- DL manuals
- IBM
- Storage
- DTLA-305040 - Deskstar 41.1 GB Hard Drive
- Specifications
IBM DTLA-305040 - Deskstar 41.1 GB Hard Drive Specifications
Hard disk drive specifications
Deskstar 40GV & 75GXP
3.5 inch Ultra ATA/100 hard disk drive
DTLA-307015
DTLA-307020
DTLA-307030
DTLA-307045
DTLA-307060
DTLA-307075
DTLA-305010
DTLA-305020
DTLA-305030
DTLA-305040
Models:
Revision 2.0
S07-4778-04
IBM storage products - official published specifications
Summary of DTLA-305040 - Deskstar 41.1 GB Hard Drive
Page 1
Hard disk drive specifications deskstar 40gv & 75gxp 3.5 inch ultra ata/100 hard disk drive dtla-307015 dtla-307020 dtla-307030 dtla-307045 dtla-307060 dtla-307075 dtla-305010 dtla-305020 dtla-305030 dtla-305040 models: revision 2.0 s07-4778-04 ibm storage products - official published specification...
Page 2
5th edition (revision 2.0) s07n-4778-04 (20 june, 2000, 2 november 2000) 4th edition (revision 1.2) s07n-4778-03 (30 may, 2000) 3rd edition (revision 1.1) s07n-4778-02 (17 may, 2000) 2nd edition (revision 1.0) s07n-4778-01 (10 may, 2000) 1st edition (revision 0.1) s07n-4778-00 (15 march, 2000) preli...
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Table of contents 42 7.3.2 jumper positions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 7.3.1 jumper pin assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 7.3 jumper...
Page 4
73 9.10 features register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72 9.9 error register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72 9.8 d...
Page 5
110 12.2 execute device diagnostic (90h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109 12.1 check power mode (e5h/98h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105 12.0 command descriptions . . . . ....
Page 6
178 12.32.16 error reporting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177 12.32.15 self-test log data structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174 12.32.14 smart error log sector...
Page 7
199 i ndex . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197 14.2 set features command support coverage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195 14.1 commands support covera...
Page 8
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 9: Figures
Figures 46 figure 48. Operating and nonoperating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45 figure 47. Jumper settings for disabling auto spin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44 figure 46. Jumper positions for capacity ...
Page 10
120 figure 92. Identify device information (5 of 6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119 figure 92. Identify device information (4 of 6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118 figure 92. Identify device information (...
Page 11
187 figure 144. Write long command (32h/33h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185 figure 143. Write dma queued command (cch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183 figure 142. Write dma command (cah/cbh) . . . . . . . . ...
Page 12
197 figure 149. Set features command coverage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196 figure 148. Command coverage (2 of 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195 figure 148. Command coverage (1 of 2) . . . . . . . ...
Page 13: 1.0
1.0 general this document describes the specifications of the following ibm 3.5-inch ata interface hard disk drives: Ÿ dtla-305010 (10.2 gb) (5400 rpm) Ÿ dtla-305020 (20.5 gb) (5400 rpm) Ÿ dtla-305030 (30.7 gb) (5400 rpm) Ÿ dtla-305040 (41.1 gb) (5400 rpm) Ÿ dtla-307015 (15.3 gb) (7200 rpm) Ÿ dtla-3...
Page 14: 1.2 General Caution
1.2 general caution the drive can be damaged by shock or esd (electrostatic discharge). Any damage sustained by the drive after removal from the shipping package and opening the esd protective bag are the responsibility of the user. 1.3 references Ÿ ata/atapi-5 (t13/1321d revision 2) deskstar 40gv &...
Page 15: 2.0
2.0 general features Ÿ data capacities of 10.2 gb - 76.8 gb Ÿ spindle speeds of 5400 rpm (dtla-305xxx) and 7200 rpm (dtla-307xxx) Ÿ enhanced ide (ultra ata100) interface Ÿ sector format of 512 bytes/sector Ÿ closed-loop actuator servo Ÿ automatic actuator lock Ÿ interleave factor 1:1 Ÿ seek time of ...
Page 16
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 17
Part 1. Functional specification deskstar 40gv & 75gxp hard disk drive specifications 5.
Page 18
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 19: 3.0
3.0 fixed disk subsystem description 3.1 control electronics the drive is electronically controlled by a microprocessor, several logic modules, digital/analog modules, and various drivers and receivers. The control electronics performs the following major functions: Ÿ controls and interprets all int...
Page 20
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 21: 4.0
4.0 drive characteristics this chapter describes the characteristics of the drive. 4.1 default logical drive parameters the default of the logical drive parameters in identify device data are as shown below. 76,869,918,720 150,136,560 63 16/15 16,383 76.8 dtla-307075 61,492,838,400 120,103,200 63 16...
Page 22: 4.2 Data Sheet
4.2 data sheet 1 upper 132kb is used for firmware embedded sector servo embedded sector servo servo method 4/3/2 10/8/6/4/3/2 number of data heads 2/1 5/4/3/2/1 number of data disks 15 15 number of zones 14.5 11 areal density - max (gbits/in 2 ) 35 28.35 track density (ktpi) 415 391 recording densit...
Page 23
4.3.2 cylinder allocation 351 26320–27724 370 32512–34326 data zone 14 378 25216–26319 400 31344–32511 data zone 13 396 23520–25215 420 29744–31343 data zone 12 432 21200–23519 440 27552–29743 data zone 11 459 19568–21199 480 23024–27551 data zone 10 486 18320–19567 540 18592–23023 data zone 9 504 1...
Page 24
4.4.1 command overhead command overhead is defined as the time required Ÿ from the time the command is written into the command register by a host Ÿ to the assertion of drq for the first data byte of a read command when the requested data is not in the buffer Ÿ excluding - physical seek time - laten...
Page 25
Seek time is measured from the start of the motion of the actuator to the start of a reliable read or write operation. “reliable read or write” implies that error correction/recovery is not used to correct arrival problems. The average seek time is measured as the weighted average of all possible se...
Page 26
4.4.2.4 cylinder switch time (cylinder skew) 1.7 dtla-307xxx 2.0 dtla-305xxx typical (ms) cylinder switch time figure 8. Cylinder skew a cylinder switch time is defined as the amount of time required by the fixed disk to access the next sequential block after reading the last sector in the current c...
