- DL manuals
- IAI
- Controller
- IS Cast SSPDACR
- Operating Manual
IAI IS Cast SSPDACR Operating Manual
Summary of IS Cast SSPDACR
Page 1
Iai america, inc. Isdb series actuator operating manual tenth edition isdb, isdbcr ispdb, ispdbcr is cast sspdacr.
Page 3
Please read before use thank you for purchasing our product. This operating manual explains the handling methods, structure and maintenance of this product, among others, providing the information you need to know to use the product safely. Before using the product, be sure to read this manual and f...
Page 4
Ce marking if a compliance with the ce marking is required, please follow overseas standards compliance manual (me0287) that is provided separately..
Page 5
Table of contents safety guide .............................................................................................................................1 caution in handling ..................................................................................................................8 names ...
Page 6
8. Operating conditions........................................................................................................46 8.1 duty ratio during continuous operation............................................................................................. 46 9. Setting the home position .....
Page 7
15. Appendix ..........................................................................................................................93 15.1 external dimensions............................................................................................................................ 93 15.1.1 isd...
Page 9
1 safety guide “safety guide” has been written to use the machine safely and so prevent personal injury or property damage beforehand. Make sure to read it before the operation of this product. Safety precautions for our products the common safety precautions for the use of any of our robots in each...
Page 10
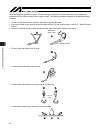
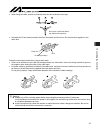
2 no. Operation description description 2 transportation Ɣ when carrying a heavy object, do the work with two or more persons or utilize equipment such as crane. Ɣ when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate...
Page 11
3 no. Operation description description (2) cable wiring Ɣ use our company’s genuine cables for connecting between the actuator and controller, and for the teaching tool. Ɣ do not scratch on the cable. Do not bend it forcibly. Do not pull it. Do not coil it around. Do not insert it. Do not put any h...
Page 12
4 no. Operation description description 4 installation and start (4) safety measures Ɣ when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with each other to ensure the safety of the workers. Ɣ when the product...
Page 13
5 no. Operation description description 6 trial operation Ɣ when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with each other to ensure the safety of the workers. Ɣ after the teaching or programming operation...
Page 14
6 no. Operation description description 8 maintenance and inspection Ɣ when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with each other to ensure the safety of the workers. Ɣ perform the work out of the safe...
Page 15: Alert Indication
7 alert indication the safety precautions are divided into “danger”, “warning”, “caution” and “notice” according to the warning level, as follows, and described in the operation manual for each model. Level degree of danger and damage symbol danger this indicates an imminently hazardous situation wh...
Page 16
8 caution in handling 1. Do not set speeds and accelerations/decelerations equal to or greater than the respective ratings. If the actuator is operated at a speed or acceleration/deceleration exceeding the allowable value, abnormal noise or vibration, failure, or shorter life may result. In the case...
Page 17
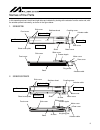
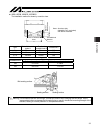
9 names of the parts in this operating manual, the left and right sides are indicated by looking at the actuator from the motor end, with the actuator placed horizontally, as shown in the figure below. 1. Isdb/ispdb 2. Isdbcr/ispdbcr right side (r) left side (l) motor cover slider front cover base a...
Page 18
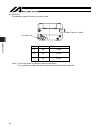
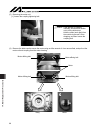
10 3. Sspdacr right side left side front side motor side slider front cover actuator cable motor cover rear cover front cover base rear cover motor cover grease nipple sheet cover plate stainless sheet.
Page 19
1. Checking the product 11 1. Checking the product if based on a standard configuration, this product consists of the items listed below. Caution: check the packed items against the packing specification. Should you find a wrong model or any missing item, please contact your iai dealer or iai. 1.1 c...
Page 20
1. Checking the product 12 (2) xsel-p/q, xsel-r/s controllers no. Name control no. 1 operation manual for xsel-p/q controller me0148 2 operation manual for xsel-r/s controller me0313 3 operation manual for xsel-p/q/px/qx rc gateway function me0188 4 operation manual for pc software ia-101-x-mw/ia-10...
Page 21
1. Checking the product 13 1.4 how to read the model number isdb - m - a - 200 - 20 - 500 – t2 - m - b - ** *1 this maybe displayed for the manufacturing reason. (this is not to indicate the manufacturing model code.) simple dust-proof type aluminum-based isdb: standard specification ispdb: high-pre...
