- DL manuals
- Hach
- Measuring Instruments
- QC8500 Series 2
- User Manual
Hach QC8500 Series 2 User Manual
Summary of QC8500 Series 2
Page 1
Catalog number doc026.53.00808 quikchem ® 8500 series 2 fia automated ion analyzer user manual june 2008, edition 4 © hach company, 2004, 2007, 2008. All rights reserved. Printed in the u.S.A.
Page 3: Table of Contents
1 table of contents section 1 specifications .................................................................................................................... 5 1.1 bench requirements..................................................................................................................
Page 4
2 table of contents 4.8 inert probe ..................................................................................................................................45 4.9 pump operation ...................................................................................................................
Page 5
3 table of contents 6.6 injection valve troubleshooting................................................................................................... 75 6.7 detector fault...............................................................................................................................
Page 6
4 table of contents.
Page 7: Section 1
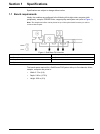
5 section 1 specifications specifications are subject to change without notice. 1.1 bench requirements ideally, the modules are configured in the following left-to-right order: computer (with peripherals), sampler, pds200 dilutor, reagent pump and system unit (refer to figure 1 ). Note: the sampler ...
Page 8: 1.2 Module Dimensions
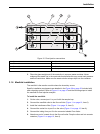
6 specifications 1.2 module dimensions table 1 contains the general dimensions for individual modules. Use table 1 for any system configuration that differs from the one explained above. Allow a minimum of 10 cm of free space in the back of the instrument and between modules for cabling and tubing. ...
Page 9
7 specifications table 2 individual electrical specifications module ac input voltage rating or range ac input frequency rating or range maximum active power (w), apparent power (va) or current (a) rating fuse rating pds200 110–240 vac 50–60 hz 0.5 a t, ½ a, 250 v asx-500 sampler 100–240 vac 50–60 h...
Page 10
8 specifications.
Page 11: Section 2
9 section 2 general information 2.1 safety information read this entire manual before unpacking, setting up or operating this equipment. Pay attention to all danger and caution statements. Failure to do so could result in serious injury to the operator or damage to the equipment. To make sure that t...
Page 12
10 general information 2.2 general product information the system unit manages five sample processing modules or channels, configured for performing flow injection analysis with photometric detection. The number of channels can be expanded to a maximum of eight by adding a second core. Alternate con...
Page 13: Section 3
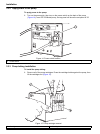
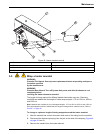
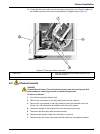
11 section 3 installation danger only qualified personnel should conduct the tasks described in this section of the manual. 3.1 system unit installation 3.1.1 carrying instructions caution potential lifting hazard. A five-channel system weighs 47 kg (103 lb). Do not unpack, carry or move the system ...
Page 14
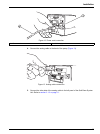
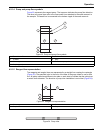
12 installation 3.1.4 flow cell installation to install the flow cell: 1. Insert the flow cell into the detector with the printed side (bottom) down. Since the flow cell is keyed, insert the flow cell only in the corresponding slot of the detector ( figure 5 ). 2. Make sure the flow cell is pushed a...
Page 15
13 installation 3.1.5 waste and sample line installation 3.1.5.1 sample line a sample line consists of a union connector, 130 or 190 cm of teflon ® tubing 0.8 mm (0.032 in.) id, two pump tube adapters, a green-green pump tube with its ends trimmed to 2 cm past both green tabs and 30 cm of teflon tub...
Page 16
14 installation 3.1.5.2 waste line a waste line consists of a 13 cm of teflon tubing 0.8 mm id, a pump tube adapter, 150 cm of tygon tubing 1.5 mm id, a glass weight and a plastic nipple. Refer to figure 9 . To install a waste line: 1. Connect a waste line to port 5 of the injection valve and the to...
