- DL manuals
- IAI
- Controller
- ERC2
- Operation Manuals
IAI ERC2 Operation Manuals
Summary of ERC2
Page 1
Operation manual seventh edition erc2 actuator with integrated controller (sio type).
Page 3
Please read before use thank you for purchasing our product. This operation manual explains the handling methods, structure and maintenance of this product, among others, providing the information you need to know to use the product safely. Before using the product, be sure to read this manual and f...
Page 4: Caution
Caution 1. Using multiple 24-v power supplies if multiple 24-v power supplies are used, always connect the 0-v lines of all power supplies. If not, damage to the controller board, sio converter or other components may occur. [connection example] 24v 0v 24v 0v 24v 0v 24v 0v 24v 0v 24-v power supply [...
Page 5: Caution
Caution 2. Pc software and teaching pendant models this product offers new functions not available in the conventional erc series. To support these new functions, the communication protocol has been changed to a general modbus- compliant protocol. Accordingly, the pc software programs and teaching p...
Page 6: Ce Marking
Ce marking if a compliance with the ce marking is required, please follow overseas standards compliance manual (me0287) that is provided separately..
Page 7: Table of Contents
Table of contents safety guide .................................................................................................................................................. 1 1. Overview ...............................................................................................................
Page 8
4.2.3 connecting an emergency stop circuit, etc................................................................. 46 5. Explanation of operating functions..................................................................................................... 47 5.1 description of position table ...........
Page 9
.......................................................................................................................... 117 10.1.3 erc2-ra6c .......................................................................................................................... 118 10.1.4 erc2-ra7c ...............
Page 11
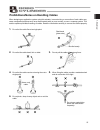
1 safety guide ³6dihw\*xlgh´kdvehhqzulwwhqwrxvhwkhpdfklqhvdiho\dqgvrsuhyhqwshuvrqdolqmxu\rusurshuw\ gdpdjhehiruhkdqg0dnhvxuhwruhdglwehiruhwkhrshudwlrqriwklvsurgxfw safety precautions for our products 7khfrpprqvdihw\suhfdxwlrqviruwkhxvhridq\rirxuurerwvlqhdfkrshudwlrq 1r 2shudwlrq 'hvfulswlrq 'hvfulsw...
Page 12
2 no. Operation description description 2 transportation Ɣ when carrying a heavy object, do the work with two or more persons or utilize equipment such as crane. Ɣ when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate...
Page 13
3 no. Operation description description (2) cable wiring Ɣ 8vhrxufrpsdq\¶vjhqxlqhfdeohvfor connecting between the actuator and controller, and for the teaching tool. Ɣ do not scratch on the cable. Do not bend it forcibly. Do not pull it. Do not coil it around. Do not insert it. Do not put any heavy ...
Page 14
4 no. Operation description description 4 installation and start (4) safety measures Ɣ when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with each other to ensure the safety of the workers. Ɣ when the product...
Page 15
5 no. Operation description description 6 trial operation Ɣ when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with each other to ensure the safety of the workers. Ɣ after the teaching or programming operation...
Page 16
6 no. Operation description description 8 maintenance and inspection Ɣ when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with each other to ensure the safety of the workers. Ɣ perform the work out of the safe...
Page 17: Alert Indication
7 alert indication 7khvdihw\suhfdxwlrqvduhglylghglqwr³'dqjhu´³:duqlqj´³&dxwlrq´dqg³1rwlfh´dffruglqjwrwkh zduqlqjohyhodviroorzvdqgghvfulehglqwkh,qvwuxfwlrq0dqxdoiruhdfkprgho /hyho 'hjuhhri'dqjhudqg'dpdjh 6\pero 'dqjhu 7klvlqglfdwhvdqlpplqhqwo\kd]dugrxvvlwxdwlrqzklfkliwkh surgxfwlvqrwkdqgohgfruuhfwo\z...
Page 18: &dxwlrqlq+Dqgolqj
8 &dxwlrqlq+dqgolqj 'rqrwvhwvshhgvdqgdffhohudwlrqvghfhohudwlrqvhtxdowrrujuhdwhu wkdqwkhuhvshfwlyhudwlqjv ,iwkhdfwxdwrulvrshudwhgdwdvshhgrudffhohudwlrqghfhohudwlrqh[fhhglqjwkhdoorzdeoh ydoxhdeqrupdoqrlvhruyleudwlrqidloxuhruvkruwhuolihpd\uhvxow ,qwkhfdvhrilqwhusrodwhgrshudwlrqrifrpelqhgd[hvwkhvshhgdqg...
Page 19
9 1. Overview 1. Overview 1.1 introduction thank you for purchasing the easy all-in-one robo cylinder (hereinafter referred to as “erc2-se”). This product retains all benefits of the conventional erc series, while incorporating new features that provide greater convenience and enhanced safety to the...
