- DL manuals
- IBM
- Desktop
- RS6000 - 7026 - H70
- Service Manual
IBM RS6000 - 7026 - H70 Service Manual
Summary of RS6000 - 7026 - H70
Page 1
Rs/6000 7025 f50 series ibm service guide sa38-0541-01.
Page 2
Second edition (february 1998) the following paragraph does not apply to the united kingdom or any country where such provisions are inconsistent with local law: this publication is provided “as is” without warranty of any kind, either express or implied, including, but not limited to, the implied w...
Page 3
Contents communications statements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Vii federal communications commission (fcc) statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Vii international electrotechnical commission (iec) statement . . . . . . . . . . . . Vii united kingdom telecommunications s...
Page 4
Physical location codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-46 aix and physical location code reference table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-48 aix location codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-54 ssa location code format . . . ...
Page 5
Chapter 7. Parts information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1 power cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7 appendix a. Ssa problem determination procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1 disk drive module power-on self-tests (...
Page 6
Vi service guide.
Page 7
Communications statements federal communications commission (fcc) statement note: this equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class a digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interfer...
Page 8
Other optional cards, not supplied by the manufacturer, do not use main voltages or any other excessive voltages. Seek advice from a competent engineer before installing other adapters not supplied by the manufacturer. European union (eu) statement this product is in conformity with the protection r...
Page 9
This is a class b product based on the standard of the voluntary control council for interference from information technology equipment (vcci). If this is used near a radio or television receiver in a domestic environment, it may cause radio interference. Install and use the equipment according to t...
Page 10
Note: if any of the following feature codes are installed: 3615, 4356, 4357, 4358, 4359, 6218, 8130, or 8134, or if a configuration using more than one syskonnect fddi adapter (feature codes 2741, 2742, or 2743) where any one of them is feature code 2743 (syskonnect sk-net fddi-up sas pci), the foll...
Page 11
Safety notices a danger notice indicates the presence of a hazard that has the potential of causing death or serious personal injury. A caution notice indicates the presence of a hazard that has the potential of causing moderate or minor personal injury. Electrical safety observe the following safet...
Page 12
Danger to prevent electrical shock hazard, disconnect the power cable from the electrical outlet before relocating the system. Xii service guide.
Page 13
Laser safety information the optical drive in this system unit is a laser product. The optical drive has a label that identifies its classification. The label, located on the drive, is shown below. Class 1 laser product laser klasse 1 luokan 1 laserlaite appareil a laser de classe 1 iec 825:1984 cen...
Page 14
Xiv service guide.
Page 15
About this book this book provides maintenance information that is specific to the system unit, adapters, and attached devices that do not have their own service information. It also contains maintenance analysis procedures (maps) that are not common to other systems. Maps that are common to all sys...
Page 16
Xvi service guide.
Page 17
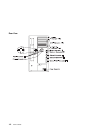
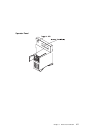
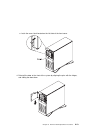
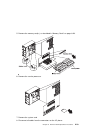
Chapter 1. Reference information system unit locations front view with media door off chapter 1. Reference information 1-1.
Page 18
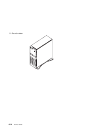
Rear view 1-2 service guide.
Page 19
Scsi ids and bay locations note: the scsi bus id's in bays a1, b1 and b2 are the recommended values. Features installed at the manufacturing site correspond to these ids. Field installations may not comply with these recommendations. Chapter 1. Reference information 1-3.
Page 20
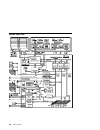
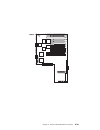
I/o planar locations j1, j2 64-bit pci connectors j3, j4, j5, j6, j7, j8p, j9p 32-bit pci connectors j8i, j9i isa connectors j10 service processor j11 external scsi connector j12 fan #1 (bottom fan) j13 diskette drive connector j15 fan #3 j16 scsi security jumper j17 fan #2 j18 ethernet connector (t...
Page 21
J19 fan #4 (top fan) j21 ethernet connector (twisted pair) j22a operator panel j23 keyboard connector j25 internal scsi connector (port 1) j26 system card connector j27 mouse connector j30 internal scsi connector (port 2) j41 serial connector (serial port 1 and 2) j43 battery socket j47 parallel con...
Page 22
System card locations j5, j6 processor card connector #2 j8, j9 processor card connector #1 j12 memory card connector #1 j13 memory card connector #2 memory card locations 1-6 service guide.
Page 23
Operator panel chapter 1. Reference information 1-7.
Page 24
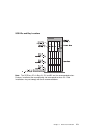
System data flow 1-8 service guide.
Page 25
Typical boot sequence for rs/6000 7025 f50 series after the a/c power is turned on, the system support controller (ssc) startup begins, and releases reset to the service processor. If the ssc cannot communicate with the service processor, the lcd displays 4ba00000. If the service processor is not pr...
Page 26
7. Ipl boot code the system firmware attempts to boot from the devices listed in the boot list. Lcd code range is e1xx. 8. Boot image execution once a boot image is located on a device in the boot list, the system firmware code hands off control to the aix boot code. – lcd code e105 for normal boot ...
Page 27
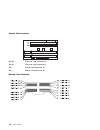
Power source loading typical emc configuration - 0.28 kva maximum - 0.65 kva power requirements typical - 154 watts maximum - 450 watts power factor 0.8 - 0.98 operating voltage 100 to 127v ac; 50 to 60 hz 200 to 240v ac; 50 to 60 hz heat output (maximum) typical - 800 btu/hr maximum - 2300 btu/hr a...
Page 28
Power cables to avoid electrical shock, a power cable with a grounded attachment plug is provided. Use only properly grounded outlets. Power cables used in the united states and canada are listed by underwriter's laboratories (ul) and certified by the canadian standards association (csa). These powe...
Page 29
Service inspection guide perform a service inspection on the system when: the system is inspected for a maintenance agreement. Service is requested and service has not recently been performed. An alterations and attachments review is performed. Changes have been made to the equipment that may affect...
Page 30
B. Check for the correct grounded power cable. C. With the external power cable connected to the device, check for 0.1 ohm or less resistance between the ground lug on the external power cable the metal frame of the device. 13. Install the covers. 1-14 service guide.
Page 31
Chapter 2. Maintenance analysis procedures (maps) entry map use the following table to determine your starting point. Note: when possible, run online diagnostics in service mode. Online diagnostics perform additional functions, compared to standalone diagnostics. This ensures that the error state of...
Page 32
Symptom action you need to verify correct system operation. Go to "map 410: repair checkout" in the ibm rs/6000 diagnostic information for multiple bus systems. Symptom analysis you have ok displayed the service processor (sp) is ready. The system is waiting for power on. You have stby displayed the...
Page 33
Symptom action the system does not respond to the password being entered or the system login prompt is displayed when booting in service mode. Verify that the password is being entered from the ascii terminal or keyboard defined as the system console. If so, then the keyboard or its controller may b...
Page 34
Symptom action the system stops and a 4-digit number is displayed in the operator panel display. If the number displayed begins with the character "e0xx" then go to “sp checkpoints” on page 3-29. Or "e1xx-efff" then go to “checkpoints” on page 3-29. For all other numbers record srn 101-xxx, where xx...
Page 35
Symptom action you suspect a cable problem. See the ibm rs/6000 adapter, device, and cable information for multiple bus systems. You cannot find the symptom in this table all other problems. Go to “map 1020: problem determination” on page 2-6. Chapter 2. Maintenance analysis procedures 2-5.
Page 36
Map 1020: problem determination purpose of this map use this map to get an error code if you were not provided one by the customer or you are unable to load diagnostics. If you are able to load the diagnostics, go to map 0020 in the ibm rs/6000 diagnostic information for multiple bus systems. The se...
Page 37
1. Insert the diagnostic cd-rom into the cd-rom drive. 2. Turn the power off. 3. Turn the power on. 4. When the keyboard indicator is displayed (the word keyboard on an ascii terminal or the keyboard icon on a graphical display), press the f5 key on the directly-attached keyboard or the number 5 key...
Page 38
5. Enter any requested passwords. 6. Wait until the diagnostics are loaded or the system appears to stop. 7. Find your symptom in the following table; then follow the instructions given in the action column. Symptom action the diskette led is blinking rapidly, or eiea or eieb is displayed on the ope...
Page 39
Symptom action the system stops and a 4-digit number is displayed in the operator panel display. If the number displayed begins with the character "e0xx" then go to “sp checkpoints” on page 3-29. Or "e1xx-efff" then go to “checkpoints” on page 3-29. For all other numbers record srn 101-xxx, where xx...
Page 40
Step 1020-2 there is a problem with the keyboard. Find the type of keyboard you are using in the following table; then follow the instructions given in the action column. Step 1020-3 take the following actions: 1. Find the eight-digit error code in chapter 3, “error code to fru index” on page 3-1. N...
Page 41
Step 1020-4 1. Turn off, then turn on the system unit. 2. When the keyboard indicator appears, press the f1 key on a directly attached keyboard or the 1 key on an ascii terminal. 3. When the system management services appear, check the error log for any errors. Choose utilities choose error log if a...
Page 42
Map 1520: power note: this is not a start of call map. Use this power map only if you have been directed here from a map step in the ibm rs/6000 diagnostic information for multiple bus systems. This procedure is used to locate power problems in system units. If a problem is detected, this procedure ...
Page 43
Step 1520-1 you may be directed to this map for several reasons: 1. There is no indication of activity when the start/stop switch is pressed. None of the leds light and none of the fans, including the fan in the power supply, start to turn. Go to “step 1520-2.” 2. When the start/stop switch is press...
Page 44
Step 1520-3 note: either the cooling fans, the power supply, the i/o planar, service processor, or the system card is defective. To test each fru, exchange the frus that have not already been exchanged in the following order. Verify that the fan jumper is connected to connector j55. Power supply i/o...
Page 45
Step 1520-4 1. Turn the power off. 2. Unplug the system unit power cable from the wall outlet. 3. Record the slot numbers of all the isa and pci adapters. Label and record the location of any cables attached to the adapters. Remove all the adapters. 4. Remove all installed memory cards. 5. Remove th...
Page 46
Step 1520-5 one of the parts that was removed or unplugged is causing the problem. Install or connect the parts in the following order. 1. Cpu card(s). 2. Memory cards. (one at a time) 3. Scsi devices, lowest bay to highest bay. 4. Pci cards, lowest slot to highest slot. 5. Isa cards, lowest slot to...
