- DL manuals
- IBM
- Server
- SC34-7012-01
- Recovery And Restart Manual
IBM SC34-7012-01 Recovery And Restart Manual
Summary of SC34-7012-01
Page 1
Cics transaction server for z/os version 4 release 1 recovery and restart guide sc34-7012-02.
Page 3
Cics transaction server for z/os version 4 release 1 recovery and restart guide sc34-7012-02.
Page 4
Note before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “notices” on page 243. This edition applies to version 4 release 1 of cics transaction server for z/os (product number 5655-s97) and to all subsequent releases and modifications until otherwise indicated in new e...
Page 5: Contents
Contents preface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Vii what this book is about . . . . . . . . . . Vii who should read this book . . . . . . . . . Vii what you need to know to understand this book vii how to use this book . . . . . . . . . . . Vii changes in cics transaction server for z/os, version 4 rel...
Page 6
Journal names and journal models. . . . . . 58 terminal control resources . . . . . . . . 58 distributed transaction resources . . . . . . 59 urimap definitions and virtual hosts . . . . 59 chapter 6. Cics emergency restart . . 61 recovering after a cics failure . . . . . . . . 61 recovering informa...
Page 7
Input extrapartition data sets . . . . . . . 134 output extrapartition data sets . . . . . . 135 using post-initialization (pltpi) programs . . 135 recovery for temporary storage . . . . . . . 135 backward recovery . . . . . . . . . . 135 forward recovery . . . . . . . . . . . 136 recovery for web s...
Page 8
Forward recovery logging . . . . . . . . 215 forward recovery . . . . . . . . . . . 216 recovering vsam spheres with aixs . . . . 217 an assembler program that calls dfsms callable services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218 chapter 19. Disaster recovery . . . . 223 why have a disaster recovery plan?...
Page 9: Preface
Preface what this book is about this book contains guidance about determining your cics ® recovery and restart needs, deciding which cics facilities are most appropriate, and implementing your design in a cics region. The information in this book is generally restricted to a single cics region. For ...
Page 10
Viii cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 11: Release 1
Changes in cics transaction server for z/os, version 4 release 1 for information about changes that have been made in this release, please refer to what's new in the information center, or the following publications: v cics transaction server for z/os what's new v cics transaction server for z/os up...
Page 12
X cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 13
Part 1. Cics recovery and restart concepts it is very important that a transaction processing system such as cics can restart and recover following a failure. This section describes some of the basic concepts of the recovery and restart facilities provided by cics. © copyright ibm corp. 1982, 2011 1.
Page 14
2 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 15
Chapter 1. Recovery and restart facilities problems that occur in a data processing system could be failures with communication protocols, data sets, programs, or hardware. These problems are potentially more severe in online systems than in batch systems, because the data is processed in an unpredi...
Page 16
In general, forward recovery is applicable to data set failures, or failures in similar data resources, which cause data to become unusable because it has been corrupted or because the physical storage medium has been damaged. Minimizing the effect of failures an online system should limit the effec...
Page 17
Another way is to shut down cics with an immediate shutdown and perform the forward recovery, after which a cics emergency restart performs the backward recovery. Recoverable resources in cics, a recoverable resource is any resource with recorded recovery information that can be recovered by backout...
Page 18
V in the event of an emergency restart, when cics backs out all those transactions that were in-flight at the time of the cics failure (emergency restart backout). Although these occur in different situations, cics uses the same backout process in each case. Cics does not distinguish between dynamic...
Page 19
The recovery manager also drives: v the backout processing for any units of work that were in a backout-failed state at the time of the cics failure v the commit processing for any units of work that had not finished commit processing at the time of failure (for example, for resource definitions tha...
Page 20
Forward recovery journal names are of the form dfhjnn where nn is a number in the range 1–99 and is obtained from the forward recovery log id (fwdrecovlog) in the file resource definition. In this case, cics creates a journal entry for the forward recovery log, which can be mapped by a journalmodel ...
Page 21
2. If the failure occurs during the execution of a cics syncpoint, where the conversation is with another resource manager (perhaps in another cics region), cics handles the resynchronization. This is described in the cics intercommunication guide. If the link fails and is later reestablished, cics ...
Page 22
When the operator replies to ixc402d, the cics interregion communication program, dfhirp, is notified and the suspended tasks are abended, and mro connections closed. Until the reply is issued to ixc402d, an inquire connection command continues to show connections to regions in the failed mvs as in ...
Page 23
The cics recovery manager then uses the information retrieved from the system log to: v back out recoverable resources. V recover changes to terminal resource definitions. (all resource definitions installed at the time of the cics failure are initially restored from the cics global catalog.) a spec...
Page 24
12 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 25
Chapter 2. Resource recovery in cics before you begin to plan and implement resource recovery in cics, you should understand the concepts involved, including units of work, logging and journaling. Units of work when resources are being changed, there comes a point when the changes are complete and d...
Page 26
V working storage v any lu6.2 sessions v any lu6.1 links v any mro links the resources cics retains include: v locks on recoverable data. If the unit of work is shunted indoubt, all locks are retained. If it is shunted because of a commit- or backout-failure, only the locks on the failed resources a...
Page 27
When a lock is first acquired, it is an active lock. It remains an active lock until successful completion of the unit of work, when it is released, or is converted into a retained lock if the unit of work fails, or for a cics or smsvsam failure: v if a unit of work fails, rls vsam or the cics enque...
Page 28
– exec cics create connection complete – exec cics discard connection – exec cics discard terminal a uow that does not change a recoverable resource has no meaningful effect for the cics recovery mechanisms. Nonrecoverable resources are never backed out. A unit of work can also be ended by backout, ...
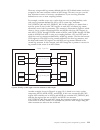
Page 29
Cics recovery manager the recovery manager ensures the integrity and consistency of resources (such as files and databases) both within a single cics region and distributed over interconnected systems in a network. Figure 3 on page 18 shows the resource managers and their resources with which the ci...
Page 30: Fc/rls
V managing the state, and controlling the execution, of each uow v coordinating uow-related changes during syncpoint processing for recoverable resources v coordinating uow-related changes during restart processing for recoverable resources v coordinating recoverable conversations to remote nodes v ...
Page 31
V notification that the resource is not available, requiring temporary suspension (shunting) of the uow v notification that the resource is available, enabling retry of shunted uows v notification that a connection is reestablished, and can deliver a commit or rollback (backout) decision v syncpoint...
Page 32
Others. This can happen, for example, if two data sets are updated and the uow has to be backed out, and the following happens: v one resource backs out successfully v while committing this successful backout, the commit fails v the other resource fails to back out these events leave one data set co...
Page 33
Resynchronization after system or connection failure units of work that fail while in an indoubt state remain shunted until the indoubt state can be resolved following successful resynchronization with the coordinator. Resynchronization takes place automatically when communications are next establis...
Page 34
Cics also writes “backout-failed” records to the system log if a failure occurs in backout processing of a vsam data set during dynamic backout or emergency restart backout. Records on the system log are used for cold, warm, and emergency restarts of a cics region. The only type of start for which t...
Page 35
V user journaling is entirely under your application programs’ control. You write records for your own purpose using exec cics write journalname commands. See “flushing journal buffers” on page 28 for information about cics shutdown considerations. V automatic journaling means that cics automaticall...
Page 36
24 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 37
Chapter 3. Shutdown and restart recovery cics can shut down normally or abnormally and this affects the way that cics restarts after it shuts down. Cics can stop executing as a result of: v a normal (warm) shutdown initiated by a cemt, or exec cics, perform shut command v an immediate shutdown initi...
