navigation tree, select authentication > aaa. B. Enter the domain name test. C. Click apply..
Page 240
227 figure 222 create an isp domain 7. Configure an authentication method for the isp domain: a. Click the authentication tab. B. Select the domain name test. C. Select the default authn box and then select the authentication mode hwtacacs. D. Select the hwtacacs scheme system from the name list to ...
Page 241
228 8. Configure an authorization method for the isp domain: a. Click the authorization tab. B. Select the domain name test. C. Select the default authz box and select the authorization mode hwtacacs. D. Select the hwtacacs scheme system from the name list to use it as the authorization scheme. E. C...
Page 242
229 figure 225 configure an accounting method for the isp domain 10. Log in to the cli, enable telnet service, and configure the ap to use aaa for telnet users. System-view [ap] telnet server enable [ap] user-interface vty 0 4 [ap-ui-vty0-4] authentication-mode scheme [ap-ui-vty0-4] quit verifying t...
Page 243
230 number of users real-time accounting interval (in minutes) 500 to 999 12 ≥1000 ≥15.
Page 244
231 user configuration user overview this module allows you to configure local users, user groups, and guests. Local user a local user is an account configured on the device. It is uniquely identified by the username and has a set of user attributes, such as the password, user type, service type, an...
Page 245
232 figure 226 local user list 2. Click add. The local user configuration page appears. On this page, you can create a local user of any type except guest. Figure 227 local user configuration page 3. Configure a local user as described in table 88 . 4. Click apply. Table 88 configuration items item ...
Page 246
233 item description password specify a password for the local user and confirm the password. The two passwords must be identical. Important: leading spaces of a password are ignored. Confirm group select a user group for the local user. For information about user group configuration, see " configur...
Page 247
234 item description acl specify the acl to be used by the access device to restrict the access of the local user after the user passes authentication. Important: this option is only effective for common ppp and lan users. User-profile specify the user profile for the local user. Important: • this o...
Page 248
235 table 89 configuration items item description group-name specify a name for the user group. Level select an authorization level for the user group, which can be visitor, monitor, configure, or management, in ascending order of priority. Vlan specify the vlan to be authorized to a user in the use...
Page 249
236 3. Click add to enter the guest configuration page. Figure 231 guest configuration page 4. Configure a single guest or a batch of guests as described in table 90 . 5. Click apply. Table 90 configuration items item description create users in a batch specify whether to create guests in a batch. U...
Page 250
237 procedure for a guest administrator to configure a guest note: guest administrators can manage only guest accounts and can only manage guest accounts through the web interface. 1. Log in to the ap as a guest administrator and select authentication > user from the navigation tree. The guest manag...
Page 251
238 certificate management pki overview the public key infrastructure (pki) is a general security infrastructure for providing information security through public key technologies, and it is the most widely applied encryption mechanism currently. H3c's pki system provides certificate management for ...
Page 252
239 you can specify the pki certificate request mode for a pki domain. Different pki certificate request modes require different configurations. Recommended configuration procedure for manual request step remarks 1. Creating a pki entity required. Create a pki entity and configure the identity infor...
Page 253
240 step remarks 5. Requesting a local certificate required. When requesting a certificate, an entity introduces itself to the ca by providing its identity information and public key, which are the major components of the certificate. A certificate request can be submitted to a ca in online mode or ...
Page 254
241 step remarks 2. Creating a pki domain required. Create a pki domain, setting the certificate request mode to auto. Before requesting a pki certificate, an entity needs to be configured with some enrollment information, which is referred to as a pki domain. A pki domain is intended only for conve...
Page 255
242 figure 235 pki entity configuration page 3. Configure the parameters as described table 91 . 4. Click apply. Table 91 configuration items item description entity name name of the pki entity. Common name common name of the entity. Ip address ip address of the entity. Fqdn fully qualified domain n...
Page 256
243 2. Click the domain tab to enter the page displaying existing pki domains. Figure 236 pki domain list 3. Click add to enter the pki domain configuration page. Figure 237 pki domain configuration page 4. Configure the parameters as described in table 92 . 5. Click apply. Table 92 configuration it...
Page 257
244 item description institution select the authority for certificate request. • ca—indicates that the entity requests a certificate from a ca. • ra—indicates that the entity requests a certificate from an ra. Ra is recommended. Requesting url url of the ra. The entity will submit the certificate re...
Page 258
245 item description crl update period crl update period, that is, the interval at which the pki entity downloads the latest crls. This item is available when the enable crl checking box is selected. By default, the crl update period depends on the next update field in the crl file. Crl url url of t...
Page 259
246 destroying the rsa key pair 1. Select authentication > certificate management from the navigation tree. 2. Click the certificate tab to enter the page displaying existing pki certificates. 3. Click destroy key to enter the rsa key pair destruction page. 4. Click apply to destroy the existing rsa...
Page 260
247 item description enable offline mode click this box to retrieve a certificate in offline mode (that is, by an out-of-band means like ftp, disk, or email). Get file from device specify the path and name of the certificate file if you retrieve the certificate in offline mode. • if the certificate ...
Page 261
248 2. Click the certificate tab to enter the page displaying existing pki certificates. 3. Click request cert to enter the local certificate request page. Figure 243 local certificate request page 4. Configure the parameters as described in table 94 . Table 94 configuration items item description d...
Page 262
249 2. Select the crl tab to enter the page displaying crls. Figure 245 crl page 3. Click retrieve crl to retrieve the crl of a domain. 4. Click view crl for the domain to display the contents of the crl. Figure 246 crl information pki configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 24...
Page 263
250 figure 247 network diagram configuring the ca server 1. Create a ca server named myca. In this example, you must first configure the basic attributes of nickname and subject dn on the ca server: the nickname is the name of the trusted ca, and the subject dn is the dn attributes of the ca, includ...
Page 264
251 figure 248 configure a pki entity 2. Create a pki domain. A. Click the domain tab b. Click add. C. Enter torsa as the pki domain name. D. Enter myca as the ca identifier. E. Select aaa as the local entity. F. Select ca as the authority for certificate request. G. Enter http://4.4.4.133:446/c95e9...
Page 265
252 figure 249 configure a pki domain 3. Generate an rsa key pair. A. Click the certificate tab. B. Click create key. C. Enter 1024 as the key length. D. Click apply to generate an rsa key pair. Figure 250 generate an rsa key pair 4. Retrieve the ca certificate. A. Click the certificate tab. B. Clic...