Page 47
Map 1540: minimum configuration notes: 1. Be sure to unplug the power cable before removing or installing service processor, cpu, system card or i/o planar to avoid damage to them. 2. This map assumes that a cd-rom drive is installed and connected to the integrated scsi adapter, and a diagnostics cd...
Page 48
Step 1540-1 1. Ensure that the diagnostics and the operating system are shut down. 2. Insert the diagnostic cd-rom into the cd-rom drive. 3. Turn the power off. 4. Turn the power on. 5. When the keyboard indicator is displayed (the word keyboard on an ascii terminal or the keyboard and hand icon on ...
Page 49
Step 1540-2 1. Turn the power off. 2. If you have not already done so, configure the service processor with the instructions on step 6 on page 2-17 and then return here and continue. 3. Exit service processor menus and remove the power cable. 4. Disconnect all external cables. 5. Remove the side cov...
Page 50
Step 1540-3 one of the frus remaining in the system unit is defective. If the following steps call for a i/o planar to be replaced, see notes on page 2-1. Turn the power off, remove the power cable, and exchange the following frus in order: 1. Processor cards 2. Memory dimms (pair) 3. Memory card 4....
Page 51
Step 1540-4 no failure was detected with this configuration. 1. Turn the power off and remove the power cable. 2. Install a pair of memory dimms. 3. Reinstall the power cable. 4. Turn the power on. 5. Wait for the operator panel to stabilize at a checkpoint. Note: checkpoints e1f2, e1f3 and stby are...
Page 52
Step 1540-5 the failure may be caused by the last pair of memory dimms installed or the memory card. To isolate the failing fru, do the following: 1. Turn the power off and remove the power cable. 2. Exchange the last memory dimm pair installed. 3. Reinstall the power cable. 4. Turn the power on. 5....
Page 53
Step 1540-6 one of the frus remaining in the system unit is defective. 1. Turn the power off and remove the power cable. 2. Exchange the following frus the order listed. A. Memory card b. System card c. I/o planar (see notes on 2-1.) d. Power supply. 3. Reinstall the power cable. 4. Turn the power o...
Page 54
Step 1540-7 1. Turn the power off. 2. Reconnect the system console. Notes: a. If an ascii terminal has been defined as the system console, attach the ascii terminal cable to the to the s1 connector on the rear of the system unit. Also connect the internal serial and ethernet cables to the i/o planar...
Page 55
Is the sms screen displayed? No one of the frus remaining in the system unit is defective. In the following order, exchange the frus that have not been exchanged: 1. Go to the problem determination procedures (test procedures) for the device attached to the s1 serial port or the display attached to ...
Page 56
Step 1540-8 1. Make sure the diagnostic cd-rom is inserted into the cd-rom drive. 2. Turn the power off and remove the power cable. 3. Plug the internal scsi cable into the scsi connector (j25) on the i/o planar. 4. Disconnect the signal and power connectors from all the scsi devices except the cd-r...
Page 57
Is the "please define the system console" screen displayed? No one of the frus remaining in the system unit is defective. In the following order, exchange the frus that have not been exchanged: 1. Scsi cable 2. Last scsi device connected (cd-rom drive, tape drive, etc.) 3. The graphics adapter, if t...
Page 58
Step 1540-9 the system is working correctly with this configuration. One of the frus (adapters) that you removed is probably defective. 1. Make sure the diagnostic cd-rom is inserted into the cd-rom drive. 2. Turn the power off and remove the power cable. 3. Plug the diskette drive cable into the di...
Page 59
Step 1540-10 the system is working correctly with this configuration. One of the frus (adapters) that you removed is probably defective, 1. Make sure the diagnostic cd-rom is inserted into the cd-rom drive. 2. Turn the power off and remove the power cable. 3. Install the second cpu card if one was r...
Page 60
Step 1540-11 the last fru installed or one of its attached devices is probably defective. 1. Make sure the diagnostic cd-rom is inserted into the cd-rom drive. 2. Turn the power off and remove the power cable. 3. Starting with the last installed adapter, disconnect one attached device and cable. 4. ...
Page 61
Step 1540-12 1. Follow the instructions on the screen to select the system console. 2. When the diagnostic operating instructions screen is displayed, press enter. 3. If the terminal type has not been defined, you must use the initial terminal option on the function selection menu to initialize the ...
Page 62
Step 1540-13 look at the fru part numbers associated with the srn. Have you exchanged all the frus that correspond to the failing function codes? No exchange the fru with the highest failure percentage that has not been changed. Repeat this step until all the frus associated with the srn have been e...
Page 63
Step 1540-14 does the system have adapters or devices that require supplemental media? No go to “step 1540-15.” yes go to “step 1540-16.” step 1540-15 consult the isa and pci adapter configuration documentation for your operating system to verify that all installed adapters are configured correctly....
Page 64
Step 1540-17 the adapter or device is probably defective. If the supplemental media is for an adapter replace the frus in the following order: 1. Adapter. 2. The planar the adapter is plugged into. If the supplemental media is for a device replace the frus in the following order: 1. Device and any a...
Page 65
Ssa maintenance analysis procedures (maps) these maintenance analysis procedures (maps) describe how to analyze a continuous failure that has occurred in a system that contains two or more disk drive modules. Failing field-replaceable units (frus) of the system unit can be isolated with these maps. ...
Page 66
Status leds led status definition power on power on off power off ready on both ssa connections good and drive is ready blinking only one ssa connection good flickering drive is executing a command check on disk drive failure self-test running drive in service mode blinking disk drive selected 2-36 ...
Page 67
Map 2010: ssa hot-swap disk drive–start this map is the entry point to the maps for the ssa hot-swap disk drive. If you are not familiar with these maps, read “how to use these maps” on page 2-35 first. You might have been sent here because: the system problem determination procedures sent you here....
Page 68
Step 2010-2 one of the following conditions exist. Take the action described. 1. You have an hdisk that has no associated pdisk. A. Issue the system cfgmgr command. B. Retry the configuration verification service aid. C. If the problem remains, a software error has probably occurred. Call your suppo...
Page 69
Step 2010-3 have the system diagnostics or problem determination procedures given you an srn for the ssa hot-swap disk drive? No go to “step 2010-4.” yes go to “service request numbers (srns)” on page a-3. Step 2010-4 if the system diagnostics are available, go to “step 2010-5.” if the stand-alone d...
Page 70
Step 2010-6 are all led's on the drives in a 6 pack off? No go to step “step 2010-9.” yes go to “step 2010-7.” step 2010-7 are any power cables loose or in need of replacement? No go to “step 2010-8.” yes fix or replace the power cables as required. Go to "map 410: repair checkout" in ibm rs/6000 di...
Page 71
Step 2010-10 is the middle led on one or more disk drives on a backplane off? No go to step “step 2010-11.” yes replace the the following fru's: 1. Backplane 2. Epow cable go to "map 410: repair checkout" in ibm rs/6000 diagnostic information for multiple bus systems to verify the repair.. Step 2010...
Page 72
Step 2010-12 replace the ssa link cable closest to the flashing led. Did the led stop flashing? No go to step “step 2010-13.” yes go to "map 410: repair checkout" in ibm rs/6000 diagnostic information for multiple bus systems to verify the repair. Step 2010-13 replace the following: 1. Backplane 2. ...
Page 73
Chapter 3. Error code to fru index the error code to fru index lists error symptoms and possible causes. The most likely cause is listed first. Use this index to help you decide which frus to replace when servicing the system. If the codes in the following tables indicate a device which is present m...
Page 74
Firmware/post error codes if you replace frus and the problem is still not corrected, go to “map 1540: minimum configuration” on page 2-17 if you replace frus and the problem is corrected, go to "map 410: repair checkout" in the ibm rs/6000 diagnostic information for multiple bus systems table 3-1 (...
Page 75
Table 3-1 (page 2 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 20d00010 self-test failed on device, can't locate package. Contact you service support representative for assistance. 20d00011 cannot determine machine model. The machine model is part of the system ...
Page 76
Table 3-1 (page 3 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 20e0000a eeprom lock problem. If for privileged-access password install, is jumper in correct position? Consult the system's user's guide for jumper location and position. 1. Turn off, turn on system...
Page 77
Table 3-1 (page 4 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 20ee000a pointer to the operating system found in non-volatile storage. Values normally found in non-volatile storage that point to the location of an operating system were not found. This can happen...
Page 78
Table 3-1 (page 5 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 21a000xxx scsi device errors notes: 1. Before replacing any system components: a. Ensure that the controller and each device on the scsi bus is assigned a unique scsi id. B. Ensure scsi bus is proper...
Page 79
Table 3-1 (page 6 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 25010xxx flash update problem 25010000 no diskette in drive. Insert diskette containing firmware image. 25010001 diskette seek error. 1. Retry function. 2. Replace diskette drive. 3. Replace diskette...
Page 80
Table 3-1 (page 7 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 25a80xxx nvram problems nvram problem resolution: 1. Errors reported against nvram can be caused by low battery voltage and (more rarely) power outages that occur during normal system usage. With the...
Page 81
Table 3-1 (page 8 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 25a80210 setenv/$setenv parameter error - name contains a null character. Refer to action under error code 25a80xxx. 25a80211 setenv/$setenv parameter error - value contains a null character. Refer t...
Page 82
Table 3-1 (page 9 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 25cyy001 memory module is not supported. Replace unsupported memory module. Note: memory module must be replaced with a supported type memory module. If an unsupported memory module is replaced the s...
Page 83
Table 3-1 (page 10 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 28030xxx rtc errors 1. Errors reported against the real time clock (rtc) can be caused by low battery voltage and (more rarely) power outages that occur during normal system usage. These errors are ...
Page 84
Table 3-1 (page 11 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 2b2xxx22 processor disabled. Cpu card. Where xxx indicates the processor type as follows: 000 166 mhz 1 or 2 way processor card 200 166 mhz 1 or 2 way processor card 211 down level vpd. Contact serv...
Page 85
Table 3-1 (page 12 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 2ba00014 service processor reports bad service processor firmware. Use service processor firmware diskette to re-program firmware. 2ba00017 service processor reports bad or low battery. 1. Replace t...
Page 86
Table 3-1 (page 13 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 2ba00064 service processor reports pci riser card vpd module not present. Replace the pci riser card. 2ba00065 service processor reports pci riser card vpd data corrupted. Replace the pci riser card...
