- DL manuals
- IAI
- Switch
- acon
- Operation Manual
IAI acon Operation Manual
Summary of acon
Page 1
Operation manual, eighth edition.
Page 2: Table of Contents
Table of contents.
Page 5
1 1. Overview the open field network profibus-dp is a multi-bit, multi-vendor network for communication of both control and data signals of the machine/line control level. A wire-saving system can be built by connecting iai’s x-sel, tt, rcs-c, e-con, acon, pcon, scon, asel, psel and ssel controllers...
Page 6
2 2. Specifications 2.1 interface specifications the table below lists the specifications of the profibus-dp interface. Item specification remarks communication profile profibus-dp communication method hybrid method master/slave method with token passing number of connectable stations 32 stations pe...
Page 7
3 3. X-sel controller 3.1 profibus-dp board types and installation positions in the x-sel there are six types of x-sel controllers that support profibus-dp, as listed below. The installation position of the profibus-dp board is different depending on whether the x-sel controller is of pr0 type or pr...
Page 8
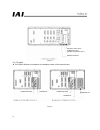
4 (1) compact type (j type) 1-axis specification *1 2-axis specification *1 3/4-axis specification *2, *3 fig. 3.1 *1) an i/o board cannot be installed in 1-axis and 2-axis specifications, because the profibus-dp board occupies the only slot available. *2) with 3-axis and 4-axis specifications, only...
Page 9
5 (2) general-purpose type (k type) z either a profibus-dp board or standard i/o board must be always installed in the standard slot (i/o1 --- slot at the far left). Z the “pr1” profibus-dp board occupies two expansion slots. If this type of profibus-dp board is selected, only one expansion slot can...
Page 10
6 fig. 3.3 (3) p/q types z the profibus-dp board is installed in the installation position of field network board. Fig. 3.4 expansion slots 2 and 3 profibus-dp board (installed in expansion slot 1.) standard i/o board standard i/o standard i/o profibus-dp board profibus-dp board expansion i/o.
Page 11
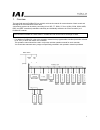
7 3.2 setting a profibus-dp board (slave station) (1) name of each part j/k/jx/kx/ type p/q/px/qx type profibus-dp communication connector termination switch address setting dials monitor leds profibus-dp communication connector termination switch address setting dials monitor leds.
Page 12
8 (2) profibus-dp communication connector interface specifications this is a 9-pin, female d-sub connector recommended by the profibus-dp standard en 50170. Connector pin no. Description contents 3 b-line rxd x txd (positive signal line) 5 gnd shield 8 a-line /rxd x /txd (negative signal line) housi...
Page 13
9 (4) node address settings the address of each profibus-dp slave station is set using the “x10” and “x1” rotary switches shown in the figure under (1). Set a desired address according to the following rule: node address number = (“value set by x10” rotary switch x 10) + (“value set by x1” rotary sw...
Page 14
10 3.3 setting x-sel i/o parameters (assigning i/o ports) set the x-sel input/output ports to be used in profibus-dp communication. The x-sel supports many variations of input/output port settings depending on how the applicable i/o parameters are set. (for details, refer to “operation manual for x-...
Page 15
11 (2) k/kx type note) one profibus-dp board occupies two slots. Accordingly, nos. 4 and 5 are set to “-1,” and no. 11 to “0,” when a profibus-dp board is set in the slots denoted by a above. If a profibus-dp board is set in the slots denoted by b, nos. 8 and 9 are set to “-1,” while no. 13 is set t...
Page 16
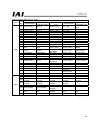
12 3.3.2 factory-set parameters (default settings) (1) factory-set parameters for the j/k/jx/kx types • i/o parameter settings no. Parameter name input range a b c remarks 1 input/output port assignment type 0 ~ 20 0 0 0 0: fixed assignment 1: automatic assignment (priority: slot 1 ~) * ports are as...
Page 17
13 (2) factory-set parameters for the p/px/q/qx types no. Parameter name input range settings remarks 1 input/output port assignment type 0 ~ 20 0 0: fixed assignment 1: automatic assignment (priorities: network i/f module → slot 1 (standard i/o) ~) * ports are assigned automatically only for the co...
Page 18
14 3.3.3 automatically assigning x-sel i/os set the x-sel input/output ports to be used in profibus-dp communication. The x-sel supports many variations of input/output port settings depending on how the applicable i/o parameters are set. (for details, refer to “operation manual for x-sel controller...
Page 19
15 x-sel (k type) no. Parameter name input range settings remarks 1 input/output port assignment type 0 ~ 20 1 0: fixed assignment 1: automatic assignment (priority: slot 1 ~) * ports are assigned automatically only for the contiguous slots in use, starting from slot 1 = for safety reasons. 2 standa...
