- DL manuals
- IBM
- Server
- BladeCenter PS703
- Technical Overview And Introduction
IBM BladeCenter PS703 Technical Overview And Introduction
ibm.com/redbooks
Red
paper
Front cover
IBM BladeCenter PS703
and PS704 Technical
Overview and Introduction
David Watts
Kerry Anders
David Harlow
Joe Shipman II
Features the POWER7 processor providing
advanced multi-core technology
Details the follow-on to the BladeCenter
PS700, PS701 and PS702
Describes management using
the new Systems Director
Management Console
Summary of BladeCenter PS703
Page 1
Ibm.Com/redbooks red paper front cover ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction david watts kerry anders david harlow joe shipman ii features the power7 processor providing advanced multi-core technology details the follow-on to the bladecenter ps700, ps701 and ps702 descr...
Page 3
International technical support organization ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction may 2011 redp-4744-00
Page 4
© copyright international business machines corporation 2011. All rights reserved. Note to u.S. Government users restricted rights -- use, duplication or disclosure restricted by gsa adp schedule contract with ibm corp. First edition (may 2011) this edition applies to: ibm bladecenter ps703, 7891-73...
Page 5: Contents
© copyright ibm corp. 2011. All rights reserved. Iii contents notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Vii trademarks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 6
Iv ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 2.3 power7 processor-based blades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 2.4 memory subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 7
Contents v 4.3.4 cache protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127 4.3.5 special uncorrectable error handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128 4.3.6 pci extended error handling . . . . . . . . ....
Page 8
Vi ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction.
Page 9: Notices
© copyright ibm corp. 2011. All rights reserved. Vii notices this information was developed for products and services offered in the u.S.A. Ibm may not offer the products, services, or features discussed in this document in other countries. Consult your local ibm representative for information on th...
Page 10: Trademarks
Viii ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction trademarks ibm, the ibm logo, and ibm.Com are trademarks or registered trademarks of international business machines corporation in the united states, other countries, or both. These and other ibm trademarked terms are marked o...
Page 11: Preface
© copyright ibm corp. 2011. All rights reserved. Ix preface the ibm® bladecenter® ps703 and ps704 are premier blades for 64-bit applications. They are designed to minimize complexity, improve efficiency, automate processes, reduce energy consumption, and scale easily. These blade servers are based o...
Page 12
X ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction has worked at ibm for 5 years. His areas of expertise include ibm bladecenter, system x, bladecenter fibre channel fabrics, bladecenter networking, and power blade servers. Previously he worked as an electrical and environmental s...
Page 13: Comments Welcome
Preface xi now you can become a published author, too! Here's an opportunity to spotlight your skills, grow your career, and become a published author—all at the same time! Join an itso residency project and help write a book in your area of expertise, while honing your experience using leading-edge...
Page 14
Xii ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction.
Page 15: Introduction and General
© copyright ibm corp. 2011. All rights reserved. 1 chapter 1. Introduction and general description this chapter introduces and provides a general description of the new ibm bladecenter power7 processor-based blade servers. These new blades offer processor scalability from 16 cores to 32 cores: ibm b...
Page 16
2 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 1.1 overview of ps703 and ps704 blade servers figure 1-1 shows the ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 blade servers. Figure 1-1 the ibm bladecenter ps703 (right) and bladecenter ps704 (left) the ps703 blade server the ibm bladecenter...
Page 17
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 3 ps703 also supports one pcie ciov expansion card slot and one pcie cffh expansion card slot. See 1.6.7, “i/o features” on page 21 for supported i/o expansion cards. The ps704 blade server the ibm bladecenter ps704 (7891-74x) is a double-wide blade se...
Page 18
4 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction table 1-1 compares the processor core options and frequencies, and l3 cache sizes of the power7 blade servers. Table 1-1 comparison of power7 blade servers for a detailed comparison, see 2.6, “technical comparison” on page 54. Ful...
Page 19
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 5 1.3.1 supported bladecenter chassis the ps703 and ps704 blades are supported in the ibm bladecenter chassis as listed in table 1-2. Table 1-2 the blade servers supported in each bladecenter chassis ibm bladecenter h delivers high performance, extreme...
Page 20
6 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 1-2 displays the front view of an ibm bladecenter h and figure 1-3 displays the rear view. Figure 1-2 bladecenter h front view figure 1-3 bladecenter h rear view.
Page 21
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 7 the key features of the ibm bladecenter h chassis are as follows: a rack-optimized, 9 u modular design enclosure for up to 14 hot-swap blades. A high-availability mid-plane that supports hot-swap of individual blades. Two 2,900 watt or 2,980 watt hot...
Page 22
8 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction chassis is positioned for expansion, capacity, redundancy, and carrier-grade nebs level 3/etsi compliance in dc models. Bladecenter ht provides a solid foundation for next-generation networks (ngn), enabling service providers to b...
Page 23
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 9 figure 1-5 shows the rear view of the bladecenter ht. Figure 1-5 bladecenter ht rear view bladecenter ht delivers rich telecommunications features and functionality, including integrated servers, storage and networking, fault-tolerant features, optio...
Page 24
10 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction the key features of the bladecenter ht are as follows: support for up to 12 blade servers, compatible with the other chassis in the bladecenter family four standard and four high-speed i/o module bays, compatible with the other c...
Page 25
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 11 figure 1-7 shows the rear view of the chassis. Figure 1-7 the rear of the bladecenter s chassis the key features of ibm bladecenter s chassis are as follows: a rack-optimized, 7 u modular design enclosure for up to six hot-swap blades two optional d...
Page 26: 1.4 Operating Environment
12 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 1.3.2 number of ps703 and ps704 blades in a chassis the number of power7 processor-based blades that can be installed in a bladecenter chassis depends on several factors: bladecenter chassis type number of power supplies installe...