Page 87
Table 3-1 (page 14 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 2ba00203 service processor firmware update error occurred, update not completed. Error occurred while reading new service processor crc after updating service processor firmware. See error code 2ba0...
Page 88
Table 3-1 (page 15 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 2ba00313 service processor reports generic power alert. 1. Replace power supply. 2. Replace i/o board. (see notes on 3-1.) 2ba00314 service processor reports 5v over voltage alert. 1. Replace power ...
Page 89
Table 3-1 (page 16 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 2ba00327 service processor reports pci expansion card 5v under voltage alert. 1. Replace power supply. 2. Replace i/o board. (see notes on 3-1.) 2ba00328 service processor reports pci expansion card...
Page 90
Table 3-1 (page 17 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 2ba00337 service processor reports memory critical over temperature slow shutdown request. 1. Check for cool air flow obstructions to the system. 2. Check fans for obstructions that prevent them fro...
Page 91
Table 3-1 (page 18 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 2ba00399 service processor reports unsupported value in epow. 1. Check epow cabling on scsi or ssa backplanes. 2. Replace i/o board. (see notes on 3-1.) 40100005 a loss of system power detected. Pos...
Page 92
Table 3-1 (page 19 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 401110c2 a low − 12 voltage reading detected. 1. Power supply. 2. I/o board. (see notes on 3-1.) 40111101 power good signal low on either processor card 1 or processor card 2. (if the system is runn...
Page 93
Table 3-1 (page 20 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 40b00000 the operating system surveillance interval exceeded. 1. Surveillance mode control is from the service processor(sp) menus. 2. Verify that the operating system (os) heartbeat utility is inst...
Page 94
Table 3-1 (page 21 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 40d00003 an unknown slow shutdown commanded. Critical cooling problem. Check to ensure the the temperature is in the ambient range 40d00004 an unknown fast shutdown commanded. Locked fan failure det...
Page 95
Table 3-1 (page 22 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 4b2xxx01 checkstop - slot 1 fail 1. Attempt to reboot the system in service mode, this preserves the aix error log. If the reboot fails, attempt to reboot from the cd-rom. If the reboot is successfu...
Page 96
Table 3-1 (page 23 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 4b2xxx43 service processor reports jtag fail 1. Service processor is the least likely failure, but it is the tester in this case. Replace the service processor to assure true failure indication. If ...
Page 97
Table 3-1 (page 24 of 24). Firmware error codes. Error code description action / possible failing fru 4ba10005 i ò c path fail. 1. I/o board. (see notes on 3-1.) 2. Cpu card. 3. System board. Chapter 3. Error code to fru index 3-25.
Page 98
Memory pd bits the following table expands the firmware error code 25cyyxxx on page 3-9, where yy is the pd values in the table below. Use these values to identify the type of memory that generated the error. If you replace frus and the problem is still not corrected, go to &hdref refid=1540. Unless...
Page 99
Bus srn to fru reference table this table is used to locate defective frus within the i/o board pci and isa buses. The table indicates which devices should be tested for each srn. For this procedure, if possible, diagnostics are run on the i/o board bus devices with all adapters removed from the fai...
Page 100
Table 3-3. Bus srn to fru reference table srn bus identification possible failing device and aix location code associated fru 9cc-100 pci bus 00 internal scsi port 1 (10-60) i/o board. (see notes on 3-1.) internal ethernet port (10-80) i/o board. (see notes on 3-1.) device installed in i/o slot 3p (...
Page 101
Checkpoints checkpoints are intended to let users and service personal know what the server is doing, with some detail, as it initializes. These checkpoints are not intended to be error indicators, but in some cases a server could hang at one of the checkpoints without displaying an 8-character erro...
Page 102
Table 3-4 (page 2 of 3). Sp checkpoints. Checkpoint description action/ possible failing fru e021 configuring nvram 1. I/o board. (see notes on 3-1.) 2. Service processor. E030 beginning to build i2c resources 1. Service processor. 2. Cpu card. 3. I/o board. (see notes on 3-1.) e031 finished buildin...
Page 103
Table 3-4 (page 3 of 3). Sp checkpoints. Checkpoint description action/ possible failing fru e072 preparing to call home 1. Modem. 2. Service processor. 3. I/o board. (see notes on 3-1.) 4. Cpu card. E075 entering sp menus 1. Service processor. 2. I/o board. (see notes on 3-1.) 3. Cpu card. E076 lea...
Page 104
Firmware checkpoints firmware uses progress codes (checkpoints) in the range of e1xx to efff. These checkpoints occur during system startup and maybe be useful in diagnosing certain problems. Service processor checkpoints are listed in “sp checkpoints” on page 3-29. If you replace frus and the probl...
Page 105
Table 3-5 (page 2 of 10). Firmware checkpoints. Checkpoint description action/ possible failing fru e116 bad crc - copy recovery block data section to ram see the note on 3-29. E117 bad crc - invalidate and flush cache, set toc see the note on 3-29. E118 bad crc - branch to high level recovery contr...
Page 106
Table 3-5 (page 3 of 10). Firmware checkpoints. Checkpoint description action/ possible failing fru e130 build device tree see the note on 3-29. E131 create root node see the note on 3-29. E132 create cpus node see the note on 3-29. E133 create l2 cache node see the note on 3-29. E134 create memory ...
Page 107
Table 3-5 (page 4 of 10). Firmware checkpoints. Checkpoint description action/ possible failing fru e155 probe pci bridge secondary bus 1. Pci adapters 2. I/o board. If a network adapter or i\o board is replaced, see 3-1. See the note on 3-29. E156 create pci ethernet node see the note on 3-29. E15a...
Page 108
Table 3-5 (page 5 of 10). Firmware checkpoints. Checkpoint description action/ possible failing fru e175 bootp request refer to “e1xx code boot problems” on page 3-44 for general considerations. 1. Turn off then on, and retry the boot operation. 2. Verify the network connection (network could be dow...
Page 109
Table 3-5 (page 6 of 10). Firmware checkpoints. Checkpoint description action/ possible failing fru e1bf create pwr-mgmt node. See the note on 3-29. E1c0 create isa ethernet node. See the note on 3-29. E1c5 create isa interrupt controller (pic) node. See the note on 3-29. E1c6 create dma node. See t...
Page 110
Table 3-5 (page 7 of 10). Firmware checkpoints. Checkpoint description action/ possible failing fru e1dd early processor exception i/o board (see notes on 3-1.) see the note on 3-29. E1de alternating pattern of e1de and e1ad is used to indicate a default catch condition before the firmware "checkpoi...
Page 111
Table 3-5 (page 8 of 10). Firmware checkpoints. Checkpoint description action/ possible failing fru e1eb verify flash eprom recovery image. Ensure that the diskette installed contains recovery image appropriate for this system unit. The system management services recovery procedure for the flash eep...
Page 112
Table 3-5 (page 9 of 10). Firmware checkpoints. Checkpoint description action/ possible failing fru e1fd default catch the operator panel will alternate between the code e1fd and another exxx code, where exxx is the point at which the error occurred. If the exxx is not listed in this table, go to “m...
Page 113
Table 3-5 (page 10 of 10). Firmware checkpoints. Checkpoint description action/ possible failing fru e213 initial memory configuration. 1. Replace the memory card (see notes on 3-1.) 2. Replace the system board. See the note on 3-29. E214 memory test. Replace the memory card (see notes on 3-1.) see ...
Page 114
Memory test hang problem general memory information: memory card cards can be installed in either slot (or both) on the system board, there is no requirement that one be installed before the other. It is perfectly acceptable for there to be 2 partially populated memory cards, the first one does not ...
Page 115
E. Remove the suspect bad tag, re-install the 2nd memory card and power the system up. If the system no longer stops at an e3xx code, re-seating the memory cards (again) has corrected the problem. If the system stops at an e3xx code again, skip to step 7 on page 3-44. 4. Attempt to isolate the probl...
Page 116
6. Replace the memory card. 7. Replace the system board. 8. Replace the cpu card(s). E1xx code boot problems: depending on the boot device, a checkpoint may be displayed on the operator panel for an extended period of time while the boot image is retrieved from the device. This is particularly true ...
Page 117
G. It is possible that another installed adapter is causing the problem. Remove all installed adapters except the one the boot device is attached to, try to boot the standalone diagnostics from a cd-rom drive attached to the scsi controller on the i/o board, and run the diagnostics against the syste...
Page 118
Location codes this system unit uses physical location codes in conjunction with aix location codes to provide mapping of the failing field replaceable units. The location codes are produced by the system unit's firmware and aix. Physical location codes physical location codes provide a mapping of l...
Page 119
Specifically, the format of a location code is defined as follows: pn[.N][- or /]pn[.N][- or /]... Where p is a defined alpha location type prefix, n is a location instance number, and [.N] is a sub-location instance number (where applicable). Sub-location notation is used only for location types wh...
Page 120
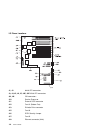
Aix and physical location code reference table 3-48 service guide.
Page 121
Chapter 3. Error code to fru index 3-49.
Page 122
Fru name aix location code physical location code physical connection logical identification central electronics complex (cec) system planar 00-00 p1 processor card 1 00-00 p1-c1 processor connectors j8 and j5 cpu id 0x00 and 0x01 (if 2-way card) processor card 2 00-00 p1-c2 processor connector j9 a...
Page 123
Fru name aix location code physical location code physical connection logical identification serial port 2 01-s2 p2/s2 i/o board connector j41 0x0218 serial port 3 01-s3 p2/s3 i/o board connector j50 0x0898 parallel port 01-r1 p2/r1 i/o board connector j47 0x0378 ethernet port 10-80 p2/e1 i/o board ...
Page 124
Fru name aix location code physical location code physical connection logical identification base cd-rom (bay a1) 10-60-00-6, 0 p2-z1-a6 primary scsi bus id 6 (refer to the note at the end of this table) media device in bay b1 10-60-00-4, 0 p2-z1-a4 primary scsi bus id 4 (refer to the note at the en...
Page 125
Fru name aix location code physical location code physical connection logical identification scsi backplane d when connected to pci adapter in slot p2-in ab-cd-00-15, 0 where ab-cd identifies the adapter's slot p2-in-z1-b2 bus id 15 dasd in bays d1 through d6 when connected to scsi port 2 (p2/z2) 30...