Page 22
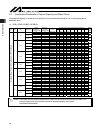
2. Specification 14 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750 800 850 900 950 1000 1050 1100 s 60 4 240 230 200 170 150 135 120 8 480 460 400 345 305 270 240 16 960 920 795 690 610 540 480 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750 800 850 900 950 1000 1050 1100 m 100 5 30...
Page 23
2. Specification 15 (2) sspdacr the maximum speed of the actuator is limited to prevent resonance of the ball screw shaft that may occur beyond a certain motor speed. Be sure to observe the applicable maximum speed shown in the table below. Stroke and maximum speed (or speed to reach) limits (unit: ...
Page 24
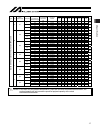
2. Specification 16 2.2 acceleration/deceleration, payload capacity and rated thrust if the payload capacity is smaller than as specified, the acceleration/deceleration can be raised beyond the applicable level. (1) isdb, ispdb, isdbcr, ispdbcr payload capacity by acceleration/deceleration [kg] type...
Page 25
2. Specification 17 payload capacity by acceleration/deceleration [kg] type size motor capacity [w] lead [mm] rated acceleration/ deceleration [g] maximum acceleration/d eceleration [g] horizontal vertical 0.2g 0.3g 0.4g 0.5g 0.6g 0.7g 0.8g 0.9g 1.0g rated thrust [n] 0.2 0.5 horizontal 55 50 38 30 -...
Page 26
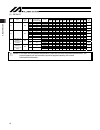
2. Specification 18 (2) sspdacr payload capacity by acceleration/deceleration [kg] size type motor capacity [w] lead [mm] maximum acceleration/ deceleration [g] horizontal vertical 0.2g 0.3g 0.4g 0.5g 0.6g 0.7g 0.8g 0.9g 1.0g 1.1g 1.2g rated thrust [n] 0.4 0.7 horizontal 90 90 90 72 60 50 - - - - - ...
Page 27
2. Specification 19 2.3 driving system/position detector the actuator is driven by the ac servo control method. (1) isdb, ispdb, isdbcr, ispdbcr ball screw specification size motor capacity [w] lead [mm] encoder pulses *1 type diameter isd series ispd series 4 8 s 60 16 rolled 12 mm c10 c5 or equiva...
Page 28
2. Specification 20 2.4 positioning preciseness functions item isd ispd sspdacr positioning repeatability r 0.01 mm r 0.005 mm r 0.005 mm backlash *1 0.05 mm or less 0.02 mm or less 0.02 mm or less *1 initial value.
Page 29
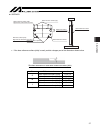
2. Specification 21 l l mb or mc direction direction of moment direction of allowable overhang ma direction mb direction mc direction ma direction size [mm] reference position for moment calculation reference position 2.5 allowable moment of the actuator (1) isdb, ispdb, isdbcr, ispdbcr static allow...
Page 30
2. Specification 22 (2) sspdacr static allowable moment (nxm) dynamic allowable moment (nxm) size ma mb mc ma mb mc allowable overhang load length (l) s 190 190 530 43.4 43.4 116.0 ma direction: 450 mb or mc direction: 450 m 470 470 1210 107.0 107.0 276.0 ma direction: 600 mb or mc direction: 600 l ...
Page 31
3. Life 23 3. Life the mechanical life of the actuator is represented by that of the guide receiving the greatest moment load. Operation life of the linear guide is to be determined by the total driving distance which can reach without having 90% flaking (peeling on rail surface). Operation life can...
Page 32
3. Life 24 [load coefficient f w ] it is a coefficient to consider the life drop due to operational conditions. Load coefficient f w operation condition reference for acceleration/deceleration 1.0 to 1.5 small vibration or impact in slow operation 1.0g or less 1.5 to 2.0 medium level vibration or im...
Page 33
4. Installation and storage/preservation environment 25 4. Installation and storage/preservation environment 4.1 installation environment the actuator should be installed in a location other than those specified below. In general, the installation environment should be one in which an operator can w...
Page 34
5. Transport 26 5. Transport 5.1 handling a single axis 5.1.1 handling a package unless otherwise specified, each axis is packed and shipped individually. X do not bump or drop the package. The package is not specially designed to withstand the impact of dropping or bumping. X an operator must not a...