Page 38
V the dfhcesd program started by the cics-supplied transaction, cesd, attempts to purge and back out long-running tasks using increasingly stronger methods (see “the shutdown assist transaction” on page 30). V tasks that are automatically initiated are run—if they start before the second quiesce sta...
Page 39
This indicator to determine the type of startup it is to perform. See “how the state of the cics region is reconstructed” on page 34. V cics writes warm keypoint records to: – the global catalog for terminal control and profiles – the cics system log for all other resources. See “warm keypoints.” v ...
Page 40
Flushing journal buffers during a successful normal shutdown, cics calls the log manager domain to flush all journal buffers, ensuring that all journal records are written to their corresponding mvs system logger log streams. During an immediate shutdown, the call to the log manager domain is bypass...
Page 41
2. If the default shutdown assist transaction cesd is run, it allows as many tasks as possible to commit or back out cleanly, but within a shorter time than that allowed on a normal shutdown. See “the shutdown assist transaction” on page 30 for more information about cesd, which runs the cics-suppli...
Page 42
The next initialization of cics must be an emergency restart, in order to preserve data integrity. An emergency restart is ensured if the next initialization of cics specifies start=auto. This is because the recovery manager’s type-of-restart indicator is set to “emergency-restart-needed” during ini...
Page 43
You are recommended always to use the cesd shutdown-assist transaction when shutting down your cics regions. You can use the dfhcesd program “as is”, or use the supplied source code as the basis for your own customized version (cics supplies versions in assembler, cobol, and pl/i). For more informat...
Page 44
- file control recovery blocks (only if a shcds nonrlsupdatepermitted command has been used). – transient data queue definitions – dump table information – interval control elements and automatic initiate descriptors at shutdown – appc connection information so that relevant values can be restored d...
Page 45
If you ever need to redefine and reinitialize the cics local catalog, you should also reinitialize the global catalog. After reinitializing both catalog data sets, you must perform an initial start. Shutdown initiated by cics log manager the cics log manager initiates a shutdown of the region if it ...
Page 46
And therefore recovery of the most recent units of work cannot be carried out. However, data might be missing from any part of the system log and cics cannot identify what is missing. Cics cannot examine the log and determine exactly what data is missing, because the log data might appear consistent...
Page 47
Overriding the type of start indicator the operation of the recovery manager's control record can be modified by running the recovery manager utility program, dfhrmutl. About this task this can set an autostart record that determines the type of start cics is to perform, effectively overriding the t...
Page 48
Performs the recovery process for work that was in-flight when the previous run of cics was abnormally terminated. Recovery of data during an emergency restart during the final stage of emergency restart, the recovery manager uses the system log data to drive backout processing for any units of work...
Page 49
You can do this by specifying start=initial as a system initialization parameter, or by running the recovery manager's utility program (dfhrmutl) to override the type of start indicator to force an initial start. See the cics operations and utilities guide for information about the dfhrmutl utility ...
Page 50
Recovery with vtam persistent sessions with vtam persistent sessions support, if cics fails or undergoes immediate shutdown (by means of a perform shutdown immediate command), vtam holds the cics lu-lu sessions in recovery-pending state, and they can be recovered during startup by a newly starting c...
Page 51
During an emergency restart of cics, cics restores those sessions pending recovery from the cics global catalog and the cics system log to an in-session state. This process of persistent sessions recovery takes place when cics opens its vtam acb. With multinode persistent sessions support, if vtam o...
Page 52
V if cics determines that it cannot recover the session without unbinding and rebinding it. The result in each case is as if cics has restarted following a failure without vtam persistent sessions support. In some other situations appc sessions are unbound. For example, if a bind was in progress at ...
Page 53
You can then start further cics regions with or without persistent sessions support as appropriate, provided that you do not exceed the limit for the number of regions that do have persistent sessions support. If you specify nops (no persistent session support) for the pstype system initialization p...
Page 54
42 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 55
Part 2. Recovery and restart processes you can add your own processing to the cics recovery and restart processes. This part contains the following sections: v chapter 4, “cics cold start,” on page 45 v chapter 5, “cics warm restart,” on page 53 v chapter 6, “cics emergency restart,” on page 61 v ch...
Page 56
44 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 57
Chapter 4. Cics cold start this section describes the cics startup processing specific to a cold start. It covers the two forms of cold start: v “starting cics with the start=cold parameter” v “starting cics with the start=initial parameter” on page 50 starting cics with the start=cold parameter sta...
Page 58
– cics requests the smsvsam server, if connected, to release all rls retained locks. – cics does not rebuild the non-rls retained locks. V cics requests the smsvsam server to clear the rls sharing control status for the region. V cics does not restore the dump table, which may contain entries contro...
Page 59
Specify on the grplist system initialization parameter. The csd file definition is built and installed from the csdxxxx system initialization parameters. Data tables as for vsam file definitions. Bdam file definitions are installed from file control table entries, specified by the fct system initial...
Page 60
Transient data resource definitions are installed from resource groups defined in the csd, as specified in the csd group list (named on the grplist system initialization parameter). Any extrapartition td queues that require opening are opened; that is, any that specify open(initial). All the newly-i...
Page 61
If you define new resource definitions and install them dynamically, ensure the group containing the resources is added to the appropriate group list. Monitoring and statistics the initial status of cics monitoring is determined by the monitoring system initialization parameters (mn and mnxxxx). The...
Page 62
Installable set install the following vtam terminal control resources are committed in installable sets: v connections and their associated sessions v pipeline terminals—all the terminal definitions sharing the same pool name if one definition in an installable set fails, the set fails. However, eac...
Page 63
Information saved in the system log from a previous run. The primary and secondary system log streams are purged and cics begins writing a new system log. V because cics is starting a new catalog, it uses a new logname token in the “exchange lognames” process when connecting to partner systems. Thus...
Page 64
52 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 65
Chapter 5. Cics warm restart this section describes the cics startup processing specific to a warm restart. If you specify start=auto, which is the recommended method, cics determines which type of start to perform using information retrieved from the recovery manager's control record in the global ...
Page 66
Files file control information from the previous run is recovered from information recorded in the cics catalog only. File resource definitions for vsam and bdam files, data tables, and lsr pools are installed from the global catalog, including any definitions that were added dynamically during the ...
Page 67
Temporary storage auxiliary temporary storage queue information (for both recoverable and non-recoverable queues) is retrieved from the warm keypoint. Note that ts read pointers are recovered on a warm restart (which is not the case on an emergency restart). Cics opens the auxiliary temporary storag...
Page 68
V all intrapartition td queues are initialized empty. V the queue resource definitions are installed from the global catalog, but they are not updated by any log records or keypoint data. They are always installed enabled. This option is intended for use when initiating remote site recovery (see cha...
Page 69
Autoinstall for programs if program autoinstall is enabled (pgaipgm=active), program, mapset, and partitionset resource definitions are installed from the csd only if they were cataloged; otherwise they are installed at first reference by the autoinstall process. All definitions installed from the c...
Page 70
Journal names and journal models the cics log manager restores the journal name and journal model definitions from the global catalog. Journal name entries contain the names of the log streams used in the previous run, and the log manager reconnects to these during the warm restart. Terminal control...
Page 71
V different tct from last run . Cics installs the tct only, and does not apply the warm keypoint information, effectively making this a cold start for these devices. Note: cics ts for z/os, version 4.1 supports only remote tcam terminals—that is, the only tcam terminals you can define are those atta...
Page 72
60 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 73
Chapter 6. Cics emergency restart this section describes the cics startup processing specific to an emergency restart. If you specify start=auto, cics determines what type of start to perform using information retrieved from the recovery manager’s control record in the global catalog. If the type-of...
