- DL manuals
- IBM
- Software
- High Performance Storage System HPSS
- Installation Manual
IBM High Performance Storage System HPSS Installation Manual
Summary of High Performance Storage System HPSS
Page 1
Hpss installation guide high performance storage system release 6.2 july 2008 (revision 2.0) hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 1.
Page 2
© copyright (c) 1992, 2008 international business machines corporation, the regents of the university of california, los alamos national security, llc, lawrence livermore national security, llc, sandia corporation, and ut-battelle. All rights reserved. Portions of this work were produced by lawrence...
Page 3
Table of contents chapter 1. Release 6.2...........................................................................................................15 1.1.New features.................................................................................................................15 1.1.1.Dce replacem...
Page 4
2.3.3.Hpss storage subsystems.................................................................................................................44 2.3.4.Hpss infrastructure ..........................................................................................................................44 2.3....
Page 5
3.4.2.3.Stk l40, stk sl500, stk sl8500..........................................................................................63 3.4.2.4.Stk............................................................................................................................................63 3.4.2.5.Adic am...
Page 6
3.7.6.6.Scsi pvr..................................................................................................................................88 3.7.7.Mover ..............................................................................................................................................
Page 7
3.10.4.File families...................................................................................................................................112 3.11.Hpss performance considerations...........................................................................112 3.11.1.Db2.......................
Page 8
5.1.4.Installation target directory preparation........................................................................................136 5.2.Install prerequisite software........................................................................................137 5.2.1.Install java.....................
Page 9
Chapter 6. Upgrading to hpss release 6.2 .....................................................................179 6.1.Special instructions for upgrading to hpss 6.2.2......................................................179 6.2.Planning for the hpss 6.2 upgrade..........................................
Page 10
6.3.16.Enable db2 backup......................................................................................................................215 6.3.17.Perform the dce export: hpss_dce_export..................................................................................215 6.3.18.Perform the uni...
Page 11
D.6. Transfer agent stanza..............................................................................................287 d.7. Stanzas reserved for future use..............................................................................291 appendix e. Hpss_env_defs.H..................................
Page 12
List of figures figure 1. File migration and stage operations..................................................................37 figure 2. Class of service / hierarchy / storage class.......................................................38 figure 3. Hpss components....................................
Page 13
List of tables table 1. Hpss client interface and mover platforms.......................................................49 table 2. Supported platform/driver/tape drive combinations......................................64 table 3. Cartridge/drive affinity table..........................................
Page 14
Preface about this book the hpss installation guide is for use both at system installation time as well as throughout the lifetime of the system. It will guide system administrators through the planning and installation of a new hpss system. It also guides system administrators through the conversio...
Page 15
Chapter 1. Release 6.2 this chapter summarizes hpss changes for release 6.2 into four categories: new features, retired features, deferred features, and changed features. Changes since release 4.5 and 5.1 are described. 1.1. New features this section describes the new hpss features added to release ...
Page 16
• storage class (but not subsystem-specific storage class options) • global configuration • accounting policy • location policy • all server configuration. Newly supported options include core server, gatekeeper, location server, log daemon, migration/purge server, pvl, all pvrs, and ssm. The mover,...
Page 17
1.1.12. Drive pools hpss provides hpss end clients the ability to direct tape read i/o requests to a predefined group of tape drives referred to as a drive pool. This ability helps hpss administrators manage tape drive scheduling and thus availability. For more information, please refer to section 7...
Page 18
1.1.18. Mover enhancement multiple movers for one or more hpss instances can now be configured to run on the same machine. The -c flag is added to the mover entry in the inetd configuration file to specify an alternate "/var/hpss" path to be used by the mover. In addition, the -s flag is added to en...
Page 19
Core server's memory image • modified the dmg table. In support of the new hpss rpc library, the tcp port was eliminated and the program and version numbers were added to dmg specific configuration. • modified the dmgfileset table. The tcp port was eliminated and the tcp hostname and rpc endpoint in...
Page 20
Filesystems do not support mirrored namespaces, fields which were specific to managing mirrored filesets are also no longer available. This includes the following configuration options: · global mount point · local mount point · fileset owner · fileset permissions • communication between the hdm and...
Page 21
1.4.4. Ssm changes significant changes were made in ssm between releases 4.5 and 5.1 and again between 5.1 and 6.2. For the reader's convenience, all changes between 4.5 and 6.2 are summarized in section 3.3.4.1: changes affecting sites upgrading directly from 4.5 . Changes between 5.1 and 6.2 are s...
Page 22
Changes since 4.5 server gui adm the ssm client scripts now use an internal polling mechanism for getting window updates (as opposed to being notified of the update by the server). This means that: • the ssm client application no longer requires a second port for two-way communication, • the rate of...
Page 23
Changes since 4.5 server gui adm the ssm client scripts can use ports exempted by the network administrator as firewall exceptions. See the -n option on the hpssadm/hpssgui man pages. The port on which the system manager will listen may be controlled by setting the $hpss_ssm_server_listen_port envir...
Page 24
Changes since 4.5 server gui adm the ability to see which users are logged into ssm, referred to in hpss 4.5 as a list of ssm "consoles", is available in 6.2 as part of the system manager statistics window from both the hpssgui and hpssadm. N n the menu bar has been reorganized extensively. The "set...
Page 25
Changes since 4.5 server gui adm column ordering is now controlled by dragging columns to the desired location. The modified order is preserved automatically in the user preferences across hpssgui restarts. N when messages have been written to the status bar, the most recent messages can be viewed i...
Page 26
Changes since 4.5 server gui adm the hpss 4.5 hpssadm commands • pvr_cartridge • pvl_volume • ss_pv • ss_map • ss_vv have been replaced by a single command "volume". The volume command has a required option "-type" for which these types may be specified: • pvl volume information • pvr cartridge info...
Page 27
Changes since 4.5 server gui adm the hpssadm config command now supports the additional structures: • class of service config • storage class (but not subsystem-specific storage class options) • global config • accounting policy • location policy • all server configurations; servers which were not s...
Page 28
Changes since 5.1 server gui adm options to the hpssgui and hpssadm startup scripts have changed significantly. See the man pages for details. Following are some highlights: n n the scripts are dependent upon an ssm configuration file (ssm.Conf), created by mkhpss, which contains some site-specific ...
Page 29
Changes since 5.1 server gui adm the ssm client script options for connecting to the system manager across a virtual private network connection (vpn) have changed. See the -p and -h options on the hpssgui and hpssadm man pages. N n n the ssm client script option for using ports exempted by the netwo...
Page 30
Changes since 5.1 server gui adm the menu bar has been reorganized slightly. The "data server statistics" menu item has been replaced by the "system manager statistics" menu item, available from the monitor->ssm information menu path. "column view" was added to the menu bar for ssm windows that disp...
Page 31
Changes since 5.1 server gui adm the mechanism for selecting columns to be displayed in each list window has moved from the list's preferences window to the "column view" menu of the list window itself. See the description of the "column view" menu item in section 3.6: common window elements of the ...
Page 32
Changes since 5.1 server gui adm since ssm now represents the three core server volume structures as a single structure, the types specified to the hpssadm volume command have changed. The 5.1 types: • disk storage map information • disk physical volume information • disk virtual volume information ...
Page 33
Changes since 5.1 server gui adm a new subcommand “update” has been added to the hpssadm device command for updating the mover device and pvl drive objects. N hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 33.
Page 34
Hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 34.
Page 35
Chapter 2. Hpss basics 2.1. Introduction the high performance storage system (hpss) provides hierarchical storage management and services for very large storage environments. Hpss may be of interest to organizations having present and future scalability requirements that are very demanding in terms ...
Page 36
2.2.4. Based on standard components hpss runs on unix and is written in ansi c and java. It uses remote procedure calls, a selectable security service (kerberos or unix), unix or ldap for user configuration information, and db2 as the basis for its portable, distributed, transaction-based architectu...
Page 37
2.3. Hpss components the components of hpss include files, filesets, junctions, virtual volumes, physical volumes, storage segments, metadata, servers, infrastructure, user interfaces, a management interface, and policies. Media and file metadata are represented by data structures that describe the ...
Page 38
Figure 2. Class of service / hierarchy / storage class 2.3.1. Hpss files, filesets, volumes, storage segments and related metadata the various metadata constructs used to describe the hpss namespace and hpss storage are described below: • files (bitfiles) . Files in hpss, called bitfiles in deferenc...
Page 39
Recorded on these tapes. Hpss supports grouping files on tape volumes only. Families can only be specified by associating the family with a fileset. All files created in the fileset belong to the family. When one of these files is migrated from disk to tape, it is recorded on a tape with other files...
Page 40
• class of service (cos) . Each bitfile has an attribute called class of service. The cos defines a set of parameters associated with operational and performance characteristics of a bitfile. The cos results in the bitfile being stored in a storage hierarchy suitable for its anticipated and actual s...
Page 41
Consisting of directories, files, and links. These name space objects may exist within filesets that are connected via junctions. Second, the core server provides the abstraction of logical bitfiles to its clients. A bitfile is identified by a core server generated name called a bitfile id. Clients ...
Page 42
The purpose of tape file migration is to make an additional copy (or multiple additional copies) of a file, in a tape storage class, to a lower level in the hierarchy. It is also possible to move files downwards instead of copying them. In this case there is no duplicate copy maintained. There is no...
Page 43
• physical volume repository (pvr) . Pvrs manage hpss cartridges. Though an hpss system may contain multiple pvrs, each cartridge is managed by only one. Pvrs provide apis for clients to request cartridge mounts and dismounts and query the status of cartridges. For convenience, pvrs are often config...
Page 44
2.3.3. Hpss storage subsystems the goal of storage subsystems (or just “subsystems”) is to increase the scalability of hpss by allowing multiple core servers to be used within a single hpss system. Every hpss system is partitioned into one or more subsystems. Each subsystem contains a single core se...
Page 45
Hpss core server performs most of the hpss metadata changes using the transaction management tools provided by db2. For the most part, these metadata transactions are managed entirely within the core server. Other servers such as mps and pvl modify their metadata transactionally, and those transacti...