Page 20
10 1. Overview 1.2 key features and functions (1) input/output of control signals by means of rs485 serial communication (conforming to the modbus protocol) (2) 64 positioning points (3) variable zone output boundaries before, zone output boundaries were set by parameters and therefore fixed. For gr...
Page 21
11 1. Overview 1.3 differences from air cylinder control this section explains the key differences between an air cylinder and this controller for users who are familiar with air cylinders but have never used a motorized cylinder before. Refer to the table below to perform appropriate controls. Item...
Page 22
12 1. Overview item air cylinder this controller position check upon power on determined using a reed switch or other external detection sensor. Immediately after the power has been turned on, the current position is indeterminable because no mechanical coordinates are stored in the controller. Afte...
Page 23
13 1. Overview 1.4 meaning of the model number pm: pulse motor blank: no option b: with brake nm: reversed-home specification ft: foot bracket (specified only for rod types.) blank: no cable p: 1 m s: 3 m m: 5 m x : length specification (example) x08 = 8 m r : robot cable specification 50 to 600...
Page 24
14 1. Overview 1.5 specifications (note 1) the figures in blank bands indicate the maximum speeds for respective strokes. The maximum speeds during vertical operation are shown in parentheses. (note 2) the payload capacity is based on operation at the rated acceleration. In the case of a guide type,...
Page 25
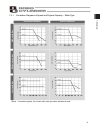
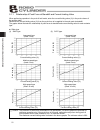
15 1. Overview 1.5.1 correlation diagrams of speed and payload capacity – slider type (note) in the above graphs, the number after each type name indicates the lead. Horizontal installation vertical installation high-speed type loa d ca pacity (kg) speed (mm/sec) medium-sp eed typ e low-speed type l...
Page 26
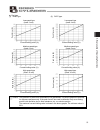
16 1. Overview 1.5.2 correlation diagrams of speed and payload capacity – rod type (note) in the above graphs, the number after each type name indicates the lead. Horizontal installation vertical installation high-speed type loa d ca pacity (kg) speed (mm/sec) medium-sp eed typ e low-speed type loa ...
Page 27
17 1. Overview load applied to the actuator (1) slider type x keep the load applied to the slider below the value stated in the applicable specification item. In particular, pay attention to the moment applied to the slider, allowable overhang length and payload capacity. X if the slider is used in ...
Page 28
18 1. Overview 1.6 warranty 1 warranty period one of the following periods, whichever is shorter: y 18 months after shipment from our company y 12 months after delivery to the specified location 2 scope of warranty our products are covered by warranty when all of the following conditions are met. Fa...
Page 29
19 1. Overview 5 conditions of conformance with applicable standards/regulations, etc., and applications (1) if our product is combined with another product or any system, device, etc., used by the customer, the customer must first check the applicable standards, regulations and/or rules. The custom...
Page 30
20 1. Overview 1.7 transportation and handling 1.7.1 handling before unpacking exercise due caution when transporting or handling the box containing the actuator, by not applying impact on the box as a result of collision or dropping. X if the box is heavy, one person should not carry it by himself....
Page 31
21 1. Overview 1.8 installation environment and noise elimination pay due attention to the installation environment of the controller. 1.8.1 installation environment the installation environment must satisfy the following conditions: no. Use environment/condition [1] not exposed to direct sunlight. ...
Page 32
22 1. Overview actuator with integrated controller other equipment other equipment actuator with integrated controller 1.8.3 power supply the control/motor-drive power supply specification is 24 vdc r 10% (2 a max). 1.8.4 noise elimination this section explains how to eliminate noise in the use of t...
Page 33
23 1. Overview diode (2) noise sources and elimination among the numerous noise sources, solenoid valves, magnet switches and relays are of particular concern when building a system. Noise from these sources can be eliminated by implementing the measures specified below. [1] ac solenoid valves, magn...
Page 34
24 1. Overview 1.9 cabling x when storing a extension cable in a moving wiring duct, use a robot cable. X in an application where the cable cannot be fixed, keep the cable from receiving a deflecting load exceeding its own weight, use a self-standing cable hose, provide a large bending radius along ...
Page 35
25 1. Overview prohibitions/notes on handling cables when designing an application system using this actuator, incorrect wiring or connection of each cable may cause unexpected problems such as a disconnected cable or poor contact, or even a runaway system. This section explains prohibited handling ...
Page 36
26 1. Overview 59 39 7. Notes on use of cable tracks z always use a robot cable for each extension bl bending radius (r) z use a cable track with a bending radius (r) of 50 mm or more. Robot cable z pio line, communication line, power and driving lines are to be put separately from each other and do...
Page 37
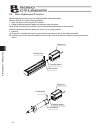
27 2. Installation led non-motor end motor end right left coupling bolt front bracket rear bracket motor bracket motor cover cable rod frame rod end bracket top bottom non-motor screw cover coupling bolt right left motor end side cover led top bottom front bracket slider rear bracket motor bracket r...