Page 74
Any non-rls locks associated with in-flight (and other failed) transactions are acquired as active locks for the tasks attached to perform the backouts. This means that, if any new transaction attempts to access non-rls data that is locked by a backout task, it waits normally rather than receiving t...
Page 75
Reconnecting to smsvsam for rls access as on a warm restart, cics connects to the smsvsam server. In addition to notifying cics about lost locks, vsam also informs cics of the units of work belonging to the cics region for which it holds retained locks. See “lost locks recovery” on page 89 for infor...
Page 76
Start requests in general, start requests are recovered only when they are associated with recoverable data or are protected and the issuing unit of work is indoubt. However, recovery can be further limited by the use of the specific cold option on the system initialization parameter for ts, icp, or...
Page 77
Is successful, but cics abnormally terminates before the catalog can be updated, cics recovers the information from the forward recovery records on the system log. If the installation or deletion of installable sets or individual resources is unsuccessful, or has not reached commit point when cics a...
Page 78
66 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 79
Chapter 7. Automatic restart management cics uses the automatic restart manager (arm) component of mvs to increase the availability of your systems. Mvs automatic restart management is a sysplex-wide integrated automatic restart mechanism that performs the following tasks: v restarts an mvs subsyste...
Page 80
If cics is restarted by arm with the same persistent jcl, cics forces start=auto to ensure data integrity. Registering with arm to register with arm, you must implement automatic restart management on the mvs images that the cics workload is to run on. You must also ensure that the cics startup jcl ...
Page 81
Cancel, cics de-registers from arm before terminating, because if cics remained registered, an automatic restart would probably encounter the same error condition. For other error situations, cics does not de-register, and automatic restarts follow. To control the number of restarts, specify in your...
Page 82
Cics start options you are recommended to specify start=auto, which causes a warm start after a normal shutdown and an emergency restart after failure. You are also recommended always to use the same jcl, even if it specifies start=cold or start=initial, to ensure that cics restarts correctly when r...
Page 83
The covr transaction to ensure that cics reconnects to vtam in the event of a vtam abend, cics keeps retrying the open vtam acb using a time-delay mechanism via the non-terminal transaction covr. After cics has completed clean-up following the vtam failure, it invokes the cics open vtam retry (covr)...
Page 84
You can also restart a server explicitly using either the server command cancel restart=yes , or the mvs command cancel jobname,armrestart by default, the server uses an arm element type of syscicss, and an arm element identifier of the form dfhxxnn_poolname where xx is the server type (xq, cf or nc...
Page 85
Chapter 8. Unit of work recovery and abend processing a number of different events can cause the abnormal termination of transactions in cics. These events include: v a transaction abend request issued by a cics management module. V a program check or operating system abend (this is trapped by cics ...
Page 86
See “commit-failed recovery” on page 83. Backout-failed a unit of work fails while backing out updates to file control recoverable resources. (the concept of backout-failed applies in principle to any resource that performs backout recovery, but cics file control is the only resource manager to prov...
Page 87
Terminating transaction takes place immediately. Therefore, it does not cause any active locks to be converted into retained locks. In the case of a cics region abend, in-flight tasks have to wait to be backed out when cics is restarted, during which time the locks are retained to protect uncommitte...
Page 88
Intrapartition transient data intrapartition destinations specified as logically recoverable are restored by transaction backout. Read and write pointers are restored to what they were before the transaction failure occurred. Physically recoverable queues are recovered on warm and emergency restarts...
Page 89
Intended for the started task, but does not back out the start request itself. Thus the new task will start at its specified time, but the data will not be available to the started task, to which cics will return a notfnd condition in response to the retrieve command. Start with recoverable data (pr...
Page 90
Table 1. Effect of restart option on started transactions (continued) description of non-terminal start command events effect of restart(yes) effect of restart(no) specifies nonrecoverable data started task abends without retrieving its data transaction is restarted with its data still available, up...
Page 91
V protect operand in the cmsg transaction note: if backout fails, cics does not try to restart regardless of the setting of the restart program. Backout-failed recovery backout failure support is currently provided only by cics file control. If backout to a vsam data set fails for any reason, cics p...
Page 92
Auxiliary temporary storage all updates to recoverable auxiliary temporary storage queues are managed in main storage until syncpoint. Ts always commits forwards; therefore ts can never suffer a backout failure. Transient data all updates to logically recoverable intrapartition queues are managed in...
Page 93
V after a number of i/o errors that you consider to be significant v after a significant number of backout failures v not at all it might be worth initially deciding to leave a data set online for some time after a backout failure, to evaluate the level of impact the failures have on users. To recov...
Page 94
Failure of the smsvsam server might be detected by the backout request, in which case cics file control starts to close the failed smsvsam control acb and issues a console message. If the failure has already been detected by some other (earlier) request, cics has already started to close the smsvsam...
Page 95
This situation can be resolved only by deleting the rival record with the duplicate key value. Lock structure full error the backout required vsam to acquire a lock for internal processing, but it was unable to do so because the rls lock structure was full. This error can occur only for vsam data se...
Page 96
Distinguishes between a commit failure where recoverable work was performed, and one for which only repeatable read locks were held. Indoubt failure recovery the cics recovery manager is responsible for maintaining the state of each unit of work in a cics region. For example, typical events that cau...
Page 97
Reads against vsam data sets and has made no updates to other resources, it is safe to force the unit of work using the set dsname or set uow commands. Cics saves enough information about the unit of work to allow it to be either committed or backed out when the indoubt unit of work is unshunted whe...
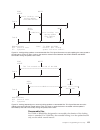
Page 98
To retrieve information about a unit of work (uow), you can use either the cemt, or exec cics, inquire uow command. For the purposes of this illustration, the cemt method is used. You can filter the command to show only uows that are associated with a particular transaction. For example, figure 4 sh...
Page 99
When a uow has been shunted indoubt, cics retains locks on the recoverable resources that the uow has updated. This prevents further tasks from changing the resource updates while they are indoubt. To display cics locks held by a uow that has been shunted indoubt, use the cemt inquire uowenq command...
Page 100
Recovery from failures associated with the coupling facility this topic deals with recovery from failures arising from the use of the coupling facility, and which affect cics units of work. It covers: v smsvsam cache structure failures v smsvsam lock structure failures (lost locks) v connection fail...
Page 101
Cics recovers after a cache failure automatically. There is no need for manual intervention (other than the prerequisite action of resolving the underlying cause of the cache failure). Lost locks recovery the failure of a coupling facility lock structure that cannot be rebuilt by vsam creates the lo...
Page 102
Region that was not sharing the data set at the time the lost locks condition occurred, and on rls access requests issued by any new units of work in cics regions that were sharing the data set. Performing lost locks recovery for failed units of work lost locks recovery requires that any units of wo...
Page 103
Simultaneously all data sets in use when the lock structure fails, each data set can be restored to service individually as soon as all its sharing cics regions have completed lost locks recovery. Connection failure to a coupling facility cache structure if connection to a coupling facility cache st...
Page 104
Recovery from the failure of a sysplex is just the equivalent of multiple mvs failure recoveries. Transaction abend processing if, during transaction abend processing, another abend occurs and cics continues, there is a risk of a transaction abend loop and further processing of a resource that has l...
Page 105
The exit code then executes as an extension of the abending task, and runs at the same level as the program that issued the handle abend command that activated the exit. After any program-level abend exit code has been executed, the next action depends on how the exit code ends: v if the exit code e...
