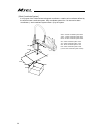
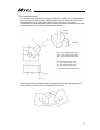
- DL manuals
- IAI
- Controller
- MSEL
- Instruction Manual
IAI MSEL Instruction Manual
Summary of MSEL
Page 1
Msel controller instruction manual fifth edition.
Page 3
Please read before use thank you for purchasing our product. This instruction manual describes all necessary information items to operate this product safely such as the operation procedure, structure and maintenance procedure. To ensure the safe operation of this product, please read and fully unde...
Page 5
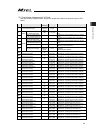
Table of contents safety guide ꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏ1 controller model codes and applicable actuators ꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏ8 precautions in operation ꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏ...
Page 6
3.4 program operation ꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏ 71 3.4.1 auto start upon power on ꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏ 71 3.4.2 starting a program by specifying its program number ꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏ 73 3....
Page 7
Chapter 6 troubleshooting ꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏ 151 6.1 action to be taken upon occurrence of problemꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏ151 6.2 error level control ꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏꞏ...
Page 8
Starting procedures when using this product for the first time, make sure to check the safety guide in the next section, and then start working with care to avoid mistakes and incorrect wiring by referring to the procedure below. Warning : make sure to put the brake release switch on the bottom side...
Page 9
1 safety guide “safety guide” has been written to use the machine safely and so prevent personal injury or property damage beforehand. Make sure to read it before the operation of this product. Safety precautions for our products the common safety precautions for the use of any of our robots in each...
Page 10
2 no. Operation description description 2 transportation ● when carrying a heavy object, do the work with two or more persons or utilize equipment such as crane. ● when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate...
Page 11
3 no. Operation description description (2) cable wiring ● use our company’s genuine cables for connecting between the actuator and controller, and for the teaching tool. ● do not scratch on the cable. Do not bend it forcibly. Do not pull it. Do not coil it around. Do not insert it. Do not put any h...
Page 12
4 no. Operation description description 4 installation and start (4) safety measures ● when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with each other to ensure the safety of the workers. ● when the product...
Page 13
5 no. Operation description description 6 trial operation ● when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with each other to ensure the safety of the workers. ● after the teaching or programming operation...
Page 14
6 no. Operation description description 8 maintenance and inspection ● when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with each other to ensure the safety of the workers. ● perform the work out of the safe...
Page 15: Alert Indication
7 alert indication the safety precautions are divided into “danger”, “warning”, “caution” and “notice” according to the warning level, as follows, and described in the instruction manual for each model. Level degree of danger and damage symbol danger this indicates an imminently hazardous situation ...
Page 16
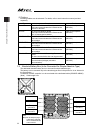
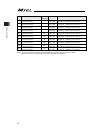
8 controller model codes and applicable actuators the controllable actuator differs depending on the model code for this controller. No. Model type controllable actuator 1 msel-pcx3 standard specification 2 msel-pgx3 safety category compliant specification *2 power-con scara robot 3 msel-pcx4 standa...
Page 17
9 precautions in operation 1. Make sure to follow the usage condition, environment and specification range of the product. In case it is not secured, it may cause a drop in performance or malfunction of the product. 2. Wait for 5 seconds or more before rebooting the power. For the reason of controll...
Page 18
10 6. Transference of pio signal between controllers please note the following when conducting transference of pio signal between controllers. To certainly transfer the signal between controllers with different scan time, it is necessary to have longer scan time than the one longer than the other co...
Page 19
11 8. Regarding battery-less absolute type actuator at the excluding of the scara axis the battery-less absolute type actuator can have the setting switched over between the absolute type and incremental type with the parameters. parameter no.38 encoder abs/inc type set to 0 = incremental type set...
Page 20
12 international standards compliances msel comply with the following international standards: refer to overseas standard compliance manual (me0287) for more detailed information. Rohs directive ce marking ul (except for pcx) to be scheduled.
Page 21
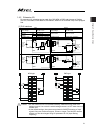
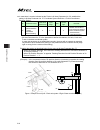
13 name for each parts and their functions [1] pc/pg/pcf/pgf type (cartesian, single-axis robot control type) 1) ac power input connector 2) absolute battery connector (when simple absolute type is used) 6) simple absolute status led lamps for each axis 10) system i/o connector 5) panel window 9) us...
Page 22
14 [2] pcx/pgx type (ixp series scara robot control type) 1) ac power input connector supply the main power source, single-phase 100v to 230v ac. Warning : do not attempt to touch this connector or wires while the power is on as it may cause electric shock. Make sure to ground the protection earthin...
Page 23
15 4) brake release switch (each axis of 1 to 4) it is the switch to release the brake compulsorily (excitation release) for the actuator equipped with a brake. When it is desired to move an actuator manually in such cases as to set up the equipment, in teaching and in an error, the brake can be com...
Page 24
16 10) system i/o connector it is the input and output connectors to manage the safety control on the controller. For pg / pgx types (safety category complied), it is available to comply with up to category 3 by connecting an external safety circuit to this controller. 11) standard i/o connector it ...
Page 25
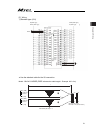
17 actuator axes refer to the pictures below for the actuator axes that can be controlled 0 defines the home position, and items in ( ) are for the home-reversed type (option). (1) rod type (2) slider type (3) table type (4) rotary type (330° rotation specification ) (multi rotation specification) f...
Page 26
18 (5) gripper type (3-finger gripper) note finger attachment is not included in the actuator package. Please prepare separately. ( 6) cartesian robot (dedicated for combination with indicated controller p1 in ik2/ik3 series) there are three types of coordinate systems, base coordinate system, work ...
Page 27
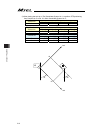
19 (7) horizontal articulated (scara) robot ⋅ ⋅ ixp type dedicated there are three types of coordinate systems, base coordinate system, work coordinate system and tool coordinate system. [base coordinate system (= work coordinate system no. 0)] it is the 3-dimensional orthogonal coordinates + rotati...
Page 28
20 [work coordinate system] it is 32 types of the 3-dimensional orthogonal coordinates + rotation axis coordinate defined by the offset to base coordinate system. Work coordinate system no. 0 is reserved as base coordinates (= work coordinate system offset = 0) by the system. Xb zb yb zofwn xwn zwn ...
Page 29
21 [tool coordinate system] it is 128 types of the 3-dimensional orthogonal coordinates + rotation axis coordinate defined by the tool (such as hand) dimension (offset) attached to the tool attachment surface. Work coordinate system no. 0 is reserved as offset 0 of tool coordinates by the system. If...
Page 30
22.
Page 31
Chapter 1 specifications check 23 chapter 1 specifications check 1.1 product check the standard configuration of this product is comprised of the following parts. If you find any faulty or missing parts, contact your local iai distributor. 1.1.1 parts (excluding options) no. Part name model quantity...
Page 32
Chapter 1 specifications check 24 1.1.3 instruction manuals related to this product, which are contained in the instruction manual (dvd). No. Name manual no. 1 sel language programming manual me0224 2 pc software ia-101-x-mw-js/ia-101-x-usbs instruction manual me0154 3 touch panel teaching tb-01/tb-...