Page 266
253 e. Click apply. Figure 251 retrieve the ca certificate 5. Request a local certificate. A. Click the certificate tab. B. Click request cert. C. Select torsa as the pki domain. D. Click password and then enter "challenge-word" as the password. E. Click apply. The system gives a prompt that the req...
Page 267
254 verifying the configuration after the configuration, select authentication > certificate management > certificate from the navigation tree to view detailed information about the retrieved ca certificate and local certificate, or select authentication > certificate management > crl from the navig...
Page 268
255 wireless service wireless local area networks (wlan) have become very popular because they are very easy to setup and use, and low cost. Generally, one or more access points (aps) can cover a building or an area. The wlan solution allows you to conveniently provide the following wireless access ...
Page 269
256 figure 254 establish a client access scanning a wireless client can get the surrounding wireless network information in two ways, passive scanning or active scanning. With passive scanning, a wireless client gets wireless network information through listening to beacon frames sent by surrounding...
Page 270
257 a client sends a probe request (with a specified ssid): when the wireless client is configured to access a specific wireless network or has already successfully accessed a wireless network, the client periodically sends a probe request carrying the specified ssid of the configured or connected w...
Page 271
258 figure 258 open system authentication process • shared key authentication figure 259 shows a shared key authentication process. The two parties have the same shared key configured. 1. The client sends an authentication request to the ap. 2. The ap randomly generates a challenge and sends it to t...
Page 272
259 • receiving a data frame from a client which is unauthenticated. • receiving a ps-poll frame from a client which is unauthenticated. 2. Dissociation a dissociation frame can be sent by an ap or a wireless client to break the current wireless link. In the wireless system, dissociation can occur d...
Page 273
260 ctr with cbc-mac protocol (ccmp) is based on the ccm of the aes encryption algorithm. Ccm combines ctr for confidentiality and cbc-mac for authentication and integrity. Ccm protects the integrity of both the mpdu data field and selected portions of the ieee 802.11 mpdu header. The aes block algo...
Page 274
261 figure 260 local mac authentication • remote mac authentication: remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) based mac authentication. When radius-based mac authentication is used, the device operates as the radius client, and cooperates with the radius server to perform the mac authenti...
Page 275
262 802.11n as the next generation wireless lan technology, 802.11n supports both 2.4ghz and 5ghz bands. It provides higher throughput to customers by using the following methods: 1. Increasing bandwidth: 802.11n can bond two adjacent 20-mhz channels together to form a 40-mhz channel. During data fo...
Page 276
263 point to point bridge connection in this network, wds uses two devices to form a bridge between two lans, and interconnect the two lans. In actual applications, each device can determine the bridge connection to be set up by configuring the mac address of the peer device. As shown in figure 262 ...
Page 277
264 figure 264 self topology detection and bridging repeater mode overview an ap acting as a repeater can set up a link with another ap through a wds link and provide wireless access service for clients at the same time, that is, an ap acting as a repeater can not only create wireless networks but a...
Page 278
265 figure 266 network diagram lan segmen t.
Page 279
266 configuring wireless service configuring access service recommended configuration procedure step remarks 1. Creating a wireless service required. 2. Configuring wireless service configuring clear type wireless service configuring crypto type wireless service required. Use either approach. Comple...
Page 280
267 figure 268 create a wireless service 3. Configure the wireless service as described in table 95 . 4. Click apply. Table 95 configuration items item description wireless service name set the service set identifier (ssid). An ssid should be as unique as possible. For security, the company name sho...
Page 281
268 figure 269 configure clear type wireless service 3. Configure the basic settings for the clear type wireless service as described in table 96 . 4. Click apply. Table 96 configuration items item description wireless service display the selected service set identifier (ssid). Vlan (untagged) enter...
Page 282
269 figure 270 advanced settings for the clear type wireless service 3. Configure the advanced settings for the clear type wireless service as described in table 97 . 4. Click apply. Table 97 configuration items item description client max users maximum number of clients of an ssid to be associated ...
Page 283
270 figure 271 security settings for the clear type wireless service 3. Configure the security settings for the clear type wireless service as described in table 98 . 4. Click apply. Table 98 configuration items item description authentication type for the clear type wireless service, you can select...
Page 284
271 item description port mode • mac-authentication—perform mac address authentication on users. • mac-else-userlogin-secure—this mode is the combination of the mac-authentication and userlogin-secure modes, with mac authentication having a higher priority. Upon receiving a non-802.1x frame, a port ...
Page 285
272 figure 272 mac-authentication port security configuration page table 99 configuration items item description port mode mac-authentication—mac-based authentication is performed on access users. Select wireless service > access service from the navigation tree, and click mac authentication list to...
Page 286
273 figure 273 userlogin-secure/userlogin-secure-ext port security configuration page (userlogin-secure is taken for example) table 100 configuration items item description port mode • userlogin-secure—perform port-based 802.1x authentication for access users. In this mode, multiple 802.1x authentic...
Page 287
274 item description handshake • enable—enable the online user handshake function so that the device can periodically send handshake messages to a user to check whether the user is online. By default, the function is enabled. • disable—disable the online user handshake function. Multicast trigger • ...
Page 288
275 table 101 configuration items item description port mode • mac-else-userlogin-secure—this mode is the combination of the mac-authentication and userlogin-secure modes, with mac authentication having a higher priority. Upon receiving a non-802.1x frame, a port in this mode performs only mac authe...
Page 289
276 item description multicast trigger • enable—enable the multicast trigger function of 802.1x to send multicast trigger messages to the clients periodically for initiating authentication. By default, the multicast trigger function is enabled. • disable—disable the 802.1x multicast trigger function...
Page 290
277 2. Click the icon corresponding to the target crypto type wireless service. The page for configuring advanced settings for the crypto type wireless service appears. Figure 276 advanced settings for the crypto type wireless service 3. Configure the advanced settings for the crypto type wireless s...
Page 291
278 item description management right web interface management right of online clients. • disable—disable the web interface management right of online clients. • enable—enable the web interface management right of online clients. Mac vlan • enable—enable the mac vlan feature for the wireless service...
Page 292
279 figure 277 security settings for the crypto type wireless service 3. Configure the security settings for the crypto type wireless service as described in table 103 . 4. Click apply. Table 103 configuration items item description authentication type link authentication method, which can be: • ope...
Page 293
280 item description security ie wireless service type (ie information carried in the beacon or probe response frame): • wpa—wi-fi protected access. • rsn—an rsn is a security network that allows only the creation of robust security network associations (rsnas). It provides greater protection than w...
