- DL manuals
- Icom
- Transceiver
- IC-208H
- Instruction Manual
Icom IC-208H Instruction Manual
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
i208H
VHF/UHF FM TRANSCEIVER
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is sub-
ject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Summary of IC-208H
Page 1
Instruction manual i208h vhf/uhf fm transceiver this device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is sub- ject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may c...
Page 2: D Features
I foreword thank you for purchasing this icom product. The ic-208h vhf / uhf fm transceiver is designed and built with icom’s state of the art technology and craftsmanship. With proper care, this product should provide you with years of trouble-free operation. We want to take a couple of moments of ...
Page 3
Rwarning rf exposure! This device emits radio frequency (rf) energy. Extreme caution should be observed when operating this device. If you have any questions regarding rf expo- sure and safety standards please refer to the federal communica- tions commission office of engineering and technology’s re...
Page 4
Iii table of contents supplied accessories q dc power cable (3 m) ………………………………………1 w mobile mounting bracket …………………………………1 e microphone (hm-133)* ……………………………………1 r fuse (20 a) …………………………………………………1 t mounting screws, nuts and washers …………………1 set y microphone hanger …………………………………………1 u separation ca...
Page 5
Iv 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 ■ one-touch ptt function ............................................................... 18 ■ audio mute function ..................................................................... 18 4 repeater operation ...........................................................
Page 6: Quick Reference Guide
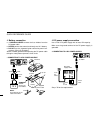
I quick reference guide ■ installation d installation methods • single body installation • the supplied mounting bracket (or optional mb-17a) can be used for the main unit installation. • remote installation • the supplied opc-600/r separation cable can be used for remote installation. • optional op...
Page 7
Ii quick reference guide d location select a location which can support the weight of the trans- ceiver and does not interfere with driving. We recommend the locations shown in the diagram below. Never place the transceiver or remote controller where nor- mal operation of the vehicle may be hindered...
Page 8
Iii quick reference guide d microphone connection connect the supplied microphone as illustrated below. D separation cable connection using the supplied separation cable (3.5 m; 11.5 ft) or the op- tional separation cable (7 m; 23 ft) the controller can be sep- arated from the main unit, doubling as...
Page 9
Iv quick reference guide d optional mb-58 installation the optional mb-58 remote controller bracket is avail- able for separate installation. Q drill 2 or 4 holes where the bracket is to be installed. • approx. 4 mm ( 1 ⁄ 8 ″) when using nuts; approx. 1–2 mm ( 1 ⁄ 16 ″) when using self-tapping screw...
Page 10
V d battery connection ☞ rwarning never remove the fuse holders from the dc power cable. ☞ never connect the transceiver directly to a 24 v battery. ☞ do not use the cigarette lighter socket for power con- nections. (see p. 5 for details) attach a rubber grommet when passing the dc power cable throu...
Page 11
Vi quick reference guide d antenna installation • antenna location to obtain maximum performance from the transceiver, select a high-quality antenna and mount it in a good location. A non- radial antenna should be used when using a magnetic mount. • antenna connector the antenna uses a pl-259 connec...
Page 12: ■ Your First Contact
Vii quick reference guide ■ your first contact now that you have your ic-208h installed in your car or shack, you are probably excited to get on the air. We would like to take you through a few basic operation steps to make your first “on the air” an enjoyable experience. 1. Turning on the transceiv...
Page 13
Viii quick reference guide 3. Tune the frequency the tuning dial will allow you to dial in the frequency you want to operate. Pages 12 and 13 will instruct you on how to set the tuning speed. Using the hm-133 you can directly enter the frequency with the hm-133 keypad for the main band. [example]: s...
Page 14: ■ Repeater Operation
Ix quick reference guide ■ repeater operation 1. Setting duplex push [band] to select the frequency band. Push [low•dup] for 1 sec. Once or twice to select minus du- plex or plus duplex. • the usa version has an auto repeater function, therefore, setting duplex is not required. 2. Repeater tone push...
Page 15
X quick reference guide quick reference guide ■ programming memory channels the ic-208h has a total of 512 memory channels (including 10 scan edges and 2 call channels) for storing often used op- erating frequency, repeater settings, etc. 1. Setting a frequency in vfo mode, set the desired operating...