Page 46
Hpss. A delog function is provided to extract and format log records from a central or archived log file. Delog options support filtering by time interval, record type, server, and user. • accounting . The hpss accounting system provides the means to collect usage information in order to allow a par...
Page 47
Gui. The hpssgui simplifies the management of hpss by organizing a broad range of technical data into a series of easy-to-read graphic displays. The hpssgui allows monitoring and control of virtually all hpss processes and resources from windows that can easily be added, deleted, moved, or overlappe...
Page 48
Hpss provides facilities for recording information about authentication and object (file/directory) creation, deletion, access, and authorization events. The security audit policy for each server determines the records that each individual server will generate. All servers can generate authenticatio...
Page 49
The following matrix illustrates which platforms support hpss interfaces. Table 1. Hpss client interface and mover platforms platform pftp client client api hpss mover hpss vfs client ftp clients ibm aix x x x any platform running standard ftp clients. Gui- based clients may not function correctly f...
Page 50
Hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 50
Page 51
Chapter 3. Hpss planning 3.1. Overview this chapter provides hpss planning guidelines and considerations to help the administrator effectively plan, and make key decisions about, an hpss system. The planning process for hpss must be done carefully to ensure that the resulting system satisfies the si...
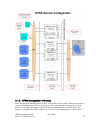
Page 52
Figure 4. Hpss generic configuration 3.1.2. Hpss configuration planning before beginning the planning process, there is an important issue to consider. Hpss was designed to optimize the transfer of large files at the expense of some small file transfer performance. If at all possible, try to reduce ...
Page 53
Aggregate the individual files into large individual files before moving them into the hpss name space. The following planning steps must be carefully considered for the hpss infrastructure configuration and the hpss configuration phases: 1. Identify the site’s storage requirements and policies, suc...
Page 54
More information about configuring families. • plan for filesets and junctions, if any. Refer to chapter 10: filesets and junctions in the hpss management guide for more information. • plan for hpss storage classes. Refer to section 3.10.1: storage class on page 102 for more information on the stora...
Page 55
3.1.4. Hpss operational planning the following planning steps must be carefully considered for the hpss operational phase: 1. Define the site guidelines for the hpss users and ssm users. • each hpss user who uses the storage services provided by hpss should be assigned an accounting id and one or mo...
Page 56
Guide that the hpss support/deployment team uses to monitor and check the progress of an installation. 3.2. Requirements and intended uses for hpss this section provides some guidance for the administrator to identify the site’s requirements and expectations of hpss. Issues such as the amount of sto...
Page 57
3.2.5. Duplicate file policy the policy on duplicating user data files impacts the amount of data stored and the amount of data moved. If all user files are duplicated, the system will require twice as much tape storage. If users perform their own duplication of files, the system may consume a small...
Page 58
Authentication and authorization (subject to certain caveats – see ftp documentation for details). The pftp_client binary must be built using the distributed source code. However, it is the site's responsibility to obtain the necessary kerberos components. Acls entries in the authzacl table and/or a...
Page 59
If unix authentication will be used, this product is not required. 3.3.1.3. Ldap and ibm kerberos hpss can be configured to use an ldap directory to store its authorization information such as users' names, uids, gids, and home directories. The supported ldap server product for this release is ibm t...
Page 60
• ibm atl: atldd.Driver 6.5.2.0 and atape.Driver 10.2.8.0 (if planning to control the ibm tape library and drives from this node) 3.3.2.1.2. Linux requirements each linux server node must have the following installed: • linux machine (eserver zseries) with a minimum of 2 gb ram • red hat enterprise ...
Page 61
• 1 gb ram 3.3.2.2.3. Solaris requirements each solaris mover node must have the following prerequisites: • solaris ultrasparc based processor • solaris 8+ (32-bit or 64-bit) • c compiler: forte developer 7 c 5.4 2002/03/09 (if planning to recompile mover code) 3.3.2.2.4. Irix requirements each irix...
Page 62
• xfsdump-2.2.25-0.2 or higher • xfsprogs-2.6.25-0.2 or higher 3.4. Hardware considerations this section describes the hardware infrastructure needed to operate hpss and includes considerations about infrastructure installation and operation that may impact hpss. 3.4.1. Network considerations becaus...
Page 63
• stk sl500 and sl8500 • stk tape libraries that support acsls • adic i500 • adic aml (supported by special bid only) 3.4.2.1. Ibm 3494 the 3494 pvr supports ethernet and rs-232 (tty) attached robots. If appropriately configured, multiple robots can be accessible from a single node. 3.4.2.2. Drive-c...
Page 64
9840c drives should not be used in conjunction with either 9840a or 9840b drives. Table 2. Supported platform/driver/tape drive combinations platform driver device(s) aix ibm 3580 (gen3, gen4), 3592 (gen2, gen3) native 3580 (gen3, gen4), 9840 (c, d), 9940 (a, b), t10000 (a, b) linux native 3580 (gen...
Page 65
(lto) gen4 drive can read 3580 (lto) gen4, 3580 (lto) gen3, and 3580 (lto) gen2 cartridges, but can only write 3580 (lto) gen4 and 3580 (lto) gen3 cartridges), hpss will mount a 3580 (lto) gen2 cartridge into a 3580 (lto) gen4 drive only if 3580 (lto) gen2 drives are not defined in hpss and 3580 (lt...
Page 66
Table 3. Cartridge/drive affinity table cartridge type drive preference list ampex dst-312 ampex dst-312 ampex dst-314 ampex dst-314 ampex dst-314 single-length 3590 single-length 3590 double-length 3590 single-length 3590e double-length 3590e single-length 3590h double-length 3590h double-length 35...
Page 67
3580 (lto) gen 4 3580 (lto) gen 4 3592 j1a short tape 3592 j1a standard tape 3592 j1a 3592 eo5 3592 eo6 3592 eo5 jj short tape 3592 eo5 ja standard tape 3592 eo5 jb xl tape 3592 eo5 3592 eo6 3592 eo6 jj short tape 3592 eo6 ja standard tape 3592 eo6 jb xl tape 3592 eo6 stk 9840a stk 9840a stk 9840b s...
Page 68
Fibre channel. For these devices, operating system disk partitions of the desired size must be created (e.G., aix logical volume or linux/solaris/irix disk partition), and the raw device name must be used when creating the mover device configuration (see section 7.1: configure a new device & drive o...
Page 69
Starting with hpss 6.2 there are many enhancements to the storage system to take advantage of storage area networks. Though separated in figure 4, in reality there is usually only one san at an installation and all the resources are attached to it. Besides the hpss movers being connected to san, the...
Page 70
Figure 5. Basic hpss metadata & filesystem allocation on the left hand side of the diagram, the raw physical volumes are shown attached to the disk array controller. The configuration of the disks by the controller and its software should be divided into three separate luns: 1) hpss filesystems and ...
Page 71
Mirrored log components will need to be determined by hpss and the customer based on transaction performance requirements. Potentially, disk resources primarily allocated for hpss disk cache can be used or the site may want to dedicate a second disk array for this purpose to prevent any possible int...
Page 72
To create a site policy configuration file, usually named /var/hpss/gk/gksitepolicy . The size of this file depends on the site-implemented gatekeeping policy. If the gatekeeper service is not used, there is a minimal amount of disk space used in this directory. • if an accounting report is requeste...
Page 73
3.5.3.7. /db2/backups/subsys1 & subsysx similar to /db2/backups/cfg , the /db2/backups/subsys1 filesystem temporarily stores backup images of the subsystem archived logs and database as they are generated. The backup files are then transferred to long-term media, such as tape, using a backup file ma...
Page 74
Section 5.3.1.2: install hpss documentation and db2 software on page 141. The tables and indexes are separated into separate logical volumes/partitions to ease future expansion of the database and to maximize performance of database operations. For linux, access to a /dev/hdxy partition is through t...
Page 75
Disk devices. The “6.2 sizing spreadsheet” input tab is shown below. Based on the input, the resulting output is show below: hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 75.
Page 76
Definitions for the db2 tables are as follows: bitfile disk allocation maps . (bfdiskallocrec) for each bitfile stored on disk, one or more rows will be created in the disk allocation maps table. The number of rows is determined by the storage segment size in the storage class in which the files are...
Page 77
Bytes. Disk storage segments . (storagesegdisk) expect the size of the disk storage segment metadata table to be quite volatile. As files are added to hpss, disk storage segments will be created, and as files are migrated to tape and purged from disk, they will be deleted. A rough estimate of the nu...
Page 78
Created will require approximately 10mb of disk space in a filesystem that should be used only for database home directories and other db2 home directories (such as the db2 administration server and fenced user). This filesystem should be protected by raid since db2 may require information in the da...
Page 79
The amount of memory for nodes running hpss movers, and no db2 servers, is dependent on the number and types of devices configured on the mover node, the expected usages of those devices, and the configuration of the movers . In general, movers supporting disk devices will require more memory than m...
Page 80
Class of service and accounting code information. In addition, the chgrp , chmod , and chown commands are supported as quote site options. The ftp daemon is built on top of the client api and must be run on a node that supports kerberos clients. Note that ftp clients can run on computers that do not...
Page 81
3.7.1. Core server the core server is responsible for managing the hpss name space (files, directories, links, etc.), bitfiles, and storage (physical volumes, virtual volumes, etc.) for a single subsystem. Each of these areas of responsibility are outlined in greater detail below. Core server at lar...
Page 82
Figure 6. The relationship of various server data structures disk storage allocation each core server manages disk storage units for hpss. It maps each disk storage unit onto an hpss disk physical volume (pv) and records configuration data for the pv. Groups of one or more pvs (disk stripe groups) a...
Page 83
The core server is designed to scale up its ability to manage tapes as the number of tapes increases. As long as sufficient memory and cpu capacity exist, threads can be added to the server to increase its throughput. Additional subsystems can also be added to a system, increasing concurrency even f...