Page 27
4.4.4 data transfer speed 100 100 buffer-host (max) 18.8 14.8 sustained - write typical 18.8 14.8 sustained - read typical 21.7 17.0 instantaneous - typical disk-buffer transfer (zone 14) 37.7 31.8 sustained - typical 43.4 36.5 instantaneous - typical disk-buffer transfer (zone 0) dtla-307xxx (mbyte...
Page 28
4.4.6 throughput 4.4.6.1 simple sequential access 1.00 1.26 0.95 1.20 zone 14 0.50 0.60 0.48 0.57 zone 0 dtla-307xxx dtla-305xxx dtla-307xxx dtla-305xxx max (sec) typical (sec) sequential read figure 13. Simple sequential access performance the above table gives the time required to read/write for a...
Page 29
4.4.7 operating modes 4.4.7.1 operating mode descriptions operating mode description spin-up start up time period from spindle stop or power down seek seek operation mode write write operation mode read read operation mode idle spindle motor and servo system are working normally. Commands can be rec...
Page 30
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 31: 5.0
5.0 defect flagging strategy media defects are remapped to the next available sector during the format process in manufacturing. The mapping from lba to the physical locations is calculated by an internally maintained table. Shipped format Ÿ data areas are optimally used. Ÿ no extra sector is wasted...
Page 32
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 33: 6.0
6.0 data integrity 6.1 data loss at power off Ÿ the drive retains recorded information under all non-write operations. Ÿ no more than one sector can be lost by power down during write operation while write cache is dis- abled. Ÿ power off during write operations may make an incomplete sector which w...
Page 34
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 35: 7.0
7.0 specification 7.1 electrical interface 7.1.1 connectors 7.1.1.1 dc power connector the dc power connector is designed to mate with amp (part 1-480424-0) using amp pins part 350078-4 (strip) or part 61173-4 (loose piece) or their equivalents. Pin assignments are shown in the figure below. 4 3 2 1...
Page 36
7.1.2 signal definition the pin assignments of interface signals are listed in the figure below: gnd 40 oc i/o dasp- 39 ttl i cs1- 38 ttl i cso- 37 ttl i da2 36 ttl i da0 35 oc i/o pdiag- 34 ttl i da1 33 oc o iocs16-(**) 32 3-state o intrq 31 gnd 30 ttl i dmack- 29 ttl i csel 28 3-state o iordy(*) 2...
Page 37
Dd0-dd15 16-bit bi-directional data bus between the host and the drive. The lower 8 lines, dd00-07, are used for register and ecc access. All 16 lines, dd00-15, are used for data transfer. These are 3-state lines with 24 ma current sink capability. Da0-da2 address used to select the individual regis...
Page 38
If dasp- was not asserted by device 1 during reset initialization, device 0 shall post its own status immediately after it completes diagnostics and clear the device 1 status register to 00h. Device 0 may be unable to accept commands until it has finished its reset procedure and is ready (drdy=1). D...
Page 39
Ddmardy- is a flow control signal for ultra dma data out bursts. This signal is held asserted by the device to indicate to the host that the device is ready to receive ultra dma data out transfers. The device may negate ddmardy- to pause an ultra dma data out transfer. Dstrobe (ultra dma) this signa...
Page 40: 7.2 Signal Timings
7.2 signal timings 7.2.1 reset timings drive reset timing. T10 t14 reset- busy figure 20. System reset timing chart 31 – reset high to not busy t14 25 reset low width t10 max (sec) min (usec) parameter description figure 21. System reset timing deskstar 40gv & 75gxp hard disk drive specifications 28.
Page 41
7.2.2 pio timings the pio cycle timings meet mode 4 of the ata/atapi-4 description. Iocs16-(*) t1 t9 t0 t2 t2i t3 t4 t5 t6 t8(*) t7(*) t1 t10 t11 read data dd0-15 dior-, diow- cs0-,cs1- da0-2 write data dd0-15 iordy (*) up to ata-2 (mode-0,1,2) figure 22. Pio cycle time chart 1250 – iordy pulse widt...
Page 42
7.2.2.1 write drq interval time for write sectors and write multiple operations 3.8 us is inserted from the end of negation of the drq bit until setting of the next drq bit. 7.2.2.2 read drq interval time for read sectors and read multiple operations the interval from the end of negation of the drq ...
Page 43
7.2.3 multiword dma timings the multiword dma timing meets mode 2 of the ata/atapi-4 description. Write data read data dmack- dmarq dior-/diow- t0 tl tj ti td tk tf tg th tg tz cs0-/cs1- tm tn figure 24. Multiword dma cycle timing chart 25 – –dmack to tristate tz – 10 cs (1:0) hold tn – 25 cs (1:0) ...
Page 44
7.2.4 ultra dma timings the ultra dma timing meets mode 0,1,2,3 4, and 5 of the ultra dma protocol. 7.2.4.1 initiating read dma dstrobe hdmardy- dmack- dmarq stop tui tack tenv tack tenv tziordy tfs tcyc tcyc t2cyc dd(15:00) tzad taz xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx xxx xxx host drives dd device drives...
Page 45
7.2.4.2 host pausing read dma dstrobe hdmardy- dmack- dmarq tsr stop trfs figure 28. Ultra dma cycle timing chart (host pausing read) 50 – 60 – 60 – 60 – 70 – 75 – ready to final strobe time trfs – – – – – – 20 – 30 – 50 – strobe to ready response time tsr max min max min max min max min max min max...
Page 46
7.2.4.3 host terminating read dma dstrobe hdmardy- dmack- dmarq stop tmli trp dd(15:00) tzah xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx host drives dd device drives dd tdh tds crc tli tack tack trfs tli tiordyz xxx rd data xxxxxxxxxx taz figure 30. Ultra dma cycle timing chart (host terminating read) 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 ...
Page 47
7.2.4.4 device terminating read dma dstrobe hdmardy- dmack- dmarq stop tmli tli dd(15:00) tzah xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx host drives dd device drives dd tdh tds crc tss tack tack tli tiordyz xxxxx xxxxxxxxxx taz tli figure 32. Ultra dma cycle timing chart (device terminating read) 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – ...
