- DL manuals
- IBM
- Storage
- IC25N020ATDA04 - Travelstar 20 GB Hard Drive
- Specifications
IBM IC25N020ATDA04 - Travelstar 20 GB Hard Drive Specifications - 11.1 Reset Response
11.0 General operation descriptions
11.1 Reset response
ATA has the following three types of resets:
The SRST bit in the Device Control Register is set and then is reset. The
device resets the interface circuitry according to the Set Features
requirement.
Soft Reset (Software Reset)
The RESET- signal is negated in the ATA Bus. The device resets the
interface circuitry and sets the default values.
Hard Reset (Hardware Reset)
The device executes a series of electrical circuitry diagnostics, spins up
the HDA, tests speed and other mechanical parametric, and sets default
values.
Power On Reset (POR)
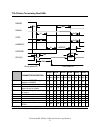
The actions of each reset are shown in Figure 59 on page 78.
Travelstar 48GH, 30GN & 15GN hard disk drive specifications
77
Summary of IC25N020ATDA04 - Travelstar 20 GB Hard Drive
Page 1
Revision 2.0 10 january 2002 s07n-7909-09 publication #1530 ic25n012atda04 ic25n005atda04 ic25n015atda04 ic25n006atda04 ic25n020atda04 ic25n007atda04 ic25n030atda04 ic25n010atda04 ic25t048atda05 models: ibm hard disk drive specifications travelstar 48gh, 30gn & 15gn 2.5 inch ata/ide hard disk drive ...
Page 2
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 3
Revision 2.0 10 january 2002 s07n-7909-09 publication #1530 ic25n012atda04 ic25n005atda04 ic25n015atda04 ic25n006atda04 ic25n020atda04 ic25n007atda04 ic25n030atda04 ic25n010atda04 ic25t048atda05 models: ibm hard disk drive specifications travelstar 48gh, 30gn & 15gn 2.5 inch ata/ide hard disk drive.
Page 4
1st edition (revision 0.1) s07n-7909-01 ( february 19, 2001) preliminary 2nd edition (revision 0.2) s07n-7909-02 (april 5, 2001) preliminary 3rd edition (revision 1.0) s07n-7909-03 (april 6, 2001) 4th edition (revision 1.1) s07n-7909-04 (april 9, 2001) 5th edition (revision 1.2) s07n-7909-05 (may 14...
Page 5: Table of Contents
Table of contents 32 6.4.5 preventive maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 6.4.4 service life and usage condition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 6.4.3 cable noise interference . . . . . ...
Page 6
67 8.2 terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67 8.1 introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67 8.0 general . . . . . . . . ...
Page 7
95 11.9.2 set max security extension commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94 11.9.1 example for operation (in lba mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94 11.9 protected area function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 8
170 13.33.1 s.M.A.R.T. Function subcommands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169 13.33 s.M.A.R.T. Function set (b0h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168 13.32 sleep (e6h/99h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 9
203 index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201 15.2 set features command support coverage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199 15.1 commands support coverage . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 10
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 11: Figures
Figures 56 figure 45. Ultra dma cycle timing (host terminating read) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 figure 44. Ultra dma cycle timings (host pausing read) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54 figure 43. Ultra dma cycle timing (initiating read) . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 12
137 figure 91. Initialize device parameters command (91h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136 figure 90. Idle immediate command (e1h/95h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135 figure 89. Idle command (e3h/97h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 13
201 figure 138. Set features command coverage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200 figure 137. Command coverage (2 of 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199 figure 137. Command coverage (1 of 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 14
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 15: 1.0 Introduction
1.0 introduction this document describes the specifications of the ibm travelstar 2.5-inch, ata/ide interface hard disk drive with the following model numbers: ! Ic25n005atda04 (5 gb) ! Ic25n006atda04 (6 gb) ! Ic25n007atda04 (7.5 gb) ! Ic25n010atda04 (10 gb) ! Ic25n012atda04 (12 gb) ! Ic25n015atda04...
Page 16
Tracks per inch tpi self-monitoring, analysis, and reporting technology s.M.A.R.T secondary low voltage selv sectors per track sect/trk second sec read/write r/w reset rst revolutions per minute rpm root mean square rms per cent relative humidity % rh relative humidity rh radio frequency interferenc...
Page 17: 1.2 References
Transistor-transistor tristate logic 3-state watt w verband deutscher electrotechniker vde volt v underwriters laboratory ul transistor-transistor logic ttl track trk. 1.2 references ! Ata/atapi-5 (t13/1321d revision 3) 1.3 general caution ! Do not apply force to the top cover (see the figure title ...
Page 18
1.4 drive handling precautions do not press on the drive cover during handling. Figure 1 . Handling precaution 1 figure 2 . Handling precaution 2 travelstar 48gh, 30gn & 15gn hard disk drive specifications 4.
Page 19: 2.0 General Features
2.0 general features ! Height mcc compliance - 2.5 inch form factor - height of 12.5 ± 0.2 mm (48 gb model) and 9.5 ± 0.2 mm (all other models) ! Capacities of 48 gb, 30 gb, 20 gb, 15 gb, 12 gb, 10 gb, 7.5 gb, 6 gb, and 5 gb ! 512 bytes/sector ! Ultra ata/100 (enhanced ide) conforming to ata-5 ! Int...
Page 20
Note: mounting screw position is # incompatible with dboa, dmca, dcra, dsoa, and dpra models # compatible with dtna, dlga, ddla, dtca, dpla, dyka, dyla, dada, dkla, dbca, dcxa, dcya, dara, and djsa models travelstar 48gh, 30gn & 15gn hard disk drive specifications 6.
Page 21
Part 1. Functional specification travelstar 48gh, 30gn & 15gn hard disk drive specifications 7.
Page 22
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 23: 3.1 Control Electronics
3.0 fixed disk subsystem description 3.1 control electronics the control electronics works with the following functions: ! At interface protocol ! Embedded sector servo ! No-id formatting ! Multizone recording ! Code: 96/104 mtr ! Ecc on-the-fly ! Enhanced adaptive battery life extender 3.2 head dis...
Page 24
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 25: 4.2 Formatted Capacity
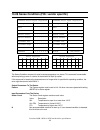
4.0 fixed disk characteristics 4.1 default logical drive parameters the following table lists the default logical drive parameters by drive model number. 5,000,970,240 950a60h 63 15 10,336 5 ic25n005atda04-0 6,007,357,440 b30880h 63 15 12,416 6 ic25n006atda04-0 7,501,455,360 df8f90h 63 15 15,504 7.5...