Page 84
Metadata updates and can impose extra overhead on db2. Also, unpredictable purge behavior may be observed if the purge record ordering is changed with existing purge records in the system until these existing records are cleared. A purge run ends when either the supply of purge records is exhausted ...
Page 85
Sites can choose to configure zero (0) or more gatekeepers per hpss system. Gatekeepers are associated with storage subsystems. Each storage subsystem can have zero or one gatekeeper associated with it and each gatekeeper can support one or more storage subsystems. Gatekeepers are associated with st...
Page 86
Requests from a particular host or user. The site interfaces will be located in a shared library that is linked into the gatekeeper. It is important that the site interfaces return a status in a timely fashion. Create, open, and stage requests from mps are timing sensitive, thus the site interfaces ...
Page 87
Pvl. It is possible for multiple hpss pvrs to manage a single robot. This is done if it is necessary to organize the tape drives in the robot into partitions. Each tape drive in the robot is assigned to exactly one pvr. Additionally, each cartridge is assigned to only one pvr. The pvrs can be config...
Page 88
3.7.6.3. 3494 pvr the 3494 pvr can manage an ibm 3494 tape robot attached via ethernet or scsi. The pvr will create a process to receive asynchronous notifications from the robot. At least one pvr should be created for every robot managed by hpss. If multiple 3494 robots are managed, care must be ta...
Page 89
3.7.7. Mover the mover configuration is largely dictated by the hardware configuration of the hpss system. Each mover can handle both disk and tape devices and must run on the node to which the storage devices are attached. The mover is also capable of supporting multiple data transfer mechanisms fo...
Page 90
Driver has a built-in configuration table for all hpss supported tape drives. This configuration provides variable block size for most hpss supported drives. In order to override the built-in configuration, device information can be supplied in the /dev/kernel/st.Conf as global properties that apply...
Page 91
Hbas with a 7000 series chip set, uncomment the following lines in the " .Config " file and follow the procedure for rebuilding your linux kernel. Config_scsi_aic7xxx=y config_aic7xxx_cmds_per_device=253 config_aic7xxx_reset_delay_ms=15000 3.7.7.4. Performance the configuration of the movers and att...
Page 92
3.7.9. Startup daemon the startup daemon is responsible for starting, monitoring, and stopping the hpss servers. The daemon responds only to requests from the ssm system manager. It shares responsibility with each hpss server for ensuring that only one copy of the server runs at a given time. It hel...
Page 93
Values may need to be overridden in env.Conf. Key sm environment variables variable default value functionality hpss_sm_srv_connect_fail_count 3 connection fail count: number of connection failures to a server before the max connection interval takes affect (*) hpss_sm_srv_connect_interval_mi n 20 i...
Page 94
Variable default value functionality hpss_sm_srv_max_connections 50 number of hpss server connections to maintain at once. If this number of connections is exceeded, then old connections will be closed to maintain this number of connections * the sm attempts to throttle the connection attempts to ot...
Page 95
Disk migration is controlled by several parameters. By default, these parameters are the same across all subsystems. However, subsystem-specific policies may be created which override all of these values. For a list of these parameters, refer to section 6.4.2.2: disk migration policy configuration i...
Page 96
Storage class by periodically extracting this information from the hpss core server. Based upon parameters in the purge policy, a purge run will be started when appropriate. The administrator can also force the start of a purge run via ssm. The disk purge is controlled by several parameters: • the d...
Page 97
Out of the hpssgecos field, it does not exist in unix. It only exists in ldap. The metadata for each file and directory in an hpss system contains an account field, which determines how the storage will be charged. Each user has at least one default account index, which is put into the account field...
Page 98
The principal's ldap hpssgecos attribute, then site-style accounting will be used. Otherwise unix-style accounting will be used. To keep the accounting information consistent, it is important to set up all users in the hpss authorization services with the same style of accounting (i.E. They should a...
Page 99
3.9.4.5. Security audit hpss provides the ability to record information about authentication, file creation, deletion, access, and authorization events. The security audit policy in each hpss server determines what audit records a server will generate. In general, all servers can create authenticati...
Page 100
Gatekeeper configured in its storage subsystem. If one is found, the core server asks the gatekeeper for its monitor types by calling the gk_getmonitortypes function which calls the locally implemented gk_site_getmonitortypes function which determines which types of requests to monitor. This query b...
Page 101
Down or when the user application is aborted. Notes: 1. All open requests to the core server will call the gatekeeping service open api ( gk_open ). This includes opens that end up invoking a stage. 2. Any stage call that is invoked on behalf of open will not call the gatekeeping service stage api (...
Page 102
(vvs). Each vv contains one or more pvs. The vv characteristics described by a storage class include the vv block size and vv stripe width. If pvs are grouped one at a time, so that their stripe width is one, they are still defined as vvs. A number of additional parameters are defined in storage cla...
Page 103
Ssm provides the capability to define storage classes and to add and delete virtual volumes to and from the defined storage classes. A storage class is identified by a storage class id and its associated attributes. For detailed descriptions of each attribute associated with a storage class, see sec...
Page 104
Utility programs copy data from one tape vv to another, so the number of available tape drives of the appropriate type must be at least twice the tape stripe width, for these programs to function. Migration of files between tape storage classes in a hierarchy, that are of the same media type, requir...
Page 105
Streaming to maximize performance. For recommended values for various media types, see section 3.10.1.12: some recommended parameter values for supported storage media on page 106. 3.10.1.6. Minimum storage segment size selection (disk only) the core server maps disk files onto a series of disk stor...
Page 106
3.10.1.8. Maximum vvs to write (tape only) this parameter restricts the number of tape vvs, per storage class, that can be concurrently written by the core server. Its purpose is to minimize the number of tape mounts and to limit the number of tape vvs being written, to prevent files from being scat...
Page 107
3.10.1.12.1. Disk media parameters table 7 contains attributes settings for the supported disk storage media types. Table 6. Suggested block sizes for disk disk type media block size minimum access size minimum virtual volume block size scsi attached 4 kb 0 1 mb ssa attached 4 kb 0 1 mb fibre channe...
Page 108
Table 7. Suggested block sizes for tape tape type media block size blocks between tape marks estimated physical volume size ampex dst-312 1 mb 1024 50, 150, 330 gb ampex dst-314 1 mb 1024 100, 300, 660 gb ibm 3580 (lto) 256 kb 1024 100 gb ibm 3580 (lto gen 2) 256 kb 1024 200 gb ibm 3580 (lto gen 3) ...
Page 109
Storagetek t10000a 256 kb 2560 500 gb storagetek t10000b 256 kb 2560 1000 gb in the above table: • media block size is the block size to use in the storage class definition. This is the size of the data blocks written to tape. Note that for tape devices, the mover configuration does not contain the ...
Page 110
3.10.3. Class of service each hpss file belongs to a single class of service (cos) which is selected when the file is created. It is selected via class of service hints information passed to the core server when the bitfile is created. If using the client api, the application program has full access...
Page 111
Guaranteed that the file is completely and successfully staged before it is read. If the stage operation fails, the open will return with an error. Guideline 3: select the stage on open async option if you wish to stage the entire file to the top level in the hierarchy and do not want the client api...
Page 112
Latency field from the storage class at the top level in the hierarchy. 3.10.3.6. Selecting transfer rate this field can be used via the cos hints mechanism to affect cos selection. Guideline 1 : this field should generally be set to the value of the transfer rate field in the storage class that is ...
Page 113
· maximum users and applications connected to db2 · nature of usage: read or update • database logging · hardware or software mirroring · disk speed and reliability: select the fastest, most reliable disk · location of physical disks and database data: it is recommended that they be separate • datab...
Page 114
Directly to tape, the buffer size used by the ftp server and the virtual volume block size defined for the storage class being written to will have a significant impact. If the buffer size used by the ftp server is not a multiple of the virtual volume block size, each buffer written will result in a...
Page 115
3.11.5. Client api the client api provides the capability to perform data transfer of any size (the size being parameters supplied by the client to the read and write interfaces). The size of the data transfers can have a significant impact on the performance of hpss. In general, larger transfers wi...
Page 116
Stage requests. The site policy could limit the maximum number of non-authorized caller requests allowed at once by either delaying or denying particular requests. To delay the request, the site policy may return a special retry status along with the number of seconds to wait before the client api r...
Page 117
3.12. Hpss metadata backup considerations this section contains guidelines for proper maintenance of the hpss metadata stored in db2. The policies described should be fully understood and implemented to protect the hpss metadata. Failure to follow these policies can lead to unrecoverable data loss. ...
Page 118
Hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 118.
Page 119
Chapter 4. System preparation this section covers the steps that must be taken to appropriately prepare your system for installation and configuration of hpss and its infrastructure. • general setup (section 4.1) • setup filesystems (section 4.2) • setup tape libraries (section 4.3) • verify tape dr...
Page 120
• configure the perl prerequisite software on hpss nodes. • configure the ssh prerequisite software on the core hpss server node (at a minimum) and configure ssh to accept connections from ibm houston. Include the houston subnet ip addresses 192.94.47 and 12.39.169 in the local firewall routing rule...
Page 121
/db2/mirror-backups/subsys1 4.2.2. Hpss filesystem configure /var/hpss as a separate file system on each hpss server node. This filesystem will store hpss configuration files, log files, mps reports, and other hpss related files. It is recommended that this filesystem be at least 1gb in size. Config...
Page 123
To start the lmcp daemon: root% /etc/methods/startatl to test whether lmcp daemon is configured and working correctly: % mtlib -l -ql where lmcpdevice is usually /dev/lmcp0 . To test ability to use lmcp daemon to mount a tape: % mtlib -l/dev/lmcp0 -m -v -x test ability to dismount the tape: % mtlib ...
Page 124
For aml tape libraries: • if using an aml pvr, configure the insert/eject ports using the configuration files /var/hpss/ etc/aml_ejectport.Conf and /var/hpss/etc/aml_insertport.Conf . Refer to section 5.2.8.3: aml pvr specific configuration of the hpss management guide for more information. 4.4. Ver...