Page 48
7.2.4.5 initiating write dma dstrobe hdmardy- dmack- dmarq stop tui tack tenv tziordy tli tui tcyc tcyc t2cyc dd(15:00) xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx xxx host drives dd tdh tds wt data wt data wt data tack figure 34. Ultra dma cycle timing chart (initiating write) – 4.6 – 5 – 5 – 5 – 5 – 5 dat...
Page 49
7.2.4.6 device pausing write dma hstrobe ddmardy- dmack- dmarq tsr stop trfs figure 36. Ultra dma cycle timing chart (device pausing write) 50 – 60 – 60 – 60 – 70 – 75 – ready to final strobe time trfs – – - – – – 20 – 30 – 50 – strobe to ready response time tsr max min max min max min max min max m...
Page 50
7.2.4.7 device terminating write dma hstrobe ddmardy- dmack- dmarq stop tmli trp dd(15:00) xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx host drives dd tdh tds crc tli tack tack trfs tli tiordyz xxx wt data xxxxxxxxxx figure 38. Ultra dma cycle timing chart (device terminating write) 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – pull...
Page 51
7.2.4.8 host terminating write dma hstrobe ddmardy- dmack- dmarq stop tmli tli dd(15:00) host drives dd tdh tds crc tss tack tack tli tiordyz xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxx tli figure 40. Ultra dma cycle timing chart (host terminating write) 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – pull-up ti...
Page 52
7.2.5 addressing of registers the host addresses the drive through a set of registers called the task file. These registers are mapped into the i/ o space of the host. Two chip select lines (cs0– and cs1–) and three address lines (da0-02) are used to select one of these registers, while a dior– or d...
Page 53: 7.3 Jumper Settings
7.3 jumper settings 7.3.1 jumper pin assignment there are four jumper settings as shown in the following sections: 16 logical heads (normal use), 15 logical heads, 2gb clip, and auto spin disable. Each category is exclusive. The pin assignment of the 9-pin jumper used to select "device 0" or "device...
Page 54
7.3.2 jumper positions 7.3.2.1 16 logical head default (normal use) the figure below shows the jumper positions used to select device 0, device 1, cable selection, or device 0 forcing device 1 present. G i e c a h f d b device 0 (master) shipping default g i e c a h f d b device 1 (slave) g i e c a ...
Page 55
7.3.2.2 15 logical head default the positions of jumper blocks shown below is used to select device 0, device 1, cable selection, or device 0 forcing device 1 present, setting 15 logical heads instead of default 16 logical head models. G i e c a h f d b device 0 (master) g i e c a h f d b device 1 (...
Page 56
7.3.2.3 capacity clip to 2gb/32gb with 16 default logical heads the positions of the jumper blocks shown below are used to select device 0, device 1, cable selection, or device 0 forcing device 1 present, setting the drive capacity down either to 2gb or 32gb for the pur- pose of compatibility. G i e...
Page 57
7.3.2.4 power up in standby the jumpers are installed as shown below for enabling power up in standby. G i e c a h f d b device 0 (master) g i e c a h f d b device 1 (slave) g i e c a h f d b cable sel g i e c a h f d b device 0 forcing device 1 present figure 47. Jumper settings for disabling auto ...
Page 58: 7.4 Environment
7.4 environment 7.4.1 temperature and humidity -40 to 65°c 5 to 95% non-condensing 35°c non-condensing 35°c/hour -300 to 12,000 m temperature relative humidity maximum wet bulb temperature maximum temperature gradient altitude nonoperating conditions 5 to 55°c 8 to 90% non-condensing 29.4°c non-cond...
Page 59
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 temperature (c) 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 relative humidity (%) environment specification wet bulb 29.4c wet bulb 35c 36c/95% 31c/90% 55c/15% 65c/14% nonoperating operating figure 49. Limits of temperature and humidity deskstar 40gv & 75gxp hard disk drive specifications 47.
Page 60: 7.5 Dc Power Requirements
7.5 dc power requirements the following voltage specifications apply at the drive power connector. Damage to the drive electronics may result if the power supply cable is connected or disconnected while power is being applied to the drive (no hot plug/unplug is allowed). Connections to the drive sho...
Page 61
Dtla-307015, -307020, -307030 , -307045 1.0 0.015 0.17 sleep average 1.5 0.015 0.26 standby average 10.5 0.70 0.41 random r/w average 2 --- 2.04 1.01 random r/w peak --- 1.90 0.81 start up (max) 10.2 0.73 0.26 seek average 1 --- 2.04 0.46 seek peak --- 0.41 0.33 idle ripple (peak-to-peak) 6.7 0.46 0...
Page 62
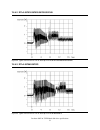
7.5.3 power supply generated ripple at drive power connector 0-10 150 +12v dc 0-10 100 +5v dc mhz maximum (mv pp) figure 52. Power supply generated ripple at drive power connector during drive start up and seeking 12-volt ripple is generated by the drive (referred to as dynamic loading). If the powe...
Page 63
7.5.4.2 dtla-307015/307020/307030/307045 figure 54. Typical current form of 12v at start up of dtla-307015/307020/307030/307045 7.5.4.3 dtla-307060/307075 figure 55. Typical current form of 12v at start up of dtla-307060/307075 deskstar 40gv & 75gxp hard disk drive specifications 51.
Page 64
7.5.5 energy consumption efficiency 0.11 307075 0.13 307060 0.15 307045 0.22 307030 0.33 307020 0.43 307015 0.12 305040 0.16 305030 0.24 305020 energy consumption efficiency (w/gb) dtla- figure 56. Energy consumption efficiency energy consumption efficiency is calculated as power consumption of idle...
Page 65: 7.6 Reliability
7.6 reliability 7.6.1 cable noise interference to avoid any degradation of performance throughput or error rate when the interface cable is routed on top or comes in contact with the hda assembly, the drive must be grounded electrically to the system frame by four screws. The common mode noise or vo...