Page 26: 4.3 Data Sheet
5,000,970,240 6,007,357,440 7,501,455,360 10,056,130,560 12,072,517,632 total logical data bytes 9,767,520 11,733,120 14,651,280 19,640,880 23,579,136 number of sectors 16,383 16,383 16,383 16,383 16,383 number of cylinders 63 63 63 63 63 number of sectors/ track 16 16 16 16 16 number of heads logic...
Page 27: 4.4 Cylinder Allocation
4.4 cylinder allocation 48-gb model 288 28160-28671 15 288 27648-28159 14 320 25600-27647 13 336 23552-25599 12 352 21760-23551 11 364 19712-21759 10 384 17664-19711 9 384 15616-17663 8 403 13568-15615 7 416 11520-13567 6 432 9216-11519 5 460 7680-9215 4 480 6144-7679 3 480 4096-6143 2 499 2048-4095...
Page 28
20-gb model 320 27648-28671 15 336 26624-27647 14 360 24576-26623 13 360 22528-24575 12 400 20480-22527 11 420 18176-20479 10 440 17152-18175 9 456 15616-17151 8 480 13568-15615 7 480 11264-13567 6 504 8960-11263 5 520 6656-8959 4 540 4352-6655 3 576 3072-4351 2 600 2048-3071 1 600 0-2047 0 number o...
Page 29
12-gb, 10-gb, 6-gb, 5-gb models 280 28160-28671 15 300 27136-28159 14 300 25600-27135 13 320 24064-25599 12 336 22272-24063 11 360 19968-22271 10 360 17664-19967 9 400 15616-17663 8 420 13312-15615 7 440 11520-13311 6 456 9472-11519 5 480 7680-9471 4 480 5888-7679 3 504 4096-5887 2 520 2048-4095 1 5...
Page 30
4.5 performance characteristics file performance is characterized by the following parameters: ! Command overhead ! Mechanical positioning ! Seek time ! Latency ! Data transfer speed ! Buffering operation (look ahead/write cache) note: all the above parameters contribute to file performance. There a...
Page 31
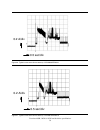
4.5.2 mechanical positioning 4.5.2.1 average seek time (including settling) 17 14 write 16 12 read max (ms) typical (ms) command type figure 12. Mechanical positioning performance typical and max are defined throughout the performance specification as follows: maximum value measured on any one drive...
Page 32
4.5.2.3 single track seek time (without command overhead, including settling) 4.5 3.0 write 4.0 2.5 read maximum (ms) typical (ms) command type figure 14. Single track seek time single track seek is measured as the average of one (1) single track seek from every track in both directions (inward and ...
Page 33
4.5.3 operating modes operating mode description spin-up start up time period from spindle stop or power down. Seek seek operation mode write write operation mode read read operation mode performance the device is capable of responding immediately to idle media access requests all electronic compone...
Page 34
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 35: 5.0 Data Integrity
5.0 data integrity 5.1 data loss on power off ! Data loss will not be caused by a power off during any operation but the write operation. ! A power off during a write operation causes the loss of any received or resident data that has not been written onto the disk media. ! A power off during a writ...
Page 36: 5.4 Write Safety
5.4 write safety the drive ensures that the data is written into the disk media properly. The following conditions are monitored during a write operation. When one of these conditions exceeds the criteria, the write operation is terminated and the automatic retry sequence is invoked. ! Head off trac...
Page 37: 5.8
5.8 ecc the 40-byte three interleaved ecc processor provides user data verification and correction capability. The first 4 bytes of ecc are check bytes for user data and the other 36 bytes are read solomon ecc. Each interleave has 12 bytes for ecc. Hardware logic corrects up to 15 bytes (5 bytes for...
Page 38
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 39: 6.0 Specification
6.0 specification 6.1 environment 6.1.1 temperature and humidity –40 to 65°c 5 to 95% noncondensing 40°c noncondensing 20°c/hour –300 to 12,192 m (40,000 ft) temperature relative humidity maximum wet bulb temperature maximum temperature gradient altitude non operating conditions 5 to 55°c (see note)...
Page 40
6.1.1.1 corrosion test the hard disk drive must be functional and show no signs of corrosion after being exposed to a temperature humidity stress of 50°c/90%rh (relative humidity) for one week followed by a temperature humidity drop to 25°c/40%rh in 2 hours. 6.1.2 magnetic fields the disk drive will...
Page 41: 6.2 Dc Power Requirements
6.2 dc power requirements connection to the product should be made in isolated secondary circuits (selv). The voltage specifica- tions are applied at the power connector of the drive. Population mean (nominal condition) supply current (+5.00 v dc case) 7–100 ms supply rise time *2 ±5% tolerance *1 1...
Page 42
6.2.1 power consumption efficiency 0.130 0.108 0.087 0.065 0.054 0.043 0.033 0.022 0.019 power consumption efficiency (watts/gb) 5 gb 6 gb 7.5 gb 10 gb 12 gb 15 gb 20 gb 30 gb 48 gb capacity figure 24. Power consumption efficiency note: power consumption efficiency is calculated as power consumption...
Page 43: 6.3
6.3 start up current 0.5 sec/div 0.2 a/div figure 25. T ypical current wave form at start up of ic25n048atda04-0 travelstar 48gh, 30gn & 15gn hard disk drive specifications 29.
Page 44
0.5 sec/div 0.2 a/div figure 26. T ypical current wave form at start up of ic25n030atda04-0 0.5 sec/div 0.2 a/div figure 27. T ypical current wave form at start up of ic25n015atda04-0 travelstar 48gh, 30gn & 15gn hard disk drive specifications 30
Page 45: 6.4 Reliability
6.4 reliability 6.4.1 data reliability ! Probability of not recovering data is 1 in 10 13 bits read ! Ecc implementation on-the-fly correction performed as a part of read channel function recovers up to 15 symbols of error in 1 sector (1 symbol is 8 bits). 6.4.2 failure prediction (s.M.A.R.T.) the d...
Page 46
6.4.5 preventive maintenance none. 6.4.6 load/unload the product supports a minimum of 300,000 normal load/unloads. Load/unload is a functional mechanism of the hard disk drive. It is controlled by the drive micro code. Specifically, unloading of the heads is invoked by the following commands: ! Har...
Page 47
This power-down sequence should be followed for entry into any system power-down state, system suspend state, or system hibernation state. In a robustly designed system, emergency unload is limited to rare scenarios, such as battery removal during operation. 6.4.6.3 power switch design consideration...
Page 48
6.5 mechanical specifications 6.5.1 physical dimensions and weight the following table gives the dimensions for the 2.5 inch hard disk drive form factor. 95 max. 100.2±0.25 69.85±0.25 9.5±0.2 all other models 99 max. 100.2±0.25 69.85±0.25 9.5±0.2 30 gb and 20 gb models 155 max. 100.2±0.25 69.85±0.25...