Page 125
To measure read performance on drive rmt1 using the previously-written uncompressed and compressed files: % iocheck -r -t 20 -b 1mb /dev/rmt1.1 % iocheck -r -t 20 -b 1mb /dev/rmt1.1 to unload a tape: % tctl -f rewoffl repeat the above steps for each tape drive. 4.4.2. Solaris on each tape mover node...
Page 126
4.4.3. Irix on each tape mover node, verify that each tape drive has the variable-length block size option enabled. To determine if the variable block size option is enabled, the following should complete successfully: % dd if=/dev/null of=/dev/rmt/tps2d6nr bs=80 count=1 % dd if=/dev/null of=/dev/rm...
Page 127
4.5.1. Aix • verify that the correct number and type of disk devices are available on each db2 and disk mover node. The disk devices section of the lsnode report displays all available disk devices. To determine the type and number of available disk devices: % lsdev -c -s a -c disk • if using ssa di...
Page 128
Use the iocheck.Ksh script from the deployment tools package to show the performance of one or more individual disk devices and the peak aggregate performance of concurrent i/o across multiple disks (e.G., to show the peak performance of adapters). Warning: the contents of this logical volume will b...
Page 129
4.6. Setup network parameters • install and configure all network interfaces and corresponding network connections. Refer to ibm's internal network technologies home page for resources on configuring and tuning networks and tcp/ip. The network interfaces section of the lsnode report from each node s...
Page 130
Will be used. For linux, a similar change should be made to /etc/nsswitch.Conf : hosts: nis dns files • for each aix ethernet network interface, verify that the en0 and et0 interfaces are not both configured at the same time (we recommend only using en0 unless the other nodes in the network are all ...
Page 131
... Ccs0 64k 64k on -- -- ccs0 64k 32k on -- -- ... You are looking for the best values possible for each network connection. These values will be used by hpss to optimize its data transfers. This example is, by no means, a complete picture of what controls network performance. In fact, it is assume...
Page 132
Udp_recvspace controls the default size of the receive buffer for upd/ip sockets. A value that is too small can cause server rpc sockets to be overrun. Tcp_recvspace, tcp_sendspace controls the default size for the receive and send buffers for tcp/ip sockets. Internally, hpss servers and clients att...
Page 133
4.6.2. Sp/x switch device buffer driver buffer pools ibm sp/x systems provide the capability to tune the buffer pool allocation in the switch device driver. Two variables can be changed: rpoolsize, which is the size of the buffer pool for incoming data, and spoolsize which is the buffer pool size fo...
Page 134
Hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 134.
Page 135
Chapter 5. Hpss installation and infrastructure configuration this chapter provides instructions and supporting information for installing the hpss prerequisite software, the hpss and db2 software from the hpss distribution media, and performing the hpss infrastructure configuration. To install and ...
Page 136
Table 9. Installation package sizes and disk requirements platfor m hpss package name package size /opt/hpss space requirement s package description aix hpssserver-6.2.0.0.Lpp 450 mb all hpss components hpssclientmover-6.2.0.0.Lp p 70 mb client and mover components hpsssource-6.2.0.0.Lpp 130 mb hpss...
Page 137
• the disk, where the installation target directory resides, has enough space to hold all the hpss packages to be installed on this node. • warning: do not use nfs mounted directories for installing nor allocating space for hpss related components. Installing on nfs is problematic and the errors can...
Page 138
If unix authorization will be used, this product is not required. Ldap authorization is supported on aix only. If ldap will be used for hpss authorization, download the ibm tivoli directory server from http://www.Ibm.Com. Search for "ibm tivoli directory server" on the site to find the download page...
Page 139
Xfs uses the linux udev daemon to dynamically configure the dmapi device node. Use the chkconfig command to make sure that boot.Udev is "on". Note that if a change is required, then the machine needs to be rebooted in order for it to take effect. 5.3. Install hpss/db2 and configure hpss infrastructu...
Page 140
5. From the "root subsystem machine" submenu, click on the 'pre-install config' icon in the left panel. Mkhpss will display the following screen: 6. Verify that the default values are correct for the given installation and modify if necessary. Click the 'configure' button to perform the pre-installa...
Page 141
Scripts to verify/create the 'hpss' account and group, setup the /var/hpss (default location) directory with the required subdirectories and initialize the hpss environment file, env.Conf in /var/hpss/etc. 7. If the pre-installation configuration succeeds, you will see the following message in the c...
Page 142
Db2 software will be installed in the /usr/opt/db2_08_01 (aix) or /opt/ibm/db2/v8.1 (linux) directory. 2. For 6.2.0, the hpss software and documentation should already be installed according to the installation step in section 5.3.1.1. Installing from cd will be an option starting in 6.2.1. 3. For 6...
Page 143
% su - % cd /usr/opt/db2_08_01/adm % ./db2licm -a the generic db2 license file (*/db2/license/db2ese.Lic) can be found on the db2 installation cd or image. It can also be obtained by contacting your hpss support representative. To update the license with the appropriate number of of processors, issu...
Page 144
3. Using the scrollbar, move the right-panel display until the "authorization service" information is seen. It should look like the following: hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 144.
Page 145
4. Select the "configure authorization service" checkbox. Set the "authorization service" to "unix and config files". 5. Review and modify (if necessary) the active fields: • local site name. The value is usually set to the full machine name of the local host which can be determined using the 'hostn...
Page 146
Configuration step. Other hpss utilities are available to administer these hpss configuration files. See section 2.2.2: security mechanisms in the hpss management guide for more information. To use the hpss configuration files, select the "enable local unix passwd files" checkbox. The default names ...
Page 147
• kdc directory. The pathname of the kdc directory. This directory should be set to /var/hpss/krb5kdc. • master password. The kerberos administration password. Be sure to remember this password to be able to administer the kerberos environment later. • verify password. Re-enter the kerberos administ...
Page 148
5. Select the "configure authorization service" checkbox. Set the "authorization service" to "unix and config files". 6. Review and modify (if necessary) the following authorization fields: • local site name. The value is usually set to the full host name of the local host. This can be determined by...
Page 149
8. Select the "configure server accounts" checkbox to create unix accounts for hpss servers. 9. Click on the "configure security services" button at the bottom of the screen to perform the specified security configuration. 10. If the configuration was a success, you should see the following message ...
Page 150
4. Select the "configure authorization service" checkbox. Set the "authorization service" to "ldap". 5. Review and modify (if necessary) the following authentication fields: • kerberos install path. The pathname where kerberos is installed. The default directory is /usr/kerberos. • kdc directory. Th...
Page 151
• authentication type. There are two supported options: keytab file or password. The keytab file option allows hpss servers or utilities to read a keytab file to authenticate. The password option requires a password to be supplied each time an hpss server or utility is invoked. • password. The passw...
Page 152
Unix passwd files" checkbox as shown in the example above. The default names for the files should be used as displayed. 8. Select the "configure server accounts" checkbox to create accounts for hpss servers. 9. Click on the "configure security services" button at the bottom of the screen to perform ...
Page 153
3. Review and modify (if necessary) the following fields: • instance owner . The name of the db2 instance owner, normally 'hpssdb'. • schema name . The name of the db2 schema containing the hpss metadata table, normally 'hpss'. • create db2 instance . Select this checkbox to create the db2 instance....
Page 154
• create subsys database . Select this checkbox to create the "subsys1" database. • subsystem database alias . The "real" database is configured as 'hsubsys1', while the database alias is the name used by hpss servers and utilities to reference the database. The default value of 'subsys1' should nor...
Page 155
B. On the “tablespace config” window, set the tablespace type from the drop down menu. For the userspace1 tablespace, select “sms” system managed space. For the remaining tablespace entries, select tablespace type to "dms" database managed space. C. For userspace1, which uses system managed space, f...
Page 156
Hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 156.
Page 157
F. Select the "add" button to add "raw devices" to container path list. The "raw devices" must already exist. For aix, the logical volumes must have already been created and the "raw" form be specified (i.E. Lv "dbs1.Tables", specify / dev/rdbs1.Tables") for linux, not only must the partition exist,...
Page 158
A variable named db2_use_local_resync set to the value of 'true' when starting db2 in order for the aforementioned fileset operations to complete successfully: csh & tcsh: setenv db2_use_local_resync true sh & bash: export db2_use_local_resync=true 5.3.1.6. Configure other services this menu configu...
Page 159
4. After exiting mkhpss , verify permissions on the generated files. In particular, note the permissions on the keytab files. The hpss.Keytab is used by hpss servers to establish credentials. The mm.Keytab is used by hpss utility programs. The kadm5.Keytab is used to establish credentials as the ker...
Page 160
5.3.2. Install and configure hpss – secondary subsystem machine for the secondary subsystem machine, the following configuration steps must be performed: • pre-installation configuration • install hpss documentation and db2 • set up db2 permanent license • install configuration bundle • configure se...
Page 161
3. Verify that the default values are as desired. Modify them, if necessary. Click the 'configure' button to perform the pre-installation setup. 4. If the pre-installation configuration was a success, you will see the following message in the command output window: ## run command exited with status ...
Page 162
This panel allows you to install the db2 software, hpss software (option starting in 6.2.1), and hpss documentation. Perform the following steps to install the software: 1. To install db2, check the 'install db2' checkbox. Click on the 'source path' button and select the directory that contains the ...
Page 163
% su - % cd /usr/opt/db2_08_01/adm % ./db2licm -a the generic db2 license file (*/db2/license/db2ese.Lic) can be found on the db2 installation cd or image. It can also be obtained by contacting your hpss support representative. To update the license with the appropriate number of of processors, issu...
Page 164
5.3.2.5. Configure hpss security services this section describes the procedure to configure a kerberos or unix security client on the secondary subsystem machine. The security client must match the security mechanism on the root machine. To configure the security client for the secondary subsystem m...
Page 165
• configure server accounts . This checkbox is flagged when the server accounts should be created on the local machine. This is usually not required when the kerberos server has already been configured with the hpss server accounts. 3. To configure the unix client, un-check the "configure kerberos c...
