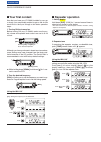
Previous view previous view 42 10 pocket beep and tone squelch tone scan by monitoring a signal that is being operated with the pocket beep, tone or dtcs squelch function turned on, you can determine the tone frequency or dtcs code necessary to open the squelch. Q set the channel to be checked for a...
Previous view functions and features of adobe ® reader ® the following functions and features can be used with adobe ® reader ® . • keyword search click “find (ctrl+f)” or “advanced search (shift+ctrl+f)” in the edit menu to open the search screen. This is convenient when search- ing for a particula...
Fm transceiver this device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation. Instructi...
Previous view i foreword thank you for purchasing this icom radio. The ic-2300h fm transceiver is designed and built with icom’s state of the art technology and craftsmanship. With proper care this radio should provide you with years of trouble-free operation. D features ❍ 65 w* — high transmit outp...
Previous view ii rwarning rf exposure! This device emits radiofrequency (rf) energy. Extreme caution should be ob- served when operating this device. If you have any questions regarding rf exposure and safety standards, please refer to the federal communications commission offi ce of engineering and...
Previous view iii table of contents foreword ......................................................................................... I important .......................................................................................... I explicit definitions ..........................................
Previous view iv quick reference guide ■ installation d location select a location which can support the weight of the transceiver and does not interfere with driving in any way. We recommend the locations shown in the dia- gram below. Rwarning! Never place the transceiver where normal operation of ...
Previous view v quick reference guide d antenna installation • antenna location to obtain maximum performance from the transceiver, select a high-quality antenna and mount it in a good location. When you use a magnetic mount, use a non- radial antenna. Roof-mount antenna (drill a hole or use a magne...
Previous view vi quick reference guide ■ your fi rst contact now that you have your ic-2300h installed in your car or shack, you are probably excited to get on the air. We would like to take you through a few basic operation steps. 1. Turning on the transceiver before turning on your ic-2300h, make ...
Previous view vii quick reference guide the ic-2300h has a total of 207 memory channels for storing often used operating frequencies, repeater set- tings, and so on. Memories include 6 scan edges and 1 call channel. 1. Setting the frequency in the vfo mode, set the desired operating frequency, repea...
Previous view q power key [ ] hold down for 1 second to turn power on or off. W memory write key [s.Mw mw] (p. 17) ➥ push to enter the memory write mode. ➥ hold down for 1 second to program a selected memory channel. • continue to hold down the key to automatically increment the memory channels. E m...
Previous view 2 q frequency readout shows the operating frequency, channel name, set mode contents, and so on. • the frequency decimal point blinks during a scan. (p. 30) • while the dtmf memory function is in use, “d” ap- pears in the 100 mhz digit. (p. 36) w transmit icon ➥ appears while transmitt...
Previous view 3 1 panel description q antenna connector [ant] connect a 50 Ω antenna with a pl-259 connector, through a 50 Ω coaxial cable. W power receptacle [dc13.8v] connect a 13.8 v dc ±15% power source with the supplied dc power cable. Note: do not use a cigarette lighter socket as a power sour...
Previous view 4 1 panel description ■ microphone keypad key function secondary function ( +key) other function opens and closes the squelch. (p. 8) turns the channel names or number display on or off, in the memory mode. (p. 21) after pushing [dtmf-s] , transmits the appropriate dtmf code. (pp. 14, ...
Previous view 5 setting a frequency 2 preparation ■ d turning power on/off ➥ hold down [ ] for 1 second to turn the power on or off. D vfo mode selection the ic-2300h has 2 basic operating modes; vfo mode and memory mode. ➥ push [v/mh z] to select the vfo mode. • push [m/call] to select the memory m...
Previous view 6 ■ tuning step selection the tuning step is the smallest selectable frequency increment you can set the operating frequency. The fol- lowing tuning steps are selectable. • 5 khz • 6.25 khz • 10 khz • 12.5 khz • 15 khz • 20 khz • 25 khz • 30 khz • 50 khz note: for convenience, select t...
Previous view 7 2 setting a frequency ■ lock functions use the lock function to prevent accidental channel changes and unnecessary function access. The ic- 2300h has two different lock functions. D lock function this function electronically locks [dial] and the key- pad. This function can be used to...
Previous view 8 basic operation 3 ■ receiving q hold down [ ] for 1 second to turn on the power. W rotate [vol] to adjust the audio level. ➥ push [moni] to open the squelch, and then rotate [vol] to adjust the audio level. E set the squelch level. ➥ first, rotate [sql] fully counterclockwise, and th...