Page 49
Figure 30. Mounting hole locations for the 48 gb model 6.5.3 connector and jumper description a jumper is used to designate the drive address as either master or slave. The jumper setting method is described in section 7.10, "drive address setting" on page 62. Connector specifications are included i...
Page 50
The user must use appropriate screws or equivalent mounting hardware to mount the drive securely enough to prevent excessive motion or vibration of the drive at seek operation or spindle rotation. 6.5.5 load/unload mechanism the head load/unload mechanism is provided to protect the disk data during ...
Page 51: 6.6 Vibration And Shock
6.6 vibration and shock all vibration and shock measurements in this section are for hard disk drives without mounting attach- ments for the systems. The input level shall be applied to the normal drive mounting points. Vibration tests and shock tests are to be conducted by mounting the drive to a t...
Page 52
6.6.2 nonoperating vibration the disk drive withstands the following vibration levels without any loss or permanent damage. 6.6.2.1 random vibration the test consists of a random vibration applied in each of three mutually perpendicular axes with the time duration of 15 minutes per axis. The psd lev...
Page 53
6.6.4 nonoperating shock the drive withstands the following half-sine shock pulse without any data loss or permanent damage. 120 g 800 g all other models 120 g 700 g 48 gb model duration of 11 ms duration of 1 ms model figure 35. Nonoperating shock the shocks are applied in each direction of the thr...
Page 54: 6.7 Acoustics
6.7 acoustics 6.7.1 sound power level the criteria of a-weighted sound power level are described below. Measurements are to be taken in accordance with iso 7779. The mean of the sample of 40 drives is to be less than the typical value. Each drive is to be less than the maximum value. The drives are ...
Page 55
6.7.2 discrete tone penalty discrete tone penalties are added to the a-weighted sound power (lw) with the following formula only when determining compliance: lwt(spec) = lw + 0.1pt + 0.3 where lw = a-weighted sound power level pt = value of desecrate tone penalty = dlt – 6.0(dba) dlt = tone-to-noise...
Page 56: 6.8 Identification Labels
6.8 identification labels the following labels are affixed to every drive: ! A label is placed on the top of the hda containing the statement "made by ibm" or equivalent, part no., ec no. And fru no. ! A bar code label placed on the disk drive based on user request. The location on the drive is to b...
Page 57: 6.10 Safety
6.10 safety 6.10.1 ul and csa approval the product is qualified per ul (underwriters labratory) 1950 third edition and can/csa c22.2 no.950-m95 third edition, for the use in information technology equipment, including electric business equipment. The ul recognition or the csa certification is mainta...
Page 58
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 59: 7.1 Cabling
7.0 electrical interface specifications 7.1 cabling the maximum cable length from the host system to the hard disk drive shall not exceed 18 inches. 7.2 interface connector the signal connector for at attachment is designed to mate with the 50 pin plug specified in annex a, connectors and cable asse...
Page 60: 7.3 Signal Definitions
7.3 signal definitions the pin assignments of interface signals are listed as follows: (reserved) 44 gnd 43 power + 5v motor 42 power + 5v logic 41 gnd 40 od i/o dasp- 39 ttl i cs1- 38 ttl i cs0- 37 ttl i da02 36 ttl i da00 35 od i/o pdiag- 34 ttl i da01 33 od o iocs16(*)- 32 3–state o intrq 31 gnd ...
Page 61
Diow- stop iordy dstrobe dior- hdmardy- read operation diow- stop dior- hstrobe iordy ddmardy- write operation conventional definition special definition (for ultra dma) figure 39. Special signal definitions for ultra dma travelstar 48gh, 30gn & 15gn hard disk drive specifications 47.
Page 62: 7.4
7.4 signal descriptions dd00–dd15 a 16-bit bi-directional data bus between the host and the hdd. The lower 8 lines, dd00-07, are used for register and ecc access. All 16 lines, dd00–15, are used for data transfer. These are 3-state lines with 24 ma current sink capability. Da00–da02 these are addres...
Page 63
Following a power on reset, software reset, or reset-, drive 1 shall negate pdiag- within 1 ms (to indicate to device 0 that it is busy). Drive 1 shall then assert pdiag- within 30 seconds to indicate that it is no longer busy and is able to provide status. Following the receipt of a valid execute d...
Page 64
Hstrobe (ultra dma) this signal is used only for ultra dma data transfers between host and drive. The signal hstrobe is the data out strobe signal from the host for ultra dma data out transfers. Both the rising and falling edge of hstrobe latch the data from dd (15:0) into the device. The host may s...
Page 65: 7.6 Reset Timings
7.5 interface logic signal levels the interface logic signals have the following electrical specifications: 24 ma min. –400 µ a min. Driver sink current driver source current current 2.4 v min. 0.5 v max. Output high voltage output low voltage outputs: 2.0 v min./5.5 v max. –0.5 v min./0.8 v max. In...
Page 66: 7.7 Pio Timings
7.7 pio timings the pio cycle timings meet mode 4 of the ata-5 description. Iocs16-(*) t9 t0 t2 t2i t3 t4 t5 t8(*) t7(*) t1 tb read data dd(15:0) dior-, diow- cs(1:0)- da(2:0) write data dd(15:0) iordy (*) up to ata-2 (mode-0,1,2) t6z trd ta t6 1,250 – iordy pulse width tb 35 – iordy setup width ta ...
Page 67: 7.8
7.8 multiword dma timings the multiword dma timings meet mode 2 of the ata-5 description. Write dd(15:0) read dd(15:0) dmack- dmarq dior-/diow- t0 tlr/tlw tj ti td tkr/tkw tf tg th tg tz te 25 – dmack- to read data released tz 35 – dior- to dmarq delay / diow- to dmarq delay tlr/tlw – 25 dior- negat...
Page 68: 7.9 Ultra Dma Timings
7.9 ultra dma timings the ultra dma timings meet mode 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 of the ultra dma protocol. 7.9.1 initiating read dma dstrobe hdmardy- dmack- dmarq stop tui tack tenv tack tenv tziordy tfs tcyc t2cyc dd(15:0) tzad taz xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx xxxx xxx host drives dd device drives dd...
Page 69
7.9.2 host pausing read dma dstrobe hdmardy- dmack- dmarq tsr stop trfs 50 – 60 – 60 – 60 – 70 – 75 – hdmardy- to final dstrobe time trfs – – – – – – 20 – 30 – 50 – dstrobe to hdmardy- time tsr max (ns) min (ns) max (ns) min (ns) max (ns) min (ns) max (ns) min (ns) max (ns) min (ns) max (ns) min (ns...