Page 20
16 (2) setting example when a profibus-dp board is used with an expansion i/o board (automatic assignment) the port numbers of the expansion board are assigned automatically in accordance with the numbers of i/o ports of the profibus-dp slave station set by i/o parameter nos. 14 and 15. Example: if ...
Page 21
17 no. Parameter name input range settings remarks 1 input/output port assignment type 0 ~ 20 1 0: fixed assignment 1: automatic assignment (priority: slot 1 ~) * ports are assigned automatically only for the contiguous slots in use, starting from slot 1 = for safety reasons. 2 standard i/o fixed as...
Page 22
18 (3) setting example when a profibus-dp board is used with an expansion i/o board (fixed assignment) under fixed assignment (where i/o parameter no. 1 is set to “0”), you can set desired initial i/o port numbers. Under automatic assignment the initial i/o port numbers (input number 0 ~ / output nu...
Page 23
19 no. Parameter name input range settings remarks 1 input/output port assignment type 0 ~ 20 1 0: fixed assignment 1: automatic assignment (priority: slot 1 ~) * ports are assigned automatically only for the contiguous slots in use, starting from slot 1 = for safety reasons. 2 standard i/o fixed as...
Page 24
20 3.3.5 setting examples for p/px/q/qx type controllers (1) setting example when only a profibus-dp board is used (automatic assignment) example: the following settings apply when the i/o ports of the profibus-dp board are used by 32 input points and 16 output points, each from the beginning, by le...
Page 25
21 i/o parameters of x-sel p/px/q/qx type controllers no. Parameter name default (reference) input range setting remarks 1 input/output port assignment type 0 0 ~ 20 1 0: fixed assignment 1: automatic assignment (priorities: network i/f module → slot 1 (standard i/o) ~) * ports are assigned automati...
Page 26
22 (2) setting example when a profibus-dp board is used with a standard i/o board (automatic assignment) example: these settings are used when 256 input points and 256 output points are assigned, both from the initial standard i/o ports, to the profibus-dp board, and the remaining i/o port numbers a...
Page 27
23 i/o parameters of x-sel p/px/q/qx type controllers no. Parameter name default (reference) input range setting remarks 1 input/output port assignment type 0 0 ~ 20 1 0: fixed assignment 1: automatic assignment (priorities: network i/f module → slot 1 (standard i/o) ~) * ports are assigned automati...
Page 28
24 (3) setting example when a profibus-dp board is used with a standard i/o board (fixed assignment) in automatic assignment, the initial i/o port numbers (no. 0 or greater for input / no. 300 or greater for output) must be set on the standard i/o board. By using fixed assignment, however, you can s...
Page 29
25 i/o parameters of x-sel p/px/q/qx type controllers no. Parameter name default (reference) input range setting remarks 1 input/output port assignment type 0 0 ~ 20 1 0: fixed assignment 1: automatic assignment (priorities: network i/f module → slot 1 (standard i/o) ~) * ports are assigned automati...
Page 30
26 3.3.6 x-sel i/o port numbers the standard i/o port numbers of the x-sel are listed below. The port numbers and function assignments of the x-sel can be changed using i/o parameters. (for details, refer to “operation manual for x-sel controller.”) port no. Function port no. Function 000 program st...
Page 31
27 3.3.7 correspondence of x-sel i/o port numbers and plc addresses when the x-sel’s profibus-dp board i/os are assigned in the input/output (memory) areas of the plc, the areas that occupy the plc memory will change depending on the numbers of i/o points set on the x-sel side. Profibus-dp board i/o...
Page 32
28 2) address assignment in the master station when setting the configuration in 1) using a configurator, the numbers of inputs and outputs of the x-sel set for slave station 2 must be determined. (here, it is assumed that the number of occupiable slave stations is set to 16 words in the master stat...
Page 33
29 4) i/o port numbers are assigned in units of 16 points starting from the channel address in the plc buffer memory corresponding to the specified node address. Here, the plc buffer memory bits are sequentially assigned to the i/o port numbers, starting from the smallest port number and lowest memo...
Page 34
30 5) description example of bit addresses --- fuji electric the inputs and outputs of the x-sel are respectively assigned i/o addresses (word addresses) as viewed from the plc. The bit address description rules are specified below. Prefix bus station number this number indicates which of the units ...
Page 35
31 reference when bit addresses are set in the plc, port numbers are assigned in units of 16 points, starting from the channels corresponding to the node address set by the dip switches. (this does not apply when a configurator is used.) (input) (output) (input) (output) port number port number node...
Page 36
32 4. Tabletop robot tt 4.1 model models: tt--i--pr maximum numbers of network i/o points: 240/240 a profibus board is installed in the installation position for field network board. Profibus board standard i/o board.
Page 37
33 4.2 profibus board 4.2.1 name of each part monitor leds address setting dials termination switch profibus-dp communication connector.
