- DL manuals
- IBM
- Server
- 7013 J Series
- Operator's Manual
IBM 7013 J Series Operator's Manual
Summary of 7013 J Series
Page 1
7013 j series operator guide sa23-2724-02.
Page 2: Third Edition (April 1997)
Third edition (april 1997) this edition notice applies to the 7013 j series operator guide. This edition obsoletes all previous editions. The following paragraph does not apply to the united kingdom or any country where such provisions are inconsistent with local law: this publication is printed “as...
Page 3: Table of Contents
Preface iii table of contents communications statements ix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Safety notices xiii . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . About this book x...
Page 4
Iv operator guide preventive maintenance 2-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Cleaning the tape path on the 5gb 8 mm tape drive 2-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Loading the 8 mm cleaning cartridge 2-21 . . . . . . . ...
Page 5
Preface v chapter 3. Using systemguard 3-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Introduction 3-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Systemguard power 3-2 . . . . . . ...
Page 6
Vi operator guide chapter 5. Using diagnostics 5-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Diagnostic programs operating considerations 5-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Diagnostics on a system unit attached to another sys...
Page 7
Preface vii display software product data pre-version 4.2 6-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Display software product data beginning with version 4.2 6-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Display configuration service aid and display configuration and resource list task 6...
Page 8
Viii operator guide chapter 10. Moving the system unit 10-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Moving the system unit safely 10-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Appendix a. Systemguard test groups a-1 . ....
Page 9: Communications Statements
Preface ix communications statements the following statement applies to this product. The statement for other products intended for use with this product appears in their accompanying manuals. Federal communications commission (fcc) statement note: this equipment has been tested and found to comply ...
Page 10
X operator guide european union (eu) statement this product is in conformity with the protection requirements of eu council directive 89/336/eec on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to electromagnetic compatibility. Neither the provider nor the manufacturer can accept respo...
Page 11
Preface xi radio protection for germany dieses gerät ist berechtigt in Übereinstimmung mit dem deutschen emvg vom 9.Nov.92 das eg-konformitätszeichen zu führen. Der aussteller der konformitätserklärung ist die ibm germany. Dieses gerät erfüllt die bedingungen der en 55022 klasse a. Für diese klasse ...
Page 12
Xii operator guide.
Page 13: Safety Notices
Preface xiii safety notices note: for a translation of these notices, see the system unit safety information, order number sa23-2652. Definitions of safety notices a danger notice indicates the presence of a hazard that has the potential of causing death or serious personal injury. Danger notices ap...
Page 14: Laser Safety Information
Xiv operator guide laser safety information the optical drive in this system unit is a laser product. The optical drive has a label that identifies its classification. The label, located on the drive, is shown below. Class 1 laser product laser klasse 1 luokan 1 laserlaite appareil a laser de classe...
Page 15: Power Cables and Plugs
Preface xv power cables and plugs 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 index part number country 1 14f1548 bahamas, barbados, bolivia, brazil, canada, costa rica, dominican republic, el salvador, ecuador, guatemala, guyana, haiti, honduras, jamaica, japan, netherlands antilles, panama, peru, philippines, taiwan, thail...
Page 16
Xvi operator guide.
Page 17: About This Book
Preface xvii about this book this book contains information on 7013 j series system and its operation together with a description of the main operations that the operator may perform. How to use this book this book provides information about the operator controls, the internal and external devices i...
Page 18
Xviii operator guide.
Page 19: Description of The Base Unit
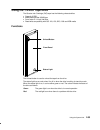
Description of the 7013 j series system 1-1 chapter 1. Description of the 7013 j series system this chapter contains information to help you become familiar with the 7013 j series system. This chapter groups miscellaneous reference information related to both the base and expansion units. It details...
Page 20
1-2 operator guide the base unit consists of a floor standing unit, which may be expanded with the addition of an expansion unit, positioned to the left of the base unit. Both units have the same dimensions: • height: 610 mm (24.1 in.) • width: 360 mm (14.2 in.) • depth: 750 mm (29.5 in.)..
Page 21
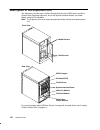
Description of the 7013 j series system 1-3 base unit without covers the following figures show the base system unit with covers and doors removed. Operator panel micro channel card cage fan module media devices power supply disk devices main fan module front view back plane micro channel card cage ...
Page 22
1-4 operator guide operator controls the basic hardware interface between the user and the system unit, is the operator panel. The operator panel is the primary hardware interface used by the system operator to bring the system to an operable state. The interface with the user is provided via the sy...
Page 23: Media Devices
Description of the 7013 j series system 1-5 media devices the scsi interface is the main bus for the mass storage devices and is used to connect disk drives, tapes and optical disks. The scsi bus internal to the unit is etched or embedded on the back plane, so it supports device connection through d...
Page 24
1-6 operator guide description of the expansion unit the expansion unit holds up to 14 mass storage devices on the scsi buses, one micro channel card cage with eight slots, one or two system interface boards, one power supply, and three fan modules. Note: the expansion unit must always be positioned...
Page 25
Description of the 7013 j series system 1-7 expansion unit the expansion unit houses a device complex with 14 device slots. The media devices (tape drives and a cd-rom drive) are always located in the upper row at the front side of the expansion unit. Two optional 5.25-inch half high media devices i...
Page 26
1-8 operator guide nine slots for 3.5-inch disk drives are located in the rear of the expansion unit. Disk drives installed devices in the rear of the expansion unit a scsi-2 differential fast/wide adapter/a is required to support the drives installed in the expansion unit. This adapter can be eithe...
Page 27: Main Power Switch Module
Description of the 7013 j series system 1-9 main power switch module the power system provides power and power regulation for all units of the 7013 j series. It enables you to power on and power off (also under operating system control) individual units. This is particularly useful for handling powe...
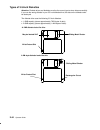
Page 28: Location Codes
1-10 operator guide location codes a location code is used to physically locate a failing device or unit. The location code is displayed along with the service request number (srn) when the diagnostic programs isolate a failure. If the location code is not known, you can run the display previous dia...
Page 29
Description of the 7013 j series system 1-11 location code table for scsi and non-scsi devices use the following table to determine the physical location of a device or unit. Note: the location code format for 9333 devices is described on the previous page and in 9333 documentation. Use the followin...
Page 30
1-12 operator guide pair description value s1 s2 s3 serial port 1 connector. Serial port 2 connector. Serial port 3 connector. 11 12 13 14 21 22 23 24 remote async node 1 on line 1. Remote async node 2 on line 1. Remote async node 3 on line 1. Remote async node 4 on line 1. Remote async node 1 on li...
Page 31
Description of the 7013 j series system 1-13 cluster power control the cluster power controller (cpc) is an external option which provides: • connectivity between a remote support facility and multiple cpus through a modem • connectivity from any attached cpu to any disk drive drawer • central power...
Page 32
1-14 operator guide.
Page 33: Main Power Switch Module
Using the system unit 2-1 chapter 2. Using the system unit this chapter explains how to use the operator panel and other devices for control, input, display, and data storage in the 7013 j series system unit. Caution: this product is equipped with a three-wire power cable and plug for the user’s saf...
Page 34
2-2 operator guide 3. Plug the power cords into the elelectical outlet. 4. Perform this step first on the expansion unit if there is one attached. Press the switch located on the main power switch module to on, switching it to the ”i” position. Main power switch.
Page 35: The Operator Panel
Using the system unit 2-3 the operator panel the operator panel complex is installed on the front of the main unit. To access the operator panel you have to open the front door. The operator panel elements are controlled by the cpu and by a special microprocessor located on the i/o card called syste...
Page 36
2-4 operator guide reading the operator panel display attention: if you have a flashing 888 in the operator panel display, do not push the reset/scroll button before you carefully read the related documentation. The operator panel display has two 16 position rows. The display is used for: • event in...
Page 37
Using the system unit 2-5 using the reset/scroll button attention: when the mode switch is in normal or service position, pressing the reset/scroll button causes the unit to reset and do an ipl (initial program load). Pressing the reset/scroll button while the operating system is running can result ...
Page 38
2-6 operator guide setting the key mode switch the key mode switch has three positions: normal position secure position service position the switch is used to establish the initial program load (ipl) path. The ipl loads the system programs, checks the system hardware and prepares the system for user...
Page 39
Using the system unit 2-7 the following list explains the uses of the key mode switch positions: attention: the reset/scroll button is active when the mode switch is in the normal or service position, and pressing the reset/scroll button can cause data to be damaged or lost if the operating system i...
Page 40
2-8 operator guide electronic mode switch the electronic mode switch (e-key) enables you to remotely change the status of the key mode switch and: • places the system for maintenance or debug purpose from a remote location, from normal to service mode, without a person physically being present near ...
Page 41
Using the system unit 2-9 starting and stopping the system unit note: this section presents an overview of the procedures to follow when starting up and shutting down the system. Before performing initial start up procedures, check with the system administrator to determine if the system operating s...
Page 42
2-10 operator guide manually starting the system unit 1. Set the power switches of the external devices to on (if connected). 2. If an expansion unit is attached, set the main power switch on the back of the unit to on. Set the base unit main power switch at the rear side of the system to on. 3. The...