Page 33
Chapter 1 specifications check 25 [1-2] single-axis and cartesian type controllers (high-thrust specification) connected axis content series controller type axis no. Pulse motor type encoder type (note 3) optional standard i/o content extension i/o content i/o cable length power supply voltage absol...
Page 34
Chapter 1 specifications check 26 [2] scara robot controller added axis content power-con scara model series controller type following type symbols come in □ n : standard c : cleanroom w : dust proof/splash proof optional pulse motor type encoder type optional standard i/o content extension i/o cont...
Page 35
Chapter 1 specifications check 27 1.2 basic specifications specification item number of controlled axes 1 axis to 4 axes (total of rc axis or scara axis + rc axis is four axes max.) power supply voltage single-phase 100v ac to 230v±10% power current (typ value) 2.9a (100v ac), 1.4a (200v ac), 1.2a (...
Page 36
Chapter 1 specifications check 28 note 1 rush current at the power connection continues for 5 msec. Note that the value of in-rush current differs depending on the impedance of the power supply line. Note 2 leak current varies depending on the capacity of connected motor, cable length and the surrou...
Page 37
Chapter 1 specifications check 29 116 185 4- 4.5 130 19 5 (10.9) 5. 9 125 (75mm from din rail center) 3 3 1.3 external dimensions 1) main body 2) absolute battery box (simple absolute type) (59mm from din rail center) 5 111 123 98 10.5 5 5 108 115 (4 ) 4 5.
Page 38
Chapter 1 specifications check 30 1.4 interfaces standard i/o can be equipped with pio (npn or pnp). 1.4.1 standard i/o input output input voltage 24v dc ±10% load voltage 24v dc ±10% input current 7ma / 1 circuit on min. 16v dc on/off voltage off max. 5v dc load current 100ma / 1 circuit, 400ma / 8...
Page 39
Chapter 1 specifications check 31 1.4.2 extension i/o for extension i/o, selection can be made from pio (npn or pnp) and six types of fieldbus (cc-link, devicenet, frofibus-dp, ethernet/ip, ethercat or profinet-io) to be equipped with. [1] pio interfaces input output input voltage 24v dc ±10% load v...
Page 40
Chapter 1 specifications check 32 [2] fieldbus following fieldbus can be selected. For details, refer to each instruction manual provided separately. Type overview details devicenet devicenet field network board this board communicates the i/o data as the remote i/o terminal. Refer to the separate. ...
Page 41
Chapter 1 specifications check 33 1.6 installation and storage environment this product is capable for use in the environment of pollution degree 2 *1 or equivalent. *1 pollution degree 2: environment that may cause non-conductive pollution or transient conductive pollution by frost (iec60664-1). [1...
Page 42
Chapter 1 specifications check 34 1.7 noise prevention and the installation (1) protective grounding for grounding, conduct a protective grounding using a strand or annealed copper wire with the diameter 1.25mm 2 (awg16) or more. Controller other equipment controller other equipment other equipment ...
Page 43
Chapter 1 specifications check 35 (4) heat radiation and installation conuct design and manufacture in consideration of the control box size, controller layout and cooling in such a way that the temperature around the controller will be 40 c or less. In case of layout with multiple controllers alig...
Page 44
Chapter 1 specifications check 36.
Page 45
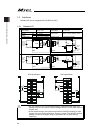
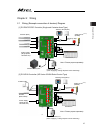
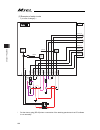
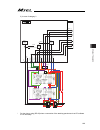
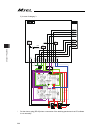
Chapter 2 wiring 37 chapter 2 wiring 2.1 wiring (example connection of devices) diagram [1] pc/pg/pcf/pgf controller (single and cartesian axes type) [2] pcx/pgx controller (ixp series scara robot control type) actuator (ixp) actuator (rcp series ) power supply (single-phase 100~230v ac) contact for...
Page 46
Chapter 2 wiring 38 caution: make sure to turn the power to the controller off when inserting or removing the connector that connects the pc software or teaching pendant to the controller. Inserting or removing the connector while the power is turned on causes a controller failure. Caution: a number...
Page 47
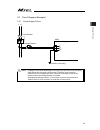
Chapter 2 wiring 39 2.2 circuit diagram (example) 2.2.1 power supply circuit caution: leakage current varies depending on the capacity of the motor to be connected, cable length and surrounding environment. Therefore, when protective measures from the leakage are taken, measure the leakage current a...
Page 48
Chapter 2 wiring 40 2.2.2 emergency stop and enable circuit (pc/pcf/pcx type) the following diagram shows the case when the teaching pendants emergency stop switch is reflected on the machine’s emergency stop circuit design. Caution: for pc/pcf/pcx type, the dead man’s switch on the teaching pendant...
Page 49
Chapter 2 wiring 41 note 1: emgs1+ and emgs1- make short-circuit inside the controller if a teaching pendant is not connected. Note 2: in auto mode, short-circuit is made between enbs1+ and enbs1- inside the controller. Note 3: when it is necessary to cut off the motor power source externally for su...
Page 50
Chapter 2 wiring 42 2.2.3 emergency stop and enable circuit (pg/pgf/pgx type) the following diagram shows the case when the teaching pendants emergency stop switch is reflected on the machine’s emergency stop circuit design. Caution: for pg/pgf/pgx type, the emergency stop switch and the dead man’s ...
Page 51
Chapter 2 wiring 43 note 1: when it is necessary to cut off the motor power source externally for such reason as to comply with safety category, connect a contact such as a connector on the wire between mpo and mpi terminals on the motor driving power line connector. Shown below is table for the pow...
Page 52
Chapter 2 wiring 44 2.2.4 motor encoder circuit (1) connection of linear axes (2) connection to ixp-4n3515, 4515 and ixp-3n3515, 4515 equipped with grippers. Msel mpg1 mpg2 mpg3 mpg4 actuator connection connector when equipped with grippers cb-ixp-at008-as msel mpg1 mpg2 mpg3 mpg4 actuator connectio...
Page 53
Chapter 2 wiring 45 (3) connection to ixp-3n3515, 4515 and additional axes note 1 applicable connection cable model no. : cable length example. 030 = 3 m model cable remarks rcp2 cb-psep-mpa robot cable from 0.5 to 20m cb-apsep-mpa robot cable from 0.5 to 20m rcp3 cb-apsep-mpa-lc standa...
Page 54
Chapter 2 wiring 46 2.2.5 pio circuit on msel controller, standard (i/o1) and extension (i/o2) are available to mount. The setting of the i/o parameters is required to use this pio board. [1] i/o port function assignment [2] port number assignment for i/o ports [1] i/o port function allocation to in...
Page 55
Chapter 2 wiring 47 parameter input function select no. No. Set value function of an input signal at the delivery no consideration of value in input function select 000 0 universal input no consideration of value in input function select 000 1 driving source cut-off cancellation input (on-edge) (eff...