Page 38
34 4.2.2 profibus-dp communication connector the board-end connector is a d-sub 9-pin (female) connector recommended under the profibus-dp standard en50170. The network connector on the other end is not supplied. Pin no. Signal name explanation 1 nc not connected 2 nc not connected 3 b-line communic...
Page 39
35 4.2.4 address setting dials (node address settings) the address of each profibus-dp slave station is set using the left (x1) and right (x10) address setting dials. These rotary switches set the node address of the applicable controller. Each of these two switches can be set to a desired value in ...
Page 40
36 4.3 i/o parameter settings (i/o port assignments) the tt i/o ports used by profibus are set. (1) board installation position (slot) and parameter numbers 64 input ports and 64 output ports are set at the factory for use with profibus. Profibus board parameter no. 14 no. 15 standard i/o board.
Page 41
37 (2) factory-set parameters for the tt type no. Parameter name factory-set value input range remarks 1 input/output port assignment type 0 read only 0: fixed assignment 2 standard i/o1 fixed assignment: initial input port number 000 -1 ~ 599 0 + (multiple of 8) (the parameter is invalid if a negat...
Page 42
38 (3) example of parameter settings for the tabletop robot tt the settings below assume that 240 input points and 240 output points are assigned on the profibus board as general-purpose i/o ports. With the tt, the initial i/o port numbers are fixed. Initial input port number: 48 initial output port...
Page 43
39 i/o parameters for tt type no. Parameter name factory-set value input range set value remarks 1 input/output port assignment type 0 read only 0 0: fixed assignment 2 standard i/o1 fixed assignment: initial input port number 000 read only 000 0 + (multiple of 8) (the parameter is invalid if a nega...
Page 44
40 4.4 i/o port numbers for tt the i/o port numbers applicable to the tt are shown below. (for details, refer to the “operation manual for tabletop robot tt.”) port no. Function port no. Function 000 start 300 alm (front panel led) 001 (software reset) 301 rdy (front panel led) 002 (servo on) 302 em...
Page 45
41 reference when bit addresses are set in the plc, port numbers are assigned in units of 16 points, starting from the channels corresponding to the node address set by the dip switches. (this does not apply when a configurator is used.) (input) (output) (input) port number node address nn node addr...
Page 46
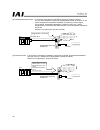
42 5. Rcs-c, e-con and scon 5.1 models external views (front views) of the rcs, e-con and scon controllers that support profibus-dp are shown below. (1) rcs-c models: rcs-c---pr- i/o points: eight dedicated input points, 10 dedicated output points rcs-c 24-v type rcs-c 100/200-v type.
Page 47
43 (2) e-con models: econ---pr- i/o points: 10 dedicated input points, 12 dedicated output points (3) scon models: scon-c--pr-- i/o points: 16 dedicated input points, 16 dedicated output points.
Page 48
44 5.2 setting a profibus-dp board (slave station) (1) name of each part (2) profibus-dp communication connector interface specifications this is a 9-pin, female d-sub connector recommended by the profibus-dp standard en 50170. Connector pin no. Description contents 3 b-line rxd/txd (positive signal...
Page 49
45 (3) bus termination settings among the units connected to a profibus-dp network, the devices at both ends require termination to prevent reflected waves from entering the bus line again. This profibus-dp module provides a termination switch that makes this termination easy. The user need not inst...
Page 50
46 (5) monitor led indications of the leds provided on the front face of the board, the two leds, err and power, can be used to check the operating condition of the communication module. The board has three leds, whose conditions and their meanings are explained below. Led color status definition de...
Page 51
47 (6) input/output (i/o) signal assignments the rcs-c, e-con and scon have the following numbers of inputs and outputs, respectively: [1] rcs-c 8 dedicated input points, 11 dedicated output points (100/200-v specification) or 10 dedicated output points (24-v specification) [2] e-con 10 dedicated in...
Page 52
48 [2] e-con signal assignments input number signal name output number signal name 0 command position 1 0 completed position 1 1 command position 2 1 completed position 2 2 command position 4 2 completed position 4 3 command position 8 3 completed position 8 4 command position 16 4 completed positio...
Page 53
49 [3] scon signal assignments the scon has 16 dedicated input points and 16 dedicated output points. The details of inputs and outputs are shown below. Signals are assigned in one of six patterns in accordance with the setting of scon parameter no. 25 (pio pattern selection). Setting of parameter n...
Page 54
50 setting of parameter no. 25 512-point mode solenoid valve mode 1 solenoid valve mode 2 3 4 5 category port no. Signal name symbol signal name symbol signal name symbol 0 pc1 start position 0 st0 start position 0 st0 1 pc2 start position 1 st1 start position 1 st1 2 pc4 start position 2 st2 start ...
Page 55
51 (7) correspondence of rcs-c, e-con and scon i/o port numbers and plc addresses in the assignment of the rcs-c, e-con or scon’s profibus-dp board i/os in the input/output (memory) areas of the plc, one word of input/output area is occupied by 16 i/o points (dedicated inputs/outputs) of the slave s...