Page 166
2. Using the scrollbar, move the right-hand panel until you see the following screen: 3. Review and modify (if necessary) the following fields: • instance owner . The name of the instance owner hpss will use. Should use the default value of 'hpssdb' in most cases. • schema name. The name of the hpss...
Page 167
• authentication type . Currently there is only one authentication type allowed. • user name . The unix userid to be used for db2 authentication. This userid must have a valid unix account before running this configuration option. • password and verify password . Enter and verify the unix password f...
Page 168
"configuration" icon and then the "other services" icon. The following window will be shown: 2. Click on the "configure other services" button to complete the configuration of the secondary subsystem machine. If the configuration was a success, you should see the following message in the command out...
Page 169
Source tree to obtain the source code from the root machine and install on the mover/client machine. 5.3.3.2. Install configuration bundle the configuration bundle is created on the root subsystem and contains configuration files used by the root, mover/client and subsystem machines. See page 159, s...
Page 170
/opt/hpss/config/ /opt/hpss/stk/ /opt/hpss/src/ included only if the hpss-src package is installed. /var/hpss/ 2. Verify that the hpss file ownerships and file permissions are set as follows: • executable files: rwxr-xr-x bin bin • include files: r--r--r-- bin bin • library files: r--r--r-- bin bin ...
Page 171
Bundle the html files for delivery to the hpssgui host machine. The recommended installation location for the html files on each hpssgui host is /var/hpss/doc for aix and linux platforms and c:\hpss\doc for windows platforms. 5.5.2. Manual page setup perform the following steps to set up hpss manual...
Page 172
Wishing to learn more about db2 tuning are referred to the hpss db2 tuning guide , available from your support representative, the db2 administrative guide: performance , available on-line from the ibm db2 website, the ibm db2 tuning redbook , and the many ibm and after-market books available on thi...
Page 173
Makefile.Macros: build_platform = aix build_top_root = /opt/hpss krb5_auth_support=on unix_auth_support=on ldap_auth_support=off gsi_auth_support=off conversion_from_45 = off conversion_from_51 = off build_unsupported = off mvr1_program_name = $(local_bin)/hpss_mvr_tcp mvr1_options = "" # mvr2_progr...
Page 174
1. Log on as hpss. 2. Change directory to /opt/hpss/bin. 3. Run the following command: % hpss_db2_bindall.Ksh 5.8.2. Construct and build the hpss mover/client source tree this section describes the procedures to extract the mover/client code from the hpss base source tree and to build the mover/clie...
Page 175
5.8.3. Construct and build the hpss hdm source tree xfs is not supported in hpss 6.2. Xfs references have been left in the hpss documentation to support the option of re-enabling xfs in future releases. This section describes the procedures to extract the hdm source code from the hpss base source tr...
Page 176
Unix authentication with ldap authorization is not supported at this time, so it only makes sense to do this if you are using unix authorization. To set up support for both authentication mechamisms, change the following fields in db2: table field old new where server num_auth_mechs 1 2 server authn...
Page 177
Serverinterfaces where server_id = (select server_id from server where desc_name = 'ssm system manager') and descriptive_name = 'administrative client interface' authn_mech_set_num_mechs authn_mech_set_mechs1 ------------------------ --------------------- 1 0 1 record(s) selected. Db2 => update serv...
Page 178
Hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 178.
Page 179
Chapter 6. Upgrading to hpss release 6.2 this chapter is only intended for sites upgrading hpss from either version 4.5 or 5.1 to version 6.2. Sites wishing to upgrade from prior hpss releases must first upgrade to hpss 4.5 or hpss 5.1. Sites that are going to install and configure hpss 6.2 from scr...
Page 180
6.2. Planning for the hpss 6.2 upgrade this section provides information necessary to plan the upgrade of an hpss 4.5 or hpss 5.1 system to hpss 6.2. It is important that all planning information be reviewed carefully before performing the upgrade. 6.2.1. Metadata changes in hpss 6.2 from 4.5 to 6.2...
Page 181
• modification of nfs metadata. In support of new authentication mechanisms, elimination of credential object id. Change privileged caller principal length from 15 to 255 characters. Nfs is no longer supported. The nfs table contains converted metadata, but will be renamed to pre62_nfs to prevent us...
Page 182
Information. New index definition for table. The metadata conversion is performed by the hpss_51_62_server conversion program. • new serverinterfaces table. This table is populated by the hpss_51_62_server conversion with default server interface information. • modification of site table. In support...
Page 183
Hpss_ldap_import to convert dce authorization information into ldap. • kerberos authentication and unix authorization. In this case, the site determines on its own how to convert dce authentication information into kerberos. The site will then use hpss_unix_import to convert dce authorization inform...
Page 184
• the hpss_dce_export and hpss_unix_import utilities are provided to convert dce authorization information. Ldap: • configuring ldap is more complex than unix. • managing ldap is fairly simple and does not require regular maintenance. • the hpss_dce_export and hpss_ldap_import utilities areprovided ...
Page 185
Three minutes, and the subsystem conversion took approximately 40 minutes. 6.2.6.1. Running time for the long running metadata conversion utilities (for 4.5 upgrades only) a system with more than 3 million hpss files will see a significant performance gain from choosing to run the long running metad...
Page 186
Running the metadata conversion. This directory will be used to store one text-based restart file, various text-based db2 output files, and other text files. Prior to performing the metadata conversion, become familiar with the conversion program output for the hpss 4.5 conversion in section 6.5: hp...
Page 187
% db2 update db cfg for using to reset to default settings, execute: % db2 reset db cfg for review and update the following: • associated with the database log are the log file size (logfilsiz), the number of primary logs (logprimary), and number of secondary log files (logsecond). A good size for l...
Page 188
Attributes pertinent to authorization are retained in hpss 6.2. The program also optionally supports unix authentication in hpss 6.2 by obtaining each hpss users’ password from dce and preserving it in the unix system or optionally into a local hpss password file • hpss_ldap_import – this program is...
Page 189
Load into the new table. • db_convert_nsobject - this program converts the name server object metadata from the hpss 4.5 nsobjects sfs file to the hpss 6.2 db2 nsobject and nsacl tables by reading records from sfs and performing db2 loads into the new tables. • db_convert_nstext - this program conve...
Page 190
Hpss_md_convert_51. This program will rename the hpss 5.1 tables by prepending the original table name with pre62_ so that the original metadata in hpss 5.1 is preserved. The hpss_md_convert_51 utility calls the following programs to perform the conversion: • hpss_51_62_dmg – reads the 5.1 metadata ...
Page 191
• acquire kerberos or ldap software, as needed. See section 6.2.3: new authentication and authorization mechanisms on page 182 for a list of valid authentication and authorization combinations. See section 5.2: install prerequisite software on page 137 for more information on obtaining mit or ibm ke...
Page 192
Instance (e.G. . /home/hpssldap/sqllib/db2profile) 7. Setup db2 instance for ldap: % /opt/ibm/ldap/v6.0/sbin/idsicrt –n -e -i -t -l e.G. % /opt/ibm/ldap/v6.0/sbin/idsicrt -n -e [asuf4as].F -i idsldap -t idsldap -l /home/idsldap 8. Set the ldap admin distinguished name (dn) and password by: % /opt/ib...
Page 193
% /opt/ibm/ldap/v6.0/bin/idsldapmodify –c –i /opt/hpss/config/ hpss_ldap_schema.Ldif –d “cn=hpssldap” –w -v note: where passwd is the password for the dn. In the example above, it would be the hpssldap user’s password since hpssldap is the dn used above and configured with ldap on this system. 14. S...
Page 194
6.3.5. Upgrade aix this step cannot be performed while the hpss 4.5 or 5.1 system is running. This section applies to site that are upgrading to hpss 6.2 from both hpss 4.5 and hpss 5.1. See section 3.3.2: prerequisite summary by hpss node type on page 59 for the the appropriate version of aix requi...
Page 195
6.3.8.1. Install hpss 6.2 distribution image this step can be performed while the hpss 4.5 or 5.1 system is running. Prior to installing the hpss 6.2 code, sites should not disturb the current hpss release code. It is possible for a site to revert to the previous release of hpss at any point prior t...
Page 196
Code. Check $hpss_root/bin/convert62 to ensure the conversion programs compiled properly. The conversion utilities must include several encina sfs files to compile and link using /usr/lpp/encina as the default pathname. If this problem is encounted during building the source code, create a link from...
Page 197
Next, use mkhpss and select the configuration option and then other services option to configure the ieee address for hpss. This will create the /var/hpss/etc/ieee_802_addr file. This is only used by hpss and will not affect other services on this system. Without performing this option the hpss rpc ...
Page 198
Environment variables are no longer kept in the $hpss_root/config subdirectory. Many are now kept in /var/hpss/etc/env.Conf. The mkhpss utility will assist in creating the env.Conf file and hpss specific environment variables can be added to it. Before running the conversion utilities, ensure the fo...
Page 199
• mkhpss_root – set to the path of hpss 6.2 code (e.G. "/opt/hpss") • hpss_db_instance_owner – the unix user id of the db2 hpss instance (e.G. "hpssdb") • hpss_ldap_bind_type – should correspond with the type of bindings allowed for ldap (e.G. "simple") • hpss_ldap_url – the valid url for the hpss l...
Page 200
Hpss_primary_authn_mech=krb5 hpss_primary_authenticator=/krb5/hpss.Keytabs valid settings for unix authentication are: hpss_primary_authn_mech=unix hpss_primary_authenticator=/etc/passwd the new authorization is performed based on the contents of /var/hpss/etc/site.Conf. This file will tell hpss to ...
Page 201
Using the scrollbar, move the right-panel scrollbar until the "authorization service" information is seen. It should look like the following: hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 201.
Page 202
6.3.11. Pre-conversion system check • i t is strongly recommended that a test conversion be performed prior to running the conversion on a production system. See section 184: testing the metadata conversion on page 184 • ensure that the db2 database has been configured prior to the conversion • conv...