Page 43
Using the system unit 2-11 manually stopping the system unit attention: use the shutdown command to stop the system unit; loss of data can occur if this command is not used. 1. Ensure that the key mode switch is in normal or service position. Note: it is possible to run the shutdown procedure from t...
Page 44
2-12 operator guide off, and push the power button on the system unit operator panel to set it to the off position.. To turn power completely off attention: unpredictable results can occur that effect your data files if you use this method to stop the system unit. 1. To switch the power to the syste...
Page 45: Terminals and Printers
Using the system unit 2-13 terminals and printers several terminals and printers can be connected to the system. All information concerning their technical characteristics and setup is contained in aix version 4 system management guide: operating system and devices. System consoles in 7013 j series ...
Page 46
2-14 operator guide using internal mass storage devices the internal mass storage devices include the media devices like the diskette drive, tape drives and cd-rom-2 drive and all the disk devices. After a general description on the special capability called hot removability, which is valid for the ...
Page 47: Using The 8 Mm Tape Drive
Using the system unit 2-15 using the 8 mm tape drive internal magnetic tape drives are typically used as back-up drives. The 8 mm helical scan has the following characteristics: • capacity 5/10gb • media data transfer 500kb/sec • capability to read and write 7g bytes cartridges (14g bytes with compr...
Page 48
2-16 operator guide status lights the following table explains the meaning of the green and amber status lights. Disturbance ready busy what has occurred: on on on the power-on self-test (post) is running or the system has issued a reset to the drive. Off off off one of the following has occurred: •...
Page 49
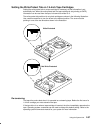
Using the system unit 2-17 setting the write-protect tab on 8 mm tape cartridges setting the write-protect tab on a tape cartridge is necessary so that information is not accidentally lost. When the write-protect tab of a tape cartridge is set (window closed), information can be read from the tape, ...
Page 50
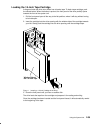
2-18 operator guide loading the 8 mm tape cartridge before loading the tape cartridge, make sure the power is on and the write-protect switch on the tape cartridge is properly set. The tape drive loads the tape from the cartridge and prepares it for reading and writing. Grasp the edges of the 8 mm t...
Page 51
Using the system unit 2-19 unloading the 8 mm tape cartridge push the unload button. The drive will rewind the tape within the cartridge and ejects the cartridge from the drive opening. The time required for a tape to rewind and unload is between 18 seconds and 3 minutes, depending on the position o...
Page 52: Preventive Maintenance
2-20 operator guide types of 8 mm tape cartridges test tape cartridge only use this specially labeled tape cartridge (found in the media kit with the 8 mm tape drive) to check out the operation of the drive or when running diagnostics. Do not use it to save programs or data. Data tape cartridge use ...
Page 53
Using the system unit 2-21 loading the 8 mm cleaning cartridge 1. Grasp the edges of the 8 mm cleaning cartridge with the window side of the cartridge on your left. 2. Slide the cleaning cartridge into the opening of the front of the 8 mm tape drive until the loading mechanism pulls the cartridge in...
Page 54
2-22 operator guide it must never be left in a car window, where sunshine can rapidly heat the air, and never left in a car overnight. It should be noted that airport-style metal detectors and hand held scanners will not affect the data stored on the 8 mm tape. 8mm data cartridge should be stored ve...
Page 55
Using the system unit 2-23 • keep the drive clean. • store data in a streaming (not start/stop) mode. Run the tape from bot to eot at normal speed. • exercise the tapes once every 12 months by reading the entire tape, to remove any stress which has built up in the tape pack during the storage interv...
Page 56
2-24 operator guide general information for 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive the 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive is an internal streaming tape drive that is used to: • save and restore system data files. • archive important records. • distribute operating system software upgrades. The 4 mm tape drive is designed to be a...
Page 57
Using the system unit 2-25 recommendations attention: tape cartridges that do not carry the proper dds symbol cannot be written to and their use will cause the 4 mm tape drive to report an error. • use only 4 mm digital data storage (dds) cartridges. Attention: use of other than recommended cleaning...
Page 58
– american national standard (ansi) standard, x3.203-191, hel...
Page 59
Using the system unit 2-27 increased if 4 mm tape cartridges are operated, stored, or shipped outside the temperature or humidity ranges shown in the following table. Before using a cartridge, always let it adjust (acclimate) to the operating environment. Do this by placing the cartridge with its co...
Page 60
2-28 operator guide using the 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive the optional 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive is a half-high device. Status lights the 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive has two green status lights and one amber status light. The on and off combinations of the status lights indicate the conditions of the 4 mm tape driv...
Page 61
Using the system unit 2-29 off • the power is off. • the post has completed successfully, but no tape cartridge has been loaded. Status lights on the 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive status the power-on self-test (post) is running or the diagnostic cartridge is running. Led test. Disturbance (amber) ready (gre...
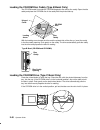
Page 62: The 4 Mm Tape
2-30 operator guide loading the 4 mm tape cartridge before loading the tape cartridge, make sure the power is on and the write-protect switch on the tape cartridge is properly set. Refer to “setting the write-protect tab on 4 mm tape cartridges” on page 2-26. The tape drive loads the tape from the c...
Page 63
Using the system unit 2-31 unloading the 4 mm tape cartridge before performing the unload operation, make sure the power to the 4 mm tape drive is on. To unload and eject the tape cartridge, press the unload button. The 4 mm tape drive rewinds the tape and then ejects the tape cartridge from the tap...
Page 64
2-32 operator guide cleaning the tape path on the 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive the 4 mm tape path should be cleaned either approximately every 30 hours of tape motion or once a month, whichever occurs first. The 4 mm tape drive monitors the recording quality of the tape cartridge and indicates that the tap...
Page 65
Using the system unit 2-33 using the 1/4-inch tape drive the quarter-inch cartridge (qic) tape has the following characteristics: • capacity 2.5gb • media data transfer 300kb/sec • form factor 5 1/4 inch half size • read/write compatibility with qic 120, 150, 525, 1000 and 2gb media functions unload...
Page 66
2-34 operator guide tape cartridge compatibility the 1/4-inch tape drive is a medium-capacity small computer system interface (scsi) tape drive. This drive is compatible with existing 1/4-inch streaming tape subsystems, which use the quarter-inch cartridge drive standards, inc. (qic) formats. The dr...
Page 67
Using the system unit 2-35 loading the 1/4-inch tape cartridge a diagram inside the drive door shows how to load a tape. To load a tape cartridge, push the unload button. When the button is pushed, the front panel of the drive partially opens towards the front of the system unit. 1. Pull the front p...
Page 68
2-36 operator guide unloading the 1/4-inch tape cartridge to unload the tape, use the same procedure as you did for loading except pull the cartridge from the drive opening. 1. Push the unload button. 2. Pull the front panel open (flat). 3. Pull the tape cartridge out of the drive. 4. Push the front...
Page 69
Using the system unit 2-37 setting the write-protect tab on 1/4-inch tape cartridges setting the write-protect tab on a tape cartridge is necessary so that information is not accidentally lost. When the write-protect tab of a tape cartridge is set (pointing to safe), information can be read from the...
Page 70
2-38 operator guide cleaning the 1/4-inch cartridge drive it is recommended to clean the read/write heads: • after any period of 8 hours use • after the first use of a new cartridge. The frequency of cleaning depends on the number of hours of daily use, on average, once a week. For effective cleanin...
Page 71: Using The Cd-Rom Drives
Using the system unit 2-39 using the cd-rom drives notes: 1. For a translation of this notice, see system unit safety information. 2. This caution only applies to the cd-rom drive. Caution: a class 3 laser is contained in the device. Do not attempt to operate the device while it is disassembled. Do ...
Page 72
2-40 operator guide loading the cd-rom disc caddy (type b bezel only) the cd-rom media kit contains a cd-rom diagnostic disc and a disc caddy. Open the disc caddy and place the cd-rom disc in the caddy with the printed side up. Cd-rom disc disc caddy hinged cover loading arrow with the loading arrow...
Page 73
Using the system unit 2-41 unloading the cd-rom disc caddy push and hold the unload button until the caddy unloads. The drive partially ejects the caddy from the drive opening. Pull the caddy out of the drive. Note: the unload button must be pushed and held for a minimum of two seconds before the ca...
Page 74
2-42 operator guide emergency eject (type c bezel only) note: execute the following procedure only in an emergency (caddy will not eject although pressing the unload button). 1. Power-off the cd-rom drive. 2. Insert a small diameter rod, such as a straightened paper clip, into the emergency eject ho...
Page 75
Using the system unit 2-43 using the 3.5-inch diskette drive functions in–use light unload button diskette opening unload button used to unload the diskette from the drive in-use light lights when the system is accessing the drive note: do not stop the system unit or remove a diskette when the in-us...
Page 76
2-44 operator guide types of 3.5-inch diskettes attention: diskette drives and diskettes must be the correct type to store data successfully. If you use the wrong diskette in your 3.5-inch diskette drive, the data on the diskette could be destroyed. The diskette drive uses the following 3.5-inch dis...