Page 16: Panel Description
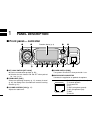
■ front panel— controller qset•lock switch [set•lock] ➥ enters set mode when pushed. (p. 56) ➥ switches the lock function on and off when pushed for 1 sec. (p. 14) wtuning dial [dial] selects the operating frequency (p. 12), memory channel (p. 26), the setting of the set mode item and the scanning d...
Page 17
2 1 panel description 1 ysquelch control [sql] varies the squelch level. (p. 15) • the rf attenuator activates and increases the attenuation when rotated clockwise to the center position and further. (p. 16) umonitor•dtmf switch [moni•dtmf] ➥ push to switch the monitor function on and off. (p. 15) ➥...
Page 18: ■ Function Display
3 1 panel description ■ function display qtransmit indicator ➥ appears while transmitting. (p. 17) ➥ blinks while transmitting with the one-touch ptt func- tion. (p. 18) wduplex indicators (p. 20) “dup” appears when plus duplex, “dup –” appears when minus duplex (repeater) operation is selected. Eto...
Page 19
4 1 panel description 1 rnarrow mode indicator (p. 65) appears when the fm/am narrow mode is selected. Narrow mode is available with usa version only. Tam indicator (p. 65) appears when am mode is selected. Ysquelch attenuator indicator (p. 16) appears when the squelch attenuator function is activat...
Page 20: ■ Rear Panel
5 1 panel description ■ rear panel qdata socket [data] connects a tnc (terminal node controller), etc. For data communications. • see p. 6 for connection information. Wexternal speaker jack [sp] connects an 8 Ω speaker. • audio output power is more than 2.0 w. Ecooling fan rotates while transmitting...
Page 21
6 1 panel description 1 d data jack pin assignment q data in input terminal for data transmit. See p. 63 for details on how to toggle data speed between 1200 (afsk) and 9600 bps (g3ruh, gmsk). W gnd common ground for data in, data out and af out. E ptt p ptt terminal for packet operation only. Conne...
Page 22: ■ Microphone (Hm-133*)
7 1 panel description ■ microphone (hm-133*) qvfo/lock switch [vfo/lock] ➥ push to select vfo mode. (p. 11) ➥ push for 1 sec. To switch the lock function on and off. (p. 14) wptt switch ➥ push and hold to transmit; release to receive. ➥ switches between transmitting and receiving while the one-touch...
Page 23: ■ Microphone Keypad
8 1 panel description 1 ■ microphone keypad key function secondary function ( +key) other functions switches between opening and closing the squelch. (p. 15) starts and stops scanning. (p. 41) starts and stops priority watch. (p. 47) selects high output power. (p. 17) selects mid. Output power. (p. ...
Page 24
9 1 panel description ➥ cancels frequency entry. (p. 12) ➥ cancels the scan or priority watch. (pgs. 41, 47) ➥ exit set mode. (p. 56) ➥ enters set mode (p. 56) ➥ advances the set mode selection order after entering set mode. (p. 56) ➥ sets the keypad for numeral input. (p. 12) ➥ reverses the set mod...
Page 25: ■ Optional Microphones
10 1 panel description 1 ■ optional microphones (hm-118n/tn/tan) qptt switch push and hold to transmit; release to receive. Wup/down switches [up]/[dn] ➥ push either switch to change operating frequency, memory channel, set mode setting, etc. (pgs. 12, 26, 56) ➥ push either switch for 1 sec. To star...
Page 26: Setting A Frequency
11 setting a frequency 2 ■ preparation d turning power on/off ➥ push [pwr] for 1 sec. To turn power on and off. D operating frequency band selection the ic-208h has 2 m and 70 cm bands for transmission and reception. In addition, extra frequency bands 127, 220, 350, 500 and 900 mhz bands are availab...
Page 27: ■ Using The Tuning Dial
12 2 setting a frequency 2 ■ using the tuning dial q rotate [dial] to set the frequency. • if vfo mode is not selected, push [v/mhz•scan] to select vfo mode. • the frequency changes in the selected tuning steps. (p. 13) w to change the frequency in 1 mhz (10 mhz for some versions) steps, push [v/mhz...
Page 28: ■ Tuning Step Selection
13 2 setting a frequency ■ tuning step selection [ tuning steps are the minimum frequency change increments when you rotate [dial] or push [y]/[z] on the microphone. Independent tuning step for each frequency bands can be set for individual tuning convenience. The following tuning steps are availabl...