Page 17
15 installation 3. Place the glass weight end of the waste line in a proper waste container. Never submerge the waste line in the waste solution because this may cause back pressure and flow restrictions. Make sure the waste solution always drips into the container. 3.1.6 manifold installation the m...
Page 18
16 installation 3.1.7 data system installation follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the setup of the computer, keyboard, monitor and mouse. For data systems purchased from the manufacturer, the omnion software is installed at the factory. For customer-supplied systems, refer to the omnion user...
Page 19
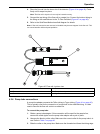
17 installation 4. Connect the analog cable to the back of the pump ( figure 13 ). 5. Connect the other side of the analog cable to the left panel of the quikchem system unit. Refer to section 3.1.3 on page 11 . Figure 12 power cord connection 1 power cord 2 main supply socket figure 13 analog cable...
Page 20
18 installation 3.2.2 apply power to the pump to apply power to the pump: 1. Turn on the power strip, then turn on the power switch on the back of the pump ( figure 14 ). In an rp-150 model pump, the top panel will show the set speed of 35. 3.2.3 pump tubing installation to install the pump tubing: ...
Page 21
19 installation 2. Place the pump tubing on the cartridges ( figure 16 ). Make sure that the tabs lock into the adaptor. 3. Move the tension lever to the far right position (up position). 4. Install the pump cartridge. Engage one side of the cartridge on the cartridge holder, then clamp down the oth...
Page 22
20 installation 5. Move the tension lever to the left until it clicks into place ( figure 18 ). Make sure the tension lever is in the 12 o'clock position. Note: move the lever to the right to remove tension. 6. Store unused cartridges. 3.2.4 reagent pump initial test to test the reagent rp-150 pump:...
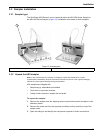
Page 23: 3.3 Sampler Installation
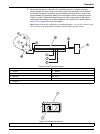
21 installation 3.3 sampler installation 3.3.1 sampler type the quikchem 8500 series 2 can be used with either the asx-500 series sampler or the asx-400 series sampler ( figure 19 ). Installation is the same for both samplers. 3.3.2 unpack the asx sampler note: if any of these items are missing or d...
Page 24
22 installation 3.3.3 sampler setup to connect the sampler: 1. Connect the power cord to the power strip. Leave the power strip switched off. 2. Connect the supplied rs232c cable to the 9-pin connector (com1) on the back of the sampler. 3. Connect the other end of the rs232c cable to com1 on the com...
Page 25
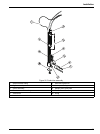
23 installation figure 20 probe tube assembly 1 sample transfer tubing 7 slider block guide rail 2 sipper assembly tube 8 home position flag 3 z-drive assembly 9 sample probe guide plate 4 thumbscrews with bushings 10 z-axis slider 5 x-axis block 11 o-ring 6 y-axis lead screw.
Page 26
24 installation 3.3.6 fluidic connections 3.3.6.1 connect the rinse station rinse solution is pumped into the bottom of the rinse station and drains to a waste container through drain tubing attached at the top of the station ( figure 21 ). To connect the rinse station: 1. Connect the rinse-in end o...
Page 27: 3.4 Dilutor Installation
25 installation 3.3.7 connect the sampler to a pds200 dilutor systems that use a pds200 dilutor require the asx-500 series sampler and a dual probe. Refer to section 3.4 for installation instructions. 3.4 dilutor installation the pds200 uses positive displacement to draw deionized water or other dil...
Page 28
26 installation 3.4.2 pds200 connections note: probe speed on existing autosamplers has been reduced to improve performance. The autosampler may produce a different sound as a result. To connect the pds200: 1. Connect the di water line to port a of the solenoid valve of the dilutor. Place the other ...
