- DL manuals
- IBM
- Enclosure
- 7015-R30
- Installation And Service Manual
IBM 7015-R30 Installation And Service Manual
Summary of 7015-R30
Page 1
7015 models r30, r40, and r50 cpu enclosure installation and service guide.
Page 2: Third Edition (April 1997)
I third edition (april 1997) this edition notice applies to the 7015 model r30, r40, and r50 cpu enclosure installation and service guide. The following paragraph does not apply to the united kingdom or any country where such provisions are inconsistent with local law: this publication is printed “a...
Page 3: Table of Contents
Preface iii table of contents communications statements vii . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Safety notices xi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . About this book xi...
Page 4
Iv service guide maintenance menu 2-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Display configuration 2-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Display bump error log 2-25 . ...
Page 5
Preface v adapter cable 4-73 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Adapter 4-75 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . I/o module...
Page 6
Vi service guide appendix d. Off line diagnostic error codes d-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Error logging d-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Appendix e. System power states e-1 . . ...
Page 7: Communications Statements
Preface vii communications statements the following statement applies to this product. The statement for other products intended for use with this product appears in their accompanying manuals. Federal communications commission (fcc) statement note: this equipment has been tested and found to comply...
Page 8
Viii service guide for class a equipment were derived for commercial and industrial environments to provide reasonable protection against interference with licensed communication equipment. Attention: this is a class a product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in w...
Page 9
Preface ix radio protection for germany dieses gerät ist berechtigt in Übereinstimmung mit dem deutschen emvg vom 9.Nov.92 das eg-konformitätszeichen zu führen. Der aussteller der konformitätserklärung ist die ibm germany. Dieses gerät erfüllt die bedingungen der en 55022 klasse a. Für diese klasse ...
Page 10
X service guide.
Page 11: Safety Notices
Preface xi safety notices note: for a translation of danger and caution notices, see the system unit safety information manual, form number sa23-2652. Definitions of safety notices a danger notice indicates the presence of a hazard that has the potential of causing death or serious personal injury. ...
Page 12
Xii service guide laser safety information the optical drive in this system unit is a laser product. The optical drive has a label that identifies its classification. The label, located on the drive, is shown below. Class 1 laser product laser klasse 1 luokan 1 laserlaite appareil a laser de classe ...
Page 13: About This Book
Preface xiii about this book this book provides maintenance information that is specific to the 7015 models r30, r40, and r50 cpu enclosures. It also contains maintenance analysis procedures (maps) that are not common to other systems. Maps that are common to all systems are contained in the diagnos...
Page 14
Xiv service guide.
Page 15: Description
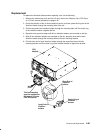
Reference information 1-1 chapter 1. Reference information this chapter contains information about part locations; connector locations; slot locations on the system planar, i/o planars; data and power flow; and cpu enclosure specifications. Description 7015 cpu enclosures equipped with a typical con...
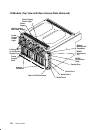
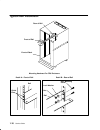
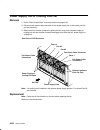
Page 16: Cpu Enclosure Locations
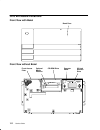
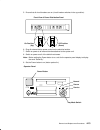
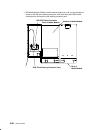
1-2 service guide cpu enclosure locations front view with bezel bezel door front view without bezel cd-rom drive optional media position operator panel 3.5-inch diskette drive front access plate.
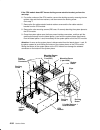
Page 17
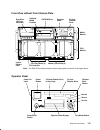
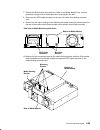
Reference information 1-3 front view without front access plate memory card slots (4) cpu card slots (4) i/o card slot cd-rom drive operator panel 3.5-inch diskette drive disk drive (r50 can have two) lateral planar 1 card optional media position cpu module media module note: the r50 cpu enclosure f...
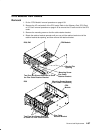
Page 18
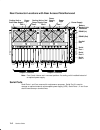
1-4 service guide rear connector locations with rear access plate removed power supply cooling unit or 2nd power supply fans power supply fans parallel port serial port 1 serial port 2 adapter locations adapter locations serial port 3 rs485 (out) battery backup unit connector rs485 (in) 0/1 1/1 0/2 ...
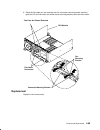
Page 19
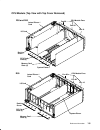
Reference information 1-5 cpu module (top view with top cover removed) cpu module fans memory card slots (4) cpu card slots (4) i/o card lateral planar 1 card system planar docking screw r30 and r40 fan 10 fan 08 fan 09 memory card slots (4) cpu card slots (4) i/o card lateral planar 1 card system p...
Page 20
1-6 service guide i/o module (top view with rear access plate removed) power supply fans adapter locations parallel port serial port 1 serial port 2 serial port 3 rear of cpu enclosure power supply rs485 connectors (out) battery backup unit connector power supply power light power supply power light...
Page 21
Reference information 1-7 media module disk drive operator panel cd-rom drive optional media position 3.5-inch diskette drive media module fans (3) fan 6 fan 5 fan 7 optional disk drive (r50) note: the model r50 cpu enclosure has a bay for an optional disk drive located above the standard disk drive...
Page 22
1-8 service guide system planar connector locations (top view) memory card slots cpu card slots i/o card slot lateral planar 1 interface connectors s r q p d c b a r30 and r40 memory card slots cpu card slots i/o card slot lateral planar 1 interface connectors s r q p d c b a r50
Page 23
Reference information 1-9 memory cards there are four types of memory card available for use with the r30, r40 or r50 systems. They are the mrx card, the rlx card, the nfx card, and the sf5 card. The base mrx memory card looks like the following figure. Base mrx memory card 1 . . . 4 bank 0 bank 0 b...
Page 24
1-10 service guide the next three types of memory cards are shown below. A two bank (8 slots) rlx card, a four bank (16 slots) nfx card, and a four bank (16 slots) sf5 card. Each bank can house four memory module kits composed of four memory memory modules each, which comply with the jedec standard ...
Page 25
Reference information 1-11 according to both the size and the number of memory module kits installed on the rlx, nfx, or sf5 cards, these can be divided into the following models: • nf64 board, based on 4m bit technology, which gives 64mb memory. It houses two mm32 memory module kits. • nf128 board,...
Page 26
1-12 service guide 7015 model r00 rack with power distribution bus (pdb) power distribution bus power distribution bus outlet power cords power supply power cords outlets (6) rear of cpu enclosure.
Page 27: Data Flow
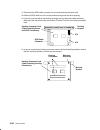
Reference information 1-13 data flow cpu card 60x l2 tag l2 cac address bus data bus smc dcb memory bus bump standard io system io mca bus mca bus memory cards and dimms system planar i/o card cpu array memory array secondary controller jtag bus cop bus ssga i2c bus eprom ram s2 service console s3 s...
Page 28
1-14 service guide 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 mca cards secondary micro channel planar xvr misc 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 mca cards primary micro channel planar xvr misc.
Page 29: Power Flow
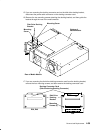
Reference information 1-15 power flow remote consoles access local consoles access operator panel tod eeprom standby voltages +5 +12 –12 power power distribution power voltages +5 +3,3/3,6 –12 +12 cd-rom drive disk drive 3,5 inch cpu card system interface optional media i/o module diskette drive pow...
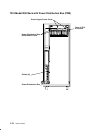
Page 30: Typical Rail Installation
1-16 service guide typical rail installation mounting hardware for cpu enclosure detail a – front of rail detail b – rear of rail a b front of rail rear of rail front of rack rail rail nut rail mounting screw guide pins lock washer.
Page 31: Specifications
Reference information 1-17 specifications dimensions height: 266.7 mm (10.5 inches) depth: 1041 mm (41 inches) width: 445 mm (17.5 inches) ac frequency 50 to 60 hz heat output 718 w (2450 btu per hour) typical operating environment class c: 10 ° to 40 ° c (50 ° to 104 ° f) wet bulb temperature: 27 °...
Page 32: External Ac Power Cables
1-18 service guide external ac power cables to avoid electrical shock, the manufacturer provides a power cable with a grounded attachment plug. Use only properly grounded outlets. Power cables used in the united states and canada are listed by underwriter’s laboratories (ul) and certified by the can...
Page 33: Service Inspection Guide
Reference information 1-19 service inspection guide perform a service inspection on the system when: • the system is inspected for a maintenance agreement. • service is requested and service was not recently performed. • an alterations-and-attachments review is performed. • changes are made to the e...
Page 34
1-20 service guide.
Page 35: Chapter 2 Using Systemguard
Using systemguard 2-1 chapter 2 using systemguard this chapter introduces the systemguard service processor which is included in all symmetric multiprocessor models. Introduction smp servers include a service processor, called systemguard, as a standard feature. Systemguard continually monitors the ...
Page 36: Systemguard Power
2-2 service guide systemguard power systemguard has its own dc power boundary. This means that even if the system power is off (power button of the system in the off position), systemguard is still powered on, as long as the cpu enclosure still has power. This allows control of the system even thoug...
Page 37: The Operator Panel
Using systemguard 2-3 the operator panel the operator panel is the first level of user interface to systemguard. The operator panel has the following features: power button it should generally stay pushed in all the time if you want to be able to power on or off the system remotely. Reset button it ...
Page 38: Systemguard Consoles
2-4 service guide systemguard consoles systemguard works with two types of consoles: • the bump console, which is an ascii terminal attached to the s1 serial port. This console provides the normal input to the bump. It can be local or remote. The line speed for the bump console must be set to 9600 b...