Page 294
281 item description port security see table 98 . Parameters such as authentication type and encryption type determine the port mode. For more information, see table 106 . After you select the cipher suite option, the following four port security modes are added: • mac and psk—mac-based authenticati...
Page 295
282 item description domain select an existing domain from the list. The default domain is system. To create a domain, select authentication > aaa from the navigation tree, click the domain setup tab, and enter a new domain name in the domain name field. • the selected domain name applies to only th...
Page 296
283 security parameter dependencies for a clear-type wireless service or crypto-type wireless service, the security parameter dependencies are described in table 106 . Table 106 security parameter dependencies service type authenticat ion mode encryption type security ie wep encryption /key id port ...
Page 297
284 binding an ap radio to a wireless service 1. Select wireless service > access service from the navigation tree. 2. Click the bind link of the wireless service to be bound to enter the page as shown in figure 280 . Figure 280 bind an ap radio to a wireless service 3. Select the ap radio to be bou...
Page 298
285 configuring wds service configuring wds service 1. Select wireless service > wds from the navigation tree. 2. Click the wds setup tab to enter the wds setup page. Figure 282 wds setup page 3. Click the icon corresponding to the radio mode to be configured in the operation column to enter the wds...
Page 299
286 configuring a neighbor mac address note: if no neighbor mac address is configured for an ap, the ap can establish a wds link with any other ap; if a neighbor mac address is configured for an ap, the ap can establish a wds link with only the specified peer ap. 1. Select wireless service > wds fro...
Page 300
287 figure 285 configure advanced wds 4. Configure advanced wds settings as described in table 108 . 5. Click apply. Table 108 configuration items item description mesh identifier set the mesh id. The default mesh identifier of a device depends on its radio mode. Link keep alive interval configure t...
Page 301
288 item description stp the following loop types may exist in a wds network: . .When a loop exists in the network, you can block redundant links to remove the loop by stp, and can provide link backup when a wds link fails. Set stp. • enable—enable stp. • disable—disable stp. By default, stp is enab...
Page 302
289 item description vlan (tagged) enter the id of the vlan whose packets are to be sent tagged. Vlan (tagged) indicates that the port sends the traffic of the vlan without removing the vlan tag. Vlan (untagged) enter the id of the vlan whose packets are to be sent untagged. Vlan (untagged) indicate...
Page 303
290 note: • a radio enabled with auto dfs and wds works in a non-radar channel. • when you select auto-dfs, if no wds link is established, a temporary working channel is automatically selected for a radio. The validation time of the temporary working channel is from 10 to 20 seconds. After the tempo...
Page 304
291 figure 288 repeater mode configuring the workgroup bridge enabling the client mode 1. Select wireless service > client mode from the navigation tree. 2. Click connect setup. Figure 289 enable the client mode 3. Select the radio unit for which the client mode is to be enabled. 4. Click enable. No...
Page 305
292 with the client mode enabled, you can check the existing wireless services in the wireless service list. Figure 290 check the wireless service list connecting the wireless service method 1 1. Click the connect icon of the wireless service in the wireless service list. The set code dialog box app...
Page 306
293 item remarks ciphersuit set the data encryption mode, which can be: • clear—no encryption • wep—wep encryption • tkip/aes-ccmp—tkip/aes-ccmp encryption password configure the wep/aes-ccmp/tkip key according to the data encryption mode. Keyid there are four static keys in wep. Their key indexes a...
Page 307
294 figure 293 display statistics wireless access configuration examples wireless service configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 294 , enable the client to access the internal network resources at any time. The ap provides plain-text wireless access service with ssid service1....
Page 308
295 3. Bind an ap radio to a wireless service a. Select wireless service > access service from the navigation tree. B. Click the bind link at the right side of the wireless service service1 to enter the page as shown in figure 297 . C. Select the box with radio mode 802.11n(2.4ghz). D. Click bind. F...
Page 309
296 figure 298 enable 802.11n radio verifying the configuration • the client can successfully associate with the ap and access the wlan network. • you can view the online clients on the page you enter by selecting summary > client from the navigation tree. Figure 299 view the online clients configur...
Page 310
297 figure 300 network diagram configuring the ap 1. Configure the fat ap interface: a. Assign an ip address to the fat ap: select network > vlan to create a vlan on the fat ap. Select device > interface management to assign an ip address to the vlan interface. B. Configure the link type of the ethe...
Page 311
298 b. Click add. C. On the page that appears, enter the service name office, select the wireless service type clear, and click apply. D. On the page that appears, enter 3 in the vlan (untagged) field, enter 3 in the default vlan field, enter 1 in the delete vlan field, and click apply. Before you p...
Page 312
299 figure 304 network diagram configuring the ap 1. Assign an ip address to the fat ap: a. Select network > vlan to create a vlan on the fat ap. B. Select device > interface management to assign an ip address to the vlan interface. 2. Configure a wireless service: a. Select wireless service > acces...
Page 313
300 figure 306 security setup 4. Bind an ap radio to a wireless service a. Select wireless service > access service from the navigation tree. B. Click the bind link at the right side of the wireless service psk to enter the page as shown in figure 307 . C. Select the box with radio mode 802.11n(2.4g...
Page 314
301 figure 308 enable the wireless service 6. Enable 802.11n radio (by default, 802.11n radio is enabled. Therefore, this step is optional. ) select radio > radio from the navigation tree to enter the radio page. Make sure 802.11n radio is enabled. Configuring the client 1. Launch the client, and re...
Page 315
302 figure 309 configure the client the client has the same preshared psk key as the ap, so the client can associate with the ap..
Page 316
303 figure 310 the client is associated with the ap verifying the configuration • the same psk pre-shared key is configured on the client. The client can successfully associate with the ap and can access the wlan network. • you can view the online clients on the page you enter by selecting summary >...
Page 317
304 b. Select device > interface management to assign an ip address to the vlan interface. 2. Configure a wireless service: a. Select wireless service > access service from the navigation tree. B. Click add. C. On the page that appears, set the service name to mac-auth, select the wireless service t...
Page 318
305 figure 313 security setup 4. Bind an ap radio to a wireless service a. Select wireless service > access service from the navigation tree. B. Click the bind link at the right side of the wireless service mac-auth to enter the page as shown in figure 314 . C. Select the box with radio mode 802.11n...
