- DL manuals
- Icom
- Transceiver
- IC-2710H
- Instruction Manual
Icom IC-2710H Instruction Manual
Summary of IC-2710H
Page 1
Instruction manual ic- 2710h dual band fm transceiver ic-2710h.Qxd 02.2.8 16:55 page a (1,1).
Page 2
R warning! Never connect the transceiver to an ac outlet. This may pose a fire hazard or result in an electric shock. R warning! Never operate the transceiver while driving a vehicle. Safe driving requires your full attention— anything less may result in an accident. Never connect the transceiver to...
Page 3
Ii unpacking accessories included with the transceiver: qty. ➀ dc power cable (opc-346)............................................. 1 ➁ mobile mounting bracket ................................................. 1 ➂ microphone (hm-98)........................................................ 1 ➃ fuse (...
Page 4
Table of contents iii important .................................................................................... I explicit definitions ................................................................. I cautions ......................................................................................
Page 5
Iv ■ calling up a scratch pad memory ....................................................... 39 ■ transferring scratch pad memory contents ........................................ 40 9 scan operation ........................................................ 41 – 46 ■ scan types .........................
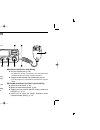
Page 6: Panel Description
Panel description 1 1 q power switch [power] turns power on and off when pushed for 1 sec. W tuning dials ➥ select the operating frequency (p. 17), the memory channel (p. 32), the contents of the set mode display (p. 82) and the scanning direction. (p. 42) ➥ select the main band when pushed. (p. 15)...
Page 7
1 panel description 2 t vfo/mhz switches [v/mhz(scan)] ➥ select and toggle vfo mode and 1 mhz tuning display. ➥ start a scan when pushed and held. (p. 42) y memory/call channel switches [m/call(prio)] ➥ select and toggle memory mode or a call channel. (pgs. 32, 37) ➥ activate the priority watch func...
Page 8: Function Display
1 panel description 3 q sub band access indicators (p. 22) appear when the sub band access function is activated and indicate the function control band via the microphone and some front panel switches (except transmitting). W main band indicators (p. 15) indicate the main band for transmit and funct...
Page 9
4 1 panel description u external dtmf control indicator (p. 63) appears when the optional external dtmf control function is in use. • available for the u.S.A. Version only. I tot (time-out timer) indicator (p. 72) appears while the time-out timer has been activated. O audio mute indicators (p. 21) a...
Page 10: Rear Panel
1 panel description 5 ■ rear panel q w e r q antenna connector [ant] accepts a 50 Ω dual band antenna with a pl-259 connec- tor. (p. 14) w speaker jack 1 [144 mhz sp] connects a 4–8 Ω speaker, if required. Outputs the 144 mhz band’s audio. See the table at right for details. E speaker jack 2 [430(44...
Page 11: Microphone
1 panel description 6 ■ microphone lock vfo call mr sub band mw func a clr d-off b set ptt-m 3 prio dtmf 6 low afc-off 2 scan csql 5 mid afc 1 moni pgr 4 high t-off c ent tsql 9 simp 16key lock # tsql s 8 dup+ tone-2 0 tone 7 dup tone-1 f-2 f-1 dtmf-s mute d sql sql vol vol mic element q w e r t y u...
Page 12: Microphone Keypad
1 panel description 7 ■ microphone keypad function secondary function (after ) func other functions toggles between opening and closing the accessed band’s squelch. (p. 20) no secondary function. After : transmit the appropriate dtmf code or push [1] to [8] to transmit the dtmf memory contents when ...
Page 13
1 panel description 8 key function secondary function (after ) func other functions • clears a digit before entry. (p. 19) • cancels the scan, priority watch, pager, code squelch or dtmf memory function. (pgs. 42, 48, 51, 59, 62) • writes the vfo contents into the memory channel or call channel. (pg...
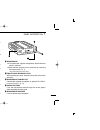
Page 14: Installation
D separate installation • optional opc-600 separation cable (3.5 m; 11.5 ft) or opc-601 (7.0 m; 23.0 ft) is necessary. • optional mb-58 remote controller bracket is available for front panel mounting. • optional mb-65 mounting base is available for increasing front panel mounting possibilities (mb-5...
Page 15: Location
2 installation 10 ■ location select a location which can support the weight of the trans- ceiver and does not interfere with driving in any way. We rec- ommend the locations shown in the diagram below. ■ single body installation ➀ drill 4 holes where the mounting bracket is to be installed. • approx...