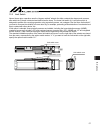
Page 35
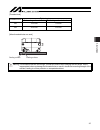
5. Transport 27 (2) sspdacr x four eye bolts are installed, so use these bolts to transport the actuator. The sspdacr, when unpacked, looks like the condition shown in the figure below. X do not hold the motor cover when transporting the sspdacr. Doing so may damage the cover due to the weight of th...
Page 36
5. Transport 28 5.2 handling an cartesian robot (ics) take note of the following points when transporting a set of axes that have been combined. 5.2.1 handling a package before shipment, combined axes are packed in an outer frame nailed to the base made of square lumbers. Each slider is secured to p...
Page 37
5. Transport 29 5.3 handling an actuator assembled to a mechanical system when transporting an actuator that has been assembled to a mechanical system, as the whole system, take note of the following points: x secure the sliders to prevent sudden movement during transport. X if any end of the actuat...
Page 38
6. Installation 30 6. Installation 6.1 installation orientations actuators are subject to certain limitations regarding their installation orientations. If an actuator is installed in an orientation not allowed for that actuator, the stainless sheet may break or other problems may occur. { : install...
Page 39
6. Installation 31 caution: (1) when installing the actuator vertically, make sure the motor comes to the top. When the actuator is installed with the motor at the bottom, there shouldn’t be any problems during normal operations. If the actuator is not operated for an extended period of time, howeve...
Page 40
6. Installation 32 6.2 installing the actuator 6.2.1 installation method x use the threaded holes on the back of the base to install the actuator. X isdb and isdbcr actuators of intermediate support type (mx/lx) are installed in the same way as the corresponding actuators without intermediate suppor...
Page 41
6. Installation 33 bolt seating surface bolt seating surface seating surface a c b z isdb, ispdb, isdbcr, ispdbcr the installation method is shown by a section view. Type pitch of threaded holes a depth of threaded hole b thread size c s 70 mm 17 mm m6 m, mx 90 mm 20 mm m8 l, lx 120 mm 20 mm m8 tigh...
Page 42
6. Installation 34 z sspdacr the installation method is shown by a section view. Type thread size depth of threaded hole s m6 9 mm m m8 12 mm l m8 16 mm (note) the through holes are lidded for keep the cleanliness. It is not possible to attach with the screws applied from the actuator body side. Bas...
Page 43
6. Installation 35 [threaded hole] tightening torque installation bolt bolt seating surface is steel bolt seating surface is aluminum m6 12.3 nxm 5.4 nxm m8 30.0 nxm 11.5 nxm [when threaded holes are used] seating surface seating surface bolt warning: the threaded holes are not through, so exercise ...
Page 44
6. Installation 36 6.2.2 preciseness of the installation surface x the frame on which the actuator is installed shall have sufficient structural rigidity to remain free from vibration, etc. X the basis of measurement of the running accuracy of the slider is from the lower side and motor side to righ...
Page 45
6. Installation 37 z sspdacr slider reference surface (side) right side as viewed from the motor slider reference surface (top) reference surface (side) right side as viewed from the motor reference surface (bottom) motor side view from the upper side quasi-reference surface reference surface quasi-...
Page 46
6. Installation 38 6.3 installing the load on the slider x the slider has two types of threaded holes, so affix the load using these holes. The affixing method shall conform to the method for installing the actuator. X similarly when the slider is affixed and actuator is moved, install the slider us...
Page 47
6. Installation 39 work installation dimensions thread a thread b reamed hole c type hole dimension p [mm] thread size depth [mm] dimension a [mm] thread size depth [mm] dimension b [mm] hole diameter depth [mm] isdb-s, ispdb-s/ isdbcr-s, ispdbcr-s 60 m6 19 70 - - - 6h7 10 isdb-m, ispdb-m/ isdb-mx, ...
Page 48
6. Installation 40 bolt seating surface seating surface bolt seating surface seating surface z sspdacr bolt seating surface type thread size depth of threaded hole s m6 9 mm m m8 12 mm l m8 16 mm tightening torque applicable bolt bolt seating surface is steel bolt seating surface is aluminum m6 12.3...
Page 49
6. Installation 41 4.5 1.5 3. 4 3. 7 6.4 using t-slots m4 t-slots for installing the connector box, etc. Are provided on the side face of the base, when configuring the orthogonal axes. (see the figure below.) you can also use these t-slots freely for installing sensors, securing wires or for other ...