Page 319
306 b. Select the mac-auth box. C. Click enable. Figure 315 enable the wireless service 6. Configure a mac authentication list a. Select wireless service > access service from the navigation tree. B. Click mac authentication list to enter the page as shown in figure 316 . C. Add a local user in the ...
Page 320
307 figure 317 configure the client verifying the configuration • if the mac address of the client is in the mac authentication list, the client can pass authentication and access the wlan network. • you can view the online clients on the page you enter by selecting summary > client from the navigat...
Page 321
308 • the ip address of the ap is 10.18.1.1. On the ap, configure the shared key for communication with the radius server as expert, and configure the ap to remove the domain name of a username before sending it to the radius server. Figure 318 network diagram configuring the ap 1. Assign an ip addr...
Page 322
309 b. Optional: on the domain setup tab, create a new isp domain. This example uses the default domain system. C. On the authentication tab, select the isp domain system, select the lan-access authn box, select the authentication mode radius, select the authentication scheme mac-auth from the name ...
Page 323
310 figure 322 configure the aaa accounting method for the isp domain 4. Configure wireless service a. Select wireless service > access service from the navigation tree. B. Click add. C. On the page that appears, set the wireless service name to mac-auth, select the wireless service type clear, and ...
Page 324
311 figure 324 security setup 6. Bind an ap radio to a wireless service a. Select wireless service > access service from the navigation tree. B. Click the bind link at the right side of the wireless service mac-auth to enter the page as shown in figure 325 . C. Select the box with radio mode 802.11n...
Page 325
312 figure 326 enable the wireless service 8. Optional: enable 802.11n radio (by default, 802.11n radio is enabled.) select radio > radio from the navigation tree to enter the radio page. Make sure 802.11n is enabled. Configuring the radius server (imcv3) note: the following takes the imc (imc plat ...
Page 326
313 figure 327 add access device 2. Add service. A. Select the service tab. B. Select access service > access device from the navigation tree. C. Click add. D. On the page that appears, set the service name to mac, keep the default values for other parameters, and click apply. Figure 328 add service...
Page 327
314 figure 329 add account configuring the radius server (imc v5) note: the following takes the imc (imc plat 5.0 and imc uam 5.0) as an example to illustrate the basic configuration of the radius server. 1. Add an access device. A. Select the service tab in the imc platform. B. Select user access m...
Page 328
315 b. Select user access manager > service configuration from the navigation tree. C. Click add. D. On the page that appears, set the service name to mac, keep the default values for other parameters, and click apply. Figure 331 add service 3. Add an account. A. Select the user tab. B. Select user ...
Page 329
316 remote 802.1x authentication configuration example network requirements perform remote 802.1x authentication on the client. • a radius server (an imc server for authentication, authorization, and accounting) is required. On the radius server, the client's username user and password dot1x, and th...
Page 330
317 figure 334 configure radius 3. Configure aaa a. Select authentication > aaa from the navigation tree. B. Optional: on the domain setup tab, create a new isp domain. This example uses the default domain system. C. On the authentication tab, select the isp domain system, select the lan-access auth...
Page 331
318 figure 336 configure the aaa authorization method for the isp domain e. On the accounting tab, select the isp domain name system, select the accounting optional box and then select enable from the accounting optional list, select the lan-access accounting box, select the accounting method radius...
Page 332
319 figure 338 create a wireless service 5. Configure 802.1x authentication after you create a wireless service, you enter the wireless service configuration page. A. In the security setup area on the page, select the open-system from the authentication type list. B. Select the cipher suite box, sel...
Page 333
320 b. Click the bind link at the right side of the wireless service mac-auth to enter the page as shown in figure 340 . C. Select the box with radio mode 802.11n(2.4ghz). D. Click bind. Figure 340 bind an ap radio 7. Enable the wireless service a. Select wireless service > access service from the n...
Page 334
321 d. On the page that appears, enter the shared key expert, enter the authentication and accounting ports 1812 and 1813, select lan access service from the service type list, select h3c from the access device type list, select or manually add an access device with the ip address 10.18.1.1, and cli...
Page 335
322 figure 343 add service 3. Add account. A. Select the user tab. B. Select user > all access users from the navigation tree. C. Click add. D. On the page that appears, enter a username user, add an account user and password dot1x, and select the service dot1x, and click apply. Figure 344 add accou...
Page 336
323 configuring the radius server (imc v5) note: the following takes the imc (imc plat 5.0 and imc uam 5.0) as an example to illustrate the basic configuration of the radius server. 1. Add an access device. A. Select the service tab in the imc platform. B. Select user access manager > access device ...
Page 337
324 figure 346 add a service 3. Add an account. A. Select the user tab. B. Select user > all access users from the navigation tree. C. Click add. D. On the page that appears, enter username user, set the account name to user and password to dot1x, select the service dot1x, and click apply. Figure 34...
Page 338
325 3. On the wireless networks tab, select wireless network with the ssid dot1x, and then click properties. The dot1x properties window appears. 4. On the authentication tab, select protected eap (peap) from the eap type list, and click properties. 5. In the popup window, clear validate server cert...
Page 339
326 figure 348 configure the wireless card (i).
Page 340
327 figure 349 configure the wireless card (ii).
Page 341
328 figure 350 configure the wireless card (iii) verifying the configuration • after entering the username user and password dot1x in the popup dialog box, the client can associate with the ap and access the wlan. • you can view the online clients on the page you enter by selecting summary > client ...
Page 342
329 figure 351 network diagram configuring the ap 1. Assign an ip address to the fat ap: a. Select network > vlan to create a vlan on the fat ap. B. Select device > interface management to assign an ip address to the vlan interface. 2. Configure a radius scheme: see " configure a radius scheme: ." 3...
Page 343
330 g. Disable handshake and multicast trigger (recommended). H. Click apply. Figure 353 security setup 6. Bind an ap radio to a wireless service a. Select wireless service > access service from the navigation tree. B. Click the bind link at the right side of the wireless service dot1x to enter the ...
Page 344
331 figure 355 enable the wireless service 8. Optional: enable 802.11n radio (802.11n radio is enabled by default.). Select radio > radio from the navigation tree to enter the radio page, and make sure 802.11n is enabled. Configuring the wireless card 1. Double click the icon at the bottom right cor...
Page 345
332 figure 356 configure the wireless card (i) 4. On the authentication tab, select protected eap (peap) from the eap type list, and click properties. 5. In the popup window, clear validate server certificate, and click configure. 6. In the popup dialog box, clear automatically use my windows logon ...
Page 346
333 figure 357 configure the wireless card (ii).