Page 29: ■ Lock Functions
14 2 setting a frequency 2 ■ lock functions to prevent accidental frequency changes and unnecessary function access, use the lock function. The transceiver has 2 different lock functions. D frequency lock this function locks [dial] and switches electronically and can be used together with the microp...
Page 30: Basic Operation
15 basic operation 3 ■ receiving q set the audio level. ➥ push [moni•dtmf] to open the squelch. ➥ rotate [vol] to adjust the audio level. ➥ push [moni•dtmf] to close the squelch. W set the squelch level. ➥ rotate [sql] fully counterclockwise in advance, then ro- tate [sql] clockwise until the noise ...
Page 31: ■ Squelch Attenuator
16 3 basic operation 3 ■ squelch attenuator the transceiver has an rf attenuator related to the squelch level setting. Approx. 10 db attenuation is obtained at maxi- mum setting. The squelch attenuator allows you to set a minimum signal level needed to open the squelch. The attenuator function can b...
Page 32: ■ Transmitting
17 3 basic operation ■ transmitting ☞ note: to prevent interference, listen on the channel be- fore transmitting by pushing [moni•dtmf] on the front panel or [ moni 1(bank)] on the microphone. Q select the frequency band. (p. 11) w set the operating frequency. (pgs. 11, 12) • select output power if ...
Page 33: ■ One-Touch Ptt Function
■ one-touch ptt function the ptt switch can be operated as a one-touch ptt switch (each push toggles between transmit/receive). Using this function you can transmit without pushing and holding the ptt switch. To prevent accidental, continuous transmission with this func- tion, the transceiver has a ...
Page 34: Repeater Operation
19 repeater operation 4 repeaters allow you to extend the operational range of your radio because a repeater has much higher output power than the typical transceiver. Normally, a repeater has independent frequencies for each receiver and transmitter. A subaudible tone may also be required to access...
Page 35: ■ Accessing A Repeater
20 4 repeater operation 4 ■ accessing a repeater q set the receive frequency (repeater output frequency). (pgs. 11, 12) w push [low•dup] for 1 sec. One or two times, to select minus duplex or plus duplex. • “dup–” or “dup” appears to indicate the transmit frequency for minus shift or plus shift, res...
Page 36
21 4 repeater operation z set the receive frequency (repeater output fre- quency). (pgs. 11, 12) x push [ dup – 7(tone)] to select minus duplex; push [ dup + 8(tsqls)] to select plus duplex. C push [func] then [ dup – 7(tone)] to turn on the subaudible tone encoder according to re- peater requiremen...
Page 37: ■ Subaudible Tones
22 4 repeater operation 4 ■ subaudible tones [ (encoder function) d subaudible tones q select the frequency band, mode/channel you wish to set the subaudible tones, such as vfo mode or memory/call channel. W push [set•lock] to enter set mode. E push [set•lock] or [dup•moni] several times until “t” a...
Page 38
D dtmf tones ➥ push [dtmf-s], then push the keys of the de- sired dtmf digits. • the function indicator lights green. • 0–9, a–d, m(e) and #(f) are available. • when “d” is displayed in place of the 100 mhz digit, cancel the dtmf memory encoder in advance. (p. 50) • push [dtmf-s] again to return the...
Page 39: ■ Offset Frequency
24 4 repeater operation 4 ■ offset frequency [ when communicating through a repeater, the transmit fre- quency is shifted from the receive frequency by an amount determined by the offset frequency. Independent offset frequencies can be set for each operating frequency. Q push [band] to select the de...
Page 40: ■ Auto Repeater
■ auto repeater (u.S.A. Version only) the usa version automatically activates the repeater settings (dup– or dup+ and tone encoder on/off) when the operating frequency falls within the general repeater output frequency range and inactivate them when outside of the range. D setting the auto repeater ...
Page 41: Memory Operation
26 5 memory operation 4 5 ■ general description the transceiver has 512 memory channels including 10 scan edge memory channels (5 pairs), and 2 call channels. Each of these channels can be individually programmed with operat- ing frequency (pgs. 11, 12), duplex direction (p. 21) and off- set (p. 24)...
