- DL manuals
- IBM
- Storage
- DDRS-39130 - Ultrastar 9.1 GB Hard Drive
- Specifications
IBM DDRS-39130 - Ultrastar 9.1 GB Hard Drive Specifications
Summary of DDRS-39130 - Ultrastar 9.1 GB Hard Drive
Page 1
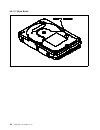
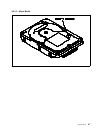
Oem hard disk drive specifications for ddrs-39130 / ddrs-34560 3.5-inch hard disk drive ( 9130 / 4560 mb ) revision (2.0) s00k-0097-03.
Page 3: Ddrs-39130 / Ddrs-34560
Oem hard disk drive specifications for ddrs-39130 / ddrs-34560 3.5-inch hard disk drive ( 9130 / 4560 mb ) revision (2.0) s00k-0097-03.
Page 4
1st edition (rev.0.1) s00k-0097-00 (aug. 29, 1997) preliminary 2nd edition (rev.1.0) s00k-0097-01 (oct. 15, 1997) 3rd edition (rev.1.1) s00k-0097-02 (oct. 30, 1997) 4th edition (rev.2.0) s00k-0097-03 (mar. 06, 1998) the following paragraph does not apply to the united kingdom or any country where su...
Page 5: Contents
Contents 1.0 general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 1.1 introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 1.2 references . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 6
6.3.3 80-pin model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38 6.4 environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39 6.5 cooling requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 7
7.6.3 inquiry data format - evpd = 1 - page code = 80h . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75 7.7 l o g select (4c) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76 7.8 l o g sense (4d) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 8
7.32 synchronize cache (35) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148 7.33 test u n i t r e a d y (00) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149 7.34 verify (2f) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 9
10.1.6 command processing during start-up and format operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183 10.1.7 internal error condition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184 10.1.8 deferred error . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 10
12.2.4 sense key (bit 3 - 0 of byte 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206 12.2.5 information bytes (byte 3 thru 6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207 12.2.6 additional sense length (byte 7) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 14
4 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 15
Part 1. Functional specification copyright ibm corp. 1997 5.
Page 16
6 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 17: 2.1 Control Electronics
2.0 fixed disk subsystem description 2.1 control electronics the drive is electronically controlled by a microprocessor, several logic modules, digital/analogue modules, and various drivers and receivers. The control electronics perform the following major functions: conducts a power-up sequence and...
Page 18
8 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 19: 3.0 Drive Characteristics
3.0 drive characteristics this chapter provides the characteristics of the drive. 3.1 formatted capacity figure 1. Formatted capacity 3.2 data sheet description ddrs-39130 ddrs-34560 label capacity (mb) 9130 4560 bytes per sector 512 512 sectors per track 165-264 165-264 number of heads 10 5 number ...
Page 20: 3.3 Cylinder Allocation
3.3 cylinder allocation mode page 03 (format device parameters) and 0c (notch parameters) provide methods to determin medium format and zone parameters. See 7.9.6, “page 3 (format device parameters)” on page 102, and 7.9.11, “page 0c (notch parameters)” on page 110. 3.4 performance characteristics a...
Page 21
3.4.1 command overhead command overhead is defined as the time required: from last byte of command phase to the first byte of data phase excluding − physical seek time − latency time − initiator delay with reconnections figure 3. Command overhead 3.4.2 mechanical positioning 3.4.2.1 average seek tim...
Page 22
3.4.2.2 full stroke seek full stroke seek is measured as the average of 1000 full stroke seeks with a random head switch from both directions (inward and outward). 3.4.2.3 cylinder switch time (cylinder skew) a cylinder switch time is defined as the amount of time required by the fixed disk access t...
Page 23
3.4.3 drive ready time ready the condition in which the drive is able to perform a media access command (eg. Read, write) immediately. If a command is received during power on before ready, the drive ready time becomes longer than the specified value. Power on this includes the time required for the...
Page 24
Sustained disk-buffer transfer rate (mbyte/sec) is defined by considering head/cylinder change time. This gives a local average data transfer rate. It is derived by: (sustained transfer rate) = a/ ( b + c + d ) a = (number of data sectors per cylinder) * 512 b = ((# of surface per cylinder) - 1) * (...
Page 25
3.4.7 throughput 3.4.7.1 simple sequential access the above table gives the time required to read/write for a total of 8000x consecutive blocks (16,777,216 bytes) accessed by 128 read/write commands. Typical and max values are given by 105% and 110% of t respectively throughput following performance...
Page 26
16 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 27: 4.0 Data Integrity
4.0 data integrity the drive retains recorded information under all non-write operations. N o more than one sector can be lost by power down during write operation while write cache is disabled. If power down occurs before completion of data transfer from write cache to disk while write cache is ena...
Page 28
18 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 29: 5.0 Physical Format
5.0 physical format media defects are remapped to the next available sector during format process in manufacturing. The mapping from lba to the physical locations is calculated by an internal maintained table. 5.1 shipped format (plist) data areas are optimally used. N o extra sector is wasted as a ...
Page 30
20 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 31: 6.0 Specification
6.0 specification 6.1 electrical interface specification 6.1.1 connectors 6.1.1.1 power connector power pin assignment of 80-pin (sca-2) model is shown in 6.1.1.5, “scsi signal connector (80-pin se)” on page 25 and 6.1.1.6, “scsi signal connector (80-pin lvd)” on page 26. Power connector of 50-pin m...
Page 32
6.1.1.2 scsi signal connector (50-pin) the scsi signal connector complies with ansi scsi-2. Figure 15. Table of signals pin signal pin signal 01 03 05 07 09 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 ground ground ground ground ground ground ground ground ground ground ground ground...