Page 77
Using the system unit 2-45 setting the write-protect tab write-protecting diskettes is necessary to avoid data loss. When diskettes are write-protected, you can read data from the diskettes, but you cannot write data on them. There is a write-protect tab on the 3.5-inch diskette. To locate the write...
Page 78
2-46 operator guide loading and unloading the 3.5-inch diskette to load a diskette into the drive, first insert the diskette in the diskette drive with the labeled metal shutter facing upward and with the bevelled corner on your right and away from you. Metal shutter loading the 3.5-inch diskette pu...
Page 79: Using Internal Disk Drives
Using the system unit 2-47 using internal disk drives the following disk drives can be installed in the 7013 j series system: • ibm 1.1gb scsi-2 se with a 1.1gb storage capacity • ibm 2.2gb scsi-2 se with a 2.2gb storage capacity • ibm 4.5gb scsi-2 se with a 4.5gb storage capacity operator controls ...
Page 80
2-48 operator guide.
Page 81: Introduction
Using systemguard 3-1 chapter 3. Using systemguard this chapter introduces the systemguard service processor which is included in all symmetric multiprocessor models. Introduction smp servers include a service processor, called systemguard, as a standard feature. Systemguard continually monitors the...
Page 82: Systemguard Power
3-2 operator guide systemguard power systemguard has its own dc power boundary. This means that even if the system power is off (power button of the system in the off position), systemguard is still powered on, as long as the unit is still plugged into a power outlet and the main power switch on the...
Page 83: The Operator Panel
Using systemguard 3-3 the operator panel the operator panel is the first level of user interface to systemguard. The operator panel has the following features: power button it should generally stay pushed in all the time if you want to be able to power on or off the system remotely. Reset button it ...
Page 84: Systemguard Consoles
3-4 operator guide systemguard consoles systemguard works with two types of consoles: • the bump console, which is an ascii terminal attached to the s1 serial port. This console provides the normal input to the bump. It can be local or remote. The line speed for the bump console must be set to 9600 ...
Page 85
Using systemguard 3-5 init phase init phase is entered when the power button on the operator panel is pressed on or when the power-on command is entered on the bump console or service console. If the system key is in normal mode, the bump runs the built-in or resident power-on (pon)-tests on the sys...
Page 86
3-6 operator guide phase change (stand-by to init) the phase change from stand-by to init is called crossing the power boundary. This is achieved by pushing the power button on the operator panel or by typing the keyword power at the stand-by prompt (>). Note that if you type power while the power b...
Page 87
Using systemguard 3-7 power-on (pon) tests pon tests are run by systemguard whenever the system power comes on. There are two types of tests: • a comprehensive set of tests are performed on the processors, cache, memory and related hardware when the fast-ipl flag is disabled. • a minimum core set of...
Page 88
3-8 operator guide there are other resident pon tests to check other system resources. These tests are a subset of the systemguard maintenance offline tests, and reside within the flash eeprom. These tests are divided into the following groups: bump quick i/o test group these tests check the accessi...
Page 89
Using systemguard 3-9 phase change (init to boot) the maintenance phase is entered from the init phase if the system key is in service mode. If the bump console present flag is set, the maintenance menu is displayed on the bump console, and the system waits for an operator action. The maintenance me...
Page 90
3-10 operator guide working with systemguard systemguard parameters and flags may be changed from different locations. They can be changed from the systemguard stand-by menu, the systemguard maintenance menu, the diagnostics interface, and also from aix. When the key signal is received, systemguard ...
Page 91
Using systemguard 3-11 when the system is in stand-by mode and the system key (physical or electronic key) is in service mode, the stand-by menu can be accessed and systemguard executed. If you turn the system unit power on from stand-by mode with the system key in the normal position, the system bo...
Page 92
3-12 operator guide stand-by menu the stand-by menu can only be entered when the system is in stand-by mode (the word stand-by must be displayed on the lcd display). Perform the following steps to bring up the stand-by menu. 1. With stand-by displayed on the lcd display press the enter key on the bu...
Page 93
Using systemguard 3-13 how to display the system configuration the system configuration can be displayed through the stand-by menu or through the maintenance menu. Displaying configuration through the stand-by menu this option displays the system configuration table. This configuration can be viewed...
Page 94
3-14 operator guide display configuration sib14 ps04 sib24 sib15 ps05 sib25 sib16 ps06 sib26 fc8e000000000000 sib17 ps07 sib27 mp d78605 19h0464 mpe d78605 mca 01 c fc8e000000000000 mcae 01 c e1ff000000000000 mca 02 c f48e000000000000 mcae 02 c 708f000000000000 mca 03 c fc8e000000000000 mcae 03 c ec...
Page 95
Using systemguard 3-15 • cpux ec+s: the agent status information of the cpu cards and the vpd information is given. • mcx ec+s: this field gives the memory card vpd values. • mcax loc. Code+status: this parameter contains the location code and the status information of the micro channel adapters (mc...
Page 96
3-16 operator guide and parameters (set during manufacturing), see the table in “default parameter values” on page b–1 of the service guide for your system. The following flags can be managed: • remote authorization: only the local operator can enable this flag to enable remote maintenance to be per...
Page 97
Using systemguard 3-17 set configuration this menu option enables you to configure or unconfigure units and devices. 1. Enter 3 in the main menu to select this option. 2. You should then see a first-level screen similar to the following. It displays the units and devices that can be configured, alon...
Page 98
3-18 operator guide ssbus maintenance this option is used to investigate and check devices on the ssbus and is meant only for trained service personnel. Use this option to investigate and check devices on the ssbus. 1. Enter 4 in the main menu to select this option. Systemguard displays the followin...
Page 99
Using systemguard 3-19 i 2 c maintenance use this option to do maintenance operations on the i 2 c buses of a selected unit, in order to investigate and check the connected devices. When exiting this menu, the previous status of the op and sib microcontrollers are restored (except for voltage margin...
Page 100
3-20 operator guide set voltage margins note: this option can be only used for error analysis or factory test and must be used only by trained service personnel. Restore nominal voltage values before restarting other operations. Any data written on the disk in marginal mode must be removed before re...
Page 101
Using systemguard 3-21 maintenance menu the maintenance menu also enables you to display the configuration of the system in a non-cryptic, easily understandable way, to perform various tests, to continue ipl either from network, a specific scsi device or from the boot list, and to set flags concerni...
Page 102
3-22 operator guide display configuration use this option to view the system hardware configuration. This option provides different screens with the following levels of information: • system-level information • unit-level information • device-level information. Enter 0 in the maintenance menu to sel...
Page 103
Using systemguard 3-23 • voltage margins for cpus, asics, and other components. • device status information. • options to select various types of devices. Display configuration – main unit margins value: +5 volt –> normal cpu (3.65 volt) –> normal asic (3.6 volt) –> normal scsi devices: present –> #...
Page 104
3-24 operator guide 1. To see device-level information, enter the corresponding command number for the device. The device-level screen is displayed. 2. Enter x to return to the system-level configuration display screen. Display configuration – device level this screen is shown when you select one of...
Page 105
Using systemguard 3-25 display bump error log use this option to view the bump firmware error log. 1. Enter 1 in the maintenance menu to select this option. The contents of the logging buffer are displayed as shown in the following screen: display bump error log event # 1: 40140100000000000000000000...
Page 106
3-26 operator guide system boot this command enables you to begin boot activity. Enter 6 in the main menu to select this option. The following screen is displayed: system boot 0> boot from list 1> boot from network 2> boot from scsi device select [x:exit]: the menu enables you to boot in three diffe...
Page 108
3-28 operator guide off-line tests attention: these menus are only to be used when directed by service support personnel. Some of the tests described require test equipment or resources not available on your system. This option under the maintenance menu enables you to run the off-line tests in a co...
Page 109
Using systemguard 3-29 0 displays the build test menu, which enables you to specify the test list (see “build test list” below). 1 displays and enables modification of the tests in the build list (see page 3-31). 2 deletes the tests in the build list, after operator confirmation. Attempting to delet...
Page 110
3-30 operator guide 3. Once you have selected the test groups, you can specify individual tests within a group. For example, the following screen enables you to specify individual bump quick io tests: build test list group 01 bump quick io test description test description 01 debug line 02 s1 asl (b...
Page 111
Using systemguard 3-31 modify/display test list once the test list is built, you can use this option to view or modify it. Each test is identified by a number xxyy, where xx is the group number and yy is the test number. 1. Enter 2 in the off-line tests menu to view or modify the test list. The foll...
Page 112
3-32 operator guide execute test list this command enables you to run the test list once it is built (and possibly modified). All the tests in the test list are run one at a time with the selected execution options. • enter 3 in the off-line tests main menu to run the selected tests. The following s...
Page 113
Using systemguard 3-33 power-on command parameters during the standby idle phase, the system power can be turned on (and the ipl started) by entering a bump console power-on string through line s1 or a service console power-on string through line s2 (see “working with systemguard” on page 3-10 for a...