Page 126
Aix location codes the basic formats of the aix location codes are: for non-scsi devices/drives ab-cd-ef-gh for scsi devices/drives ab-cd-ef-g,h fru name aix location code physical location code physical connection logical identification fan 3 connector p2/x3 fan connector j15 at i/o board fan 4 con...
Page 128
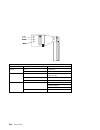
Ef is the connector id. It is used to identify the adapter's connector that a resource is attached to. Gh is used to identify a port, device, or fru. For example: for async devices gh defines the port on the fanout box. The values are 00 to 15. For a diskette drive h defines which diskette drive 1 o...
Page 129
Examples of aix location codes displayed are: integrated pci adapter pluggable pci adapters integrated isa adapters non-integrated isa adapters device attached to scsi controller 10-80 ethernet 10-60 integrated scsi port 1 30-58 integrated scsi port 2 20-58 to 20-5f any pci card in slot 1 20-60 to 2...
Page 130
Ssa location code format location codes identify the locations of adapters and devices in the using system and their attached subsystems and devices. These codes are displayed when the diagnostic programs isolate a problem. For information about the location codes that are used by the using system, ...
Page 131
Ssa loops and links the disk drive modules of the system unit are connected through two ssa links to an ssa adapter that is located in the using system. The disk drive modules, ssa links, and ssa adapter are configured in loops. Each loop provides a data path that starts at one connector of the ssa ...
Page 132
The ssa links must be configured as loops. The loop is connected to the internal connectors at the ssa adapter card. These connectors must be a valid pair (that is, a1 and a2, or b1 and b2); otherwise, the disk drive modules on the loop are not fully configured, and the diagnostics fail. Operations ...
Page 133
Pdisks, hdisks, and disk drive module identification the physical disk drives (pdisks) in an ssa subsystem can be configured as logical units (luns). A lun is also known as an hdisk, and can consist of one or more physical disk drives. An hdisk in an ssa subsystem might, therefore, consist of one pd...
Page 134
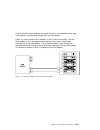
Loops and data paths all devices that are attached to an ssa adapter card are connected through ssa links. See figure 3-2 on page 3-60. The ssa links are configured as loops. Data and commands to a particular device pass through all other devices on the link between the adapter and the target device...
Page 135
If two or more disk drive modules are turned off, fail, or are removed from the loop, some modules might become isolated from the ssa adapter. Figure 3-4 shows that disk drive modules in slots 2 and 4 have failed. The disk drive module in slot 1 can communicate with the using system only through con...
Page 136
Ssa service aids ssa service aids help you service the ssa hot-swap disk drive. This section describes those service aids, and tells how to use them. Attention: do not run the service aids from more than one using system at a time; otherwise, unexpected results might occur. The ssa service aids are:...
Page 137
The identify function the identify function can be accessed from any of the service aids. This function enables you to determine the location of a particular disk drive module that you want to identify but do not want to remove from the system unit. The identify function causes the check light of th...
Page 138
Note: in some configurations of the using-system console: esc and 0 = exit esc and 3 = cancel in such configurations, however, the displayed instructions for the function keys remain the same as those shown in the screen above. 5. Select the service aid that you require, then go to the relevant inst...
Page 139
Set service mode service aid the set service mode service aid enables you to determine the location of a particular disk drive module and to remove that module from the system unit. It causes the check light of that disk drive module to come on for identification, and it stops all ssa link activity ...
Page 140
The columns of information displayed on the screen have the following meanings: pdisk0 through pdisk8 physical disk drive resource identifiers. 11111111 through 99999999 serial numbers of the physical disk drive modules. The actual serial number of a disk drive module is shown on the front of the di...
Page 141
2. Select the pdisk that you want to identify or put into service mode (for example, pdisk3). The following display appears with details of the disk drive module that you have just selected. ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ ssa service aids 8ð238...
Page 142
3. Select either the service mode or the identify function. (for this example, assume that you have selected the service mode function.) the list of pdisks is displayed again, and the disk drive module that you selected is marked by a > , which shows that the module is in the service mode. ┌────────...
Page 143
4. Select a second disk drive module, if required (for example, pdisk5). The following display appears: ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ ssa service aids 8ð238ð │ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────...
Page 144
5. Select either the service mode or the identify function. If the original disk drive module is to remain in service mode, you can select only the identify function now. (only one disk drive module at a time can be in the service mode.) the list of pdisks appears again. The pdisk that is in identif...
Page 145
Link verification service aid the link verification service aid helps you determine: where an ssa link has been broken the status of the disk drive modules on that ssa link the location of a power fault that has been detected by the disk drive modules on that ssa link to use the link verification se...
Page 146
3. When you have selected an adapter, a list is displayed showing the status of all the disk drive modules that are attached to the adapter: ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ ssa service aids 8ð238ð │ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────...
Page 147
From either direction, the broken loop does not prevent access to any data, unless that data is on the failed disk drive module. If the loop is broken between two disk drive modules, the ready lights on those modules flash to show that only one ssa path is active. Also, the link verification service...
Page 148
B. If you have just made changes to or have just turned on the system unit, you might need to wait up to 30 seconds before detailed information about the ssa network becomes available to the service aids. 4. When you have solved a problem, press f3 (esc and 3 on some consoles) to leave the display; ...
Page 149
Configuration verification service aid the configuration verification service aid enables you to determine the relationship between ssa logical units (hdisks) and ssa physical disk drives (pdisks). It also displays the connection information and operational status of the disk drives. Note: user appl...
Page 150
2. Select the hdisk or pdisk that you want to test. 3. If you select an hdisk, a list of pdisks is displayed: ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ ssa service aids 8ð238ð │ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────...
Page 151
Format disk service aid the format disk service aid formats ssa disk drive modules. Attention: formatting a disk drive module destroys all the data on that module. Use this procedure only when instructed to do so by the service procedures. To use the format disk service aid: 1. Select format disk fr...
Page 152
2. Select the pdisk that you want to format. The following instructions are displayed: ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ ssa service aids 8ð238ð │ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ format disk 8...
Page 153
Certify disk service aid the certify disk service aid verifies that all the data on a disk drive module can be read correctly. Instruction given elsewhere in this book tell you when you need to run this service aid. To use the certify disk service aid: 1. Select certify disk from the ssa service aid...
Page 154
2. Select the pdisk that you want to certify. The following instructions are displayed: ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ ssa service aids 8ð238ð │ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ certify disk...
Page 155
Service aid error codes if the ssa service aids detect an unrecoverable error and are unable to continue, one of the following error codes might occur. Ssa01 not enough using-system memory is available for this service aid to continue. Take one of the actions described here: this problem might be ca...
Page 156
Using the service aids for ssa-link problem determination if you have a problem with an ssa link, use the link verification service aid (see “link verification service aid” on page 3-73). The following examples show various loops and the associated information that is displayed by the link verificat...
Page 157
For this example, the link verification service aid displays the following information: ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ link verification 8ð2386 │ │ │ │ ssa link verification for: │ │ ssa1 ðð-ð5 ssa adapter │ │ │ │ to set or reset identify, move...
Page 158
Example 2. Broken loop (cable removed): each disk drive module normally communicates with the adapter through one data path. Because data can pass around the loop in either direction, however, the adapter automatically reconfigures the loop to enable communication to continue to each disk drive if t...
Page 159
For this example, the link verification service aid displays the following information: ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ link verification 8ð2386 │ │ │ │ ssa link verification for: │ │ ssa1 ðð-ð5 ssa adapter │ │ │ │ to set or reset identify, move...
Page 160
Example 3. Broken loop (disk drive module removed): figure 3-7 shows eight disk drive modules connected to connectors a1 and a2 of the ssa adapter, but the loop is broken because disk drive module in slot 3 has been removed. Four disk drive modules are connected to connectors b1 and b2 of the same s...
Page 161
For this example, the link verification service aid displays the following information: ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ link verification 8ð2386 │ │ │ │ ssa link verification for: │ │ ssa1 ðð-ð5 ssa adapter │ │ │ │ to set or reset identify, move...
Page 162
Finding the physical location of a device the physical location of a device (for example, a disk drive module or an ssa adapter) cannot be reported directly by the using system because of the way in which the ssa interface works. The address of an ssa device is related to the position of that device...
Page 163
The first disk drive module or adapter that you reach represents ssa-address count 0. Continue to follow the ssa link from disk drive module or adapter, increasing the ssa-address count by 1 for each device, until you reach the disk drive module or adapter that is indicated in the srn. Chapter 3. Er...
Page 164
Microcode maintenance updates to the microcode are loaded into the using system from diskettes. If the level of the microcode that is stored in the using system is higher than the level of the microcode that is installed on the ssa adapter or the disk drive modules, the higher-level microcode is aut...
Page 165
Vital product data (vpd) the vital product data (vpd) for the system unit and for the ssa adapter can be displayed by using the using-system service aids. This section shows the types of information that are contained in the vpd. Abbreviations used in this section are: dram dynamic random-access mem...
Page 166
Device driver level minimum level of device driver needed for this level of card description of function ssa adapter device specific (z0) if the adapter contains additional dram modules, z0 indicates the total dram size in megabytes device specific (z1) if the adapter contains a pluggable fast-write...
Page 167
Chapter 4. Loading the system diagnostics the system diagnostics can be booted either from the default boot list or from the service mode boot list. (the service mode boot list can be modified using the system diagnostics "display or change bootlist" service aid. The service mode boot list cannot be...
Page 168
If all types of devices in the boot list have been polled without finding a bootable image, the system restarts, this gives the user the opportunity to start the system management services ( by pressing the f1 key on a directly attached keyboard or the number 1 on an ascii terminal) before the syste...
Page 169
Chapter 5. System management services the system management services make it possible for you to view information about your computer and to perform such tasks as setting passwords and changing device configurations. If you have chosen a graphical display as your system console, you can use the grap...
Page 170
To enter the graphical system management services instead of the open firmware command line, you must press the f1 key after the keyboard icon appears during startup. After the system management services starts, the following screen appears. You may also press f8 here to enter the ok > prompt. 5-2 s...
Page 171
The system management services screen contains the following choices. Config: enables you to view your system configuration. Multiboot: invokes the mulitboot menu which provides several functions: to select a particular operating system to boot. In the case of aix this is a supported option, if you ...