Page 66
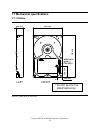
7.7 mechanical specifications 7.7.1 outline 25.4 ±0.4 101.6 ±0.4 146 ±0.6 breather hole (*) left front * do not block the breather hole . 38.9 ±0.4 19.7 ±0.4 dia.2.0±0.1 figure 57. Outline of the dtla-3xxxxx deskstar 40gv & 75gxp hard disk drive specifications 54.
Page 67
7.7.2 physical dimensions the following chart describes the dimensions for ibm dtla-307xxx hard disk drive form factor. 670 307060 307075 590 307015 307020 307030 307045 550 146.0 ± 0.8 101.6 ± 0.4 25.4 ± 0.4 305010 305020 305030 305040 weight (grams) length (mm) width (mm) height (mm) dtla- figure ...
Page 68
7.7.3 hole locations the figure below shows the outline of the drive including the hole locations. Thickness of bracket screw 6-32 unc max allowable penetration of noted screw to be 4.5 mm. Max allowable penetration of noted screw to be 4.0 mm. Recommended torque 0.6 - 1.0 nm rear right (6x) 6.35 ±0...
Page 69
7.7.4 connector locations figure 60. Connector locations 7.7.5 drive mounting the drive will operate in all axes (6 directions). Performance and error rate will stay within specification limits if the drive is operated in the other orientations from which it was formatted. For reliable operation, th...
Page 70: 7.8 Vibration And Shock
7.8 vibration and shock all vibration and shock measurements recorded in this section are made with a drive that has no mounting attachments for the systems. The input power for the measurements is applied to the normal drive mounting points. 7.8.1 operating vibration 7.8.1.1 random vibration the dr...
Page 71
7.8.2.1 random vibration the test consists of a random vibration applied for each of three mutually perpendicular axes with the time duration of 10 minutes per axis. The psd levels for the test simulate the shipping and relocation environment shown below. The overall rms (root mean square) level of ...
Page 72
7.8.4.2 sinusoidal shock wave the shape is approximately half-sine pulse. The figure below shows the maximum acceleration level and duration: 11 75 all models 2 225 dtla-307060, -307075 2 350 dtla-307015, -307020, -307030, -307045 2 400 dtla-305xxx duration (ms) accleration level (g) models figure 6...
Page 73: 7.9 Acoustics
7.9 acoustics the upper limit criteria of the octave sound power levels are given in bels relative to one pico watt and are shown in the following table. The sound power emission levels are measured in accordance with iso 7779. 4.8 4.5 3.7 3.4 4.0 3.7 operating 3.9 3.6 3.4 3.1 3.4 3.0 idle max typic...
Page 74: 7.10 Identification Labels
7.10 identification labels the following labels are affixed to every drive shipped from the drive manufacturing location in accord- ance with the appropriate hard disk drive assembly drawing: • a label containing the ibm logo, the ibm part number, and the statement “made by ibm japan ltd.”, or ibm a...
Page 75: 7.13
7.12 electromagnetic compatibility when installed in a suitable enclosure and exercised with a random accessing routine at maximum data rate, the hard disk drive meets the following worldwide emc requirements: Ÿ united states federal communications commission (fcc) rules and regulations (class b), p...
Page 76
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 77
Part 2. Interface specification deskstar 40gv & 75gxp hard disk drive specifications 65.
Page 78
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 79: 8.0
8.0 general this specification describes the host interface of the dtla-30xxxx. The interface conforms to the working document of information technology - at attachment with packet interface extension (ata/atapi-5), revision 2, dated 13 december 1999, with certain limitations described in 8.2, “devi...
Page 80
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 81: 9.0
9.0 registers invalid address x x x a a command status 1 1 1 n a 2 lba bits 24–27 1 lba bits 24–27 1 0 1 1 n a device/head device/head. 0 1 1 n a 2 lba bits 16–23 1 lba bits 16–23 1 1 0 1 n a cylinder high cylinder high 1 0 1 n a 2 lba bits 8–15 1 lba bits 8–15 1 0 0 1 n a cylinder low cylinder low ...
Page 82: 9.2 Command Register
9.1 alternate status register err idx cor dbq dsc/ serv df rdy bsy 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 alternate status register figure 67. Alternate status register this register contains the same information as the status register. The only difference is that reading this register does not imply interrupt acknowledge...
Page 83: 9.5 Data Register
9.5 data register this register is used to transfer data blocks between the device data buffer and the host. It is also the register through which sector information is transferred on a format track command and configuration information is transferred on an identify device command. All data transfer...
Page 84: 9.8 Device/head Register
-h3,-h2,-h1,-h0 - -head select. These four bits are the 1's complement of the binary coded address of the currently selected head. -h0 is the least significant. -ds1 -drive select 1. Drive select bit for device 1, active low. Ds1=0 when device 1 (slave) is selected and active. -ds0 -drive select 0. ...
Page 85: 9.10 Features Register
At the completion of any command except execute device diagnostic the contents of this register are always valid even if err=0 is in the status register. Following a power on, a reset, or completion of an execute device diagnostic command, this register contains a diagnostic code. See figure 75 on p...
Page 86: 9.13 Status Register
9.13 status register err idx corr drq dsc/ serv df drdy bsy 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 status register figure 72. Status register this register contains the device status. The contents of this register are updated whenever an error occurs and at the completion of each command. If the host reads this register w...
Page 87: 10.0
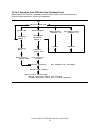
10.0 general operation 10.1 reset response there are three types of resets in ata: power on reset (por) the device executes a series of electrical circuitry diagnostics, spins up the hda, tests speed, and other mechanical parametrics, and sets default values. Hard reset (hardware reset) reset- signa...
Page 88
10.1.1 register initialization 50h alternate status 50h status a0h device/head 00h cylinder high 00h cylinder low 01h sector number 01h sector count diagnostic code error default value register figure 74. Default register values after power on, hard reset, or software reset, the register values are ...
Page 89
10.2 diagnostic and reset considerations for each reset and execute device diagnostic the diagnostic is done as follows: power on reset dasp- is read by device 0 to determine if device 1 is present. If device 1 is present, device 0 shall read pdiag- to determine when it is valid to clear the bsy bit...
Page 90
10.3 sector addressing mode all addressing of data sectors recorded on the drive media is by a logical sector address. The logical chs address for the drive is different from the actual physical chs location of the data sector on the disk media. The drive supports both logical chs addressing mode an...