Page 114
3-34 operator guide set configuration this command is used to configure electronic boards like i/o cards or micro channel adapter (mca) devices. 1. Enter 2 in the set parameters menu to display the set configuration menu as shown below: set configuration 0> cpu card 1> memory card 2> basic mca adapt...
Page 115
Using systemguard 3-35 1. Enter 3 in the set parameters menu to display the phone numbers menu shown here: phone numbers 0> service center dial–out (1) –> 1> service center dial–out (2) –> 2> customer hub dial–out (1) –> 3> customer hub dial–out (2) –> 4> system dial–in –> 5> system operator voice –...
Page 116
3-36 operator guide • enter 4 in the set parameters menu to display the miscellaneous parameters menu. The value set for all the flags, except fast ipl, is permanent until a new change is made. Miscellaneous parameters 0> bump console –> present 1> autoservice ipl –> disabled 2> dial_out authorizati...
Page 117
Using systemguard 3-37 2. The new flag status (opposite of the previous state) is displayed. Boot multiuser aix in service flag enables multiuser aix boots to proceed even if the mode switch is in the service position (when booting by selecting option 6 in the maintenance menu). When the flag is ena...
Page 118
3-38 operator guide set national language use this option in the main menu to set the national language used for “systemguard”. Once selected, the effect is immediate and all the console messages are presented in the selected language. 1. Enter 9 in the maintenance menu to select this option. The fo...
Page 119
Using systemguard 3-39 some common systemguard tasks the following tasks are done through the stand-by and maintenance menus that are part of systemguard. Note that these tasks can also be carried out from aix diagnostics. How to set the electronic key the key can be set electronically, making it ea...
Page 120
3-40 operator guide the configuration display is a good picture of the systemguard configuration on one screen. Here is an example: display configuration machine type/model: 7013j30 45067 firmware release: standby –> 1600 backup eprom –> 0701 flash eprom –> 0704 service contract: last update (yymmdd...
Page 121
Using systemguard 3-41 setting fast ipl through the maintenance menu 1. Enter the maintenance menu. 2. Enter 8 to select the set parameters menu. 3. Enter 4 from the set parameters menu to select the miscellaneous parameters menu. 4. Option 3 in this menu should show the current status of the fast i...
Page 122
3-42 operator guide how to set the service line speed by default, the service line speed is 1200 baud or 2400 baud depending on the level of systemguard. This speed can be changed through the systemguard maintenance menu. In order to use the service console properly, the terminal connected to the s2...
Page 123
Using systemguard 3-43 setting line speed through aix 1. With aix up and running, log in as user root. 2. Type the following command to view current settings: mpcfg –dm the following is the output of the command: index name value 1 modem parameters file name 2 service line speed 3 protocol inter dat...
Page 124
3-44 operator guide how to set up console mirroring console mirroring concepts console mirroring is a way to provide the customer a view of what the person working remotely from the service console is doing on the system. When mirroring is active, the service console and the bump console are logical...
Page 125
Using systemguard 3-45 setting up console mirroring in order to setup console mirroring, you need first to authorize the service console, and set up the right line speed. Refer to previous chapters on how to set up the service line speed and how to authorize the service console. Then do the followin...
Page 126
3-46 operator guide how to enable surveillance surveillance is implemented by the survd daemon. This daemon, when started, establishes a heartbeat between aix and systemguard. In case of an aix hang, systemguard detects it and reboots the system. To implement the surveillance, do the following: 1. E...
Page 127
Using systemguard 3-47 modem configuration the modem on line s2 must be configured using an ascii modem configuration file which describes various parameters using a specific syntax. Aix uses this file directly. The bump uses the same information (in condensed form) stored in non-volatile memory (nv...
Page 128
3-48 operator guide how to reboot aix from the remote service console it is possible for the remote personnel connected via the service console to reboot aix from the remote site. Prerequisites the following procedure must be carried out from the bump console in order to allow aix to boot remotely f...
Page 129
Using systemguard 3-49 rebooting to single-user and then to multi-user this allows the remote support personnel connected to the system via a modem to the s2 port to shut down and reboot the system in diagnostics mode for hardware diagnostics purposes. After running diagnostics, the remote personnel...
Page 130
3-50 operator guide 3. From this menu, enter 4 . To select the miscellaneous parameters menu, which is similar to the following: miscellaneous parameters 0> bump console –> present 1> autoservice ipl –> disabled 2> dial_out authorization –> disabled 3> fast ipl –> enabled 4> set mode to normal when ...
Page 131
Using systemguard 3-51 10.At this point, a boot from scsi device screen appears. This displays the present device location code. If it is not the device you want to boot from, go through each option and change it to the desired bus, slot, scsi id, and lun id. Option 4 allows you to change all these ...
Page 132
3-52 operator guide how to boot from the network the system can be booted from the network through the maintenance menu. Network boot allows a system to be reinstalled via the network and also allows various maintenance tasks to be carried out on the local machine. Use the following procedure to boo...
Page 133
Using systemguard 3-53 5. The select boot (startup) device menu appears, which is similar to the following: select boot (startup) device select the device to boot (startup) this machine. Warning: if you are using token–ring, selection of an incorrect data rate can result in total disruption of the t...
Page 134
3-54 operator guide 7. Enter the appropriate ip addresses, and enter 99 to return to the main menu. A screen similar to the following appears: main menu 1. Select boot (startup) device 2. Select language for these menus 3. Send test transmission (ping) 4. Exit main menu and start system (boot) type ...
Page 135
Using systemguard 3-55 how to disable and enable processors in the smp servers, it is possible to disable/enable processors. A suspected faulty processor can be disabled so that the system can run without it. The processors can be disabled/enabled through the stand-by menu, maintenance menu, diagnos...
Page 137
Using systemguard 3-57 5. The cpu card screen appears and looks similar to the following: cpu card – (cpu1) present conditions: pr #0 –> valid & enabled pr #1 –> valid & enabled commands: 0> enable 1> disable 2> temporary disable select [x:exit]: 6. From this screen, you can disable or enable a part...
Page 138
3-58 operator guide customizing systemguard for your needs systemguard is controlled by several flags. The flags consist of contract flags, operational flags, remote maintenance flags, and test flags. Remote service flag this flag is disabled at the factory and must be enabled for remote service ope...
Page 139
Using systemguard 3-59 phone numbers if remote maintenance is used, systemguard requires several phone numbers to be entered. Additional information is provided in “phone numbers” on page 3-34. Service line speed parameters if remote maintenance is used, systemguard requires that the line speed be c...
Page 140
3-60 operator guide reloading the flash eeprom follow this procedure to load a new version of systemguard into the flash eeprom. Only system administrators should perform this procedure. Prerequisites to install a new version of the flash eeprom firmware, you need either a firmware diskette containi...
Page 141
Removal and installation procedures 4-1 chapter 4. Removal and installation procedures this chapter contains the instructions for removing or installing a micro channel adapter (the system power must be turned off). The procedures in this chapter are not presented in a step-by-step order. As needed,...
Page 142: Hot Removability Capability
4-2 operator guide hot removability capability the disk and media drives in the 7013 j series base unit and expansion unit are designed for removal and installation while the system is operating. This feature is called hot removability capability. The hot removability capability offers additional ad...
Page 143
Removal and installation procedures 4-3 locating a micro channel adapter the software uses a software location code to identify each device, but, you also need to know where the device is physically located in the base unit or expansion unit. Before you remove or install a micro channel adapter (mca...
Page 144
4-4 operator guide locating a disk or media drive the 7013 models jxx units have two scsi buses in each unit. The scsi buses are controlled by scsi-2 differential fast/wide controllers installed in the mca slots. In the base unit, the standard configuration has a scsi controller in mca slot 7 attach...
Page 145
Removal and installation procedures 4-5 scsi bus controllers to determine the physical location of a drive from a software location code you must determine how the scsi bus controllers are cabled. Record the location of the scsi controller for each scsi bus you have in your system (unit is base or e...
Page 146
4-6 operator guide converting a software location code to a physical drive location 1. From the configuration listing, determine the software location code for the drive you want to locate. Look at the -cd- portion of the software location code to determine the location of the scsi controller. Ab - ...
Page 147
Removal and installation procedures 4-7 unconfiguring or configuring a drive there are three conditions where you need to use these procedures: • you are removing or installing a drive while the system power is turned on. This is called hot removability capability. • you are installing a new drive. ...
Page 148
4-8 operator guide removing or installing a front media or disk device this procedure is for the media or disk drives installed in the front drive positions on the base unit and expansion unit. Attention: the 9.1gb disk drive can only be installed in positions in the front of the unit. Note: for a t...
Page 149
Removal and installation procedures 4-9 5. Locate the drive retaining screw at the lower side of the drive. 6. Loosen the retaining screw using a screwdriver. Firmly grip the drive and pull it out of the unit. Installation 1. Align the drive with the guides in the desired drive position; then slide ...
Page 150
4-10 operator guide removing or installing a rear drive this procedure is for the disk drives installed in the rear drive positions on the base unit and expansion unit. Attention: do not operate the system unit with the covers removed for a long time. Operating with the covers on ensures adequate co...