Page 70
7.9.3 host terminating read dma dstrobe hdmardy- dmack- dmarq stop tmli trp dd(15:0) tzah xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx device drives dd host drives dd tch tcs crc tack tack trfs tli tiordyz xxx rd data xxxxxxxxxxx taz tli 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – maximum time before releasing iordy tiordyz – 20 – 20 ...
Page 71
7.9.4 device terminating read dma dstrobe hdmardy- dmack- dmarq stop tmli dd(15:0) tzah xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx device drives dd host drives dd tch tcs crc tack tack tli tiordyz xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxx tss tli tli taz – – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – maximum time before releasing iordy tiordyz – – – 20 – 20 – 20 –...
Page 72
7.9.5 initiating write dma hstrobe ddmardy- dmack- dmarq stop tui tack tenv tziordy tli tui tcyc t2cyc dd(15:0) xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx xxx host drives dd tdh tds wt data wt data wt data tack tcyc – 4.6 – 5 – 5 – 5 – 5 – 5 data hold time at device tdh – 4 – 5 – 7 – 7 – 10 – 15 data setup...
Page 73
7.9.6 device pausing write dma hstrobe ddmardy- dmack- dmarq tsr stop trfs 50 – 60 – 60 – 60 – 70 – 75 – ddmardy- to final hstrobe time trfs – – – – – – 20 – 30 – 50 – hstrobe to ddmardy- time tsr max (ns) min (ns) max (ns) min (ns) max (ns) min (ns) max (ns) min (ns) max (ns) min (ns) max (ns) min ...
Page 74
7.9.7 device terminating write dma hstrobe ddmardy- dmack- dmarq stop tmli trp dd(15:0) xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx host drives dd tch tcs crc tli tack tack trfs tli tiordyz xxx wt data xxxxxxxxxx 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – maximum time before releasing iordy tiordyz – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 ...
Page 75
7.9.8 host terminating write dma hstrobe ddmardy- dmack- dmarq stop tmli dd(15:0) host drives dd tch tcs crc tss tack tack tli tiordyz xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxx tli tli 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – maximum time before releasing iordy tiordyz – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 – 20 hold ...
Page 76: 7.10 Drive Address Setting
7.10 drive address setting a jumper is available at the interface connector to determine the drive address. The set position of the jumper is as shown below. Using cable selection, the drive address depends on the condition of pin 28 of the at interface cable. In the case when pin 28 is ground, or l...
Page 77
7.12 addressing of hdd registers the host addresses the drive through a set of registers called a task file. These registers are mapped into the host's i/o space. Two chip select lines (cs0- and cs1-) and three address lines (da00–02) are used to select one of these registers, while a dior- or diow-...
Page 78
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 79
Part 2. Interface specification travelstar 48gh, 30gn & 15gn hard disk drive specifications 65.
Page 80
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 81: 8.0 General
8.0 general 8.1 introduction this specification describes the host interface of the travelstar 48gh, 30gn & 15gn (model numbers ic25xxxxatdaxx-x). The interface conforms to the working document of information technology, at attachment with packet interface extension (ata/atapi-5), revision 3 dated f...
Page 82
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 83
9.0 deviations from standard the device conforms to the referenced specifications with deviations described below. The interface conforms to the working document of information technology, at attachment with packet interface extension (ata/atapi-5), revision 3 dated february 29, 2000, with deviation...
Page 84
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 85: 10.0 Registers
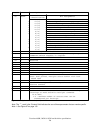
10.0 registers invalid address invalid address x x x a a command status 1 1 1 n a lba bits 24-27 (*2) lba bits 24-27 (*2) 0 1 1 n a device/head device/head. 0 1 1 n a lba bits 16-23 (*2) lba bits 16-23 (*2) 1 0 1 n a cylinder high cylinder high 1 0 1 n a lba bits 8-15 (*2) lba bits 8-15 (*2) 0 0 1 n...
Page 86: 10.2 Command Register
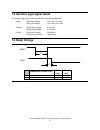
10.1 alternate status register 0 err 1 idx 2 cor 3 drq 4 dsc 5 df 6 rdy 7 bsy alternate status register figure 54. Alternate status register this register contains the same information as the status register. The only difference between this register and the status register is that reading the alter...
Page 87: 10.5 Data Register
10.5 data register this register is used to transfer data blocks between the device data buffer and the host. It is also the register through which sector information is transferred on a format track command and the configuration information is transferred on an identify device command. All data tra...
Page 88: 10.7 Device/head Register
10.7 device/head register hs0 hs1 hs2 hs3 drv 1 l 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 device/head register figure 56. Device/head register this register contains the device and head numbers. Bit definitions head select. These four bits indicate the binary encoded address of the head. Bit hs0 is the least significant ...
Page 89: 10.8 Error Register
10.8 error register amn tk0n abrt 0 idnf 0 unc crc 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 error register figure 57. Error register this register contains the status from the last command executed by the device or a diagnostic code. At the completion of any command except execute device diagnostic, the contents of this reg...
Page 90: 10.12 Status Register
10.11 sector number register this register contains the starting sector number for any disk data access for the subsequent command. The sector number is from one to the maximum number of sectors per track. In lba mode this register contains bits 0–7. At the end of the command this register is update...
Page 91: 11.1 Reset Response
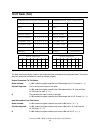
11.0 general operation descriptions 11.1 reset response ata has the following three types of resets: the srst bit in the device control register is set and then is reset. The device resets the interface circuitry according to the set features requirement. Soft reset (software reset) the reset- signa...
Page 92
O o o reset standby timer value (*5) (*4) (*4) (*6) power mode (*3) o o reverting programmed parameters to default Ÿ number of chs (set by initialize device parameters) Ÿ multiple mode Ÿ write cache Ÿ delayed write Ÿ read look-ahead Ÿ ecc bytes Ÿ volatile max. Address Ÿ address offset mode o o o pdi...
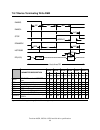
Page 93
11.1.1 register initialization after a power on, a hard reset, or a software reset, the register values are initialized as shown in the table below. 50h alternate status 50h status a0h device/head 00h cylinder high 00h cylinder low 01h sector number 01h sector count diagnostic code error default val...
Page 94
11.2 diagnostic and reset considerations the set max password, the set max security mode and the set max unlock counter are not retained over a power on reset but are retained over a hard reset or soft reset. For each reset and execute device diagnostic, the diagnostic is done as follows: if device ...
Page 95
11.3 power-off considerations 11.3.1 load/unload load/unload is a functional mechanism of the hdd. It is controlled by the drive microcode. Specifically, unloading of the heads is invoked by the following commands. Ul -> comp. Sleep ul -> comp. Standby immediate ul -> comp. Standby response command ...