Previous view 9 ■ audio mute function this function temporarily mutes the audio without dis- turbing the volume setting. ➥ push [func] then [mute] to mute the au- dio. • the “mute” icon appears. • push [clr] to cancel the function. ■ squelch attenuator the transceiver has an rf attenuator related to...
Previous view 10 3 basic operation ■ transmitting caution: transmitting without an antenna will dam- age the transceiver. Note: to prevent interference, listen on the channel before transmitting by opening the squelch. To open the squelch, rotate [dial] counterclockwise or push [sql z ] on the micro...
Previous view 11 3 basic operation lock set anm moni dup low t-scan tone prio m/call scan v/ mhz digital prio ao busy mute nar mid low ■ selecting output power the ic-2300h has 4* output power levels to suit your operating requirements. Lower output powers during short-distance communications may re...
Previous view 12 3 basic operation ■ accessing a repeater q set the receive frequency (repeater output frequen- cy). (p. 5) • for only usa versions: when the auto repeater function is set to “r1” (p. 16), steps w and e are not necessary. When the auto repeater function is set to “r2” (p. 16), steps ...
Previous view 3 basic operation 13 ■ subaudible tones (encoder function) d subaudible tones q select the channel that you want to set the subaudible tone to, such as the vfo, memory or call channel. • the subaudible tone frequency or code is indepen- dently programmed into each mode or channel. W pu...
Previous view 14 3 basic operation d dtmf tones z when “d” is displayed in the 100 mhz digit, fi rst can- cel the dtmf memory encoder. (p. 37) x push [dtmf-s] , and then push the keys of the desired dtmf digits. • the function indicator lights green. • 0–9, a–d, m(e) and #(f) are selectable. • push ...
Previous view 15 repeater setting 4 ■ frequency offset when communicating through a repeater, the transmit frequency is shifted up or down from the receive fre- quency. Q push [set] to enter the set mode. W push [set] or [moni] until the “±” icon and the fre- quency offset appear. E rotate [dial] to...
Previous view ■ reversed duplex function when the reversed duplex function is on, the receive frequency shifts. (the transmit frequency shifts in normal duplex mode.) an example receive and transmit frequency is shown in the table below with the following settings: input frequency : 145.30 mhz offse...
Previous view ■ general description the transceiver has 207 memory channels including 6 scan edge memory channels (3 pairs), and 1 call chan- nel. These channels can be individually programmed with: • operating frequency (p. 5) • duplex direction (p. 12) and offset (p. 15) • subaudible tone or tone ...
Previous view 18 ■ memory channel selection using the tuning dial d q push [m/call] once or twice to select the memory mode. • the “ ” icon appears. W rotate [dial] to select the desired memory channel. • only programmed memory channels can be se- lected. D using [y] or [z] on the hm-133v z push [mr...
Previous view ■ copying memory contents this function copies a memory channel’s contents to the vfo, another memory or call channel. This function is useful when searching for signals around the memory channel frequency, and for easy recalling the frequency offset, subaudible tone frequency, and so ...
Previous view 20 d memory/call channel➪call/memory channel q select the memory or call channel to be copied. W push [s.Mw]. • the “ ” icon and “– –” indication blink. E rotate [dial] to select the target memory channel. • “c” blinks when the call channel is selected. • scan edge channels; 1a/1b, 2a/...
Previous view 21 5 memory operation ■ programming channel names each memory channel and the call channel can be programmed with an alphanumeric channel name, for easy recognition. Names can be a maximum of 6 char- acters— see the table to the right, for the selectable characters. Q push [m/call] to ...
Previous view 5 memory operation 22 ■ memory clearing contents of programmed memories can be cleared (blanked). Q push [v/mh z] to select the vfo mode. W push [s.Mw]. • the “ ” icon and the memory channel number blink. E rotate [dial] to select the memory channel to be cleared. • memory channels not...
Previous view 23 5 memory operation ■ memory bank setting q push [m/call] to select the memory mode, and then rotate [dial] to select the desired memory channel. W push [set] to enter the set mode. E push [set] or [moni] until “bak” appears. • “– –” indication blinks. R rotate [dial] to select the d...
Previous view 24 5 memory operation ■ memory bank selection the ic-2300h has a total of 10 banks (a to j). Regular memory channels; 0 to 199, and scan edges; 1a to 3b can be assigned into the desired bank for easy memory management. Q push [m/call] to select the memory mode. W push [bank] to select ...