Page 172
To select an icon, move the cursor with the arrow keys to choose which icon is highlighted, then press the enter key. You can also select an icon by clicking on it with your left mouse button. To leave the current screen, either press the esc key or select the exit icon. 5-4 service guide.
Page 173
Config selecting this icon makes it possible for you to view information about the setup of your system unit. A list similar to the following appears when you select the config icon. Chapter 5. System management services 5-5.
Page 174
Selecting the down arrow key or page down key displays the next configuration screen, which lists your computer's firmware version, the date of its development, and the firmware part number. The following screen is provided by the service processor. 5-6 service guide.
Page 175
Multiboot: this selection invokes the mulitboot menu which provides several functions: to select a particular operating system to boot. In the case of aix this is a supported option, if you receive a an informational icon after making this selection this would mean that information in non-volatile s...
Page 176
This would mean that information in non-volatile storage could have been lost, as would happen if the battery had been removed. In order to recreate this value issue the bootlist command under aix with the appropriate parameters as to the location of the operating system in a particular hard disk. P...
Page 177
Attention: if you change your startup sequence, you must be extremely careful when performing write operations (for example, copying, saving, or formatting). You can accidentally overwrite data or programs if you select the wrong drive. The default boot sequence is: the primary diskette drive cd-rom...
Page 178
Utilities selecting this icon enables you to perform various tasks and view additional information about your computer. The following describes the choices available on this screen. Password: enables you to set password protection for turning on the computer and for using system administration tools...
Page 179
Update: allows you to update the firmware programs on your computer. Console: if you have more than one display attached to your system unit, or if you have an ascii terminal attached to your system unit in addition to a keyboard and display, this tool allows you to define which one is active. Chapt...
Page 180
Password when you select this icon, the following screen is displayed. Power-on password: setting a power-on password helps protect information stored in your computer. If a power-on password is set for your computer, the power on icon is shown in the locked position; if a power-on password is not s...
Page 181
Press enter when you are finished; you are required to type the password again for verification. If you make a mistake, press the esc key and start again. After you have entered and verified the password, the power-on password icon flashes and changes to the locked position to indicate that the powe...
Page 182
Remote mode: the remote mode, when enabled, allows the system to start from the defined boot device. This mode is ideal for network servers and other computers that operate unattended. You must set a power-on password before you can enable the remote mode. When the remote mode is set, the icon chang...
Page 183
After you have entered and verified the password, the privileged-access password icon flashes and changes to the locked position to indicate that your computer now requires the password you just entered before running system programs. Note: if you forget the power-on password, you have to remove the...
Page 184
Error log selecting this icon displays the log of errors your computer has encountered during operations. Selecting the clear icon erases the entries in this log. 5-16 service guide.
Page 185
Ripl selecting the remote initial program load (ripl) icon above gives you access to the following selections. Chapter 5. System management services 5-17.
Page 186
The set address icon allows you to define addresses from which your computer can receive ripl code. Notes: 1. Some applications may require that ip addresses contain leading zeroes for numbers less than 100. For example, 129.132.4.20 may need to be entered as 123.132.004.020. If any of the addresses...
Page 187
The ping icon allows you to confirm that a specified address is valid by sending a test transmission to that address. After choosing the ping option, you may be asked to indicate which communications adapter (token ring or ethernet) should be used to send the test transmission. Chapter 5. System man...
Page 188
The config icon allows you to configure network adapters which require setup. Selecting the config icon presents a list of the adapters requiring configuration. Use the arrow keys to highlight an adapter, press the spacebar to select the adapter, then highlight the ok icon and press the enter key. T...
Page 189
Scsi id this selection allows you to view and change the addresses (ids) of the scsi controllers attached to your system unit. To change an id, highlight the entry by moving the arrow keys, then use the space bar to scroll through the available id's. After you have entered the new address, use the a...
Page 190
Update this selection allows you to update the service processor and system firmware in your system unit from an image on a 3.5 inch diskette. After choosing to update the firmware and confirming this choice, you must insert the diskette containing the firmware image. Attention: while the new firmwa...
Page 191
Firmware recovery if a troubleshooting procedure has indicated that the firmware information in your system unit has been corrupted, then you must perform a firmware recovery. To perform a firmware recovery, do the following: 1. Locate your firmware update diskette. 2. Using another system unit, ren...
Page 192
Text-based system management services the text-based open firmware command line and system management services are available if an ascii terminal is attached to your system unit. The text-based open firmware command line allows you to configure some adapters, and the system management services makes...
Page 194
Display configuration this option provides information about the setup of your computer. A screen similar to the following is displayed. à ð device powerpc 6ð4 l2-cache, ð512k memory slota=8mb slotb=8mb lpt addr=3bc com addr=3f8 com addr=2f8 audio keyboard mouse diskette addr=3fð integrated ethernet...
Page 196
The ok prompt procvides access to the open firmware command prompt. The open firmware command prompt is used for debug purposes, and device driver development. Information about the commands that are available in the ieee standard 1275. The multiboot start option toggles between off and on and selec...
Page 199
Utilities the utilities screen enables you to select from the following system management tools. à ð utilities 1. Set password and unattended start mode 2. Audio 3. Display error log 4. Remote initial program load setup 5. Change scsi id 6. Update system firmware 7. Update service processor 8. Selec...
Page 200
Set power on password: setting a power-on password helps protect information stored in your computer. You can use any combination of up to eight characters (a–z, a–z, and 0–9) for your password. The password you type is not displayed on the screen. Press enter when you are finished; you are required...
Page 201
Set privileged-access password: the privileged-access password protects against the unauthorized starting of the system programs. If you previously had set a privileged-access password and want to remove it, select remove privileged-access password. Note: if you forget your password, you have to shu...
Page 205
After choosing which adapter to use to ping the remote system, you must provide the addresses needed to communicate with the remote system. à ð ping 1. Client ip address 129.132.4.2ð 2. Server ip address 129.132.4.1ð 3. Gateway ip address 129.132.4.3ð 4. Subnet mask 255.255.255.ð .---------. .------...
Page 208
5-40 service guide.
Page 209
Chapter 6. Removal and replacement procedures before performing any of the removal or replacement procedures in this chapter, read the following notice. Danger an electrical outlet that is not correctly wired could place hazardous voltage on metal parts of the system or the devices that attach to th...
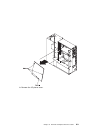
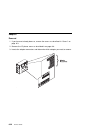
Page 210
Handling static–sensitive devices attention: adapters, planars, diskette drives, and disk drives are sensitive to static electricity discharge. These devices are wrapped in antistatic bags, as shown in this illustration, to prevent this damage. Take the following precautions: if you have an antistat...
Page 211
Covers removal 1. Open the door. Chapter 6. Removal and replacement procedures 6-3.
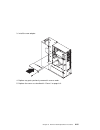
Page 212
2. Remove the door by carefully lifting it up and off the hinges. Store it in a safe place. 3. Remove all media (diskettes, cds, optical discs, or tapes) from drives; then turn the power off to the system and all attached devices. 4. Shutdown the operating system. 5. Turn off power to the system and...
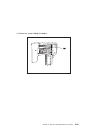
Page 213
6. If you have a modem or fax machine attached to the system, disconnect the telephone line. 7. Unplug all power cords (cables) from electrical outlets. Note the location of the following; then disconnect them from the back of the system: power cord display cable keyboard cable any other cables and ...
Page 214
8. Remove the front cover: a. Unlock the keylock on the front cover. B. Lift up on the latch on the left side of the front cover. 6-6 service guide.
Page 215
C. Grasp the sides of the front cover near the top of the system and pull it forward. (the front cover is held in place by two spring detented ball studs.) d. Detach the front cover's bottom hooks from the grooves located on the bottom of the system, and lift the front cover off the bottom of the sy...
Page 216
9. Remove the side cover: a. Open the side cover to a 90 degree angle. B. Remove the cover by carefully lifting it up and off the hinges. Store it in a safe place. 10. Remove the i/o planar cover: attention if your system has the ssa bulkhead cable installed, make sure that you do not damage the cab...
Page 217
B. Remove the i/o planar cover. Chapter 6. Removal and replacement procedures 6-9.
Page 218
Replacement 1. I/o planar cover a. Place the lip at the top of the i/o planar cover over the top of the system adapter housing. Push the bottom of the i/p planar cover in, aligning the key on the system with the key slot on the cover. Replace the i/o planar cover. B. Latch the cover and tighten the ...
Page 219
2. Reinstall the side cover: a. Place the side cover at a 90 degree angle. Align the pins on the rear of the side cover with the two hinges on the rear of the system. B. Slide the side cover down. C. Push the side cover to close it. Chapter 6. Removal and replacement procedures 6-11.
Page 220
3. Reinstall the front cover: note: before installing the front cover, verify that the side cover is installed correctly. If the side cover is not properly installed, the front cover will not align correctly when you attempt to install it. A. Align the bottom of the front cover with the bottom of th...
Page 221
E. Latch the cover latch located on the left side of the front cover. 4. Reinstall the door at the front of the system by aligning the pins with the hinges, and sliding the door down. Chapter 6. Removal and replacement procedures 6-13.
Page 222
5. Close the door. 6-14 service guide.
Page 223
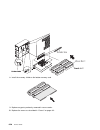
Power supply danger do not attempt to open the covers of the power supply. Power supplies are not serviceable and are to be replaced as a unit. Removal 1. If you have not already done so, remove the covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. 2. Disconnect the two cables from i/o planar connectors ...
Page 224
5. Disconnect the power cables at the power supply that connect to the backplanes. . 6. Disconnect the power cord from rear of the power supply. 7. Remove the three screws from the power supply. 8. Remove the power supply from the system. Slide the power supply forward, toward the front. Lift it up ...
Page 225
Replacement 1. Place the power supply in the bottom of the system. Slide the power supply backward, toward the rear of the system. 2. Secure the power-supply assembly by installing the three screws that you removed in step 7 on page 6-16. 3. Reconnect the cables. A. Reconnect the power supply cables...
Page 226
B. Reconnect the cable labeled p1 to i/o planar connector p1. C. Reconnect the cable labeled p2 to i/o planar connector p2. D. Reconnect the cable labeled p17 to system card connector j1. E. Reconnect the cable labeled p16 to system card connector j2. F. Reconnect the cable labeled p15 to system car...