Page 106
1. Cics invokes dfhrest only when restart(yes) is specified in a transaction’s resource definition. 2. Ensure that resources used by restartable transactions, such as files, temporary storage, and intrapartition transient data queues, are defined as recoverable. 3. When transaction restart occurs, a...
Page 107
V cics remains operational, but the task currently in control terminates. V cics terminates (see “shutdown requested by the operating system” on page 29). If a program check occurs when a user task is processing, the task abends with an abend code of asra. If a program check occurs when a cics syste...
Page 108
96 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 109
Chapter 9. Communication error processing the types of communication error that can occur include terminal error processing and intersystem communication failures. Terminal error processing there are two main cics programs that participate in terminal error processing. These are the node error progr...
Page 110
The tep is entered once for each terminal error, and therefore should be designed to process only one error for each invocation. Intersystem communication failures an intersystem communication failure can be caused by the failure of a cics region, or the remote system to which it is connected. A net...
Page 111
Part 3. Implementing recovery and restart this part describes the way you implement recovery and restart for cics regions. © copyright ibm corp. 1982, 2011 99.
Page 112
100 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 113
Chapter 10. Planning aspects of recovery when you are planning aspects of recovery, you must consider your applications, system definitions, internal documentation, and test plans. Application design considerations think about recoverability as early as possible during the application design stages....
Page 114
Question 5: if a data set becomes unusable, should all applications be terminated while recovery is performed? If degraded service to any application must be preserved while recovery of the data set takes place, you will need to include procedures to do this. Question 6: which of the files to be upd...
Page 115
Before any design or programming work begins, all interested parties should agree on the statement—including: v those responsible for business management v those responsible for data management v those who are to use the application—including the end users, and those responsible for computer and onl...
Page 116
V if a user’s printer becomes unusable (because of hardware or communication problems), consider the use of alternatives, such as the computer center’s printer, as a standby. Security decide the security procedures for an emergency restart or a break in communications. For example, when confidential...
Page 117
And general log data to log streams defined to the mvs system logger. For more information, see chapter 11, “defining system and general log streams,” on page 107. Files for vsam files defined to be accessed in rls mode, define the recovery attributes in the icf catalog, using idcams. For vsam files...
Page 118
Normal conditions. They should, nevertheless, be tested as far as possible, to ensure that they handle the functions for which they are designed. Cics facilities, such as the execution diagnostic facility (cedf) and command interpreter (ceci), can help to create exception conditions and to interpret...
Page 119
Chapter 11. Defining system and general log streams all cics system logging and journaling is controlled by the cics log manager, which uses mvs system logger log streams to store its output. About this task cics logging and journaling can be divided into four broad types of activity: system logging...
Page 120
System log streams these are used by the cics log manager and the cics recovery manager exclusively for unit of work recovery purposes. Each system log is unique to a cics region, and must not be merged with any other system log. General log streams these are used by the cics log manager for all oth...
Page 121
Cics log manager connects to its log stream automatically during system initialization, unless it is defined as type(dummy) in a cics journalmodel resource definition. Although the cics system log is logically a single logical log stream, it is written to two physical log streams—a primary and a sec...
Page 122
Model log streams for cics system logs if cics fails to connect to its system log streams because they have not been defined, cics attempts to have them created dynamically using model log streams. To create a log stream dynamically, cics must specify to the mvs system logger all the log stream attr...
Page 123
However, using model log streams defined with the cics default name are always assigned to the same structure within an mvs image. This may not give you the best allocation in terms of recovery considerations if you are using structures defined across two or more coupling facilities. For example, co...
Page 124
Varying the model log stream name: to balance log streams across log structures, using model log streams means customizing the model log stream names. You cannot achieve the distribution of log streams shown in this scenario using the cics default model name. About this task you can use an xlgstrm g...
Page 125
Work. With this information, cics continues reading backwards, but this time reading only the records for units of work that are identified in the activity keypoint. Reading continues until cics has read all the records for the units of work identified by the activity keypoint. This process means th...
Page 126
V if a system log stream exceeds the primary storage space allocated, it spills onto secondary storage. (for a definition of primary and secondary storage, see the cics transaction server for z/os installation guide.) the resulting i/o can adversely affect system performance. V if the interval betwe...
Page 127
Writing user-recovery data about this task you should write only recovery-related records to the system log stream. You can do this using the commands provided by the application programming interface (api) or the exit programming interfaces (xpi). This is important because user recovery records are...
Page 128
About this task the dddd value specifies the minimum number of days for which data is to be retained on the log. You are strongly recommended not to use the system log for records that need to be kept. Any log and journal data that needs to be preserved should be written to a general log stream. See...
Page 129
2. Define a general log stream for forward recovery data. If you do not define a general log stream, cics attempts to create a log stream dynamically. See “model log streams for cics general logs” for details. 3. Decide how you want to merge forward recovery data from different cics regions into one...
Page 130
Merging data on shared general log streams unlike system log streams, which are unique to one cics region, general log streams can be shared between many cics regions. This means that you can merge forward recovery data from a number of cics regions onto the same forward recovery log stream. About t...
Page 131
About this task the cics-supplied group, dfhlgmod, includes a journalmodel for the log of logs, called dfhlglog, which has a log stream name of &userid..Cicsvr.Dfhlglog. Note that &userid resolves to the cics region userid, and if your cics regions run under different racf user ids, the dfhlglog def...
Page 132
V in a format compatible with utility programs written for versions of cics that use the log manager for logging and journaling. See the cics operations and utilities guide for more information about using the logr ssi to access log stream data, and for sample jcl. If you plan to write your own util...
Page 133
Operating a recovery process that is independent of time-stamps in the system log data ensures that cics can restart successfully after an abnormal termination, even if the failure occurs shortly after local time has been put back. Offline utility program, dfhjup changing the local time forward has ...
Page 134
122 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 135: Resources
Chapter 12. Defining recoverability for cics-managed resources this section describes what to do to ensure that you can recover the resources controlled by cics on behalf of your application programs. About this task it covers the recoverability aspects of the various resources as follows: v “recove...
Page 137
Recovery for files a cics file is a logical view of a physical data set, defined to cics in a file resource definition with an 8-character file name. A cics file is associated with a vsam or bdam data set by one of the following: v by dynamic allocation, where the data set name is predefined on the ...
Page 138
Forward recovery for vsam files, you can use a forward recovery utility, such as cicsvr, when online backout processing has failed as a result of some physical damage to the data set. For forward recovery: v create backup copies of data sets. V record after-images of file changes in a forward recove...
Page 139
Uses the icf catalog entry recovery attributes instead of the file resource. To force cics to use the file resource attributes instead of the catalog, set the nonrlsrecov system initialization parameter to filedef. V you define the recovery attributes for bdam files in file entries in the file contr...
Page 140
Vsam files accessed in rls mode if you specify file definitions that open a data set in rls mode, specify the recovery options in the icf catalog. The recovery options on the cics file resource definitions (recovery, fwdrecovlog, and backuptype) are ignored if the file definition specifies rls acces...
Page 141
Inquire dsname command returns values from the vsam base cluster block (bcb). However, because base cluster block (bcb) recovery values are not set until the first open, if you issue an inquire dsname command before the first file is opened, cics returns notapplic for recovstatus. Bdam files you can...
Page 142
About this task if you use xfcnrec to suppress open failures that are a result of inconsistencies in the backout settings, cics issues a message to warn you that the integrity of the data set can no longer be guaranteed. Any inquire dsname recovstatus command that is issued from this point onward wi...