Page 29
27 installation figure 24 dilutor and solenoid valve fluidic connections 1 to sample probe 7 dilutor power connection 2 to diluent 8 dilutor power supply 3 dual probe assembly 9 sampler power supply 4 dilutor/sampler serial cable 10 to pump/analyzer 5 sampler/computer connection 11 di water line 6 s...
Page 30
28 installation.
Page 31: Section 4
29 section 4 operation the quikchem ® system automates wet chemical determinations using the principle of flow injection analysis. The peristaltic reagent pump draws the sample from the sampler into the injection valve. Simultaneously, reagents are continuously pumped through the system. The sample ...
Page 32
30 operation the injection valve has two states: the inject state and the load state. The valve will be moving bi-directionally between those two states. When the system is not in operation, the valves rest in the inject state. 4.1.1 inject state when the valve is in the inject state, the carrier st...
Page 33
31 operation 4.1.2 load state during the load state, the sample loop is being filled with sample. When the valve switches back to the inject state, the sample flowing through the sample loop is trapped momentarily. This sample, whose volume can be calculated from the length and inner diameter of the...
Page 34: 4.2 Manifold Diagram
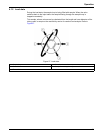
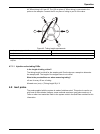
32 operation 4.2 manifold diagram a manifold is the reaction module where the chemistry occurs. This section explains how to read a manifold diagram. Each quikchem method contains a manifold diagram ( figure 28 ). The manifold diagrams depict reagent flow rather than the manifold layout. Both diagra...
Page 35
33 operation 4.2.1 manifold symbols 4.2.1.1 mixing coil symbol mixing coils are typically constructed with 0.8 mm id teflon tubing wrapped on a coil support. The mixing coil symbol ( figure 29 ) may also represent a back pressure loop. Read the notes regarding mixing coils in the quikchem methods. T...
Page 36
34 operation note: refer to the quikchem method to obtain the correct length of tubing needed for the analysis. Some manifold diagrams have all dimensions in the metric system. 4.2.1.3 injection valve symbols the injection valve ( figure 31 ) will be located on the left side of every channel of the ...
Page 37
35 operation 4.2.1.4 pump and pump flow symbols figure 32 represents the reagent pump. The top arrow indicates the pump flow direction. The other two upper lines refer to the rinse water lines attached to the wash reservoir in the sampler. The wash line is connected to the bottom nipple of the wash ...
Page 38
36 operation the reagent lines are labeled to indicate the solution going through that line. The carrier line is always connected to port 2 of the valve. The sample line is always connected to port 6 of the valve. 4.2.1.6 tee connector symbol note: the manifold diagram examples have only one tee con...
Page 39: 4.3 Fluidic Connections
37 operation 4.3 fluidic connections 4.3.1 flow fit connections tee connectors, union connectors and pump tube adapters are all examples of flow fit connections. Tube connectors used on tee connectors, union connectors and pump tube adapters pass teflon tubing through two viton ® o-rings into a seat...
Page 40
38 operation 4.3.2 flared tubing connections/switching valve connections the switching valve is a manual valve designed to direct the flow in the manifold. Some manifolds that include a column (e.G., cadmium column for nitrate reduction) may have this type of valve. A flared tubing connection requir...
Page 41
39 operation 4. Place the flow cell into the lower slot of the detector ( figure 44 on page 43 ). Press firmly until it snaps into place. Note: the flow cell is keyed so it can only be inserted one way. 5. Connect the top tubing of the flow cell to a waste line. Connect the bottom tubing to the fitt...
Page 42
40 operation 4. Insert the pump tube adapter into the pump tube. Slide the pump tube as far as it can go. 5. Screw the collar on the pump tube adapter. Table 7 pump tube colors collar pump tube color white orange - white white black white orange white white black red black gray black yellow black ye...
Page 43: 4.4 Instrument Startup Test
41 operation 4.3.5 transmission lines connections depending on the inner diameter of the tygon tubing, two pieces of tubing can be connected by a metal or a plastic nipple. The metal nipple is used for small inner diameter tubing. The plastic nipple is for large inner-diameter tubing ( figure 42 ). ...