Page 227
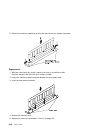
Cd-rom drive, tape drive, diskette drive caution: do not open the drive; no user adjustments or serviceable parts are inside. Removal 1. If you have not already done so, remove the covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. 2. Disconnect the power and signal cables to the drive you are removing. 3...
Page 228
Backplane removal 1. If you have not already done so, remove the covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. 2. Remove the screw from the backplane. 3. Slide the backplane out to gain cable access. 4. Disconnect the scsi cable, epow cable, and power supply cable from the backplane. 5. Remove the ba...
Page 229
Replacement if you installed a scsi backplane, check the jumpers on the new backplane for proper setting. The jumpers should be set as shown. Replace in reverse order. If you installed an ssa backplane, be sure to connect the internal ssa cable between the backplane and the internal connectors on th...
Page 230
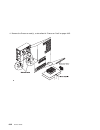
Adapters removal 1. If you have not already done so, remove the covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. 2. Remove the i/o planar cover as described in on page 6-8. 3. Locate the adapter connectors and determine which adapter you want to remove. 6-22 service guide.
Page 231
4. Remove the screw holding the adapter. Chapter 6. Removal and replacement procedures 6-23.
Page 232
5. Remove the adapter. Replacement 1. With one hand, touch any metal surface of the chassis to minimize static electrical charges, and then pick up the adapter. 2. Locate the adapter connector location on the i/o planar. 6-24 service guide.
Page 233
3. Install the new adapter. 4. Replace any parts previously removed in reverse order. 5. Replace the covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. Chapter 6. Removal and replacement procedures 6-25.
Page 234
Memory cards removal 1. If you have not already done so, remove the covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. 2. Remove the i/o planar cover as described on page 6-8; then return here to determine your next step. 3. Remove the memory adapter card shield. 4. The card is secured in place with card ...
Page 235
Replacement 1. With one hand, touch any metal surface of the chassis to minimize static electrical charges, and then pick up the memory card. 2. Open the retainer hooks. Attention: to prevent damage to the card and the card connectors, open and close the retainer hooks at the same time. 3. Remove th...
Page 236
8. Install the memory shield on the bottom memory card. . 9. Replace any parts previously removed in reverse order. 10. Replace the covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. 6-28 service guide.
Page 237
Memory module removal 1. If you have not already done so, remove the covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. 2. Remove the i/o planar cover as described on page 6-8. 3. Remove the memory card as described in “memory cards” on page 6-26. 4. Locate the memory module connectors and determine which...
Page 238
5. Remove the memory module by pushing the tabs out on the memory connectors. Replacement 1. With one hand, touch any metal surface of the chassis to minimize static electrical charges, and then pick up a memory module. 2. Locate the memory module connector location on the memory card. 3. Install th...
Page 239
I/o planar 1. If you have not already done so, remove the covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. 2. Remove the i/o planar cover as described on page 6-8. Note: adapter cables (scsi) should be labeled to insure correct installation of cables to adapters slots. Rearranging the order of the scsi ...
Page 240
4. Remove the processor card(s), as described in “processor card” on page 6-35. 6-32 service guide.
Page 241
5. Remove the memory card(s), as described in “memory cards” on page 6-26. 6. Remove the service processor. 7. Remove the system card. 8. Disconnect all cables from the connectors on the i/o planar. Chapter 6. Removal and replacement procedures 6-33.
Page 242
9. Remove eight screws connecting the i/o planar to the rear of the system. Note that the screws in the scsi connector are black. 10. Remove 12 screws from the i/o planar. 11. Remove i/o planar. Note: the system card can be removed without removing the i/o planar. However, you must remove the system...
Page 243
Processor card removal 1. If you have not already done so, remove the covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. 2. Remove the i/o planar cover as described on page 6-8. Attention: make sure the power cord is unplugged and the power (power led) is off before removing the cpu card. 3. Remove the po...
Page 244
Replacement 1. With one hand, touch any metal surface of the chassis to minimize static electrical charges, and then pick up the cpu card. 2. Install the new cpu card. 3. Replace any parts previously removed in reverse order. 4. Replace the covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. Note: if the s...
Page 245
Service processor removal 1. If you have not already done so, remove the covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. 2. Remove the i/o planar cover as described on page 6-8. Attention: make sure the power cord is unplugged and the power led is off before removing the service processor. 3. Remove th...
Page 246
Battery caution: a lithium battery can cause fire, explosion, or a severe burn. Do not recharge, disassemble, heat above 100°c (212°f), solder directly to the cell, incinerate, or expose cell contents to water. Keep away from children. Replace only with the part number specified for your system. Use...
Page 247
Chapter 6. Removal and replacement procedures 6-39.
Page 248
4. Use one finger to slightly slide the battery toward the front of the server. (the spring mechanism behind the battery pushes it out toward you as you slide it forward.) use your thumb and index finger to hold the battery as it pushes out of the socket. Replacement tilt the battery so that you can...
Page 249
2. Ensure that the battery polarity is correct; place the battery in the holder with the positive side facing up. Chapter 6. Removal and replacement procedures 6-41.
Page 250
Fans removal 1. Do the cover removal procedure in “covers” on page 6-3. 2. If removing one of the two upper fans, remove the adapter cards, remove the three screws from the adapter card bracket and remove the bracket. Note: the fans are numbered from bottom to top as fan 1, fan 2, fan 3, and fan 4. ...
Page 251
Replacement replace in reverse order. Chapter 6. Removal and replacement procedures 6-43.
Page 252
Operator panel display removal 1. If you have not already done so, remove the front covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. 2. Press the snap in detent on the right side of the display card mounting bracket and remove the display card. 3. Rotate the display forward and out of the mounting brack...
Page 253
Operator panel control assembly removal 1. Do the cover removal procedure in “covers” on page 6-3. 2. Remove the assembly by compressing the spring clip at the top and bottom of the assembly and pulling out toward the rear of the system. 3. Unplug the lcd cable from the assembly. 4. Unplug the contr...
Page 254
Serial/parallel card removal 1. If you have not already done so, remove the covers as described in “covers” on page 6-3. 2. Remove the i/o planar cover as described on page 6-8. 3. Remove the external serial and parallel connectors from the rear of the system. 4. Remove the cables from the i/o plana...
Page 255
Chapter 7. Parts information chapter 7. Parts information 7-1.
Page 256
7-2 service guide.
Page 257
Index part number units per description 1 93h5758 1 chassis assembly (includes covers and side door) 2 73h0898 1 emc clip 3 06h7082 1 display panel 4 93h1816 1 cable (display) 5 93h2922 1 operator panel control assembly 6 07l6594 1 i/o board 7 06h7697 13 standoff 8 33f8354 1 battery 9 73h3520 1 cpu ...
Page 258
Note: see ibm rs/6000 diagnostic information for multiple bus systems for part numbers. 7-4 service guide.
Page 259
Index part number units per description 1 06h6660 73h1894 39h9994 92f1294 93h9816 93h4339 93h4341 93h9821 93h4340 up to 3 1 1 3 a/r up to 3 1 1-2 up to 3 1 cable (scsi adapter to backplane) cable (diskette) cable (power 2-drop) cable clamp screw (3.5 x 6) cable ssa ground strap (backplane to chassis...
Page 260
Index part number units per description 1 82g3278 1 keyboard, united states english 1391402 1 keyboard, french 1393395 1 keyboard, italian 1391403 1 keyboard, german/austrian 1391406 1 keyboard, united kingdom english 1391405 1 keyboard, spanish 79f0167 1 keyboard, japanese 64f7707 1 keyboard, brazi...
Page 261
Power cables 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 index part number country 1 1838574 bahamas, barbados, bolivia, brazil, canada, costa rica, dominican republic, el salvador, ecuador, guatemala, guyana, haiti, honduras, jamaica, japan, netherlands antilles, panama, peru, philippines, taiwan, thailand, trinidad, ...
Page 262
Index part number country 8 14f0051 liechtenstein, switzerland 9 14f0069 chile, ethiopia, italy 10 14f0087 israel 11 6952291 paraguay, colombia, uruguay 7-8 service guide.
Page 263
Appendix a. Ssa problem determination procedures problem determination procedures are provided by power-on self-tests (posts), service request numbers (srns), and maintenance analysis procedures (maps). Some of these procedures use the using system service aids that are described in “ssa service aid...
Page 264
Adapter power-on self-tests (posts) two power-on self-tests (posts) are resident in the ssa adapter. The tests are post-1 and post-2. Post-1 tests all the functions that are necessary to enable the adapter to communicate with the micro channel. Post-1 can fail for either of two reasons: a hardware e...
Page 265
Service request numbers (srns) service request numbers (srns) are generated for the ssa hot-swap disk drive by the system error-log analysis, system configuration code, diagnostics, and customer problem-determination procedures. Srns help you to identify the cause of a problem, the failing field-rep...
Page 266
3. Normally exchange only one fru at a time, starting from the top of the fru list for that srn. Always use instructions given in the page reference when exchanging frus. After each fru is exchanged, go to "map 410: repair checkout" in ibm rs/6000 diagnostic information for multiple bus systems to v...
Page 267
Software and microcode errors some srns indicate that a problem might have been caused by a software error or by a microcode error. If you have one of these srns, perform the following actions: 1. Make a note of the contents of the error log for the device that has the problem. 2. Go to the using-sy...
Page 268
Table a-1 (page 1 of 9). Service request numbers srn fru list % problem 10101 disk drive module 100 description: disk drive motor stopped. The disk drive module is bad. Action: if this srn was received by one disk drive module only, then exchange that disk drive module. 10112 none – description: for...
Page 269
Table a-1 (page 2 of 9). Service request numbers srn fru list % problem 2a002 disk drive module ssa adapter card 50 50 description: async code 02 has been received. A software error has probably occurred. Action: go to “software and microcode errors” on page a-5 before exchanging any frus. 2a003 dis...
Page 270
Table a-1 (page 3 of 9). Service request numbers srn fru list % problem 2a006 disk drive module backplane 70 30 description: async code 06 has been received. This code indicates that a disk drive module has detected the loss of one of its power inputs. Action: if the failing device is an ssa hot-swa...
Page 271
Table a-1 (page 4 of 9). Service request numbers srn fru list % problem 300c0 backplane 100 description: a disk drive module has detected the loss of one of its power inputs. Action: if the failing device is an ssa hot-swap disk drive, exchange the backplane. If the failing device is not an ssa hot-...