Page 347
334 figure 358 configure the wireless card (iii) verifying the configuration • after the user enters the username user and password dot1x in the popup dialog box, the client can associate with the ap and access the wlan. • you can view the online clients on the page you enter by selecting summary > ...
Page 348
335 configuring the ap 1. Assign an ip address to the fat ap: a. Select network > vlan to create a vlan on the fat ap. B. Select device > interface management to assign an ip address to the vlan interface. 2. Configure a wireless service a. Select wireless service > access service from the navigatio...
Page 349
336 figure 362 enable the wireless service 5. Enable 802.11n(2.4ghz) radio (by default, 802.11n(2.4ghz) radio is enabled.) select radio > radio from the navigation tree to enter the radio page. Make sure 802.11n(2.4ghz) is enabled. Figure 363 enable 802.11n(2.4ghz) radio verifying the configuration ...
Page 350
337 configuration guidelines note the following guidelines when you configure 802.11n: • select radio > radio from the navigation tree, select the ap radio unit to be configured, and click the corresponding icon to enter the radio configuration page, where you can modify the 802.11n-related paramete...
Page 351
338 figure 366 wds setup page b. Click the corresponding icon of the target radio unit. C. On the page that appears, select the pass phrase box, and enter 12345678 in the preshared key field, leave the neighbor mac address box blank (indicating that the ap can establish a wds link with any other ap)...
Page 352
339 figure 368 configure the working channel 4. Enable 802.11n(5ghz) radio (by default, 802.11n(5ghz) is enabled.). Select radio > radio from the navigation tree to enter the radio page. Make sure 802.11n(5ghz) is enabled. 5. Enable wds a. Select wireless service > wds from the navigation tree to en...
Page 353
340 figure 370 the page displaying wds information configuration guidelines the output information of a wds link includes: neighbor mac address, local mac address, link state, link uptime, and signal quality. When five green bars are displayed for the signal quality, the signal is of the highest qua...
Page 354
341 configuration guidelines note the following guidelines when you configure wds: • configure a neighbor mac address for each radio interface (otherwise, wds links may be set up between ap 2, ap 3, and ap 4). • set the maximum number of wds links allowed. The default value is 2. It must be set to 3...
Page 355
342 figure 373 wds setup page b. Click the icon in the operation column of the target 802.11n (2.4ghz) radio mode. C. Select the pass phrase box and enter 12345678 in the preshared key field. D. Click apply. Figure 374 wds setup page 2. Configure the working channel: a. Select radio > radio from the...
Page 356
343 figure 375 configure the same channel 3. Enable 802.11n (2.4ghz) radio (by default, 802.11n (2.4ghz) is enabled.). Select radio > radio from the navigation tree to enter the radio page. Make sure 802.11n (2.4ghz) is enabled. 4. Enable wds: a. Select wireless service > wds from the navigation tre...
Page 357
344 figure 377 configure the access service note: when you configure access service on the repeater, make sure the radio mode of the repeater is the same as that of wds. In this example, radio unit 2 in 802.11n(2.4ghz) mode is specified. Verifying the configuration 1. The wds link has been establish...
Page 358
345 figure 379 the page displaying radio information workgroup bridge mode configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 380 , an ap working as a workgroup bridge accesses the wireless network as a client. The ethernet interface of the workgroup bridge connects to multiple hosts or p...
Page 359
346 a. Select wireless service > client mode from the navigation tree. B. Click connect setup. C. On the page that appears, select the box corresponding to 802.11n (2.4ghz) and click enable. Figure 381 enable the client mode when the client mode enabled, you can check the existing wireless services ...
Page 360
347 figure 383 set code verifying the configuration on the ap shown in figure 380 , select summary > client from the navigation tree to enter the page shown in figure 384 , where you can verify that the workgroup bridge is online. Figure 384 verify that the workgroup bridge is online • you can see t...
Page 361
348 note: to configure vlan information about the wlan uplink interface of the workgroup bridge, make sure the vlan id of the wlan uplink interface of the workgroup bridge is the same as the vlan id of the downlink ethernet interface..
Page 362
349 configuring acl and qos note: unless otherwise stated, acls refer to both ipv4 and ipv6 acls throughout this document. Overview introduction to acl an access control list (acl) is a set of rules (or permit or deny statements) for identifying traffic based on criteria such as source ip address, d...
Page 363
350 qos refers to the ability to provide improved service by solving the core issues such as delay, jitter, and packet loss ratio in the packet forwarding process. Traditional packet forwarding services on traditional ip networks, devices treat all packets equally and handle them using the first in ...
Page 364
351 step remarks 3. Configuring a rule for a basic ipv4 acl required. Complete one of the three steps according to the acl category. 4. Configuring a rule for an advanced ipv4 acl 5. Configuring a rule for an ethernet frame header acl recommended ipv6 acl configuration procedure step remarks 1. Addi...
Page 365
352 figure 386 adding a time range 3. Configure the time range information. 4. Click apply. Table 111 configuration items item description time range name set the name for the time range. Periodic time range start time set the start time of the periodic time range. These items are available after yo...
Page 366
353 2. Click the add tab to enter the ipv4 acl adding page. Figure 387 adding an ipv4 acl 3. Configure the ipv4 acl information as described in table 112 . 4. Click apply. Table 112 configuration items item description acl number set the number of the ipv4 acl. Match order set the match order of the...
Page 367
354 figure 388 configuring an basic ipv4 acl 3. Configure a basic ipv4 acl as described in table 113 . 4. Click add. Table 113 configuration items item description acl select the basic ipv4 acl for which you want to configure rules. Available acls are basic ipv4 acls. Rule id select the rule id opti...
Page 368
355 item description check logging select this option to log matching ipv4 packets. A log entry contains the acl rule number, action on the matching packets, protocol that ip carries, source/destination address, source/destination port number, and number of matching packets. Source ip address select...
Page 369
356 figure 389 configuring an advanced ipv4 acl 3. Configure an advanced ipv4 acl rule as described in table 114 . 4. Click add. Table 114 configuration items item description acl select the advanced ipv4 acl for which you want to configure rules. Available acls are advanced ipv4 acls..
Page 370
357 item description rule id select the rule id option and enter a number for the rule. If you do not specify the rule number, the system assigns one automatically. Important: if the rule number you specify already exists, the following operations modify the configuration of the rule. Action select ...
Page 371
358 item description tcp/udp port tcp connection established select this option to make the rule match packets used for establishing and maintaining tcp connections. These items are available only when you select 6 tcp from the protocol list. A rule with this item configured matches tcp connection p...