Page 56
Chapter 2 wiring 48 (2) output port function allocation parameter output function select no. No. Set value function of an input signal at the delivery 0 universal output 1 error output at the operation cancellation level or more (on) 2 error output at the operation cancellation level or more (off) 3...
Page 57
Chapter 2 wiring 49 [2] port number assignment for i/o ports with the following i/o parameters, assign the ranges and numbers of the ports used on pio board. No. Parameter name default (reference) input range remarks 1 i/o port assignment type 0 (reference value) 0 to 20 0: fixed assignment (no othe...
Page 58
Chapter 2 wiring 50 no. Parameter name default (reference) input range remarks 305 output function select 306 physical input port no. 322 0, 316 to 331, 348 to 599 indicate port number to assign function set in i/o parameter no. 52 (output port 307 when 0) 306 output function select 307 physical inp...
Page 59
Chapter 2 wiring 51 [3] wiring 1) standard type (i/o1) 24vdc (npn type) 0v (pnp type) 0v 24vdc (pnp type) 24vdc 0v (npn type) 016 017 018 019 020 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 029 030 031 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 output function is parameter setup input funct...
Page 60
Chapter 2 wiring 52 2) extensioni/o (i/o2) 24vdc (npn type) 0v (pnp type) 0v 24vdc (pnp type) general-purpose input general-purpose output 24vdc 0v (npn type) 048 049 050 348 349 350 ● use the attached cable for the i/o connection. Model : cb-pac-pio ( indicates the cable length l. Example. 02...
Page 61
Chapter 2 wiring 53 2.2.6 connection to absolute battery box (only for pc/pg/pcf/pgf type simple absolute) (note) do not attempt to plug in or take off the cable with force in the tilted direction to the connector. Msel absolute battery connector absolute battery box msel-abb-□-□ cb-msel-ab005 cable...
Page 62
Chapter 2 wiring 54 2.3 wiring method 2.3.1 connection to ac power input connector the wire of the power supply is to be connected to the enclosed connector (plug). Strip the sheath of the applicable wires for 7mm and insert them to the connector. When inserting, turn the screw on the side of the in...
Page 63
Chapter 2 wiring 55 2.3.2 wiring the emergency stop circuit (system i/o) construction is made with the emergency stop input and the input terminal of the enable signal. The wires are to be connected to the enclosed connectors (plugs). Peel the sheath on the applicable cable for 10mm, and insert to a...
Page 64
Chapter 2 wiring 56 the following pin numbers are connected with a short-circuiting cable at the delivery. pins 4 and 5 pins 3 and 6 pins 10 and 11 pins 9 and 12 2.3.3 wiring for actuator connect the relay cables to the actuator connectors. Check in the instruction manual of each actuator fo...
Page 65
Chapter 2 wiring 57 2.3.4 wiring for motor driving power line connector this wiring is to be constructed when it is required to have the driving power source shut externally. In case of using the driving source cutoff circuit inside the controller, use the controller under the condition of the enclo...
Page 66
Chapter 2 wiring 58 2.3.6 wiring for pio the connection of i/o to the controller is to be carried out using the dedicated i/o cable. The cable length is shown in the model code of the controller. Please check the controller model code. There are 2m for standard, 3m and 5m as an option. Up to 10m can...
Page 67
Chapter 2 wiring 59 2.3.7 wiring for the teaching tool (sio connector, usb connector) connect a teaching tool such as the pc software. Connection of either rs232c or usb is available. (usb is prioritized when both are connected at the same time.) apply the enclosed dummy plug (dp-4s) to the teaching...
Page 68
Chapter 2 wiring 60 [2] usb connector usb connector model remarks controller side ubbs-4r-d14-4d b type pin no. Signal name description applicable wire diameter 1 v bus 5v 2 d- communication data - 3 d+ communication data + 4 gnd 0v usb cable caution: 1) set “operation mode setting switch” to “manu”...
Page 69
Chapter 3 operation 61 chapter 3 operation 3.1 types of operations the msel controller is a programming controller that can operate without a host controller. Programming for this controller uses iai’s dedicated programming language (sel language). [refer to the separate sel language programming man...
Page 70
Chapter 3 operation 62 3.2 receiving and forwarding of i/o signals necessary for operation the i/o port can deliver the data with the msel controller and external signals through interface. One port can exchange data for one contact (1 bit). Data is exchanged via pios (24v i/os) or over a fieldbus. ...
Page 71
Chapter 3 operation 63 (1) i/o map the factory-set i/o port numbers and functions of the msel controller are shown below. The functions of the i/o port can be changed using the i/o parameter setting. [refer to 2.2.5 pio circuit and chapter 6. I/o parameter] 1) when i/o2 is not fieldbus type (type of...
Page 72
Chapter 3 operation 64 2) when i/o2 is fieldbus type (type of extension i/o is either of cc/cc2/dv/dv2/pr/ep/ec/prt) type port no. Function type port no. Function 000 300 alm (led on the front panel) 001 301 rdy (led on the front panel) 002 302 emg (led on the front panel) 003 303 system reservation...
Page 73
Chapter 3 operation 65 3.3 starting the controller 3.3.1 turning on the power and cutoff (1) power on procedure the following procedure is applied for cases where the parameters are the same as those at delivery, and the unit is not in the error occurrence mode or emergency stop mode. Also, the numb...
Page 74
Chapter 3 operation 66 3.3.2 panel window display the 4-digit, 7-segment led shows the controller status. When the unit is started up normally, “ ” is displayed after the initial processing display. If an indication “e***” is displayed, check “trouble shooting” in chapter 7. For others shown on 7-se...
Page 75
Chapter 3 operation 67 panel window display list (2/2) control codes for core display priority (note ) description [control codes for core] e e * * 1 a cold-start level error is present. E c * * 1 an operation-cancellation level error is present. E a * * 2 a message level error is present. J p a 2 j...
Page 76
Chapter 3 operation 68 3.3.3 status led it shows the status of pio or fieldbus plugged to the extension i/o connector. (1) pio type status led : illuminating : off name lamp condition color description run green in the normal operation (flashes when initialization completes) err orange pio power...
Page 77
Chapter 3 operation 69 (5) ethernet/ip type status led : illuminating : off : flashing name lamp condition color description in operation condition and under control of scanner (master) green setting of construction information incomplete, or scanner (master) in idling condition fatal malfunct...
Page 78
Chapter 3 operation 70 3.3.4 position table and program creation and writing create a position table and create a program using the sel language. Perform the teaching, etc., and register the required coordinates in the position table. Also, create the program using the sel language. [refer to the se...
Page 79
Chapter 3 operation 71 3.4 program operation for the operation there are two ways of start-up. One is the automatic start-up of the set program no. And the other is to start up with the program no. Selected externally. 3.4.1 auto start upon power on after the power is turned on, the program with its...
Page 80
Chapter 3 operation 72 caution: after the power is turned on, unexpected movements of the robot may create dangerous situations. For safety, provide an interlock whereby the program is started only after a start confirmation signal has been input from a pushbutton switch, etc. An example of operatio...