Page 143
- file is defined with recovery(all): the open fails. – base cluster has recovery(all): - file is defined with recovery(none): the open fails. - file is defined with recovery(backoutonly): the open fails. - file is defined with recovery(all): the open proceeds unless fwdrecovlog specifies a differen...
Page 144
For more information about allocation and space requirements, see the cics system definition guide.) for extrapartition transient data considerations, see “recovery for extrapartition transient data” on page 134. You must specify the name of every intrapartition transient data queue that you want to...
Page 145
Making intrapartition td physically recoverable can be useful in the case of some cics queues. For example, after a cics failure, you might choose to restart cics as quickly as possible, and then look for the cause of the failure. By specifying queues such as csmt as intrapartition and physically re...
Page 146
Recovery for extrapartition transient data cics does not recover extrapartition data sets. If you depend on extrapartition data, you will need to develop procedures to recover data for continued execution on restart following either a controlled or an uncontrolled shutdown of cics. There are two are...
Page 147
Output extrapartition data sets the recovery of output extrapartition data sets is somewhat different from the recovery of input data sets. For a tape output data set, use a new output tape on restart. You can then use the previous output tape if you need to recover information recorded before termi...
Page 148
Define temporary storage queues as recoverable using temporary storage model resource definitions as shown in the following example define statements: ceda define description(recoverable ts queues for start requests) tsmodel(recov1) group(tsrecov) prefix(df) location(auxiliary) recovery(yes) ceda de...
Page 149
About this task cics uses business transaction services (bts) to ensure that persistent messages are recovered in the event of a cics system failure. For this to work correctly, follows these steps: procedure 1. Use idcams to define the local request queue and repository file to mvs. You must specif...
Page 150
2. For each local request queue, define a qlocal object. Use the following command: define qlocal('queuename') descr('description') process(processname) initq('initiation_queue') trigger trigtype(first) trigdata('default_target_service') bothresh(nnn) boqname('requeuename') where: v queuename is the...
Page 151
Not usable, message dfhpi0117 is issued, and cics continues without bts, using the existing channel-based container mechanism. If a cics failure occurs before the web service starts or completes processing, bts recovery ensures that the process is rescheduled when cics is restarted. If the web servi...
Page 152
140 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 153
Chapter 13. Programming for recovery when you are designing your application programs, you can include recovery facilities that are provided by cics; for example, you can use global user exits for backout recovery. This section covers the following topics: v “designing applications for recovery” v “...
Page 154
V progress transaction, to check on progress through the application. Such a function could be used after a transaction failure or after an emergency restart, as well as at any time during normal operation. For example, it could be designed to find the correct restart point at which the terminal use...
Page 155
Saa-compatible applications the resource recovery element of the systems application architecture ® (saa) common programming interface (cpi) provides an alternative to the standard cics application program interface (api) if you need to implement saa-compatible applications. The resource recovery fa...
Page 156
Committed in one unit of work, but the transaction is to continue with one or more units of work for further processing. 3. Where file or database updates must be kept in step, make sure that your application does them in the same unit of work. This approach ensures that those updates will all be co...
Page 157
Back out only the updates made during that individual step; the application is responsible for restarting at the appropriate point in the conversation, which might involve recreating a screen format. However, other tasks might try to update the database between the time when update information is ac...
Page 158
V data tables (user-maintained) v coupling facility data tables cics can return all these resources to their status at the beginning of an in-flight unit of work if a task ends abnormally. Temporary storage (auxiliary) you can use a temporary storage item to communicate between transactions. (for th...
Page 159
About this task consider using the following techniques: procedure v arrange for all transactions to access files in a sequence agreed in advance. This could be a suitable subject for installation standards. Be extra careful if you allow updates through multiple paths. V enforce explicit installatio...
Page 160
The protect option on a start request ensures that, if the task issuing the start fails during the unit of work, the new task will not be initiated, even though its start time may have passed. (see “start requests” on page 76 for more information about the protect option.) consider also the possibil...
Page 161
Using transient data queues when a number of tasks direct large amounts of data to a single terminal (for example, a printer receiving multipage reports initiated by the users), it may be necessary to queue the data (on disk) until the terminal is ready to receive it. About this task such queuing ca...
Page 162
The resp option on a command returns a condition id that can be tested. Alternatively, a handle condition command is used in the local context of a transaction program to name a label where control is passed if certain conditions occur. For example, if file input and output errors occur (where the d...
Page 163
Remember that: v for transactions that access a recoverable resource, dtb helps to preserve logical data integrity. V resources that are to be updated should be made recoverable. V dtb takes place only after program level abend exits (if any) have attempted cleanup or logical recovery. Transaction r...
Page 164
If you want to initiate a dump, do so in the exit code at the same program level as the abend. If you initiate the dump at a program level higher than where the abend occurred, you may lose valuable diagnostic information. V attempt local recovery, and then continue running the program. V send a mes...
Page 165
Processing the ioerr condition any program that attempts to process an ioerr condition for a recoverable resource must not issue a return or syncpoint command, but must terminate by issuing an abend command. A return or syncpoint command causes the recovery manager to complete the unit of work and c...
Page 166
For details of pl/i coding restrictions in a cics environment, see the appropriate pl/i programmer’s guide for your compiler. Locking (enqueuing on) resources in application programs this topic describes locking (enqueuing) functions provided by cics (and access methods) to protect data integrity. A...
Page 167
Recoverable files for vsam or bdam files designated as recoverable, the duration of the locking action is extended. For vsam files, the extended locking is on the updated record only, not the whole control interval. Read write update ====== locking ===== during update (see note below) task a sot rea...
Page 168
The extended period of locking is needed to avoid an update committed by one task being backed out by another. (consider what could happen if the nonextended locking action shown in figure 13 on page 155 was used when updating a recoverable file. If task a abends just after task b has reached syncpo...
Page 169
The backout fails because a duplicate key is detected in the aix indicated by message dfhfc4701, with a failure code of x'f0'. There is no locking on the aix ® key to prevent the second task taking the key before the end of the first task’s unit of work. If there is an application requirement for th...
Page 170
Enqueuing on temporary storage queues where concurrently executing tasks can read and change queue(s) with the same temporary storage identifier. (see “explicit enqueuing (by the application programmer).”) temporary storage control commands that invoke implicit enqueuing are: v writeq ts v deleteq t...
Page 171
After a task has issued an enq resource(data-area) command, any other task that issues an enq resource command with the same data-area parameter is suspended until the task issues a matching deq resource(data-area) command, or until the unit of work ends. Note: enqueueing on more than one resource c...
Page 172
V if both deadlocked resources are cics resources (but not both vsam resources), or one is cics and the other dl/i, cics abends the task whose dtimout period elapses first. It is possible for both tasks to time out simultaneously. If neither task has a dtimout period specified, they both remain susp...
Page 173
Procedure v enable them in plt programs in the first part of plt processing. V specify them on the system initialization parameter, tbexits. This takes the form tbexits=(name1,name2,name3,name4,name5,name6), where name1, name2, name3, name4, name5, and name6 are the names of your global user exit pr...
Page 174
Xfcldel global user exit xfcldel is invoked when backing out a unit of work that performed a write operation to a vsam esds, or a bdam data set. Xfcbover global user exit xfcbover is invoked whenever cics is about to decide not to backout an uncommitted update, because the record could have been upd...
Page 175
Chapter 14. Using a program error program (pep) the program error program (pep) gains control after all program-level abend exit code has executed and after dynamic transaction backout has been performed. About this task there is only one program error program for the whole region. Procedure 1. Deci...