Page 96: 11.4 Sector Addressing Mode
11.3.3 required power-off sequence problems can occur on most hdds when power is removed at an arbitrary time. Listed below are examples of such problems: ! Data loss from the write buffer. ! If the drive is writing a sector, a partially-written sector with an incorrect ecc block results. The sector...
Page 97
Lba addressing mode logical sectors on the device shall be linearly mapped with the first lba addressed sector (sector 0) being the same sector as the first logical chs addressed sector ( cylinder 0, head 0, sector 1). Irre- spective of the logical chs translation mode currently in effect, the lba a...
Page 98
The idle and idle immediate commands move a device to idle mode immediately from the active or standby modes. The idle command also sets the standby timer count and starts the standby timer. The sleep command moves a device to sleep mode. The device's interface becomes inactive at the com- pletion o...
Page 99
Though the interface is inactive in sleep mode, the access to the interface registers and the validity of intrq is guaranteed for two seconds after the sleep command is completed. After this period, the contents of interface registers may be lost. Since the contents of interface registers may be inv...
Page 100: 11.7 S.M.A.R.T. Function
11.6.3 low power idle mode power consumption is 60–65% less than that of performance idle mode. The heads are unloaded on the ramp, however the spindle is still rotated at the full speed. Recovery time to active mode is about 300 ms. 11.6.4 transition time the transition time is dynamically managed ...
Page 101
Degrading or fault condition existing. There is no implied linear reliability relationship corresponding to the numerical relationship between different attribute values for any particular attribute. 11.7.3 attribute thresholds each attribute value has a corresponding attribute threshold limit which...
Page 102
11.8.1 security mode following security modes are provided. The device enables all commands except those which can update the device lock function, set/change password. The device enters this mode via a security freeze lock command. It cannot quit this mode until power off. Device frozen mode the de...
Page 103
11.8.5.2 user password setting when a user password is set, the device will automatically enter lock mode the next time the device is powered on. Por set password with user password normal operation power off device locked mode por ( ref.) por normal operation power off device unlocked mode por figu...
Page 104
11.8.5.3 operation from por after user password is set when the device lock function is enabled, the device rejects the media access command until a security unlock command is successfully completed. Por device locked mode unlock cmd command (*1) command (*1) password erase unit password match ? Rej...
Page 105
11.8.5.4 user password lost if the user password is forgotten and high level security is set, the system user can't access any data. However the device can be unlocked using the master password. If a system user forgets the user password and maximum security level is set, data access is impossible. ...
Page 106
11.8.6 command table this table shows the device's response to commands when the security mode feature set (device lock function) is enabled. O o o set max set password o o o set max lock o o o set max freeze lock o o o set max address o o o set features o o o sense condition o o o seek x o o securi...
Page 107
O o x write verify o o x write sector(s) (w/o retry) o o x write sector(s) (w/o retry) o o x write multiple o o x write long (w/retry) o o x write long (w/o retry) o o x write dma (w/retry) o o x write dma (w/o retry) o o o write buffer o o o standby immediate o o o standby o o o s.M.A.R.T. Save att...
Page 108
11.9 protected area function protected area function is to provide the 'protected area' which cannot be accessed via conventional methods. This 'protected area' is used to contain critical system data such as bios or system management information. The contents of the entire system main memory may al...
Page 109
Change maximum lba using set max address command to 0fbfffh with nonvolatile option. From this point, the protected area cannot be accessed until next set max address command is issued. Any bios, device driver, or application software accesses the hdd as if it is a 528 mb device because the device b...
Page 110
The set max freeze lock command allows the host to disable the set max commands (including set max unlock) until the next power cycle. When this command is accepted the device is in the set max frozen mode. The set max password, the set max security mode and the unlock counter do not persist over a ...
Page 111
11.10 address offset feature (vendor specific) computer systems perform initial code loading (booting) by reading from a predefined address on a disk drive. To allow an alternate bootable operating system to exist in a reserved area on a disk drive this feature provides a set features function to te...
Page 112
11.10.2 identify device data identify device data, word 83, bit 7 indicates that the device supports the address offset feature. Identify device data, word 86, bit 7 indicates that the device is in address offset mode. 11.10.3 exceptions in address offset mode any commands which access sectors acros...
Page 113: 11.11
11.11 seek overlap the drive provides accurate seek time measurement method. The seek command is usually used to measure the device seek time by accumulating execution time for a number of seek commands. With typical implementation of the seek command, this measurement must include the device and ho...
Page 114: 11.12 Write Cache Function
11.12 write cache function write cache is a performance enhancement whereby the device reports completion of the write command (write sectors and write multiple) to the host as soon as the device has received all of the data in its buffer. The device assumes responsibility to write the data subseque...
Page 115: 11.14 Reassign Function
11.14 reassign function the reassign function is used with read commands and write commands. The sectors of data for reassignment are prepared as the spare data sector. The one entry can register 256 consecutive sectors maximum. This reassignment information is registered internally, and the informa...
Page 116
This page intentionally left blank..
Page 117: 12.0 Command Protocol
12.0 command protocol the commands are grouped into different classes according to the protocols followed for command execution. The command classes with their associated protocols are defined below. For all commands, the host must first check to see if bsy = 1, and should proceed no further unless ...
Page 118
E. The host reads one sector (or block) of data via the data register. F. The device sets drq = 0 after the sector (or block) has been transferred to the host. 4. For the read long command: a. The device sets bsy = 1 and prepares for data transfer. B. When the sector of data is available for transfe...
Page 119: 12.2 Data Out Commands
12.2 data out commands the following are examples of data out commands: ! Device configuration set ! Format track ! Security disable password ! Security erase unit ! Security set password ! Security unlock ! Set max set password ! Set max unlock ! S.M.A.R.T. Write log sector ! Write buffer ! Write l...
Page 120
F. The device clears the interrupt in response to the status register being read. The write multiple command transfers one block of data for each interrupt. The other commands transfer one sector of data for each interrupt. If the device detects an invalid parameter, then it will abort the command b...
Page 121: 12.3 Nondata Commands
12.3 nondata commands the following are examples of nondata commands: ! Check power mode ! Device configuration freeze lock ! Device configuration restore ! Enable/disable delayed write ! Execute device diagnostic ! Flush cache ! Format unit ! Idle ! Idle immediate ! Initialize device parameters ! R...
Page 122
12.4 dma data transfer commands these commands are ! Identify device dma ! Read dma ! Write dma data transfers using dma commands differ in two ways from pio transfers: ! Data transfers are performed using the slave dma channel ! No intermediate sector interrupts are issued on multisector commands i...
Page 123: 13.0 Command Descriptions
13.0 command descriptions 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 f9 set max freeze lock 3 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 f9 set max address 3 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 ef set features 3 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 f0 sense condition 3 0 1 1 1 - - - - 7x seek 3 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 f2 security unlock 2 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 f1 security set password 2 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 f5 ...