Page 81
Chapter 3 operation 73 3.4.2 starting a program by specifying its program number the program to be started up, can be started with its number specified externally and start-up signal input. 1) connect the pc software and perform the setting, referring to the set values in the following table. Parame...
Page 82
Chapter 3 operation 74 3.4.3 7-segment display sel program the 7-segment led in the panel window on the normally displays the information from the system, but it is able to change the display of the 7-segment led by the sel program created. (sel program and system are displayed in turn.) for control...
Page 83
Chapter 3 operation 75 2) in port no. 339, establish the setting for the switchover of sel program display and system display. Setting value function 0 display of system is conducted port no. 339 1 display of sel program is conducted 3) when setting is established no. 339 = 1, and port no. 338 gets ...
Page 84
Chapter 3 operation 76 how to use 1) establish the display mode setting in port no. 338 and 339. 2) set the digit to display (update) in port no. 332 and 333. 3) establish the display pattern setting of the 7-segment display in port no. 340 to 346. 4) have port no. 337 (refresh) turned off → on → of...
Page 85
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 77 chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset there are three types for the encoder to measure the current position of the actuator. 1) for incremental type, it is necessary to conduct home-return operation when the power is turned on. 2) for battery-less absolute ...
Page 86
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 78 4.2 absolute reset preparation (for battery-less absolute type except for scara robot) caution : it is not necessary to have an absolute reset in ordinary case, however, make sure to have the absolute reset conducted when an absolute error is occurred or aft...
Page 87
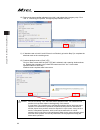
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 79 5) “calibration home / abs. Encoder reset” window appears. Select the tab for the axis 4 (o1). 6) click on “start” button while the [axis 4 (o1)] tab is selected, and a warning window shows up. Release the emergency stop, check the content and click “yes” to...
Page 88
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 80 7) close “calibration home / abs. Encoder reset” window after the home-return operation is complete. After that, the window switches to “flash rom writing” window. Put a check mark on “parameter” and click “yes” to start writing. After it is finished, conduc...
Page 89
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 81 4.3 absolute reset for scara robot (battery-less absolute type) it is available to perform operation on scara robot without having anything special as an absolute reset has already been conducted before delivered out from our factory. It is necessary to have...
Page 90
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 82 4.3.1 absolute reset preparation caution: • it is not necessary to have an absolute reset in ordinary case, however, make sure to have the absolute reset conducted when an absolute error is occurred or after dismantlement of the robot for a reason such as mo...
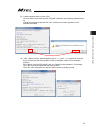
Page 91
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 83 4) a warning window shows up. Check the content and click “ok”. 5) “calibration home/abs. Encoder reset” appears. Select the tab for the axis that requires the absolute reset. Select a tab for the axis to have home position adjustment from j1 (axis 1) axis o...
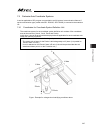
Page 92
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 84 6) click on “start” button while the [axis 1 (j1)] or [axis 2 (j2)] tab is selected, and a warning window shows up. Release the emergency stop, check the content and click “yes”. Home-return operation starts on the axis subject to absolute reset. Caution: as...
Page 93
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 85 home-position adjusting tool (φ4) j2 axis 8) have the emergency stop conducted, and insert the home-position adjustment tool (φ4) at the datum position of j1 axis or j2 axis. 9) with the home-position adjustment tool (φ4) being inserted, click “ok” in “emerg...
Page 94
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 86 10) remove the home-position adjustment tool (φ4), and release the emergency stop. Click “ok” in “positioning pin ejection, emergency stop release” window. 11) if absolute reset on both j1 and j2 axes is not finished, go back to step 5) to complete the absol...
Page 95
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 87 13) conduct absolute reset on [axis 4 (r)]. Click on “start” button while the [axis 4 (r)] tab is selected, and a warning window shows up. Cancel the emergency stop and click “yes”, and the home-return operation on the selected axes starts. 14) “jog -> basic...
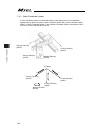
Page 96
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 88 15) input the emergency stop, adjust it manually so it becomes the datum position for r axis, and insert the home-position adjusting tool (φ3). As shown in the figure below align the position of either the d-cut surface on the r-axis tip or the d-cut surface...
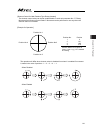
Page 97
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 89 17) remove the home-position adjustment tool (φ3), and release the emergency stop. Click “ok” in “positioning pin removeal -> emergency stop release” window. 18) after the adjustment on all the axes necessary to have an absolute reset is finished, close “cal...
Page 98
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 90 4.4 simple absolute type (pc/pg/pcf/pgf type dedicated) a simple absolute type controller retains the position data of an encoder in battery backup. It is not necessary to perform a home-return operation every time you turn it on. To retain the encoder posit...
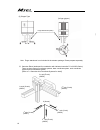
Page 99
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 91 4.4.3 simple absolute type absolute batteries and absolute battery box are enclosed in a simple absolute type controller. For an absolute battery, there is a specific position for each axis number. Refer to the figure below to insert the batteries to the abs...
Page 100
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 92 4.4.4 absolute encoder backup type item specification battery model ab-7 number of units 1 unit/axis (4 units/4 axes max.) battery voltage 3.6v current capacity 3300mah reference for battery replacing timing (note 1) approx. 3 years (it may differ depending ...
Page 101
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 93 4.4.6 detection of absolute battery voltage drop an error will be detected corresponding to the voltage when the absolute battery voltage starts to drop. Voltage alarm 2.5v ±8% or less 41c abs unit encoder error (2) an absolute reset is necessary after batte...
Page 102
Chapter 4 home-return / absolute reset 94.
Page 103
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 95 chapter 5 i/o parameter parameter data should be set appropriately according to the applicaiton requirements. When a change is required to the parameters, make sure to back up the data before the change so the settings can be returned anytime. With using pc software, it is...
Page 104
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 96 ◎ parameters set in bits how to use bits refer below for how to turn on the bits (in case the last digit of the set value is h). Set the value of hexadecimal number transformed from the binary number. ■ binary number in the binary number system, the figure is expressed u...
Page 105
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 97 5.1 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 i/o port assignment type 0 0 ~ 20 0: fixed assignment 2 input port start number at i/o1 affixed assignment 000 -1 ~ 599 0 + (multiple of 8) (invalid if a negative value is set) 3 out...
Page 106
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 98 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 32 input function selection 002 0 0 ~ 5 0: general-purpose input 1: servo on * on edge: equivalent to the all-valid-axis servo on command, off edge: equivalent to the all-valid-axis servo ...
Page 107
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 99 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 43 input function selection 013 1 0 ~ 5 0: general-purpose input 1: program number specified for program start 2: error reset (on edge) note: the port number assigned to this function can ...
Page 108
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 100 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 51 output function selection 305 0 0 ~ 5 0: general-purpose output 1: axis 1 in-position output (off if the work part is missed during push-motion operation) 2: output when axis-1 servo i...
Page 109
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 101 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 65 physical input port number for axis-4 brake forced release 0 0 ~ 299 forcibly unlock the brake when the applicable port is on (be aware of a falling load). * invalid if “0” is set (inv...