Page 176
7. The cics transaction failure program, dfhtfp, links to dfhpep before transaction backout is performed. This means resources used by the abending transaction may not have been released. Dfhpep needs to be aware of this, and might need logic to handle resources that are still locked. 8. Do not use ...
Page 177
When you have corrected the error, you can re-enable the relevant installed transaction definition to allow terminals to use it. You can also disable transaction identifiers when transactions are not to be accepted for application-dependent reasons, and can enable them again later. The cics resource...
Page 178
166 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 179: Resources
Chapter 15. Resolving retained locks on recoverable resources this section describes how you can locate and resolve retained locks that are preventing access to resources, either by cics transactions or by batch jobs. About this task although the main emphasis in this section is on how you can switc...
Page 180
The rls quiesce and unquiesce functions the rls quiesce and unquiesce functions are initiated by a cics command in one region, and propagated by the vsam rls quiesce interface to other cics regions in the sysplex. When these functions are complete, the icf catalog shows the quiesce state of the targ...
Page 181
Note: 1. A suitably-authorized user application program (aor1 in the diagram) issues an exec cics set dsname(...) quiesced command (or a terminal operator issues the equivalent cemt command). If the command specifies the busy(nowait) option, all phases of the quiesce operation are asynchronous, and ...
Page 182
(4a) smsvsam uses the coupling facility to propagate the request to the other smsvsam servers in the sysplex. 5. The cics rls quiesce exit program schedules a cics region task (cfqr) to perform asynchronously the required quiesce actions in that cics region. 6. When cics has closed all open rls acbs...
Page 183
With the new rls quiesce mechanism, you do not have to close a data set to take a non-bwo backup. However, because this causes new transactions to be abended, you may prefer to quiesce your data sets before taking a non-bwo backup. Non-bwo data set backup end a quiesce interface function initiated b...
Page 184
Lost locks recovery complete a quiesce interface function initiated by vsam. Vsam takes action associated with a sphere having completed lost locks recovery on all cics regions that were sharing the data set. Smsvsam invokes the cics rls quiesce exit program in each region that is registered with an...
Page 185
Note: if your file definitions specify an lsr pool id that is built dynamically by cics, consider using the rlstolsr system initialization parameter. V open the files non-rls read-only mode in cics. V concurrently, run batch non-rls. V when batch work is finished: – close the read-only non-rls mode ...
Page 186
The remainder of this topic on switching to non-rls access mode describes the options that are available if you need to switch to non-rls mode and are prevented from doing so by retained locks. Resolving retained locks before opening data sets in non-rls mode vsam sets an ‘rls-in-use’ indicator in t...
Page 187
About this task however, it does know about the uncommitted changes that are protected by such locks, and why the changes have not yet been committed successfully. Cics uses this information to help you resolve any retained locks that are preventing you from switching to non-rls access mode. Inquire...
Page 188
V commit failure , where a unit of work has failed during the commit action. The commit action may be either to commit the changes made by a completed unit of work, or to commit the successful backout of a unit of work. This failure is caused by a failure of the smsvsam server, which is returned as ...
Page 189
4. If a unit of work has been shunted with a different cause and reason, review the descriptions of these values in the inquire uowdsnfail command to determine what action to take to allow the shunted unit of work to complete. Choosing data availability over data integrity there may be times when yo...
Page 190
Diagnostic messages dfhfc3003 and dfhfc3010 are issued for each log record. If a data set has both indoubt-failed and other (backout- or commit-) failed units of work, deal with the indoubt uows first, using set dsname uowaction, because this might result in other failures which can then be cleared ...
Page 191
Cemt inquire uowdsnfail dsn(’rls.Accounts.Esds.Dbase1’) status: results dsn(rls.Accounts.Esds.Dbase1 ) dat del uow(aa6db080c40cee01) rls dsn(rls.Accounts.Esds.Dbase1 ) dat ind uow(aa6db08ac66b4000) rls the display shows a reason code of delexiterror (del) for one unit of work, and indexrecfull (ind)...
Page 192
X’aa6db08ac66b4000’ and file accnt1 . Update was a write-add made by transaction wkly at terminal t583 under task number 00027. Key length 4, data length 7, base esds rba x’00000ddf’, record key x’00000ddf’ a special case: lost locks if a lost locks condition occurs, any affected data set remains in...
Page 193
V do not use denynonrlsupdate if you run non-rls work after specifying permitnonrlsupdate. The permit status is automatically reset by the cics regions that hold retained locks when they open the data set in rls mode. Post-batch processing after a non-rls program has been permitted to override retai...
Page 194
Coupling facility data table retained locks recoverable coupling facility data table records can be the subject of retained locks, like any other recoverable cics resource that is updated in a unit of work that subsequently fails. A recoverable cfdt supports indoubt and backout failures. If a unit o...
Page 195: Locks
Chapter 16. Moving recoverable data sets that have retained locks there may be times when you need to re-define a vsam data set by creating a new data set and moving the data from the old data set to the new data set. About this task for example, you might need to do this to make a data set larger. ...
Page 196
The following access method services examples assume that cics.Dataset.A needs to be redefined and the data moved to a data set named cics.Dataset.B, which is then renamed: define cluster (name(cics.Dataset.B) ... Repro indataset(cics.Dataset.A) outdataset(cics.Dataset.B) delete cics.Dataset.A alter...
Page 197
This makes the data set unavailable while the move from old to new is in progress, and also allows the following unbind operation to succeed. 4. Issue the shcds frunbind subcommand to unbind any retained locks against the old data set. For example: shcds frunbind(cics.Dataset.A) this enables smsvsam...
Page 198
V create a new empty data set into which the copy is to be restored, and use import to copy the data from the exported version of the data set to the new empty data set. V use shcds frsetrr to mark the original data set as being under maintenance. V use shcds frunbind to unbind the locks from the or...
Page 199
Chapter 17. Forward recovery procedures if a data set that is being used by cics fails, perhaps because of physical damage to a disk, you can recover the data by performing forward recovery of the data set. About this task your forward recovery procedures can be based either on your own, or an isv-s...
Page 200
Recovery of data set with volume still available the procedure described here is necessary to preserve any retained locks that are held by smsvsam against the data in the old data set. Unless you follow all the steps of this procedure, the locks will not be valid for the new data set, with potential...
Page 201
9. Alter the new data set name use access method services to rename the new data set to the name of the old data set. Alter cics.Datasetb newname(cics.Dataseta) you must give the restored data set the name of the old data set to enable the following bind operation to succeed. 10. Issue the frbind su...
Page 202
There are several methods you can use to recover data sets after the loss of a volume. Whichever method you use (whether a volume restore, a logical data set recovery, or a combination of both), you need to ensure smsvsam puts data sets into a lost locks state to protect data integrity. This means t...
Page 203
This is because cics cannot run the lost locks recovery process until the data sets are available, and the data sets are made available only after the cics vr recovery jobs are finished. If you physically restore the volume, however, the data sets that need to be forward recovered are immediately av...
Page 204
This clears the smsvsam cfvol-quiesced state and allows smsvsam rls access to the volume. Cics ensures that access is not allowed to the data sets that will eventually be forward recovered, but the volume is available for other data sets. 6. Run data set forward recovery jobs. The following two exam...
Page 205
Pids/565501800 lvls/510 ms/dfhfc0152 rids/dfhfcca ptfs/un92873 regs/gr15 valu/00000008 pcss/idaretlk prcs/000000a9 +dfhfc0312 adswa03a message dfhfc0152 data set rlsadsw.Vf04d.Dataendb we used the cemt command inquire uowdsnfail ioerror to display the uows that were shunted as a result of the i/o er...