Page 38
28 2. Installation 2.1.3 (1) rod type with a single guide (rgs6c/rgs7c) (2) rod type with double guides (rgd6c/rgd7c) non-motor end coupling bolt right left motor end led top bottom cable motor cover rod frame rear bracket motor bracket rear cover guide bracket guide bearing guide rod non-motor end ...
Page 39
29 2. Installation 2.2 installation 2.2.1 slider type z installing the actuator the actuator-mounting surface must be a machined surface or have an equivalent flatness. The side and bottom faces of the actuator base are parallel with the guides. If high slide precision is required, install the actua...
Page 40
30 2. Installation hex cap bolt hole in flange 2.2.2 rod type a rod-type actuator can be installed in the following two ways: z affixing with a flange install the actuator by tightening from the motor end side with hex cap bolts using the holes provided in the flange. Caution: if the actuator is ins...
Page 41
31 2. Installation z affixing with foot brackets (optional) if optional foot brackets are used, install the foot brackets using hex cap bolts. Foot-bracket tightening bolts model nominal thread size tightening torque ra6c rgs6c rgd6c m6 5.4 n m (0.55 kgf-m) ra7c rgs7c rgd7c m8 11.5 n m (1.17 kgf-m...
Page 42
32 2. Installation 2.2.3 installing the load z slider type four tapped holes are provided in the slider, so affix the load using these holes (indicated by arrows in the figure shown to the left). Type slider mounting hole sa6c, sa7c m5, depth 9 mm nominal thread size tightening torque bolt bearing s...
Page 43
33 2. Installation z rod type a bolt is attached on the rod end bracket, so use this bolt to affix the load. (use the supplied nut, if necessary.) rod end bracket model rod end bracket ra6c m8, length 18 mm ra7c m10, length 21 mm note) apply a spanner wrench at the rod end bracket to prevent the rod...
Page 44
34 3. Electrical specifications 3. Electrical specifications 3.1 controller specification item description number of controlled axes 1 axis/unit supply voltage 24 vdc r10% supply current 2 a max. Control method weak field-magnet vector control positioning command position number specification, numer...
Page 45
35 3. Electrical specifications 3.2 input/output interfaces connector pin no. Signal name description 1 sga 2 sgb 3 5v 4 gnd rs485 serial communication 5 24v control power, 24 v 6 bkr brake release (the brake is released when 24 v, 150 ma is supplied.) 7 mpi motor drive power, 24 v 8 gnd control pow...
Page 46
36 3. Electrical specifications orange blue brown green red gray yellow black shield signal name wire color wire control power brake shield shielded wire blue yellow red black purple gray green orange shielded wire standard cable robot cable 3.2.1 extension cable this cable is a standard accessory o...
Page 47
37 3. Electrical specifications 3.3 sio converter (optional) model number: rcb-tu-sio-a (vertical installation) rcb-tu-sio-b (horizontal installation) this unit is a rs232c-rs485 converter. When multiple controllers are linked together, you can use the sio converter to perform movement operations an...
Page 48
38 3. Electrical specifications signal signal d-sub 9-pin, female d-sub 9-pin pc: female plc: male [4] d-sub, 9-pin connector (rs232c) a connection port with the plc’s communication module. You can also connect a pc here. For the communication cable, use a rs232c crossed cable as explained below. [5...
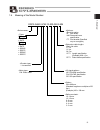
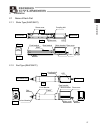
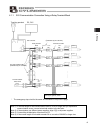
Page 49
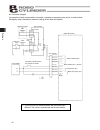
39 4. Wiring 4. Wiring 4.1 basic configuration with sio converter connect a teaching pendant, pc or plc using a sio converter (for rs232c/rs485 conversion), as shown below. Caution: do not connect any device to the mini-din connector and d-sub connector at the same time. If a device is connected to ...
Page 50
40 4. Wiring z connection diagram an example of serial communication connection, including an emergency stop circuit, is shown below. Emergency stop is actuated by means of cutting off the motor drive power. *1 the wire colors for standard cables and robot cables are different. The colors in parenth...
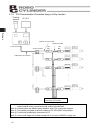
Page 51
41 4. Wiring 4.1.1 sio communication connection using a relay terminal block * the emergency stop circuit is the same as illustrated on the previous page. (note 1) if the total length of the communication cable is 10 m or longer and you experience communication errors, connect a terminal resistor to...
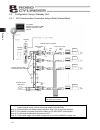
Page 52
42 4. Wiring 4.1.2 sio communication connection using a 4-way junction (note 1) if the total length of the communication cable is 10 m or longer and you experience communication errors, connect a terminal resistor to the last axis. (note 2) if the actuators use different power supplies, align 0 [v] ...