Page 151
Removal and installation procedures 4-11 4. Be sure the yellow indicator on the drive you are removing is off (powered off). 5. Firmly grip the disk drive and pull it out of the unit. Installation 1. Align the disk drive with the guides in the desired drive position; then slide it inside the unit. T...
Page 152
4-12 operator guide 2. Insert the two positioning pins located on the lower edge of the rear cover into the corresponding holes of the unit. 3. When the pins are in place, close and lock the rear cover. 4. Use the “configuring” procedure on page 4-7 to add the drive to the system configuration..
Page 153
Using the diagnostics 5-1 chapter 5. Using diagnostics this topic describes how to run the diagnostics from the network server. Diagnostic programs operating considerations the following items identify some things to consider before using the diagnostic programs. Note: when possible, run the online ...
Page 154
5-2 operator guide running diagnostic programs from cd-rom consider the following when you run diagnostic programs from the cd-rom disc: • the diagnostic disc must remain in the cd-rom drive for the entire time that diagnostics are executing. • the diagnostic cd-rom disc cannot be ejected from the c...
Page 155
Using the diagnostics 5-3 running the diagnostic programs from the network consider the following when you run the diagnostic programs from a network: • diagnostics cannot be loaded and run from the network until aix version 3.2 or higher has been installed and configured on the server. • your syste...
Page 156
5-4 operator guide general attributes always required the general attributes in the following table are the default settings for the diagnostic programs. Be sure your terminal is set to these attributes. Note: these attributes should be set before the diagnostic programs are loaded. General setup at...
Page 157
Using the diagnostics 5-5 general setup attributes description 3161/3164 settings 3151 /51/61 settings 3151 /11/31/41 settings tab field field field the column tab stops are ignored, and the tab operation depends on the field attribute character positions. Trace all both inbound data (data to the sy...
Page 158
5-6 operator guide additional keyboard attributes the following keyboard attributes are for the keyboard attached to the 3151, 3161, and 3164 terminals. Keyboard setup attributes 3151 /11/ 31 /41 settings 3151 /51/61) settings 3161 /3164 settings description enter return return return the enter key ...
Page 159
Using the diagnostics 5-7 diagnostic modes of operation the diagnostics can be run in three modes: • maintenance mode allows checking of most system resources • concurrent mode allows the normal system functions to continue while selected resources are being checked. • standalone mode allows checkin...
Page 160
5-8 operator guide there are three levels of testing in concurrent mode: • the share-test level tests a resource while the resource is being shared by programs running in the normal operation. This testing is mostly limited to normal commands that test for the presence of a device or adapter. • the ...
Page 161
Using the diagnostics 5-9 running the diagnostics in standalone mode to run diagnostics in standalone mode, take the following steps: 1. Stop all programs including the aix operating system (get help if needed). 2. Set the power switch on the system unit to off. 3. Set the key mode switch to the ser...
Page 162
5-10 operator guide starting the system exerciser when the system exerciser is selected from the menu, another menu displays all devices to be tested. Pressing the enter key starts tests for all of the devices. The time required to test all of the devices depends on the number of devices to be teste...
Page 163: Reading A Flashing
Using the diagnostics 5-11 reading a flashing 888 message on a multi-line operator panel display an 888 flashing in the first line of the operator panel display indicates that a hardware or software error has been detected and that an error message is being displayed. For additional information abou...
Page 164
5-12 operator guide is the second line of the operator panel display blank? No the message has a type 103 or 105 message included in it. Press the reset button once, then go to step 3. Read out the srn and fru information for these message types. Yes this completes the read-out of this message. You ...
Page 165: Step 4. Other Numbers
Using the diagnostics 5-13 step 3. Reading the type 103 and 105 message a type 103 and 105 message is generated when a hardware error is detected. Use the following steps and information to record srn and fru location code information. 1. Record all characters following the first 103 or 105 in the f...
Page 166
5-14 operator guide.
Page 167: Tasks
Using the service aids 6-1 chapter 6. Introduction to tasks and service aids beginning with version 4.2 there are two top level menus seen by the user – tasks and resources. Once a task has been selected, then a list of resources is displayed for selection to run the task on. Or after selecting a re...
Page 168
6-2 operator guide run diagnostics task the run diagnostics task invokes the resource selection list menu. When the commit key is pressed, diagnostics are run on all selected resources. The procedures for running the diagnostics depends on the states of the diagnostics run time options. The run time...
Page 169
Using the service aids 6-3 • run tests multiple times this option allows the user to select if the diagnostic should be run in loop mode or not (the default is no). Note: this option is only displayed when running online diagnostics in service mode. Process supplemental media task this prompts for e...
Page 170: Aix Shell Prompt Service Aid
6-4 operator guide periodic diagnostics service aid 6-13 product topology service aid 6-13 scsi bus service aid and scsi bus analyzer task 6-13 scsi tape utilities service aid 6-14 service aids for use with ethernet 6-14 service hints service aid 6-15 ssa service aid 6-15 trace service aid 6-15 7318...
Page 171
Using the service aids 6-5 • save or restore diagnostics modes and remote support phone number this function allows the diagnostics modes and remote support phone number to be saved and restored. The location of the save area is to be defined. • flash eprom download this function updates the flash e...
Page 172: Based Diagnostic Task
6-6 operator guide disk based diagnostic update service aid and update disk based diagnostic task this service aid allows fixes (apars) to be applied. Disk based diagnostic update service aid before version 4.2 prior to version 4.2 this service aid is used to update the diagnostics on the disk drive...
Page 173: Disk Media Service Aids
Using the service aids 6-7 to prevent problems that may occur when running this service aid from disk, it is suggested that this service aid be run from the diagnostics that are loaded from removable media when possible. Display/alter sector service aid note: to access this service aid refer to the ...
Page 174
6-8 operator guide 2. Do a format without certify. 3. Run a second pass of the erase service aid. For a newly installed drive, you can insure that all blocks on the drive are overwritten with your pattern if you use the following procedure: 1. Format the drive. 2. Check the defect map by running the...
Page 175: Diskette Media Service Aid
Using the service aids 6-9 indicates that the disk needs to be backed up and replaced. Formatting the disk does not improve the availability of spare sectors. Diskette media service aid this service aid provides a way to verify the data written on a diskette. When this service aid is selected, a men...
Page 176
6-10 operator guide display software product data beginning with version 4.2 this service aid displays information about the installed software and provides the following functions: • list installed software • list applied but not committed software updates • show software installation history • sho...
Page 177: Mode Switch Task)
Using the service aids 6-11 diagnostic test list menu lists all resources that can be deleted from the diagnostic test list. Note: only resources that were previously detected by the diagnostics and have not been deleted from the diagnostic test list are listed. If no resources are available to be d...
Page 178: Log Task
6-12 operator guide hardware error report service aid and display hardware error log task this service aid provides a tool for viewing the hardware error log and performing error log analysis. It uses the errpt command to do this. The display error summary and display error detail selection provide ...
Page 179: Product Topology Service Aid
Using the service aids 6-13 periodic diagnostics service aid this service aid provides a tool for configuring periodic diagnostics and automatic error log analysis. A hardware resource can be chosen to be tested once a day, at a user specified time. If the resource cannot be tested because it is bus...
Page 180
6-14 operator guide when the scsi bus service aid is entered a description of the service aid is displayed. Pressing the enter key displays the adapter selection menu. This menu allows the user to enter which address to transmit the scsi inquiry command. When the adapter is selected the scsi bus add...
Page 181: Service Hints Service Aid
Using the service aids 6-15 when the ethernet service aid is executed, one of the following messages is returned: • no errors occurred. • an adapter error occurred. • a transmit time–out occurred. • a transmit error occurred. • a receive time–out occurred. • a receive error occurred. • a system erro...
Page 182
6-16 operator guide 7318 serial communications network server service aid this service aid provides a tool for diagnosing terminal server problems..
Page 183
Using the system verification procedure 7-1 chapter 7. Using the system verification procedure this chapter contains information about pre-procedure considerations and running the system verification. System verification procedure the system verification procedure is used to check the system for cor...
Page 184
7-2 operator guide step 2. Loading the diagnostic programs 1. Stop all application programs running on the operating system. 2. Stop the operating system (if help is needed; call your 800 support number). 3. Power the system off. 4. Set the key mode switch to the service position. 5. If you want to ...
Page 185
Using the system verification procedure 7-3 step 4. Additional system verification the checkout programs end with either the testing complete menu and a message stating no trouble was found or the a problem was detected on (time stamp) menu with an srn. 1. Press enter to return to the diagnostic sel...
Page 186
7-4 operator guide.
Page 187: Step 2
Hardware problem determination 8-1 chapter 8. Hardware problem determination if you have an error or failure on your system, this chapter contains steps for obtaining a service request number (srn). You report the srn to the service organization. The service organization uses the srn to determine wh...
Page 188: Step 4
8-2 operator guide step 4 (from step 3) diagnostic tests can be run on many resources while the operating system is running. However, problem isolation is obtained by running diagnostics in service mode. Do you want to run the diagnostics in service mode? No go to step 5. Yes do the following to shu...