Page 27: 1.5 Physical Package
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 13 ibm bladecenter h operating temperature – 10.0°c - 35 °c (50°f - 95 °f) at 0 - 914 m (0 - 3000 ft.) – 10.0°c - 32 °c (50°f - 90 °f) at 914 - 2133 m (3000 - 7000 ft.) relative humidity 8% - 80% maximum altitude: 2133 meters (7000 ft.) ibm bladecenter...
Page 28: 1.6 System Features
14 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 1.6 system features the ps703 and ps704 blade servers are 16-core and 32-core power7 processor-based blade servers.This section describes the features on each of the power7 blade servers. The following topics are covered: 1.6.1, ...
Page 29
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 15 form factor single-wide (30 mm) blade processors: – two eight-core 64-bit power7 processors operating at a 2.4 ghz clock speed for a total of 16 cores in the blade server – based on cmos 12s 45 nm soi (silicon-on-insulator) technology – power consum...
Page 30
16 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 1.6.2 ps704 system features the ps704 is a double-wide server. The two halves of the bladecenter ps704 are shown in figure 1-9 on this page and figure 1-10 on page 17. Figure 1-9 top view of ps704 blade server base unit two 8-cor...
Page 31
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 17 figure 1-10 top view of ps704 blade server smp unit the features of the server are as follows: machine type and model number 7891-74x form factor double-wide (60 mm) blade processors: – four eight-core 64-bit power7 processors operating at a 2.4 ghz...
Page 32
18 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction – two disk drive bays supporting up to two 2.5-inch sas hdd (hard disk drive) or up to four 1.8-inch sas ssd (solid state drive) – hardware mirroring: • one hdd: raid 0 • one ssd: raid 0 • two hdds: raid 0 or raid 10 • one hdd an...
Page 33
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 19 table 1-6 minimum features for ps703 and ps704 blade server 1.6.4 power supply features the peak power consumption is 428 w for the ps703 and 848 w for the ps704 blade server; power is provided by the bladecenter power supply modules. The maximum me...
Page 34
20 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 1.6.5 processor the processors used in the ps703 and ps704 are 64-bit power7 processors operating at 2.4 ghz. They are optimized to achieve maximum performance for both the system and its virtual machines. Couple that performance...
Page 35
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 21 the optional active memory expansion is a power7 technology that allows the effective maximum memory capacity to be much larger than the true physical memory. Compression and decompression of memory content using processor cycles can allow memory ex...
Page 36
22 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction the card has the following features: ciov form factor qlogic 2532 8 gb asic pci express 2.0 host interface support for two full-duplex fibre channel ports at 8 gbps maximum per channel support for fibre channel protocol small com...
Page 37
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 23 comprehensive virtualization capabilities with support for n_port id virtualization (npiv) and virtual fabric simplified installation and configuration using common hba drivers efficient administration by using hbanyware for hbas anywhere in the san...
Page 38
24 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction qlogic 1 gb ethernet and 8 gb fibre channel expansion card (cffh) the qlogic 1gb ethernet and 8gb fibre channel expansion card, feature #8271, is a cffh high speed blade server expansion card with two 8gb fibre channel ports and ...
Page 39
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 25 qlogic 2-port 10 gb converged network adapter (cffh) the qlogic 2-port 10 gb converged network adapter (cffh) for ibm bladecenter, feature #8275, offers robust fibre channel storage connectivity and 10 gb networking over a single converged enhanced ...
Page 40
26 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction ability to function as a 2-port ethernet nic in bladecenter s chassis or a 4-port ethernet nic in a bladecenter h chassis supports bladecenter open fabric manager (bofm) network install and boot support with adapter firmware upda...
Page 41
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 27 for more details about service processors, see 2.8, “service processor” on page 65. Ethernet ports the ps703 has a 2-port onboard integrated ethernet adapter for a total of two ethernet ports. The ps704 has two 2-port onboard integrated ethernet ada...
Page 42
28 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction serial over lan (sol) the integrated sol function routes the console data stream over standard dual 1 gb ethernet ports to the advance management module. The ps703 and ps704 do not have on-board video chips and do not support kvm...
Page 43
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 29 configuration of bladecenter. Complete compatibility matrixes are available on the following web pages: serverproven®: http://www.Ibm.Com/servers/eserver/serverproven/compat/us/eserver.Html bladecenter interoperability guide http://www.Ibm.Com/suppo...
Page 44
30 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction table 1-11 sas i/o modules supported by the sas pass through card 1.7.3 fibre channel switch and pass-through modules fibre channel i/o modules are available from several manufacturers. These i/o modules can provide full san fabr...
Page 45
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 31 table 1-12 fibre channel i/o modules 1.7.4 converged networking i/o modules there are two basic solutions to implement fibre channel over ethernet (fcoe) over a converged network with a bladecenter. The first solution uses a top-of-rack fcoe-capable...
Page 46
32 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction table 1-13 converged network modules supported by the qlogic cna for the latest interoperability information see the bladecenter interoperability guide, available from: http://ibm.Com/support/entry/portal/docdisplay?Lndocid=migr-...
Page 47
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 33 1.7.6 multi-switch interconnect module the msim is a switch module container that fits in the high speed switch bays (bays 7 and 8 or bays 9 and 10) of the bladecenter h chassis. Up to two msims can be installed in the bladecenter h. The msim suppor...
Page 48: 1.8 Building to Order
34 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 1.7.7 multi-switch interconnect module for bladecenter ht the multi-switch interconnect module for bladecenter ht (msim-ht) is a switch module container that fits in the high-speed switch bays (bays 7 and 8 or bays 9 and 10) of t...
Page 49: 1.9 Model Upgrades
Chapter 1. Introduction and general description 35 system to order. Use this tool to specify each configuration feature that you want on the system, building on top of the base-required features. 1.9 model upgrades the ps703 and ps704 are new serial-number blade servers. There are no upgrades from p...