Page 110
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 102 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 95 parity type of sio channel 1 opened to use 0 0 ~ 2 0: none 1: odd 2: even 96 receive operation type of sio channel 1 opened to user 0 0 ~ 1 0: forcibly enable receive after send 1: do ...
Page 111
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 103 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 123 network attribute 4 0h 0h ~ ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: selection for permission of 0.0.0.0 (ip address of connection destination ignored) for ip address of connection destination during e...
Page 112
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 104 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 130 own mac address (h) 0h referency only (hex) only lower two bytes are valid. 131 own mac address (l) 0h referency only (hex) 132 own ip address (h) 192 1 ~ 255 * setting of 0 and 127 i...
Page 113
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 105 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 163 vision system i/f connected ip address (l) (for pc/pg/pcf/pgf type) 102 0 ~ 254 * setting of 0 and 255 is prohibited. * pcx/pgx type is system reservation 164 vision system i/f connec...
Page 114
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 106 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 225 extension i/o control 0h 0h ~ ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: i/o2 module type ( 0: not mounted 1: cc-link, 2: devicenet, 3: profibus, 4: ia-net 5 to 6: system reservation 7: ethernet/ip, 8: s...
Page 115
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 107 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 274 (for extention) 0 275 (for extention) 0 276 (for extention) 0 277 (for extention) 0 278 (for extention) 0 279 (for extention) 0 280 (for extention) 0 281 (for extention) 0 282 (for ex...
Page 116
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 108 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 294 physical input port number to input function selection 011 27 -1 ~ 299 specify the port number to be assigned to the function of i/o parameter no. 41, “input function selection 011”. ...
Page 117
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 109 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 309 physical output port number to output function selection 310 326 0 ~ 599 specify the port number to be assigned to the function of i/o parameter no. 56, “output function selection 310...
Page 118
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 110 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 331 output function selection 300 (area 2) 1 0 ~ 20 0: general-purpose output 1: output error of operation-cancellation level or higher (on) 2: output error of operation-cancellation leve...
Page 119
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 111 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 351 vision system i/f 1 function selection 1 (for pc/pg/pcf/pgf type) 3105500h 0h ~ ffffffffh * pcx/pgx is system reservation bits 0 to 3: function select (0: not in use, 1: use) bits 4 t...
Page 120
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 112 i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 388 (for extention) 0 389 (for extention) 0 390 (for extention) 0 391 (for extention) 0 392 (for extention) 0 393 (for extention) 0 394 (for extention) 0 395 (for extention) 0 396 (for ex...
Page 121
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 113 5.2 all axes common parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks ~ 1 effective axis pattern 0000b 0b ~ 11111111b 2 default override 100 1 ~ 100 used if not specified in program. (invalid for sio operation) 3 system reservation 0 (pc/pg/...
Page 122
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 114 all axes common parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 20 maximum operation acceleration/deceleration ctheck timing (for pc/pg/pcf/pgf type) 1 (pc/pg/ pcf/pgf), 0 (pcx/pgx) 0 ~ 1 * pc/pg is system reservation 0: check at input 1: ...
Page 123
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 115 all axes common parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 34 scara axis ptp safety speed in manual mode (for pcx/pgx type) 5 1 ~ 10 % * pc/pg/pcf/pgf is system reservation 35 scara axis each axis related max. Jog speed (for pcx/pgx t...
Page 124
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 116 all axes common parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 54 all axes setting bit pattern 3 100h 0h ~ ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: system reservation bits 4 to 7: select position output operation data valid (0: disable, 1: enable) * cautio...
Page 125
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 117 all axes common parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 98 (for extension) 0 ~ 99 (for extension) 0 ~ 100 (for extension) 0 ~ 101 (for extension) 0 ~ 102 (for extension) 0 ~ 103 (for extension) 0 ~ 104 (for extension) 0 ~ 105 (for ...
Page 126
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 118 all axes common parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 130 vision system i/f 1 control 2 (for pc/pg/pcf/pgf type) 0h 0h ~ ffffffffh * pcx/pgx is system reservation bits 0 to 7: position judgment datum distance in z-axis direction ...
Page 127
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 119 5.3 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 axis operation type 0 (pc/pg/ pcf/pgf), 1, 1, 0, 1 (pcx/pgx) 0 ~ 1 0: linear movement axis 1: rotational movement axis (angle control) 2 (for extension) 0 ~ 3 (for extensi...
Page 128
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 120 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 17 initial home sensor escape velocity at power recovery 10 (pc/pg/ pcf/pgf), 10, 10, 10, 10 (pcx/pgx) 1 ~ 100 mm/sec 18 system reservation 100 1 ~ 500 mm/sec 19 end search spee...
Page 129
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 121 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 40 system reservation 0 0 ~ 1 41 system reservation 25 0 ~ 100 drvvr 42 system reservation (change prohibited) 800 0 ~ 99999999 43 system reservation (change prohibited) 0 -7 ~ ...
Page 130
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 122 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 65 system reservation (pcx/pgx type) synchro axis number of mating axis (pc/pg/pcf/pgf type) 0 0 ~ 8 * pcx/pgx is system reservation smaller axis number in a pair is the main ax...
Page 131
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 123 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 83 system reservation (pcx/pgx type) abs synchro slave axes same coordinates reset cancel (pc/pg/pcf/pgf type) 0 0 ~ 5 * pcx/pgx is system reservation it is available only for s...
Page 132
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 124 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 95 zone 4 max. (pc/pg/pcf/pgf type) linear sliding axis zone 4 max. (pcx/pgx type) 0 -99999999 ~ 99999999 0.001mm 0.001 deg valid only when maximum. > minimum * must be inside t...
Page 133
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 125 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 137 system reservation (change prohibited) 0 138 arm length (for pcx/pgx type) 0 (pc/pg/ pcf/pgf) 160000, 190000, 0, 0 (pcx/pgx) 1 ~ 99999999 0.001mm * pc/pg/pcf/pgf is system r...
Page 134
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 126 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 180 system reservation (change prohibited) 0 0 ~ 100 for adjustment by the manufacturer 181 system reservation (change prohibited) 0 0 ~ 400 for adjustment by the manufacturer 1...
Page 135
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 127 5.4 driver card parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 type (upper) (manufacturing information) space 4 digits ’ ’ ~ ’ z’ 2 type (middle) (manufacturing information) space 4 digits ’ ’ ~ ’ z’ 3 type (lower) (manufacturing inform...
Page 136
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 128 driver card parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 30 configuration information 08: system reservation 0000h 0000h ~ ffffh 31 configuration information 09: control characteristics word 1400h 0000h ~ ffffh 32 configuration informat...
Page 137
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 129 driver card parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 65 system reservation 0h 0000h ~ ffffh 66 system reservation 0h 0000h ~ ffffh 67 system reservation 0h 0000h ~ ffffh 68 system reservation 0h 0000h ~ ffffh 69 system reservation 0...
Page 138
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 130 5.5 encoder parameters no parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 manufacturing information 01 (system reservation) space 4 digits ’ ’ ~ ’ z’ 2 manufacturing information 02 (system reservation) space 4 digits ’ ’ ~ ’ z’ 3 manufacturing informat...