Page 50
6. Installation 42 6.5 suctioning for clean room application actuators designed for clean room application can demonstrate performance corresponding to cleanliness class 10 (0.1 pm or more per 1 ft 3 ) by suctioning air from the suction joint. The suction flow rate at the rated speed of each model i...
Page 51
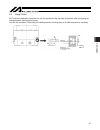
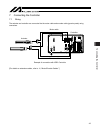
7. Connecting the controller 43 5% )86( 32:(5 0 0 3* &2'( %. 02'( 73 +267 %. 3* /6 /6 7. Connecting the controller 7.1 wiring the actuator and controller are connected via the motor cable and encoder cable (genuine parts) using connectors. Example of connection with xsel controller [for details on e...
Page 52
7. Connecting the controller 44 when designing an application system, incorrect wiring or connection of each cable may cause unexpected problems such as a disconnected cable or poor contact. The following explains examples of prohibited handling of cables. X do not cut and reconnect the cable for ex...
Page 53
7. Connecting the controller 45 x when fixing the cable, provide a moderate slack and do not tension it too tight. X separate the i/o and communication lines from the power and drive lines. Do not wire them together in the same duct. Follow the instructions below when using a cable track. X if there...
Page 54
9. Setting the home position 46 8. Operating conditions 8.1 duty ratio during continuous operation operate at duty ratios equal to or greater than the allowable value. “duty ratio” refers to a utilization ratio indicating the percentage of the time during which the actuator is operating in one cycle...
Page 55
9. Setting the home position 47 9. Setting the home position 9.1 home return home return involves the operation explained below: [1] when a home return command is issued, the actuator moves (in the direction set by the applicable parameter). [2] the software detects the mechanical end in the return ...
Page 56
9. Setting the home position 48 9.4 how to use the homing mark stickers the following stickers are supplied with the actuator. Use these stickers, as necessary, to mark the home position of the actuator, etc. Examples of use [1] for marking the home position of the actuator attach two stickers when ...
Page 57
9. Setting the home position 49 9.5 fine-tuning the home position correct the position deviation by changing the parameter for home preset in the case of a x-sel or ssel controller, or by changing the parameter for home return offset in the case of a scon, mscon controller. How to set these paramete...
Page 58
9. Setting the home position 50 (4) select the axis-specific parameter tab. (5) in the axis-specific parameter tab, select no. 12, “preset home.” (6) change the setting of axis-specific parameter no. 12 (preset home). Add or subtract the value measured in (2) to/from the value currently input. The s...
Page 59
9. Setting the home position 51 (8) transfer the data to the controller. (9) click ok. (10) write the data to the flash rom. (11) restart the controller. Select the parameters check box. Select yes..
Page 60
9. Setting the home position 52 9.5.2 econ, scon and mscon controllers (1) open the position edit screen. On the pc software screen, click , select a desired position number, and then click ok to display the following screen. Click the home return button to perform home return. (2) turn off the serv...
Page 61
9. Setting the home position 53 (3) open the parameter screen. (4) the user parameter screen appears. (5) change user parameter no. 22 (home offset). * the setting unit is mm. Add or subtract the value measured in (2) to/from the value currently input. Example: when subtracting 0.5 mm home offset = ...
Page 62
9. Setting the home position 54 (6) write the new data. Click the controller transfer button, and then click ok. * after the data has been written, turn off the controller power. Click the controller transfer button. Click ok..
Page 63
9. Setting the home position 55 9.6 absolute reset method (absolute specification) if the battery has been replaced or encoder cable unplugged following an absolute encoder battery voltage error, etc., absolute reset must be performed. For the method to perform absolute reset, check 1.2, “related op...
Page 64
10. Options 56 10 20 mm/s 10. Options 10.1 brake the brake is a mechanism to retain the slider of a vertically installed actuator so that the slider will not drop when the power is cut off or servo turns off. If any axis is used vertically, an optional brake is required. 10.2 creep sensor this senso...
Page 65
10. Options 57 21 10.3 limit switch normal home return operation uses the “stopper method” wherein the slider contacts the stopper and reverses, after which the z-phase is detected and defined as the home. The home limit switch (l) is an option which is designed to perform this reversing operation u...
Page 66
10. Options 58 10.4 reversed-home specification in the reversed-home specification, the home is located on the front side. This is indicated by “nm” in the model number. If you wish to change the home direction after the delivery, consult iai because the moving direction parameter must be adjusted, ...