Page 124
0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 3c write verify 2 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 31 write sectors (no retry) 2 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 30 write sectors (retry) 2 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 c5 write multiple 2 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 33 write long (no retry) 2 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 32 write long (retry) 2 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 cb write dma (no retry) 4 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 ...
Page 125
C3 b1 device configuration set c2 b1 device configuration identify c1 b1 device configuration freeze lock c0 b1 device configuration restore (device configuration overlay) 04 f9 set max freeze lock 03 f9 set max unlock 02 f9 set max lock 01 f9 set max set password (set max security extension) cc ef ...
Page 126
The following symbols are used in the command descriptions: output registers 0 this indicates that the bit must be set to 0. Output registers – continued 1 this indicates that the bit must be set to 1. D the device number bit. Indicates that the device number bit of the device/head register should b...
Page 127
13.1 check power mode (e5h/98h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector ...
Page 128: (B1H)
13.2 device configuration overlay (b1h) ...See below... Status 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head - - - - d - - - device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - -...
Page 129
13.2.2 device configuration freeze lock (subcommand c1h) the device configuration freeze lock command prevents accidental modification of the device configuration overlay settings. After successful execution of a device configuration freeze lock command, all device configuration set, device configur...
Page 130
Error information example 2: if the device has enabled the security feature set and if a user attempts to disable that feature, the device aborts that command and returns an error reason code as below. = now security feature set is enabled : 04h sector count = bit 3 is invalid : 03h cylinder low = w...
Page 131
Other reason ffh subcommand code is invalid 08h dco is not supported 07h protected area is now established 06h device is now set max locked or frozen mode 05h user attempt to disable any feature enabled 04h device's feature is already modified with dco 03h device is now security locked mode 02h dco ...
Page 132
13.3 enable/disable delayed write (fah: vendor specific) see below status 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector numbe...
Page 133
13.4 execute device diagnostic (90h) see below status 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 - - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - se...
Page 134: 13.5 Flush Cache (E7H)
13.5 flush cache (e7h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number - ...
Page 135
13.6 format track (50h: vendor specific) see below status 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v ...
Page 136
H in lba mode this register specifies the current lba address bits as 24–27 (l = 1). Error this indicates the error register. An abort error (abt = 1) will be returned under the following conditions: Ÿ the descriptor value does not match the certain value (except 00h). In lba mode this command forma...
Page 137: 13.7
13.7 format unit (f7h: vendor specific) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - -...
Page 138
The execution time of this command is shown below: 8 min 5 gb model 8 min 6 gb model 10 min 7.5 gb model 14 min 10 gb model 16 min 12 gb model 20 min 15 gb model 24 min 20 gb model 38 min 30 gb model 52 min 48 gb model travelstar 48gh, 30gn & 15gn hard disk drive specifications 124.
Page 139: 13.8 Identify Device (Ech)
13.8 identify device (ech) see below status 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector numbe...
Page 140
Maximum number of sectors that can be transferred per interrupt on read and write multiple commands 15-8(=80h) 7-0 : maximum number of sectors that can be transferred per interrupt. 8010h 47 model number in ascii note 1 27-46 micro code version in ascii xxxx 23-26 number of ecc bytes as currently se...
Page 141
Multiword dma transfer capability 15-11(=0) reserved 10 1 = multiword dma mode 2 is selected 9 1 = multiword dma mode 1 is selected 8 1 = multiword dma mode 0 is selected 7- 0(=7) multiword dma transfer modes supported (support mode 0, 1 and 2) xx07h 63 reserved * 0000h 62 total number of user addre...
Page 142
Command set supported 15(=0) reserved 14(=1) 1=nop command supported 13(=1) 1=read buffer command supported 12(=1) 1=write buffer command supported 11(=0) reserved 10(=1) 1=host protected area feature set supported 9(=0) 1=device reset command supported 8(=0) 1=service interrupt supported 7(=0) 1=re...
Page 143
Command set/feature enabled 15(=1) reserved 14(=1) 1=nop command supported 13(=1) 1=read buffer command supported 12(=1) 1=write buffer command supported 11(=0) reserved 10(=1) 1=host protected area feature set supported 9(=0) 1=device reset command supported 8(=0) 1=service interrupt enabled 7(=0) ...
Page 144
Current master password revision codes xxxxh 92 current advanced power management level 15- 8(=40h) reserved 7- 0(=xxh) correct advanced power management level set by set features command (01h to feh) 40xxh 91 time required for enhance security erase completion 0000 : not supported 0000h 90 time req...
Page 145
Security mode feature. Bit assignments 15-9(=0) reserved 8(=x) security level 1= maximum, 0= high 7-6(=0) reserved 5(=0) 1=enhanced security erase supported 4(=x) 1=security count expired 3(=x) 1=security frozen 2(=x) 1=security locked 1(=x) 1=security enabled 0(=x) 1=security supported 0xxxh 128 re...
Page 146
Integrity word 15-8(=xxh) checksum 7-0(=a5h) signature xxa5h 255 reserved * 0000h 132-254 initial power mode selection. Bit assignments 15-2(=0) reserved 1(=1) always 0(=x) initial power mode 1=standby, 0=idle * 000xh 131 reserved * xxxxh 130 current set feature option. Bit assignments 15-4(=0) rese...
Page 147
950a60h number of user addressable sectors 02b6h (=347kb) buffer size fh number of heads 2860h number of cylinders ic25n005atda04-0 b30880h number of user addressable sectors 02b6h (=347kb) buffer size fh number of heads 3080h number of cylinders ic25n006atda04-0 df8f90h number of user addressable s...
Page 148
13.9 identify device dma (eeh) see below status 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector n...
Page 149: 13.10 Idle (E3H/97H)
13.10 idle (e3h/97h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number - - ...
Page 150
13.11 idle immediate (e1h/95h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector n...
Page 151
13.12 initialize device parameters (91h) see below status 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d h h h h device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - ...
Page 152: 13.13 Read Buffer (E4H)
13.13 read buffer (e4h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number -...
Page 153: 13.14 Read Dma (C8H/c9H)
13.14 read dma (c8h/c9h) see below status 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector number ...
Page 154
H this indicates the head number of the first sector to be transferred. (l = 0) in lba mode this register specifies the lba bits 24–27 to be transferred. (l = 1) r this indicates the retry bit. If set to one, then retries are disabled. Input parameters from the device sector count this indicates the...
Page 155: 13.15 Read Long (22H/23H)
13.15 read long (22h/23h) see below status 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector number...
Page 156
R this indicates the retry bit. If it is set to one then retries are disabled. Input parameters from the device sector count this indicates the number of requested sectors not transferred. Sector number this indicates the sector number of the transferred sector. (l = 0) in lba mode, this register co...