Page 39
6.1.6 auxiliary connector on 68-pin model the 68-pin models contain auxiliary connector between power connector and 68-pin scsi connector in addition to option jumper block. The setting at option jumper block and the auxiliary connector work as logical or. The drive conforms sff-8009 rev3.0. Pin #1,...
Page 40: 6.2 Option Jumper Block
6.2 option jumper block the 12 positions jumper block shown below is used to select the scsi device id, auto spin up option control, unit attention option control, scsi terminator o n / o f f setting, auto start delay option control and scsi parity option control. It also provides an external light ...
Page 41
N o t e : ( x ) s h o w s p o s i t i o n n u m b e r ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ ³ ÀÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ ³ ³ g r o u n d ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ ³ 2 3 ( 1 ) 2 4 ³ ÄÄÄ Ä d a s 3 ÄÄ¿ ³ ³ ³ ³ ³ ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ ÃÄÄÄ ³ ³ 2 1 ( 2 ) 2 2 ³ ³ ÄÄÄ Ä d a s 2 ÄÄ´ ³ ³ ÀÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÙ ³ ³ ³ ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ ÃÄÄÄ ³ ³ 1 9 ( 3 ) 2 0 ³ ³ ÄÄÄ Ä ...
Page 42
6.2.1 jumper signal description throughout this paragraph o n means a shunt jumper is installed and o f f means that no shunt jumper is installed. 6.2.1.1 device address select lines. (-das0, -das1, -das2, -das3) these four lines defines ddrs-3xxxx device id on the scsi bus. -das0 is the least signi...
Page 43
6.2.1.6 disable unit attention. (position 7) grounding this pin (jumper on) enables control of uai (unit attention inhibit) bit in mode page 0. 6.2.1.7 enable ti-sdtr (50-pin) / enable ti-sdtr/wdtr (68,80-pin) grounding this pin (jumper on) enables the following. Target initiated wide data transfer ...
Page 44
6.2.1.9 disable scsi parity check (position 11) grounding this pin will disable scsi parity checking. 6.2.1.10 led pins (position 12) the l e d pins are used to drive an external light emitting diode. U p to 30 ma of sink current capability is provided. The l e d anode must be tied to the current li...
Page 46: 6.3
6.3 led circuit jumper pin #1 and #2 are used to drive an external led. Instead of the the jumper pins, the following pins can be used to drive led. 68-pin model : auxiliary connector pin #8 and #11. 80-pin model : sca-2 connector pin #77 as shown in 6.3.3, “80-pin model” on page 38. The schematics ...
Page 47
6.3.2 68-pin model d d r s Ä 3 9 1 3 0 / d d r s Ä 3 4 5 6 0 6 8 Ä p i n m o d e l : : e x a m p l e o f u s a g e : : a t s y s t e m s i d e : : : : 5 v : : o : : ³ a u x i l i a r y : : ³ c o n n e c t o r p i n # 1 1 : ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ o o ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ f o r l e d a n o d e :...
Page 48
6.3.3 80-pin model d d r s Ä 3 9 1 3 0 / d d r s Ä 3 4 5 6 0 8 0 Ä p i n ( s c a Ä 2 ) m o d e l : : e x a m p l e o f u s a g e : : a t s y s t e m s i d e : : : : + 5 v + 5 v : : + 5 v o o : : o ³ ³ : : ³ ³ ³ : : ³ > > : : > 1 k o h m : : > > : : > ³ ³ : : ³ ³ ³ : : ³ ÄÄÄÁÄÄÄ ³ : : ÄÄÄÁÄÄÄ \ / ³ :...
Page 49: 6.4 Environment
6.4 environment figure 31. Environmental condition operating conditions temperature 5 to 55[ ˚ c] (see note) relative humidity 8 to 90 [ % r h ] non-condensing maximum wet bulb temperature 29.4[ ˚ c] non-condensing maximum temperature gradient 15[ ˚ c / hour] altitude − 300 to 3048 [ m] non-operatin...
Page 50: 6.5 Cooling Requirements
6.5 cooling requirements the system has to provide sufficient ventilation to maintain a surface temperature below 60˚ c at the center of the top cover of the drive. The system has to provide sufficient ventilation to keep the limits of component temperature as shown below. Figure 32. Maximum allowab...
Page 51: 6.6 Dc Power Requirements
6.6 dc power requirements connection to the product should be made in isolated secondary circuits (selv). The following voltage specification is applied at the power connector of the drive. N o special power on/off sequencing is required. Notes: 1. 12v + / - 7 % is acceptable during spin up, but the...
Page 52
During drive start up and seeking, 12 volt ripple is generated by the drive (referred to as dynamic loading). If several files have their power daisy chained together then the power supply ripple plus other drive's dynamic loading must remain within the regulation tolerance of ± 0.5%. A common suppl...
Page 53: 6.7 Reliability
6.7 reliability 6.7.1 contact start stop (css) the drive is designed to withstand a minimum of 40,000 contact start/stop cycles at 40˚ c with 13-25% rela- tive humidity. The drive is designed to withstand a minimum of 10,000 contact start/stop cycles at operating environment conditions specified in ...
Page 54
6.7.6 automatic drive maintenance (adm) a d m function can be enabled by e a d m bit in mode page 0, and the shipping default is disable. A d m function is equipped to enhance the reliability in continuous usage. A d m function is to perform a css automatically after detection of idling time for 1 m...
Page 55
6.8 mechanical specifications 6.8.1 outline 6.8.1.1 50-pin model figure 39. Outline of 50-pin model specification 45.
Page 56
6.8.1.2 68-pin model figure 40. Outline of 68-pin model 46 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 57
6.8.1.3 80-pin model figure 41. Outline of 80-pin model specification 47.