Page 42
27 5 memory operation ■ programming a memory channel [example]: programming 145.870 mhz into memory channel 20 (blank channel) via the controller. Push rotate for setting frequency, etc. Push . Rotate push for 1 sec. And continue to push ➠ beep “ beep beep beep “ “ “ “ “ beep “ vfo settings, includi...
Page 43
28 5 memory operation 5 d programming a memory channel via the microphone [example]: programming 145.870 mhz into memory channel 20 (blank channel) via the microphone. Push 10 times beep “ beep “ beep beep beep “ “ “ “ “ push push then push then for 1 sec. And continue to push ➠ the microphone can a...
Page 44: ■ Copying Memory Contents
29 5 memory operation ■ copying memory contents this function copies a memory channel’s contents to vfo (or another memory/call channel). This is useful when searching for signals around a memory channel frequency and for re- calling the offset frequency, subaudible tone frequency etc. D memory/call...
Page 45
30 5 memory operation 5 d memory/call ➪memory/call q select the memory/call channel to be transferred. ➥ push [m/call•prio] several times to select memory mode or call channel, then rotate [dial] or push [band] to select the desired memory or call channel respec- tively. W push [s.Mw•mw] momentarily...
Page 46
31 5 memory operation ■ programming channel names each memory channel and the call channel can be pro- grammed with an alphanumeric channel name for easy recognition and can be indicated independently by channel. Names can be a maximum of 6 characters— see the table below for available characters. Q...
Page 47
32 5 memory operation 5 channel names can also be programmed via the mi- crophone. Z push [func] then [ clr a(mw)] momentarily. • “!” and memory channel number blink. X push [y]/[z] to select the memory/call channel to be as- signed memory names. C push [band]. • frequency readouts disappear and a c...
Page 48
5 memory operation 33 d d to indicate the channel name [ the channel name indication can be set for independent memory channels. Q push [m/call•prio] to select the memory mode. W rotate [dial] to select the desired memory channel to be indicated the channel name. E push [set•lock] to enter set mode....
Page 49: ■ Memory Clearing
5 memory operation 34 5 ■ memory clearing contents of programmed memories can be cleared (blanked), if desired. Q push [v/mhz•scan] to select vfo mode. W push [s.Mw•mw] momentarily. • “!” indicator and the memory channel number blink. E rotate [dial] to select the memory channel to be cleared. • mem...
Page 50: ■ Memory Bank Selection
35 5 memory operation ■ memory bank selection the ic-208h has a total of 10 banks (a to j) . Regular memory channels, 1 to 500, are assigned into the desired bank for easy memory management. Q push [m/call•prio] several times to select memory mode, if desired. W push [band] to select memory bank con...
Page 51: ■ Memory Bank Setting
36 5 memory operation 5 ■ memory bank setting [ q push [m/call•prio] several times to select memory mode, then select the desired memory channel via [dial]. W push [set•lock] to enter set mode. E push [set•lock] or [s.Mw•mw] several times until “bak” appears. R rotate [dial] to select the desired ba...
Page 52
37 5 memory operation ■ transferring bank contents [ contents of programmed memory banks can be cleared or transferred to another bank. Information: even if the memory bank contents are cleared, the memory channel contents still remain pro- grammed. Q select the desired bank contents to be transferr...
Page 53: Call Channel Operation
38 6 call channel operation 5 6 ■ call channel selection call channel is pre-programmed memory channel that can be accessed by simply pushing call channel button. ➥ push [m/call•prio] several times to select the call chan- nel mode then push [band] to select the desired call channel. • “c1” or “c2” ...
Page 54
39 6 call channel operation ■ programming a call channel operating frequency, duplex information, subaudible tone in- formation (tone encoder or tone squelch on/off and its fre- quency) can be programmed into the call channel. Q set the desired frequency in vfo mode. ➥ push [v/mhz•scan] to select vf...
Page 55: Scan Operation
40 7 scan operation 6 7 ■ scan types scanning searches for signals automatically and makes it easier to locate new stations for contact or listening purposes. There are 3 scan types and 4 resume conditions to suit your operating needs. Band scan (p. 41) repeatedly scans all frequen- cies over the en...
Page 56: ■ Scan Start/stop
41 7 scan operation ■ scan start/stop d preparation scan resume condition (p. 45); program the scan edges (pgs. 42, 43); program 2 or more memory channels (pgs. 27, 28); set skip settings (p. 44), if desired. D operation q select vfo mode for full/programmed scan with [v/mhz•scan]; or memory mode fo...