Page 206
Effect in cics region adswa03c was shown by the following response to an inquire uowdsnfail command for data set rlsadsw.Vf01d.Bankacct: inquire uowdsnfail dsn(rlsadsw.Vf01d.Bankacct) status: results dsn(rlsadsw.Vf01d.Bankacct ) dat ope uow(add19b8166268e02) rls dsn(rlsadsw.Vf01d.Bankacct ) rls com ...
Page 207
Work. Assuming that all cics regions are active, and there are no indoubt uows, lost locks processing, for all data sets except the ones on the failed volume, should complete quickly. 9. In this example, cemt inquire uowdsnfail on cics region adswa01d showed uow failures only for the rlsadsw.Vf04d.T...
Page 208
Waits for indoubt resolution before allowing general access to the data set. In such a situation you can still release the locks immediately, using the set dsname command, although in most cases you will lose data integrity. See “lost locks recovery” on page 89 for more information about resolving i...
Page 209
Route *all,vary sms,smsvsam,terminateserver 8. When all smsvsam servers were down, we deleted the igwlock00 lock structure with the mvs command: vary sms,smsvsam,forcedeletelockstructure 9. We restarted the smsvsam servers with the mvs command: route *all,vary sms,smsvsam,active cics was informed du...
Page 210
That before running shcds cfrepair, the restored user catalog must be import connected to the master catalog on all systems (see the “recovering shared catalogs” topic in dfsms/mvs managing catalogs). Forward recovery of data sets accessed in non-rls mode for data sets accessed in non-rls mode, use ...
Page 211
In these cases, you can resolve the cause of the failure and try the whole process again. This topic describes what to do when the failure in forward recovery cannot be resolved. In this case, where you are unsuccessful in applying all the forward recovery log data to a restored backup, you are forc...
Page 213
Procedure for failed non-rls mode forward recovery operation if you are not successful in applying all the forward recovery log data to a restored backup, you are forced to abandon the forward recovery, and revert to your most recent full backup. However, during its recovery processing, cics assumes...
Page 214
202 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 215
Chapter 18. Backup-while-open (bwo) the bwo facility, together with other system facilities and products, allows you to take a backup copy of a vsam data set while it remains open for update. Many cics applications depend on their data sets being open for update over a long period of time. Normally,...
Page 216
Forward-recovery logs. Long-running transactions, automated teller machines, and continuously available applications require the database to be up and running when the backup is being taken. The concurrent copy function used along with bwo by dfsmsdss allows backups to be taken with integrity even w...
Page 217
Hardware requirements the concurrent copy function is supported by the ibm ® 3990 model 3 with the extended platform and the ibm 3990 model 6 control units. Which data sets are eligible for bwo you can use bwo only for: v data sets that are on sms-managed storage and that have an integrated catalog ...
Page 218
How you request bwo you can define files as eligible for bwo in one of two ways. Procedure decide which method you want to use for data sets: v if your data set is accessed in rls mode, you must define the bwo option in the icf catalog. Defining bwo in the icf catalog requires dfsms 1.3. V if your d...
Page 219
V but if you specify bwo(typecics), and the ptf has not been applied, and you have not specified log(all) and a forward recovery log stream name, bwo processing for rls remains disabled for such files. To achieve bwo for the file, you must either: – apply the ptf, – or specify log(all) and a forward...
Page 220
Removing bwo attributes if you want to remove bwo attributes from your data sets, you must follow the correct procedure to avoid problems when taking subsequent back ups. Procedure 1. Close the vsam data set either by shutting down cics normally or issuing the command cemt set file closed. Do not pe...
Page 221
After an uncontrolled or immediate shutdown, further bwo backups might be taken by dfsmshsm, because the bwo status in the icf catalog is not reset. These backups should be discarded; only the non-bwo backups taken at the end of the batch window should be used during forward recovery, together with ...
Page 222
Each of these operations is discussed in the following sections. File opening different processing is done for each of the three cases when a file is opened for an update. The following processing takes place: v first file opened for update against a cluster v subsequent file opened for update again...
Page 223
V if the file was defined with backuptype(static) and the icf catalog indicates that the data set is already ineligible for bwo, cics sets the backuptype attribute in the dsnb to indicate ineligibility for bwo. However, if the icf catalog indicates that the data set is currently eligible for bwo, ig...
Page 224
V if the file was defined with backuptype(static) and the icf catalog indicates that the data set is already ineligible for bwo, the icf catalog is not updated. However, if the icf catalog indicates that the data set is currently eligible for bwo, igwabwo makes it ineligible for bwo and sets the rec...
Page 225
Shutdown and restart the way cics closes files is determined by whether the shutdown is controlled, immediate, or uncontrolled. Controlled shutdown during a controlled shutdown, cics closes all open files defined in the fct. This ensures that, for files that are open for update and eligible for bwo,...
Page 226
When you use dfsmshsm, you still use dfsmsdss as the data mover. You can specify this using the dfsmshsm setsys command: setsys datamover(dss) the dfsms processing at the start of backup is dependent on the dfsms release level. For releases before dfsms 1.2, dfsmsdss first checks the bwo attributes ...
Page 227
Dfsmsdfp must now disallow the pending change to ‘bwo enabled’ (and dfsmsdss must fail the backup) because, if the split did not finish before the end of the backup, the invalid backup would not be discarded. V from ‘bwo disabled and vsam split occurred’ to ‘bwo enabled’. This state change could be ...
Page 228
Each cics allows all units of work with updates for the data set to complete, and then they write the tie-up records to the forward recovery log and the log of logs, and replies to dfsmsdss. For bwo backups, it is usually not necessary for the forward recovery utility to process a log from file-open...
Page 229
The forward recovery utility should allocate, with disp=old, the data set that is to be recovered. This prevents other jobs accessing a back level data set and ensures that data managers such as cics are not still using the data set. Before the data set is opened, the forward recovery utility should...
Page 230
An assembler program that calls dfsms callable services *asm xopts(cics,noepilog,sp) * * a program that can be run as a cics transaction to read and set * the bwo indicators and bwo recovery point via dfsms callable * services (igwabwo). * * invoke the program via a cics transaction as follows: * * ...
Page 231
Ds 30c dateval ds 8c date value from bwo recovery point sucmsg1 ds 8c message text timeval ds 8c time value from bwo recovery point sucmsg2 ds c message text readmsg ds 0cl11 if function = read put out bwo flags ds 7c message text bwoval1 ds c bwo indicator 1 bwoval2 ds c bwo indicator 2 bwoval3 ds ...
Page 232
Mvc bwoflags(12),zeroes la r4,1(0) cli bwoc1,c’0’ be prgbit2 st r4,bwof1 set bwo indicator 1 if required prgbit2 ds 0h cli bwoc2,c’0’ be prgbit3 st r4,bwof2 set bwo indicator 2 if required prgbit3 ds 0h cli bwoc3,c’0’ be prgcont st r4,bwof3 set bwo indicator 3 if required b prgcont prgread ds 0h cli...
Page 233
Mvc sucmsg1(8),suctxt1 mvc sucmsg2(1),suctxt2 unpk keywork(9),bwotime(5) make date printable tr keywork(8),hextab-c’0’ mvc dateval(8),keywork unpk keywork(9),bwotime+4(5) make time printable tr keywork(8),hextab-c’0’ mvc timeval(8),keywork cli tranfunc,c’s’ if read then print bwo flags bne prgreado ...
Page 234
222 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 235
Chapter 19. Disaster recovery if your cics system is normally available about 99 percent of the time, it would be wise to look at your disaster recovery plan. The same pressure that drives high availability drives the need for timely and current disaster recovery. You must plan what level of disaste...