Page 53
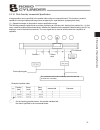
43 4. Wiring 4.1.3 address assignment if multiple axes are connected, a slave number must be assigned to each axis so that the host can recognize the corresponding actuator. Assign addresses in the setting screen of the teaching pendant or pc. Z overview of operation on the pc [1] open the main wind...
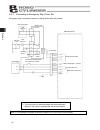
Page 54
44 4. Wiring 4.2 configuration using a gateway unit 4.2.1 sio communication connection using a relay terminal block (note 1) if the total length of the communication cable is 10 m or longer and you experience communication errors, connect a terminal resistor to the last axis. (note 2) if the actuato...
Page 55
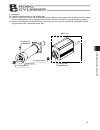
45 4. Wiring 4.2.2 sio communication connection using a 4-way junction (note 1) if the total length of the communication cable is 10 m or longer and you experience communication errors, connect a terminal resistor to the last axis. (note 2) if the actuators use different power supplies, align 0 [v] ...
Page 56
46 4. Wiring 4.2.3 connecting an emergency stop circuit, etc. Emergency stop is actuated by means of cutting off the motor drive power. *1 the wire colors for standard cables and robot cables are different. The colors in parentheses are for robot cables. (note 1) the gateway unit power must be the s...
Page 57
47 5. Explanation of operating functions 5. Explanation of operating functions erc2-se actuators support two operation modes: [1] “position number specification mode” in which the actuator is operated by specifying position numbers, and [2] “numerical specification mode” in which the actuator is ope...
Page 58
48 5. Explanation of operating functions position speed acceleration deceleration push threshold positioning band zone+ zone– acceleration/ deceleration mode incremental command mode standstill mode comment 5.1 description of position table create a position table using the pc software or teaching p...
Page 59
49 5. Explanation of operating functions (4) acceleration/deceleration x enter the acceleration/deceleration at which the actuator will be moved, in [g]. Basically, you should set values within the rated range specified in the catalog. The input range is greater than the rated range in the catalog, ...
Page 60
50 5. Explanation of operating functions “push & hold operation” the set value defines the maximum distance the actuator will push the work part in the push & hold mode upon reaching the target position. Consider the mechanical variations of the work part and set an appropriate positioning band so t...
Page 61
51 5. Explanation of operating functions (9) acceleration/deceleration mode x this field is not used for this controller. The factory setting is “0.” (10) incremental x this setting defines whether to use the absolute mode or incremental mode. The factory setting is “0.” 0: absolute mode 1: incremen...
Page 62
52 5. Explanation of operating functions 5.1.1 relationship of push force at standstill and current-limiting value when performing operation in the push & hold mode, enter the current-limiting value (%) in the push column of the position table. Determine the current-limiting value (%) from the push ...
Page 63
53 5. Explanation of operating functions z rod type (1) ra6c type (2) ra7c type low-speed type low-speed type (lead: 3 mm) (lead: 4 mm) medium-speed type medium-speed type (lead: 6 mm) (lead: 8 mm) high-speed type high-speed type (lead: 12 mm) (lead: 16 mm) caution: the precision of push force at st...
Page 64
54 5. Explanation of operating functions 5.2 data set in the numerical specification mode when the actuator is operated in the numerical specification mode, specify data relating to the intended operation (target position, speed, acceleration/deceleration, positioning band, current-limiting value du...
Page 65
55 5. Explanation of operating functions erc2 -se fu nction li st { : direct control, ' : indirect control, x: not available position numb er sp e cification mod e numeric al spe cificati on mod e de v icen et gat e w a y cc-link gate wa y serial communi catio n gate w a y position numb er specifica...
Page 66
56 5. Explanation of operating functions 5.3.1 control signals and control data to operate the actuator via serial communication, the internal 16-bit memory (modbus registers and statuses) of the controller must be written/read. The key signals and symbols used in these operations are explained belo...
Page 67
57 5. Explanation of operating functions (plc o controller) register bit address bit position signal symbol signal name description 15 to 6 - - - 043ah 5 pc32 - 043bh 4 pc16 - 043ch 3 pc8 - 043dh 2 pc4 - 043eh 1 pc2 - position number specification register posr address 0d03h [pos specification] 043f...
Page 68
58 5. Explanation of operating functions (plc o controller) register address description pcmd position data specification [numerical specification] inp positioning band specification [numerical specification] vcmd speed specification [numerical specification] acmd acceleration/ deceleration [numeric...
Page 69
59 5. Explanation of operating functions (plc o controller) (note) set in a range of 20% to 70% (33h to b3h) if the actuator imposes limitations. Register address description current- limiting value during push & hold operation [numerical specification] ctlf control flag [numerical specification] 16...
Page 70
60 5. Explanation of operating functions (2) controller output signals (controller o plc) register bit address bit position signal symbol signal name description 0100h 15 emgs emergency stop status an emergency stop is being actuated when this bit is “1.” 0101h 14 sfty safety speed enabled the safet...