Page 57: ■ Scan Edges Programming
42 7 scan operation 7 ■ scan edges programming scan edges can be programmed in the same manner as memory channels. Scan edges are programmed into scan edges, 1a/1b to 5a/5b, in memory channels. Q set the edge frequency of the desired frequency range in vfo mode: ➥ set the frequency using [dial]. ➥ s...
Page 58
43 7 scan operation d programming scan edges via microphone z set the desired frequency in vfo mode. ➥ push [vfo/lock] to select vfo mode. ➥ set the frequency via the keypad or [y]/[z]. X push [func] then [ clr a(mw)] momentarily. C push [y] or [z] to select scan edge channels, 1a, 2a, 3a, 4a or 5a....
Page 59: ■ Skip Channel Setting
44 7 scan operation 7 ■ skip channel setting [ the memory skip function speeds up scanning by checking only those memory channels not set as skip channels. Set skip channels as follows. Q select a memory channel: ➥ push [m/call•prio] to select memory mode. ➥ rotate [dial] to select the desired chann...
Page 60: ■ Scan Resume Condition
45 7 scan operation ■ scan resume condition [ the scan resume condition can be selected as timer or pause scan. The selected resume condition is also used for priority watch. (p. 47) q push [set•lock] to enter set mode. W push [set•lock] or [s.Mw•mw] several times until “sct” or “scp” appears as sho...
Page 61: Priority Watch
46 8 priority watch 7 8 ■ priority watch types priority watch checks for signals on a vfo frequency every 5 sec. While operating in memory mode. The transceiver has 3 priority watch types to suit your needs. You can also trans- mit on the vfo frequency while the priority watch operates. The watch re...
Page 62
47 8 priority watch ■ priority watch operation q select vfo mode; then, set an operating frequency. W set the watching channel(s). For memory channel watch: select the desired memory channel. For memory scan watch: select memory mode; then, push [v/mhz•scan] for 1 sec. To start memory scan. For call...
Page 63: Dtmf Memory Encoder
48 9 dtmf memory encoder 8 9 ■ programming a dtmf code dtmf tones are used for autopatching, controlling other equipment, etc. The transceiver has 16 dtmf memory chan- nels (d0–df) for storage of often-used dtmf codes of up to 24 digits. Q push [moni•dtmf] for 1 sec. To turn the dtmf encoder on. • “...
Page 64
49 9 dtmf memory encoder d programming a dtmf code— via microphone z push [func] then [ low 6(dtmf)] to turn the dtmf encoder on. • “d” appears in place of 100 mhz digit. X push [ set b(d-off)] to enter the dtmf memory programming condition. C push [y] or [z] to select the desired dtmf memory channe...
Page 65
50 9 dtmf memory encoder 9 ■ transmitting a dtmf code d automatic transmission (dtmf memory) q push [moni•dtmf] for 1 sec. To turn the dtmf memory encoder on. • “d” appears in place of 100 mhz digit. W push [set•lock] to enter dtmf memory programming condition. E rotate [dial] to select the desired ...
Page 66: ■ Dtmf Speed
51 9 dtmf memory encoder d manual transmission z deactivate the dtmf memory encoder by pushing [func] then [ set b(d-off)]. X push [dtmf-s] to turn the dtmf direct selec- tion on. • the function indicator (microphone) lights green. C push one of “0” to “9” and “a” to “f” keys mo- mentarily, then pus...
Page 67: ■ Pocket Beep Operation
52 10 pocket beep and tone squelch 9 10 ■ pocket beep operation this function uses subaudible tones for calling and can be used as a “common pager” to inform you that someone has called while you were away from the transceiver. D waiting for a call from a specific station q set the operating frequen...
Page 68
53 10 pocket beep and tone squelch z set the operating frequency. X program the ctcss tone frequency or dtcs code in set mode. ➥ push [ set b(d-off)] to enter set mode. ➥ push [ set b(d-off)] or [ ent c(t-off)] several times until “ct” for tone squelch or “dt” for dtcs squelch appears. • “t sql” bli...
Page 69
54 10 pocket beep and tone squelch 10 ■ tone/dtcs squelch operation the tone or dtcs squelch opens only when receiving a sig- nal with the same pre-programmed subaudible tone or dtcs code, respectively. Q set the operating frequency. W program the ctcss tone frequency or dtcs code in set mode. • see...