Page 139
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 131 5.6 i/o-slot card parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 type (upper) (manufacturing information) space four-digit ascii code 2 type (middle) (manufacturing information) space four-digit ascii code 3 type (lower) (manufacturing ...
Page 140
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 132 i/o-slot card parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 36 card parameter (by board type) 0000h 0000h ~ ffffh 37 card parameter (by board type) 0000h 0000h ~ ffffh 38 card parameter (by board type) 0000h 0000h ~ ffffh 39 card paramet...
Page 141
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 133 i/o-slot card parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 72 card parameter (by board type) 0000h 0000h ~ ffffh 73 card parameter (by board type) 0000h 0000h ~ ffffh 74 card parameter (by board type) 0000h 0000h ~ ffffh 75 card paramet...
Page 142
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 134 i/o-slot card parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 108 card parameter (by board type) 0000h 0000h ~ ffffh 109 card parameter (by board type) 0000h 0000h ~ ffffh 110 card parameter (by board type) 0000h 0000h ~ ffffh 111 card par...
Page 143
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 135 5.7 other parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 auto-start program number 0 0 ~ 255 (invalid if “0” is set) 2 i/o processing program number at operation/program abort 0 0 ~ 255 the start trigger is determined from the “i/o proc...
Page 144
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 136 other parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 21 manual operation type 0 0 ~ 5 0: always enable edit and sio/pio start (initial condition after connection = with safety speed) 1: select edit and start (with password) (eu, etc.) 2: ...
Page 145
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 137 other parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 47 other setting bit pattern 2 1h 0h ~ ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: calendar function use selection (0: not in use 1: use 2: not in use (use the elapsed time after the reset) 3: system reserv...
Page 146
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 138 other parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 57 pc/tp data protect setting 3 0h 0h ~ ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: protect range maximum number (position) (10’s place, bcd) bits 4 to 7: protect range maximum number (position) (100’s plac...
Page 147
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 139 5.8 parameters for linear / rotation controls shown in the list below are the combinations of parameters for linear and rotation controls: inpu t uni t • dist ance mm • s pe ed m m /se c • a ccelera tion / d ecel eration g • angle mm → de g • an gular velocity m m/sec → d...
Page 148
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 140 [parameters related to rotary axis movement] ● rotation movement axis mode select (axis-specific parameter no.66) set the rotation axis mode. The current value expression gets fixed at 0 to 359.99 by selecting index mode when the setting of the axis operation type (each a...
Page 149
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 141 [shortcut control for multi-rotation type rotary actuator] the shortcut control select can be set enable/disable in each axis parameter no. 67 “rotary movement axis shortcut control select”. Movement can be performed in one way when the shortcut select is set enable. [exa...
Page 150
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 142 5.9 permission of sio/pio program startup with password by setting to parameter “manual operation type” (other parameter no. 21), the parameter can be changed so sio program startup and pio program startup cannot be conducted without inputting a password. (1) pc software ...
Page 151
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 143 5.10 parameter setting (applied) you can add functions or set dedicated functions to i/o ports by changing parameter values. Setting examples under different operating conditions are explained below. When executing the desired operation, change the parameter settings in t...
Page 152
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 144 5.10.1 want to operate the system tentatively without using i/os if you want to perform a test operation before wiring the i/os and fieldbus, disable the error monitor functions for i/os and fieldbus. (the i/os and fieldbus whose error monitor function was disabled cannot...
Page 153
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 145 5.10.4 want to start an emergency program to operate an emergency program when an emergency stop signal is input or the safety gate becomes open, set an emergency program number and range of output ports to be used. * programs which do not involve actuator operations are ...
Page 154
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 146 5.10.6 want to enable auto recovery (error reset) upon cancellation of emergency stop you can automatically reset the error when the emergency stop is cancelled, and execute the program. Parameter no. Set value description other parameter no.1 execution program number oth...
Page 155
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 147 5.10.10 want to make a home-return on actuators externally actuator of incremental type will make home-return operation once on-edge off → on) is input to input port 031*. Parameter no. Set value description 1 home-return operation of incremental type scara robot and line...
Page 156
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 148 5.10.14 want to reset errors externally errors other than cold-start level errors are reset when input port 029 is turned on (errors are reset at the off on edge). Parameter no. Set value description i/o parameter no.43 2 set input port 013 as the error reset signal inpu...
Page 157
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 149 5.10.16 want to change output port assignments you can select output functions by i/o parameter nos. 46 to 61 and assign them to desired output ports. Parameter no. Set value description i/o parameter no.299 output port number to assign output function selection 300 to i/...
Page 158
Chapter 5 i/o parameter 150 5.10.18 want to output the error level the level of each error can be indicated using output ports 316* and 317*. Error level output port 316* output port 317* message level or lower on on operation-cancellation level off on cold-start level off off parameter no. Set valu...
Page 159
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 151 chapter 6 troubleshooting 6.1 action to be taken upon occurrence of problem when a trouble is occurred, take an action following the steps described below in order to have a rapid recovery and to avoid the recurrence of the same trouble. 1) check on 7-segment led displa...
Page 160
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 152 6.2 error level control program run (application only) error level system error assignment source error no. (hex) display (7-segment display, etc.) error list (applicati on only) error led output (main only) other parameter no. 4 = 0 other parameter no. 4 = 1 error rese...
Page 161
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 153 program run (application only) error level system error assignment source error no. (hex) display (7-segment display, etc.) error list (application only) error led output (main only) other parameter no. 4 = 0 other parameter no. 4 = 1 error reset (application only) rema...
Page 162
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 154 6.3 error list (main application) in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 205 update system software version error (iai protocol) an update was tried to an old version of system software that has no ...
Page 163
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 155 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 22d error in number of maintenance information change [detail & cause] there is an error in the number of maintenance information change to be indicated in suc...
Page 164
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 156 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 406 flash busy reset timeout it is an error in deleting or writing of flash rom. 40d vision system response timeout error communication response from the visio...
Page 165
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 157 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 41d abs unit encoder error (3) [detail & cause] it is detected the axis has moved with speed more than the set rotation speed for an external reason during pow...
Page 166
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 158 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 4a4 maintenance information data control domain sum check error [detail & cause] an error was detected in maintenance information data stored in the retention ...
Page 167
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 159 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 548 ia net resizing overlapping error several stations executed the resizing. There is a concern multiple stations are subject to resizing execution. Check the...
Page 168
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 160 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 56a cc-link system domain use error cc-link system domain cannot be used as the system input and output port of x-sel. It can be considered as the cause that c...
Page 169
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 161 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 614 driver synchronizing communication lrc error [detail & cause] an error was detected in the communication between the driver cpu and main board fpga. [count...
Page 170
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 162 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 650 encoder receive timeout error (during initialization communication) an encoder communication failure. 66d slave communication target id error the target id...
Page 171
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 163 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 69e position data control domain sum check error [detail & cause] an error was detected in the position data. Contents in info.1 in the error list show the dat...