Page 157: 13.16 Read Multiple (C4H)
13.16 read multiple (c4h) see below status 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector number...
Page 158
Input parameters from the device sector count this indicates the number of requested sectors not transferred. This number is zero unless an unrecoverable error occurs. Sector number this indicates the sector number of the last transferred sector. (l = 0) in lba mode this register contains the curren...
Page 159
13.17 read native max address (f8h) see below status 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d - - - - device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number - - - - - - - - sec...
Page 160
H in lba mode this register contains the native max lba bits 24–27. (l = 1) in the chs mode this register contains the native maximum head number. (l = 0) v valid. Indicates that the bit is part of an input parameter and will be set to 0 or 1 by the device. - this indicates that the bit is not used....
Page 161
13.18 read sectors (20h/21h) see below status 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector num...
Page 162
Input parameters from the device sector count this is the number of requested sectors not transferred. This will be zero, unless an unrecoverable error occurs. Sector number this is the sector number of the last transferred sector. (l = 0) in lba mode this register contains the current lba bits 0–7....
Page 163
13.19 read verify sectors (40h/41h) see below status 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sec...
Page 164
H this is the head number of the first sector to be transferred. (l = 0) in lba mode this register contains the lba bits 24–27. (l = 1) r this is the retry bit. If it is set to one then retries are disabled. Input parameters from the device sector count this is the number of requested sectors not ve...
Page 165: 13.20 Recalibrate (1Xh)
13.20 recalibrate (1xh) see below status 0 0 0 1 - - - - command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number -...
Page 166
13.21 security disable password (f6h) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - s...
Page 167
13.22 security erase prepare (f3h) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sect...
Page 168
13.23 security erase unit (f4h) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector ...
Page 169
Identifier zero indicates that the device should check the supplied password against the user password stored internally. One indicates that the device should check the given pass- word against the master password stored internally. The security erase unit command erases all user data and disables t...
Page 170
13.24 security freeze lock (f5h) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector...
Page 171
13.25 security set password (f1h) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - secto...
Page 172
Reserved 19-255 master password revision code (valid if word 0 bit 0 = 1) 17-18 password ( 32 bytes ) 01-16 control word bit 0 : identifier (1- master, 0- user) bit 1-7 : reserved bit 8 : security level (1- maximum, 0- high) bit 9-15 : reserved 00 description word figure 107. Security set password i...
Page 173
13.26 security unlock (f2h) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector numb...
Page 174
Reserved 17-255 password ( 32 bytes ) 01-16 control word bit 0 : identifier (1- master, 0- user) bit 1-15 : reserved 00 description word figure 109. Security unlock information identifier azero indicates that the device regards password as the user password. A one indicates that the device regards p...
Page 175: 13.27 Seek (7Xh)
13.27 seek (7xh) see below status 0 1 1 1 - - - - command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector number - - - - ...
Page 176
13.28 sense condition (f0h: vendor specific) see below status 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 command - - - d - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - n sector number - - - - - ...
Page 177: 13.29 Set Features (Efh)
13.29 set features (efh) see below status 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number ...
Page 178
Output parameters to the device feature destination code for this command. 02h enable write cache (see note 2) 03h set transfer mode based on value in sector count register 05h enable advanced power management 09h enable address offset mode 44h 40 bytes of ecc apply on read long/write long commands ...
Page 179
13.30 set max address (f9h) see below status 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector numb...
Page 180
Output parameters to the device feature destination code for this command 01h set max set password 02h set max lock 03h set max unlock 04h set max freeze lock when the set max address command is executed, this register is ignored. B this indicates the option bit for selection whether nonvolatile or ...
Page 181: 13.31 Set Multiple (C6H)
13.31 set multiple (c6h) see below status 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number ...
Page 182: 13.32 Sleep (E6H/99H)
13.32 sleep (e6h/99h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number - -...
Page 183
13.33 s.M.A.R.T. Function set (b0h) see below status 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sec...
Page 184
D8h s.M.A.R.T. Enable operations d9h s.M.A.R.T. Disable operations dah s.M.A.R.T. Return status dbh s.M.A.R.T. Enable/disable automatic off-line 13.33.1 s.M.A.R.T. Function subcommands 13.33.1.1 s.M.A.R.T. Read attribute values (subcommand d0h) this subcommand returns the device's attribute values t...
Page 185
13.33.1.5 s.M.A.R.T. Execute off-line immediate (subcommand d4h) this subcommand causes the device to immediately initiate the set of activities that collect attribute data in an off-line mode (off-line routine) or execute a self-test routine in either captive or off-line mode. The sector number reg...
Page 186
13.33.1.7 s.M.A.R.T. Write log sector (subcommand d6h) this command writes 512 bytes of data to the specified log sector. The 512 bytes of data are transferred at a command and the sector count value shall be set to one. The sector number must be set to specify the "log sector address" (see figure 1...
Page 187
13.33.1.11 s.M.A.R.T. Enable/disable automatic off-line (subcommand dbh) this subcommand enables and disables the optional feature that cause the device to perform the set of off-line data collection activities that automatically collect attribute data in an off-line mode and then save this data to ...
Page 188
13.33.2 device attributes data structure the following defines the 512 bytes that make up the attribute value information. This data structure is accessed by the host in its entirety using the s.M.A.R.T. Read attribute values subcommand. All multibyte fields shown in these data structures follow the...
Page 189
13.33.2.2 individual attribute data structure the following defines the 12 bytes that make up the information for each attribute entry in the device attribute data structure. 12 total bytes binary 0bh 1 reserved (00h) binary 05h 6 reserved (may not be 0) binary 04h 1 reserved (may not be 0) ffh inva...
Page 190
10 spin retry count 12 device power cycle count 191 gsense error rate 192 power off retract count 193 load/unload cycle count 194 device temperature 196 reallocation event count 197 current pending sector count 198 off-line scan uncorrectable sector count 199 ultra dma crc error count status flag de...
Page 191
13.33.2.3 off-line data collection status the value of this byte defines the current status of the off-line activities of the device. Bit 7 indicates an automatic off-line data collection status. Bit 7 automatic off-line data collection status 0 automatic off-line data collection is disabled. 1 auto...
Page 192
13.33.2.6 current segment pointer this byte is a counter indicating the next segment to execute as an off-line data collection activity. Because the number of segments is 1, 01h is always returned in this field. 13.33.2.7 off-line data collection capability bit definition 0 the execute off-line imme...
Page 193
13.33.2.9 error logging capability if bit = 1, the device supports the error logging the error logging support bit 0 reserved (0) 7–1 definition bit 13.33.2.10 self-test failure check point this byte indicates the section of self-test where the device detected a failure. 13.33.2.11 self-test complet...