Page 189: Step 6
Hardware problem determination 8-3 step 6 (from steps 3, 4, 5, 7) this step loads the diagnostics. 1. Set the mode switch to the service position. 2. Be sure the power switches of the attached devices are set to on. 3. Set the power switch on the system unit to on. 4. If c31 is displayed, follow the...
Page 190
8-4 operator guide 6. Starting at the top of the following table, find your symptom and follow the instructions given in the action column. Symptom action the system stops with a blank operator panel display and the words diagnostic operating instructions are displayed with no obvious problem on the...
Page 191: Step 7
Hardware problem determination 8-5 step 7 (from step 6, 18) the following steps analyze a steady (not flashing) number displayed in the operator panel display while attempting to load the diagnostics. Operator panel display number action 200 be sure the key mode switch is set to the service position...
Page 192: Step 9
8-6 operator guide step 9 (from steps 6, 18, 20) the following steps analyze a console display problem. Find your type of console display in the following table; then, follow the instructions given in the action column. Console display action display device go to the your display documentation for p...
Page 193
Hardware problem determination 8-7 3. Press the enter key. 4. In the following table, find the menu or system response you received when you selected diagnostic routines; then follow the instructions given in the action column. System response action the diagnostic mode selection menu is displayed. ...
Page 194: Step 13
8-8 operator guide step 13 (from step 12) the system checkout option checks all of the resources (available in standalone mode only). Select and run the diagnostic tests on the resources you are having problems with or run system checkout to check all of the configured resources. Find the response i...
Page 195: Step 15
Hardware problem determination 8-9 step 15 (from steps 12, 13) the diagnostic programs produced an srn for this problem. 1. Record the srn and any other numbers. 2. Report the srn to the service organization. 3. Stop. You have completed these procedures. Step 16 (from step 6) the system stopped with...
Page 196: Step 18
8-10 operator guide step 18 (from step 17) the following steps analyze a failure to load the diagnostic programs from a disk, or a failure to determine whether the diagnostic programs are on a disk. 1. Set the power switch on the system unit to off. 2. Set the key mode switch to the service position...
Page 197: Step 19
Hardware problem determination 8-11 7. Starting at the top of the following table, find your symptom; then perform the specific action. Symptom action the system stops with a blank operator panel display, and the words diagnostic operating instructions are displayed with no obvious problem on the co...
Page 198: Step 21
8-12 operator guide step 21 (from steps 2 and 7) an english-only version of diagnostics are provided on cd-rom disc. Do you want to run diagnostics from cd-rom disc? No if you have a problem, call for service, and report the problem. Yes go to step 17. Step 22 (from step 16) an english-only version ...
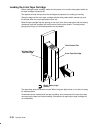
Page 199: Chapter 9. Expansion Unit
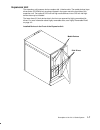
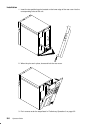
Expansion unit 9-1 chapter 9. Expansion unit this chapter describes how to connect the expansion unit to the base unit. In addition it illustrates briefly the general rules to disconnect the expansion unit from the system configuration. Overview looking at the cabinets from front, the expansion unit...
Page 200: Installation Procedures
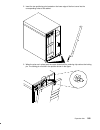
9-2 operator guide installation procedures preliminary operations before connecting an expansion unit to a base unit, perform the following preliminary operations. Note: for a translation of these notices, see system unit safety information. Danger an electrical outlet that is not correctly wired co...
Page 201
Expansion unit 9-3 3. For each unit, press the switch located on the main power switch module off, switching it to the ”0” position. 4. Make sure the power switches for all external devices connected to the system unit, if any, are set to off. 5. Unplug the power cable to all external devices connec...
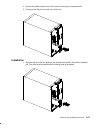
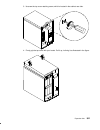
Page 202
9-4 operator guide rear cover attention: do not operate the system unit with the covers removed for a long time. Operating with the covers on ensures adequate cooling of the components. Remove the covers only when required by the removal and installation procedures illustrated in this guide. Removal...
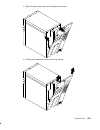
Page 203
Expansion unit 9-5 3. With a firm grip on the cover, tilt it towards you as shown. 4. Pull the cover upward, to remove it from the cabinet..
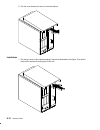
Page 204
9-6 operator guide installation 1. Insert the two positioning pins located on the lower edge of the rear cover into the corresponding holes of the unit. 2. When the pins are in place, close and lock the rear cover. 3. Do in reverse order the steps listed in “preliminary operations” on page 9-2..
Page 205
Expansion unit 9-7 front cover removal 1. Before removing the front cover, be sure to remove the rear cover. Follow the removal procedure described in “rear cover” on page 9-4. 2. On the rear side of the unit, turn the locking handle clockwise 90 degrees to unlock the front cover. Later models early...
Page 206
9-8 operator guide 4. Pull the cover up to remove it from the cabinet. Installation 1. Before installing the front cover, be sure that the locking handle in the rear side of the cabinet is in the position shown in the figure. If not, turn it in that position. Later models early models.
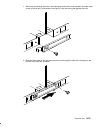
Page 207
Expansion unit 9-9 2. Insert the two positioning pins located on the lower edge of the front cover into the corresponding holes of the cabinet. 3. When the pins are in place push the cover closed until the retaining clip catches the locking pin. The locking pin must be in the position shown in the f...
Page 208
9-10 operator guide 4. On the rear of the unit, turn the locking handle counterclockwise 90 degrees to lock the front cover. Later models early models 5. Re-install the rear cover, as described on page 9-6, after having performed all needed operations. Top cover removal attention: if you try to remo...
Page 209
Expansion unit 9-11 3. Unscrew the top cover retaining screw, which is located in the cabinet rear side. 4. Firmly grip the top cover with your hands. Pull it up, inclining it as illustrated in the figure..
Page 210
9-12 operator guide 5. Pull the cover forward to remove it from the cabinet. Installation 1. Put the top cover on the cabinet keeping it inclined as illustrated in the figure. Then slide it back until it catches the locking bar on the unit..
Page 211
Expansion unit 9-13 2. Push the cover down. 3. Tighten the top cover retaining screw, which is located in the cabinet rear side. 4. Re-install the front and rear covers, as described on pages 9-6, and 9-8, after having performed all needed operations..
Page 212: Mechanical Connection
9-14 operator guide mechanical connection the units must be mechanically connected at the bottom. Securing the units at the bottom the units are secured to one another at the bottom, using the locking bar shown. The locking bar must be installed on both the front and the rear of the units, in the po...
Page 213
Expansion unit 9-15 1. Start the screw through the hole in the locking bar and into the hole located in the lower right corner of the left unit, as illustrated in the figure. Push the locking bar against the units. 2. Slide the locking bar to the right and start the screw through the hole of the loc...
Page 214
9-16 operator guide 3. Pull the units apart, until locking bars stop you. This allows the doors to open and close smoothly. 4. Using a screwdriver, tighten the screws clockwise as shown in the figure, to secure the locking bar. 5. Continue with “units interconnection” on page 9-17..
Page 215: Units Interconnection
Expansion unit 9-17 units interconnection the units must be connected using appropriate cables, according to the system configuration. Do the following procedure to perform the units interconnection. Fxe cable interconnection the fxe cable interconnection must be performed between the base unit and ...
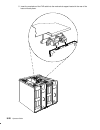
Page 216
9-18 operator guide b. Using the cpu module puller as indicated in the following figure, unlock the cpu module from the base unit. Base unit, rear c. Firmly grip the front handle on the cpu module. Then slide the cpu module out of the base unit until the handle on the top is visible. Gripping both t...
Page 217
Expansion unit 9-19 2. Remove the metal bridge from the base unit,in the area circled in step 4. 3. Remove the adapter cards nearest the outside of the expansion unit. See adapters in 7013 j series service guide. This will enable easier access for the fxe cable installation. 4. Insert the fxe cable ...
Page 218
9-20 operator guide 5. Insert the mechanics of the fxe cable into the mechanical support located in the rear of the base unit back plane..
Page 219
Expansion unit 9-21 6. Slide the mechanics of the fxe cable following the direction shown in the figure. 7. Secure the mechanics of the fxe cable to the base unit back plane mechanical support tightening clockwise the screw illustrated in the figure..
Page 220
9-22 operator guide 8. Connect the fxe cable connector to the connector marked y1 on the mpe board in the expansion unit micro channel adapter card cage. Note: before attempting to connect the fxe cable, remove the dust covers from connectors on the fxe cable and the mpe board..
Page 221
Expansion unit 9-23 9. Replace the metal bridge as shown here. Use the new bridge that is shipped with the expansion unit (the side piece is shorter, to allow the fxe cable to fit under it). Be sure to attach the ground cable from the expansion unit to the base unit. Ground cable 10.Be sure to adjus...
Page 222
9-24 operator guide rs-485 cables interconnection the rs-485 cables interconnection must be performed from unit to unit. 1. Insert a terminator plug on the upper 6 pins mini connector located on the system interface board installed in the base unit. (this connector is marked ‘‘in’’ on the system int...