Page 91
10.4 overlapped and queued feature overlap allows devices to perform a bus release so that the other device on the bus may be used. To perform a bus release the device clears both drq and bsy to zero. When selecting the other device during overlapped operations, the host shall disable interrupts via...
Page 92
10.5 power management feature the power management feature functions permit a host to reduce the power required to operate the drive. It provides a set of commands and a timer that enables a device to implement low power consumption modes. The drive implements the following set of functions: Ÿ stand...
Page 93: 10.6 S.M.A.R.T. Function
10.5.4 interface capability for power modes each power mode affects the physical interface as defined in the following table. Inactive no 1 o sleep inactive yes 1 o standby active yes 1 o idle active yes x x active media interface active rdy bsy mode figure 77. Power conditions ready (rdy) is not a ...
Page 94
10.6.4 threshold exceeded condition if one or more attribute values, whose pre-failure bit of their status flag is set, are less than or equal to their corresponding attribute thresholds, then the device reliability status is negative, indicating an impending degrading or faulty condition. 10.6.5 s....
Page 95
10.7 security mode feature set security mode feature set is a powerful security feature. With a device lock password, a user can pre- vent unauthorized access to a hard disk drive even if the device is removed from the computer. The following commands are supported for this feature: ('f6'h) security...
Page 96
The system manufacturer or dealer who intends to enable the device lock function for end-users must set the master password even if only single level password protection is required. 10.7.4 operation example 10.7.4.1 master password setting the system manufacturer or dealer can set a new master pass...
Page 97
10.7.4.3 operation from por after user password is set when device lock function is enabled, the device rejects media access command until a security unlock command is successfully completed. Por device locked mode unlock cmd command (*1) command (*1) password erase unit password match ? Reject comp...
Page 98
10.7.4.4 user password lost if the user password is forgotten and high level security is set, the system user cannot access any data. However the device can be unlocked using the master password. If a system user forgets the user password and maximum security level is set, data access is impossible....
Page 99
10.7.5 command table this table shows the response of the device to commands when the security mode feature set (device lock function) is enabled. Executable executable executable standby executable executable executable smart enable/disable automatic off-line data collection executable executable e...
Page 100
Executable executable command aborted write verify executable executable command aborted write sector(s) (w/retry) executable executable command aborted write sector(s) (w/o retry) executable executable command aborted write multiple executable executable command aborted write long (w/retry) executa...
Page 101
10.8 host protected area function the host protected area function provides a protected area which cannot be accessed via conventional methods. This protected area is used to contain critical system data such as bios or system manage- ment information. The contents of the main memory of the entire s...
Page 102
4. Advanced usage using protected area the data in the protected area is accessed by the following method: i. Issue read native max address command to get the real device maximum lba. Returned value shows that native device maximum lba is 12,692,735 (c1acffh) regardless of the current setting. Ii. M...
Page 103: 10.9 Seek Overlap
10.9 seek overlap the dtla-3xxxxx provides an accurate seek time measurement method. The seek command is usually used to measure the device seek time by accumulating the execution time for a number of seek com- mands. With typical implementation of seek command this measurement must include the devi...
Page 104: 10.11 Reassign Function
10.11 reassign function reassign function is used with read commands and write commands. The sectors of data for reassign- ment are prepared as the spare data sector. This reassignment information is registered internally and the information is available right after complet- ing the reassign functio...
Page 105: 10.13
The identify device information indicates the states as follows: Ÿ identify device information is complete or incomplete Ÿ this feature set is implemented Ÿ this feature set is enabled or disabled Ÿ the device needs the set features command to spin-up into active state 10.13 advanced power managemen...
Page 106
3. Automatic acoustic management is enabled and the associated algorithm indicates that the standby mode should be entered to reduce acoustical emanations. The identify device response word 83, bit 9 indicates that automatic acoustic management feature is supported if set. Word 86, bit 9 indicates t...
Page 107
Before enable address offset mode a reserved area has been created using a non-volatile set max command. Non-accessible (sytem reserved area) accessible (user area) lba 0 lba r lba m after enable address offset mode non-accessible (user area) accessible (system reserved area) lba 0 lba m–r lba m aft...
Page 108
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 109: 11.0
11.0 command protocol the commands are grouped into different classes according to the protocols followed for command exe- cution. The command classes with their associated protocols are defined below. For all commands, the host must first check if bsy=1, and should proceed no further unless and unt...
Page 110
E. The host reads one sector of data via the data register. F. The device sets drq=0 after the sector has been transferred to the host. 4. For the read long command a. The device sets bsy=1 and prepares for data transfer. B. When the sector of data is available for transfer to the host, the device s...
Page 111: 11.2 Pio Data Out Commands
11.2 pio data out commands these commands are: Ÿ format track Ÿ security disable password Ÿ security erase unit Ÿ security set password Ÿ security unlock Ÿ set max set password command Ÿ set max unlock command Ÿ smart write log sector Ÿ write buffer Ÿ write long Ÿ write multiple Ÿ write sectors exec...
Page 112
The write multiple command transfers one block of data for each interrupt. The other commands transfer one sector of data for each interrupt. If the device detects an invalid parameter, it will abort the command by setting bsy=0, err=1, abt=1, and interrupting the host. If an uncorrectable error occ...
Page 113: 11.3 Non-Data Commands
11.3 non-data commands non-data commands are Ÿ check power mode Ÿ execute device diagnostic Ÿ flush cache Ÿ idle Ÿ idle immediate Ÿ initialize device parameters Ÿ nop Ÿ read native max address Ÿ read verify sectors Ÿ recalibrate Ÿ security erase prepare Ÿ security freeze lock Ÿ seek Ÿ set features Ÿ...
Page 114: 11.4 Dma Commands
11.4 dma commands dma commands are Ÿ read dma Ÿ write dma data transfers using dma commands differ in two ways from pio transfers: Ÿ data transfers are performed using the slave dma channel Ÿ no intermediate sector interrupts are issued on multisector commands initiation of the dma transfer commands...
Page 115: 11.5 Dma Queued Commands
11.5 dma queued commands these commands are Ÿ read dma queued Ÿ service Ÿ write dma queued 1. Command issue a. The host writes any required parameters to the features, sector count, sector number, cylinder, and device/head registers. B. The host writes command code to the command register. C. The de...