Page 194
13.33.3.2 individual thresholds data structure the following defines the 12 bytes that make up the information for each threshold entry in the device attribute thresholds data structure. Attribute entries in the individual threshold data structure are in the same order and correspond to the entries ...
Page 195
13.33.4 s.M.A.R.T. Error log sector the following defines the 512 bytes that make up the s.M.A.R.T. Error log sector. All multibyte fields shown in these data structures follow the ata/atapi-5 specifications for byte ordering. 512 1ffh 1 data structure checksum 1c6h 57 reserved 1c4h 2 device error c...
Page 196
13.33.4.4 error log data structure the data format of each error log structure is shown below. 90 3ch 30 error data structure 30h 12 5th error log data structure 24h 12 4th error log data structure 18h 12 3rd error log data structure 0ch 12 2nd error log data structure 00h 12 1st error log data stru...
Page 197
13.33.4.4.1 error data structure data format of error data structure is shown below. 30 1ch 2 life time stamp (hours) 1bh 1 state 08h 19 extended error data (vendor specific) 07h 1 status register 06h 1 device/head register 05h 1 cylinder high register 04h 1 cylinder low register 03h 1 sector number...
Page 198
13.33.5 self-test log data structure the following defines the 512 bytes that make up the self-test log sector. All multibyte fields shown in these data structures follow the ata/atapi-5 specifications for byte ordering. 512 1ffh 1 data structure checksum 1fdh 2 reserved 1fch 1 self-test log pointer...
Page 199
13.33.6 error reporting the following table shows the values returned in the status and error registers when specific error conditions are encountered by a device. 10h or 01h 51h the device is unable to write to its attribute values data structure. 10h or 40h 51h the device is unable to read its att...
Page 200: 13.34 Standby (E2H/96H)
13.34 standby (e2h/96h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number -...
Page 201
13.35 standby immediate (e0h/94h) see below status 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - secto...
Page 202: 13.36 Write Buffer (E8H)
13.36 write buffer (e8h) see below status 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 command - - - - - - - - device/head 1 - 1 d - - - - device/head - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder high - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - cylinder low - - - - - - - - sector number - - - - - - - - sector number ...
Page 203: 13.37 Write Dma (Cah/cbh)
13.37 write dma (cah/cbh) see below status 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector number...
Page 204
H this indicates the head number of the first sector to be transferred. (l = 0) in lba mode this register contains the lba bits 24–27. (l = 1) input parameters from the device sector count this indicates the number of requested sectors not transferred. The sector count will be zero unless an unrecov...
Page 205: 13.38 Write Long (32H/33H)
13.38 write long (32h/33h) see below status 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector numbe...
Page 206
H this indicates the head number of the sector to be transferred. (l = 0) in lba mode this register contains the lba bits 24–27. (l = 1) r the retry bit. If the retry bit is set to one, then retries are disabled. Input parameters from the device sector count this indicates the number of requested se...
Page 207: 13.39 Write Multiple (C5H)
13.39 write multiple (c5h) see below status 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector numbe...
Page 208
Input parameters from the device sector count this indicates the number of requested sectors not transferred. The sector count will be zero, unless an unrecoverable error occurs. Sector numberthis indicates the sector number of the last transferred sector. (l = 0) in lba mode this register contains ...
Page 209
13.40 write sectors (30h/31h) see below status 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 r command - - - - h h h h device/head 1 l 1 d h h h h device/head v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder high v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v cylinder low v v v v v v v v sector number v v v v v v v v sector nu...
Page 210
Input parameters from the device sector count this indicates the number of requested sectors not transferred. The sector count will be zero unless an unrecoverable error occurs. Sector number this indicates the sector number of the last transferred sector. (l = 0) in lba mode this register contains ...
Page 211: 14.0 Time-Out Values
14.0 time-out values the timing of bsy and drq in status register are shown in the table below. 400 ns status register bsy=1 out to command register device busy after command code out dma data transfer command 30 sec (note 2.) interrupt status register bsy=1 interrupt for command complete 400 ns sta...
Page 212
We recommend that the host system execute soft reset and then retry to issue the command if the host system time-out would occur for the device. Note 1. For security erase unit command, the execution time is referred to 13.23, "security erase unit (f4h)" on page 154. Note 2. For format unit command,...
Page 213: 15.0 Appendix
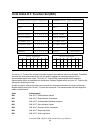
15.0 appendix 15.1 commands support coverage the following table is provided to facilitate the understanding of command support coverage of the drive compared to the ata-5 defined command set. The column entitled "implementation for travelstar 48 gh, 30 gn & 15 gn" shows the capability of the drive ...
Page 214
Reserved reserved reserved: all remaining codes --- vendor specific reserved vendor specific fbh-ffh vendor specific yes enable/disable delayed write fah optional yes set max address f9h optional yes read native max address f8h vendor specific vendor specific format unit f7h optional (6) yes securit...
Page 215
15.2 set features command support coverage the following table provides a list of feature registers and feature names as well as a column titled "implementation for travelstar 48gh, 30gn & 15gn" which indicates whether the drive has the capability of executing the command in comparison to the ata/at...
Page 216
This page intentionally left blank. Travelstar 48gh, 30gn & 15gn hard disk drive specifications 202.
Page 217: Index
A able-3, 85 abrt, 75 abt, 75 active idle mode, 85 adaptive power management feature low power idle mode, 86 address offset feature, 97 address setting, 62 advanced power management, 85 advanced power management feature active idle mode, 85 performance idle mode, 85 transition time, 86 amn, 75 amnf,...
Page 218
Error register diagnostic codes, 79 example for operation (in lba mode), 94 execute device diagnostic, 119 f flush cache, 120 format track, 121 format unit (f7h: vendor specific), 123 full stroke seek, 17 h hs0, 74 hs1, 74 hs2, 74 hs3, 74 i icrce, 75 identify device, 103, 125 identify device dma, 10...
Page 219
S.M.A.R.T. Operation with power management modes, 87 s.M.A.R.T. Capability, 178 s.M.A.R.T. Function, 86 attribute thresholds, 87 attribute values, 86 attributes, 86 s.M.A.R.T. Commands, 87 threshold exceeded condition, 87 s.M.A.R.T. Function set, 169 s.M.A.R.T. Function subcommands, 114, 115, 170 sa...
Page 220
© international business machines corporation 2002 www.Ibm.Com/harddrive ibm technology group support center telephone: 888.Ibm.5214 or 507.286-5825 fax: 507.253.Drive e-mail: drive@us.Ibm.Com singapore technical support center telephone: (65)6418.9595 or 1800.418.9595 e-mail: drive@sg.Ibm.Com uk te...