Page 50
36 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction.
Page 51: Architecture and Technical
© copyright ibm corp. 2011. All rights reserved. 37 chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview this chapter discusses the overall system architecture of the power7 processor-based blade servers and provides details about each major subsystem and technology. The topics covered are: 2.1, “architec...
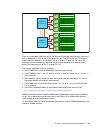
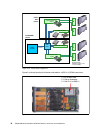
Page 52: 2.1 Architecture
38 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 2.1 architecture the overall system architecture is shown in figure 2-1, with the major components described in the following sections. Figure 2-1 shows the ps703 layout. Figure 2-1 ps703 block diagram the ps704 double-wide blade...
Page 53
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 39 figure 2-2 ps704 block diagram 2.2 the ibm power7 processor the ibm power7 processor represents a leap forward in technology achievement and associated computing capability. The multi-core architecture of the power7 processor has been matched with a ...
Page 54
40 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction processor-based systems is one of system-wide balance in which the power7 processor plays an important role. Ibm has used innovative methods to achieve required levels of throughput and bandwidth. Areas of innovation for the powe...
Page 55
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 41 table 2-1 summarizes the technology characteristics of the power7 processor. Table 2-1 summary of power7 processor technology 2.2.2 power7 processor core each power7 processor core implements aggressive out-of-order (ooo) instruction execution to dri...
Page 56
42 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 2.2.3 simultaneous multithreading an enhancement in the power7 processor is the addition of the smt4 mode to enable four instruction threads to execute simultaneously in each power7 processor core. Thus, the instruction thread ex...
Page 57
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 43 2.2.4 memory access each power7 processor chip has two ddr3 memory controllers, each with four memory channels (enabling eight memory channels per power7 processor). Each channel operates at 6.4 gbps and can address up to 32 gb of memory. Thus, each ...
Page 58
44 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction optimized for servers the power7 processor forms the basis of a flexible compute platform and can be offered in a number of guises to address differing system requirements. The power7 processor can be offered with a single active...
Page 59
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 45 figure 2-7 shows the flr-l3 cache regions for the cores on the power7 processor die. Figure 2-7 flr-l3 cache regions on the power7 processor the innovation of using edram on the power7 processor die is significant for several reasons: latency improve...
Page 60
46 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 2.2.7 power7 processor and intelligent energy energy consumption is an important area of focus for the design of the power7 processor, which includes intelligent energy features that help to optimize energy usage and performance ...
Page 61: 2.4 Memory Subsystem
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 47 2.3 power7 processor-based blades the ps703 and ps704 are follow-ons to the previous generation blades, the ps700, ps701 and ps702. The ps700 blade contains a single processor socket with a 4-core processor and eight ddr3 memory dimm slots. The ps701...
Page 62
48 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction access to a total of 8 memory buffers and therefore 16 ddr3 dimms. The ps704’s four 8-core processor chips use a single memory controller per processor chip, which connects to four memory buffers per cpu, providing access to a to...
Page 63
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 49 figure 2-9 memory dimm topology there are 16 buffered dimm slots on the ps703 and ps704 base blade shown in figure 2-9, with an additional 16 slots on the ps704 expansion unit. The ps703 and the ps704 base blade have slots labelled p1-c1 through p1-c...
Page 64
50 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction table 2-5 ps703 dimm placement rules dimm socket number dimm socket location code ps703 number of dimms to install 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 1 p1-c1 x x x x x x x x 2 p1-c2 x x x x 3 p1-c3 x x x x 4 p1-c4 x x x x x x x x 5 p1-c5 x x x ...
Page 65
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 51 for the ps704, table 2-6 shows the required placement of memory dimms depending on the number of dimms installed. The recommended practice is to match the dimms between the two system planars. Table 2-6 ps704 dimm placement dimm socket number dimm so...
Page 66
52 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 2.5 active memory expansion optional active memory expansion is a power7 technology that allows the effective maximum memory capacity to be much larger than the true physical memory. Innovative compression/decompression of memory...
Page 67
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 53 to help you perform this study, a planning tool is included with aix 6.1 technology level 4 or later allowing you to sample actual workloads and estimate both how expandable the partition's memory is and how much cpu resource is needed. Any model pow...
Page 68: 2.6 Technical Comparison
54 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 2.6 technical comparison table 2-7 shows a comparison of the technical characteristics of the ps700, ps701, ps702, ps703, and ps704. Table 2-7 comparison of technical characteristics between ps700, ps701, ps702, ps703, and ps704 ...
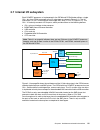
Page 69: 2.7 Internal I/o Subsystem
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 55 2.7 internal i/o subsystem each power7 processor as implemented in the ps703 and ps704 blades utilizes a single gx++ bus from cpu0 to connect to the i/o subsystem as shown in figure 2-12. The i/o subsystem is a gx++ multifunctional host bridge asic c...
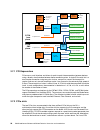
Page 70
56 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 2-13 ps704 i/o hub subsystem architecture 2.7.1 pci express bus pcie uses a serial interface and allows for point-to-point interconnections between devices using a directly wired interface between these connection points. ...
Page 71
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 57 support extends to the majority of frequently used devices, although various third-party pci devices might not provide native eeh support. Expansion card form factors there are two pcie card form factors supported on the ps703 and ps704 blades: ciov ...
Page 72
58 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 2-14 shows the locations of the pcie ciov and cffh connectors, and the physical location codes for the ps703. Figure 2-14 ps703 location codes for pcie expansion cards figure 2-15 shows the locations of the pcie ciov and c...