Page 39
Using systemguard 2-5 init phase init phase is entered when the power button on the operator panel is pressed on or when the power command is entered on the bump console or service console. If the system key is in normal mode, the bump runs the built-in or resident power-on (pon)-tests on the cpu mo...
Page 40
2-6 service guide phase change (stand-by to init) the phase change from stand-by to init is called crossing the power boundary. This is achieved by pushing the power button on the operator panel or by typing the keyword power at the stand-by prompt (>). Note that if you type power while the power bu...
Page 41
Using systemguard 2-7 power-on (pon) tests pon tests are run by systemguard whenever the system power comes on. There are two types of tests: • a comprehensive set of tests are performed on the processors, cache, memory and related hardware when the fast-ipl flag is disabled. • a minimum core set of...
Page 42
2-8 service guide • enabling at least one processor from the stand-by menu there are other resident pon tests to check other system resources. These tests are a subset of the systemguard maintenance offline tests, and reside within the flash eeprom. These tests are divided into the following groups:...
Page 43
Using systemguard 2-9 phase change (init to maint) the maintenance phase is entered from the init phase if the system key is in service mode. If the bump console present flag is set, the maintenance menu is displayed on the bump console, and the system waits for an operator action. The maintenance m...
Page 44
2-10 service guide working with systemguard systemguard parameters and flags may be changed from different locations. They can be changed from the systemguard stand-by menu, the systemguard maintenance menu, the diagnostics interface, and also from aix. When the key signal is received, systemguard c...
Page 45
Using systemguard 2-11 when the system is in stand-by mode and the system key (physical or electronic key) is in service mode, the stand-by menu can be accessed and systemguard executed. If you turn the system unit power on from stand-by mode with the system key in the normal position, the system bo...
Page 46
2-12 service guide stand-by menu the stand-by menu can only be entered when the system is in stand-by mode (the word stand-by must be displayed on the lcd display). Perform the following steps to bring up the stand-by menu. 1. With stand-by displayed on the lcd display press the enter key on the bum...
Page 47
Using systemguard 2-13 how to display the system configuration the system configuration can be displayed through the stand-by menu or through the maintenance menu. Displaying configuration through the stand-by menu this option displays the system configuration table. This configuration can be viewed...
Page 48
2-14 service guide display configuration sib14 ps04 sib24 sib15 ps05 sib25 sib16 ps06 sib26 fc8e000000000000 sib17 ps07 sib27 mp d78605 19h0464 mpe d78605 mca 01 c fc8e000000000000 mcae 01 c e1ff000000000000 mca 02 c f48e000000000000 mcae 02 c 708f000000000000 mca 03 c fc8e000000000000 mcae 03 c ec8...
Page 49
Using systemguard 2-15 • cpux ec+s: the agent status information of the cpu cards and the vpd information is given. • mcx ec+s: this field gives the memory card vpd values. • mcax loc. Code+status: this parameter contains the location code and the status information of the micro channel adapters (mc...
Page 50
2-16 service guide and parameters (set during manufacturing), see the table in “default parameter values” on page b-1 of the service guide for your system. The following flags can be managed: • remote authorization: only the local operator can enable this flag to enable remote maintenance to be perf...
Page 51
Using systemguard 2-17 set configuration this menu option enables you to configure or unconfigure units and devices. 1. Enter 3 in the main menu to select this option. 2. You should then see a first-level screen similar to the following. It displays the units and devices that can be configured, alon...
Page 52
2-18 service guide ssbus maintenance this option is used to investigate and check devices on the ssbus and is meant only for trained service personnel. Use this option to investigate and check devices on the ssbus. 1. Enter 4 in the main menu to select this option. Systemguard displays the following...
Page 53
Using systemguard 2-19 i 2 c maintenance use this option to do maintenance operations on the i 2 c buses of a selected unit, in order to investigate and check the connected devices. When exiting this menu, the previous status of the op and sib microcontrollers are restored (except for voltage margin...
Page 54
2-20 service guide set voltage margins note: this option can be only used for error analysis or factory test and must be used only by trained service personnel. Restore nominal voltage values before restarting other operations. Any data written on the disk in marginal mode must be removed before res...
Page 55
Using systemguard 2-21 maintenance menu the maintenance menu also enables you to display the configuration of the system in a non-cryptic, easily understandable way, to perform various tests, to continue ipl either from network, a specific scsi device or from the boot list, and to set flags concerni...
Page 56
2-22 service guide display configuration use this option to view the system hardware configuration. This option provides different screens with the following levels of information: • system-level information • unit-level information • device-level information. Enter 0 in the maintenance menu to sele...
Page 57
Using systemguard 2-23 • voltage margins for cpus, asics, and other components. • device status information. • options to select various types of devices. Display configuration – main unit margins value: +5 volt –> normal cpu (3.65 volt) –> normal asic (3.6 volt) –> normal scsi devices: present –> #...
Page 58
2-24 service guide 1. To see device-level information, enter the corresponding command number for the device. The device-level screen is displayed. 2. Enter x to return to the system-level configuration display screen. Display configuration – device level this screen is shown when you select one of ...
Page 59
Using systemguard 2-25 display bump error log use this option to view the bump firmware error log. 1. Enter 1 in the maintenance menu to select this option. The contents of the logging buffer are displayed as shown in the following screen: display bump error log event # 1: 40140100000000000000000000...
Page 60
2-26 service guide system boot this command enables you to begin boot activity. Enter 6 in the main menu to select this option. The following screen is displayed: system boot 0> boot from list 1> boot from network 2> boot from scsi device select [x:exit]: the menu enables you to boot in three differ...
Page 62
2-28 service guide off-line tests attention: these menus are only to be used when directed by service support personnel. Some of the tests described require test equipment or resources not available on your system. This option under the maintenance menu enables you to run the off-line tests in a con...
Page 63
Using systemguard 2-29 0 displays the build test menu, which enables you to specify the test list (see “build test list” below). 1 displays and enables modification of the tests in the build list (see page 2-31). 2 deletes the tests in the build list, after operator confirmation. Attempting to delet...
Page 64
2-30 service guide 3. Once you have selected the test groups, you can specify individual tests within a group. For example, the following screen enables you to specify individual bump quick io tests: build test list group 01 bump quick io test description test description 01 debug line 02 s1 asl (bu...
Page 65
Using systemguard 2-31 modify/display test list once the test list is built, you can use this option to view or modify it. Each test is identified by a number xxyy, where xx is the group number and yy is the test number. 1. Enter 2 in the off-line tests menu to view or modify the test list. The foll...
Page 66
2-32 service guide execute test list this command enables you to run the test list once it is built (and possibly modified). All the tests in the test list are run one at a time with the selected execution options. • enter 3 in the off-line tests main menu to run the selected tests. The following sc...
Page 67
Using systemguard 2-33 power-on command parameters during the standby idle phase, the system power can be turned on (and the ipl started) by entering a bump console power-on string through line s1 or a service console power-on string through line s2 (see “working with systemguard” on page 2-10 for a...
Page 68
2-34 service guide set configuration this command is used to configure electronic boards like i/o cards or micro channel adapter (mca) devices. 1. Enter 2 in the set parameters menu to display the set configuration menu as shown below: set configuration 0> cpu card 1> memory card 2> basic mca adapte...
Page 69
Using systemguard 2-35 1. Enter 3 in the set parameters menu to display the phone numbers menu shown here: phone numbers 0> service center dial–out (1) –> 1> service center dial–out (2) –> 2> customer hub dial–out (1) –> 3> customer hub dial–out (2) –> 4> system dial–in –> 5> system operator voice –...
Page 70
2-36 service guide • enter 4 in the set parameters menu to display the miscellaneous parameters menu. The value set for all the flags, except fast ipl, is permanent until a new change is made. Miscellaneous parameters 0> bump console –> present 1> autoservice ipl –> disabled 2> dial_out authorizatio...
Page 71
Using systemguard 2-37 2. The new flag status (opposite of the previous state) is displayed. Boot multiuser aix in service flag enables multiuser aix boots to proceed even if the mode switch is in the service position (when booting by selecting option 6 in the maintenance menu). When the flag is ena...
Page 72
2-38 service guide set national language use this option in the main menu to set the national language used for “systemguard”. Once selected, the effect is immediate and all the console messages are presented in the selected language. 1. Enter 9 in the maintenance menu to select this option. The fol...
Page 73
Using systemguard 2-39 some common systemguard tasks the following tasks are done through the stand-by and maintenance menus that are part of systemguard. Note that these tasks can also be carried out from aix diagnostics. How to set the electronic key the key can be set electronically, making it ea...
Page 74
2-40 service guide display configuration machine type/model: 7013j30 45067 firmware release: standby –> 1600 backup eprom –> 0701 flash eprom –> 0704 service contract: last update (yymmdd) –> 950707 validity –> unlimited contract remote service support –> valid quick on call service –> not valid aut...
Page 75
Using systemguard 2-41 setting fast ipl through the maintenance menu 1. Enter the maintenance menu. 2. Enter 8 to select the set parameters menu. 3. Enter 4 from the set parameters menu to select the miscellaneous parameters menu. 4. Option 3 in this menu should show the current status of the fast i...
Page 76
2-42 service guide how to set the service line speed by default, the service line speed is 1200 baud or 2400 baud depending on the level of systemguard. This speed can be changed through the systemguard maintenance menu. In order to use the service console properly, the terminal connected to the s2 ...
Page 77
Using systemguard 2-43 setting line speed through aix 1. With aix up and running, log in as user root. 2. Type the following command to view current settings: mpcfg –dm the following is the output of the command: index name value 1 modem parameters file name 2 service line speed 3 protocol inter dat...
Page 78
2-44 service guide how to set up console mirroring console mirroring concepts console mirroring is a way to provide the customer a view of what the person working remotely from the service console is doing on the system. When mirroring is active, the service console and the bump console are logicall...