Page 56
52 i/o port numbers are assigned in units of 16 points starting from the channel address in the plc buffer memory corresponding to the specified node address. Here, the plc buffer memory bits are sequentially assigned to the i/o port numbers, starting from the smallest port number and lowest memory ...
Page 57
53 reference 1 when bit addresses are set in the plc, inputs and outputs are sequentially assigned to the channels corresponding to the node address set by the dip switches. (input) (output) node address nn the numbers under (nn)/(mm) ch are plc channel addresses corresponding to node address nn. In...
Page 58
54 example of address assignment rules --- fuji electric prefix bus station number this number indicates the installation position of the profibus-dp board in the plc. Word number a sequential number specifying a word when the i/os assigned to the master station are arranged in words. Bit address a ...
Page 59
55 6. Asel, psel, ssel asel, psel and ssel controllers of profibus type can support up to 256 input points and 256 output points. 6.1 models 6.1.1 asel, psel asel and psel controllers of profibus type are indicated by the following model numbers: 1-axis type asel-c-1--pr- psel-c-1--pr- 2-axis ty...
Page 60
56 6.1.2 ssel ssel controllers of profibus type are indicated by the following model numbers: 1-axis type ssel-c-1--pr- 2-axis type ssel-c-1--pr- external view status leds profibus communication connector front panel color dark gray printed series name.
Page 61
57 6.2 profibus interface (1) name of each part • asel, psel • ssel (2) status led indications the operating condition of the profibus board, as well as the network condition, can be checked using the two leds (status0 and status1) provided on the front side of the board. Led color indicator conditi...
Page 62
58.
Page 63
59 (3) profibus-dp communication connector the board-end connector is a d-sub 9-pin (female) connector recommended under the profibus-dp standard en50170. The network connector on the other end is not supplied. Pin no. Signal name explanation 1 nc not connected 2 nc not connected 3 b-line communicat...
Page 64
60 6.3 i/o parameter settings set the node address, i/o ports and other parameters of the asel, psel and ssel used with profibus. (1) network type setting i/o parameter no. 225, “network i/f module: control” has been set to 3h (profibus) at the factory. (no additional setting is required.) (2) node ...
Page 65
61 asel, psel and ssel network i/o parameter list no. Parameter name factory-set value input range remarks 1 input/output port assignment type 0 0 ~ 20 0: fixed assignment 1: automatic assignment 14 network i/f module: remote input ports used 64 0 ~ 256 multiple of 8 15 network i/f module: remote ou...
Page 66
62 6.4 i/o port numbers and profibus-dp address assignments asel, psel and ssel controllers operate in the program mode and positioner mode, but the principles of assignment are the same with both modes. To be specific, i/o port numbers are assigned in units of 16 points starting from the channel ad...
Page 67
63 (2) positioner mode regardless of the settings of i/o parameter nos. 1, 16 and 17, physical ports are assigned from no. 0 for input ports and from no. 300 for output ports. As shown in the i/o port table on the next page and subsequent pages, input ports of nos. 0 to 23 and output ports of nos. 3...
Page 68
64 asel positioner mode i/o port table positioner mode category port no. Standard mode product-type switching mode 2-axis independent mode teaching mode dc-s-c1 compatible mode 16 position input 10 input 10 position input 7 axis 1 jog- position no. 1000 input 17 position input 11 input 11 position i...
Page 69
65 psel positioner mode i/o port table positioner mode category port no. Standard mode product-type switching mode 2-axis independent mode teaching mode dc-s-c1 compatible mode 16 position input 10 input 10 position input 7 axis 1 jog- position no. 1000 input 17 position input 11 input 11 position i...
Page 70
66 ssel positioner mode i/o port table positioner mode category port no. Standard mode product-type switching mode 2-axis independent mode teaching mode dc-s-c1 compatible mode 16 position input 10 input 10 position input 7 axis 1 jog- position no. 1000 input 17 position input 11 input 11 position i...
Page 71
67 7. Acon, pcon 7.1 operation modes and functions acon and pcon controllers supporting profibus-dp can be operated in a desired operation mode selected from the following five modes. Operation modes and key functions key function remote i/o mode position/simple direct mode half direct mode full dir...
Page 72
68 [2] position/simple direct mode: in this mode, the actuator is operated by specifying position numbers. You can select whether to specify the target position directly as a value, or use a value registered in the position data table, by switching a control signal. For the speed, acceleration/decel...
Page 73
69 [4] full direct mode: in this mode, the actuator is operated by specifying all values relating to position control (target position, speed, acceleration/deceleration, etc.) directly as values. Number of occupied bytes: 32 bytes (16 words) [5] remote i/o mode 2: in this mode, the actuator is opera...