Page 73
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 59 figure 2-16 shows the locations of the pcie ciov and cffh connectors for the ps702 expansion blade (feature code 8358) and the physical location codes. Figure 2-16 ps704 expansion blade location codes for pcie expansion cards bladecenter i/o topology...
Page 74
60 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 2-17 bladecenter h i/o topology figure 2-18 bladecenter ht i/o topology blade server 14 blade server 1 on-board 1gbe cffv cffh expansion cards i/o bay 7 i/o bay 9 i/o bay 8 i/o bay 10 i/ o b ay 5 i/ o b a y 6 i/ o b a y 3 ...
Page 75
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 61 figure 2-19 bladecenter s i/o topology 2.7.3 i/o expansion cards i/o expansion cards can provide additional resources that can be used by a native operating system, the virtual i/o server (vios), or assigned directly to a lpar by the vios. See 1.6.7,...
Page 76
62 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction the 3 gb sas passthrough expansion card is a 2-port pcie ciov form factor card. The output from the ports on this card is routed through the bladecenter mid-plane to i/o switch bays 3 and 4. Fibre channel adapters the ps703 and p...
Page 77
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 63 top-of-rack switch. A combination of the appropriate i/o switch module in these bays and the proper fibre channel-capable modules in bays 3 and 5 can eliminate the top-of-rack switch requirement. See 1.7, “supported bladecenter i/o modules” on page 2...
Page 78
64 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction the bcm5387 is connected to the fsp to provide its connection to the chassis for sol connectivity. See 2.8.1, “server console access by sol” on page 65 for more details concerning the sol connection. Mac addresses for bcm5709s et...
Page 79: 2.8 Service Processor
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 65 2.8 service processor the flexible service processor (fsp) is used to monitor and manage the system hardware resources and devices. In a power7-based blade implementation the external network connection for the service processor is routed through an ...
Page 80
66 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 2-21 sol service processor to amm connection bladecenter components are configured for sol operation through the bladecenter amm. The amm also acts as a proxy in the network infrastructure to couple a client running a teln...
Page 81
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 67 the ethernet switch module must be set up correctly. For details about setting up sol, see the bladecenter serial over lan setup guide, which can be found at the following web page: http://ibm.Com/support/entry/portal/docdisplay?Lndocid=migr-54666 th...
Page 82: 2.9 Internal Storage
68 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 2.9 internal storage ps703 and ps704 blades use a single integrated 3 gb sas controller. The controller attaches to the io hub pcie gen1 connector operating at 2.5 gbps. The ps704 has a single embedded sas controller located on t...
Page 83
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 69 figure 2-24 shows the physical locations and codes for the hdds in the ps703. Figure 2-24 hdd location and physical location code ps703 in the ps704 blade, the sas controller is located on the smp planar. A total of eight sas ports are used in the ps...
Page 84
70 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 2-25 ps704 sas configuration figure 2-26 shows the physical location and code for a hdd in a ps704 base planar. Figure 2-26 hdd location and physical location code ps704 base planar x8 gen1 p7ioc i/o hub hdd/ssd connector ...
Page 85
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 71 figure 2-27 shows the physical location and code for a hdd in a ps704 smp planar. Figure 2-27 hdd location and physical location code ps704 smp planar figure 2-28 shows the sata ssd interposer card used to connect the 1.8-inch sata ssd drives to the ...
Page 86
72 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 2.9.1 hardware raid function for the ps703, the supported raid functions are as follows: 1 hdd - raid 0 1 ssd - raid 0 2 ssds - raid 0, 10 for the ps704, the supported raid functions are as follows: 2 hdds - raid 0, 10 1 hdd and ...
Page 87
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 73 for more information, see “using the disk array manager” in the systems hardware information center at: http://publib.Boulder.Ibm.Com/infocenter/systems/scope/hw/index.Jsp?Topic=/arebj/s asusingthesasdiskarraymanager.Htm 2.9.2 external sas connection...
Page 88
74 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction on-board sas controller on the blade itself in conjunction with the sas passthrough card installed into the blade server. Table 2-9 lists the basic local storage solution components for bladecenter s. Table 2-9 basic local storag...
Page 89
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 75 figure 2-29 sas i/o connections with one sas connectivity module installed figure 2-30 shows a sample connection topology for basic local storage with two sas connectivity modules installed. Figure 2-30 sas i/o connections with two sas connectivity m...
Page 90
76 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction keep the following considerations in mind when planning bladecenter s basic local storage implementations: every blade requiring integrated storage connectivity must have one sas connectivity card installed. At least one dsm must...
Page 91
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 77 advanced shared storage using the sas raid controller module the main feature of advanced shared storage for bladecenter s is the ability to: create storage pools from hard disks in disk storage modules create logical volumes in these pools assign th...
Page 92
78 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 2-31 shows a sample topology for bladecenter s with two sas raid controller modules. Figure 2-31 bladecenter s sas raid controller connections topology keep these considerations in mind when planning bladecenter s advanced...
Page 93
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 79 – maximum number of volumes is 16 per blade server (maximum of 128 volumes per chassis). – one volume can be mapped to all 6 blades in the chassis. Mixing hdds of different capacities in a single volume is supported. However, the total volume size is...
Page 94
80 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction ibm system storage ds3000 family the ibm system storage ds3000 is an entry-level storage system designed to meet the availability and consolidation needs for a wide range of users. New features, including larger capacity 450 gb s...
Page 95: 2.11 Ivm
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 81 features and five-nines availability. In today’s dynamic, global business environment, where organizations need information to be reliably available around the clock and with minimal delay, the ds8000 series can be an ideal solution. With its tremend...
Page 96
82 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction table 2-13 comparison of ivm, hmc, and sdmc characteristic ivm hmc sdmc general characteristics delivery vehicle integrated into the server a desktop or rack-mounted appliance hardware/software appliance footprint runs in 60 mb m...