Page 44: 4.7 Manifold Installation
42 operation once the instrument is powered up: 1. Determine if the analysis to be performed requires a special detector. Most quikchem methods require a photometric detector module ( figure 44 on page 43 ). Note: the ion chromatography (ic) channel (optional) uses a conductivity module instead of a...
Page 45
43 operation 5. Determine whether the manifold is for a heated chemistry. A heated chemistry manifold board will have a hole to route the tubing from the heater to the manifold. For heated chemistries, locate the union connector that holds the two ends of the tubing needed for the method. Refer to t...
Page 46
44 operation 4.7.1 injection valve connections ports 1 and 4— the tubing that connects these two ports is called the sample loop. The length of the sample loop is specified in the method. Use 0.8 mm id teflon tubing for the sample loop unless the quikchem method specifies otherwise. Refer to figure ...
Page 47: 4.8 Inert Probe
45 operation all teflon tubing is 0.8 mm id. The 130 cm piece of teflon tubing is connected to the probe on the sampler. Connect the 20 cm piece of tubing to port 6 of the valve. 4.7.1.1 injection valve tubing faqs is the length of tubing critical? The tubing length is critical for the sample path. ...
Page 48: 4.9 Pump Operation
46 operation 4.9 pump operation to use new pump tubes for the first time, allow the pump to run approximately ten minutes in order to obtain constant flow rates. Table 8 shows the functions of each button on the pump. Place all of the reagent lines into their corresponding containers or in deionized...
Page 49: 4.10
47 operation 4.9.1 reagent pump shutdown procedure to shutdown the rp-150 reagent pump: 1. Press the manual run/ stop button to stop the pump. Turn off the green power switch or turn off the power strip. 2. Release all of the cartridges. If the pump tubes are clamped down for more than a few minutes...
Page 50: 4.12 Dye Test Standards
48 operation 4.12 dye test standards to evaluate the operation of the system, run tests with the universal dye instead of reagents. This technique is helpful in troubleshooting problems that are not related to the reagents. All of the reagent lines can be put in deionized water. The standards will b...
Page 51: 4.13 Calibration Run
49 operation 4.13 calibration run once the installation of the manifold is complete, refer to the omnion 3.0 software user manual for the calibration run details. Figure 47 system operation.
Page 52
50 operation.
Page 53: Section 5
51 section 5 maintenance danger only qualified personnel should conduct the tasks described in this section of the manual. Preventive maintenance is extremely important for long-term operation. The following tips will help keep the quikchem ® 8500 series 2 operation at maximum potential. Keep all mo...
Page 54: 5.3
52 maintenance 5.2 system shutdown procedure to shutdown the system: 1. To use a manifold with a column, such as the cadmium column for nitrate, take the column off-line by rotating the switching valve to the bypass position. If the manifold has a column, but does not have a switching valve, turn of...
Page 55: 5.4
53 maintenance 10. Carefully wrap transmission lines around the manifold. Store the manifold in the supplied plastic bubble bag. 11. To install another manifold, refer to section 3.1.6 on page 15 . 5.4 heater assembly installation and removal danger potential electrocution hazard. Turn off system un...
Page 56
54 maintenance 5.4.2 heater assembly removal refer to figure 49 on page 55 . To remove the heater assembly: 1. Allow the assembly to cool completely, then disconnect the tubing from the manifold. Remove the manifold. 2. Lift the assembly from the channel. 3. Disconnect the heater controller cable, h...
Page 57: 5.5
55 maintenance 5.5 wrap a heater mandrel warning potential fire hazard. Use only exact replacement heater wrap tubing and tape or insulation specified by the manufacturer. Warning potential burn hazard. Turn off system unit power and allow the heater to cool completely before touching the heater ele...