Page 71
61 5. Explanation of operating functions (controller o plc) register bit address bit position signal symbol signal name description 15 to 9 - - - 0147h 8 pzone position zone output if individual zone boundaries are set in the position table, this bit will turn “1” when the current position enters th...
Page 72
62 5. Explanation of operating functions 5.3.2 timings after power on follow the procedure below to turn on the power after confirming that the slider or rod is not contacting a mechanical end nor the load is contacting any peripheral equipment: [1] cancel the emergency stop or turn on the motor dri...
Page 73
63 5. Explanation of operating functions warning: since a pulse motor is used as the driving motor, the excited phase will be detected when the servo is turned on for the first time after the power on. Accordingly, the actuator must be able to move when the servo is turned on. If the slider or rod i...
Page 74
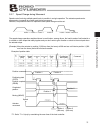
64 5. Explanation of operating functions 1 msec max. Home return command (home) home return completion (hend) position complete (pend) moving (move) actuator movement power on position [1] [2] mech ani cal e nd home pos ition 5.3.3 home return operation this controller uses an incremental position d...
Page 75
65 5. Explanation of operating functions home return command (home) home return operation will start upon detection of the “0” o “1” edge of this signal bit. When home return is completed, the home return completion (hend) signal will be output. The home signal can be input as many time as desired...
Page 76
66 5. Explanation of operating functions 5.3.4 positioning operation first, change the position complete (pend) signal bit to “1” by turning on the 24-vdc power by referring to 5.3.2. Home return is not yet complete immediately after the power has been turned on. Accordingly, home return operation m...
Page 77
67 5. Explanation of operating functions explanation of operation [1] when the servo becomes ready after the supply voltage has been turned on, the servo ready (sv) and position complete (pend) bits will turn “1.” after confirming that pend is “1,” specify position 1 and change the positioning start...
Page 78
68 5. Explanation of operating functions positioning start (cstr) upon detecting the “0” o “1” leading edge of this signal bit, the controller will read the target position number specified by a binary code consisting of six bits from pc1 to pc32 (in the position number specification register) and...
Page 79
69 5. Explanation of operating functions position complete (pend) this signal indicates that the target position has been reached, and turns on only when the following conditions are satisfied: [1] the servo ready (sv) bit is “1” and [2] the current position has reached the positioning band before...
Page 80
70 5. Explanation of operating functions 5.3.5 push & hold operation just like with an air cylinder, the end of the rod can be pressed against a work part and maintained in this condition. The push & hold operation is useful in clamping or press-fitting of work parts. (1) basic operation as shown be...
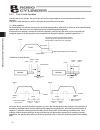
Page 81
71 5. Explanation of operating functions [1] specification of push & hold mode x set a value (current-limiting value) “other than 0” in the “push” field of the position table. X to specify the push & hold mode numerically, set bit 0 of the control flag specification register ctlf to “1.” [2] push sp...
Page 82
72 5. Explanation of operating functions speed target position positioning band (maximum push amount) push & hold operation was determined complete here. Travel (note) if the actuator is pushed back to the target position, an alarm will generate. (2) the work part is missed during push & hold operat...
Page 83
73 5. Explanation of operating functions (4) the push direction is set incorrectly exercise caution when setting the push direction, because if the direction is set incorrectly, the position will deviate by twice the positioning band, as shown below. Speed target position positioning band travel pos...
Page 84
74 5. Explanation of operating functions speed command position positioning start (cstr) position complete (pend) completed position pause command (stp) moving (move) actuator movement 4 msec max. Deceleration to a stop start of movement to complete the remaining travel 5.3.6 pause when the pause co...
Page 85
75 5. Explanation of operating functions position command positioning start (cstr) position complete (pend) completed position moving (move) actuator movement speed position 1 position 2 position 1 position 2 position 1 (200 mm) position 2 (300 mm) comment position [mm] speed [mm] acceleration [g] d...
Page 86
76 5. Explanation of operating functions (note) if a pause command is issued while home return is in progress, the movement command will be held if the actuator has not yet contacted the mechanical end. If the actuator has already contacted the mechanical end and reversed, home return will be perfor...
Page 87
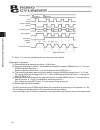
77 5. Explanation of operating functions position command acceleration/ deceleration command position complete (pend) completed position moving (move) actuator movement speed position 1 acceleration deceleration position 1 position 1 acceleration deceleration 5.3.8 operation at different acceleratio...
Page 88
78 5. Explanation of operating functions zone signal actuator operation home zone setting- zone setting+ + direction 5.3.9 zone signal this signal is output (the bit turns “1”) when the current actuator position is inside the specified zone. The zone signal can be used for the following purposes: [1...