Page 97
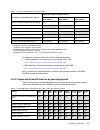
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 83 2.12 operating system support the ibm power7 processor-based systems support three families of operating systems: aix ibm i linux in addition, the virtual i/o server can be installed in special partitions that provide support to the other operating s...
Page 98
84 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction virtual i/o server virtual i/o server 2.2.0.12-fp24 sp02 or later ibm regularly updates the virtual i/o server code. To find information about the latest updates, see the virtual i/o server at the following web page: http://www14...
Page 99: 2.13 Ibm Energyscale
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 85 linux linux is an open source operating system that runs on numerous platforms from embedded systems to mainframe computers. It provides a unix®-like implementation in many computer architectures. At the time of this writing, the supported versions o...
Page 100
86 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction performance per watt, or reduce frequency to save energy. This feature is called turbo-mode. 2.13.1 ibm energyscale technology this section describes ibm energyscale design features, and hardware and software requirements. Ibm en...
Page 101
Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 87 performance is favored over energy consumption, the maximum frequency will be at least 100% of nominal. Dynamic power saver mode is mutually exclusive with power saver mode. Only one of these modes can be enabled at a given time. Power capping power ...
Page 102
88 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction report blade power consumption to the amm through the service processor. Report blade system voltage levels to the amm through the service processor. Accommodate bladecenter/amm defined thermal triggers such as warning temperatur...
Page 103: Virtualization
© copyright ibm corp. 2011. All rights reserved. 89 chapter 3. Virtualization ibm advance power virtualization (powervm) is a feature use to consolidate workload to deliver cost savings and improve infrastructure responsiveness. As you look for ways to maximize the return on your it infrastructure i...
Page 104
90 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 3.1 powervm version 2.2 enhancements the latest available powervm version 2.2 contains the following enhancements: support for up to 160 lpars on ps703 support for up to 320 lpars on ps704 support for up to 80 lpars on power 710 ...
Page 105
Chapter 3. Virtualization 91 the ibm powervm workload partitions manager™ for aix, version 2.2 has the following enhancements: when used with aix 6.1 technology level 6, the following support applies: – support for exporting vios scsi disk into a wpar. Compatibility analysis and mobility of wpars wi...
Page 106: 3.2 Power Hypervisor
92 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 3.2 power hypervisor combined with features designed into the power7 processors, the power hypervisor delivers functions that enable capabilities, including dedicated processor partitioning, micro-partitioning, virtual processors...
Page 107
Chapter 3. Virtualization 93 table 3-1 configured memory-to-default lmb size physical memory assigned to partitions are in increments of lmb. The power hypervisor provides the following types of virtual i/o adapters: virtual scsi virtual ethernet virtual fibre channel virtual (tty) console virtual i...
Page 108
94 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction each operating system partition detects the virtual local area network (vlan) switch as an ethernet adapter without the physical link properties and asynchronous data transmit operations. Any virtual ethernet can also have connec...
Page 109
Chapter 3. Virtualization 95 figure 3-1 connectivity between virtual fibre channels adapters and external san devices virtual serial adapters (tty) console virtual serial adapters provide a point-to-point connection from one logical partition to another, the hardware management console (hmc), or the...
Page 110: 3.3 Power Processor Modes
96 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 3.3 power processor modes although, strictly speaking, they are not a virtualization feature, power modes are described in this section because they affect certain virtualization features. On power system servers, partitions can ...
Page 111: 3.4 Powervm
Chapter 3. Virtualization 97 figure 3-3 shows how to choose a processor compatibility mode from ivm. Figure 3-3 configuring partition profile compatibility mode from ivm table 3-2 lists the differences between these modes. Table 3-2 differences between power6 and power7 mode 3.4 powervm the powervm ...
Page 112
98 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction powervm lx86, live partition mobility (lpm), active memory sharing (ams), suspend/resume, and n_port id virtualization (npiv) are included within the powervm family. As with advanced power virtualization in the past, powervm is a...
Page 113
Chapter 3. Virtualization 99 table 3-4 powervm capabilities by edition for power7-based blades the powervm editions web site also contains useful information: http://www.Ibm.Com/systems/power/software/virtualization/editions 3.4.2 logical partitions logical partitions (lpars) and virtualization incr...
Page 114
100 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction the power hypervisor abstracts the physical processors and presents a set of virtual processors to the operating system within the micro-partitions on the system. The operating system sees only the virtual processors and dispatc...
Page 115
Chapter 3. Virtualization 101 virtual processors do not introduce any additional abstraction level. They are only a dispatch entity. On a physical processor, virtual processors run at the same speed as the physical processor. Each partition’s profile defines cpu entitlement, which determines how muc...
Page 116
102 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction increase system use without compromising the computing power for critical workloads in a dedicated processor. Figure 3-5 shows how the dedicated shared processor mode can be configured. Figure 3-5 ivm console shows how to config...
Page 117
Chapter 3. Virtualization 103 figure 3-6 overview of the architecture of multiple shared-processor pools micro-partitions are created and then identified as members of either the default shared-processor pool 0 or a user-defined shared-processor pool n . The virtual processors that exist within the ...
Page 118
104 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction table 3-5 attribute values for the default shared-processor pool (spp 0 ) creating multiple shared-processor pools the default shared-processor pool (spp 0 ) is automatically activated by the system and is always present. All ot...
Page 119
Chapter 3. Virtualization 105 figure 3-8 shows the virtual server aix1 assigned to processor pool itsopool1. Figure 3-8 virtual server assignments to processor pools shown by an sdmc levels of processor capacity resolution there are two levels of processor capacity resolution implemented by the powe...
Page 120
106 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 3-9 the two levels of unused capacity redistribution capacity allocation above the entitled pool capacity (level 1 ) the power hypervisor initially manages the entitled pool capacity at the shared-processor pool level. Th...