Page 79
Using systemguard 2-45 setting up console mirroring in order to setup console mirroring, you need first to authorize the service console, and set up the right line speed. Refer to previous chapters on how to set up the service line speed and how to authorize the service console. Then do the followin...
Page 80
2-46 service guide how to enable surveillance surveillance is implemented by the survd daemon. This daemon, when started, establishes a heartbeat between aix and systemguard. In case of an aix hang, systemguard detects it and reboots the system. To implement the surveillance, do the following: 1. En...
Page 81
Using systemguard 2-47 modem configuration the modem on line s2 must be configured using an ascii modem configuration file which describes various parameters using a specific syntax. Aix uses this file directly. Systemguard uses the same information (in condensed form) stored in non-volatile memory ...
Page 82
2-48 service guide how to reboot aix from the remote service console it is possible for the remote personnel connected via the service console to reboot aix from the remote site. Prerequisites the following procedure must be carried out from the bump console in order to allow aix to boot remotely fr...
Page 83
Using systemguard 2-49 rebooting to single-user and then to multi-user this allows the remote support personnel connected to the system via a modem to the s2 port to shut down and reboot the system in diagnostics mode for hardware diagnostics purposes. After running diagnostics, the remote personnel...
Page 84
2-50 service guide 3. From this menu, enter 4 . To select the miscellaneous parameters menu, which is similar to the following: miscellaneous parameters 0> bump console –> present 1> autoservice ipl –> disabled 2> dial_out authorization –> disabled 3> fast ipl –> enabled 4> set mode to normal when b...
Page 85
Using systemguard 2-51 10.At this point, a boot from scsi device screen appears. This displays the present device location code. If it is not the device you want to boot from, go through each option and change it to the desired bus, slot, scsi id, and lun id. Option 4 allows you to change all these ...
Page 86
2-52 service guide how to boot from the network the system can be booted from the network through the maintenance menu. Network boot allows a system to be reinstalled via the network and also allows various maintenance tasks to be carried out on the local machine. Use the following procedure to boot...
Page 87
Using systemguard 2-53 5. The select boot (startup) device menu appears, which is similar to the following: select boot (startup) device select the device to boot (startup) this machine. Warning: if you are using token–ring, selection of an incorrect data rate can result in total disruption of the t...
Page 88
2-54 service guide 7. Enter the appropriate ip addresses, and enter 99 to return to the main menu. A screen similar to the following appears: main menu 1. Select boot (startup) device 2. Select language for these menus 3. Send test transmission (ping) 4. Exit main menu and start system (boot) type t...
Page 89
Using systemguard 2-55 how to disable and enable processors in the smp servers, it is possible to disable/enable processors. A suspected faulty processor can be disabled so that the system can run without it. The processors can be disabled/enabled through the stand-by menu, maintenance menu, diagnos...
Page 91
Using systemguard 2-57 5. The cpu card screen appears and looks similar to the following: cpu card – (cpu1) present conditions: pr #0 –> valid & enabled pr #1 –> valid & enabled commands: 0> enable 1> disable 2> temporary disable select [x:exit]: 6. From this screen, you can disable or enable a part...
Page 92
2-58 service guide customizing systemguard for your needs systemguard is controlled by several flags. The flags consist of contract flags, operational flags, remote maintenance flags, and test flags. Remote service flag this flag is disabled at the factory and must be enabled for remote service oper...
Page 93
Using systemguard 2-59 phone numbers if remote maintenance is used, systemguard requires several phone numbers to be entered. Additional information is provided in “phone numbers” on page 2-34. Service line speed parameters if remote maintenance is used, systemguard requires that the line speed be c...
Page 94
2-60 service guide reloading the flash eeprom follow this procedure to load a new version of systemguard into the flash eeprom. Only system administrators should perform this procedure. Prerequisites to install a new version of the eeprom firmware, you need either a firmware diskette containing a bi...
Page 95
3-1520-1 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) chapter 3. Maintenance analysis procedures (maps) map 1520: 7015 cpu enclosure – power map note: this is not a start of call map. Use this power map only if you have been directed here from a map step in the diagnostic information for micro channel bus...
Page 96: Step 1
3-1520-2 service guide power supply status if the system detects a power supply failure in the cpu enclosure, it turns the power off and displays service-request number (srn) 409-axy or 409-bxy , where xy is the hexadecimal value of the power status register and gives some information about the powe...
Page 97: Step 3
3-1520-3 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) step 3 (from step 2) is the operator panel display illuminated? No go to step 4. Yes go to step 7. Step 4 (from step 3) check the led on the system interface board. If the led is on, it means that the power supply unit is supplying the stand-by voltage...
Page 98: Step 6
3-1520-4 service guide step 6 (from step 5) note: either the power supply or the power distribution cable cluster is defective. 1. Unplug both power supply power cords from both pdb outlet power cords. 2. Replace the power supply. Refer to the “power supply or cooling unit” removal procedure on page...
Page 99: Step 8
3-1520-5 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) step 8 (from step 2) note: stand-by should appear on the operator panel display. Is stand-by displayed on the operator panel display? No if an srn is displayed, go to “map 0210: general problem resolution” in the diagnostic information for micro channe...
Page 100: Step 9
3-1520-6 service guide step 9 (from step 8) 1. Set the power switch on the cpu enclosure to on, with the key mode switch set to service. 2. Find your symptom in the following table; then follow the instructions given in the action column. Symptom action the power light does not come on or comes on a...
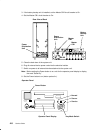
Page 101: Step 10
3-1520-7 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) step 10 (from step 1 and 9) the xy value in srn 409-axy or 409-bxy is the hex value for the power status register byte. Line 2 of the operator panel display identifies the unit that contains the error. The bits in the power status register are defined ...
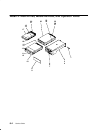
Page 102: Step 11
3-1520-8 service guide step 11 (from step 10) an over temperature problem can be caused by an environmental problem (see specifications in chapter 1) or blocked air ducts. Check each of these items. Did you find the problem? No go to step 12. Yes repair the problem. Go to “map 0410: repair checkout”...
Page 103
3-1540-1 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) map 1540: 7015 cpu enclosure – minimum configuration note: this is not a start of call map. You should use this map only if you have been directed here from a map step in the diagnostic information for micro channel bus systems. Purpose of this map thi...
Page 104: Step 1
3-1540-2 service guide step 1 (from step 3, 6, 7, 9, 10, 17) 1. Ensure that the diagnostics and the operating system are shut down. 2. Turn the key mode switch to the service position. 3. Sometimes an srn or error code will be logged in the bump error log. Before proceeding, check the bump error log...
Page 105
3-1540-3 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) note: before verifying any condition indicated in the following steps of this map (for example, a certain code displayed on the operator panel display), be sure that the system activity has stopped on that condition (same condition for more than 3 minu...
Page 106: Step 2
3-1540-4 service guide step 2 (from step 1) 1. Set the power button on the cpu enclosure to off. 2. Unplug both pdb outlet power cords from both power supply power cords. 3. Record the slot numbers of the adapters. Label and record the location of any cables attached to the adapters. Remove all the ...
Page 107: Step 3
3-1540-5 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) step 3 (from step 2) one of the frus remaining in the cpu enclosure is defective. To test each fru, exchange the frus that have not already been exchanged in the following order: 1. I/o card (ioc) 2. Cpu card (cpu) 3. Memory card (mc) 4. System planar ...
Page 108: Step 4
3-1540-6 service guide step 4 (from step 2) no failure was detected with this configuration. 1. Set the power button on the cpu enclosure to off. 2. Unplug both pdb outlet power cords from both power supply power cords. 3. Starting with the cpu cards, install one additional cpu card (cpu) or memory ...
Page 109: Step 5
3-1540-7 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) step 5 (from step 4) the failure may be caused by the last cpu card (cpu) or memory card (mc) installed. To isolate the failing card, do the following: 1. Set the power button on the cpu enclosure to off. 2. Unplug both pdb outlet power cords from both...
Page 110: Step 6
3-1540-8 service guide step 6 (from step 5) one of the frus remaining in the cpu enclosure is defective. To test each fru, exchange the frus in the following order: • system planar (sp) • i/o card (ioc) • cpu cards (cpu) • memory cards (mc) • i/o planars • cpu module flex cables • i/o module flex ca...
Page 111: Step 7
3-1540-9 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) step 7 (from steps 1, 2, and 4) 1. Set the power button on the cpu enclosure to off. 2. Unplug both pdb outlet power cords from both power supply power cords. 3. Record the slot numbers of the adapters. Label and record the location of any cables attac...
Page 112: Step 8
3-1540-10 service guide step 8 (from steps 7 and 17) the system is working correctly with this configuration. One of the adapters or devices that you removed is probably defective. 1. Set the power button on the cpu enclosure to off. 2. Unplug both pdb outlet power cords from both power supply power...
Page 113: Step 9
3-1540-11 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) step 9 (from step 8) 1. Set the power button on the cpu enclosure to off. 2. Unplug both pdb outlet power cords from both power supply power cords. 3. Starting with the last installed adapter, disconnect one attached device and cable . 4. Insert the d...
Page 114: Step 10
3-1540-12 service guide step 10 (from step 1) 1. Set the power button on the cpu enclosure to off. 2. Unplug both pdb outlet power cords from both power supply power cords. 3. Record the slot numbers of the adapters. Label and record the location of any cables attached to the adapters. Remove all th...
Page 115: Step 11
3-1540-13 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) step 11 (from step 10) 1. Follow the instructions on the display to select your console. 2. When the diagnostics operating instructions display, press the enter key. 3. If the terminal type has not been defined or you are ipling from cd-rom, you must ...