Page 58: 5.6 Dilutor Maintenance
56 maintenance 4. Leave a 30-cm length of the replacement tubing that extends beyond the end of the mandrel core and secure the tubing with high-temperature tape. Note: the length of tubing is specified in the quikchem method. 5. Wrap the tubing around the length of the mandrel core. Leave a 30-cm l...
Page 59: 5.8
57 maintenance 5.7.2 rinse station tubing replacement to replace the rinse station tubing: 1. Shut down and unplug the sampler. 2. Gently push the sampler arm about 30 cm away from the home position. 3. Carefully disconnect the rinse solution inlet and drain tubing. 4. Rotate the rinse station tube ...
Page 60
58 maintenance 5.9.1 valve module replacement refer to figure 50 . To replace the valve module: 1. Disconnect all tubing from the valve. 2. Lift the valve module from the channel and disconnect the 6-pin connector. 3. Lift the module free of the channel. 4. Connect the replacement valve module. 5. S...
Page 61: 5.10 Flow Cell Maintenance
59 maintenance • the rotor seal in the valve module wears with use. Hence, routine replacement of the module is required. The main cause of early failure is the presence of abrasive particles in the samples. Filter or centrifuge the sample to avoid scratches on the rotor seal surface. • if leaks occ...
Page 62: 5.12 Manifold Maintenance
60 maintenance 5.12 manifold maintenance follow the recommended cleaning procedures listed in the quikchem methods. In addition, every 500 hours of use, clean each fitting and replace the o-rings as necessary. If any of the tubing is stained, replace it with new tubing. Replace all manifold tubing o...
Page 63
61 maintenance lamp specifications • tungsten halogen lamp ge ® constant color lamp ™ • catalog no. 31069 to replace the lamp: 1. Remove the top panel of the system unit. 2. Locate the spare lamp, secured by a strap to the inside of the system unit. 3. Loosen the two screws on the lamp cover and sli...
Page 64: 5.15
62 maintenance 5.15 fuse replacement danger potential shock hazard. Disconnect ac input before replacing fuse. Replace and secure the fuse holder before reconnecting ac input. Table 12 shows the specifications for the user-replaceable fuses. 5.15.1 pds fuse replacement to replace the pds fuse: 1. Re...
Page 65: Section 6
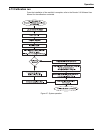
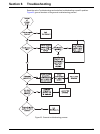
63 section 6 troubleshooting read the entire troubleshooting section before troubleshooting a specific problem. Figure 53 gives a flowchart of the general troubleshooting process. Figure 53 general troubleshooting process.
Page 66: 6.1 Valve Timing Setup
64 troubleshooting 6.1 valve timing setup to set the method valve timing correctly is critical. Poor valve timing may result in the absence of peaks, presence of air spikes or very small peaks. Set the cycle period parameter as specified in the quikchem method. When running multiple methods simultan...
Page 67
65 troubleshooting while random air spikes may not affect the analysis, constant air spikes are a problem. One of the most common causes of constant air spikes is the introduction of air into the line due to the exhaustion of the reagent. Make sure the reagent transmission lines are at the bottom of...
Page 68
66 troubleshooting 6.4 peak shapes interpretation and troubleshooting 6.4.1 refractive index a refractive index usually shows up as a negative peak before the analyte peak. There may be a small positive peak after the analyte peak. A refractive index is the difference in density between the carrier ...
Page 69
67 troubleshooting 6.4.2 ph effect this phenomenon occurs when a change in ph occurs. Most chemical reactions are ph dependent, therefore the colored complex that is formed as a result of the reaction may vary in concentration if the conditions of the analysis are altered. All of the quikchem method...
Page 70
68 troubleshooting 6.4.3 valve artifact this problem manifests itself when the valve is not operating properly. The symptom is noise that occurs before each analyte peak. A valve artifact can be mistaken for a refractive index. Valve artifacts are more noticeable when one or more reagents are colore...