Page 89
79 5. Explanation of operating functions position 1 50-mm pitch to front end last load zone output signal the coordinate of the load immediately before the last load is set as the + boundary. 5.3.10 pitch feed by incremental specification a target position can be specified in the position table usin...
Page 90
80 5. Explanation of operating functions *t1: set to t1 t 0 (ms) by considering the scan time of the host controller. [explanation of operation] [1] perform positioning operation to position 1 (100.00 mm). [2] when the positioning to position 1 has completed, the position complete (pend) bit turns “...
Page 91
81 5. Explanation of operating functions command position start position complete completed position moving actuator movement position 1 position 2 position 2 speed position speed position from home: 40 distance (2) note on positioning operation if a start signal is input after selecting and inputti...
Page 92
82 5. Explanation of operating functions command position start position complete completed position actuator movement position 1 position 2 position 2 speed position speed distance (3) note on push & hold operation if a start signal is input after selecting and inputting a position number (for push...
Page 93
83 5. Explanation of operating functions 5.3.11 power-saving mode at standby positions one general feature of pulse motors is that their holding current is greater than ac servo motors in a standstill state. Therefore, we provide a power-saving mode to reduce power consumption in situations where th...
Page 94
84 6. Parameter settings 6. Parameter settings 6.1 parameter table parameters are classified into four types according to their content. Category: a: parameter relating to the actuator stroke range b: parameter relating to the actuator operating characteristics c: parameter relating to the external ...
Page 95
85 6. Parameter settings 6.2 detailed explanation of parameters if a parameter has been changed, always restart the controller using a software reset command or by reconnecting the power. 6.2.1 parameters relating to the actuator stroke range z soft limit (no. 3/4 limm/liml) set the soft limit in th...
Page 96
86 6. Parameter settings (home) z home return offset (no.22 ofst) the controller is shipped from the factory with an optimal value set in parameter no. 22, so the distance from each mechanical end to the home becomes uniform. The minimum setting unit is “0.01 [mm].” the home return offset can be adj...
Page 97
87 6. Parameter settings 6.2.2 parameters relating to the actuator operating characteristics z default speed (no.8 vcmd) the factory setting is the rated speed of the actuator. When a target position is set in an unregistered position table, the setting in this parameter will be used as the speed da...
Page 98
88 6. Parameter settings z default direction of excited-phase signal detection (no.28 phsp1) when the servo is turned on for the first time after a power on, excited phase is detected. This parameter defines the direction of this detection. The parameter need not be changed in normal conditions. In ...
Page 99
89 6. Parameter settings z default standstill mode (no.53 ctlf) this parameter defines the power-saving mode to be applied when the actuator stands by for a long time while the machine is operating; the actuator stands by for a long time after completing home return operation; or the actuator stands...
Page 100
90 6. Parameter settings z push speed (no.34 pshv) this parameter defines the push speed to be applied after the actuator reaches the target position in push & hold operation. Before the shipment, this speed has been set to a default value appropriate for the characteristics of the actuator. Set an ...
Page 101
91 6. Parameter settings 6.2.3 parameters relating to the external interface z output mode of position complete signal (no.39 fpio) this parameter defines the status of position complete signal to be applied if the servo turns off or “position deviation” occurs while the actuator is standing still a...
Page 102
92 6. Parameter settings z silent interval multiplication factor (no.45 sivm) it is applied to controllers of rs485 serial communication type. If specified, this parameter defines the multiplication factor to be applied to the silent interval time for delimiter judgment in the rtu mode. The default ...
Page 103
93 6. Parameter settings 6.2.4 servo gain adjustment before the shipment, the servo has been adjusted in accordance with the standard specification of the actuator. Accordingly, the servo settings need not be changed in normal conditions. Nonetheless, the parameters relating to servo adjustment are ...
Page 104
94 6. Parameter settings z speed loop integral gain (no.32 vlpt) parameter no. Unit input range default 32 --- 1 ~ 217270 set individually in accordance with the actuator characteristics. This parameter is used to determine the response of the speed control loop. Reducing the set value lowers the re...
Page 105
95 7. Troubleshooting 7. Troubleshooting 7.1 action to be taken upon occurrence of problem upon occurrence of a problem, take appropriate action according to the procedure below in order to ensure speedy recovery and prevent recurrence of the problem. A) check the status indicator lamps. Illuminatin...
Page 106
96 7. Troubleshooting 7.2 alarm level classification alarms output from the controller are classified into two levels according to the symptoms they represent. Alarm level alm lamp failure status register what happens when alarm generates how to reset operation cancellation on (red) almh is “1” the ...
Page 107
97 7. Troubleshooting 7.3 alarm description and cause/action (1) operation-cancellation level alarms code error name cause/action 080 movement command at servo off cause: a movement command was issued by numerical specification when the servo was off. Action: issue a movement command after confirmin...