Page 116: Step 13
3-1540-14 service guide step 13 (from steps 19, 20, 21, 22) 1. Set the power button on the cpu enclosure to off. 2. Unplug both pdb outlet power cords from both power supply power cords. 3. Record the location of all the internal scsi devices attached to the scsi bus you are attempting to ipl from. ...
Page 117: Step 14
3-1540-15 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) step 14 (from step 13) this problem can be caused by: – the cd-rom pulling the bus down or opening the positive temperature coefficient (ptc) on the scsi adapter – a defective scsi adapter – a defective terminator – a defective sib – a defective cable...
Page 118: Step 16
3-1540-16 service guide step 16 (from steps 14 and 15) in the following order, exchange the frus that have not been exchanged: 1. Scsi adapter 2. Cd-rom drive (if still in the system). 3. System interface board (sib) 4. Scsi cable test each fru by trying to load diagnostics from cd-rom if installed ...
Page 119: Step 17
3-1540-17 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) step 17 (from step 16) 1. Set the power button on the cpu enclosure to off. 2. Unplug both pdb outlet power cords from both power supply power cords. 3. Record the slot numbers of the adapters. Label and record the location of any cables attached to t...
Page 120: Step 18
3-1540-18 service guide step 18 (from step 13) the system is working correctly with this configuration. One of the devices that you removed is probably defective. 1. Set the power button on the cpu enclosure to off. 2. Unplug both pdb outlet power cords from both power supply power cords. 3. Install...
Page 121: Step 19
3-1540-19 maintenance analysis procedures (maps) step 19 (from step 1) this problem can be caused by: – a scsi device pulling the bus down or opening the ptc on the scsi adapter. – a defective scsi adapter – a defective terminator – a defective system interface board (sib) – a defective cable the mo...
Page 122: Step 20
3-1540-20 service guide step 20 (from step 1) a message should be displayed with the flashing 269. Find the message in the table and do the listed action. Message displayed perform the listed action(s) 269 - no bootable go to step 21. 269 - no device go to step 13. 269 - no dev type go to step 22. S...
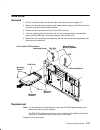
Page 123
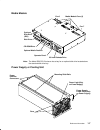
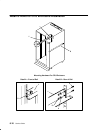
Removal and replacement procedures 4-1 chapter 4. Removal and replacement procedures this chapter contains information about removing and replacing various field replaceable units (frus) and parts. The following illustration shows the three types of power distribution systems available in the model ...
Page 124
4-2 service guide power-off procedure with a power distribution bus attention: use the appropriate shutdown command before you stop the system unit; failure to do so may result in the loss of data. See your operating system documentation for information about the shutdown command. 1. Set the key mod...
Page 125
Removal and replacement procedures 4-3 note: for a translation of this notice, see the system unit safety information manual. Danger an electrical outlet that is not correctly wired could place hazardous voltage on metal parts of the system or the devices that attach to the system. It is the respons...
Page 126
4-4 service guide power-on procedure with a power distribution bus 1. Set the key mode switch to the service position. Note: for a translation of this notice, see the system unit safety information manual. Danger an electrical outlet that is not correctly wired could place hazardous voltage on metal...
Page 127
Removal and replacement procedures 4-5 power-off procedure with a power distribution unit attention: use the appropriate shutdown command before you stop the system unit; failure to do so may result in the loss of data. See your operating system documentation for information about the shutdown comma...
Page 128
4-6 service guide note: for a translation of this notice, see the system unit safety information manual. Danger an electrical outlet that is not correctly wired could place hazardous voltage on metal parts of the system or the devices that attach to the system. It is the responsibility of the custom...
Page 129
Removal and replacement procedures 4-7 power-on procedure with a power distribution unit 1. Set the key mode switch to the service position. Key mode switch normal secure service operator panel note: for a translation of this notice, see the system unit safety information manual. Danger an electrica...
Page 130
4-8 service guide 3. If the battery backup unit is installed, set the master cb2 circuit breaker to on. 4. Set the master cb1 circuit breaker to on. Battery backup unit power distribution unit master cb2 master cb1 power distribution unit rear view of rack 5. Close the back door of the system unit. ...
Page 131
Removal and replacement procedures 4-9 power-off procedure with a power distribution panel note: notify the customer that you are going to switch off power to the attached 7015 cpu-media enclosure and to all of the disk drive drawers in the rack. Notify the customer that other attached systems might...
Page 132
4-10 service guide note: for a translation of this notice, see the system unit safety information manual. Danger an electrical outlet that is not correctly wired could place hazardous voltage on metal parts of the system or the devices that attach to the system. It is the responsibility of the custo...
Page 133
Removal and replacement procedures 4-11 power-on procedure with power distribution panel 1. Set the key mode switch to the service position. Key mode switch normal secure service operator panel power button.
Page 134
4-12 service guide note: for a translation of this notice, see the system unit safety information manual. Danger an electrical outlet that is not correctly wired could place hazardous voltage on metal parts of the system or the devices that attach to the system. It is the responsibility of the custo...
Page 135
Removal and replacement procedures 4-13 5. Ensure that all circuit breakers are on (circuit breaker switches in the up position). On position (up) off position (down) front view of power distribution panel 6. Plug all external device power cords into the electrical outlets. 7. Switch on power to all...
Page 136
4-14 service guide handling static-sensitive devices attention: adapters, boards, diskette drives, and disk drives can be damaged by electrostatic discharge. These devices are wrapped in antistatic bags to prevent this damage. Refer to the illustration. Take the following precautions: • do not remov...
Page 137
Removal and replacement 4-15 front bezel and front access plate removal note: for a translation of this notice, see the system unit safety information manual, order number sa23-2652. Caution: this drawer is fixed and should not be moved for servicing. Attempting to move the drawer partially or compl...
Page 138
4-16 service guide 3. To remove the front access plate, remove the seven retainer screws from the front of the cpu enclosure, and then remove the front access plate. Front access plate retainer screws retainer screws replacement note: ensure that the grounding strips located around the edges of the ...
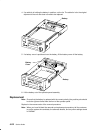
Page 139: Disk Drive
Removal and replacement 4-17 disk drive removal 1. Do the “front bezel and front access plate” removal procedure on page 4-15. 2. Remove the mounting screw attaching the media retainer bracket to the cpu enclosure, and then remove the media retainer bracket. 3. Pull the disk drive toward you and out...
Page 140
4-18 service guide cd-rom drive or optional media device removal note: observe the following safety notice before removing the cd-rom drive. For a translation of this notice, see the system unit safety information manual. Caution: a class 3 laser is contained in the device. Do not attempt to operate...
Page 141
Removal and replacement 4-19 5. If you are replacing only the cd-rom drive or the optional media device and not the mounting bracket, disconnect the power and data connectors. 6. Remove the four mounting screws attaching the cd-rom or optional media device to the mounting bracket, and then remove th...
Page 142: Operator Panel
4-20 service guide operator panel removal 1. Depending on the power distribution in your rack, do one of the following: • “power-off procedure with a power distribution bus” on page 4-2 • “power-off procedure with a power distribution unit” on page 4-5 • “power-off procedure with a power distributio...
Page 143: Lithium Battery
Removal and replacement procedures 4-21 lithium battery removal caution: a lithium battery can cause fire, explosion, or a severe burn. Do not recharge, disassemble, heat above 100 ° c (212 ° f), solder directly to the cell, incinerate, or expose cell contents to water. Keep away from children. Repl...
Page 144
Service guide 4-22 4. If a cable tie is holding the battery in position, cut the tie. The cable tie is for the original shipment of the unit and does not need to be replaced. Battery 5. If a battery cover is positioned over the battery, lift the battery cover off the battery. Battery battery cover 6...
Page 145: 3.5-Inch Diskette Drive
Removal and replacement procedures 4-23 3.5-inch diskette drive removal 1. The 3.5-inch diskette drive is part of the operator panel subassembly. It is accessible from the upper side of the operator panel, after having removed it from the base unit. Remove the operator panel from the base unit, as d...
Page 146
Service guide 4-24 4. Disconnect the 3.5-inch diskette drive connector. 5. For later models, remove the two mounting screws attaching the diskette drive to the operator panel assembly, then remove the diskette drive from the operator panel assembly. 6. From the bottom of the diskette drive, remove t...
Page 147: Operator Panel Bezel
Removal and replacement procedures 4-25 operator panel bezel removal 1. Do the steps detailed in the removal procedure in “operator panel” on page 4-20. The operator panel bezel is then accessible from the upper side of the operator panel. 2. Remove the two mounting screws and clamps attaching the t...
Page 148
Service guide 4-26 4. Disconnect the two power connectors and the data connector. 5. For later models, remove the two mounting screws attaching the bezel to the operator panel assembly at the top corners of the operator panel assembly, and then remove the bezel. Bezel mounting screw bezel mounting s...
Page 149: Media Module
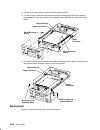
Removal and replacement 4-27 media module removal 1. Do the “front bezel and front access plate” removal procedure on page 4-15. 2. Disconnect the following cables: • operator panel cable (push connector tabs away from the center of the connector) • media power cable. 3. Disconnect the scsi cable: •...
Page 150
4-28 service guide • r50 media module: slide the media module toward you until you can access the bottom of the disk drive docking connector card, then remove the scsi cable connector from the bottom of the docking connector card. Bottom of media module rear of media module r50 scsi cable connector ...
Page 151
Removal and replacement 4-29 4. Slide the media module toward you until you can place your hand under it, and then slide the media module out of the cpu enclosure. Media module front view of cpu enclosure 5. Place the media module on a stable surface. Replacement replace in the reverse order..
Page 152: Media Module Fans
4-30 service guide media module fans removal 1. Do the “media module” removal procedure on page 4-27. 2. Disconnect the fan power cable for the fan you are removing. 3. Remove all four vibration isolators by pulling the fan either downward or away from the media module until the vibration isolators ...