Page 121
Chapter 3. Virtualization 107 where there is unused processor capacity in underutilized shared-processor pools, the micro-partitions within the shared-processor pools cede the capacity to the power hypervisor. In busy shared-processor pools where the micro-partitions have used all of the entitled po...
Page 122
108 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction because several simultaneous micro-partition migrations are supported by powervm live partition mobility, it is conceivable to migrate the entire shared-processor pool from one server to another. 3.4.4 vios the vios is part of a...
Page 123
Chapter 3. Virtualization 109 layer 2, the original mac address and vlan tags of the packet are visible to other systems on the physical network. Ieee 802.1 vlan tagging is supported. The sea also provides the ability for several client partitions to share a physical adapter. Using an sea, you can c...
Page 124
110 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction for a more detailed discussion about virtual networking, see the following web page: http://www.Ibm.Com/servers/aix/whitepapers/aix_vn.Pdf virtual scsi virtual scsi is provided by the power hypervisor and provides a virtualized ...
Page 125
Chapter 3. Virtualization 111 figure 3-12 architectural view of virtual scsi at the time of writing, virtual scsi supports fibre channel, parallel scsi, iscsi, sas, scsi raid devices, and optical devices (including dvd-ram and dvd-rom). Other protocols such as ssa and tape devices are not supported....
Page 126
112 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction for more information about the virtual i/o server and its implementation, see ibm powervm virtualization introduction and configuration, sg24-7940, available from the following web page: http://www.Redbooks.Ibm.Com/abstracts/sg2...
Page 127
Chapter 3. Virtualization 113 optimize the server. Consolidate workloads running on several small, under-used servers onto a single large server. System requirements for partition mobility both source and destination systems must have the powervm enterprise edition license code installed. The source...
Page 128
114 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction the sdmc or ivm is used to configure, validate, and orchestrate live partition mobility on power-based blades. Use the sdmc to enable mover service function for virtual i/o server; an sdmc or ivm wizard validates your configurat...
Page 129
Chapter 3. Virtualization 115 figure 3-13 active memory sharing block diagram with shared and dedicated memory 3.4.8 suspend/resume suspend/resume partition or virtual server can provide long-term suspension of partitions. Partition state (memory, nvram, and vsp state) is saved on persistent storage...
Page 130
116 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 3.4.9 n_port id virtualization (npiv) n_port id virtualization (npiv) is a technology that allows multiple logical partitions to access independent physical storage through the same physical fibre channel adapter. Npiv provides ...
Page 131
Chapter 3. Virtualization 117 table 3-7 npiv compatibility matrix for ibm i client for additional information about npiv, see the following resources: powervm migration from physical to virtual storage, sg24-7825 http://www.Redbooks.Ibm.Com/abstracts/sg247825.Html ibm powervm virtualization managing...
Page 132
118 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction for more information see “supported features for linux on power systems servers” in the linux on power infocenter: http://publib.Boulder.Ibm.Com/infocenter/lnxinfo/v3r0m0/index.Jsp?Topic=/liaam/sup portedfeaturesforlinuxonpowers...
Page 133: Continuous Availability and
© copyright ibm corp. 2011. All rights reserved. 119 chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability this chapter provides information about ibm reliability, availability, and serviceability (ras) design and features. This set of technologies, implemented on ibm power systems servers, provides ...
Page 134: 4.1 Introduction
120 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 4.1 introduction each successive generation of ibm servers is designed to be more reliable than the previous server family. Power7 processor-based servers have new features to support new levels of virtualization, ease administr...
Page 135: 4.3 Availability
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 121 4.2.1 designed for reliability systems designed with fewer components and interconnects have fewer opportunities to fail. Simple design choices (such as integrating processor cores on a single power chip) can reduce the opportunity for system ...
Page 136
122 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction self-diagnose and self-correct during run time automatically reconfigure to mitigate potential problems from suspect hardware self-heal or substitute good components for failing components automatically throughout this chapter, ...
Page 137
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 123 action to deconfigure the faulty hardware to avoid a potential system outage and to enhance system availability. Persistent deallocation to enhance system availability, a component that is identified for deallocation or deconfiguration on a po...
Page 138
124 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction if there are available inactivated processor cores or capacity-on-demand (cod) processor cores, the system effectively puts a cod processor into operation after it has been determined that an activated processor is no longer ope...
Page 139
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 125 dynamically when a fault occurs. In addition, the memory bus has spare capacity to substitute a spare data bit-line that is determined to be faulty. Chipkill chipkill is an enhancement that enables a system to sustain the failure of an entire ...
Page 140
126 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 4-1 shows a power7 chip as implemented on a ps703 or ps704 blade, with its memory interface comprised of one controller and four advanced memory buffers. Advanced memory buffer chips are exclusive to ibm. They help to inc...
Page 141
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 127 lpar operation), the power hypervisor warns the operating system when memory pages are included that need to be deallocated. If an uncorrectable error in memory is discovered, the logical memory block that is associated with the address with t...
Page 142
128 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction system memory to reload the cache line from main memory. Modified data would be handled through special uncorrectable error handling. L2 and l3 deleted cache lines are marked for persistent deconfiguration on subsequent system r...
Page 143: 4.4 Serviceability
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 129 4.3.6 pci extended error handling ibm estimates that pci adapters can account for a significant portion of the hardware-based errors on a large server. Although servers that rely on boot-time diagnostics can identify failing components to be r...
Page 144
130 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction client control of the service environment extends to firmware maintenance on all of the power processor-based systems. This strategy contributes to higher systems availability with reduced maintenance costs. This section provide...
Page 145
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 131 platform errors are faults related to: the sysplanar: that part of the server composed of the central processor units, memory, storage controls, and the i/o hubs the power and cooling subsystems the firmware used to initialize the system and d...