Page 108
98 7. Troubleshooting code error name cause/action 0a1 parameter data error cause: the parameter data does not meet the specified input range. (example) this alarm generates when a pair of values clearly has an inappropriate magnitude relationship, such as when the soft limit + setting is 200.3 mm, ...
Page 109
99 7. Troubleshooting code error name cause/action 0c9 excessive motor supply voltage this alarm indicates that the motor supply voltage is excessive (24 v + 20%: 28.8 v or more). Cause: [1] high voltage of the 24-v input power supply [2] faulty internal part of the controller action: check the volt...
Page 110
100 7. Troubleshooting (2) cold-start level alarms code error name cause/action 0b8 excitation detection error this controller detects excited phase when the servo is turned on for the first time after a power on. This alarm indicates that the specified encoder signal level cannot be detected after ...
Page 111
101 7. Troubleshooting code error name cause/action 0f5 verification error of data written to nonvolatile memory when data was written to the nonvolatile memory, the written data is read and compared (verified) against the original data. This alarm indicates that the read data does not mach the orig...
Page 112
102 7. Troubleshooting 7.4 messages displayed during operation using the teaching pendant or pc software this section explains the warning messages that may be displayed during operation using the teaching pendant or pc software. Code error name cause/action 112 invalid data an inappropriate value w...
Page 113
103 7. Troubleshooting code error name cause/action 20c cstr-on during operation this message indicates that the start signal (cstr) was turned on by the plc while the actuator was moving, and that duplicate movement commands occurred as a result. 20d stp-off during operation this message indicates ...
Page 114
104 7. Troubleshooting 7.5 specific problems z the led lamp does not illuminate after the power is input. Cause: [1] reverse connection of the 24-v power supply [2] faulty controller board if the power supply is connected properly, probably the controller board is faulty. Please contact iai. (note) ...
Page 115
105 7. Troubleshooting z the actuator overshoots when decelerated to a stop. Cause: the load inertia is high in view of the balance of loading mass and deceleration. Action: decrease the deceleration setting. Z the home and target positions sometimes shift on the rod-type actuator. Cause: the curren...
Page 116
106 8. Maintenance and inspection 8. Maintenance and inspection 8.1 inspection items and schedule perform maintenance and inspection per the schedule specified below. This schedule assumes eight hours of operation a day. Shorten the inspection intervals if the utilization is higher, such as when the...
Page 117
107 8. Maintenance and inspection 8.4 internal check (slider type) [1] with the sa6 and sa7, the screw cover and side covers can be removed using a hex wrench with 1.5 mm width across flats. X the front and rear brackets are supporting the ball screw, so do not disassemble these brackets. X precisio...
Page 118
108 8. Maintenance and inspection 8.5 internal cleaning (slider type) Ɣ wipe off dirt using a soft cloth, etc. Ɣ do not blow compressed air at high speed. Doing so may cause dust to enter the actuator through gaps. Ɣ do not use petroleum solvent, neutral detergent or alcohol. Caution: do not use cle...
Page 119
109 8. Maintenance and inspection (2) greasing method grease the guide by following the procedure below: [1] apply grease between the slider and base, as shown to the left. Apply grease on the opposite side in the same manner. [2] spread the grease evenly between the slider and base using a spatula,...
Page 120
110 8. Maintenance and inspection 8.7 greasing the ball screw (slider type) (1) applicable grease the following special grease is applied to the ball screw prior to shipment: kyodo yushi multemp lrl3 this grease generates less heat and has other excellent properties suitable for ball screws. For equ...
Page 121
111 8. Maintenance and inspection 8.8 greasing the rod slide surface (1) applicable grease the following grease is applied to the rod slide surface prior to shipment: kyodo yushi multemp lrl3 use lithium grease for maintenance. Note: never use fluorine grease. If fluorine grease is mixed with lithiu...
Page 122
112 8. Maintenance and inspection 8.9 motor replacement procedure before replacing the motor, save the latest parameter and position data. Save the data by one of the following methods: x save the data to a file using the pc software. X prepare position/parameter tables and manually write the values...
Page 123
113 8. Maintenance and inspection x installation [1] place the coupling spacer in the coupling hub. [2] insert the motor unit into the rear bracket while paying attention to the phase of the coupling hub with respect to the coupling spacer. (when inserting the motor unit, exercise due caution to pre...
Page 124
114 9. Operation examples 9. Operation examples refer to the operation manuals specified below for operation examples using this product: x operation manual for devicenet gateway unit x operation manual for cc-link gateway unit x operation manual for serial communication protocol.
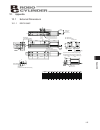
Page 125
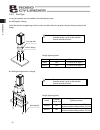
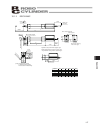
115 appendix 10.1 external dimensions 10.1.1 erc2-sa6c 10. Appendix 50.9 2.5 49.1 2.3 37.5 25 13.5 118.5 80.6 30 a 50 b 50 60 5 50 5 9 9 32 32 s.E. M.E. L 10 stroke 60 59 50 48.5 58 13.5 43.5 118.5 22 31 37.4 (300) (6) 25 36 55 p 0.02 (6) n s100 p pio type sio type m.E.*2 stroke 50 100 150 200 250 3...