Page 153
Removal and replacement 4-31 replacement to replace the vibration isolators when replacing a fan, do the following: 1. Check the direction of the air flow marked on the fan, and then place the long end of the vibration isolator through the mounting hole of the fan. 2. Pull the long end of the vibrat...
Page 154
4-32 service guide media module cables and docking connector cards removal notes: if you are removing the scsi cable connected to the disk drive and media docking cards, perform steps 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12. If you are removing the operator panel cable that is not connected to a dock...
Page 155
Removal and replacement 4-33 7. Remove the disk drive fan and media fan. Refer to the “media module fans” removal procedure on page 4-30 for information about removing the two fans. 8. Disconnect the scsi cable connector on the rear of the disk drive docking connector card. 9. Remove the two rear mo...
Page 156
4-34 service guide 11. Disconnect the scsi cable connector on the media docking connector card. 12.Guide the scsi cable out of the media module through the disk drive opening. 13.If you are removing either the docking connector card or the power cable assembly, disconnect the two power cable connect...
Page 157
Removal and replacement 4-35 15.If you are removing the docking connector card on the disk drive docking bracket, disconnect the power cable connector on the docking connector card. 16.Remove the two mounting screws attaching the docking bracket, and then guide the bracket through the rear of the me...
Page 158
4-36 service guide 18.If you are removing the operator panel cable for a media module that does not contain a docking connector card and bracket, remove the cable from the plastic cable retainers, and then guide the cable out of the media module through the operator panel position. Bottom view of me...
Page 159
Removal and replacement 4-37 21.Remove the two mounting screws attaching the operator panel docking bracket to the bottom of the media module. 22.Remove the cable from the cable retainers, and then guide the cable out of the media module through the operator panel position. Top view of media module ...
Page 160
4-38 service guide 23.If you are removing the docking connector card and cable from the operator panel docking bracket, remove the four mounting screws, and then remove the card and cable. Docking connector card mounting screws docking bracket mounting screws 24.If you are removing the power cable a...
Page 161: Cpu Module
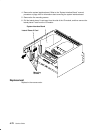
Removal and replacement 4-39 cpu module removal 1. Do the “front bezel and front access plate” removal procedure on page 4-15. 2. Disconnect the operator panel cable and the media power cable, and then move the cables away from the front of the cpu module. Front view of cpu enclosure operator panel ...
Page 162
4-40 service guide 3. Remove the two retainer screws. 4. Loosen the docking screw until the cpu module is disengaged from the i/o planar interface connectors. 5. Grasp the front of the cpu module, and then pull the cpu module toward you until you can grasp the bottom of the cpu module on each side. ...
Page 163
Removal and replacement 4-41 note: make sure that the operator panel cable and the media power cable are placed out of the path of the cpu module. 6. While grasping the bottom of the cpu module on each side, pull the cpu module toward you until it is out of the cpu enclosure, and then place the cpu ...
Page 164
4-42 service guide replacement note: when placing the cpu module in the cpu enclosure, make sure that the operator panel cable and the media power cable are placed out of the path of the cpu module. 1. Grasp the bottom of the cpu module with both hands and slowly slide it into the cpu enclosure unti...
Page 165: Interlock Cable
Removal and replacement 4-43 interlock cable note: refer to “handling static-sensitive devices” on page 4-14 before removing or installing memory cards. Removal 1. Do the “cpu module” removal procedure on page4-39. 2. Remove the seven screws from the cpu module top cover, and then remove the top cov...
Page 166
4-44 service guide – r50 cpu enclosure: disconnect the interlock cable connector from the lateral planar 1 card, and then remove the interlock cable connector from the cpu-module frame. Interlock cable connector lateral planar 1 card replacement replace in the reverse order..
Page 167
Removal and replacement 4-45 memory card, cpu card, or i/o card note: refer to “handling static-sensitive devices” on page 4-14 before removing or installing memory cards. Note: removing the memory card, cpu card, or i/o card requires using the extraction tools. The extraction tools are stored on th...
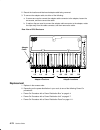
Page 168
4-46 service guide 3. If you are removing the i/o card, disconnect both flex cables connected to the i/o card. 4. Locate the card you are removing and position the extraction tools: – r30 and r40 cpu enclosures: position the single-piece extraction tool by placing the pin of the extraction tool thro...
Page 169
Removal and replacement 4-47 – r50 cpu enclosure: position single-piece extraction tools on either end of the card you are removing by placing the pin of the extraction tool through the hole in the top corner of the card you are removing. Single-piece extraction tool single-piece extraction tool pin...
Page 170
4-48 service guide replacement notes: install the memory cards in a right-to-left sequence beginning with slot a, and then continuing with slots b, c, and d. Memory cards must be installed with no empty slots between installed memory cards. Install the cpu cards in a right-to-left sequence beginning...
Page 171: Memory Modules
Removal and replacement 4-49 memory modules removal 1. Remove the memory card from the cpu module, refer to the “memory card, cpu card, or i/o card” removal procedure on page4-45. 2. Push the release tabs away from the memory module until the memory module disengages from the slot, and then remove t...
Page 172: Cpu Module Fans
4-50 service guide cpu module fans removal 1. Do the “cpu module” removal procedure on page4-39. 2. Remove the cable tie holding the fan power cable connector. 3. Disconnect the fan power cable. 4. Remove all four vibration isolators by pulling the fan away from the media module until the vibration ...
Page 173
Removal and replacement 4-51 replacement to replace the vibration isolators when replacing a fan, do the following: 1. Remove the module top cover and the i/o card, refer to the “memory card, cpu card, or i/o card” removal procedure on page 4-45. 2. Check the direction of the air flow marked on the ...
Page 174: System Planar
4-52 service guide system planar note: refer to “handling static-sensitive devices” on page 4-14 before removing or installing memory cards. Removal 1. Do the “interlock cable connector” removal procedure on page 4-43. 2. Do the “memory card, cpu card, and i/o card” removal procedure on page4-45 to ...
Page 175
Removal and replacement 4-53 if the cpu enclosure has a docking screw retention bracket, perform the next two steps. 4. Remove the screw holding the docking screw retention bracket. 5. Move the docking screw aside to provide access to the system planar mounting screws. Go to step 7. Lateral planar 1...
Page 176
4-54 service guide if the cpu module does not have a docking screw retention bracket, perform the next step. 6. For earlier versions of the cpu module, remove the docking screw by removing the two retainer clips and the three washers, and then remove the docking screw. Go to step 7. 7. Remove the fl...
Page 177
Removal and replacement 4-55 replacement note: only nine mounting screws are required. If the system planar was installed with 11 mounting screws, two of them may be discarded. 1. Before replacing the system planar in the cpu module, perform the following: a. Thread all of the mounting screws into t...
Page 178: Lateral Planar 1 Card
4-56 service guide lateral planar 1 card note: refer to “handling static-sensitive devices” on page 4-14 before removing or installing memory cards. Removal 1. To remove the lateral planar 1 card, perform the following removal procedures: a. The “cpu module” removal procedure on page 4-39. B. The “m...
Page 179: Cpu Module Flex Cables
Removal and replacement 4-57 cpu module flex cables removal 1. Do the “cpu module” removal procedure on page 4-39. 2. Remove the i/o card and all of the cpu cards. Refer to the “memory card, cpu card, or i/o card” removal procedure on page 4-45 to remove the i/o card and all of the cpu cards. 3. Rem...
Page 180
4-58 service guide 5. Record the location of the flex cable connectors. 6. If you are removing the flex cable connected to the horizontal connector on the i/o card, remove the two large slotted mounting screws. If you are removing the flex cable connected to the vertical connector on the i/o card, r...
Page 181
Removal and replacement 4-59 8. Guide the flex cable you are removing over the connector mounting bracket, and then guide the i/o card connector end under the fan mounting bracket; remove the flex cable. Cpu module two fans are shown removed flex cable connectors connector mounting bracket fan mount...
Page 182: Rear Access Plate
4-60 service guide rear access plate removal 1. Depending on the power distribution in your rack, do one of the following: • “power-off procedure with a power distribution bus” on page 4-2. • “power-off procedure with a power distribution unit” on page 4-5. • “power-off procedure with a power distri...
Page 183
Removal and replacement 4-61 power supply or cooling unit for systems attention: if your system has the capability to change power supplies while the system power is applied (r40, r50), see“removal and replacement while system power is applied” on page 4-62. Removal while system power is removed the...
Page 184
4-62 service guide replacement attention: ensure that you complete the replacement of the power supply before plugging in the power supply power cord. Plugging in the power cord before completing the power supply replacement can cause possible data loss. Replace in the reverse order. Removal and rep...
Page 185
Removal and replacement 4-63 5. Tighten the mounting bolt of the new power supply. As you tighten the bolt the sib led turns off. When the bolt is sufficiently tightened, the sib led lights, the fans return to normal speed and the following messages appear: note: these messages may take several minu...
Page 186
4-64 service guide power supply fan or cooling unit fan removal 1. Do the “rear access plate” removal procedure on page 4-60. 2. Disconnect the power cable connector for the power supply fan or the cooling unit fan you are removing. 3. Remove all four vibration isolators by pulling the fan away from...
Page 187: System Interface Board (Sib)
Removal and replacement 4-65 system interface board (sib) attention: lateral planar 2 and system interface board (sib) eeproms contain the sysid of the system. When one of the two components is to be replaced (for example the lateral planar 2), the sysid information is copied from sib eeprom into th...
Page 188
4-66 service guide replacement note: before replacing the sib in the i/o module, make sure the sib is placed correctly on the guide rails. 1. Replace in the reverse order. 2. Depending on the power distribution in your rack, do one of the following power-on procedures: • “power-on procedure with a p...