Page 146
132 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction – the server input voltages are out of operational specification the service processor can immediately shut down a system in the following circumstances: – temperature exceeds the critical level or if the temperature remains bey...
Page 147
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 133 root cause of the fault is captured without the need to recreate the problem or run an extended tracing or diagnostics program. For the vast majority of faults, a good ffdc design means that the root cause is detected automatically without int...
Page 148
134 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction service threshold (meaning that a service action point has been reached) a request for service is initiated through an error logging component. 4.4.2 diagnosing using the extensive network of advanced and complementary error det...
Page 149
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 135 which logs the error. I/o devices can also include specific exercisers that can be invoked by the diagnostic facilities for problem recreation if required by service procedures. 4.4.3 reporting in the unlikely event that a system hardware or e...
Page 150
136 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction a similar process is performed by the sdmc. The problem analysis component of the sdmc handles the detection and analysis of serviceable events. The problem analysis resides within the ssm. The ssm receives the errors directly f...
Page 151
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 137 client notify events are serviceable events by definition because they indicate that something has happened that requires client awareness in the event they want to take further action. These events can be reported back to ibm at the client’s ...
Page 152
138 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction tool-less design selected ibm systems support tool-less or simple tool designs. These designs require no tools or simple tools such as flathead screwdrivers to service the hardware components. Positive retention positive retenti...
Page 153
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 139 figure 4-3 amm blade led details the system can clearly identify components for replacement by using specific component-level leds, and can also guide the servicer directly to the component by signaling (turning on solid) the system fault led,...
Page 154
140 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction location codes, drawings of physical locations, concurrent maintenance status, or other data pertinent to a repair. Location diagrams are especially useful when multiple components are installed, such as dimms, cpus, processor b...
Page 155: 4.5 Manageability
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 141 the following repair scenarios are covered by r&v: replacing a defective field-replaceable unit (fru) reattaching a loose or disconnected component correcting a configuration error removing or replacing an incompatible fru updating firmware, d...
Page 156
142 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction the system unit can be in the following states: standby (power off) operating, ready to start partitions operating with running logical partitions the service processor is used to monitor and manage the system hardware resources...
Page 157
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 143 ivm service management the following functions are available through the ivm service management: electronic service agent or esa (for more information see 4.5.3, “electronic service agent and service and support manager” on page 147) service f...
Page 158
144 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction the following sources can generate events that are recorded in the event log: blade service processor bladecenter unit blade device by bay number bladecenter service advisor the bladecenter service advisor provides a method to n...
Page 159
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 145 figure 4-4 support for ibm systems web page after selecting the bladecenter link you will be directed the bladecenter section of the ibm support portal (figure 4-5 on page 146). From this page the specific bladecenter chassis or blade type and...
Page 160
146 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 4-5 bladecenter entry into ibm support portal the current running level and boot side (a or b) of the firmware can be displayed from the amm or the sdmc. The running, temporary, and permanent firmware version levels can a...
Page 161
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 147 4.5.3 electronic service agent and service and support manager ibm has transformed its delivery of hardware and software support services to help you achieve higher system availability. Electronic services is a web-enabled solution that offers...
Page 162
148 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 4.5.4 bladecenter service advisor ibm bladecenter service advisor comes standard in all bladecenter chassis that have an amm. After being configured and activated, a service event on the bladecenter chassis can be reported to ib...
Page 163
Chapter 4. Continuous availability and manageability 149 on the event log page of the advanced management module web interface, you can select the display call home flag checkbox. If you select the checkbox, events are marked with a c for call home events and an n for events that are not called home...
Page 164
150 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction.
Page 165: Systems Director Management
© copyright ibm corp. 2011. All rights reserved. 151 chapter 5. Systems director management console the systems director management console (sdmc) is the successor to the hardware management console (hmc) and the integrated virtualization manager (ivm). This chapter highlights some of the new concep...
Page 166: 5.1 Sdmc Introduction
152 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 5.1 sdmc introduction the sdmc is an extension to ibm systems director. The sdmc is available in two appliance versions, hardware and software. The sdmc is designed to replace both the hmc and ivm for power-based systems managem...
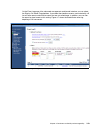
Page 167
Chapter 5. Systems director management console 153 table 5-1 power6 support by sdmc table 5-2 power7 support by sdmc power6 models machine types hmc or ivm systems director management console rack systems 595 9119-fha hmc hardware appliance only 575 9125-f2a hmc hmc only 570 9117-mma hmc hardware ap...
Page 168
154 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 5.1.4 terminology sdmc uses the terminology that has been established in ibm systems director. Many of the terms used in the hmc and ivm context have changed with sdmc. Table 5-3 correlates some of the more common hmc and ivm te...
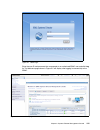
Page 169
Chapter 5. Systems director management console 155 figure 5-1 sdmc login enter the user id and password that corresponds to an authorized sdmc user and click log in. The welcome page shown in figure 5-2 will display after logging in successfully to the sdmc. Figure 5-2 sdmc welcome page.
Page 170
156 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction sdmc has the same navigation method on the left side of the user interface as ibm systems director, and essentially the same base functionality. After the login process, the sdmc begins with the sdmc welcome page. This page has ...
Page 171
Chapter 5. Systems director management console 157 5.2.2 settings tab the settings tab provides the interface to the tasks that are related to managing your sdmc appliance itself. These tasks are shown in figure 5-3. Figure 5-3 settings tab tasks you can click any of the tasks, which opens a new pag...
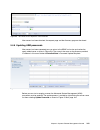
Page 172: 5.4 Ivm to Sdmc Transition
158 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction the hardware management console (hmc) functions with a typical rack-based power system. Characteristics of an ivm-managed system are: runs on top of a virtual i/o server administers power-based blade servers and entry power serv...