Page 67
10. Options 59 10.7 suction joint on opposite side this option is available for the clean room actuators including isdbcr, ispdbcr and sspdacr. On these clean room actuators, the standard installation position of the suction joint is on the left side of the actuator as viewed from the motor. If you ...
Page 68
10. Options 60 10.9 high-precision straightness specification the high-precision straightness specification type is a precision actuator with high-level settings of parallelism and straightness, which is the base and slider travel accuracies. The models are expressed with st. X aluminum-based isdb/i...
Page 69
10. Options 61 deviation measured value representative line straightness slider travel distance parallelism (reference) [measurement method] [1] parallelism (horizontal) between the base reference surface and the slider (reference surface) affix the base on the surface plate and, with the indicator ...
Page 70
11. Motor/encoder cables 62 11. Motor/encoder cables 11.1 standard the same cables are used regardless of the actuator model. The applicable cables vary depending on the combined controller. Correspondence table of controllers and motor/encoder cables controller xsel-j/k xsel-p/q/r/s ssel scon, msco...
Page 71
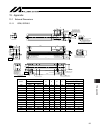
11. Motor/encoder cables 63 [3] limit switch cable cb-x-lcƑƑƑ [4] encoder cable cb-x1-paƑƑƑ [5] encoder cable with ls cb-x1-plaƑƑƑ 41 14 13 7 3 8 8 1 5 2 13 14 26 l e24v 0v ls cleep ot rsv a+ a b+ b z+ z srd+ srd bkr bkr+ 10 11 12 13 26 25 24 23 9 18 19 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 14 15 16 17 20 21 22 1 2 3 4 5...
Page 72
12. Maintenance/inspection 64 12. Maintenance/inspection 12.1 inspection items and intervals perform maintenance/inspection according to the following timetable. The operating time is assumed to be 8 hours a day. If the actuator is used continuously for 24 hours or the utilization rate is otherwise ...
Page 73
12. Maintenance/inspection 65 12.2 visual inspection of the machine exterior check the following items visually. Main body and work part loose mounting bolts, etc. Cables damage to cables, connection of connectors stainless sheet damage to the sheet, slacking general noise, vibration x check the sta...
Page 74
12. Maintenance/inspection 66 caution: if the actuator stroke is 400 mm or more, check the stainless sheet for slacking and position deviation every month. If any slack or other problem is found, adjust the stainless sheet. [for the adjustment procedure of the stainless sheet, refer to 13, “replacem...
Page 75
12. Maintenance/inspection 67 12.4 interior check turn off the power, remove the stainless sheet and visually inspect the interior. For the interior inspection, check the following items. Actuator loosening of actuator mounting bolts, intrusion of dust and other foreign matters guide lubrication con...
Page 76
12. Maintenance/inspection 68 warning: y do not disassemble the front cover because the ball screw is supported by the front cover. If a proper adjustment of the front cover is lost, the shaft center may become offset and the traveling resistance may increase or life of each part may become shorter,...
Page 77
12. Maintenance/inspection 69 12.5 grease supply (1) applicable grease our guides use urea grease that offers excellent low-dust-raising property, stable torque characteristics, excellent lubrication performance, and rust-preventive effect similar to lithium grease. The following grease has been app...
Page 78
12. Maintenance/inspection 70 [grease nipple positions] z isdbcr, ispdbcr (note) follow the grease nipple diameter shown in the list below when preparing a grease gun. Model nipple diameter [mm] common to all models 6.0 recommend grease gun nozzle maker mg70 n type thk caution: y charging too much g...
Page 79
12. Maintenance/inspection 71 z sspdacr (note) follow the grease nipple diameter shown in the list below when preparing a grease gun. Model nipple diameter [mm] sspdacr-s 3.5 sspdacr-m 6.0 sspdacr-l 6.0 recommend grease gun nozzle maker mg70 n type thk caution: y charging too much grease may increas...
Page 80
13. Replacement/adjustment procedure for stainless sheet 72 13. Replacement/adjustment procedure for stainless sheet the following explains how to replace and adjust the stainless sheet. The screws and other parts that are removed to take out the old stainless sheet will be needed when the component...