Page 116
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 117: 12.0
12.0 command descriptions 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 b0 smart execute off-line data collection 3 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 b0 smart enable operations 3 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 b0 smart enable/disable attribute autosave 3 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 b0 smart disable operations 3 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 99 sleep* 3 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 e6 sleep 3 1 1 0 0...
Page 118
0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 31 write sectors (no retry) 2 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 30 write sectors (retry) 2 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 c5 write multiple 2 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 33 write long (no retry) 2 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 32 write long (retry) 2 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 cc write dma queued 5 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 cb write dma (no retry) 4 1 1 0 0 1 0 ...
Page 119
02 03 44 55 5d 66 82 aa bb cc dd ef ef ef ef ef ef ef ef ef ef ef set features enable write cache set transfer mode 40 bytes of ecc apply on read/write long disable read look-ahead feature enable release interrupt disable reverting to power on defaults disable write cache enable read look-ahead feat...
Page 120
B option bit. Indicates that the option bit of the sector count register should be specified. (this bit is used by set max address command) v valid. Indicates that the bit is part of an output parameter and should be specified. X indicates that the hex character is not used. - indicates that the bit...
Page 121
12.1 check power mode (e5h/98h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector ...
Page 122
12.2 execute device diagnostic (90h) see below status 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 - - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - se...
Page 123: 12.3 Flush Cache (E7H)
12.3 flush cache (e7h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number v ...
Page 124: 12.4 Format Track (50H)
12.4 format track (50h) see below status 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector number -...
Page 125
Input parameters from the device sector number in lba mode this register specifies current lba address bits 0-7. (l=1) cylinder high/low in lba mode this register specifies current lba address bits 8-15 (low), 16-23 (high) h in lba mode this register specifies current lba address bits 24-27. (l=1) e...
Page 126: 12.5 Format Unit (F7H)
12.5 format unit (f7h) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 l 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number - ...
Page 127: 12.6 Identify Device (Ech)
12.6 identify device (ech) see below status 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector numbe...
Page 128
The identify device command requests the device to transfer configuration information to the host. The device will transfer a sector to the host containing the information described in the figure below. Ÿ the content field indicates vendor specific use of those parameters. Capabilities, bit assignme...
Page 129
Reserved 0000h 69-74 minimum pio transfer cycle time without flow control 15–0 (=78) cycle time in nanoseconds (120ns, 16.6mb/s) 0078h 68 minimum pio transfer cycle time without flow control 15–0 (=f0) cycle time in nanoseconds (240ns,8.3mb/s) 00f0h 67 manufacturer’s recommended multiword dma transf...
Page 130
Command set/feature supported extension 15-14(=01) word 83 is valid 13- 8 (=0) reserved 4000h 84 command set supported 15-14(=01) word 83 is valid 13-10 (=0) reserved 9 (=1) automatic acoustic mode 8 (=1) set max security extension 7 (=1) set features address offset mode 6 (=1) set features subcomma...
Page 131
Ultra dma transfer modes 15- 8 (=xx) current active ultra dma transfer mode 15-14 reserved (=0) 13 mode 5 1= active 0= not active 12 mode 4 1= active 0= not active 11 mode 3 1= active 0= not active 10 mode 2 1= active 0= not active 9 mode 1 1= active 0= not active 8 mode 0 1= active 0= not active 7-...
Page 132
Device lock function. Bit assignments 15- 9 reserved 8 security level 1= maximum, 0= high 7- 6 reserved 5 enhanced erase 1= support 4 expire 1= expired 3 freeze 1= frozen 2 lock 1= locked 1 enable/disable 1= enable 0 capability 1= support xxxxh 128 removable media status notification feature set 000...
Page 133
15- 8 checksum. This value is the two's complement of the sum of all bytes in byte 0 through 510 7- 0 (a5) signature xxa5h 255 reserved 0000h 160-254 reserved Ÿ xxxxh 130-159 current set feature option. Bit assignments 15- 4 reserve 3 auto reassign 1= enable 2 reverting 1= enable 1 read look-ahead 1...
Page 134: 12.7 Idle (E3H/97H)
12.7 idle (e3h/97h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number - - -...
Page 135
When the automatic power down sequence is enabled, the drive will enter standby mode automatically if the time-out interval expires with no drive access from the host. The time-out interval will be reinitialized if there is a drive access before the time-out interval expires. Deskstar 40gv & 75gxp h...
Page 136
12.8 idle immediate (e1h/95h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector nu...
Page 137
12.9 initialize device parameters (91h) see below status 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d h h h h device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - -...
Page 138: 12.10 Nop (00H)
12.10 nop (00h) see below status 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 command initial value device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head initial value cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high initial value cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low initial value sector number - - - - - - - - sector number initial value sec...
Page 139: 12.11 Read Buffer (E4H)
12.11 read buffer (e4h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number -...
Page 140: 12.12 Read Dma (C8H/c9H)
12.12 read dma (c8h/c9h) see below status 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector number ...
Page 141
Cylinder high/low the cylinder number of the first sector to be transferred. (l=0) in lba mode this register specifies lba address bits 8 - 15 (low) 16 - 23 (high) to be transferred. (l=1) h the head number of the first sector to be transferred. (l=0) in lba mode this register specifies lba bits 24-...
Page 142
12.13 read dma queued (c7h) see below status 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector numb...
Page 143
Input parameters from the device on bus release sector count bits 7 - 3 (tag) contain the tag of the command being bus released. Bit 2 (rel) is set to one. Bit 1 (i/o) is cleared to zero. Bit 0 (c/d) is cleared to zero. Sector number, cylinder high/low, h n/a. Srv cleared to zero when the device per...
Page 144: 12.14 Read Long (22H/23H)
12.14 read long (22h/23h) see below status 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector number...
Page 145
H the head number of the sector to be transferred. (l=0) in lba mode this register contains lba bits 24-27. (l=1) r the retry bit. If set to one, then retries are disabled. Input parameters from the device sector count the number of requested sectors not transferred. Sector number the sector number ...