Previous view 25 5 memory operation ■ transferring bank links the link between a memory channels and it's assigned bank can be transferred to another bank. Q push [m/call] to select the normal memory mode. • the “ ” icon and the channel number appear. W push [bank] to select the memory bank mode. • ...
Previous view 26 5 memory operation [i.E.]: erasing the link of bank “a." ■ erasing bank links the link between a memory channel and it's assigned bank can be erased. Information: even if the memory bank links are erased, the memory channel contents remain pro- grammed. Q push [m/call] to select the...
Previous view 27 call channel operation 6 ■ call channel selection ➥ push [m/call] once or twice to select the call channel. • “c” appears instead of a memory channel number. • push [m/call] to return to the memory mode, or push [v/mh z] to select the vfo mode. Using the hm-133v ➥ hold down [call] f...
Previous view 28 ■ programming a call channel operating frequency, duplex setting, subaudible tone setting (tone encoder or tone squelch on/off and its frequency) and channel names can be also pro- grammed into the call channel. Q push [v/mh z] to select the vfo mode, and set the desired frequency. ...
Previous view 29 scan operation 7 ■ scan types scanning automatically searches for signals making it easier to locate new stations for contact or listening pur- poses. There are 3 scan types and 4 resume conditions to suit your operating needs. Full scan band edge band edge scan jump repeatedly scan...
Previous view 30 ■ scan start/stop preparation d if desired, set the scan resume option (p. 33), program the scan edges (p. 31), program 2 or more memory channels (p. 17), set the skip channels (p. 32). Operation d q select the mode or bank. For full/programmed scan: ➥ push [v/mh z] to select the vf...
Previous view 31 7 scan operation ■ scan edges programming scan edges can be programmed in the same manner as memory channels. Scan edges are programmed into scan edges, 1a/1b to 3a/3b, in memory channel sheet. Q set the desired edge frequency in the vfo mode: w push [mw] (s.Mw). • the “ ” icon and ...
Previous view 32 7 scan operation ■ skip channel setting the memory skip function speeds up scanning by not scanning those memory channels set as skip channels. Set skip channels as follows. Q push [m/call] to select the memory mode, and then select the memory channel to be skipped. W push [set] to ...
Previous view 33 7 scan operation ■ scan resume function various pause and timer options can be selected with the scan resume function. The selected resume op- tion is also used for priority watch. (p. 35) q push [set] to enter the set mode. W push [set] or [moni] until “sct” or “scp” ap- pears. E r...
Previous view 34 priority watch 8 ■ priority watch types ic-2300h has three types of priority watch, to suit your needs. You can transmit on the vfo frequency, even while priority watch is functioning. The watch resumes, depending on the selected scan resume function. See the page 33 for details. No...
Previous view 35 ■ priority watch operation q select the vfo mode, and then set the operating frequency. W set the watching channel. For a memory channel watch: push [m/call] to select the memory mode, and then rotate [dial] to select the desired memory channel. For a memory scan watch: select the m...
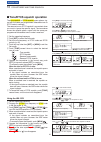
Previous view 36 dtmf memory encoder 9 ■ programming a dtmf code dtmf codes are used for autopatching, controlling other equipment, and so on. Ic-2300h has up to 16 dtmf memory channels (d0–df) for up to 24 digits often-used dtmf codes . Q hold down [opt] (bank) for 1 second to enter the option set ...
Previous view 37 ■ transmitting a dtmf code automatic transmission (dtmf memory) d q hold down [opt] (bank) for 1 second to enter the option set mode. W if necessary, push [set] or [moni] to select “dtm.” e rotate [dial] to turn on the dtmf encoder. R push [bank] to enter the dtmf memory mode. • the...
Previous view 38 9 dtmf memory encoder ■ dtmf tx speed the transmitting speed of dtmf code can be set to ac- commodate your operating needs. Q hold down [ ] for 1 second to turn off the power. W while holding down [lock] (set) and [ ] for 1 second, to turn on the power to enter the initial set mode....
Previous view 39 ■ pocket beep operation this function uses subaudible tones as calling, and can be used as a “common pager” to inform you that some- one has called while you were away from the trans- ceiver. D waiting for a call from the specifi c station q set the operating frequency. W push [set]...
Previous view 40 10 pocket beep and tone squelch 67.0 69.3 71.9 74.4 77.0 79.7 82.5 85.4 88.5 91.5 94.8 97.4 100.0 103.5 107.2 110.9 114.8 118.8 123.0 127.3 131.8 136.5 141.3 146.2 151.4 156.7 159.8 162.2 165.5 167.9 171.3 173.8 177.3 179.9 183.5 186.2 189.9 192.8 196.6 199.5 203.5 206.5 210.7 218.1...