Page 58
6.8.2 mechanical dimensions the following chart describes the dimensions and the weight. Figure 42. Physical dimension height [ m m ] 25.4 ± 0.4 width [ m m ] 101.6 ± 0.4 length [ m m ] 146.0 ± 0.6 weight [ gram] 630 max. Figure 43. Mechanical dimension 48 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 59
6.8.3 interface connector 6.8.3.1 50-pin model figure 44. Interface connector (50-pin model) specification 49.
Page 60
6.8.3.2 68-pin model figure 45. Interface connector (68-pin model) 50 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 61
6.8.3.3 80-pin model figure 46. Interface connector (80-pin model) specification 51.
Page 62
6.8.4 mounting positions and tappings figure 47. Mounting positions and tappings 52 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 63
6.8.4.1 drive mounting the drive will operate in all axes (6 directions). Performance and error rate will stay within specification limits if the drive is operated in the other orientations from which it was formatted. The recommended mounting screw torque is 0.6 - 1.0 [ n m ] (6 - 10 [ kgf.Cm]). Th...
Page 64: 6.9 Vibration And Shock
6.9 vibration and shock all vibration and shock measurements in this section are made with the drive that has no mounting attach- ments for the systems. The input power for the measurements is applied to the normal drive mounting points. 6.9.1 operating vibration 6.9.1.1 random vibration the drive i...
Page 65
6.9.2 non-operating vibrations the drive does not sustain permanent damage or loss of recorded data after being subjected to the environ- ment described below. 6.9.2.1 random vibration the test consists of a random vibration applied for each of three mutually perpendicular axes with the time duratio...
Page 66: 6.10 Acoustics
6.10 acoustics the following shows the acoustic levels. 6.10.1 sound power levels the upper limit criteria of the a-weighted sound power levels are given in bel relative to one pico watt and are shown in the following table. The measurment method is in accodance with iso7779. Background power levels...
Page 67
6.10.2 sound pressure (reference) 6.10.2.1 unit sound pressure level measurment the hard disk drives are measured in a semi-anechoic chamber, with background noise = faces to be measured are top cover side and card side. Microphone is set one meter above the drive surface. Random operation mode is s...
Page 69: 6.13 Safety
6.13 safety the following shows the safety standards for different countries. 6.13.1 underwriters lab (ul) approval ddrs-3xxxx comply with u l 1950. 6.13.2 canadian standards authority (csa) approval ddrs-3xxxx comply with csa c22.2 no.0-m91, and csa c22.2 no.950-m1993. 6.13.3 iec compliance ddrs-3x...
Page 70
60 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 71
Part 2. Scsi interface specification copyright ibm corp. 1997 61.
Page 72
62 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 73: 7.0 Scsi Command Set
7.0 scsi command set summaries of the scsi commands supported by the file are listed below. Where o=optional, m=mandatory, e=extended, r=reserved and v = v e n d o r unique. The column “scsi-1” refers to ansi version 1 standard. The column “ccs” refers to the ansi sub-committee common command subset...
Page 74: 7.1 Flag And Link Bits
ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ scsi-1 ³ ccs ³ scsi-2 ³ code ³ command ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ o ³ m ³ m ³ 00h ³ test unit ready ³ ³ o ³ o ³ o ³ 01h ³ rezero unit ³ ³ m ³ m ³ m ³ 03h ³ request sense ³ ³ m ³ m ³ m ³ 04h ³ forma...
Page 75: 7.2 Abbreviations
Link this bit is set to one to indicate that the initiator desires an automatic link to the next command upon successful completion of the current command. Upon successful completion of the command, the file will return i n t e r m e d i a t e g o o d status and then send one of the two mes- sages d...
Page 76: 7.4 Format Unit (04)
7.4 format unit (04) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code =...
Page 77
ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ reserved = 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ...
Page 78
Immed (immediate) bit set to zero requests that status be returned at the end of the format operation. An immediate bit set to one requests that status be returned immediately. Good status is returned fol- lowing the cdb validation and transfer of data in the data out phase. If the immediate format ...
Page 79
ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ (msb) ³ ³ 1 ³ cylinder number of de...
Page 80: 7.5 Inquiry (12)
7.5 inquiry (12) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = 12h...
Page 81: 7.6 Inquiry Data
7.6 inquiry data fields with a value shown inside quotes (e.G. Value = 'xyz') are character fields. A value not in quotes is a numeric value. Character fields are alpha-numeric and represented in either ascii or ebcdic as stated. Scsi c o m m a n d set 71.
Page 82
7.6.1 inquiry data format - evpd = 0 figure 61 shows the data format. ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ byte ³ ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ qualifier = 0 ³ peripheral device type = 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ...
Page 83
Ecma is set to zero to indicate that this product does not claim compliance to the european computer manufacturers association (ecma) version of scsi (ecma-111). Ansi indicates the level of the ansi standard that is supported by the product. The file supports ansi scsi version 2. Rdf is set to two t...
Page 84
7.6.2 inquiry data format - evpd = 1 - page code = 00 ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ byte ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ qualifier = 0 ³ peripheral dev type = 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 1 ³ page code = 0...
Page 85
7.6.3 inquiry data format - evpd = 1 - page code = 80h ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ byte ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ qualifier = 0 ³ peripheral dev type = 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 1 ³ page code = ...
Page 86: 7.7 Log Select (4C)
7.7 log select (4c) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = ...
Page 87: 7.8 Log Sense (4D)
7.8 log sense (4d) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = 4...
Page 88
7.8.1 log page parameters each log page begins with a four-byte page header followed by zero or more variable-length log parameters. Page header page code field identifies which log page is being transferred. The page length field specifies the length in bytes of the following log parameters. Log pa...