Page 146: 12.15 Read Multiple (C4H)
12.15 read multiple (c4h) see below status 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector number...
Page 147
Input parameters from the device sector count the number of requested sectors not transferred. This will be zero unless an unrecoverable error occurs. Sector number the sector number of the last transferred sector. (l=0) in lba mode this register contains current lba bits 0 - 7. (l=1) cylinder high/...
Page 148
12.16 read native max address (f8h) see below status 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d - - - - device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number - - - - - - - - sec...
Page 149
12.17 read sectors (20h/21h) see below status 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector num...
Page 150
Input parameters from the device sector count the number of requested sectors not transferred. This will be zero, unless an unrecoverable error occurs. Sector number the sector number of the last transferred sector. (l=0) in lba mode this register contains current lba bits 0 - 7. (l=1) cylinder high...
Page 151
12.18 read verify sectors (40h/41h) see below status 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sec...
Page 152
Input parameters from the device sector count the number of requested sectors not verified. This will be zero, unless an unrecoverable error occurs. Sector number the sector number of the last transferred sector. (l=0) in lba mode this register contains current lba bits 0 - 7. (l=1) cylinder high/lo...
Page 153: 12.19 Recalibrate (1Xh)
12.19 recalibrate (1xh) see below status 0 0 0 1 - - - - command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number -...
Page 154
12.20 security disable password (f6h) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - s...
Page 155
Identifier zero indicates that the device should check the supplied password against the user password stored internally. One indicates that the device should check the given password against the master password stored internally. Deskstar 40gv & 75gxp hard disk drive specifications 143.
Page 156
12.21 security erase prepare (f3h) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sect...
Page 157
12.22 security erase unit (f4h) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector ...
Page 158
Reserved 17-255 password ( 32 bytes ) 01-16 control word bit 0 : identifier (1- master, 0- user) bit 1 : erase mode (1- enhanced, 0- normal) enhanced mode is not supported bit 2-15: reserved 00 description word figure 110. Erase unit information identifier zero indicates that the device should check...
Page 159
12.23 security freeze lock (f5h) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector...
Page 160
12.24 security set password (f1h) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - secto...
Page 161
Reserved 18-255 master password revision code valid if word 0 bit 0 = 1 17 password ( 32 bytes ) 01-16 control word bit 0 : identifier (1- master, 0- user) bit 1-7 : reserved bit 8 : security level (1- maximum, 0- high) bit 9-15 : reserved 00 description word figure 113. Security set password inform...
Page 162
12.25 security unlock (f2h) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector numb...
Page 163
Reserved 17-255 password ( 32 bytes ) 01-16 control word bit 0 : identifier (1- master, 0- user) bit 1-15 : reserved 00 description word figure 115. Security unlock information identifier zero indicates that device regards password as user password. One indicates that device regards password as mast...
Page 164: 12.26 Seek (7Xh)
12.26 seek (7xh) see below status 0 1 1 1 - - - - command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector number - - - - ...
Page 165: 12.27 Service (A2H)
12.27 service (a2h) 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 command - - - d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector count - - - - - - - - feature - - - - - - - - data 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 register command block output registers figure 11...
Page 166: 12.28 Set Features (Efh)
12.28 set features (efh) see below status 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number ...
Page 167
5dh enable release interrupt 66h disable reverting to power on defaults 82h disable write cache 85h disable advanced power management 86h disable power-up in standby mode 89h disable address offset mode aah enable read look-ahead feature bbh 4 bytes of ecc apply on read long/write long commands c2h ...
Page 168
12.28.3.1 low power idle mode additional electronics are powered off and the heads are unloaded on the ramp. However the spindle is still rotated at the full speed. 12.28.3.2 low rpm standby mode the heads are unloaded on the ramp and the spindle is rotated at the 60-65% of the full speed. When feat...
Page 169
12.29 set max address (f9h) see below status 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector numb...
Page 170
Output parameters to the device b option bit for selection whether nonvolatile or volatile. B = 0 is volatile condition. When b=1, max lba/cyl which is set by set max lba/cyl command is pre- served by por. When b=0, max lba/cyl which is set by set max lba/cyl command will be lost by por. B = 1 is no...
Page 171
12.29.1 set max set password (feature = 01h) see below status 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 command 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - ...
Page 172
12.29.2 set max lock (feature = 02h) see below status 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 command 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - se...
Page 173
12.29.3 set max unlock (feature = 03h) see below status 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 command 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - ...
Page 174
12.29.4 set max freeze lock (feature = 04h) see below status 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 command 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - -...
Page 175: 12.30 Set Multiple (C6H)
12.30 set multiple (c6h) see below status 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number ...
Page 176: 12.31 Sleep (E6H/99H)
12.31 sleep (e6h/99h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number - -...
Page 177
12.32 s.M.A.R.T. Function set (b0h) see below status 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sec...
Page 178
12.32.1 smart read attribute values (subcommand d0h) this subcommand returns the attribute values of the device to the host. Upon receipt of the smart read attribute values subcommand from the host the device saves any updated attribute values to the attribute data sectors and then transfers the 512...
Page 179
Off-line mode: the device executes command completion before executing the specified routine. During execution of the routine the device will not set bsy nor clear drdy. If the device is in the process of performing its routine and is interrupted by a new command from the host, the device will abort...
Page 180
Non-self-preserved attribute values will no longer be monitored. The state of s.M.A.R.T. (either enabled or disabled) is preserved by the device across power cycles. Upon receipt of the smart disable operations subcommand from the host the device disables s.M.A.R.T. Capabilities and functions and th...
Page 181
12.32.12 device attributes data structure the following defines the 512 bytes that make up the attribute value information. This data structure is accessed by the host in its entirety using the smart read attribute values subcommand. All multibyte fields shown in these data structures are in byte or...
Page 182
12.32.12.2 individual attribute data structure the following defines the 12 bytes that make up the information for each attribute entry in the device attribute data structure. 12 total bytes 04h 8 vendor specific 03h 1 attribute value (valid values from 01h to fdh) 01h 2 status flags 00h 1 attribute...
Page 183
Status flag definitions bit definition 0 pre-failure/advisory bit 0 an attribute value less than or equal to its corresponding attribute threshold indicates an advisory condition where the usage or age of the device has exceeded its intended design life period. 1 an attribute value less than or equa...