Page 70: ■ Tone Scan
55 10 pocket beep and tone squelch ■ tone scan by monitoring a signal that is being operated with pocket beep, tone or dtcs squelch function, you can determine the tone frequency or dtcs code necessary to open a squelch. Q set the desired operating frequency or memory channel to be checked for a ton...
Page 71: Other Functions
56 11 other functions 10 11 ■ set mode • set mode operation q push [set•lock] to enter the set mode. W push [set•lock] or [s.Mw•mw] to select the desired item. E rotate [dial] to select the condition or value. R push [moni•dtmf] to exit set mode. • set mode items z push [ set b(d-off)] to enter set ...
Page 72
57 11 other functions d d display dimmer adjust to suit lighting conditions. The levels 1 (dark) to 8 (bright: default) are available. D d display color the display color can be set to amber (default), yellow or green. D d mic lock function sets the supplied hm-133’s (optional for some versions) key...
Page 73
58 11 other functions 11 d d dtcs code sets dtcs code (both encoder and decoder) for dtcs squelch operation. Total of 104 codes are available. (default: 023) d d dtcs polarity sets dtcs polarities for transmission and reception from “nn,” “nr,” “rn” and “rr.” (default: nn) d d offset frequency sets ...
Page 74
59 11 other functions d d scan resume timer selects scan resume timer from sct-15 (default), sct-10, sct-5 and scp-2. • sct-15/10/5 : scan pauses for 15/10/5 sec., then re- sumes. • scp-2 : pause on a signal until signal disap- pears, then resumes 2 sec. After the sig- nal disappears. D d channel sk...
Page 75
60 11 other functions 11 d d program scan skip setting sets the program scan skip setting from on and off for vfo scan operation, such as programmed scan. This item appears when set mode is accessed from vfo mode only. D d weather alert function turns weather alert function on and off. D d memory ba...
Page 76: ■ Initial Set Mode
61 11 other functions ■ initial set mode the initial set mode is accessed at power on and al- lows you to set seldom-changed settings. In this way, you can “customize” transceiver operations to suit your preference and operating style. • initial set mode items d d entering initial set mode q while p...
Page 77
62 11 other functions 11 d d key-touch beep the key-touch beep can be turned off for silent operation. D d time-out timer to prevent accidental prolonged transmission, etc., the trans- ceiver has a time-out timer. This function cuts a transmission off after 1–30 min. Of continuous transmission. This...
Page 78
63 11 other functions d d cooling fan control selects the cooling fan control condition from auto and on. • auto (at) : the fan rotates during transmit and for 2 min. After transmission, or when the internal tem- perature of the transceiver exceeds the pre- set value until the temperature drops. • o...
Page 79
64 11 other functions 11 d d active band selects the frequency selecting condition via [dial] or [y]/[z] on the microphone from all (al) and single (si). • all (al) : the operating frequency can be selected continuously. • single (si) : the operating frequency can be selected within the current band...
Page 80: ■ Am/fm Narrow Mode
65 11 other functions ■ am/fm narrow mode the ic-208h has am mode reception and fm narrow mode is available. Typically, am mode is used for the air band (118–135.995 mhz). Q select the desired frequency band in vfo mode, or the de- sired memory channel. W push [band] for 1 sec. To select am/fm narro...
Page 81
66 11 other functions 11 ■ weather channel operation (usa version only) d d weather channel selection q push [m/call•prio] several times to select weather channel group. W rotate [dial] to select the desired weather channel. E push [m/call•prio] to select memory mode, or push [v/mhz•scan] to select ...
Page 82: ■ Microphone Keys
67 11 other functions ■ microphone keys the supplied hm-133’s (optional for some versions) [f-1] and [f-2] keys memorize the transceiver conditions. The [up]/[dn] keys of the standard or an optional microphone (other than the hm-133) can be assigned functions like the function keys on the transceive...
Page 83: ■ Partial Reset
68 11 other functions 11 ■ partial reset if you want to initialize the operating conditions (vfo fre- quency, vfo settings, set mode contents) without clearing the memory contents. ➥ while pushing [v/mhz•scan] and [set•lock], push [pwr] for 1 sec. To partially reset. ■ all reset the function display...