Page 203
6.3.12. Take a full backup of sfs or db2 this step should not be performed while the hpss 4.5 or 5.1 system is running. The sfs or db2 backup should be performed on the root and each non-root subsytem. Refer to the hpss 4.5 or 5.1 management guide or contact your hpss customer support representative...
Page 204
The first program used in the 4.5 conversion is the information collection utility, db_convert_collect_info. This utility will gather configuration related information based on input provided about the 4.5 hpss system. The program will save the information to several text files located in the /var/h...
Page 205
Subsystem id of the subystem being converted as the command line arguments. For example, % su – root % db_subsys_convert /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/globalconfig 1 this program provides an option to change all partially written hpss 4.5 tapes to be read-only. When invoked, the option will force the storage ...
Page 206
-db /var/hpss/convert/6.2/convert.Db.Names \ -ss /var/hpss/convert/6.2/convert.Ss.Server.Ids \ -sub 1 % db_convert_bitfile –g /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/globalconfig \ -db /var/hpss/convert/6.2/convert.Db.Names \ -sub 1 % db_convert_nsobject –g /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/globalconfig \ -db /var/hpss/convert/6.2/c...
Page 207
Root 1456 2034 0 16:04:08 pts/13 0:00 db_convert_bitfile ... Root 1567 1456 0 16:04:08 pts/13 0:00 ksh db2 load ... Next, issue a 'kill -15 1381', sending a sigterm (kill -l, will list all signals and their appropriate number on your system) to the only the conversion c program, and not to any of th...
Page 208
-db /var/hpss/convert/6.2/convert.Db.Names \ -sub 1 -restart when given the ‘-restart’ flag, the program will first attempt to determine that no other conversions or db2 loads are currently running on the specific table. If a load or conversion is still running (due to failure to cleanup from an abn...
Page 209
Error occurs while reading metadata. A restart from a user termination (ctrl-c) works well 90% of the time. Sometimes a user termination can cause db2 to output many system log errors (usually means the db2as, administrative server died). If the program is unable to perform a restart (i.E. An attemp...
Page 210
Environment variables to hpss 4.5 values. Examples follow: • hpss_principal_ssm=hpss_ssm • hpss_principal_ftpd=hpss_ftp • hpss_principal_mps=hpss_mps • hpss_principal_ndcg=hpss_ndcg • hpss_principal_nfsd=hpss_nfs • hpss_principal_dmg=hpss_dmg this allows the db_convert_dce_cds program to add proper ...
Page 211
Machine to enable the hpss 6.2 system to work properly. On several test machines, we had to open world access to the devices used by the hpss core server and pvl in order for them to initialize properly. 6.3.14. Verify hpss 4.5 conversion results • prior to running the verification utilities, we rec...
Page 212
Ensure that the site has sfs and db2 configured as expected. This program is not able to check the name server objects (nsobject) or acls (nsacl) table. The object count between two systems does not match because objects associated with deleted bitfiles are not converted. To invoke this utility, see...
Page 213
Check every bitfile descriptor in the 6.2 system. The -f and -l options check only the first and last number of bitfile descriptors provided with these options. To invoke this utility, see the usage below: db_convert_address_check -g -db -ss -s [-a] (check all files) [-f ] (check first files) [-l ] ...
Page 214
Option 1 – rename old tables [ renaming lspolicy table to pre62_lspolicy ] [ renaming server table to pre62_server ] [ renaming dmg table to pre62_dmg ] [ renaming gatekeeper table to pre62_gatekeeper ] [ renaming moverdevice table to pre62_moverdevice ] [ renaming site table to pre62_site ] option ...
Page 215
6.3.16. Enable db2 backup set up the db2 backup process for hpss metadata. Ensure that an initial backup of all hpss databases are available at this point. Perform this step on each root and non-root subsystem. 6.3.17. Perform the dce export: hpss_dce_export this step applies to upgrades for both hp...
Page 216
5.1, set the non-default server principal values using the appropriate environment variable names: • hpss_pre62_principal_core • hpss_pre62_principal_dmg • hpss_pre62_principal_ftpd • hpss_pre62_principal_gk • hpss_pre62_principal_hpssd • hpss_pre62_principal_log • hpss_pre62_principal_ls • hpss_pre...
Page 217
The conversion program that imports dce authorization information into ldap is called hpss_ldap_import. Usage: hpss_ldap_import -realmname % hpss_ldap_import /var/hpss/convert/6.2 -realmname "cn=hpss.Acme.Com" where the realmname option should use the name of the realm desired in ldap. The program r...
Page 218
6.3.19.1. Tune db2 for normal operations refer to section 5.7: tune db2 on page 171. Perform this step on each root and non-root subsystem. 6.3.19.2. Modify accounting, if applicable if the hpss system consists of multiple subsystems and accounting by subsystems is desired, accounting metadata shoul...
Page 219
That each caller of the interface is given. Run the hpss_init_server_acls program as follows: % /opt/hpss/bin/convert62/hpss_init_server_acls error in stat of keytab file, /var/hpss/etc/mm.Keytab, 2 note: the error is expected and does not indicate that the hpss_init_server_acls program did not comp...
Page 220
Hpssgui.Pl hpssgui.Vbs hpss.Jar login.Conf the -ssmclientpkg option creates a tar file and places it in the specified directory (e.G. /tmp/ssmclientpkg.Tar) which will contain the following files: • hpss.Jar – java executables for running the ssm gui • hpssgui.Pl – perl version of the ssm gui start ...
Page 221
6.3.20.1. Invoke the ssm system manager, startup daemon and prerequisite software perform this step on the root subsystem only. Use the rc.Hpss script to invoke the startup daemon, ssm system manager and the prerequisite software. % /opt/hpss/bin/rc.Hpss or $ /etc/rc.Hpss if problems are encountered...
Page 222
The default name of the ssm configuration file is ssm.Conf. Its default location is the current directory or, if not there, in $hpss_path_ssm (/var/hpss/ssm by default). The name and location may be overridden by the -m option to the hpssgui.Pl script or by setting the value in the user's environmen...
Page 223
Mps 10 10 5 20 pvl 50 10 1 2 pvr 30 20 5 30 mover 20 20 1 5 startup daemon 10 10 0 2 ssm system manager 100 100 5 20 4. Review and update the core server(s) other configuration parameters, if necessary 5. For 4.5 upgrades only: review all migration policies to ensure that they were converted correct...
Page 224
Fields will display the current value. Change the accounting bits such that if the initial value is 1 then the new value will be 2 and conversely if the initial value is 2 then the new value will be 1. At this point, the hpss system has no accounting metadata for existing files. Any new files that a...
Page 225
• using the gui, mark the mps configuration executable and start it • verify that migration and purge are working correctly • repack and reclaim tape volumes 6.3.22. Clean up after a 4.5 to 6.2 upgrade after the 6.2 system has been operational for an extended period, clean up the following: • if it ...
Page 226
In tape mount errors for read operations once it is determined that it’s safe to revert back to release 6.2, perform the steps as follows. Note that this procedure assumes that the upgrade stopped after the 6.2 servers are up but before changes were made that may affect the 4.5 user data or invalida...
Page 227
The "pre62_". Next, beginning with step 4, follow the procedures in section 6.3.24.1: revert the hpss 6.2 system to version 4.5 on page 225. The site will also have to revert the operating system software and any other upgraded software back to the hpss 4.5 prerequisite versions so that the hpss 4.5...
Page 228
6.4.1.2. Db_config_convert, db_subsys_convert, and db_lr_convert errors and warnings 1sql3304n the table does not exist . => the program is attempting to insert data into a table that has not been created under the database name and schema it is running under. Determine the database name entered for...
Page 229
Resolution: check that the table exists in the schema and that the db_convert_collect_info utility has been run recently. The empty table scripts pull their information about which schema to use from the text file /var/hpss/convert/6.2/convert.Db.Names, created by running db_convert_collect_info. En...
Page 230
Resolution: either the wrong filename or the wrong subsystem id for that filename was entered. Rerun the conversion program with the correct subsystem id and filename. Sql0968c the file system is full. Sqlstate=57011 => this error message usually follows 10 or so other sql messages, and means that t...
Page 231
Error: write_bitfile_to_asc failed to write to pipe, fd is -1, errno = 9 => this error results when running a long running conversion program that cannot write to /var/hpss/convert/6.2 and create a file called asc_fifo_bitfile (the named pipe for the c program to communicate with the db2 load). Reso...
Page 232
Trying to insert the converted metadata. If this resulted from previously running the metadata conversion, and the metadata should be re-converted, then identify the table name (e.G. “hpss.Serverinterfaces”) and empty the table by executing a % db2 delete from statement where conversion for this tab...
Page 233
Through several syslogd error messages output to the monitor or a failed attempt at restarting the failed conversion program. Should db2 be placed in an inconsistent state, the tablespace will likely have to be dropped and recreated along with the table being converted. Then the database will need t...
Page 234
The output displays “re-running” which indicates that the utility is performing a restart. When performing a restart and there are already rows in the db2 table, rows committed should still equal rows submitted to the load. The conversion program will determine the number of records already loaded i...
Page 235
$ db_config_convert /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/globalconfig logged into dce as hpss_ssm. Emptying all configuration tables in global database... All config tables emptied in global database, under schema hpss. Running db_convert_global utility... Converting sfs file /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/globalconfig convert...
Page 236
Running db_convert_gatekeeper utility... Converting sfs file /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/gkconfig converted 1 records successfully from /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/gkconfig db_convert_gatekeeper complete, inserted 1 records into db2 gatekeeper table running db_convert_logclient utility... Converting sfs file /.:/en...
Page 237
/.:/encina/sfs/hpss/cartridge_stk converting sfs file /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/cartridge_stk_rait converted 4 records successfully from /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/cartridge_stk_rait db_convert_cartridge complete, inserted 32 records into db2 cartridge table running db_convert_cos utility... Converting sfs file ...