Page 184
12.32.12.5 total time in seconds to complete off-line data collection activity this field tells the host how many seconds the device requires to complete the off-line data collection activity. 12.32.12.6 off-line data collection capability reserved (0) 5-7 1 self-test routine is implemented 0 self-t...
Page 185
12.32.12.10 self-test completion time these bytes are the minimum time in minutes to complete the self-test. 12.32.12.11 data structure checksum the data structure checksum is the two's compliment of the result of a simple 8-bit addition of the first 511 bytes in the data structure. 12.32.13 device ...
Page 186
12.32.13.3 attribute id numbers attribute i d numbers supported by the device are the same as attribute values data structures. 12.32.13.4 attribute threshold these values are preset at the factory and are not intended to be changeable. 12.32.13.5 data structure checksum the data structure checksum ...
Page 187
12.32.14.4 error log data structure data format of error data structure is shown below. 90 3ch 30 error data structure 30h 12 5th command data structure 24h 12 4th command data structure 18h 12 3rd command data structure 0ch 12 2nd command data structure 00h 12 1st command data structure offset byte...
Page 188
Error data structure: data format of error data structure is shown below. 30 1ch 2 life timestamp (hours) 1bh 1 state 08h 19 extended error data (vendor specific) 07h 1 status register 06h 1 device/head register 05h 1 cylinder high register 04h 1 cylinder low register 03h 1 sector number register 02...
Page 189
12.32.15 self-test log data structure the following figure defines the 512 bytes that make up the self-test log sector. All multibyte fields shown in these data structures are in byte ordering. Note: n is 0 through 20 512 1ffh 1 data structure checksum 1fdh 2 reserved 1fch 1 self-test log pointer 1f...
Page 190
12.32.16 error reporting the following table shows the values returned in the status and error registers when specific error con- ditions are encountered by a device. 10h or 01h 51h the device is unable to write to its attribute values data structure. 10h or 40h 51h the device is unable to read its ...
Page 191: 12.33 Standby (E2H/96H)
12.33 standby (e2h/96h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number -...
Page 192
Output parameters to the drive sector count time-out parameter. If it is 0, the automatic power down sequence is disabled. If it is nonzero, the automatic power down sequence is enabled. The time-out interval is shown below: 21 minutes 15 seconds 255 21 minutes 10 seconds 254 8 hours 253 21 minutes ...
Page 193
12.34 standby immediate (e0h/94h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - secto...
Page 194: 12.35 Write Buffer (E8H)
12.35 write buffer (e8h) see below status 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 – 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number ...
Page 195: 12.36 Write Dma (Cah/cbh)
12.36 write dma (cah/cbh) see below status 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector number...
Page 196
H the head number of the first sector to be transferred. (l=0) in lba mode this register contains lba bits 24 - 27. (l=1) r the retry bit. If set to 1, then retries are disabled. It is ignored, when write cache is enabled. (ignoring the retry bit is in violation of ata-2.) input parameters from the ...
Page 197
12.37 write dma queued (cch) see below status 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector num...
Page 198
Input parameters from the device on bus release sector count bits 7 - 3 (tag) contain the tag of the command being bus released. Bit 2 (rel) is set to one. Bit 1 (i/o) is cleared to zero. Bit 0 (c/d) is cleared to zero. Sector number, cylinder high/low, h n/a. Srv cleared to zero when the device per...
Page 199: 12.38
12.38 write long (32h/33h) see below status 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector numbe...
Page 200
Input parameters from the device sector count the number of requested sectors not transferred. Sector number the sector number of the sector to be transferred. (l=0) in lba mode this register contains current lba bits 0 - 7. (l=1) cylinder high/low the cylinder number of the sector to be transferred...
Page 201: 12.39 Write Multiple (C5H)
12.39 write multiple (c5h) see below status 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector numbe...
Page 202
Input parameters from the device sector count the number of requested sectors not transferred. This will be zero, unless an unrecoverable error occurs. Sector number the sector number of the last transferred sector. (l=0) in lba mode this register contains current 1.5 lba bits 0 - 7. (l=1) cylinder ...
Page 203
12.40 write sectors (30h/31h) see below status 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector nu...
Page 204
Input parameters from the device sector count the number of requested sectors not transferred. This will be zero, unless an unrecoverable error occurs. Sector number the sector number of the last transferred sector. (l=0) in lba mode, this register contains current lba bits 0 - 7. (l=1) cylinder hig...
Page 205: 13.0
13.0 timings the timing of bsy and drq in status register are shown in the figure below. 400 ns status register bsy=1 out to command register device busy after command code out dma data transfer command 30 sec interrupt status register bsy=1 interrupt for command complete 400 ns status register bsy=...
Page 206
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 207: 14.0 Appendix
14.0 appendix 14.1 commands support coverage following table is provided to facilitate the understanding of dtla-3xxxxx command support coverage comparing to the ata-5 defined command set. The column entitled ‘implementation’ shows the capability of dtla-3xxxxx for those commands. Obsoleted yes read...
Page 208
Reserved reserved reserved: all remaining codes vendor specific reserved vendor specific fbh vendor specific no enable/disable delayed write fah optional yes set max address f9h optional yes read native max address f8h vendor specific vendor specific format unit f7h optional (6) yes security disable...
Page 209
14.2 set features command support coverage the following table provides a list of feature registers, feature names, and implementation for the dtla-3xxxxx models. The "implementation" column indicates with a "yes" or "no" whether or not the dtla-3xxxxx models have the capability of executing the com...
Page 210
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 211: Index
A abbreviations used, 1 acoustics, 61 actuator, 7 address offset, 94 addressing of hdd registers, 40 advanced power management, 93 at signal connector, 23 automatic acoustic management, 93 average latency, 14 b buffering, 15 c cable noise interference, 53 cabling, 40 ce mark, 63 command descriptions...
Page 212
N non-data commands, 101 o operating conditions, 46 operating mode definition, 17 p passwords, 83 performance characteristics, 11 pio data in commands, 97 pio data out commands, 99 pio timings, 29 plist physical format, 19 power management, 80 power modes, 80 power supply current, 48 power supply ge...