Page 74
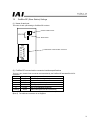
70 7.2 models the models of acon and pcon controller supporting profibus-dp are indicated as follows, respectively: z acon-c/cg- -pr- z pcon-c/cg- -pr- printed series name z acon z pcon front panel color z acon: dark blue z pcon: dark green.
Page 75
71 7.3 profibus-dp (slave station) settings (1) name of each part the name of each part relating to profibus-dp is shown. (2) profibus-dp communication connector interface specifications this is a 9-pin, female d-sub connector recommended by the profibus-dp standard en 50170. Connector pin no. Descr...
Page 76
72 (3) bus terminal processing if the connector is to be connected to the network terminal node, connect the terminal resistor to the profibus-dp communication connector as shown below or use a connector with terminal resistor. Z example of connector with terminal resistor: subcon-plus-profib/ax/sc ...
Page 77
73 (6) status led indications the board operating condition and network condition can be checked using the two leds provided on the front side of the controller. Led color indicator condition description of indication (meaning of indication) lit the board is online with the fieldbus network and comm...
Page 78
74 7.4 communication with the master station 7.4.1 operation modes and handling of plc addresses the address assignments under each operation mode are shown below. • plc output → acon/pcon input (* n indicates the initial output address for each axis.) acon/pcon di and input data resister remote i/o...
Page 79
75 • acon/pcon output → plc input (* n indicates the initial input address for each axis.) acon/pcon do and output data resister remote i/o mode position/simple direct mode half direct mode full direct mode remote i/o mode 2 plc input address (word address) number of occupied bytes: 2 number of occu...
Page 80
76 z reference: example of plc address assignment rules --- fuji electric the plc address assignment rules are shown below. Prefix bus station number this number indicates the installation position of the profibus-dp master unit within the plc units is indicated. Word address word addresses refer to...
Page 81
77 7.4.2 remote i/o mode (number of occupied bytes: 2) in this mode, the actuator is operated by specifying position numbers just like when pios (24-v i/os) are used. Set desired position data using the rc pc software or teaching pendant. The number of positions to which the actuator can be operated...
Page 82
78 (1) plc address configuration (* n indicates the initial input/output address for each axis.) parameter no. 84 acon/pcon di (port number) plc output address acon/pcon do (port number) plc input address 0 0 to 15 n 0 to 15 n pay attention to use of duplicate addresses. (2) i/o signal assignments f...
Page 83
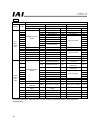
79 (3) i/o signal assignments which signals are assigned to controller i/o ports vary according to the setting of parameter no. 25. (for details, refer to the operation manual for the controller.) acon setting of parameter no. 25 positioning mode teaching mode 256-point mode 0 1 2 category port no. ...
Page 84
80 acon setting of parameter no. 25 512-point mode solenoid valve mode 1 solenoid valve mode 2 3 4 5 category port no. Signal name symbol signal name symbol signal name symbol 0 pc1 start position 0 st0 start position 0 st0 1 pc2 start position 1 st1 start position 1 st1 2 pc4 start position 2 st2 s...
Page 85
81 pcon setting of parameter no. 25 positioning mode teaching mode 256-point mode 0 1 2 category port no. Signal name symbol signal name symbol signal name symbol 0 pc1 pc1 pc1 1 pc2 pc2 pc2 2 pc4 pc4 pc4 3 pc8 pc8 pc8 4 pc16 pc16 pc16 5 command position number pc32 command position number pc32 pc32...
Page 86
82 pcon setting of parameter no. 25 512-point mode solenoid valve mode 1 solenoid valve mode 2 3 4 5 category port no. Signal name symbol signal name symbol signal name symbol 0 pc1 start position 0 st0 start position 0 st0 1 pc2 start position 1 st1 start position 1 st1 2 pc4 start position 2 st2 s...
Page 87
83 7.4.3 position/simple direct mode (number of occupied bytes: 8) in this mode, the actuator is operated by specifying position numbers. You can select whether to set the target position directly as a value or use a value registered in the position data table, by switching a control signal (pmod si...
Page 88
84 (2) i/o signal assignments for each axis an i/o signal of each axis consists of 4 words (8 bytes) of i/o addresses. Z control signals and status signals are bit on/off signals. Z the target position and current position are both a 2-word (32-bit) binary data. Although values from -999999 to +9999...
Page 89
85 plc input address (* n indicates the initial input address for each axis.) 1 word = 2 bytes = 16 bits current position (upper word) current position (lower word) complete position number status signal if the current position is a negative value, it is expressed by a 2’s complement..
Page 90
86 (3) i/o signal assignments (* in the table, on indicates that the applicable bit is “1,” while off indicates that the applicable bit is “0.”) signal type bit symbol description details target position 32-bit data - 32-bit signed integer. Specify the target position on the absolute coordinates. Th...