Page 238
Running db_convert_purgepol utility... Converting sfs file /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/purgepolicy converted 1 records successfully from /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/purgepolicy db_convert_purgepol complete, inserted 1 records into db2 purgepol table running db_convert_pvldrive utility... Converting sfs file /.:/enc...
Page 239
$ db_subsys_convert /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/globalconfig 1 logged into dce as hpss_ssm. Emptying all subsystem tables in subsys1 database... All subsystem tables emptied in subsys1 database, under schema hpss. Running db_convert_acctlog utility... Converting sfs file /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/acctlog.1 conver...
Page 240
Converted 600 records successfully from /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/bfmigrrec.1 db_convert_bfmigrec complete, inserted 600 records into db2 bfmigrec table for subsystem 1 running db_convert_bfpurgerec utility... Converting sfs file /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/bfpurgerec.1 converted 0 records successfully from /.:/e...
Page 241
Table for subsystem 1 running db_convert_storagemapdisk utility... Converting sfs file /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/storagemapdisk.1 converted 3 records successfully from /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/storagemapdisk.1 db_convert_storagemapdisk complete, inserted 3 records into db2 storagemapdisk table for subsystem 1 ...
Page 242
Converting sfs file /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/bftapesegment.1 converted 1159 records successfully from /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/bftapesegment.1 lr_db_convert_bftapeseg complete, submitted 1159 records to db2 bftapeseg load for subsystem 1, 1596 operations per sec, 0.725914 total time number of rows read = 1159...
Page 243
Converting sfs file /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/nstext.1 converted 408 records successfully from /.:/encina/sfs/hpss/nstext.1 lr_db_convert_nstext complete, submitted 408 records to db2 nstext load for subsystem 1, 1233 operations per sec, 1.001456 total time number of rows read = 408 number of rows skipped...
Page 244
Hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 244.
Page 245
Appendix a. Glossary of terms and acronyms aci automatic media library client interface acl access control list acsls automated cartridge system library software (science technology corporation) adic advanced digital information corporation accounting the process of tracking system usage per user, p...
Page 246
Bitfile service portion of the hpss core server that provides a logical abstraction of bitfiles to its clients. Bmux block multiplexer channel bytes between tape marks the number of data bytes that are written to a tape virtual volume before a tape mark is required on the physical media. Cap cartrid...
Page 247
Device a physical piece of hardware, usually associated with a drive, that is capable of reading or writing data. Directory an hpss object that can contain files, symbolic links, hard links, and other directories. Dismount an operation in which a cartridge is either physically or logically removed f...
Page 248
Gatekeeping service a registered interface in the gatekeeper that provides a site the mechanism to create local policy on how to throttle or deny create, open and stage requests and which of these request types to monitor. Gatekeeping site interface the apis of the gatekeeping site policy code. Gate...
Page 249
I/o input/output iod/ior input/output descriptor / input/output reply. Structures used to send control information about data movement requests in hpss and about the success or failure of the requests. Ip internet protocol irix sgi’s implementation of unix junction a mount point for an hpss fileset....
Page 250
Ls location server lto linear tape-open. A half-inch open tape technology developed by ibm, hp and seagate. Mac mandatory access control managed object a programming data structure that represents an hpss system resource. The resource can be monitored and controlled by operations on the managed obje...
Page 251
Notification a notice from one server to another about a noteworthy occurrence. Hpss notifications include notices sent from other servers to ssm of changes in managed object attributes, changes in tape mount information, and log messages that are alarm, event, and status log record message types. N...
Page 252
Ram random access memory reclaim t he act of making empty tape virtual volumes available for reuse. Reclaimed tape virtual volumes are assigned a new virtual volume id, but retain the rest of their previous characteristics. Registration the process by which ssm requests notification of changes to sp...
Page 253
Ss hpss storage service ssa serial storage architecture ssm storage system management ssm session the environment in which an ssm user interacts with the ssm system manager to monitor and control hpss. This environment may be the graphical user interface provided by the hpssgui program, or the comma...
Page 254
Stripe length the number of bytes that must be written to span all the physical storage media (physical volumes) that are grouped together to form the logical storage media (virtual volume). The stripe length equals the virtual volume block size multiplied by the number of physical volumes in the st...
Page 255
Hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 255.
Page 256
Appendix b. References 4. 3580 ultrium tape drive setup, operator and service guide ga32-0415-00 5. 3584 ultrascalable tape library planning and operator guide ga32-0408-01 6. 3584 ultrascalable tape library scsi reference wb1108-00 7. Aix performance tuning guide 8. Data storage management (xdsm) a...
Page 257
Storage system (hpss), ” from the 1995 ieee mss symposium, courtesy of the ieee computer society press. 33. T.W. Tyler and d.S. Fisher, “ using distributed oltp technology in a high-performance storage system, ” from the 1995 ieee mss symposium, courtesy of the ieee computer society press. 34. J.K. ...
Page 258
Appendix c. Developer acknowledgments hpss is a product of a government-industry collaboration. The project approach is based on the premise that no single company, government laboratory, or research organization has the ability to confront all of the system-level issues that must be resolved for si...
Page 259
Appendix d. Hpss.Conf configuration file the hpss.Conf configuration file contains tuning options to be used by hpss clients and servers. For additional information, please see the hpss.Conf manual page. General hpss.Conf rules/suggestions: • keywords must be specified precisely as shown (no extra s...
Page 260
Stanza (cmpd) pftp client = { e.G. Pftp client = { optional reserved stanza specifier. Must be terminated with a matching “}” substanza syslog facility = values: daemon , local0 ... Local7 e.G. Syslog facility = local2 optional substanza specifying the syslog facility for the multinode daemon substa...
Page 261
Substanza auto parallel size = value: size - may be specified as a decimal number or “ x mb” style notation. E.G. Auto parallel size = 4mb optional substanza specifying the minimum file size to start using the “auto-parallel” features of the pftp client. Substanza portrange = value: ncadg_ip_tcp[sta...
Page 262
Substanza no san3p e.G. No san3p optional substanza specifying not to use san3p even if it is available. Default is to use san3p if available. Substanza no transfer agent support e.G. No transfer agent support optional substanza specifying to not use the transfer agent. Default is to use the transfe...
Page 263
The pftp_client automatically performs conversion of get and put commands to their parallel equivalents, pget and pput . Some sites have reported degraded performance as a result of this substitution occurring with small file transfers. To accommodate this problem, the auto parallel size = value sub...
Page 264
; transfer buffer size = 1mb ; socket buffer size = 16mb # pftp sets an artificial (compiled in) maximum of 250gb max ptran size = 10gb # disable san3p ; no san3p # disable transfer agent ; no transfer agent supported # disable 64-bit protocol - default is on ; no 64-bit support # special features ;...
Page 265
Subsection or name: valid interface name dotted ip address: 132.175.1.1 e.G. Eth0 132.175.1.1 optional parameter containing the name or dot notation ip address specification for the interface on the local host ( pftp client) to use to connect to the mover(s) associated with the specified pftp daemon...
Page 266
Pftp client interfaces stanza example: ; pftp client interfaces = { # pftp client host name(s) ; water.Clearlake.Ibm.Com water = { # next specification is the pftp daemon host # water has 3 specific interfaces that can talk # to the hpss movers associated with the pftp # daemon host "water", as well...
Page 267
Configuration type description stanza (cmpd) multinode table = { e.G. Multinode table = { optional reserved stanza specifier. Must be terminated with a matching “}” substanza sleep for debugger = values value: time in seconds. E.G. Sleep for debugger = 15 optional parameter to specify a delay in the...
Page 268
Superdaemon ( /etc/inetd.Conf and /etc/services ) to initiate the multinoded. The sections may be either a simple section or a valued section. A simple substanza is a single name/dot notation ip address to be used for both “control” connection and “data” connection. The valued substanza is used to s...
Page 269
Destination ip address “masked” by the netmask value. The calling application (pftp client, client api, or mover) will apply the value of the netmask specification in the configuration file entry to the specified destination address. A “ default ” destination may be specified for all sources/destina...
Page 270
Section (cmpd) = { e.G. 100.101.102.0 = { optional substanza specifying a dotted decimal address of the destination interface. Only one address is allowed; however, networks and sub-networks may be chosen by appropriate specification of the netmask. May contain: “default = {“ ( reserved specificatio...
Page 271
Subsection tcpnodelay = values: 0, 1 e.G. Tcpnodelay = 1 optional parameter indicates whether the tcp delay option should be disabled (0) or enabled (any other value) sendspace & recvspace controls the size of the receive and send buffers for tcp/ip sockets. Internally, hpss servers and clients atte...
Page 272
• multiple sections may be included in any substanza. A “default” destination interface name section may be specified. Note: do not include the quotes when specifying default. • the netmask must be specified in decimal dot ip address notation • all subsections must be specified in every section. Net...
Page 273
Default = { netmask = 255.255.255.0 rfc1323 = 1 sendspace = 256kb recvspace = 128kb writesize = 512kb tcpnodelay = 0 } } } d.5. Pftp daemon stanza a large number of options are available for configuring the pftp daemon and tuning its performance. These options were previously specified in the ftpacc...
Page 274
Substanza syslog facility = value: daemon, local0 ... Local7 e.G. Syslog facility = local0 replaces -s option. Optional substanza s pecifying the syslog facility for the hpss pftpd. The default syslog facility is log_daemon (reference:/ usr/include/sys/syslog.H ). Alternatives are local0 - local7 . ...
Page 275
Substanza ftp access file = value: filename e.G. Ftp access file = myftpaccess replaces -f option. Optional substanza setting the { ftp_ftpaccessfile }. Default: ftpaccess . Located in the directory {ftpbasedir}/etc . Substanza disable slash home directory e.G. Disable slash home directory replaces ...
Page 276
Substanza ftp principal keytab file = value: pathname/filename e.G. Ftp principal keytab file = /var/hpss/etc/hpss.Keytabs optional substanza specifying the keytab containing the ftp principal. Substanza allow passive connections e.G. Allow passive connections replaces -a option. Optional substanza ...