Page 272
Table a-1 (page 5 of 9). Service request numbers srn fru list % problem 44paa disk drive module 100 description: a disk drive module has failed. Action: if the ssa service aids are available, run the link verification service aid (see “link verification service aid” on page 3-73) to find the failing...
Page 273
Table a-1 (page 6 of 9). Service request numbers srn fru list % problem 50005 ssa adapter card 100 description: a software error has occurred. Action: go to “software and microcode errors” on page a-5 before exchanging the fru. 50006 ssa adapter card 100 description: a channel check has occurred. Ac...
Page 274
Table a-1 (page 7 of 9). Service request numbers srn fru list % problem 50100 none – description: an attempt was made to log an error against a pdisk that is not available to the using system. Action: this problem has occurred for one of the following reasons: a user has deleted a pdisk from the sys...
Page 275
Table a-1 (page 8 of 9). Service request numbers srn fru list % problem d0100 disk drive module 100 description: unable to clear a disk drive module reservation. Action: exchange the fru for a new fru. D0101 disk drive module 100 description: the disk drive module has been reserved since the diagnos...
Page 276
Table a-1 (page 9 of 9). Service request numbers srn fru list % problem d4100 ssa adapter card 100 description: the diagnostics cannot open the ssa adapter. Action: exchange the fru for a new fru. D4300 ssa adapter card 100 description: the diagnostics have detected an ssa adapter post failure. Acti...
Page 277
Ssa loop configurations that are not valid note: this section is related to srn 48000. Srn 48000 shows that the ssa loop contains more devices or adapters than are allowed. The following condition exist: the loop contains more than 48 devices. If the srn occurred when either you or the customer swit...
Page 278
A-16 service guide.
Page 279
Appendix b. Service processor menus the service processor menus enable you to configure service processor options and to enamle and disable functions. Service processor menus are available using an ascii terminal when the server is powered off and the service processor is operating with standby powe...
Page 280
1 operating system root password 2 privileged access password 3 general access (power-on) password service processor functions service processor menus (ascii terminals) service processor service aids (ascii or graphics terminals) sms (ascii or graphics terminals) read vpd y 3 y 3 view system environ...
Page 281
Service processor menus the service processor menus are divided into two groups: general user menus - the user must know the general access password. Privileged user menus - the user must know the privileged access password. The following section describes these two groups of menus, how to access th...
Page 282
General user menus the menu options presented to the general user are a subset of the options available to the privileged user. The user must know the general access password in order to access these menus. à ð general user menu 1. Power-on system 2. Read vpd 3. Read progress indicators from last sy...
Page 283
Read progress indicators from last system boot displays the boot progress indicators (check points), up to a maximum of 100, from the system boot prior to the one in progress now. This historical information may be useful to help diagnose system faults. The progress indicators are displayed in two s...
Page 284
Privileged user menus the following menus are available to privileged users only. The user must know the privileged access password in order to access these menus. Main menu at the top of the main menu is a listing containing: your service processor's current firmware version the firmware copyright ...
Page 285
Note: the information under the service processor firmware heading in the main menu example that follows is example information only. à ð service processor firmware eprom: 1997ð915 flash: 1997ð512 copyright 1997, ibm corporation system name main menu 1. Service processor setup menu 2. System power c...
Page 286
Service processor setup menu à ð service processor setup menu 1. Change privileged access password 2. Change general access password 3. Enable/disable console mirroring: currently disabled 4. Start talk mode 5. Os surveillance setup menu 6. Reset service processor 7. Reprogram service processor flas...
Page 287
Passwords passwords can be any combination of up to 8 alphanumeric characters. You can enter longer passwords, but the entries are truncated to include only the first 8 characters. Passwords can be set from the service processor menu or from the sms menus. For security purposes, the service processo...
Page 288
When console mirroring is enabled, the service processor sends information to both serial ports. This capability may be enabled by local or remote users. This provides local users the capability to monitor remote sessions. Console mirroring may be enabled for the current session only. For more infor...
Page 289
Surveillance setup menu this option may be used to setup operating system surveillance. à ð os surveillance setup menu 1. Surveillance: currently disabled 2. Surveillance time interval: currently 5 3. Surveillance delay: currently 1ð 98. Return to previous menu á ñ – surveillance may be set to enabl...
Page 290
System power control menu à ð system power control menu 1. Enable/disable unattended start mode: currently disabled 2. Ring indicate power-on menu 3. Reboot/restart policy setup menu 4. Power-on system 5. Power-off system 98. Return to previous menu 99. Exit from menus á ñ enable/disable unattended ...
Page 291
– ring indicate power-on may be set to 'enabled' or 'disabled'. – number of rings may be set to any number from 1 to 255. Reboot/restart policy setup menu, see “reboot/restart policy setup menu” on page b-23. Power-on system lets you power-on the system immediately. For other power-on methods see “s...
Page 292
Historical comparison can be useful to system administrators and service personnel. Read progress indicators from last system boot displays the boot progress indicators (check points), up to a maximum of 100, from the system boot prior to the one in progress now. This historical information may be u...
Page 293
à ð system environmental conditions (system power is currently off.) fan ð: a stopped fan detected fan 1: a stopped fan detected fan 2: a stopped fan detected fan 3: a stopped fan detected mem temperature is operating within normal tolerances i/o temperature is operating within normal tolerances cpu...
Page 294
Call-in/call-out setup menu à ð call-in/call-out setup menu 1. Modem configuration menu 2. Serial port selection menu 3. Serial port speed setup menu 4. Telephone number setup menu 5. Call-out policy setup menu 6. Customer account setup menu 7. Call-out test 8. Ring indicate power-on menu 98. Return...
Page 295
For information on choosing a modem configuration file, see “sample modem configuration files” on page d-1 and “seamless transfer of a modem session” on page d-6. à ð modem configuration menu port 1 modem configuration file name: port 2 modem configuration file name: to make changes, first select th...
Page 296
You may enable and/or disable the call-in and call-out functions of each serial port in any combination. Serial port speed setup menu à ð serial port speed setup menu 1. Serial port 1 speed: currently 96ðð 2. Serial port 2 speed: currently 96ðð 98. Return to previous menu á ñ serial port speed can b...
Page 297
à ð telephone number setup menu 1. Service center telephone number: currently unassigned 2. Customer administration center telephone number: currently unassigned 3. Digital pager telephone number: currently unassigned 4. Customer voice telephone number: currently unassigned 5. Customer system teleph...
Page 298
For digital pagers that require a personal identification number (pin) for access, include the pin in this field as in the following example: 1 8ðð 123 4567,,,,87654 where the commas create pauses 1 for the voice response system, and the 87654 represents the pin. Customer voice telephone number is t...
Page 299
If call out policy is set to 'all', the service processor will attempt a call out to all the following numbers in the order listed: 1. Service center 2. Customer admin center 3. Pager remote timeout and remote latency are functions of your service provider's catcher computer. You should take the def...
Page 300
Customer account setup menu à ð customer account setup menu 1. Customer account number: currently unassigned 2. Customer retain login userid: currently unassigned 3. Customer retain login password: currently unassigned 98. Return to previous menu á ñ customer account number is assigned by your servi...
Page 301
Reboot/restart policy setup menu reboot describes bringing the system hardware back up from scratch, for example, from a system reset or power on. The boot process ends when control passes to the operating system process. Restart describes activating the operating system after the system hardware re...
Page 302
2. The use os-defined restart policy is set to yes and the operating system has no automatic restart policy. Refer to “service processor reboot/restart recovery” on page b-27. Call-out before restart (enabled/disabled) if a restart is necessary due to a system fault, you can enable the service proce...
Page 303
Local user function user interface local async console text based menus with nls operator panel messages power and miscellaneous power on/off configurable reboot policy status and data access vpd error data (service processor) error data (system) environmental data service processor setup utilities ...
Page 304
System power-on methods power-on switch - see 'starting the system unit' in &ugtitle.. Sp menu power-on request you can request a power-on via the service processor menus from either a local or remote terminal. If a remote terminal is to be used, the modem must be connected to serial port 1, and the...
Page 305
Follow-up to a failed boot attempt the service processor will initiate a power-on sequence upon detection of a failed boot attempt. Service processor reboot/restart recovery reboot describes bringing the system hardware back up from scratch, for example, from a system reset or power on. The boot pro...
Page 306
Use os-defined restart policy?: the use os-defined restart policy default setting is yes. This causes the sp to refer to the os automatic restart policy setting and take action, the same action the os would take if it could have responded to the problem causing the restart. When this setting is no, ...
Page 307
Service processor system monitoring - surveillance surveillance is a function in which the service processor monitors the system, and the system monitors the service processor. This monitoring is accomplished by periodic samplings called heartbeats. Surveillance is available during two phases: 1. Sy...
Page 308
3. Surveillance delay this is the length of time in minutes for the service processor to wait from when the operating system is started to when the first heartbeat is expected. Surveillance will take effect immediately after setting the parameters from the service processor menus. If operating syste...
Page 309
Call out (call-home) the service processor can call out (call-home) when it detects one of the following conditions: system firmware surveillance failure. Operating system surveillance failure (if supported by operating system). Critical environmental failures. Restarts to enable the call out featur...
Page 310
Console mirroring console mirroring allows a person on a local ascii terminal to monitor the service processor activities of a remote user. Console mirroring ends when the service processor releases control of the serial ports to the system firmware. System configuration: service processor modem con...
Page 311
Service processor firmware updates the service processor eprom may need to be updated for two different reasons: 1. The update (composite) portion of the eprom has become corrupted. 2. The service processor firmware upgrades, without any corruption present. The use of a flash eprom allows updates to...
Page 312
Refer to the downloaded update instructions, or to the system management services “config” on page 5-5 or “display configuration” on page 5-26 or service processor menus on page b-7, to determine the level of the system unit or service processor flash. Updating firmware from the service processor me...
Page 313
Updating firmware from aix you must delete the file /var/update_flash_image before proceeding. The flash update image file must have already been placed in the /var file system. This could have been done with a file transfer from another server or with the dosread command of the aix dos utilities, f...
Page 314
System post errors: if post (power-on self test) errors occur during start-up, this error log help isolate faults when used with the diagnostics. à ð read system post errors version : ð severity : ð disposition : ð initiator : ð event being reported : ð extended error log data: ðxc2 ðxðð ðx84 ðxð9 ð...
Page 315
Appendix c. Service processor setup and test for your convenience, here is an example service processor setup checklist. It is basic. Your setup may include more or less of the available features, so you may wish to adjust this checklist for your own application. This checklist will at least provide...