Page 223
Expansion unit 9-25 scsi interface card interconnection for each scsi bus used in the expansion unit, a dedicated scsi controller must be installed. Install the scsi controllers in the expansion unit observing the following rules: • install the scsi controller(s) that will manage the scsi buses in t...
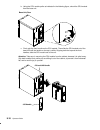
Page 224: Recognizing The New Unit
9-26 operator guide recognizing the new unit 1. Replace the rear cover as described in rear cover “installation” on page 9-6. Attention: before powering on the base system unit, be sure that the expansion unit main power switch is set to on (i). If you attempt to power the base unit on when the expa...
Page 225: Units Disconnection
Expansion unit 9-27 units disconnection when a unit needs to be disconnected from the existing system configuration composed of the base unit and the expansion unit, you have to do the following steps in the indicated order. Attention: before attempting to disconnect the expansion unit from the syst...
Page 226
9-28 operator guide.
Page 227
Moving the system unit 10-1 chapter 10. Moving the system unit this section provides important information about moving the system unit. Moving the system unit safely note: it is recommended that only trained people connect or disconnect any cables attached to the system. Attention: damage as a resu...
Page 228
10-2 operator guide to move the units of your 7013 j series system safely, follow the sequence described below: 1. Set the power switches of the attached devices to off. 2. To take off power from the base unit and the other system units you have connected, push the power control button on the operat...
Page 229
Systemguard test groups a-1 appendix a. Systemguard test groups systemguard test groups table the following diagram shows the various test groups and their associated tests. To modify the test list, the tests have to be selected in the xxyy format, where xx is the group number and yy is the test num...
Page 230
Operator guide a-2 group no test test no group 05 dcb and memory test group 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 50 mm data lines test mm address lines test mm board dec. Test mm basic acc. Test mm components test ecc component test ecc mechanism test refresh mech. Test ecc data lines access. Test mm full tes...
Page 231
Systemguard test groups a-3 6. Mm full test 7. Scsi–d ext. Test. Systemguard test group descriptions the following is a description of the different test groups and the tests available under them. All of these tests are performed automatically at power-on with default parameters. They can also be pe...
Page 232
Operator guide a-4 bump, remote, and special asynchronous lines test these tests are meant to check the asynchronous lines of the standard i/o and the asynchronous lines controller in the super i/o. These tests contain sub-tests, which are described as follows. Each sub-test saves and restores the l...
Page 233
Systemguard test groups a-5 nvram test this test checks the accessibility of nvram bytes. It contains the following sub-tests: nvram data lines access test this test saves the first nvram byte. Then a read / write operation is done word by word. It restores the first nvram byte. Nvram address lines ...
Page 234
Operator guide a-6 dtr register test this test writes, reads and compares a 1 among 0 bits in dtr registers. Ctr register test this test writes, reads and compares a 1 among 0 bits in ctr registers. It saves and restores the ctr register value. Miscellaneous registers test this test checks accessibi...
Page 235
Systemguard test groups a-7 entry parameters parameters name definition possible values default value parameter 1 sub test # subtest number 0 or 1 0 = all tests linked parameter 2 proc # processor number 8 8 = bump check–sum test it checks the crc value for all present vpds; it checks the crc value ...
Page 236
Operator guide a-8 bpp external loopback test (bpp ext l–b test ) note: this test can only be performed by field or manufacturing people. This test checks the accessibility of the super–io chip. It saves and restores used registers. This test is not performed at power on. Entry parameters parameters...
Page 237
Systemguard test groups a-9 ionian-ssga registers test this test is performed by all the processors and it checks the accessibility from the processor to the ionian and ssga chips. Following h/w parts are checked. 1. Dcb asic 2. Ionian asic 3. Ssga asic the following sub-tests are included under the...
Page 238
Operator guide a-10 super i/o and uart access test this test checks the accessibility of the super i/o chip from the processors. They don’t check the functional aspects of the super i/o chip (this is done by the bump directly). The following sub-tests are available under this test: super i/o uart 1 ...
Page 239
Systemguard test groups a-11 ssga interrupt registers test this test writes and reads specific values from each of the interrupt registers. The values are then compared. Values are saved and restored in all the operations. Floppy disk access test this test needs a formatted diskette in the diskette ...
Page 240
Operator guide a-12 level 2 cache. It calculates the memory address available and then validates the level 2 cache before writing 1 mb. Then a read operation is done in word mode and values are compared. Then a read is done in burst mode and comparison is done. Tag data test this test checks the ava...
Page 241
Systemguard test groups a-13 walking 0 data test this test isolates the open lines among the data lines. It writes “0s among 1s” pattern on the cache line. Then it is read and compared. Transfer modes on dcb test this sub-test is used to check the transfer of 1 to 8 bytes to the memory. Initially th...
Page 242
Operator guide a-14 this test consists of two sub-tests. Words manipulated / used are not restored at the end of the test. This test is applied to all the memory cards which are present. In case of errors, suitable error messages are displayed on the console. The following is a description of the su...
Page 243
Systemguard test groups a-15 basic main memory test this test is performed by all the processors and it checks the capability to access the main memory in all kinds of data formats. This test applies to one main memory location and the words used during the test are not restored. This test partially...
Page 244
Operator guide a-16 main memory components test this test is performed by all the processors to check all the main memory locations. From the h/w point of view, this test checks the memory chips mounted on the main memory cards. This test can be launched in two modes, as follows: 1. Bit map elaborat...
Page 245
Systemguard test groups a-17 ecc data lines accessibility test this test checks the accessibility for all the data lines to the ecc memory banks, through smc asics. The following h/w parts are checked by running this test. • dcb asics • smc asics • connection of data lines between cpu daughter board...
Page 246
Operator guide a-18 ecc memory component test this test is identical to the main memory components test but it is applied to the ecc memory components. Error correction mechanism test this test checks the hardware mechanisms enabling the detection of and the correction of single bit errors when work...
Page 247
Systemguard test groups a-19 interrupt tests group these tests are performed by the bump as well as the processors. They are launched at power on and under control of off line test monitor. They collectively check the interrupt system. The following tests are available under this group. Bump to cpu ...
Page 248
Operator guide a-20 cpu multiprocessor test group these tests are launched at power-on and are also available under the control of the off line tests monitor. These tests check the multi-processor mechanisms, atomic instructions, cache coherency, main memory sharing, and multi-resources sharing. The...
Page 249
Systemguard test groups a-21 instruction. This is issued by processor 0 which is set to global copy back mode. Caching is inhibited for processor 1. Paradox detection: dcbst not from line owner here, processor 1 is set to local copy back mode. Memory coherency is enabled for processor 0. This test v...
Page 250
Operator guide a-22 main memory sharing test this test is launched by the bump and performed by all configured processors. It has a sub-test to check the capability of all the processors to access the main memory. The following h/w parts are checked during the process: 1. Dcb asics 2. Ionian asics 3...
Page 251: Default Parameter Values
Modifying systemguard parameters b-1 appendix b. Modifying systemguard parameters many systemguard parameters can be modified in several ways. Some can be modified using the systemguard stand-by menu, others using the systemguard maintenance menu, and others using the aix diag or mpcfg commands or d...
Page 252
B-2 operator guide flag, parameter and keyword default values name default value bump console power-on command string power service console power-on command string blank (not set) bump console power-on command flag enabled service console power-on command flag disabled remote authorization flag disa...
Page 253
Modifying systemguard parameters b-3 changing flags and parameters under aix service aids the service aids are recommended to change the flags. The service aids can be entered using the diag command or by booting diagnostics in service mode. They display or change flag values using 0 (zero) for disa...
Page 254
B-4 operator guide systemguard maintenance menu starting from the main maintenance menu: • enter 2 to enable the flag. Or • enter 3 to disable the flag. Aix diag command starting from the service aids selection menu: 1. Select the bump service aids option. 2. Select the display or change flags and c...
Page 255
Modifying systemguard parameters b-5 modifying dial-in phone numbers these parameters can be changed under systemguard using the maintenance menu, or under aix using the diag command. Systemguard maintenance menu starting from the main maintenance menu: 1. Enter 8 to set parameters. 2. Enter 3 for p...
Page 256
B-6 operator guide modifying the electronic mode switch from service line flag this flag can be changed under systemguard using the maintenance menu, or under aix using the diag command. Systemguard maintenance menu starting from the main maintenance menu: 1. Enter 8 to set parameters. 2. Enter 4 fo...
Page 257: Reloading The Flash Eeprom
Modifying systemguard parameters b-7 reloading the flash eeprom follow this procedure to load a new version of systemguard into the flash eeprom. Only system administrators should perform this procedure. Prerequisites to install a new version of the eeprom firmware, you need either a firmware disket...
Page 258
B-8 operator guide.
Page 259: Configuration
Systemguard remote operation configuration c-1 appendix c. Systemguard remote operation configuration in order to utilize the remote operation capabilities of systemguard and also allow console mirorring, you need to have flags, parameters and tty configurations properly enabled. Below, are tty0 and...
Page 260
C-2 operator guide the configuration of the tty1 for the s2 port looks similar to the following: [top] [entry fields] tty tty1 tty type tty tty interface rs232 description asynchronous terminal status available location 00–00–s2–00 parent adapter sa1 port number [s2] enable login disable baud rate [...