Page 172
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 164 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 6bf position data sum check error [detail & cause] an error was detected in the position data. Contents in info.1 in the error list show the data domain the er...
Page 173
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 165 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 801 scif overrun status (iai protocol reception) communication failure. Check for noise, connected equipment and communication setting. 802 scif receive er sta...
Page 174
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 166 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 900 blank step shortage error there are not enough blank steps to save step data. Provide enough blank steps needed to save step data. 901 step number error th...
Page 175
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 167 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. A04 system mode error at core update [detail & cause] an update command was received when the system was not in the core update mode. [countermeasure] establis...
Page 176
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 168 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. A1e start condition non-satisfaction error start was attempted when the start condition was not satisfied, such as when an all-operation-cancellation factor (s...
Page 177
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 169 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. A40 data change refusal error during flash rom write data cannot be changed while the flash rom is being written. A41 duplicate flash-rom write commands refusa...
Page 178
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 170 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. A62 fieldbus error (herror-blink) a herror-blink was detected. A64 scif overrun error (sio bridge) communication failure. Check for noise, connected equipment ...
Page 179
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 171 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. B00 scha setting error the setting of scha command is invalid. B01 tpcd setting error the setting of tpcd command is invalid b02 slen setting error the setting...
Page 180
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 172 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. B20 ethernet non-initialization device use error an attempt was made to use the ethernet system when ethernet device initialization was not yet complete. Check...
Page 181
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 173 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. B4d arm system setting error there is an error in the setting of the arm system. When the target arm system data is set to the position to make scara cp operat...
Page 182
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 174 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. B81 each axis ptp multiple axes indication error each axis ptp operation on multiple axes was indicated. Each axis ptp operation is available to indicate only ...
Page 183
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 175 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. C02 executable program count over error execution requests were received for programs exceeding the number that can be executed simultaneously. C03 non-registe...
Page 184
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 176 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. C19 expansion-condition ld shortage error 1 there is not enough ld when expansion condition a or o is used. C1a expansion-condition ld shortage error 2 there i...
Page 185
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 177 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. C40 string-variable delimiter non-detection error delimiter cannot be detected in the string variable. C41 string-variable copy size over error the copy size o...
Page 186
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 178 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. C61 sel-data flash-rom erase count over error the number of times the flash rom containing sel data can be erased was exceeded. C62 operation command error at ...
Page 187
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 179 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. C75 motion-data-packet generation logic error the motion-data-packet generation logic is invalid. C76 movement-position count over error too many packets are g...
Page 188
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 180 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. C92 push-motion approach distance/speed specification error the specified push-motion approach distance/speed is invalid. C93 system output operation error the...
Page 189
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 181 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. Cb0 mismatched valid axes for palletizing 3-point teaching position data the valid axis patterns do not match in the position data for palletizing 3-point teac...
Page 190
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 182 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. Cca arch top/end-point reversing error the coordinates of highest point and end point are reversed during arch motion operation. Ccb arch start-point/trigger r...
Page 191
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 183 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. D03 encoder count error faulty encoder or defective encoder assembly condition is suspected. D05 encoder-eeprom write acceptance error the encoder is faulty or...
Page 192
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 184 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. D35 abs encoder error detection 2 [detail & cause] initialization of the absolute encoder could not be completed. [countermeasure] reboot the power. In case th...
Page 193
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 185 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. D58 fieldbus error (init timeout) an init timeout was detected. Check the status of the monitor led on the front face of the board by referring to the operatio...
Page 194
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 186 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. D6f optional password error the optional function specified for use requires an optional password. Check other parameter nos. 30 to 32, etc., depending on the ...
Page 195
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 187 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. E01 dma address error dma transfer error e02 scif send-buffer overflow error the scif send buffer overflowed. E03 sci send-buffer overflow error the sci send b...
Page 196
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 188 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. E21 i/o assignment count over error the i/o assignments exceed the specified range. Check i/o parameter nos. 2 to 9 and 14 to 17 and the i/o slot card type (nu...
Page 197
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 189 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. E46 maximum receive size over error at absolute-data acquisition the receive size is too large when acquiring absolute data. E47 no normal response error at ab...
Page 198
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 190 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. E72 motor configuration information outside supported function information range a motor whose configuration information is outside the range supported by the ...
Page 199
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 191 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. E8a sel program flash-rom status error data is not written to the flash rom correctly or written in an old, incompatible application version. E8b symbol defini...
Page 200
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 192 in the panel window, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. F00 shutdown error (hi_sysdwn ( ) definition) a shutdown error (hi_sysdwn ( ) definition) was detected. F03 ~ f58 shutdown error (os call error) a shutdown err...
Page 201
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 193 error list (main core) in the panel window, the error numbers follow the three digits after the e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 950 update file error [detail & cause] 1) it was attempted to update to an old system software version which ...
Page 202
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 194 in the panel window, the error numbers follow the three digits after the e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. A82 write-source data buffer address error (odd-numbered address) error writing the flash rom (when updating) a83 invalid code secto...
Page 203
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 195 in the panel window, the error numbers follow the three digits after the e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. E90 core code flash-rom status error the core program is invalid. Contact the manufacturer. E91 application code flash-rom status er...
Page 204
Chapter 6 troubleshooting 196 in the panel window, the error numbers follow the three digits after the e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. Eb3 cpu clock operation mode error [detail & cause] it has been detected the operation is made in an unsupported or inappropriate cp...
Page 205
Chapter 7 appendix 197 chapter 7 appendix 7.1 example of safety circuit for pg/pgf/pgx type (conforming to safety category) pg/pgf/pgx types are the controllers applicable for the safety categories (b to 3). In this section, describes an example of a circuit using the dedicated teaching pendant. Ple...
Page 206
Chapter 7 appendix 198 [3] examples of safety circuits 1) in case of category 1 emergency stop sw r y reset sw 24v 24g enable sw r y 24g 24v solenoid contactor tp 9.Emgs1- 10.Emgs1+ 7.Emgs2- 8.Emgs2+ 12.Emgin 3.Enbs1- 4.Enbs1+ 1.Enbs2- 2.Enbs2+ 6.Enbin 11.Emgout 5.Enbout vp24s vp24s 12.Emgs1+_tp 9.E...
Page 207
Chapter 7 appendix 199 2) in case of category 2 24v 24v reset sw enable sw emergency stop sw g9sa-301 (omron) g9sa-301 (omron) solenoid contactor solenoid contactor 24v 24v system i/o connector 24v 24v tp 9.Emgs1- 10.Emgs1+ 7.Emgs2- 8.Emgs2+ 12.Emgin 3.Enbs1- 4.Enbs1+ 1.Enbs2- 2.Enbs2+ 6.Enbin 11.Em...
Page 208
Chapter 7 appendix 200 3) in case of category 3 g9sa-301 (omron) g9sa-301 (omron) 24v 24v 24v 24v short-circuit the only when constructing category 3 tp 9.Emgs1- 10.Emgs1+ 7.Emgs2- 8.Emgs2+ 12.Emgin 3.Enbs1- 4.Enbs1+ 1.Enbs2- 2.Enbs2+ 6.Enbin 11.Emgout 5.Enbout vp24s vp24s 12.Emgs1+_tp 9.Emgs1-_tp 5...