Page 126
116 appendix 10.1.2 erc2-sa7c 40 49 51.5 22.5 16 118.5 118.5 16 92.1 a 50 50 b 㧹.E. 2.5 3 l 10 49.8 75 55.2 75 5 65 5 9 9 47 34.5 66.5 60 58.5 68 32 40 47.4 4 4.5 f4.5 f8 2.5 4 46 63 n s100 p stroke p 0.02 (300) (3.5) (3.5) 5.E. 㧹.E.*2 pio type sio type 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600...
Page 127
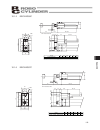
117 appendix 10.1.3 erc2-ra6c c 7 18 31.7 m8 s1.25 nut 3 types 2 37.5 20 43.5 118.5 b l f 40h7 49.7 a 8 2 118.5 20 stroke (300) pio type sio type m8 s1.25 4 - f5.5 75.6 54 44 5 1 27 58 54 44 13 (2 flat faces) (note) the angle of the 2 faces on the actual product would not be as shown in the drawing....
Page 128
118 appendix 10.1.4 erc2-ra7c c 9 21 40 49 4 51.5 20 118.5 b l 61 8.5 2 a 118.5 20 stroke m10 s1.5 (300) sio type f 45h7 m.E. Pio type 50 100 150 200 250 300 l a b c 312.5 194 423.5 106 2.7 362.5 244 523.5 156 2.9 412.5 294 623.5 206 3.0 462.5 344 723.5 256 3.2 512.5 394 823.5 306 3.3 562.5 444 923....
Page 129
119 appendix 10.1.5 erc2-rgs6c 106.5 54 2 st 51.7 st 58.3 13 54 f 10 st 3.3 55 8 23.7 20 12.5 10 57 24 3 22.5 37 40 7 12.5 91 3 58 54 52 30 20 f 34 m.E. 6-m5 50 100 150 200 250 300 0.2 1.8 0.2 1.9 0.3 2.1 0.3 2.3 0.3 2.4 0.4 2.6 stroke home me : mechanical end guide weight [kg] weight of guide main ...
Page 130
120 appendix 10.1.7 erc2-rgd6c 51.7 23.7 20 159 134 114 st m.E. 2 st 58.3 13 54 54 20 145 114 54 53 52 42 30 f 34 f 10 st 3.3 55 8 4-m5 8-m5 50 100 150 200 250 300 guide weight [kg] weight of guide main unit [kg] 0.4 2.0 0.4 2.1 0.5 2.3 0.6 2.6 0.6 2.7 0.7 2.9 stroke home me : mechanical end 10.1.8 ...
Page 131
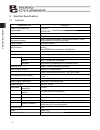
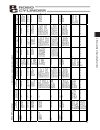
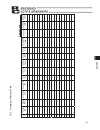
121 appendix standstill mode command mode incremental recorded date: acceler a tion/ decelerati on mode zone– [mm] zone+ [mm] positioning ban d [mm] threshold [%] push [%] decel e rati on [g] acceler a tion [g] spee d [mm/s] position [mm] 10.2 recording of position table no . 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
Page 132
122 appendix standstill mode command mode incremental recorded date: acceler ation/ decelerati on mode zone– [mm] zone+ [mm] positioning ban d [mm] threshold [%] push [%] decel erati on [g] acceler ation [g] spee d [mm/s] position [mm] no. 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 ...
Page 133
123 appendix standstill mode command mode incremental recorded date: acceler ation/ decelerati on mode zone– [mm] zone+ [mm] positioning ban d [mm] threshold [%] push [%] decel erati on [g] acceler ation [g] spee d [mm/s] position [mm] no. 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 ...
Page 134
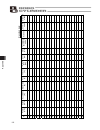
124 appendix 10.3 parameter records recorded date: category: a: parameter relating to the actuator stroke range b: parameter relating to the actuator operating characteristics c: parameter relating to the external interface d: servo gain adjustment a t a d d e d r o c e r t i n u e m a n l o b m y s...
Page 135
125 change history change history revision date description of revision january 2011 fifth edition added “before use.” changed “safety precautions” to “safety guide.” p. 9: added 1.5.3, “the sound pressure level of this product does not exceed 70 db.” p. 16: moved “prohibitions/notes on handling cab...
Page 138
Manual no.: me0159-7c (june 2015) the information contained in this document is subject to change without notice for purposes of product improvement. Copyright © 2015. Jun. Iai corporation. All rights reserved. 15.06.000 head office: 577-1 obane shimizu-ku shizuoka city shizuoka 424-0103, japan tel ...