Page 189: I/o Module
Removal and replacement 4-67 i/o module removal 1. Depending on the type of power distribution in your rack, do one of the following: • “power-off procedure with a power distribution bus” on page 4-2. • “power-off procedure with a power distribution unit” on page 4-5. • “power-off procedure with a p...
Page 190
4-68 service guide note: the retainer screw on your right is also one of the retainer screws for attaching the system interface board in the i/o module. 7. Remove the remaining retainer screw. Retainer screw retainer screw (also used for system interface board) 8. Do the “front bezel and front acces...
Page 191
Removal and replacement 4-69 10.Slide the i/o module toward you until you can grasp the bottom of the i/o module on both sides, and then remove the i/o module from the cpu enclosure. 11. Place the i/o module on a stable surface. Retainer screw rear of cpu enclosure i/o module retainer screw (also us...
Page 192
4-70 service guide replacement 1. Grasp the bottom of the i/o module with both hands and slowly slide it into the cpu enclosure until the nut on the i/o module touches the tip of the docking screw on the cpu module. Note: the i/o module should easily slide into the cpu enclosure until it touches the...
Page 193: Lateral Planar 2 Card
Removal and replacement 4-71 lateral planar 2 card attention: after the lateral planar 2 card is installed and the system is powered–up, the system id is down-loaded to the lateral planar 2 card from a backup source within the system. This id becomes permanent on the lateral planar 2 and cannot be a...
Page 194
4-72 service guide 4. Remove the system interface board. Refer to the “system interface board” removal procedure on page 4-65 for information about removing the system interface board. 5. Remove the five mounting screws. 6. Pull the lateral planar 2 card away from the side of the i/o module, and the...
Page 195: Adapter Cable
Removal and replacement 4-73 adapter cable note: for a translation of this notice, see the system unit safety information manual, form number sa23-2629. Danger an electrical outlet that is not correctly wired could place hazardous voltage on metal parts of the system or the devices that attach to th...
Page 196
4-74 service guide 2. Record the location and label each adapter cable being removed. 3. To remove the adapter cable, do either of the following: a. If screws are used to connect the adapter cable connector to the adapter, loosen the two screws, and then remove the cable. B. If retainer clips are us...
Page 197: Adapter
Removal and replacement 4-75 adapter note: refer to “handling static-sensitive devices” on page 4-14 before removing or installing adapters. Removal 1. Remove the power supply or cooling unit located above the adapter you are removing. Refer to the “power supply or cooling unit” removal procedure on...
Page 198: I/o Module Flex Cables
4-76 service guide i/o module flex cables removal 1. Perform the “i/o module” removal procedure on page 4-67. 2. If you are removing the flex cable attached to the i/o planar 0, then remove the two guide pin mounting screws. If you are removing the flex cable attached to the i/o planar 1, then remov...
Page 199: I/o Planar Power Cables
Removal and replacement 4-77 i/o planar power cables removal 1. Perform the “i/o module” removal procedure on page 4-67. 2. If any adapters are located over the i/o planar power cables, do the “adapter” removal procedure on page 4-75 to remove the adapters. Attention: to prevent damage to the flex c...
Page 200: I/o Planars
4-78 service guide i/o planars note: refer to “handling static-sensitive devices” on page 4-14 before removing or installing the sib. Removal 1. Perform the “i/o module” removal procedure on page 4-67. 2. Do the “adapter” removal procedure on page 4-75 to remove all of the adapters installed on the ...
Page 201: Power Distribution Cables
Removal and replacement 4-79 power distribution cables removal 1. Perform the “power supply or cooling unit” removal procedure on page 4-61 to remove the power supply and either the cooling unit or optional power supply. 2. Perform the “i/o module” removal procedure on page 4-67. 3. Carefully cut th...
Page 202
4-80 service guide note: the docking connector mounting screws for the primary power supply, cooling unit, and optional power supply are located inside the i/o module. 5. If you are removing the power distribution cable for the optional power supply, remove the two mounting screws on the two optiona...
Page 203
Cpu enclosure installation procedure 5–1 chapter 5. Cpu enclosure installation procedure note: the following statement applies to the cpu enclosure with power supplies or with a power supply and cooling unit installed. Caution: this unit weighs more than 55 kg (121.2 pounds). Material handling syste...
Page 204
5–2 service guide 5. Remove the front bezel of the cpu enclosure. If you need more information to remove the front bezel, refer to the “front bezel and front access plate” removal procedure on page 4-15. Caution: the unit weighs between 32 kg (70 pounds) and 55 kg (121.2 pounds). Three persons are r...
Page 205
Parts information 6-1 chapter 6. Parts information this chapter contains details showing all parts and the respective part numbers for each detail. Acronyms for fru parts occasionally, an acronym is displayed with an srn or error code on the lcd display to identify a failing fru. The listing below d...
Page 206
6-2 service guide detail 1. Front bezel, front access plate, and cpu enclosure 1 2 3 4 5 10 11 12 6 10 11 12 9 7 8.
Page 207
Parts information 6-3 index number part number units per assy description 1 93h5056 1 front bezel 2 11h3202 1 logo 93h5078 1 logo (r50) 3 11h7395 1 front access plate (r30 and r40) 93h7089 1 front access plate (r50) 4 11h3227 1 warning label 5 00g1268 7 screw, front cover mounting (m4x7) 6 11h7397 1...
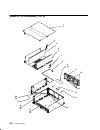
Page 208
6-4 service guide detail 2. Disk drives, media devices, and operator panel 14 15 1 13 18 19 22 2 3 4 10 5 6 7 16 20 21 25 26 27 8 9 17 23 24 11 12.
Page 209
Parts information 6-5 index number part number units per assy description 1 96g4207 1 lithium battery 2 94h9993 1 operator panel assembly (1.44 mb with keylock) 3 88g4768 1 diskette drive (1.44mb) 4 1622530 2 screw (mounting screw) 5 11h3165 1 retainer bracket 6 1621170 1 screw (attaches to operator...
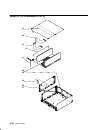
Page 210: Detail 3. Media Module
6-6 service guide detail 3. Media module 1 21 22 2 3 7 6 5 4 13 9, 8 20 16 14 10 15 17 11 18 23 24 19 12.
Page 211
Parts information 6-7 index number part number units per assy description 1 11h7394 1 media module (r30 and r40) 93h7119 1 media module (r50) 2 11h3248 1 retainer bracket (r30, r40) 93h5065 1 retainer bracket (r50) 3 00g1268 1 screw 4 78x8993 4 screw 5 00g1268 4 screw – autodocking receiver mounting...
Page 212
6-8 service guide detail 4. Cpu module (1 of 3) 17 18 19 3 12 1 2 5 6 4 7 20 21 22 14 8 9 10 16 15 24 25 11 13 23.
Page 213
Parts information 6-9 index number part number units per assy description 1 11h2653 1 top cover (part of cpu module assembly) (r30, r40) 93h5071 1 top cover (part of cpu module assembly) (r50) 2 1621285 7 screw 3 11h3280 1 extraction tool (single-piece, two required for r50) 4 35h8748 1 cpu card, ty...
Page 214
6-10 service guide detail 5. Cpu module (2 of 3) 26 27 29 30 31 32 33 34 28 35.
Page 215
Parts information 6-11 index number part number units per assy description 26 65g6068 1 lateral planar 1 (r30) 40h7013 1 lateral planar 1 (r40 and r50) 27 04g1559 4 screw 28 11h2678 1 interlock cable 29 19h0242 1 system planar for r30 35h8778 1 system planar for r40 19h0035 1 system planar for r50 3...
Page 216
6-12 service guide detail 6. Cpu module (3 of 3) 36 37.
Page 217
Parts information 6-13 index number part number units per assy description 36 93h7441 1 front guide bracket assembly (r50) 37 93h7442 1 rear guide bracket assembly (r50).
Page 218: Detail 7. I/o Module
6-14 service guide detail 7. I/o module 30 27 28 29 33 34 35 36 6 7 8 9 18 1 2 3 4 5 10 11 20 26 25 14 15 24 22 23 21 13 12 32 31 16 17 19.
Page 219
Parts information 6-15 index number part number units per assy description 1 see note 16 adapter 2 40h0723 1 flex cable (for i/o planar 1) 3 40h0727 1 flex cable (for i/o planar 0) 4 11h2684 1 power cable (long – i/o planar to sib card) 5 11h2683 1 power cable (short – i/o planar to sib card) 6 40h0...
Page 220
6-16 service guide detail 8. Rails for cpu enclosure installation mounting hardware for cpu enclosure detail a – front of rail detail b – rear of rail 1 1 1 6 3 2 5 4 a b.
Page 221
Parts information 6-17 index number part number units per asm description 1 02g7232 1 rail, left 2 0375867 4 nut clip 3 02g7295 4 screw, rail mounting 4 1622320 4 lock washer 5 1622405 4 nut 6 02g7263 1 rail, right.
Page 222: Power Cables
6-18 service guide power cables 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 note: if you should need a different power cable, use this figure and the following table to assist you when ordering. Index part number country 1 1838574 bahamas, barbados, bolivia, brazil, canada, costa rica, dominican republic, el salvador, ...
Page 223
Systemguard test groups a-1 appendix a. Systemguard test groups systemguard test groups table the following diagram shows the various test groups and their associated tests. To modify the test list, the tests have to be selected in the xxyy format, where xx is the group number and yy is the test num...
Page 224
Operator guide a-2 group no test test no group 05 dcb and memory test group 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 50 mm data lines test mm address lines test mm board dec. Test mm basic acc. Test mm components test ecc component test ecc mechanism test refresh mech. Test ecc data lines access. Test mm full tes...