Page 91
87 (* in the table, on indicates that the applicable bit is “1,” while off indicates that the applicable bit is “0.”) signal type bit symbol description details current position 32 bit - 32-bit signed integer indicating the current position. The unit is 0.01 mm. (example) reading: 000003ffh = 1023 (...
Page 92
88 7.4.4 half direct mode (number of occupied bytes: 16) in this mode, the actuator is operated by specifying the target position, positioning band, speed, acceleration/deceleration and push current directly as values from the plc. Set each value in an applicable i/o address. If the zone function is...
Page 93
89 (2) i/o signal assignments for each axis an i/o signal of each axis consists of 8 words (16 bytes) of i/o addresses. Z control signals and status signals are bit on/off signals. Z the target position and current position are both a 2-word (32-bit) binary data. Although values from -999999 to +999...
Page 94
90 plc output address (* n indicates the initial output address for each axis.) 1 word = 2 bytes = 16 bits target position (upper word) target position (lower word) control signal if the target position is a negative value, it is expressed by a 2’s complement. Positioning band (upper word) positioni...
Page 95
91 plc input address (* n indicates the initial input address for each axis.) 1 word = 2 bytes = 16 bits current position (upper word) current position (lower word) if the current position is a negative value, it is expressed by a 2’s complement. Command current (upper word) command current (lower w...
Page 96
92 (3) i/o signal assignments (* in the table, on indicates that the applicable bit is “1,” while off indicates that the applicable bit is “0.”) signal type bit symbol description details target position 32-bit data - 32-bit signed integer. Specify the target position on the absolute coordinates. Th...
Page 97
93 (* in the table, on indicates that the applicable bit is “1,” while off indicates that the applicable bit is “0.”) signal type bit symbol description details push-current limiting value 16-bit data - 16-bit integer. Specify the current-limiting value during push-motion operation. The specified ra...
Page 98
94 (* in the table, on indicates that the applicable bit is “1,” while off indicates that the applicable bit is “0.”) signal type bit symbol description details current position 32-bit data - 32-bit signed integer indicating the current position. The unit is 0.01 mm. (example) reading: 000003ffh = 1...
Page 99
95 7.4.5 full direct mode (number of occupied bytes: 32) in this mode, the actuator is operated by specifying all values relating to position control (target position, speed, etc.) directly as values from the plc. Set each value in an i/o address. The key functions that are available on robo cylinde...
Page 100
96 (2) i/o signal assignments for each axis an i/o signal of each axis consists of 16 words (32 bytes) of i/o addresses. Z control signals 1 and 2 and status signals are bit on/off signals. Z the target position and current position are both a 2-word (32-bit) binary data. Although values from -99999...
Page 101
97 plc output address (* n indicates the initial output address for each axis.) 1 word = 2 bytes = 16 bits target position (upper word) target position (lower word) if the target position is a negative value, it is expressed by a 2’s complement. Positioning band (upper word) positioning band (lower ...
Page 102
98 (*3) dedicated pcon function. Cannot be used on acon. Plc output address (* n indicates the initial output address for each axis.) 1 word = 2 bytes = 16 bits zone boundary- (upper word) zone boundary- (lower word) if the zone boundary- is a negative value, it is expressed by a 2’s complement. Dec...
Page 103
99 plc input address (* n indicates the initial input address for each axis.) 1 word = 2 bytes = 16 bits current position (upper word) current position (lower word) command current (upper word) command current (lower word) current speed (upper word) current speed (lower word) alarm code cannot be us...
Page 104
100 (3) i/o signal assignments (* in the table, on indicates that the applicable bit is “1,” while off indicates that the applicable bit is “0.”) address bit symbol function details target position 32-bit data - 32-bit signed integer. Specify the target position on the absolute coordinates. The unit...
Page 105
101 (* in the table, on indicates that the applicable bit is “1,” while off indicates that the applicable bit is “0.”) address bit symbol function details acceleration 16-bit data - deceleration 16-bit data - 16-bit integer. Specify the acceleration and deceleration at which to move the actuator. Th...
Page 106
102 (* in the table, on indicates that the applicable bit is “1,” while off indicates that the applicable bit is “0.”) address bit symbol function details b2 dir push direction specification: when the signal is off, the direction of the position obtained by subtracting the positioning band from the ...
Page 107
103 (* in the table, on indicates that the applicable bit is “1,” while off indicates that the applicable bit is “0.”) signal type bit symbol description details current position 32 bit data - 32-bit signed integer indicating the current position. The unit is 0.01 mm. (example) reading: 000003ffh = ...
Page 108
104 7.4.6 remote i/o mode 2 (number of occupied bytes: 12) in this mode, the actuator is operated by specifying position numbers just like when pios (24-v i/os) are used. Set desired position data using the rc pc software or teaching pendant. The number of positions to which the actuator can be oper...