Page 261
Systemguard remote operation configuration c-3 the modem parameters file name value should be set to the file name of your modem configuration file. The service line speed should be set to your modem and tty capabilities (9600 is recommended). • service flags: mpcfg –ds index name value 1 remote ser...
Page 262: Modem Configuration Files
C-4 operator guide modem configuration files if you want to attach a modem to the s2 port to allow automatic problem reporting from systemguard or dial-in access from a remote location, you have to provide a configuration file for the modem you are using. This file is also necessary to utilize the m...
Page 263
Systemguard remote operation configuration c-5 this is a sample /usr/share/modems/mir_modem file for console mirroring using an ibm 7851 modem. # tested at 9600bps. Icdelay 5 defaultto 10 calldelay 120 # at attention code q0 enable result codes to screen # &f1 set factory profile 1 q1 disable result...
Page 265: Appendix D: Supplies
Supplies d-1 appendix d: supplies this appendix contains a list of devices and supplies with the part numbers needed to order them. Description part number 1.0gb disk drive, 8 bit, (with carrier) 96g4067 1.1gb disk drive, 16 bit, (with carrier) 19h0182 2.0gb disk drive, 8 bit, (with carrier) 96g4360...
Page 266: Ordering Keys
D-2 operator guide ordering keys for protection against unauthorized key duplication, the key mode switch is equipped with a medeco high-security lock. Keys for this lock are a factory restricted series, and duplicate keys are not available through normal commercial channels. The metal code tag supp...
Page 267: Key Reorder Form
D-3 supplies key reorder form this form, when accompanied by the metal code tag supplied with the original keys, represents an authorized order for additional factory keys. Please indicate the quantity required and enclose a check or money order for the appropriate amount. Number of keys required___...
Page 268
D-4 operator guide.
Page 269
E-1 three-digit display numbers appendix e. Three-digit display numbers this appendix contains lists of the various numbers and characters that may display in the three-digit display. Determine the type of operation being performed, then use the list for that type operation. Power-on (pon) test indi...
Page 270
E-2 operator guide power-on self-test (post) indicators 20c l2 cache post error. (the display shows a solid 20c for 5 seconds.) 21c l2 cache is not detected. (the display shows a solid 21c for 2 seconds.) 22c attempting a normal mode ipl from fddi specified in nvram ipl device list. 23c attempting a...
Page 271
E-3 three-digit display numbers 230 attempting a normal mode ipl from adapter feature rom specified in ipl rom device list. 231 attempting a normal mode ipl from ethernet specified in ipl rom device list. 232 attempting a normal mode ipl from standard i/o planar attached devices specified in rom def...
Page 272
E-4 operator guide 259 attempting a service mode ipl from fddi specified by the operator. 260 information is being displayed on the display console. 261 no supported local system display adapter was found. 262 keyboard not detected as being connected to the system’s keyboard port. 263 attempting a n...
Page 273
E-5 three-digit display numbers 312 flash utility rom ram post memory configuration error or no memory found (irrecoverable). 313 flash utility rom ram post failure (irrecoverable). 314 flash utility rom power status register failed (irrecoverable). 315 flash utility rom detected a low voltage condi...
Page 274
E-6 operator guide 529 the configuration manager is unable to update odm data (irrecoverable error). 530 the program savebase returned an error. 531 the configuration manager is unable to access the pdat object class (irrecoverable error). 532 there is not enough memory to continue (malloc failure);...
Page 275
E-7 three-digit display numbers 597 ocs software being configured. 598 ocs hosts being configured during system reboot. 599 configuring fddi data link control. 600 starting network boot portion of /sbin/rc.Boot 602 configuring network parent devices. 603 /usr/lib/methods/defsys, /usr/lib/methods/cfg...
Page 276
E-8 operator guide 722 unknown disk being identified or configured. 723 unknown cdrom being identified or configured. 724 unknown tape drive being identified or configured. 725 unknown display device being identified or configured. 726 unknown input device being identified or configured. 727 unknown...
Page 277
E-9 three-digit display numbers 854 3270 host connection program/6000 connection being identified or configured. 855 4-port multiprotocol adapter being identified or configured. 857 fsla adapter being identified or configured. 858 5085/5086/5088 adapter being identified or configured. 859 fddi adapt...
Page 278
E-10 operator guide 925 three-button mouse being identified or configured. 926 tablet model 21 being identified or configured. 927 tablet model 22 being identified or configured. 928 standard speaker being identified or configured. 929 dials being identified or configured. 930 lighted program functi...
Page 279
E-11 three-digit display numbers diagnostic load progress indicators note: when a lowercase c is listed, it displays in the lower half of the seven-segment character position. C00 aix install/maintenance loaded successfully. C01 insert the first diagnostic diskette. C02 diskettes inserted out of seq...
Page 280: Debugger Progress Indicators
E-12 operator guide c99 diagnostics have completed. This code is only used when there is no console. Debugger progress indicators c20 the kernel debugger has started due to an unexpected system halt. Flashing 888 message descriptions a crash message (type 102) can occur at any time. See “reading the...
Page 281
External scsc address record f-1 appendix f. External scsi address record on the following sheet, record the unit in which the scsi controller is located, the adapter slot number, the device type, and the scsi address for each externally attached scsi device. T scsi i/o controller slot ____________ ...
Page 282
F-2 operator guide t scsi i/o controller slot ____________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ d...
Page 283
External scsc address record f-3 t scsi i/o controller slot ____________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address...
Page 284
F-4 operator guide t scsi i/o controller slot ____________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ device ____________ address ___________ d...
Page 285: Power States
System power states g-1 appendix g. System power states the state of the system is dependant on the condition of four variable conditions that effect how the system ipls or shutsdown. The four conditions are: • the position of the power-on button this button has two positions. It can be pressed in t...
Page 286
G-2 operator guide if the command sbb is entered on the bump console, and the system key is in the normal position, the system goes to the sbb_ecmd state. • if the power-on button is pressed and changes from the on position to the off position, the system sets the was_shutdown status to false. • if ...
Page 287
System power states g-3 • if the power_fault status is false, the system attempts to power on. If the system then detects a power fault, the power_fault status is set to true. The system displays an operator panel lcd error message, and the system goes to the main_standby status. If no power fault i...
Page 288
G-4 operator guide if the system power does not turn on, the power-on button may be in the off position. Go to the system unit and press the power-on button (only press the button once), if the system power still does not turn on there may be an earlier fault condition. Remove main power from the sy...
Page 289
Glossary x-1 glossary: special terms used in systemguard bp (back plane). A panel located in the system unit and used to interconnect boards and devices. Bist (built in self-test). Tests performed during the standby phase of the ipl process. The bist phase comes ahead of the post phase. Bump (bring-...
Page 290
Operator guide x-2 sib (system interface board). The sib is a system board which controls the power supply and the rs-485 interconnect bus. Simm (single in-line memory module). See memory module. Smp. Symmetric multiprocessor. Srn (service request number). Ssbus (subsystem bus). A special bus used t...
Page 291: Index
Index x-3 index numbers 3.5-inch diskette loading, 2-46 type, 2-44 3.5-inch diskette drive, using, 2-43 3-digit display configuration program indicators, e-5 debugger progress indicators, e-12 diagnostic load progress indicators, e-11 dump progress indicators, 5-12 flashing 888 message descriptions,...
Page 292
X-4 operator guide d debugger progress indicators, e-12 diagnostic package utility service aid, 6-5 diagnostic programs modes for running, 5-7 concurrent mode, 5-7 maintenance mode, 5-7 standalone mode, 5-8 operating considerations, 5-1 attached to a host system, 5-1 identifying a terminal, 5-1 runn...
Page 293
Index x-5 g generic microcode download service aid, 6-11 h hardware error report service aid, 6-12 hardware problem determination, considerations, 8-1 highly removable disks, 4-2 hot removability, 4-2 i indicators, configuration program, e-5 k key mode switch, 2-6 keys ordering, d-2 reorder form, d-...
Page 294
X-6 operator guide sbb_ecmd, g-2 sbb_gateway, g-1 sbb_menu, g-2 sbb_pcmd, g-2 wait_power_on, g-2 wait_rebuilding, g-3 power states, system, g-1 power-on from bump console, g-3 power-on using the power-on button, g-4 preventive maintenance, 8 mm tape drive, 2-20 printers, 2-13 problem determination p...
Page 295
Index x-7 diagnostics loading, 7-2 stopping, 7-3 running, 7-2 systemguard bump overview, 3-2 common tasks, 3-39 authorize the service console, 3-43 boot from network, 3-52 boot from scsi device, 3-49 disable processors, 3-55 enable processors, 3-55 enable surveillance, 3-46 reboot aix from remote se...
Page 296
X-8 operator guide general information, 2-24 tape drives, 2-14 tasks, 6-1 display hardware error log, 6-12 display or change bump configuration, 6-4 display or change electronic mode switch, 6-11 display or change multiprocessor configuration, 6-12 local area network analyzer, 6-12 process supplemen...
Page 297
Printed in the u.S.A. Sa23-2724-02 93h6489.