Page 81
13. Replacement/adjustment procedure for stainless sheet 73 13.2 replacement/adjustment procedure (1) move the slider to the center of the actuator. (2) turn off the controller power. (3) remove the four affixing screws to take out the slider cover. After removing the slider cover (4) use an allen w...
Page 82
13. Replacement/adjustment procedure for stainless sheet 74 (6) adjust the tension of the stainless sheet. [1] move the stainless sheet back and forth to adjust the sheet tension. If the actuator is of clean room type, push down the rollers until they contact the side cover. This is not necessary wi...
Page 83
13. Replacement/adjustment procedure for stainless sheet 75 (8) after checking the tension of the stainless sheet and confirming absence of slacking, position deviation or other problems, tighten the two screws alternately. At the end, tighten them to a uniform torque to secure the stainless sheet. ...
Page 84
14. Motor replacement procedures 76 14. Motor replacement procedures the following explains the procedure to replace the motor in the event of coil breakage, etc. Prepare a storage box, etc., and keep in this box, etc., all screws and other parts you have removed to replace the motor, because they w...
Page 85
14. Motor replacement procedures 77 cover coupling ball screw coupling on the ball screw side coupling on the motor side motor unit 14.1 removing the motor unit (1) removing the coupling cover turn off the power supply to the controller, and then disconnect the motor cable and encoder cable. Remove ...
Page 86
14. Motor replacement procedures 78 rear cover cable mounting cover rear cover rear cover cable affixing cover (2) removing the rear cover [1] remove the screws used to secure the cable mounting cover using an allen wrench of 2 mm across flats. [2] remove the four bolts used to secure the rear cover...
Page 87
14. Motor replacement procedures 79 cable mounting cover motor motor cover bolts affixing the motor cover (3) removing the cable mounting cover remove the three bolts used to secure the cable mounting cover to the cable using an allen wrench of 2.5 mm across flats. (note) after the motor is replaced...
Page 88
14. Motor replacement procedures 80 (5) removing the motor unit [1] loosen the coupling tightening bolt. Caution: if the actuator is installed vertically, exercise due caution not to let the slider drop. Hold the slider (work part) from the outside to prevent it from dropping, and then loosen the co...
Page 89
14. Motor replacement procedures 81 14.2 installing a new motor (1) new motor unit the new motor will be supplied together with the coupling installed as shown below. Caution: the motor actuator cable exit direction varies depending on the actuator cable exit direction. The cable exit direction must...
Page 90
14. Motor replacement procedures 82 [2] action to be taken upon error x with xsel or ssel controller, if the 7-segment display on the front face of the controller does not show “rdy” or “ardy” but indicates an alarm after turning on the power, reset the alarm by checking the operation manual. If the...
Page 91
14. Motor replacement procedures 83 standard home specification [if a slider jig, etc. Cannot be removed] reversed home specification set this part based on table 1 on next page. The use of a block gauge is recommended also in this case. Set this part based on table 1 on next page. The use of a bloc...
Page 92
14. Motor replacement procedures 84 (table 1) spacer thickness by model standard home specification adjust dimension to: (mm) type lead standard equipped with a limit switch = equipped with a home sensor 4 6 8 isdb, ispdb isdbcr, ispdbcr-s 8 x 16 8 8 5 7 9 isdb, ispdb isdbcr, ispdbcr-m 10 x 20 x 30 ...
Page 93
14. Motor replacement procedures 85 (3) aligning the motor position apply power to the controller, and then run the motor with the jog control using the pc software or teaching pendant to align the home position marked on the motor and the slit in the coupling. (jog at 1 mm per second (minimum speed...
Page 94
14. Motor replacement procedures 86 (4) installing the motor temporarily [1] with the motor servo turned on, fit the motor unit’s coupling in the end of the ball screw shaft and fasten the motor housing and motor unit temporarily. (tighten manually for this temporary purpose.) when fastening the mot...
Page 95
14. Motor replacement procedures 87 type bolt used isdb, isdbcr, ispdb, ispdbcr-s m4 x 12 isdb, isdbcr, ispdb, ispdbcr, -m, mx, l, lx m5 x 15 sspdacr-s m5 x 15 sspdacr-m m5 x 15 sspdacr-l m6 x 20 [2] with the motor fastened temporarily, tighten the coupling bolts on the ball screw side. [3] turn off...
Page 96
14. Motor replacement procedures 88 (5) centering and securing the motor unit loosen the motor affixing screws you have tightened only loosely in an earlier step, move the slider back and forth by hand for three to four cycles (over as long an operation stroke as possible) and eventually move the sl...