Page 225
Systemguard test groups a-3 systemguard test group descriptions the following is a description of the different test groups and the tests available under them. All of these tests are performed automatically at power on with default parameters. They can also be performed selectively (selection of tes...
Page 226
Operator guide a-4 bump, remote, and special asynchronous lines test these tests are meant to check the asynchronous lines of the standard i/o and the asynchronous lines controller in the super i/o. These tests contain sub-tests, which are described as follows. Each sub-test saves and restores the l...
Page 227
Systemguard test groups a-5 nvram test this test checks the accessibility of nvram bytes. It contains the following sub-tests: nvram data lines access test this test saves the first nvram byte. Then a read / write operation is done word by word. It restores the first nvram byte. Nvram address lines ...
Page 228
Operator guide a-6 dtr register test this test writes, reads and compares a 1 among 0 bits in dtr registers. Ctr register test this test writes, reads and compares a 1 among 0 bits in ctr registers. It saves and restores the ctr register value. Miscellaneous registers test this test checks accessibi...
Page 229
Systemguard test groups a-7 entry parameters parameters name definition possible values default value parameter 1 sub test # subtest number 0 or 1 0 = all tests linked parameter 2 proc # processor number 8 8 = bump check–sum test it checks the crc value for all present vpds; it checks the crc value ...
Page 230
Operator guide a-8 bpp external loopback test (bpp ext l–b test ) note: this test can only be performed by field or manufacturing people. This test checks the accessibility of the super–io chip. It saves and restores used registers. This test is not performed at power on. Entry parameters parameters...
Page 231
Systemguard test groups a-9 ionian-ssga registers test this test is performed by all the processors and it checks the accessibility from the processor to the ionian and ssga chips. Following hardware parts are checked. 1. Dcb asic 2. Ionian asic 3. Ssga asic. The following sub-tests are included und...
Page 232
Operator guide a-10 super i/o and uart access test this test checks the accessibility of the super i/o chip from the processors. They don’t check the functional aspects of the super i/o chip (this is done by the bump directly). The following sub-tests are available under this test: super i/o uart 1 ...
Page 233
Systemguard test groups a-11 ssga interrupt registers test this test writes and reads specific values from each of the interrupt registers. The values are then compared. Values are saved and restored in all the operations. Floppy disk access test this test needs a formatted diskette in the diskette ...
Page 234
Operator guide a-12 level 2 cache. It calculates the memory address available and then validates the level 2 cache before writing 1 mb. Then a read operation is done in word mode and values are compared. Then a read is done in burst mode and comparison is done. Tag data test this test checks the ava...
Page 235
Systemguard test groups a-13 walking 0 data test this test isolates the open lines among the data lines. It writes “0s among 1s” pattern on the cache line. Then it is read and compared. Transfer modes on dcb test this sub-test is used to check the transfer of 1 to 8 bytes to the memory. Initially th...
Page 236
Operator guide a-14 this test consists of two sub-tests. Words manipulated / used are not restored at the end of the test. This test is applied to all the memory cards which are present. In case of errors, suitable error messages are displayed on the console. The following is a description of the su...
Page 237
Systemguard test groups a-15 basic main memory test this test is performed by all the processors and it checks the capability to access the main memory in all kinds of data formats. This test applies to one main memory location and the words used during the test are not restored. This test partially...
Page 238
Operator guide a-16 main memory components test this test is performed by all the processors to check all the main memory locations. From the hardware point of view, this test checks the memory chips mounted on the main memory cards. This test can be launched in two modes, as follows: 1. Bit map ela...
Page 239
Systemguard test groups a-17 ecc data lines accessibility test this test checks the accessibility for all the data lines to the ecc memory banks, through smc asics. The following hardware parts are checked by running this test. • dcb asics • smc asics • connection of data lines between cpu daughter ...
Page 240
Operator guide a-18 ecc memory component test this test is identical to the main memory components test but it is applied to the ecc memory components. Error correction mechanism test this test checks the hardware mechanisms enabling the detection of and the correction of single bit errors when work...
Page 241
Systemguard test groups a-19 interrupt tests group these tests are performed by the bump as well as the processors. They are launched at power on and under control of off line test monitor. They collectively check the interrupt system. The following tests are available under this group. Bump to cpu ...
Page 242
Operator guide a-20 cpu multiprocessor test group these tests are launched at power-on and are also available under the control of the off line tests monitor. These tests check the multi-processor mechanisms, atomic instructions, cache coherency, main memory sharing, and multi-resources sharing. The...
Page 243
Systemguard test groups a-21 instruction. This is issued by processor 0 which is set to global copy back mode. Caching is inhibited for processor 1. Paradox detection: dcbst not from line owner here, processor 1 is set to local copy back mode. Memory coherency is enabled for processor 0. This test v...
Page 244
Operator guide a-22 main memory sharing test this test is launched by the bump and performed by all configured processors. It has a sub-test to check the capability of all the processors to access the main memory. The following hardware parts are checked during the process: 1. Dcb asics 2. Ionian as...
Page 245: Default Parameter Values
Modifying systemguard parameters b-1 appendix b. Modifying systemguard parameters many systemguard parameters can be modified in several ways. Some can be modified using the systemguard stand-by menu, others using the systemguard maintenance menu, and others using the aix diag or mpcfg commands or d...
Page 246
B-2 installation and service guide flag, parameter and keyword default values name default value bump console power-on command string power service console power-on command string blank (not set) bump console power-on command flag enabled service console power-on command flag disabled remote authori...
Page 247
Modifying systemguard parameters b-3 changing flags and parameters under aix service aids the service aids are recommended to change the flags. The service aids can be entered using the diag command or by booting diagnostics in service mode. They display or change flag values using 0 (zero) for disa...
Page 248
B-4 installation and service guide systemguard maintenance menu starting from the main maintenance menu: • enter 2 to enable the flag. Or • enter 3 to disable the flag. Aix diag command starting from the service aids selection menu: 1. Select the bump service aids option. 2. Select the display or ch...
Page 249
Modifying systemguard parameters b-5 modifying dial-in phone numbers these parameters can be changed under systemguard using the maintenance menu, or under aix using the diag command. Systemguard maintenance menu starting from the main maintenance menu: 1. Enter 8 to set parameters. 2. Enter 3 for p...
Page 250
B-6 installation and service guide modifying the electronic mode switch from service line flag this flag can be changed under systemguard using the maintenance menu, or under aix using the diag command. Systemguard maintenance menu starting from the main maintenance menu: 1. Enter 8 to set parameter...
Page 251: Reloading The Flash Eeprom
Modifying systemguard parameters b-7 reloading the flash eeprom follow this procedure to load a new version of systemguard into the flash eeprom, which may be necessary when you install a new version of aix for example. Only system administrators should perform this procedure. Prerequisites if the s...
Page 252
B-8 installation and service guide.
Page 253: Configuration
Systemguard remote operation configuration c-1 appendix c. Systemguard remote operation configuration in order to utilize the remote operation capabilities of systemguard and also allow console mirroring, you need to have flags, parameters and tty configurations properly enabled. Below, are tty0 and...
Page 254
Service guide c-2 the configuration of the tty1 for the s2 port looks similar to the following: [top] [entry fields] tty tty1 tty type tty tty interface rs232 description asynchronous terminal status available location 00–00–s2–00 parent adapter sa1 port number [s2] enable login disable baud rate [9...
Page 255
Systemguard remote operation configuration c-3 the modem parameters file name value should be set to the file name of your modem configuration file. The service line speed should be set to your modem and tty capabilities (9600 is recommended). • service flags: mpcfg –ds index name value 1 remote ser...
Page 256: Modem Configuration Files
Service guide c-4 modem configuration files if you want to attach a modem to the s2 port to allow automatic problem reporting from systemguard or dial-in access from a remote location, you have to provide a configuration file for the modem you are using. This file is also necessary to utilize the mi...
Page 257
Systemguard remote operation configuration c-5 this is a sample /usr/share/modems/mir_modem file for console mirroring using an ibm 7851 modem. # tested at 9600bps. Icdelay 5 defaultto 10 calldelay 120 # at attention code q0 enable result codes to screen # &f1 set factory profile 1 q1 disable result...
Page 259
Off line diagnostic error codes d-1 appendix d. Off line diagnostic error codes note: the failure percent value is calculated on a system model base. As some failing function codes are system model specific but are associated the the same error number, it may happen that the sum of the failure perce...
Page 260
Service guide d-2 error number source failing function codes failure percent (%) description 401-023 k c59 100 description: s2 asynchronous line junction signal error (dtr to dsr link). Action: use map 0210. 401-024 k c59 100 description: s2 asynchronous line junction signal error (rts to cts link)....
Page 261
Off line diagnostic error codes d-3 error number source failing function codes failure percent (%) description 401-049 k c59 100 description: s3 asynchronous line junction signal error (dtr to dsr link). External loop-back mode. Action: use map 0210. 401-050 k c59 100 description: s3 asynchronous li...
Page 262
Service guide d-4 error number source failing function codes failure percent (%) description 401-140 k all boards description: bad vpd board. 401-141 k all boards description: no board present. 401-142 k all boards description: no coherent configuration on board. 401-150 k c59 c61 c63 c88 40 20 20 2...
Page 263
Off line diagnostic error codes d-5 error number description failure percent (%) failing function codes source 401-182 k c59 modem 20 80 description: dial-out test. No customer hub or service center phone dial-out. 401-183 k c59 modem 20 80 description: dial-out test. Modem parameters failed. 401-18...
Page 264
Service guide d-6 error number source failing function codes failure percent (%) description 401-514 k c59 c63 c61 50 25 25 description: direct io: ionian-ssga. Apr register error. Action: use map 0210. 401-515 k c59 c63 c61 50 25 25 description: direct io: ionian-ssga. Bsr init value. Action: use m...