Page 372
359 figure 390 configuring a rule for an ethernet frame header acl 3. Configure an ethernet frame header ipv4 acl rule as described in table 115 . 4. Click add. Table 115 configuration items item description acl select the ethernet frame header ipv4 acl for which you want to configure rules. Availab...
Page 373
360 item description mac address filter source mac address select the source mac address option and enter a source mac address and wildcard. Source mask destination mac address select the destination mac address option and enter a destination mac address and wildcard. Destination mask cos(802.1p pri...
Page 374
361 figure 391 adding an ipv6 acl 3. Configure the ipv6 acl information as described in table 116 . 4. Click apply. Table 116 configuration items item description acl number enter a number for the ipv6 acl. The value ranges of the acl number vary by device. Match order select a match order for the a...
Page 375
362 figure 392 configuring a rule for a basic ipv6 acl 3. Configure the basic ipv6 acl rule information as described in table 117 . 4. Click add. Table 117 configuration items item description select access control list (acl) select the basic ipv6 acl for which you want to configure rules. Available...
Page 376
363 item description source ip address select the source ip address option and enter a source ipv6 address and prefix length. The ipv6 address must be in a format like x:x::x:x. An ipv6 address consists of eight 16-bit long fields, each of which is expressed with two hexadecimal numbers and separate...
Page 377
364 4. Click add. Table 118 configuration items item description select access control list (acl) select the advanced ipv6 acl for which you want to configure rules. Available acls are advanced ipv6 acls. Rule id select the rule id option and enter a number for the rule. If you do not specify the ru...
Page 378
365 item description tcp/udp port so urc e operation select the operations and enter the source port numbers and destination port numbers as required. These items are available only when you select 6 tcp or 17 udp from the protocol list. Different operations have different configuration requirements...
Page 379
366 figure 394 configuring priority trust mode 2. Configure the priority trust mode of the interfaces as described in table 119 . 3. Click apply. Table 119 configuration items item description please select the interface type select the type of the ports to be configured. The interface types availab...
Page 380
367 item description (select the ports) specify the ports to be configured. Click the ports to be configured in the port list. You can select one or more ports. Configuring a qos policy a qos policy defines what qos actions to take on what class of traffic for purposes such as traffic shaping or tra...
Page 381
368 step remarks 6. Configuring classifier-behavior associations for the policy required. Associate a traffic behavior with a class in the qos policy. You can associate a class with only one traffic behavior in a qos policy. If a class is associated with multiple traffic behaviors, the last associat...
Page 382
369 item description operation specify the logical relationship between rules of the classifier. • and—specifies the relationship between the rules in a class as logic and. The device considers a packet belongs to a class only when the packet matches all the rules in the class. • or—specifies the re...
Page 383
370 figure 396 configuring classification rules 3. Configuration classification rules as described in table 121 . 4. Click apply. A progress dialog box appears. 5. Click close on the progress dialog box when the progress dialog box prompts that the configuration succeeds. Table 121 configuration ite...
Page 384
371 item description dscp define a rule to match dscp values. If multiple such rules are configured for a class, the new configuration does not overwrite the previous one. You can configure up to eight dscp values each time. If multiple identical dscp values are specified, the system considers them ...
Page 385
372 item description mac source mac define a rule to match a source mac address. If multiple such rules are configured for a class, the new configuration does not overwrite the previous one. A rule to match a source mac address is significant only to ethernet interfaces. Destination mac define a rul...
Page 386
373 figure 397 adding a traffic behavior configuring actions for a traffic behavior 1. Select qos > behavior from the navigation tree. 2. Click the setup tab to enter the page for setting a traffic behavior..
Page 387
374 figure 398 setting a traffic behavior 3. Configure the traffic behavior actions as described in table 122 . 4. Click apply. A progress dialog box appears. 5. Click close on the progress dialog box when the progress dialog box prompts that the configuration succeeds. Table 122 configuration items...
Page 388
375 item description car enable/disable enable or disable car. Cir set the committed information rate (cir), the average traffic rate. Cbs set the committed burst size (cbs), number of bits that can be sent in each interval. Red discard set the action to perform for exceeding packets. After selectin...
Page 389
376 item description filter configure the packet filtering action. After selecting the filter option, select one item in the following list: • permit—forwards the packet. • deny—drops the packet. • not set—cancels the packet filtering action. Accounting configure the traffic accounting action. Selec...
Page 390
377 figure 400 setting a policy 3. Configure classifier-behavior associations as described in table 123 . 4. Click apply. Table 123 configuration items item description please select a policy select an existing policy in the list. Classifier name select an existing classifier in the list. Behavior n...
Page 391
378 figure 401 applying a policy to a port 3. Select a policy and apply the policy to the specified ports as described in table 124 . 4. Click apply. Table 124 configuration items item description please select a policy select an existing policy in the list. Direction set the direction in which you ...
Page 392
379 figure 402 service policy 2. Click the icon for a wireless service to enter the service policy setup page. Figure 403 service policy setup 3. Apply the policy to the wireless service as described in table 125 . 4. Click apply. Table 125 configuration items item remarks wlan service displays the ...
Page 393
380 item remarks inbound policy apply the qos policy to the packets received by the wireless service. Outbound policy apply the qos policy to the packets sent by the wireless service. Trust mode set the priority trust mode: • untrust—trusts the port priority. • dscp—uses the dscp values of received ...
Page 394
381 figure 405 defining a time range covering 8:00 to 18:00 every day 2. Add an advanced ipv4 acl: a. Select qos > acl ipv4 from the navigation tree. B. Click the add tab. C. Enter the acl number 3000. D. Click apply..
Page 395
382 figure 406 adding an advanced ipv4 acl 3. Define an acl rule for traffic to the ftp server: a. Click the advanced setup tab. B. Select 3000 in the acl list. Select the rule id option, and enter rule id 2. Select permit in the action list. C. Select the destination ip address option, and enter ip...
Page 396
383 figure 407 defining an acl rule for traffic to the ftp server 4. Add a class: a. Select qos > classifier from the navigation tree. B. Click the add tab. C. Enter the class name class1. D. Click add..
Page 397
384 figure 408 adding a class 5. Define classification rules. A. Click the setup tab. B. Elect the class name class1 in the list. Select the acl ipv4 option, and select acl 3000 in the following list. C. Click apply. A progress dialog box appears. D. Click close on the progress dialog box when the p...