Page 97
14. Motor replacement procedures 89 cable mounting cover bolts affixing the motor cover (6) installing the motor cover tighten the two bolts to install the motor cover using an allen wrench of 2.5 mm across flats for isdb, ispdb, isdbcr and ispdbcr-s, or 3 mm across flats for all other models. Two o...
Page 98
14. Motor replacement procedures 90 rear cover cable mounting cover (8) installing the rear cover [1] insert the cable affixing cover into the rear cover. [2] tighten the four bolts to install the rear cover using an allen wrench of 2.5 mm across flats for isdb, ispdb, isdbcr and ispdbcr-s, or 3 mm ...
Page 99
14. Motor replacement procedures 91 (9) installing the coupling cover tighten the two screws to install the cover on the motor side using an allen wrench of 2.5 mm across flats for isdb, ispdb, isdbcr and ispdbcr-s, or 3 mm across flats for all other models. Coupling cover coupling.
Page 100
14. Motor replacement procedures 92 14.3 correcting for position deviation (1) connect the motor cable and encoder cable and turn on the controller power. (2) use the pc software or teaching pendant to perform homing and check the home position. Repeat homing several times to confirm that the actuat...
Page 101
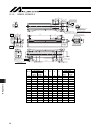
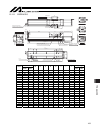
15. Appendix 93 51 38 84 90 3 6 5. 45 5. 2 5. 47 1 51 70 90 5 4 stroke 5 10 82.5 50w b 22 l 154 11 10 m.E. S.E. M.E. Home 06 20. 0± 5 45 45 70 10 10 90 06 86 86 25.5 100 d×200 f 100 7.5 07 7 8 07 20. 0± 75.5 25 57.5 50 50 06 3. 4 3. 7 1.5 4.5 6 Ø a b 15. Appendix 15.1 external dimensions 15.1.1 isdb...
Page 102
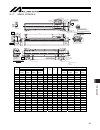
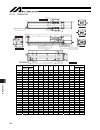
15. Appendix 94 a 49 94 69 5. 2 1 6 110 116 5 120 5. 96 54 22 5 stroke 5 8 5 194 91 100w 106 200w l b 22 11 10 5. 55 m.E. S.E. M.E. Home 300 90 15 15 120 70 25 25 08 20. 0± 08 60 60 7 107 107 120 d×200 f 120 12.5 42.5 102.5 72.5 30 09 20. 0± 09 60 12 8 h7 0 +0.015 01 60 87 3. 4 3. 7 1.5 4.5 6 Ø b 15...
Page 103
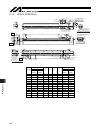
15. Appendix 95 15.1.3 isdb, ispdb-mx l weight [kg] 200 w motor 200 w motor stroke without brake with brake b d e f without brake with brake 800 1241 1276 1113 3 14 122 18.3 18.8 900 1341 1376 1213 3 14 222 19.6 20.1 1000 1441 1476 1313 4 16 122 20.9 21.4 1100 1541 1576 1413 4 16 222 22.2 22.7 1200 ...
Page 104
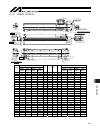
15. Appendix 96 15.1.4 isdb, ispdb-l l weight [kg] 200 w motor 400 w motor 200 w motor 400 w motor stroke without brake with brake without brake with brake b d e f without brake with brake without brake with brake 100 497 531 519 553 358 0 8 73.5 11.8 12.3 12.2 12.7 150 547 581 569 603 408 0 8 123.5...
Page 105
15. Appendix 97 15.1.5 isdb, ispdb-lx l weight [kg] 200 w motor 400 w motor 200 w motor 400 w motor stroke without brake with brake without brake with brake b d e f without brake with brake without brake with brake 1000 1489 1523 1511 1545 1350 4 16 173.5 29.7 30.2 30.1 30.6 1100 1589 1623 1611 1645...
Page 106
15. Appendix 98 15.1.6 isdbcr, ispdbcr-s l weight [kg] 50 w motor 50 w motor stroke without brake with brake b d e f without brake with brake 100 382.5 417.5 278 0 8 45 4.2 4.4 150 432.5 167.5 328 0 8 95 4.5 4.7 200 482.5 517.5 378 0 8 145 4.9 5.1 250 532.5 567.5 428 0 8 195 5.2 5.4 300 582.5 617.5 ...