Page 89
7.8.2 log sense page 0 page 0 indicates the supported log sense pages. This page is used to determine which additional pages can be requested by an initiator. Byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 reserved page code = 0 1 reserved 2-3 page length = 0006h (number of pages supported) 4 first supported page 0h 6 seco...
Page 90
7.8.3 log sense page 2 this page contains counters for write errors byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 reserved page code = 02h 1 reserved 2 - 3 pagelength = 38h 4 - 5 parameter code = 00h 6 d u = 0 ds = 0 tsd = 0 e t c = 0 t m c = 0 lbin = 0 lp = 0 7 parameter length = 04h 8 - 11 errors recovered without delay...
Page 91
Byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 44 - 45 parameter code = 05h 46 d u = 0 ds = 0 tsd = 0 e t c = 0 t m c = 0 lbin = 0 lp = 0 47 parameter length = 04h 48 - 51 total bytes written 52 - 53 parameter code = 06h 54 d u = 0 ds = 0 tsd = 0 e t c = 0 t m c = 0 lbin = 0 lp = 0 55 parameter length = 04h 56 - 59 count of ...
Page 92
7.8.4 log sense page 3 this page contains counters for read errors byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 reserved page code = 03h 1 reserved 2 - 3 pagelength = 38h 4 - 5 parameter code = 00h 6 d u = 0 ds = 0 tsd = 0 e t c = 0 t m c = 0 lbin = 0 lp = 0 7 parameter length = 04h 8 - 11 errors recovered without delay ...
Page 93
The drive will attempt to read data after a seek before the head has fully settled on track. This is done to aid performance. However as a result there is a high incidence of error recovery invoked which normally uses ecc or a retry to recover the data. As a consequence of this an error recovered by...
Page 94
7.8.5 log sense page 5 this page contains counters for verify errors byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 reserved page code = 05h 1 reserved 2 - 3 pagelength = 38h 4 - 5 parameter code = 00h 6 d u = 0 ds = 0 tsd = 0 e t c = 0 t m c = 0 lbin = 0 lp = 0 7 parameter length = 04h 8 - 11 errors recovered without dela...
Page 95
The drive will attempt to read data after a seek before the head has fully settled on track. This is done to aid performance. However as a result there is a high incidence of error recovery invoked which normally uses ecc or a retry to recover the data. As a consequence of this an error recovered by...
Page 96
7.8.6 log sense page 6 this page contains counters for non-medium errors. This includes seek errors and other hardware type fail- ures. Byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 reserved page code = 06h 1 reserved 2 - 3 pagelength = 08h 4 - 5 parameter code = 00h 6 d u = 0 ds = 0 tsd = 0 e t c = 0 t m c = 0 lbin = 0 l...
Page 97
7.8.7 log sense page 3a log sense page 3a is reserved and this page of the specification is intentionally left blank. Scsi c o m m a n d set 87.
Page 98: 7.9 Mode Sense (1A)
7.9 mode sense (1a) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = ...
Page 99
1 1 report saved value. The file returns the saved value for the page code specified. Saved values are one of following : the values saved as a result of m o d e select command identical to the default values zero when the parameters are not supported the page length byte value of each page returned...
Page 100
7.9.2 mode parameter list the mode parameter list contain a header, followed by zero or more block descriptors, followed by zero or more variable-length pages. 7.9.2.1 header the six-byte command descriptor block header is defined below. 7.9.2.1.1 mode parameter header (6) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ...
Page 101
When used with the m o d e sense command, a write protect (wp) bit of zero indicates that the medium is write enabled. Block descriptor length specifies the length in bytes of the block descriptors. When used with the m o d e select command, zero or eight are supported by the file. When used with th...
Page 102
ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ byte 0 ³ ps ³ rsvd=0 ³ page code ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 1 ³ page length ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte ³ mode parameters ³ ³ 2 Ä n ³ ³ ÀÄÄÄ...
Page 103
7.9.3 page 0 (vendor unique parameters) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ³ default ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ ps ³ rsvd=0 ³ page code = 00h ³ ³ 80h ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄ...
Page 104
Scam level, scam level control bits, specify the scam function level to be supported. (shipping default = 2) arhes (automatic reassign hard error sites) bit of one indicates the drive will automatically reassign an hard read error. The error will be recovered when the lba is written. Arhes bit of ze...
Page 105
When there is a command active or in the queue, the l e d is high. Command aging limit this value is used to control the maximum time a command should wait in the command queue when the caen bit is set. Each unit of this timer is 50ms. Qpe read threshold specifies the error reporting threshold for r...
Page 106
7.9.4 page 1 (read/write error recovery parameters) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ³ default ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ ps ³ rsvd=0 ³ page code = 01h ³ ³ 81h ³ ÃÄÄÄÄ...
Page 107
Occurred, then normal d r p could result in considerable recovery action, including proceeding through all levels of d r p . R c set to 0 indicates normal interpretation of per, dte, dcr, and tb values. The r c bit setting is used by the target when reporting errors associated with the transfer of t...
Page 108
The following summarizes valid modes of operation. If an illegal mode is set the mode select command will complete successfully but the action of the file when an error occurs is undefined. Per dte dcr tb description 0 0 0 0 retries and error correction are attempted. Recovered and/or corrected data...
Page 109
1 0 0 0 the highest level error is reported at the end of transfer. Retries and error cor- rection are attempted. Recovered and/or corrected data (if any) is transferred with c h e c k c o n d i t i o n status and r e c o v e r e d e r r o r sense key set at the end of the transfer. No err the trans...
Page 110
1 1 0 0 the highest level error is reported at the end of transfer. Retries and error cor- rection are attempted. Recovered and/or corrected data (if any) is transferred with c h e c k c o n d i t i o n status and r e c o v e r e d e r r o r sense key set at the end of the transfer. No err the trans...