Page 109
105 (1) plc address configuration (* n indicates the initial input/output address for each axis.) parameter no. 84 acon/pcon di and input register plc output address acon/pcon do and output register plc input address port number 0 to 15 n+0 port number 0 to 15 n+0 n+1 occupied area n+1 n+2 n+2 n+3 c...
Page 110
106 plc input address (* n indicates the initial input address for each axis.) 1 word = 2 bytes = 16 bits controller output port number cannot be used. Current position (upper word) current position (lower word) command current (upper word) command current (lower word) if the current position is a n...
Page 111
107 (3) i/o signal assignments for the signal assignments in each pio pattern, refer to (3), “i/o signal assignments” under 7.4.2, “remote i/o mode.” the signal assignments for command-current and current-position read functions are shown below. Signal type bit symbol description details current pos...
Page 112
108 7.4.7 i/o signal controls and functions * on indicates that the applicable bit is “1,” while off indicates that the applicable bit is “0.” the following specifies the controls and functions of i/o signals used in the position/simple direct mode, half direct mode and full direct mode. For the i/o...
Page 113
109 (5) servo on command (son) plc output signal ready (sv) plc input signal when the son signal is turned on, the servo turns on. When the servo turns on, the status indicator led (refer to (6) in 7.3) on the front side of the controller illuminates in green. The sv signal is synchronized with this...
Page 114
110 (6) home return (home) plc output signal home return complete (hend) plc input signal home return in progress (ghms) plc input signal when the home signal is turned on, the command will be processed at the leading (on) edge of the signal and home return operation will be performed automatically....
Page 115
111 (7) positioning start (cstr): used in the position/simple direct mode plc output signal this command is processed at the leading (on) edge of the signal, upon which the actuator moves to the position set by the target position corresponding to the specified position or the plc’s target position ...
Page 116
112 (10) positioning complete signal (pend) plc input signal this signal turns on when the actuator has moved to the target position and entered the positioning band or completed the push motion. When the servo turns from off to on, positioning is performed based on the current position being the ta...
Page 117
113 (12) zone 1 (zone1) plc input signal zone 2 (zone 2) plc input signal position zone (pzone) plc input signal each signal turns on when the current actuator position is inside the specified range, and turns off when the actuator is outside the range. [1] zones 1, 2 a desired zone is set using use...
Page 118
114 (13) +jog (jog+) plc output signal -jog (jog-) plc output signal these signals are used as starting commands for jog operation or inching operation. A + command starts the applicable operation in the direction opposite home, while a – command starts the applicable operation in the direction of h...
Page 119
115 (14) jog speed/inching distance switching (jvel) plc output signal this signal switches between the parameter that specifies the jog speed to be used when the jog mode is selected, and one that specifies the inching distance to be used when the inching mode is selected. The relationships of appl...
Page 120
116 (16) teaching mode command (mode) plc output signal teaching mode signal (modes) plc input signal when the mode signal is turned on, the normal operation mode switches to the teaching mode. When the mode switches to teaching, the controller of each axis turns on the modes signal. The plc should ...
Page 121
117 (19) operation mode (rmod) plc output signal operation mode status (rmds) plc input signal a different operation mode is selected as follows based on the rmod signal and the mode switch on the front side of the controller. Whether the current mode is auto or manu can be checked using the rmds si...
Page 122
118 (23) missed load during push-motion operation (psfl) plc input signal this signal turns on when the actuator has not contacted the load after having travelled the distance set by the positioning band in the controller’s position table or plc’s positioning band (refer to 7.4.1) during push-motion...
Page 123
119 (26) load output judgment (load) plc input signal dedicated pcon function this signal is valid only during push-motion operation. To use an actuator in a press-fit application, whether or not the specified load threshold has reached during the push-motion operation must be recognized. The load t...
Page 124
120 (27) torque level (trqs) plc input signal dedicated pcon function this signal is valid only during push-motion operation. This signal turns on when the motor current has reached the load threshold during push-motion operation (while the actuator is moving inside the positioning band). Since the ...
Page 125
121 (28) standstill control mode (smod) plc output signal dedicated pcon function one general characteristic of pulse motors is that their holding current in a standstill state is greater than that of ac servo motors. Accordingly, a means to reduce power consumption in a standstill state is provided...
Page 126
122 (29) acceleration/deceleration mode (mod1, mod0) plc output signal dedicated acon function this signal is used to select a desired acceleration/deceleration pattern characteristic. Select one characteristic before issuing an actuator move command. Mod1 mod0 pattern name remarks off off trapezoid...
Page 127
123 7.5 i/o signal timings the maximum response time after a given control signal is turned on to operate the robo cylinder using the plc’s sequence program, until a response (status) signal is turned, is expressed by the formula below: maximum response time (msec) = yt + xt + 2 + command processing...
Page 128
124 7.6 operation next, timings in the position/simple direct mode, half direct mode and full direct mode are explained using examples of basic operations. For the remote i/o mode and remote i/o mode 2, refer to the operation manual for the controller. (in remote i/o mode 2, read the current positio...