Page 107
15. Appendix 99 15.1.7 isdbcr, ispdbcr-m l weight [kg] 100 w motor 200 w motor 100 w motor 200 w motor stroke without brake with brake without brake with brake b d e f without brake with brake without brake with brake 100 430 454 445 480 317 0 8 22 7.6 7.9 8.0 8.4 150 480 504 495 530 367 0 8 72 8.2 ...
Page 108
15. Appendix 100 15.1.8 isdbcr, ispdbcr-mx l weight [kg] 200 w motor 200 w motor stroke without brake with brake b d e f without brake with brake 800 1241 1276 1113 3 14 122 18.5 19.0 900 1341 1376 1213 3 14 222 19.8 20.3 1000 1441 1476 1313 4 16 122 21.0 21.5 1100 1541 1576 1413 4 16 222 22.3 22.8 ...
Page 109
15. Appendix 101 15.1.9 isdbcr, ispdbcr-l l weight [kg] 200 w motor 400 w motor 200 w motor 400 w motor stroke without brake with brake without brake with brake b d e f without brake with brake without brake with brake 100 497 531 519 553 358 0 8 73.5 11.9 12.4 12.3 12.8 150 547 581 569 603 408 0 8 ...
Page 110
15. Appendix 102 15.1.10 isdbcr, ispdbcr-lx l weight [kg] 200 w motor 400 w motor 200 w motor 400 w motor stroke without brake with brake without brake with brake b d e f without brake with brake without brake with brake 1000 1489 1523 1511 1545 1350 4 16 173.5 29.8 30.3 30.2 30.7 1100 1589 1623 161...
Page 111
15. Appendix 103 15.1.11 sspdacr-s l weight [kg] stroke without brake with brake m n p r m n r t without brake with brake 100 457 492 299 140 139 74.5 1 0 4 2 7.5 8.1 150 507 542 349 190 39 24.5 2 1 6 3 8.1 8.7 200 557 592 399 240 89 49.5 2 1 6 3 8.7 9.3 250 607 642 449 290 139 74.5 2 1 6 3 9.3 9.9 ...
Page 112
15. Appendix 104 15.1.12 sspdacr-m l weight [kg] stroke without brake with brake m n p r m n r t without brake with brake 100 520 555 340 160 160 20 2 0 4 3 13.9 14.5 150 570 605 390 210 210 45 2 0 4 3 15.0 15.6 200 620 655 440 260 60 70 2 1 6 3 16.0 16.6 250 670 705 490 310 110 20 3 1 6 4 17.1 17.7...
Page 113
15. Appendix 105 15.1.13 sspdacr-l l weight [kg] stroke without brake with brake m n p r m n r t without brake with brake 100 590 627 370 150 220 85 1 0 4 2 24 25 150 640 677 420 200 70 10 2 1 6 3 26 27 200 690 727 470 250 120 35 2 1 6 3 28 29 250 740 777 520 300 170 60 2 1 6 3 29 30 300 790 827 570...
Page 114
16. Warranty 106 16. Warranty 16.1 warranty period one of the following periods, whichever is shorter: y 18 months after shipment from our company y 12 months after delivery to the specified location y 2,500 hours of operation 16.2 scope of warranty our products are covered by warranty when all of t...
Page 115
16. Warranty 107 16.4 limited liability (1) we shall assume no liability for any special damage, consequential loss or passive loss such as a loss of expected profit arising from or in connection with our product. (2) we shall not be liable for any program or control method created by the customer t...
Page 116
Change history 108 change history revision date description of revision july 2011 october 2011 november 2011 march 2012 march 2012 may 2012 january 2013 first edition second edition a page for ce marking added third edition contents changed in safety guide caution notes added for when working with t...
Page 117
Change history 109 revision date description of revision december 2013 november 2014 december 2014 april 2015 eighth edition pg. 85 note corrected in table nxm ĺ nxcm 8d edition pg. 65 joint deleted from the table eleventh edition pg. 29 the availability of installation are changed pg. 63 change mad...
Page 120
Manual no.: me3712-10a (april 2015) the information contained in this document is subject to change without notice for purposes of product improvement. Copyright © 2015. Apr. Iai corporation. All rights reserved. 15.04.000 head office: 577-1 obane shimizu-ku shizuoka city shizuoka 424-0103, japan te...