Previous view 41 ■ tone/dtcs squelch operation the tone squelch or dtcs squelch opens when a sig- nal with the same pre-programmed subaudible tone or dtcs code is received. The reverse tone or dtcs squelch is convenient when you want to ignore the specifi c signal. The transceiver closes the squelch...
Previous view 42 10 pocket beep and tone squelch ■ tone scan by monitoring a signal that is being operated with the pocket beep, tone or dtcs squelch function turned on, you can determine the tone frequency or dtcs code necessary to open the squelch. Q set the channel to be checked for a tone freque...
Previous view 43 ■ set mode • set mode operation q push [set] to enter the set mode. W push [set] or [moni] to select the desired item. E rotate [dial] to set the option or value. R push any key other than [set] or [moni], to exit the set mode. Using the hm-133v z push [set] to enter the set mode. X...
Previous view 44 11 other functions select the display backlight color. Adjust the lcd contrast. Turns the tx inhibit function on or off. Turns the skip function on or off. Assign the desired memory and scan edge channels. Assign the desired banks for a continuous banks scan. Set both the transmissi...
Previous view 11 other functions 45 repeater tone d select the subaudible tone needed to access the re- peater. A total of 50 tone frequencies (67.0–254.1 hz) are selectable. (default: 88.5 hz) lock set anm moni dup low t-scan tone prio m/call scan v/ mhz digital prio ao busy mute nar mid low tone s...
Previous view 46 11 other functions display color d select the display backlight color from amber (default), yellow or green. Lock set anm moni dup low t-scan tone prio m/call scan v/ mhz digital prio ao busy mute nar mid low lock set anm moni dup low t-scan tone prio m/call scan v/ mhz digital prio...
Previous view 11 other functions 47 ■ initial set mode entering the initial set mode d q while holding down [set], hold down [ ] for 1 sec- ond to enter the initial set mode. W push [set] or [moni] to select the desired item. E rotate [dial] to set the option or value. R push [ ] to exit the initial...
Previous view 48 11 other functions key-touch beep d turn the confi rmation beeps on (default) or off. Lock set anm moni dup low t-scan tone prio m/call scan v/ mhz digital prio ao busy mute nar mid low time-out timer d to prevent accidental prolonged transmission, the transceiver has a time-out tim...
Previous view 49 11 other functions tone burst d turn the tone burst function on or off. • of : when you transmit a signal that superimposes the ctcss tone or subaudible tone, the squelch tail noise may be audible on the rx side. • on : when you transmit a signal which superimposes the ctcss tone or...
Previous view 50 11 other functions weather channel operation ■ weather channel selection d q push [m/call] several times to select the weather channel group. W rotate [dial] to select the desired weather chan- nel. E push [m/call] to select the memory mode, or push [v/mh z] to select the vfo mode. ...
Previous view 11 other functions 51 ■ microphone keys [f-1] and [f-2] on the supplied hm-133v memorize the transceiver settings. The [up] and [down] keys on the standard or optional mi- crophone (other than the hm-133v) can be assigned func- tions like the function keys on the transceiver’s front pa...
Previous view 52 11 other functions ■ partial reset if you want to reset the vfo frequency, vfo settings and set mode items to their default values, without clearing the memory contents, you can do a partial reset of the transceiver's cpu. ➥ while holding down [v/mhz], hold down [ ] for 1 sec- ond t...
Previous view 53 11 other functions ■ data cloning cloning allows you to quickly and easily transfer the programmed contents from one transceiver to another, or data from a personal computer to a transceiver, us- ing the optional cs-2300h cloning software . D cloning between two transceivers q conne...
Previous view 54 m general • frequency coverage : (unit: mhz) usa tx: 144–148/rx: 136–174* export, china tx: 136–174*/rx: 136–174* taiwan, korea tx/rx: 144–146 *guaranteed: 144–148 mhz range only. • type of emission : fm • number of memory channels : 207 (incl. 6 scan edges and 1 call) • scan types ...
Previous view 55 troubleshooting ■ ■ fuse replacement if the fuse is blown or the transceiver stops functioning, fi nd the source of the problem if possible, repair the problem and then replace the damaged fuse with a new rated one (fgb 20 a), as shown at right. 20 a fuse problem possible cause solu...
A-6966-1ex- w printed in japan © 2011–2012 icom inc. 1-1-32 kamiminami, hirano-ku, osaka 547-0003, japan.