Page 209
Chapter 7 appendix 201 7.2 stopping method and recovery 7.2.1 stopping method actuator operation can be stopped in two methods: normal operation stop and emergency stop. 1) normal operation stop normal position control is active: set a deceleration operation plan and cause the actuator to decelerate...
Page 210
Chapter 7 appendix 202 7.2.2 recovery [1] drive-source recovery request (1) method of drive-source recovery request recovery of drive source can be requested by one of the following methods: • set i/o parameter no. 44 to “1” (input selection function 014 = drive-source cutoff reset input), and then ...
Page 211
Chapter 7 appendix 203 7.3 extension sio it can be applicable to sel program communication and iai protocol communication features if serial communication type (model code se1: rs232c, se2: rs485) is mounted to the extension i/o. 7.3.1 specification item contents interface standards rs-232c interfac...
Page 212
Chapter 7 appendix 204 7.3.4 status display there are led lamps equipped on the front panel of the controller to display the communication status. { : illuminating ¯ : off : flashing 7.3.5 parameter settings in below, shows the parameter settings necessary in order to use the extension sio feature...
Page 213
Chapter 7 appendix 205 (2) set parameters such as the communication channel using method in i/o parameter no. 101 “user release sio channel 2 attribute 2 (extended)”. No. Parameter name initial value (reference) input range remarks 101 attribute 2 of sio channel 2 opened to user (extension) 0 0 ~ ff...
Page 214
Chapter 7 appendix 206 (3) how to set parameters 1) settings in common for sel program communication / iai protocol communication ・ set the communication specifications for the extension sio user release channel number to be used. (i/o parameter no. 100, 102, 104 and 106 “user release channel n attr...
Page 215
Chapter 7 appendix 207 7.4 cartesian axis coordinate systems it can be applicable to sel program communication and iai protocol communication features if serial communication type (model code se1: rs232c, se2: rs485) is mounted to the extension i/o. 7.4.1 coordinates for coordinate system definition...
Page 216
Chapter 7 appendix 208 7.4.2 base coordinate system it is the coordinate system to indicate the position of the datum point for tool installation against the work piece mount face. Work coordinate system no. 0 (work coordinate system offset 0) = base coordinate system. X axis of base coordinate syst...
Page 217
Chapter 7 appendix 209 7.4.3 work coordinate system it is the 32 kinds of coordinate systems defined by the offset of each axis against the base coordinate system. Work coordinate system no. 0 is reserved as base coordinate system (= work coordinate system offset = 0) by the system. Set the offset o...
Page 218
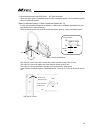
Chapter 7 appendix 210 (1) setting of work coordinate system when required to define work coordinate system no. 1 and no. 2 as shown in the figure below; xw1 yw1 xw2 yw2 ワーク座標系no.1 原点 ワーク座標系no.2 原点 120 200 300 150 xb yb rb -25° 45° the offset of work coordinate system no. 1 and no. 2 are to be set a...
Page 219
Chapter 7 appendix 211 (2) positioning on work coordinate system select the work coordinate system to be used and perform positioning. When selecting the work coordinate system number in sel program, use slwk command. Also, the selected work coordinate system number is valid after program complete a...
Page 220
Chapter 7 appendix 212 2) when having ptp positioning to position no. 5 and no. 6 on work coordinate system no. 2. Work coordinate system no. Offset x [mm] y [mm] z [mm] r [deg] 2 150.000 300.000 0.000 45.000 position no. Coordinate data axis1(x) axis2(y) axis3(z) axis4(r) 5 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 ...
Page 221
Chapter 7 appendix 213 7.4.4 tool coordinate system it is the 128 kinds of coordinate systems defined by the too (such as hand) dimensions (offset) of that attached on the tool attached position. (note) work coordinate system no. 0 is reserved as offset = 0 of tool coordinates by the system. Select ...
Page 222
Chapter 7 appendix 214 (1) setting the tool coordinate system set the offset amount from the tool attached position to the tool tip. Set the tool offset as explained below under condition that each axis system coordinates for all the unit constructing axes is 0 is taken as the datum. X example for t...
Page 223
Chapter 7 appendix 215 (2) positioning using tool coordinate system offset select the work coordinate system to be used and perform positioning. When selecting the work coordinate system number in sel program, use sltl command. Also, the selected work coordinate system number is valid after program ...
Page 224
Chapter 7 appendix 216 2) when having the tool tip on tool coordinate system no. 1 to perform ptp positioning from position no. 5 to no. 6 in work coordinate system no. 2; work coordinate system no. Offset x [mm] y [mm] z [mm] r [deg] 2 150.000 300.000 0.000 45.000 tool coordinate system no. Offset ...
Page 225
Chapter 7 appendix 217 7.4.5 setting of parameters shown below, describes how to set the parameters necessary for using the work and tool coordinate system features on the linear axis. • by setting all axes parameter no. 55 “coordinate system definition 1 control” to “1h”, the coordinate system defi...
Page 226
Chapter 7 appendix 218 in case there is an axis indicated as the r-axis in all axes parameter no. 56, establish the setting in all axes parameter no. 57 “coordinate system definition 1 r-axis coordinates direction setting”. No. Parameter name initial value (reference) input range unit access right r...
Page 227
Chapter 7 appendix 219 7.4.6 caution note (1) limitation in coordinate system constructing axes shown below are the cases when limitation is applied to indication for operation of x, y and r-axes in the coordinate system definition unit. Indicated axis operations subject for limitation x y z r press...
Page 228
Chapter 7 appendix 220 (2) while in operation of either x-axis or y-axis (or r-axis) in a sel program, or with operation of pc software or tp, x-axis and y-axis (and r-axis) cannot be operated in another sel program. (3) when operating either x-axis or y-axis (or r-axis), it is basically necessary t...
Page 229
Chapter 8 w arranty 221 chapter 8 warranty 8.1 warranty period one of the following periods, whichever is shorter: 18 months after shipment from our company 12 months after delivery to the specified location 8.2 scope of the warranty our products are covered by warranty when all of the following...
Page 230
Chapter 8 w arranty 222 8.5 conditions of conformance with applicable standards/regulations, etc., and applications (1) if our product is combined with another product or any system, device, etc., used by the customer, the customer must first check the applicable standards, regulations and/or rules....
Page 231
Change history 223 change history revision date revision description 2014.07 2014.08 2015.04 2016.01 2016.02 2016.04 2017.05 2018.05 first edition second edition pc/pg type added edition 2c pg. 23: correction made to model code of pc software. Pg. 25: scara model codes added. Pg. 27: selection of br...
Page 234
Manual no.: me0336-5b (may 2018) the information contained in this document is subject to change without notice for purposes of product improvement. Copyright © 2018. May iai corporation. All rights reserved. 18.05.000 head office: 577-1 obane shimizu-ku shizuoka city shizuoka 424-0103, japan tel +8...