Page 111
7.9.5 page 2 (disconnect/reconnect parameters) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ³ default ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ ps ³ rsvd=0 ³ page code = 02h ³ ³ 82h ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄ...
Page 112
7.9.6 page 3 (format device parameters) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ default ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ³ 4.5g 9.1g ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ ps = 0 ³ rsvd=0 ³ page code = 03h ³ ³ 03h ³ ÃÄÄ...
Page 113
A value of 0 in the following parameters indicate that those are target specific. Alternate sectors per zone alternate tracks per zone alternate tracks per logical unit sectors per track specifies the number of physical sectors within each track. This field is a function of the active notch. Track s...
Page 114
7.9.7 page 4 (rigid disk drive geometry parameters) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ default ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ³ 4.5g 9.1g ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ rsvd = 0 ³ page code = 04h ³ ³ 04h...
Page 115
7.9.8 page 7 (verify error recovery parameters) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ³ default ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ ps ³ rsvd=0 ³ page code = 07h ³ ³ 87h ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅ...
Page 116
1 0 0 soft errors are reported. Ecc is applied to recover the data. 0 0 1 soft errors are not reported. Ecc is not used to recover the data. 1 0 1 soft errors are reported. Ecc is not used to recover the data. Verify retry count sets a limit on the amount of verify recovery procedure(vrp) passes the...
Page 117
7.9.9 page 8 (caching parameters) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ³ default ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ ps ³ rsvd=0 ³ page code = 08h ³ ³ 88h ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ...
Page 118
Minimum pre-fetch specifies the minimum number of lba's that the drive should read ahead after each read command. A value of zero indicates that read ahead should be terminated immediately a new command arrives, except in the case when the new command is on the current head and track. Maximum pre-fe...
Page 119
7.9.10 page a (control mode page parameters) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ³ default ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ ps ³ rsvd=0 ³ page code = 0ah ³ ³ 8ah ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄ...
Page 120
7.9.11 page 0c (notch parameters) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ³ default ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ ps ³ rsvd=0 ³ page code = 0ch ³ ³ 8ch ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄ...
Page 121
− write buffer empty ratio page 3 − alternate sector per zone − alternate track per zone − alternate track per logical unit − sector per track − track skew factor − cylinder skew factor starting boundary contains the first physical location of the active notch. The first three bytes are the cyl- ind...
Page 122
7.9.12 page 1a (power control) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ³ default ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ ps ³ rsvd ³ page code = 01ah ³ ³ 9ah ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄ...
Page 123
7.9.13 page 1c (informational exceptions control) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ³ default ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ ps ³ rsvd=0 ³ page code = 1ch ³ ³ 9ch ³ ÃÄÄÄÄ...
Page 124
Perf (performance) bit is not used. Method of reporting informational exceptions indicates the methods used by the target to report infor- mational exception conditions. Code description 0h no reporting of informational exception condition: this method instructs the target to not report informationa...
Page 125: 7.10 Mode Sense (5A)
7.10 mode sense (5a) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code =...
Page 126: 7.11 Mode Select (15)
7.11 mode select (15) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code ...
Page 127
C h e c k c o n d i t i o n status with sense key of illegal request. See 7.9, “ m o d e sense (1a)” on page 88. Note: if an initiator sends a m o d e select command that changes any parameters that apply to other initiators, the file shall generate an unit attention condition for all initiators exc...
Page 128: 7.12 Mode Select (55)
7.12 mode select (55) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code ...
Page 129: 7.13 Pre-Fetch (34)
7.13 pre-fetch (34) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = ...
Page 130: 7.14 Read (08)
7.14 read (08) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = 08h ³...
Page 131: 7.15 Read Capacity (25)
7.15 read capacity (25) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command cod...
Page 132
ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ (msb) ³ ³ byte 1 ³ logical block address ³ ³ byte 2 ³ ³ ³ byte 3 ³ (lsb) ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ...
Page 133
7.16 read defect data (37) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command ...
Page 134
Note: the file will terminate the data in phase when the allocation length has been transferred or when all available defect data has been transferred to the initiator, whichever is less. The read defect data contains a four byte header, followed by zero or more defect descriptors. 7.16.1 defect lis...
Page 135
ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ defect descriptors ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ (msb) ³ ³ byte 1 ³ cylinder number of defect ³ ³ byte 2 ³ (lsb) ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 3 ³ h...
Page 136: 7.17 Read Extended (28)
7.17 read extended (28) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command cod...
Page 137: 7.18 Read Buffer (3C)
7.18 read buffer (3c) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code ...
Page 138
ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ rsvd = 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 1 ³ (msb) buffer capacity ³ ³ byte 2 ³ ³ ³ byte 3 ³ ...
Page 139
ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ offset boundary ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 1 ³ (msb) buffer capacity ³ ³ byte 2 ³ ³ ³ by...
Page 140: 7.19 Read Long (3E)
7.19 read long (3e) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = ...
Page 141: 7.20 Reassign Blocks (07)
7.20 reassign blocks (07) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command c...
Page 142
ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ rsvd = 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 1 ³ rsvd = 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 2 ³ (msb) defect list ...
Page 143
7.21 receive diagnostics (1c) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ comma...
Page 144
Supplied format is the value supplied by the send diagnostic command it may be one of the three fol- lowing values − 000b block format − 100b bytes from index format − 101b physical sector format it specifies the format in which the address has been supplied. Translate format is the value supplied b...
Page 145: 7.22 Release (17)
7.22 release (17) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = 17...
Page 146: 7.23 Release (57)
7.23 release (57) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = 57...
Page 147: 7.24 Request Sense (03)
7.24 request sense (03) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command cod...
Page 148: 7.25 Reserve (16)
7.25 reserve (16) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = 16...
Page 149: 7.26 Reserve (56)
7.26 reserve (56) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = 56...