Page 398
385 figure 409 defining classification rules 6. Add a traffic behavior: a. Select qos > behavior from the navigation tree. B. Click the add tab. C. Enter the behavior name behavior1. D. Click add..
Page 399
386 figure 410 adding a traffic behavior 7. Configure actions for the traffic behavior: a. Click the setup tab. B. Elect behavior1 in the list. Select the filter option, and then select deny in the following list. C. Click apply. A progress dialog box appears. D. Click close when the progress dialog...
Page 400
387 figure 411 configuring actions for the behavior 8. Add a policy: a. Select qos > qos policy from the navigation tree. B. Click the add tab. C. Enter the policy name policy1. D. Click add..
Page 401
388 figure 412 adding a policy 9. Configure classifier-behavior associations for the policy. A. Click the setup tab. B. Select policy1. Select class1 in the classifier name list. Select behavior1 in the behavior name list. C. Click apply. Figure 413 configuring classifier-behavior associations for t...
Page 402
389 figure 414 applying the qos policy in the inbound direction of wireless service service1 verifying the configuration after you complete these configurations, the qos policy is applied to wireless service service1, and the wireless clients cannot access the ftp server at ip address 10.1.1.1 from ...
Page 403
390 configuring wireless qos overview an 802.11 network offers wireless access based on the carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (csma/ca) channel contention. All clients accessing the wlan have equal channel contention opportunities, and all applications carried on the wlan use th...
Page 404
391 wmm protocol overview the distributed coordination function (dcf) in 802.11 stipulates that access points (aps) and clients use the csma/ca access mechanism. Aps or clients listen to the channel before they hold the channel for data transmission. When the specified idle duration of the channel t...
Page 405
392 to use a high-priority access category, a client must send a request to the ap. The ap returns a positive or negative response based on either of the following admission control policy: • channel utilization-based admission policy—the ap calculates the total time that the existing high-priority ...
Page 406
393 figure 416 wireless qos 2. Select the option in front of the radio unit to be configured. 3. Click enable. By default, wmm is enabled. Note: the wmm protocol is the foundation of the 802.11n protocol. When the radio works in 802.11n (5 ghz) or 802.11n (2.4 ghz) radio mode, you must enable wmm. O...
Page 407
394 3. Configure svp mapping as described in table 126 . 4. Click apply. Table 126 configuration items item description radio displays the selected radio. Svp mapping select the option before svp mapping, and then select an access category for the svp service: • ac-vo. • ac-vi. • ac-be. • ac-bk. Set...
Page 408
395 by default, the qos service tab is displayed. 2. Click the icon for the desired radio to enter the page for configuring wireless qos. 3. On the radio edca list, click the icon for the desired priority type (ac_bk, for example) to enter the page for setting radio edca parameters. Figure 420 setti...
Page 409
396 setting edca parameters for wireless clients 1. Select qos > wireless qos from the navigation tree. By default, the qos service tab is displayed. 2. Click the icon for the desired radio to enter the page for configuring wireless qos. 3. On the client edca list, click the icon for the desired pri...
Page 410
397 note: • ecwmin cannot be greater than ecwmax. • if all clients operate in 802.11b radio mode, set txoplimit to 188 and 102 for ac-vi and ac-vo. • if some clients operate in 802.11b radio mode and some clients operate in 802.11g radio mode in the network, h3c recommends the txoplimit parameters i...
Page 411
398 field description radio chip max txoplimit maximum txoplimit allowed by the radio chip. Radio chip max ecwmax maximum ecwmax allowed by the radio chip. Client accepted number of clients that have been admitted to access the radio, including the number of clients that have been admitted to access...
Page 412
399 displaying client statistics 1. Select qos > wireless qos from the navigation tree. 2. Click the client statistics tab to enter the page displaying client statistics. 3. Click a client name to see its details. Figure 423 displaying client statistics table 133 field description field description ...
Page 413
400 field description downlink cac packets number of downlink cac packets. Downlink cac bytes number of downlink cac bytes. Downgrade packets number of downgraded packets. Downgrade bytes number of downgraded bytes. Discard packets number of dropped packets. Discard bytes number of dropped bytes. Se...
Page 414
401 item description direction traffic direction, which can be: • inbound—traffic from clients to the ap. • outbound—traffic from the ap to clients. • both—includes inbound traffic (traffic from clients to the ap) and outbound traffic (traffic from the ap to clients) mode set a rate limiting mode, w...
Page 415
402 figure 425 setting the reference radio bandwidth 3. Set the reference radio bandwidth as described in table 135 . 4. Click apply. Table 135 configuration items item description 802.11a mode set the reference radio bandwidth. Important: set the reference radio bandwidth slightly lower than the ma...
Page 416
403 figure 426 setting guaranteed bandwidth 2. Set the guaranteed bandwidth as described in table 136 . 3. Click apply. Table 136 configuration items item description guaranteed bandwidth percent (%) allocate guaranteed bandwidth as a percentage of the radio bandwidth to each wireless service. The t...
Page 417
404 displaying guaranteed bandwidth settings 1. Select qos > wireless qos from the navigation tree. 2. Click the bandwidth guarantee tab. 3. Click the specified radio unit to view the wireless services bound to the radio unit and the guaranteed bandwidth setting for each wireless service. Figure 428...
Page 418
405 b. Make sure that wmm is enabled. Figure 430 wireless qos configuration page c. Select the radio unit to be configured on the list and click the icon to enter the page for configuring wireless qos. D. On the client edca list, select the priority type (ac_vo, for example) to be modified, and clic...
Page 419
406 maximum number of users allowed in high-priority access categories, which is 10 in this example, the request is allowed. The system decreases the priority of the packets from the clients exceeding the maximum number of high-priority clients. Static rate limiting configuration example network req...
Page 420
407 • check that traffic from client1 is rate limited to around 128 kbps, so is traffic from client2. Dynamic rate limiting configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 435 , clients access the wlan through a ssid named service2. Configure all clients to share 8000 kbps of bandwidth...
Page 421
408 1. When only client1 accesses the wlan through ssid service2, its traffic can pass through at a rate as high as 8000 kbps. 2. When both client1 and client2 access the wlan through ssid service2, their traffic flows can each pass through at a rate as high as 4000 kbps. Bandwidth guarantee configu...
Page 422
409 figure 438 setting the reference radio bandwidth e. Click the icon for 802.11a to enter the page for setting guaranteed bandwidth. F. Set the guaranteed bandwidth percent to 80 for wireless service research. Set the guaranteed bandwidth percent to 20 for wireless service office. Set the guarante...