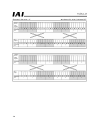
Page 129
125 [1] [2] set value of target position data specified position number positioning start positioning complete current position moving actuator movement positioning band [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] *t1: make sure “t1 ≥ 0 ms” is satisfied by considering the scan time of the host controller..
Page 130
126 (2) operation in the half direct mode operate the actuator by specifying data for the plc’s target position, positioning band, specified speed, acceleration/deceleration and push-current limiting specification. Z example of operation (push-motion operation) [1] set the target position data for t...
Page 131
127 set value of target position data [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] positioning band set value of positioning band data set value of speed data set value of acceleration/ deceleration data set value of push-current limiting value push specification push direction speci...
Page 132
128 (3) operation in the full direct mode operate the actuator by specifying from the plc all conditions required for positioning, such as the plc’s target position and positioning band. Z example of operation (push-motion operation) [1] set the target position data for the target positions (*) corr...
Page 133
129 set value of target position data [1] [2] set value of positioning band data set value of speed data [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] set value of position zone boundary data set value of acceleration data set value of deceleration data set value of push-current limiting value data set value of load curr...
Page 134
130 [9] [10] positioning band push specification push direction specification positioning command positioning complete/missed load during push-motion operation current position moving actuator operation (push) actuator operation (normal positioning operation) push *t1: make sure “t1 ≥ 0 ms” is satis...
Page 135
131 (4) data change during movement in the half direct mode and full direct mode, the values of target position data, acceleration/deceleration data, speed data, positioning band and push-current limiting value set by the plc can be changed while the actuator is moving. After a desired data has been...
Page 136
132 7.7 profibus-dp parameters the parameters relating to profibus-dp are parameter nos. 84 to 87 and 90. Category: c: external interface parameter no. Category symbol name factory default 1 ~ 83 for parameter nos. 1 to 83, refer to the operation manual for the controller. 84 c fmod fieldbus operati...
Page 137
133 z network type (no. 87 ntyp) specify the network module in parameter no. 87. Do not change the default value. Z fieldbus i/o format (no. 90 fmio) plc addresses are assigned in units of 16 points (units of words) based on the i/o addresses set to the controller and number of occupied addresses in...
Page 138
134 (example ii) set value = “2” z indicates on, while o indicates off. Acon/ pcon input register hexadecimal data hexadecimal data hexadecimal data hexadecimal data plc: output acon/ pcon output register plc: input.
Page 139
135 (example iii) set value = “1” z indicates on, while o indicates off. Acon/ pcon input register hexadecimal data hexadecimal data hexadecimal data hexadecimal data plc: output acon/ pcon output register plc: input.
Page 140
136 (example iv) set value = “0” z indicates on, while o indicates off. Acon/ pcon input register hexadecimal data hexadecimal data hexadecimal data hexadecimal data plc: output acon/ pcon output register plc: input.
Page 141
137 7.8 troubleshooting 7.8.1 status led indicators the illumination patterns of status leds (status0/1) indicate the operating condition of the profibus-dp module as well as the network condition. Should you encounter a problem, check the current conditions based on the illumination patterns of the...
Page 142
138 7.9 ce marking 7.9.1 european ec directives european ec directives are a group of new approach directives issued by the european commission for application to products sold in the eu (european union) bloc, in order to protect the health and safety of users and consumers of these products and als...
Page 143
139 7.9.3 configuration of peripherals ac power supply bus control panel circuit breaker surge protector* 24-vdc power supply (manufacturer: okaya electric industries @earth leakage breaker2 power-supply terminal (affixed by an affixing bolt on the controller).
Page 144
140 (1) environment use the acon and pcon in an environment conforming to pollution degree 2 or 1 as specified in iec 60664-1. Example) installation in a control panel whose structure does not permit entry of water, oil, carbon, dust, etc. (ip54). (2) power supply a) use the controller in an environ...
Page 145
141 (5) surge protector install a surge protector on the primary side of the 24-vdc power supply. Manufacturer: okaya electric industries model: r-a-v-781bwz-4 external view of surge protector (6) cable all cables connected to the acon and pcon, such as the motor cable, encoder cable and various net...
Page 146
142 8. Common items and others 8.1 communication cable for connection cables, use type a cables conforming to the profibus standard. 8.2 useful function when adjusting an x-sel controller (1) if a standard or expansion i/o board is installed in an x-sel k-type controller, the controller can be start...
Page 147
143.
Page 148
144.
Page 149
Catalog no.: me0153-8a (september 2008) head office: 2690 w. 237th street, torrance, ca 90505 tel (310) 891-6015 fax (310) 891-0815 chicago office: 1261 hamilton parkway, itasca, il 60143 tel (630) 467-9900 fax (630) 467-9912 atlanta office: 1220-e kenneston circle, marrietta, ga 30066 tel (678) 354...