Page 71
69 troubleshooting 6.4.4.1 common causes of carryover • wrong cycle period: if the cycle period is too small, carryover will occur when a series of high standards are injected. Look up the correct cycle period in the quikchem method. The cycle period is specified in the sample timing. If overrange s...
Page 72
70 troubleshooting • manifold: the manifold may not match the diagram in the method or the pump tubes may be a different color. Make sure the correct interference filter is installed. • overrange samples: sample may be too concentrated. Dilute those samples or choose a different method. 6.4.6 no pea...
Page 73
71 troubleshooting 6.4.7 noisy baseline any baseline will have some noise or disturbances. To observe this, zoom into the baseline section. Baseline noise becomes a problem when it interferes with the analysis. Methods that have colored reagent solutions will be typically more noisy. A noisy baselin...
Page 74
72 troubleshooting electronic noise electronic noise can be identified by the insertion of an empty and clean flow cell in the detector, as well as an interference filter. Do not pump any reagents at this time. Run any worksheet to see the baseline on the screen. If the baseline is noisy when there ...
Page 75: 6.5 Flow Blockages
73 troubleshooting 6.4.9 negative peaks and carrier contamination negative peaks ( figure 62 ) are normal for some chemistries like hypochlorite, alkalinity, etc. These methods are called inverse chemistries. On the other hand, direct chemistries always produce positive peaks. If the carrier of a di...
Page 76
74 troubleshooting after determining the suspect line, it is necessary to follow it from the glass weight at the entrance of the reagent to the waste container after the flow cell. Check every connection of the suspect line, starting from the nipple that holds the glass weight. Move towards the pump...
Page 77: 6.7 Detector Fault
75 troubleshooting 6.6 injection valve troubleshooting keep the valve clean at all times. Proper maintenance will help prevent many problems. There are two main problems that can occur with the valve: clogs and hardware failure. Refer to section 6.5.1 on page 74 to determine if blockages exist in th...
Page 78: 6.10 Dilutor
76 troubleshooting 6.10 dilutor to test the accuracy of the dilutor, run five manually-diluted and five autodiluted standards. Compare the results to determine if the problem resides in the dilutor or elsewhere. Run a dye test. Use the dilutor to make a series of standards from the stock universal d...
Page 79: 6.12 Dye Test
77 troubleshooting 4. Turn the pump on. Press normal run . The display must show a speed of 35 in order to continue this test. Refer to section 3.2 on page 16 if the display shows anything else. 5. Using an accurate watch or chronometer, measure the time the pump takes to make ten (10) revolutions. ...
Page 80
78 troubleshooting 6.12.3 dye test to determine valve problems make up a series of dye standards that can be run with the method in use. Specify two injections for each standard and use a first-order-polynomial fit. Another option is to make up four dye standards and write a new method using exactly...
Page 81: 6.13 Other Common Problems
79 troubleshooting 6.13 other common problems table 14 troubleshooting problems problem type problem description solution flow related the flow is moving backwards. There is a blockage on the manifold. Refer to section 6.5 on page 73 . Chemistry and/or flow related air bubbles are coming out of the ...
Page 82
80 troubleshooting software and/or hardware related the computer shows that an application error has occurred. Application errors can occur when the computer is asked to do something it does not understand or it cannot do. These errors are more frequently found when more than one program is running ...
Page 83
81 troubleshooting chemistry related the ammonia peaks are very small. Other ammonia method issues: too much naoh in the buffer may cause staining in the tubing after the heater. This may also be caused by using household bleach. Make sure the ph at the waste line is 13. Use the hypochlorite solutio...
Page 84
82 troubleshooting.
Page 85: Section 7
83 section 7 replacement parts and accessories 7.1 replacement parts description catalog number cadmium column 50237a cadmium column maintenance kit 50254 channel (sample processing module) a85040 clip, harness for manifold 50025 clip, large gray 50024l clip, small gray 50023l collar, large black 85...