Page 423
410 verifying the configuration • send traffic from the ap to the three clients at a rate lower than 10000 kbps. The rate of traffic from the ap to the three clients is not limited. • send traffic at a rate higher than 2000 kbps from the ap to client 1 and at a rate higher than 8000 kbps from the ap...
Page 424
411 advanced settings advanced settings overview district code radio frequencies for countries and regions vary based on country regulations. A district code determines characteristics such as frequency range, channel, and transmit power level. Configure the valid country code or area code for a wla...
Page 425
412 figure 442 network diagram for uplink interface monitoring (a radio interface acts as the uplink interface) channel busy test the channel busy test is a tool to test how busy a channel is. It tests channels currently supported by the district code one by one, and provides a busy rate for each ch...
Page 426
413 figure 443 multicast data transmission when multicast optimization is enabled with multicast optimization enabled, the ap listens to the igmp reports and leave messages sent by clients. When the ap receives an igmp report, it adds or updates a multicast optimization entry and updates the multica...
Page 427
414 figure 444 setting a district code 2. Configure a district code as described in table 137 . 3. Click apply. Table 137 configuration items item description country/region code select a district code. Configure the valid district code for a wlan device to meet the country regulations. Note: • if t...
Page 428
415 figure 446 configuring continuous transmitting mode 2. Click the icon corresponding to the target radio to enter the page for configuring transmission rate. The transmission rate varies with radio mode. When the radio mode is 802.11a/b/g, the page as shown in figure 447 appears. Select a transmi...
Page 429
416 configuring uplink interface monitoring 1. Select advanced > uplink monitor from the navigation tree. Figure 449 configuring uplink interface monitoring 2. Configure uplink interface monitoring as described in table 138 . Table 138 configuration items item description interface name display the ...
Page 430
417 figure 451 testing channel busy rate 3. Configure channel busy test as described in table 139 . 4. Click start. Table 139 configuration items item description radio unit display the radio unit of the ap. Radio mode display the radio mode of the ap. Test time per channel set a time period in seco...
Page 431
418 • the fast association function is disabled. By default, the fast association function is disabled. For more information about fast association, see "configuring access services." • band navigation is enabled for the ap. By default, band navigation is enabled for the ap. • the ssid is bound to t...
Page 432
419 item description max denial count maximum denial count of client association requests. If a client has been denied more than the maximum times on the 5 ghz radio, the ap considers that the client is unable to associate to any other ap or the 2.4 ghz radio of the ap, and allows the 5 ghz radio to...
Page 433
420 table 141 configuration items item description aging time specify the aging time for multicast optimization entries. If the ap does not receive any igmp report from a client within the aging time, the ap removes the client from the multicast optimization entry. Multicast optimization max clients...
Page 434
421 table 142 field description field description total clients total number of clients served by multicast optimization. If a client joins multiple multicast groups, the client is counted as multiple clients. For example, if a client has joined two multicast groups through a radio, the client is co...
Page 435
422 1. Configure wireless service: a. Select wireless service > access service from the navigation tree. B. Click add. C. On the page that appears, set the service name to band-navigation, select the wireless service type clear, and click apply. 2. Enable wireless service: a. Select wireless service...
Page 436
423 figure 457 configuring band navigation verifying the configuration client 1 and client 2 are associated to the 5 ghz radio of the ap, and client 4 can only be associated to the 2.4 ghz radio of the ap. Because the number of clients on the 5 ghz radio has reached the upper limit 2, and the gap be...
Page 437
424 3. Click apply. 4. Select the target wireless service. 5. Click enable. Figure 459 configuring multicast optimization verifying the configuration client 1 and client 2 are associated with a radio of the ap. Because the number of clients on the radio has reached the upper limit 2, client 3 cannot...
Page 438
425 wlan security configuration wlan security overview 802.11 networks are susceptible to a wide array of threats such as unauthorized access points and clients, ad hoc networks, and denial of service (dos) attacks. To ensure security, the wireless intrusion detection system (wids) is introduced. Wi...
Page 439
426 at present, spoofing attack detection counters this type of attack by detecting broadcast de-authentication and disassociation frames sent on behalf of an ap. When such a frame is received, it is identified as a spoofed frame, and the attack is immediately logged. Weak iv detection wired equival...
Page 440
427 figure 460 configuring wids 2. Configure wids as described in table 143 . 3. Click apply. Table 143 configuration items item description flood attack detect if you select the box, flood attack detection is enabled. It is disabled by default. Spoof attack detect if you select the box, spoofing at...
Page 441
428 figure 462 displaying statistics configuring the blacklist and white list functions configuring dynamic blacklist 1. Select security > filter from the navigation tree. You will enter the blacklist tab. Figure 463 configuring dynamic blacklist 2. Configure the dynamic blacklist as described in ta...
Page 442
429 note: at present, these attacks can be detected through a dynamic blacklist: assoc-flood, reassoc-flood, disassoc-flood, probereq-flood, action-flood, auth-flood, deauth-flood, and nulldata-flood. Configuring static blacklist 1. Select security > filter from the navigation tree. You will enter t...
Page 443
430 figure 465 configuring white list 4. Add a white list as described in table 146 . 5. Click apply. Table 146 configuration items item description mac address select mac address and then add a mac address to the white list. Select current connect client if you select the box, the table below lists...
Page 444
431 user isolation if an ap has the user isolation feature enabled, clients associated with it are isolated at layer 2. As shown in figure 466 , after user isolation is enabled on the ap, all the clients cannot ping each other or learn each other's mac or ip addresses, because they cannot exchange l...
Page 445
432 index a b c d e f h i l m o p q r s t u v w a aaa configuration example, 200 aaa overview, 193 access service, 255 acl/qos configuration example, 380 adding a dns server address, 135 adding a domain name suffix, 136 admin configuration, 4 advanced settings configuration examples, 421 advanced se...
Page 446
433 creating an ipv4 static route, 115 creating an ipv6 static route, 118 d device information, 20 dhcp server configuration example, 130 diagnostic information, 39 display the information of assigned ip addresses, 129 displaying arp entries, 101 displaying client, 30 displaying client statistics, 3...
Page 447
434 recommended configuration procedure, 133 recommended configuration procedure, 106 recommended configuration procedure, 124 removing a file, 51 removing arp entries, 103 repeater mode configuration example, 341 repeater mode overview, 264 restoring configuration, 47 s saving configuration, 48 set...