Page 316
Testing the setup the following is a sample procedure to assure your setup is working. These tests include communicating with the server operating system. Be sure the necessary serial port(s) is configured. If you need assistance, refer to “serial port configuration” on page c-3. The server should b...
Page 317
2. Call your server again. 3. At the service processor main menu, select call-in/call-out setup menu, then select call-out test. This causes a simulated error condition for the purposes of this test. 4. After a few moments, a message appears regarding an illegal entry. Press enter to clear the messa...
Page 318
C-4 service guide.
Page 319
Appendix d. Modem configurations sample modem configuration files with nearly 1000 modems to choose from, and various programming standards, configuring a modem for use with the service processor can be challenging. The service processor is designed to place little demand on an attached modem, there...
Page 320
Configuration file selection 1. Does your modem respond to the extended command set (prefixed with & )? If yes, go to 3 if not, continue with 2 below. 2. Does your modem respond to: a. Atz reset command, or b. Atzn reset commands, where n can be 0, 1, etc.? If atz, configuration file modem_z.Cfg is ...
Page 321
4. Does your modem respond to: a. At&f reset command, or b. At&fn reset commands, where n can be 0, 1, etc.? If at&f, configuration file modem_f.Cfg is recommended. If at&fn, configuration file modem_f0.Cfg or modem_f1.Cfg is recommended, depending on which provides the hardware flow control profile...
Page 322
Note: if you have already set up your serial ports, line speeds, authorizations and telephone numbers from the service processor menus, specify your customized modem configuration files from the service aid. If you have not already set up your serial ports, line speeds, authorizations and telephone ...
Page 323
Ring detection most modems produce an interrupt request each time they detect a ring signal. Some modems generate an interrupt only on the first ring signal they receive. At&t dataport 2001 is an example of such a modem. The service processor uses the ring interrupt request to count the number of ri...
Page 324
If your modem communicates properly with remote users, it is probably in control. It may be wise to occasionally change some of the functional settings and then change them back, just for the sense of security that the modem is communicating, and to assure it has been initialized recently. Another s...
Page 325
With the remote terminal connected to serial port 1 and defined as the primary console device, there are two tests you can perform: 1. Will the modem drop the connection after the "system initialization complete" message appears at the remote terminal? If yes, this is the correct response. The modem...
Page 326
Prevention strategy the disconnect is caused by the operating system when it initializes the primary console. The tests listed above are conducted with the remote terminal selected as the primary console to manifest the modem's response to dtr transitions. If a local ascii terminal or a graphics con...
Page 327
Modem configuration samples sample file modem_z.Cfg # # component_name: (espsetup) entry service processor setup z # # functions: modem configuration file for many early hayes\ compatible modems. # this example uses the atz reset command to choose the factory defaults. # this setup will work for man...
Page 328
Retry: send "a/" # repeat the previous command. # expect a connection response. Expect "16\r" or "15\r" or "14\r" or "12\r" or "1ð\r" or "5\r" or "1\r" busy "7\r" timeout 6ð done disconnect: delay 2 # separate from previous data. Send "+++" # assure command mode. Delay 2 # allow mode switching delay...
Page 329
Sample file modem_z0.Cfg # # component_name: (espsetup) entry service processor setup zð # # functions: modem configuration file for some early hayes\ compatible modems. # this example uses the atzð reset command to choose the factory defaults. # this setup is recommended for modems that will respon...
Page 330
Expect "16\r" or "15\r" or "14\r" or "12\r" or "1ð\r" or "5\r" or "1\r" busy "7\r" timeout 6ð done disconnect: delay 2 # separate from previous data. Send "+++" # assure command mode. Delay 2 # allow mode switching delay. Send "athðt\r" # set modem switch-hook down # (i.E., hang up). Ignore "ð\r" or...
Page 331
Sample file modem_f.Cfg # # component_name: (espsetup) entry service processor setup f # # functions: modem configuration file for many recent hayes\ compatible modems. # this example uses the at&f reset command to choose the factory defaults. # this set up is preferred for modems with extended (&) ...
Page 332
Done retry: send "a/" # repeat the previous command. # expect a connection response. Expect "16\r" or "15\r" or "14\r" or "12\r" or "1ð\r" or "5\r" or "1\r" busy "7\r" timeout 6ð done disconnect: delay 2 # separate from previous data. Send "+++" # assure command mode. Delay 2 # allow mode switching ...
Page 333
Expect "8\r" or "7\r" or "6\r" or "4\r" or "3\r" delay 2 done appendix d. Modem configurations d-15.
Page 334
Sample file modem_f0.Cfg # # component_name: (espsetup) entry service processor setup fð # # functions: modem configuration file for many recent hayes\ compatible modems. # this example uses the at&fð reset command to choose the factory defaults. # this set up is preferred for modems with extended (...
Page 335
Expect "16\r" or "15\r" or "14\r" or "12\r" or "1ð\r" or "5\r" or "1\r" busy "7\r" timeout 6ð done retry: send "a/" # repeat the previous command. # expect a connection response. Expect "16\r" or "15\r" or "14\r" or "12\r" or "1ð\r" or "5\r" or "1\r" busy "7\r" timeout 6ð done disconnect: delay 2 # ...
Page 336
Done # ri power on enabled. Error: # handle unexpected modem # responses. Expect "8\r" or "7\r" or "6\r" or "4\r" or "3\r" delay 2 done d-18 service guide.
Page 337
Sample file modem_f1.Cfg # # component_name: (espsetup) entry service processor setup f1 # # functions: modem configuration file for many recent hayes\ compatible modems. # this example uses the at&f1 reset command to choose the factory defaults. # this set up is for modems with extended (&) command...
Page 338
Timeout 6ð done retry: send "a/" # repeat the previous command. # expect a connection response. Expect "16\r" or "15\r" or "14\r" or "12\r" or "1ð\r" or "5\r" or "1\r" busy "7\r" timeout 6ð done disconnect: delay 2 # separate from previous data. Send "+++" # assure command mode. Delay 2 # allow mode...
Page 339
Error: # handle unexpected modem # responses. Expect "8\r" or "7\r" or "6\r" or "4\r" or "3\r" delay 2 done appendix d. Modem configurations d-21.
Page 340
D-22 service guide.
Page 341
Appendix e. Service processor operational phases this section provides a high-level flow of the phases of the service processor (sp). Sp power applied │ 6 ┌─────┐ pre-standby phase │ 6 │ │ 6 │ standby phase sp menus available │ │ │ 6 │ bring-up phase sms menus available │ │ │ 6 │ runtime phase diagn...
Page 342
Standby phase the standby phase can be reached in two ways: 1. With the server off and power connected (the normal path), recognized by ok in the lcd display. 2. With the server on after an operating system fault, recognized by stby or an 8-digit code in the lcd display. In the standby phase, the sp...
Page 343
The sp can dial a pre-programmed telephone number in the event of an ipl failure. The sp issues an error report with the last reported ipl status indicated and any other available error information. Update operator panel the sp displays operator panel data on the ascii terminal if a remote connectio...
Page 344
E-4 service guide.
Page 345: Numerics
Index numerics 1.12 gb, 2.25 gb, and 4.51 gb ssa disk drives 3-93 a about this book xv account number b-22 active ssa link 3-60 adapter code package id 3-92 description of 3-93 finding the physical location 3-90 posts (power-on self-tests) a-2 ssa 3-59 port connector 3-90 vital product data (vpd) 3-...
Page 346
Commands cfgmgr 2-38, 3-92 diag -a a-12 lsattr -e -l adapter -a ucode 3-92 send diagnostic a-1 configuration complete system 3-92 invalid ssa loop a-15 manager command 3-92 configuration verification service aid 3-77 connector port, on ssa adapter 3-90 console mirroring enable/disable b-9 quick disc...
Page 347
Error code to fru index 3-1 error codes firmware 3-2 post 3-1 error logs b-14 f failed application program 3-83 status 3-74 failure continuous 2-35 link 3-83 fans removal and replacement 6-42 fast-write cache module 3-94 finding the physical location of a device 3-90 format disk service aid 3-79 for...
Page 348
Location codes 3-46, 3-48 aix 3-54 physical 3-46 ssa 3-58 locations i/o 1-4 memory 1-6 system card 1-6 system unit 1-1 logical units (lun) 3-61 loop broken 3-86 configurations, ssa, invalid a-15 data paths, description of 3-62 links 3-59 ssa, rules 3-61 loops 3-60 lsattr -e -l adapter -a ucode comma...
Page 349
Messages, sp checkpoints 3-29 microcode maintenance 3-92 software errors a-5 minimum configuration map 2-17 missing disk drive module 3-75 mode, set service 3-67 modem configuration file selection d-2 configurations d-1 seamless transfer d-6 modem_f.Cfg, sample file d-13 modem_f0.Cfg, sample file d-...
Page 350
Port (p) value 3-90 connector on ssa adapter 3-90 pos (programmable option select) a-2 post error codes 3-1 post errors read b-5, b-14 posts (power-on self-tests) a-1 power status 3-74 power cables 1-12, 7-7 power map 2-12 power supply removal and replacement 6-15 power-on methods b-26 power-on self...
Page 351
Safety notices xi seamless transfer of a modem session d-6 select, function menu 3-65 send diagnostic command a-1 sequence, startup 5-8 serial cable removal and replacement 6-46 serial number 3-61 service aids available 3-90 certify disk 3-81 configuration verification 3-77 format disk 3-79 link fai...
Page 352
Ssa (serial storage architecture) (continued) service aids (continued) finding the physical location of a device 3-90 format disk 3-79 identify function 3-65 link verification 3-73 set service mode 3-67 starting 3-65 ssa hot-swap disk drive vital product data (vpd) 3-93 ssa-address (aa) value 3-91 s...
Page 353
Vpd, vital product data 3-93 index x-9.
Page 354
X-10 service guide.
Page 355
Reader's comments — we'd like to hear from you &title. Part number: &partnum. Overall how satisfied are you with the information in this book? How satisfied are you that the information in this book is: please tell us how we can improve this book: thank you for your response. May we contact you? Ø y...
Page 356
X-12 service guide.
Page 358
Ibm part number: 07l8343 printed in the united states of america on recycled paper containing 10% recovered post-consumer fiber. February 1998 sa38-ð541-ð1 ð7l8343.