Page 173
Chapter 5. Systems director management console 159 5.4.1 ivm to sdmc transition process the transition process is performed manually for the ivm to sdmc transition. The transition wizard available for hmc to sdmc moves cannot be used for ivm to sdmc transitions. Prior to the transition the managed s...
Page 174
160 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction the event log page for the success or failure of the transition process. When the transition completes successfully, the following message is posted in the event log: the ivm to sdmc transition completed successfully the status ...
Page 175
Chapter 5. Systems director management console 161 2. Click the desired blade from the list displayed. Figure 5-4 shows the network configuration information and settings that relate to the fsp, allowing it to be present on the network. Figure 5-4 setting fsp ip address 5.4.4 discovery the server di...
Page 176
162 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 5-6 shows the ps703 server after the discovery process has been completed. After discovery the next step is to request access. Figure 5-6 ps703 fsp after initial discovery 5.4.5 request access to server after discovery bu...
Page 177
Chapter 5. Systems director management console 163 figure 5-8 successful access request to fsp on ps703 after access has been obtained, the request page and the discovery page can be closed. 5.4.6 updating asm passwords after access has been requested you can return to the sdmc main view and review ...
Page 178
164 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 5-10 starting asm/fsp password update process figure 5-11 show the page used to set/update the various asm passwords. After the password values are entered click ok. Figure 5-11 updating/setting asm passwords the discover...
Page 179
Chapter 5. Systems director management console 165 serial number. The change in the name is the result of the previous step, which allows full access to the fsp. Figure 5-12 starting inventory collection from the sdmc select view and collect inventory to access an additional page that will show you ...
Page 180
166 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction 5.5.1 virtual server creation previous to sdmc, integrated virtualization manager was required as the management device for power-based blades. Ivm would install as part of the virtual i/o server lpar in position 1, then additio...
Page 181
Chapter 5. Systems director management console 167 figure 5-14 virtual server creation wizard step 1 next you assign memory to the virtual server (figure 5-15). Virtual servers for vios only have the option for dedicated memory. Virtual servers for ibm i or aix/linux can be assigned dedicated or sha...
Page 182
168 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 5-16 virtual server creation wizard step 3: processor assignment virtual ethernet adapter assignment is the next step. Figure 5-17 shows the default number of virtual adapters is two. Figure 5-17 virtual server creation w...
Page 183
Chapter 5. Systems director management console 169 figure 5-18 editing a virtual ethernet adapter virtual storage adapters can be added next, as shown in figure 5-19. Figure 5-19 virtual server creation wizard step 5: virtual storage adapter creation the types of virtual storage adapters available a...
Page 184
170 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 5-20 virtual server creation wizard step 5: virtual storage adapter type selection physical adapter selection is the next step in the wizard. All the physical adapters in the system can be displayed, or toggled to only sh...
Page 185
Chapter 5. Systems director management console 171 figure 5-22 virtual server creation wizard step 7: summary page click finish on the summary page to view a panel displaying the new virtual server (figure 5-23). Figure 5-23 sdmc showing new virtual server and status information a profile is created...
Page 186
172 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 5-24 accessing a virtual server profile when the managed profiles page opens a list of profiles associated with the virtual server is shown. Figure 5-25 shows a single profile that has a status of being the default profil...
Page 187
Chapter 5. Systems director management console 173 figure 5-26 editing and creating new virtual server profiles after a new profile is created it will be included in the profile list as shown in figure 5-27. Figure 5-27 list of available profiles for a virtual server 5.5.3 dual vios on power-based b...
Page 188
174 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction a dual vios environment setup requires the creation of the two virtual servers, both of which are set for a vios environment. After the virtual servers are created with the appropriate environment setting and physical resources ...
Page 189
Chapter 5. Systems director management console 175 figure 5-28 dual vios configuration on a ps704 once the two virtual i/o servers are installed, the normal methods of creating a share ethernet adapter (sea) failover for virtual networking, and redundant paths for the client virtual server disks (np...
Page 190
176 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 5-30 starting the suspend operation on a virtual server 5.5.5 active memory expansion (ame) active memory expansion is the ability to expand the memory available to an aix virtual server beyond the amount of assigned phys...
Page 191
Chapter 5. Systems director management console 177 5.5.6 virtual consoles from the sdmc ivm-managed power-based blades can have console sessions to the vios from either the vios virtual console function or serial over lan (sol) through the bladecenter amm. Client lpars in a vios/ivm environment can ...
Page 192
178 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction figure 5-33 opening a console to a virtual server when the operation completes a separate window will be opened for the console that will require the same password as the current id login to the sdmc before the connection comple...
Page 193: Abbreviations and Acronyms
© copyright ibm corp. 2011. All rights reserved. 179 ac alternating current amd advanced micro devices amm advanced management module arp address resolution protocol asic application-specific integrated circuit asmi advanced system management interface bios basic input output system bist built-in se...
Page 194
180 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction lun logical unit number mac media access control mes miscellaneous equipment specification mpi message passing interface msim multi-switch interconnect module msp mover service partition mtu maximum transmission unit nasa nation...
Page 195: Related Publications
© copyright ibm corp. 2011. All rights reserved. 181 related publications the publications listed in this section are considered particularly suitable for a more detailed discussion of the topics covered in this paper. Ibm redbooks documents for information about ordering these publications, see “ho...
Page 196: Online Resources
182 ibm bladecenter ps703 and ps704 technical overview and introduction online resources this web site is also relevant as further information sources: ibm bladecenter ps700, ps701, and ps702 express home page http://ibm.Com/systems/bladecenter/hardware/servers/ps700series how to get redbooks you ca...
Page 198: Red
® redp-4744-00 international technical support organization building technical information based on practical experience ibm redbooks are developed by the ibm international technical support organization. Experts from ibm, customers and partners from around the world create timely technical informat...