Page 236
Acceptable. If you are located in an area prone to hurricanes or earthquakes, for example, a disaster recovery site next door would be pointless. When you are planning for disaster recovery, consider the cost of being unable to operate your business for a period of time. You have to consider the num...
Page 237
V how critical and sensitive your business processes are: the more critical they are, the more frequently testing may be required. Six tiers of solutions for off-site recovery one blueprint for recovery planning describes a scheme consisting of six tiers of off-site recoverability (tiers 1-6), with ...
Page 238
Your disaster recovery plan has to include information to guide the staff responsible for recovering your system, from hardware requirements to day-to-day operations. The backups required for off-site storage must be created periodically. After a disaster, your data can only be as up-to-date as the ...
Page 239
Tier 1 tier 1 provides a very basic level of disaster recovery. You will lose data in the disaster, perhaps a considerable amount. However, tier 1 allows you to recover and provide some form of service at low cost. You must assess whether the loss of data and the time taken to restore a service will...
Page 240
The advantage of tier 3 is that you should be able to provide a service to your users quite rapidly. You must assess whether the loss of data will prevent your company from continuing in business. Figure 20 summarizes the tier 3 solution. Tier 3 is similar to tier 2. The difference is that data is e...
Page 241
The advantage of these methods is their low cost. The disadvantages of these methods are: v recovery is slow, and it can take days or weeks to recover. V any recovery is incomplete, because any updates made after the point-in-time backup are lost. V disaster recovery is risky, and difficulties in te...
Page 242
Tier 4 closes the gap between the point-in-time backups and current online processing recovery. Under a tier 4 recovery plan, site one acts as a backup to site two, and site two acts as a backup to site one. Tier 4 duplicates the vital data of each system at the other's site. You must transmit image...
Page 243
V cost is higher than for the tier 1 to 3 solutions, because you need dedicated hardware, software, and communication links. Tier 5 - two-site, two-phase commit a tier 5 solution is appropriate for a custom-designed recovery plan with special applications. Because these applications must be designed...
Page 244
Figure 24 summarizes the tier 6 solution. Tier 6, minimal to zero data loss, is the ultimate level of disaster recovery. There are two tier 6 solutions, one hardware-based and the other software-based. For details of the hardware and software available for these solutions, see “peer-to-peer remote c...
Page 245
Support the xrc dfsms/mvs host, and one for the recovery 3990, this allows a total of 86 km (53.4 miles) between the 3990s. If you use channel extenders with xrc, there is no limit on the distance between your primary and remote site. For rrdf there is no limit to the distance between the primary an...
Page 246
Disaster recovery and high availability this topic describes the tier 6 solutions for high availability and data currency when recovering from a disaster. Peer-to-peer remote copy (pprc) and extended remote copy (xrc) pprc and xrc are both 3990-6 hardware solutions that provide data currency to seco...
Page 247
V ims write-ahead data set (wads) and ims online log data set (olds) v acblib for ims v boot-strap data set (bsds), the catalog and the directory for db2 v db2 logs v any essential non-database volumes cics applications can use non-dasd storage for processing data. If your application depends on thi...
Page 248
Where there is a high volume of transactions, but each transaction is typically less than 200 dollars in value. Other benefits of pprc and xrc pprc or xrc may eliminate the need for disaster recovery backups to be taken at the primary site, or to be taken at all. Pprc allows you to temporarily suspe...
Page 249
Between the primary and secondary sites is interrupted. Remote logging is only as effective as the currency of the data that is sent off-site. Rrdf transports log stream data to a remote location in real-time, within seconds of the log operation at the primary site. When the rrdf address space at th...
Page 250
You should ensure that a senior manager is designated as the disaster recovery manager. The recovery manager must make the final decision whether to switch to a remote site, or to try to rebuild the local system (this is especially true if you have adopted a solution that does not have a warm or hot...
Page 251
Cics vsam recovery qsam copy cics vsam recovery (cics vr) provides a qsam copy function that can copy mvs log streams to a qsam data set. Copies of the qsam data can be sent either electronically or physically to the remote site. On arrival at the remote site, you can use the mvs system logger impor...
Page 252
If a disaster occurs at the primary site, your disaster recovery procedures should include recovery of vsam data sets at the designated remote recovery site. You can then emergency restart the cics regions at the remote site so that they can backout any uncommitted data. Special support is needed fo...
Page 253: Part 4. Appendixes
Part 4. Appendixes © copyright ibm corp. 1982, 2011 241.
Page 254
242 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 255: Notices
Notices this information was developed for products and services offered in the u.S.A. Ibm may not offer the products, services, or features discussed in this document in other countries. Consult your local ibm representative for information on the products and services currently available in your a...
Page 256
Such information may be available, subject to appropriate terms and conditions, including in some cases, payment of a fee. The licensed program described in this document and all licensed material available for it are provided by ibm under terms of the ibm customer agreement, ibm international progr...
Page 257: Bibliography
Bibliography cics books for cics transaction server for z/os general cics transaction server for z/os program directory, gi13-0536 cics transaction server for z/os what's new, gc34-6994 cics transaction server for z/os upgrading from cics ts version 2.3, gc34-6996 cics transaction server for z/os up...
Page 258
Cics shared data tables guide, sc34-7017 cicsplex sm books for cics transaction server for z/os general cicsplex sm concepts and planning, sc34-7044 cicsplex sm web user interface guide, sc34-7045 administration and management cicsplex sm administration, sc34-7005 cicsplex sm operations views refere...
Page 259: Accessibility
Accessibility accessibility features help a user who has a physical disability, such as restricted mobility or limited vision, to use software products successfully. You can perform most tasks required to set up, run, and maintain your cics system in one of these ways: v using a 3270 emulator logged...
Page 260
248 cics ts for z/os 4.1: recovery and restart guide.
Page 261: Index
Index a abend handling 95, 151 acid properties, of a transaction 20 activity keypoints description 22 adcd abend 159 afcf abend 159 afcw abend 159 airdelay 39 aix (alternate index) 130, 147 alternate index (aix) 130, 147 alternate indexes preserving locks over a rebuild 186 application processing un...
Page 262
Dl/i (continued) implicit enqueuing upon 158 intertransaction communication 146 scheduling program isolation scheduling 158 documenting recovery and restart programs 105 dsnbs, data set name blocks recovery 54 dtimout option (define transaction) 123 dump table 50 dynamic rls restart 37 dynamic trans...
Page 263
Locking (continued) implicit locking on recoverable files 156 in application programs 154 locks 14 log of logs failures 119 logical levels, application program 92 logical recovery 132 lost locks recovery from 89 m managing uow state 18 mnps 38, 39, 40 moving data sets using export and import command...
Page 264
System log stream basic definition 104 system logs log-tail deletion 114 system or abend exit creation 95 system recovery table (srt) definition of 104 user extensions to 95 system warm keypoints 27 systems administration for bwo 208 t tables for recovery 104 task termination, abnormal 94 dfhpep exe...
Page 265
Readers’ comments — we'd like to hear from you cics transaction server for z/os version 4 release 1 recovery and restart guide publication no. Sc34-7012-02 we appreciate your comments about this publication. Please comment on specific errors or omissions, accuracy, organization, subject matter, or c...
Page 266
Readers’ comments — we'd like to hear from you sc34-7012-02 sc34-7012-02 cut or fold along line cut or fold along line fold and tape please do not staple fold and tape fold and tape please do not staple fold and tape place postage stamp here ibm united kingdom limited user technologies department (m...
Page 268
Sc34-7012-02.