Page 84: ■ Data Cloning
69 11 other functions ■ data cloning cloning allows you to quickly and easily transfer the pro- grammed contents from one transceiver to another; or data from a personal computer to a transceiver using the optional cs-208 cloning software . D cloning between transceivers q connect the opc-474 clonin...
Page 85
70 11 other functions 11 d cloning using a personal computer data can be cloned to and from a personal computer (mi- crosoft ® windows ® 98/2000/me/xp) using the optional cs-208 cloning software and the optional cloning cable opc-478u (usb type) or opc-478 (rs-232c type). Consult the cs-208 cloning ...
Page 86: ■ Packet Operation
71 11 other functions ■ packet operation d data speed for packet operation, the transceiver can be set to one of two data speeds: 1200 bps or 9600 bps. Q while pushing [set•lock], push [pwr] for 1 sec. To enter initial set mode. W push [set•lock] or [s.Mw•mw] to select the ‘bps’ item. E rotate [dial...
Page 87
72 11 other functions 11 • read the instructions supplied with your tnc carefully before attempting packet operation with the transceiver. • pin t af out is for 1200 bps operation only. This pin cannot be used for 9600 bps operation. • over modulation may degrade signal quality. If you find that man...
Page 88
73 11 other functions d 9600 bps high speed packet operation the transceiver supports 2 modes of 9600 bps packet opera- tion: g3ruh and gmsk. Q connect the transceiver and a tnc as illustrated below. W g3ruh mode can handle 16 kinds of modulated wave forms in order to maintain a communication link. ...
Page 89
74 11 other functions 11 d adjusting the transmit signal output from the tnc when setting data transmission speed to 9600 bps, the data signal coming from the tnc is applied exclusively to the in- ternal limiter circuitry to automatically maintain band width. Never apply data levels from the tnc of ...
Page 90: Maintenance
75 maintenance 12 problem possible cause solution ref. ■ troubleshooting if your transceiver seems to be malfunctioning, please check the following points before sending it to a service center. Does not turn on. No sound comes from the speaker. Sensitivity is low and only strong signals are audible....
Page 91: ■ Fuse Replacement
76 12 maintenance 12 ■ fuse replacement if the fuse blows or the transceiver stops functioning, find the source of the problem if possible, and replace the damaged fuse with a new, rated one (fgb 20 a) as shown at right. 20 a fuse problem possible cause solution ref. Some memory channels cannot be s...
Page 92: Specifications And Options
77 specifications and options 13 ■ specifications d d general • frequency coverage : usa rx 118.000–173.995 mhz* 1 , 230.000–549.995 mhz* 2 , 810.000–999.990 mhz* 3 tx 144–148 mhz, 440–450 mhz australia, asia rx 118.000–173.995 mhz* 1 , 230.000–549.995 mhz* 2 , 810.000–999.990 mhz tx 144–148 mhz, 43...
Page 93: ■ Options
78 13 specifications and options 13 ■ options hm-133 remote - control microphone wired remote control microphone with key backlight. Same as that supplied with the transceiver. Hm-118tan/tn dtmf microphone hm-118n hand microphone hs-62 flexible mobile microphone + hs-15sb switch box + opc-589 adapto...
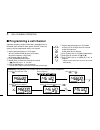
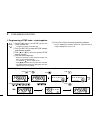
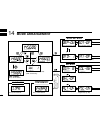
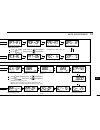
Page 94: Mode Arrangement
79 mode arrangement 14 key-touch beep (p. 62) time-out timer (p. 62) dtmf speed (p. 64) narrow transmission (p. 64) set mode dtmf memory clone mode call channel (p. 38) weather channel (p. 66) (usa version only) bank channel memory mode (p. 26) vfo mode (p. 11) initial set mode display dimmer (p. 57...
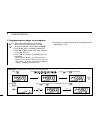
Page 95
80 14 mode arrangement 14 auto repeater (p. 62) (usa version only) auto power off (p. 62) cooling fan (p. 63) data speed (p. 63) squelch delay (p. 63) microphone sensitivity (p. 63) squelch attenuator (p. 63) active band (p. 64) repeater tone frequency (p. 57) tone squelch frequency (p. 57) dtcs cod...
Page 96
1-1-32 kamiminami, hirano-ku, osaka 547-0003 japan a-6265d-1ex printed in japan © 2003 icom inc..