Page 86
84 replacement parts and accessories kits accessory kit, qc8500 a85025 degassing tube 50100l flare kit for nitrate 50962 flare kit for sulfate 50963 maintenance kit, cadmium column 50254 pump tubing pvc 534xx 1 duraprene 544xx 1 silicone 494xx 1 acidflex 654xx 1 tefzel 41300l zeus 30928 teflon ® tub...
Page 87: 7.2 Accessories
85 replacement parts and accessories 7.2 accessories description catalog number cable, interface- asx510 21415l kit, tubing, asx samplers 89040 label, tie wrap with customized text 50050 rack, 60 position, 16 mm 21302 rack, 90 position, 13 mm 21301l rack, 90 position, 13 mm with inserts 21311 sample...
Page 88
86 replacement parts and accessories.
Page 89: Section 8
87 section 8 contact information authorization must be obtained from hach company before sending any items for repair. Please contact the lachat instruments-hach service center serving your location u.S.A. Customers by telephone: 6:30 a.M. To 5:00 p.M. Mst monday through friday (800) 247-7613 by fax...
Page 90
88.
Page 91: Section 9
89 section 9 warranty limited warranty lachat instruments, a hach company brand, warrants the quikchem ® 8500 system to the original purchaser against any defects that are due to faulty material or workmanship for a period of one year from date of shipment. In the event that a defect is discovered d...
Page 92
90 warranty.
Page 93: Section 10 Certification
91 section 10 certification hach company certifies this instrument was tested thoroughly, inspected and found to meet its published specifications when it was shipped from the factory. The model qc8500 series 2 has been tested and is certified as indicated to the following instrumentation standards:...
Page 94
92 certification.
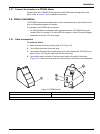
Page 95: A.1
93 appendix a channel installation the qc8500 series 2 analyzer can be expanded with modular channels and daisy-chain connections. Heater controller, valve controller and leak detector signals share one ribbon cable. The controller cable and power cable connections are made from the new channel to t...
Page 96
94 channel installation 5. Loosen the screws on the system unit cover and remove the cover. Note: it is not necessary to disconnect the ground cord on the cover. 6. Fit the tongue on the back of the new channel into the groove on the front of the existing channel. 7. Tighten the bottom screw on each...
Page 97: A.2
95 channel installation 11. Thread the fiber optic cable into the opening on the system unit. Plug the cable into an available opening on the terminal opposite the tungsten lamp ( figure 67 ). A.2 channel removal danger potential shock hazard. Turn off and disconnect power from the system unit befor...
Page 98
96 channel installation 8. Loosen the bottom screw on each end of the channel. 9. Lift the channel and set aside. 10. Snap the cover panels into place. Replace the system unit cover and tighten the screws..
Page 99
97 appendix b ion chromatography the channel for ion chromatography (ic) consists of a 6-port injection valve and a 10-port suppressor valve connected through a split cable and a conductivity module. The 10-port valve is mounted in the heater assembly drip tray. The conductivity module connects to t...
Page 100
98 ion chromatography b.1 suppressor valve assembly replacement caution potential chemical hazard. Turn off the system unit and disconnect from power before connecting or disconnecting channels or channel components. To replace the suppressor valve assembly: 1. Turn off the system unit and disconnec...
Page 101: B.3 Manifold Installation
99 ion chromatography b.3 manifold installation most ic manifolds will have two columns: a guard column and an analytical column. The purpose of the guard column is to protect the analytical column. Any unwanted particulates will be retained in the guard column. Some organic compounds, oils and grea...
Page 102
100 ion chromatography.
Page 103: Index
101 index a air bubbles ............................................................... 12 air spikes .................................................................. 64 alternating coil ........................................................ 84 ammonia ..............................................
Page 104
102 index r reagent limitation ..................................................... 69 reagent line .............................................................. 35 refractive index ........................................................ 66 rinse station .............................................