Page 265
Off line diagnostic error codes d-7 error number description failure percent (%) failing function codes source 401-550 k c59 c61 c90 c91 60 20 10 10 description: direct io. Flash eprom access error. Action: use map 0210. 401-560 k c59 c61 80 20 description: direct io. Eprom access error. Action: use...
Page 266
Service guide d-8 error number source failing function codes failure percent (%) description 401-591 k c59 c63 c61 50 25 25 description: diskette drive access. Error on sense interrupt command. Action: use map 0210. 401-592 k c59 c63 c61 50 25 25 description: diskette drive access. Error on write co...
Page 267
Off line diagnostic error codes d-9 error number description failure percent (%) failing function codes source 401-807 k lsa c59 c90 c61 c63 40 20 20 10 10 description: channel reset and pos. Missing dma interrupt error during transfer. Action: use map 0210. 401-808 k lsa c59 c90 c61 c63 40 20 20 10...
Page 268
Service guide d-10 error number description failure percent (%) failing function codes source 401-824 k lsa c59 c90 c61 c63 40 20 20 10 10 description: channel reset and pos. Scsi bus control lines error. Action: use map 0210. 401-825 k lsa c59 c90 c61 c63 40 20 20 10 10 description: channel reset a...
Page 269
Off line diagnostic error codes d-11 error number description failure percent (%) failing function codes source 401-841 k lsa c59 c90 c61 c63 40 20 20 10 10 description: channel reset and pos. Pos4 register error. Action: use map 0210. 401-842 k lsa c59 c90 c61 c63 40 20 20 10 10 description: channe...
Page 270
Service guide d-12 error number description failure percent (%) failing function codes source 401-851 k lsa c59 c90 c61 c63 40 20 20 10 10 description: channel reset and pos. Buffer exchange error. Action: use map 0210. 401-852 k lsa c59 c90 c61 c63 40 20 20 10 10 description: channel reset and pos....
Page 271
Off line diagnostic error codes d-13 error number source failing function codes failure percent (%) description 402-110 k c63 c61 50 50 description: caches coherencies. Concurrent coherent write accesses error. Action: use map 0210. 402-111 k c63 c61 50 50 description: caches coherencies. Concurrent...
Page 272
Service guide d-14 error number source failing function codes failure percent (%) description 402-132 k c63 c61 50 50 description: dcb ports arbitration error. Memory coherency error. Action: use map 0210. 402-133 k c63 c61 50 50 description: dcb ports arbitration error. Odd processor dcbf or even p...
Page 273
Off line diagnostic error codes d-15 error number source failing function codes failure percent (%) description 402-530 k c59 c61 ??? 50 25 25 description: cpus to cpus interrupt error. Even processors auto interrupt. Action: use map 0210. 402-531 k c59 c61 ??? 50 25 25 description: cpus to cpus int...
Page 274
Service guide d-16 error number source failing function codes failure percent (%) description 403-013 k b94 c61 c63 40 30 30 description: main memory address lines accessibility error. Unexpected interrupt. Action: use map 0210. 403-020 k b94 c61 c63 40 30 30 description: main memory board address a...
Page 275
Off line diagnostic error codes d-17 error number source failing function codes failure percent (%) description 403-038 k b94 c61 c63 40 30 30 description: main memory basic tests error. Work mode main memory addressing error. Action: use map 0210. 403-039 k b94 c61 c63 40 30 30 description: main me...
Page 276
Service guide d-18 error number source failing function codes failure percent (%) description 403-074 k b94 b96 or b97 50 50 description: error correction code mechanism. Multiple error generation error. Action: use map 0210. 403–075 k b94 c64 d28 b96 b97 d33 50 50 50 50 50 50 description: dcb or sm...
Page 277
Off line diagnostic error codes d-19 error number description failure percent (%) failing function codes source 403-506 k c59 c61 c63 50 25 25 description: bump to cpu interrupt error. Iod-hw-sts register error. Action: use map 0210. 403-507 k c59 c61 c63 50 25 25 description: bump to cpu interrupt ...
Page 278
Service guide d-20 error number description failure percent (%) failing function codes source 403-527 k c59 c61 c63 50 25 25 description: cpu to bump interrupt. Xirr4 register error. Action: use map 0210. 403-528 k c59 c61 c63 50 25 25 description: cpu to bump interrupt. Iod-hw-sts register error. A...
Page 279
Off line diagnostic error codes d-21 error number description failure percent (%) failing function codes source 403-555 k c59 c61 c63 50 25 25 description: cpu to cpu interrupt. Xirr register error. Action: use map 0210. 403-560 k c59 c61 c63 50 25 25 description: tod to bump interrupt. Unexpected i...
Page 280
Service guide d-22 error number description failure percent (%) failing function codes source 404-018 k c63 c61 80 20 description: caches coherencies. Dcbi not from line owner error. Action: use map 0210. 404-019 k c63 c61 80 20 description: caches coherencies. Dcbt not from line owner error. Action...
Page 281
Off line diagnostic error codes d-23 error number description failure percent (%) failing function codes source 407-015 k c59 c61 c63 40 30 30 description: cpu interrupt test manager stopping t-o. Action: use map 0210. 407-016 k c59 c61 c63 40 30 30 description: cpu multi-processor test manager laun...
Page 282
Service guide d-24 error number description failure percent (%) failing function codes source 408-060 k b94 b96 or b97 50 50 description: main memory knaizuk-hartmann test error. Action: use map 0210. 408-080 k c63 c61 90 10 description: multi resources full test error. Action: use map 0210. 409-000...
Page 283
Off line diagnostic error codes d-25 error number description failure percent (%) failing function codes source 409-083 b c60 100 description: op microcontroller not working. Action: use map 0210. 409-087 k c63 100 description: mvr not compatible with the cpu boards. Action: use map 0210. 409-088 k ...
Page 284: Error Logging
Service guide d-26 error logging when a failure occurs on a fan or on a power supply, the system produces a logging report for this event. The logging report can be viewed using errpt. An errpt report about power and fan is the following: label: epow_sus description: loss of electrical power probabl...
Page 285
Off line diagnostic error codes d-27 1010 fan 2 fault 1011 fan 3 fault 1100 fan 4 fault 1100 fan 5 fault 1100 fan 6 fault 1111 reserved power up bits 4–6 values description 000 manual on button pushed 001 remote on signal from external 010 timed power on from tod clock 011 remote on signal from powe...
Page 286
Service guide d-28 power system operating in backup mode bit 14 values description 0 no power warning 1 power system operating in backup mode warning cooling system operating in backup mode bit 15 values description 0 no cooling warning 1 cooling system operating in backup mode warning power fault a...
Page 287
Off line diagnostic error codes d-29 understanding pksr the pksr status is logged in hexadecimal value: 8 digits are logged. Each hexadecimal digit must be converted in 4 binary digits: 32 bits are obtained. Divide the bits as indicated in the pksr layout and check the bit values to understand the m...
Page 288
Service guide d-30
Page 289: Power States
System power states e-1 appendix e. System power states the state of the system is dependant on the condition of four variable conditions that effect how the system ipls or shuts down. The four conditions are: • the position of the power-on button this button has two positions. It can be pressed in ...
Page 290
E-2 operator guide if the command sbb is entered on the bump console, and the system key is in the normal position, the system goes to the sbb_ecmd state. • if the power-on button is pressed and changes from the on position to the off position, the system sets the was_shutdown status to false. • if ...
Page 291
System power states e-3 • if the power_fault status is false, the system attempts to power on. If the system then detects a power fault, the power_fault status is set to true. The system displays an operator panel lcd error message, and the system goes to the main_standby status. If no power fault i...
Page 292
E-4 operator guide if the system power does not turn on, the power-on button may be in the off position. Go to the system unit and press the power-on button (only press the button once), if the system power still does not turn on there may be an earlier fault condition. Remove main power from the sy...
Page 293
Glossary x-1 glossary: special terms used in systemguard bp (back plane). A panel located in the system unit and used to interconnect boards and devices. Bist (built in self-test). Tests performed during the standby phase of the ipl process. The bist phase comes ahead of the post phase. Bump (bring-...
Page 294
X-2 service guide which can be removed without turning the power off to the entire system). Ros (read-only storage). Storage which does not support writing. Scsi (small computer system interface). A standard bus interface used to connect peripherals such as disk drives or tape drives. Sib (system in...
Page 295: Index
Glossary x-3 index numbers -48 v dc power supply power-off procedure with power distribution panel, 4-9 power-on procedure, 4-11 a about this book, xiii adapter, 4-75 adapter cable, 4-73 autoserviceipl flag, 2-36 b boot multiuser aix in service flag, 2-37 bump console flag, 2-36 c cd-rom drive, 4-18...
Page 296
X-4 service guide h handling static-sensitive devices, 4-14 hardware components, cpu module, memory cards, 1-9 i i/o card, 4-45 i/o module, 1-6, 4-67, 6-14 i/o module flex cables, 4-76 i/o planar power cables, 4-77 i/o planars, 1-11, 4-78 installation, rails, 1-16 installation, cpu enclosure, 5–1 in...
Page 297
Glossary x-5 power-off with a power distribution bus, 4-2 power-on from bump console, e-3 power-on procedure with power distribution panel, 4-11 power-on using the power-on button, e-4 power-on with a power distribution bus, 4-4 power-off procedure with a power distribution unit, 4-5 power-on proced...
Page 298
X-6 service guide electronic mode switch, modifying, b-6 flags, 2-9 flash eeprom, reloading, b-7 maintenance menu, 2-21 disable service console, 2-25 display bump error log, 2-25 display configuration, 2-22 device level, 2-24 system level, 2-22 unit level, 2-22 enable service console, 2-25 off-line ...
Page 300
Printed in the u.S.A. Sa23-2743-02 40h7126.