Page 150
Only the initiator that issued the reserve command for a l u n may release the lun, regardless of the 3rdpty option. This initiator may also release the l u n by issuing another reserve command. This super- seding reserve command releases the previous reservation when the new reservation is granted....
Page 151: 7.27 Rezero Unit (01)
7.27 rezero unit (01) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code ...
Page 152: 7.28 Seek (0B)
7.28 seek (0b) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = 0bh ³...
Page 153: 7.29 Seek Extended (2B)
7.29 seek extended (2b) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command cod...
Page 154: 7.30 Send Diagnostic (1D)
7.30 send diagnostic (1d) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command c...
Page 155
Both tests are performed as a result of the send diagnostic command. The send diagnostics will fail with c h e c k c o n d i t i o n status if it is issued while the spindle motor is not turning. (such as after stop command has been received.) note: the self diagnostic is also performed at power on ...
Page 156
Terminate with c h e c k c o n d i t i o n status with a sense of illegal request and illegal field in param- eter list. Address to translate contains the address to translate. If the logical block format is specified then the first 4 bytes of the field, i.E. Bytes 6 to 9, contain the lba and the re...
Page 157: 7.31 Start/stop Unit (1B)
7.31 start/stop unit (1b) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command c...
Page 158
7.32 synchronize cache (35) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command...
Page 159
7.33 test unit ready (00) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command c...
Page 160: 7.34 Verify (2F)
7.34 verify (2f) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = 2fh...
Page 161: 7.35 Write (0A)
7.35 write (0a) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code = 0ah ...
Page 162: 7.36 Write Extended (2A)
7.36 write extended (2a) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command co...
Page 163
7.37 write and verify (2e) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command ...
Page 164: 7.38 Write Buffer (3B)
7.38 write buffer (3b) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code...
Page 165
Buffer offset must be zero. If another value is specified, no download function are performed and the command is terminated with c h e c k c o n d i t i o n status. And file shall set sense key to illegal request and additional sense code to illegal f i e l d in cdb. Parameter list length specifies ...
Page 166
00h : main microprocessor code 81h : reserved area data any other value for the buffer id will cause the command to terminate with c h e c k c o n d i t i o n status. The file shall set sense key to illegal request and additional sense code to illegal f i e l d in cdb. Buffer offset must be zero. If...
Page 167
Any other value for the buffer id will cause the command to terminate with c h e c k c o n d i t i o n status. The file shall set sense key to illegal request and additional sense code to illegal f i e l d in cdb. 7.38.4.1 download microprocessor microcode and save (buffer_id = 00h) there are 3 type...
Page 168
If an invalid value is specified, the command is terminated with c h e c k c o n d i t i o n status . File shall set sense key to illegal request and additional sense code to illegal f i e l d in cdb. Parameter list length must be specified for the total byte length of each data set. It may also be ...
Page 169: 7.39 Write Long (3F)
7.39 write long (3f) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code =...
Page 170: 7.40 Write Same (41)
7.40 write same (41) ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ ³ bit ³ ³ byte ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ ³ 7 ³ 6 ³ 5 ³ 4 ³ 3 ³ 2 ³ 1 ³ 0 ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 0 ³ command code =...
Page 171: 8.0 Scsi Status Byte
8.0 scsi status byte upon the completion of a command, a status byte is sent to the initiator. Additional sense information may also be available depending on the contents of the status byte. The following section describes the possible values for the status byte and sense data. ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ...
Page 172
162 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 173: 9.0 Scsi Message System
9.0 scsi message system this chapter details how the message system is implemented on the file. Included is a functional description of the supported messages. 9.1 supported messages the message supported by the file is shows in figure 125. Message code direction negate atn (hex) before last ack com...
Page 174
9.1.1 command complete (00) the file sends this message to the initiator to indicate that the execution of a command has terminated and that valid status has been sent to the initiator. After successfully sending this message, the file releases all bus signals and goes to bus f r e e phase. 9.1.2 sy...
Page 175
9.1.2.1.1 on lvd receiver mode.: the tareget responds to each initiator requested transfer period as shown in the following figure figure 127 on page 165: target maximum initiator target transfer burst request response period rate ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ...
Page 176
9.1.2.2 synchronous negotiation started by the target if the file recognizes that negotiation is required, the file sends a s d r message to the initiator with minimum transfer period on the current receiver mode. The file interprets the initiator corresponding transfer period as shown in the follow...
Page 177
Target maximum initiator's transfer burst response period rate ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ 0 send message reject(async mode) n/a 12 50 nsec 20.00 mt/s 13 75 nsec 13.33 mt/s 19 100 nsec 10.00 mt/s 26 125 nsec 8.00 mt/s 32 150 nsec 6.67 mt/s 38 175 nsec 5.71 m...
Page 178
E the transfer width exponent (e) is two to the transfer width exponent bytes wide. Valid data transfer widths are 8 bits (e = 00h) and 16 bits (e = 01h). Value of e greater than 01h are reserved. 9.1.3.1 transfer width negotiation started by the initiator if the initiator recognizes that negotiatio...
Page 179
Note: if the corresponding transfer width exponent received from the initiator indicates a data transfer width that is greater than 16 bits (e > 01h) the target sends a message reject message to the initiator to indicate 8 bit data transfer mode. If the first message received from the initiator is e...
Page 180
9.1.7 initiator detected error (05) this message is sent from an initiator to inform the file that an error has been detected that does not pre- clude the file from retrying the previous c o m m a n d , d a t a and status phase. The source of the error may be either related to previous activities on...
Page 181
9.1.11 message parity error (09) this message is sent from the initiator to inform the file that the last message byte received had a parity error. If the initiator intends to send this message, the initiator must assert the a t n signal prior to its release of ack for the r e q / a c k handshake of...