Page 277
Substanza pftp io buffer size = e.G. Pftp io buffer size = 4mb replaces -b option. Optional substanza setting the preferred io buffer size for the pftp server substanza debug value = e.G. Debug value = 3 replaces -d option(s). Optional substanza specifying the level of debugging desired (1-3). Used ...
Page 278
Substanza client api verbose value = e.G. Client api verbose value = 1 replaces -v option(s). Optional substanza specifying the level of hpss client api logging to use (1-3). The client api will perform logging specified by the hpss_debug environment variable in a file specified by the hpss_debugpat...
Page 279
Substanza maximum time out = value: time in seconds e.G. Maximum time out = 86400 replaces -t option and hpss_option mto time in ftpaccess . Optional substanza specifying the maximum timeout in seconds. Substanza use udp only e.G. Udp only replaces -u option. Optional substanza specifying use of udp...
Page 280
Substanza portrange = e.G. Portrange = ncadg_ip_udp[10100-12100]:ncacn_ip_tcp[10100-12100] optional substanza specifying the port range to be used for the non-hpss parallel ftp daemon which is necessary for parallel transfers. Note: this is ignored for passive listings, etc. Substanza socket buffer ...
Page 281
Subsection cos = e.G. Cos = 2 optional subsection specifying the class of service to be used based on file size. 0 means allow the core server to determine the optimal cos. (has no meaning for the non-hpss pftd daemon.) substanza service name = e.G. Sunrahe service name = sunrahe.Sandia.Gov optional...
Page 282
Substanza pftp group file = value: pathname/filename e.G. Pftp group file = /var/hpss/etc/pftp_groups optional substanza used to specify the file containing the group information for pftp clients. Default is /var/hpss/etc/group . Substanza primary authentication mechanism = values: krb5, ibm_hpss_pk...
Page 283
Subsection mapfile specifier = values: pathname/filename e.G. Mapfile specifier = /var/hpss/etc/mapfilename optional substanza used to specify a file containing username mappings. A different file can exist for each authentication type. This file provides the ability to authenticate as one user and ...
Page 284
Sizes in the range [1mb, 2mb). Pftp daemon stanza example: pftp daemon = { # allow the daemon to take core dumps ; allow core files # directory to put core files in (default = .) ; core file directory = /var/hpss/adm/core # specify the syslog facility to use for all syslog messages # except authenti...
Page 285
; default time out = 1500 # specify (in octal) the default umask ; default umask = 077 # specification of the level of hpss client api logging to use ( 0 - 3 ) ; client api verbose value = 0 # do not allow the user to specify classes of service (hpss only) ; disallow user setting of cos # name the k...
Page 286
; 100mb = { ; blocksize = 4mb ; stripewidth= 0 ; cos = 0 ; } ; 1gb = { ; blocksize = 8mb ; stripewidth= 0 ; cos = 0 ; } ; } # use the system password file routines (true or false) # the default for pftp is false ( case sensitive !) use system password files = false # path and name for the pftp passw...
Page 287
; gsi = { ; mapfile specifier = ldap:/var/hpss/etc/krb2unixmapfile ; use site auth method = cryptocard ; default authorization mechanism = ldap ; } ; ident = { ; mapfile specifier = file:/var/hpss/etc/ident2unixmapfile ; use site auth method = securid ; default authorization mechanism = dbas ; } use...
Page 288
Substanza nodeset file = value: pathname/filename e.G. Nodeset file = /var/hpss/etc/pmta_nodesets optional substanzaused to specify the location of the transfer agent file containing nodesets. Substanza node affinity file = value: pathname/filename e.G. Node affinity file = /var/hpss/etc/pmta_nodeaf...
Page 289
Substanza debug logfile = value: pathname/filename e.G. Debug logfile = /var/hpss/log/pmta_debugfile optional substanzaused to specify the location of the transfer agent debugging file. Substanza syslog facility = values: daemon , local0 ... Local7 , none e.G. Syslog facility = local0 optional subst...
Page 290
# parallel multinode transfer agent (pmta) section transfer agent = { # the (optional) nodeset file contains named sets of # nodes that can be referred to via the "set:setname" # notation. Nodeset file = /var/hpss/etc/ta/nodeset.Conf # the (optional) node affinity file is used to specify # groups of...
Page 291
D.7. Stanzas reserved for future use the following stanza names (specifiers) are reserved for future implementation in hpss and should not be used by application developers. • transfer agent (partially implemented) • pipe file • local file path • psi hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (re...
Page 292
Hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 292.
Page 293
Appendix e. Hpss_env_defs.H the hpss environment variables are defined in /opt/hpss/include/hpss_env_defs.H. These environment variables can be overridden in /var/hpss/etc/env.Conf or in the local environment. Static env_t hpss_env_defs[] = { /* ******************************************************...
Page 294
{ "hpss_grp_name_client", "hpss_client", null}, /* ************************************************************************** * * hpss server principal names * * hpss_principal - principal name for sec server * hpss_principal_core - principal name for core server * hpss_principal_dmg - principal nam...
Page 295
* hpss_principal_mps_uid - principal uid for migration/purge server * hpss_principal_mvr_uid - principal uid for mover * hpss_principal_nfsd_uid - principal uid for nfs daemon * hpss_principal_ns_uid - principal uid for name server * hpss_principal_pfsd_uid - principal uid for pfs daemon * hpss_prin...
Page 296
* hpss_exec_pvr_scsi - executable name for pvr scsi * hpss_exec_ssmsm - executable name for ssm storage manager * ************************************************************************** * */ { "hpss_exec_acct", "${hpss_path_bin}/hpss_acct", null}, { "hpss_exec_core", "${hpss_path_bin}/hpss_core",...
Page 297
* hpss_exec_delog - pathname for the delog utility * hpss_exec_reclaim - pathname for the reclaim utility * hpss_exec_repack - pathname for the repack utility * ************************************************************************** * */ { "hpss_exec_acl_edit", "${hpss_path_slash_bin}/acl_edit", ...
Page 298
* hpss_unix_nfs_checkpoint - checkpoint * hpss_nfs_disable_junctions - disable traversal of junctions * hpss_mnt_disable_junctions - disable mounting junctions ************************************************************************** */ { "hpss_path_nfs", "${hpss_path_var}/nfs", null}, { "hpss_unix...
Page 299
{ "hpss_subsys_db_name", "subsys", null}, { "hpss_mm_schema_name", "hpss", null}, { "hpss_mm_low_water_mark", "1", null}, { "hpss_mm_high_water_mark", "5", null}, { "hpss_mm_cache", "", null}, { "hpss_server_db_group", "hpsssrvr", null}, { "hpss_server_db_keytab", "${hpss_path_etc}/mm.Keytab", null}...
Page 300
*/ { "hpss_host_tmp", "%h", null}, { "hpss_desc_core", "core server", null}, { "hpss_desc_dmg", "dmap gateway", null}, { "hpss_desc_ftpd", "ftp daemon", null}, { "hpss_desc_gk", "gatekeeper", null}, { "hpss_desc_hpssd", "startup daemon ($ {hpss_host_tmp})", null}, { "hpss_desc_hpssd_short", "startup...
Page 301
Updates * hpssssm_ui_mo_rate - time the gui will wait between mo update tries * hpssssm_ui_list_rate - time the gui will wait between list update tries * hpssssm_ui_alarm_rate - time the gui will wait between alarm update tries * hpssgui_sec_mech - security mechanism used for sm communication * hpss...
Page 302
* to maintain at once. If this number of connections is * exceeded, then old connections will be close to * maintain this number of connections * ************************************************************************** * */ { "hpss_path_ssm", "${hpss_path_var}/ssm", null}, { "hpss_ssm_alarms", nul...
Page 303
* hpss_api_max_conn - defines the number of connections that * are supported by the client api within * a single client process * hpss_api_debug - used to enable debug messages * hpss_api_retries - used to control the number of retries * when operations fail with a "retryable" * return code * hpss_a...
Page 304
{ "hpss_api_total_delay", "0", null}, { "hpss_api_limited_retries", "1", null}, { "hpss_api_dmap_write_updates","20", null}, { "hpss_api_reuse_connections", "0", null}, { "hpss_api_use_port_range", "0", null}, { "hpss_api_retry_stage_inp", "1", null}, { "hpss_api_disable_cross_realm","0", null}, { "...
Page 306
* hpss_authz_types - supported authorization types * hpss_site_location - site location * krb5_install_path - kerberos installation path * no default - platform dependent * krb5_kdc_dir - kerberos directory containing local config * files for kdc * krb5_kdc_host - host for kerberos kdc (just used by...
Page 307
Null}, { "hpss_primary_authenticator", "${hpss_krb5_keytab_file}", null}, { "hpss_client_authn_mech", "${hpss_primary_authn_mech}", null}, { "ieee_802_file", "${hpss_path_etc}/ieee_802_addr", null}, { "hpss_auth_service_conf", "${hpss_path_etc}/auth.Conf", null}, { "hpss_authz_service_conf", "${hpss...
Page 308
* hpss_path_core - path where subsystem core files are placed * hpss_path_tmp - path where temporary files are placed * hpss_path_etc - path where runtime config files are placed * hpss_env_conf - the path to the environment override file * hpss_pthread_stack - stack size for hpss pthreads *********...
Page 309: /var/hpss
Appendix f. /var/hpss files the /var/hpss directory tree is the default location of a number of hpss configuration files, log files, and other files needed by the servers. The directories and configuration files can be created with the mkhpss utility or hand created. Be very careful when using mkhps...
Page 310
Authorization mechanism and authorization url to utilize. • rc.Db2 . Created by mkhpss. Script for starting db2. • rc.Krb . Created by mkhpss. Script for starting the kerberos servers. • passwd. Created by mkhpss. A local hpss-only password file for use with unix authentication and authorization. Op...
Page 311
Of the hpss servers it brought up in the node. Hpss may also write diagnostic log files and disk allocation maps in this directory, when configured to do so. The lock files are very small, but the log files and maps can be very large. Hpss installation guide july 2008 release 6.2 (revision 2.0) 311.