Page 182
Byte value description ÄÄÄÄ ÄÄÄÄÄ ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ 0 20h simple queue tag message 21h head of queue tag message 22h ordered queue tag message 1 xxh queue tag figure 134. Queue tag messages queue tag messages are used to specify an identifier, called a queue tag, for an i/o process which establish the i_t...
Page 183
Byte value description ÄÄÄÄ ÄÄÄÄÄ ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ 0 23h ignore wide residue message 1 01h ignore figure 135. Ignore wide residue message format the ignore wide residue message is sent from the target to indicate that the number of valid bytes sent during the last r e q / a c k handshake of a data in pha...
Page 184
Note: the initiator may send the i n i t i a t o r d e t e c t e d e r r o r message as a result of an initiator detected scsi bus parity error or an internal error. Retry message in phase − the retry will be caused by the receipt of a message parity e r r o r message immediately following a message...
Page 185: 9.3 Attention Condition
9.3 attention condition the attention condition allows an initiator to inform the file that a message o u t phase is desired. The initiator may create the attention condition by asserting the a t n signal at any time except during the a r b it ra tio n or bus f r e e phases. The initiator must creat...
Page 186
9.4.1 unexpected bus free phase error condition there are several error conditions that will cause the file to immediately change to the bus f r e e phase, regardless of the state of the a t n signal. The file will not attempt to reconnect to the initiator to complete the operation that was in progr...
Page 187
9.4.6 initiator detected error message an i n i t i a t o r d e t e c t e d e r r o r message is valid after a c o m m a n d , d a t a i n / o u t or status phase has occurred. If another phase has occurred, the message is rejected. The file will, depending on the model, optionally retry the previou...
Page 188
178 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 189: 10.1 Scsi Protocol
10.0 additional information this chapter provides additional information or descriptions of various functions, features, or operating models supported by the target that are not fully described in previous chapters. 10.1 scsi protocol there are various operating conditions that prevent the target fr...
Page 190
10.1.2.1 case 1 - selection message sequence with inquiry command the i n q u i r y command is a special case in scsi. It is used to configure the bus when file ids and luns are not known. The proper response is to return the inquiry data with a peripheral drive type of 1fh which indicates that the ...
Page 191
Queue full status is returned busy status is returned if an active i/o process does exist when the target receives a new command, then the target determines how the new command should be handled based on the following rules: check condition status is returned with sense key set to aborted command fo...
Page 192
− the command would otherwise be queued(according to the rules described above)but disconnection is not allowed for the current i/o process, or if a command is queued, command execution may still be prevented at a later time when the command is dequeued to become an active i/o process. This occurs i...
Page 193
10.1.5 unit attention condition the file will generate a unit attention condition for each initiator whenever: the file has been reset. This includes power on reset, scsi bus reset, scsi bus device reset message. The mode parameters in effect for this initiator has been changed by another initiator....
Page 194
Request sense executes the command, returns a sense key of n o t r e a d y and an additional sense code of logical u n i t n o t r e a d y and returns g o o d status. The additional sense code qualifier that is returned depends on type of i/o proc- esses that are active: for the start/stop u n i t a...
Page 195
10.1.9 degraded mode there are certain errors or conditions which may impair the file's ability to function normally. Rather than fail hard, the file is designed to be as responsive as possible. Also, in most cases, some action on the part of the initiator may be used to restore normal operation. Th...
Page 196
10.1.11 command processing while reserved a logical unit is reserved after successful execution of the reserve command. Each time a reserve command is executed successfully, the target records the scsi id of the initiator that made the reservation and the scsi id of the initiator that is to receive ...
Page 197: 10.2 Priority Commands
If a reservation conflict status is not reported and the command is permitted, then the target checks the next highest priority internal condition to determine whether execution is allowed. See 10.1.1, “priority of scsi status byte reporting” on page 179 10.2 priority commands certain scsi commands ...
Page 198
10.3.2 tagged queuing commands with a tag message are saved in the command queue. Queued commands will be reordered by the target defined rule. See the section on reordering 10.4, “command reordering” on page 189 for details. 10.3.3 untagged queuing the target supports queuing one i/o process from e...
Page 199: 10.4 Command Reordering
10.4 command reordering command reordering function is supported under tagged command queuing enabled (dque = 0). The reorder feature reorders read/write commands in order to minimize seek time between commands. This function will improve total thruput of the drive. 10.5 concurrent i/o process the c...
Page 200: 10.8 Power Saving Mode
10.8 power saving mode power save function will save power consumption while the drive is idle. The drive automatically transfers its operating mode according to the event and timer. 10.9 automatic rewrite/reallocate the target supports auto and recommended reallocate for read, write, write verify a...
Page 201
Write portion of write and verify for all other commands the awre setting is ignored and the target will not automatically reallocate or recommend reassign. Auto/recommend reallocate information is communicated via the sense data returned following a command during which a site was determined to nee...
Page 202: 10.10 Segmented Caching
10.10 segmented caching 10.10.1 overview segmented caching divides the data buffer into several smaller buffers. Each buffer is used as read/write/read-ahead buffer. 10.10.2 read ahead the read ahead function consists of reading data that the initiator has not yet requested to the file buffer. This ...
Page 203
10.14 selection without atn if the target is selected without a t n signal active, no identify message is received from the initiator. In this case, the l u n is identified from the cdb and disconnect permission is disabled. The target does not perform any phase retries. The target still responds to...
Page 204
10.16 contingent allegiance condition the contingent allegiance condition shall exist following the return of check condition, except check con- dition caused by invalid lun. Execution of all queued commands shall be suspended until the contingent allegiance condition is cleared. The contingent alle...
Page 205: 10.17 Reset
10.17 reset the reset condition is used to clear all scsi devices from the bus. This condition takes precedence over all other phases and conditions. After a reset condition is detected and the reset actions completed, the target returns to a 'scsi bus enabled' state that allows the target to accept...
Page 206: 10.18 Diagnostics
10.18 diagnostics the file will execute a self test at power on or when a send diagnostics command is issued with the self test bit set. The diagnostics are to assure the correct operation of the file and to verify that the check circuits detect fault conditions. 10.18.1 power on diagnostics at powe...
Page 207: 10.19 Idle Time Functions
10.19 idle time functions 10.19.1.1 automatic drive maintenance (adm) enable and disable of a d m function is in control of mode page 0, and the shipping default is disable. A d m function is equipped to enhance the reliability in continuous usage. A d m function is to perform a css automatically af...
Page 208
198 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 209: 11.0 Scam
11.0 scam 11.1 scam operation 11.1.1 level 1 a reset condition shall cause an exit from any state and places the drive in the reset delay state. When a drive is powered-on, it immediately enters the power-on delay state and may perform local initialization. The drive shall leave this state and enter...
Page 210
Enter the scam monitor state. Note that a drive make only one attempt to initiate scam protocol after power-on. While in the scam monitor state, a drive shall monitor the scsi bus for both scam selection and normal scsi selection. If the drive detects the initiation of scam protocol, it shall enter ...
Page 211: 11.2 Identification String
11.2 identification string following string shall be sent out as the identification string when the isolation stage. ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ byte ³ note ³ ddrs-34560 ³ ddrs-39130 ³ ddrs-34560w ³ ddrs-39130w ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÁÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ...
Page 212: 11.3 Function Codes
11.3 function codes the following function codes are supported. ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ function code ³ description ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 00000b ³ isolate ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 00001b ³ isolate and set prio...
Page 213: 11.4 Action Codes
11.4 action codes the following action codes are supported. ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ first quintet ³ second quintet ³ description ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ 11000b ³ ccnnnb ³ assign id 00nnnb ³ ÃÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄ...
Page 214
204 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 215: 12.0 Scsi Sense Data
12.0 scsi sense data 12.1 scsi sense data format format of the sense data returned by the file in response to the request sense command. ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 0 ³ valid ³ er...
Page 216
12.2 sense data description 12.2.1 valid (bit 7 of byte 0) 0 the information bytes (byte 3 thru 6) are not defined. 1 the information bytes (byte 3 thru 6) contain a valid logical block address. 12.2.2 error code (bit 6 - 0 of byte 0) 70h current error. This indicates an error for the current comman...
Page 217
Nated without altering the medium. If an invalid parameter is found in parameters supplied as data, then the file might have altered the medium. 6h unit attention indicates that the file entered in the 'unit attention condition'. (see 10.1.5, “unit atten- tion condition” on page 183.) 7h-8h not used...
Page 218
12.2.8 additional sense code/qualifier (byte 12 and 13) the following table shows the description of the combination of sense key / sense code / qualifier. Key code qual description 0 00 00 n o error. 0h 5dh 00h n o sense. Predictive failure analysis threshold reached. 1h 01h 00h recovered write err...
Page 219
Key code qual description 2h 40h 85h diag fail - r a m microcode not loaded. 3h 0ch 03h medium error. Recommend reassign. 3h 10h 00h medium error. Id c r c error. 3h 11h 00h medium error. Unrecovered read error. 3h 14h 01h medium error. Record not found. 3h 16h 00h medium error. Data synchronization...
Page 220
Key code qual description bh 25h 00h aborted command. Unsupported lun. The drive supports l u n 0 only. Bh 43h 00h aborted command. Message reject error. A message reject error occurs when an inappropriate or unexpected message reject is received from the ini- tiator or the initiator rejects a messa...
Page 221
12.2.9 fru : field replaceable unit (byte 14) the f r u (field replaceable unit) field value will always be zero. 12.2.10 sense key specific (byte 15 thru 17) the definition of this field is determined by the value of the sense key field. 12.2.10.1 sense key specific - illegal request (sense key = 5...
Page 222
12.2.10.2 sense key specific - recovered (sense key = 1h) hardware (sense key = 4h) or medium error (sense key = 3h) actual retry count is reported. ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ¿ ³ bit ³ ³ 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ³ ÚÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÅÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ´ ³ byte 15...
Page 223
12.2.12 vender unique error information (byte 20 thru 23) this field gives detail information of the error. It contains a unique code which describes where the error was detected and which piece of hardware or microcode detected the error. 12.2.13 physical error record (byte 24 thru 29) ili = 1 - th...
Page 224
214 o e m spec. Of ddrs-3xxxx.
Page 225: Index
Index a abort 170 abort t a g 171 attention condition 175 automatic rewrite/reallocate 190 b back to back write 189 bus device reset 171 c c l e a r q u e u e t a g 171 command 61 f o r m a t u n i t 66 i n q u i r y 70 l o g select 76 l o g sense 77 m o d e select (10) 118 m o d e select (6) 116 m ...
Page 226
Message system (continued) i d e n t i f y 173 i g n o r e w i d e r e s i d u e 172 initiator d e t e c t e d e r r o r 169 l i n k e d c o m m a n d c o m p l e t e 171 l i n k e d c o m m a n d c o m p l e t e w i t h f l a g 171 message p a r i t y e r r o r 170 message reject 170 n o o p e r a ...
Page 227
W w i d e d a t a t r a n s f e r request 167 w r i t e 151 write a n d verify 153 w r i t e b u f f e r 154 write cache 189 w r i t e e x t e n d e d 152 w r i t e l o n g 159 w r i t e same 160 index 217.
Page 228
Part number 00k0097 published in japan s00k-0097-03.