Page 16: Microphone Connection
2 installation 11 ■ microphone connection the microphone connector is located behind the front panel. Connect the supplied microphone as follows: ➀ push the release button, then detach the remote controller as shown below. ➁ connect the supplied microphone to the microphone con- nector. ➂ reattach t...
Page 17: Optional Mb-58 Installation
2 installation 12 ■ optional mb-58 installation the optional mb-58 remote controller bracket is avail- able for separate installation. ➀ drill 2 or 4 holes where the bracket or mounting base is to be installed, respectively. • approx. 4 mm ( 1 ⁄ 8 in) when using nuts; approx. 1–2 mm ( 1 ⁄ 16 in) whe...
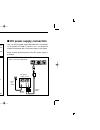
Page 18: Battery Connection
2 installation 13 ■ battery connection ■ dc power supply connection use a 13.8 v dc power supply with more than 12 a capabil- ity. An optional ic-ps30 dc power supply is available for using the transceiver with a dc power supply in your home. Make sure the ground terminal of the dc power supply is g...
Page 19: Antenna Installation
2 installation 14 ■ antenna installation d antenna location to obtain maximum performance from the transceiver, select a high-quality antenna and mount it in a good location. A non- radial antenna should be used when using a magnetic mount. D antenna splitter you can use a dual band antenna because ...
Page 20: Setting A Frequency
Setting a frequency 3 15 ■ preparation d turning power on push [power] for 1 sec. To turn power on. D main band the ic-2710h can receive 144 mhz and 430(440) mhz band signals simultaneously. Function access or frequency changes affect the main band only. In addition, signals can be transmitted on th...
Page 21: Lock Functions
3 setting a frequency 16 ■ lock functions to prevent accidental frequency changes and unnecessary function access, use the lock function. The transceiver has 2 different lock functions. D frequency lock this function locks the tuning dials and switches electronically and can be used together with th...
Page 22: Using A Tuning Dial
3 setting a frequency 17 ■ using a tuning dial ➀ rotate the desired band’s tuning dial to set the frequency. • if vfo mode is not selected, push the same band’s [v/mhz] to select vfo mode. • frequency changes according to the selected tuning steps. (p. 18) ➁ for the 1 mhz frequency setting, rotate t...
Page 23: Tuning Step Selection
3 setting a frequency 18 ■ tuning step selection tuning steps are the minimum frequency change increments when you rotate the tuning dial or push the [ y ] or [ z ] switches on the microphone. The following tuning steps are available: • 5 khz • 10 khz • 12.5 khz • 15 khz • 20 khz • 25 khz • 30 khz •...
Page 24: Using The Keypad
3 setting a frequency 19 ■ using the keypad the frequency can be directly set via numeral keys on the microphone. Ä push [band] to set the main band, if necessary. Å push [vfo] to select vfo mode. Ç push [ent] to activate the keypad for digit input. É push 5 keys to input a frequency. • when a digit...
Page 25: Basic Operation
Basic operation 4 20 ■ receiving the ic-2710h can receive 144 mhz and 430(440) mhz band signals simultaneously. ➀ push [power] for 1 sec. To turn power on. ➁ set the audio levels. ➥ push [ (sql) moni] to open the squelch. ➥ rotate the [vol] control to adjust the audio output level. ➥ push [ (sql) mo...
Page 26: Avionics Band Receive
4 basic operation 21 ■ avionics band receive (u.S.A. Version only) am mode can be selected over the range of 118.000 to 135.995 mhz for reception of avionics-related broadcasts. ➥ push and hold [ (sql) moni] to toggle between am and fm modes. • mode selection cannot be performed via the microphone. ...
Page 27: Sub Band Access
4 basic operation 22 ■ sub band access this function allows you to change sub band settings such as duplex settings, especially useful from the microphone, during transmission standby on the main band. It’s easy to access the sub band and return to the main band with the band switch. ➀ push and hold...
Page 28: Sub Band Mute/
4 basic operation 23 ■ sub band mute/ sub band busy beep the sub band mute function automatically cuts out sub band af signals when both main and sub band signals are re- ceived simultaneously. The sub band busy beep sounds when the sub band’s squelch is closed to inform you that the sub band’s sque...
Page 29: Para-Watch
4 basic operation 24 ■ para-watch the ic-2710h can simultaneously receive 2 signals on the same band, 144 mhz or 430(440) mhz band, using the para- watch function. [example] can be switched between vhf and uhf. ➀ push the desired band's tuning dial to assign the main band. ➁ push and hold the main b...
Page 30: Transmitting
4 basic operation 25 ■ transmitting note: ➥ to prevent interference, listen on the frequency before transmitting by pushing the main band’s [ (sql) moni] or the microphone’s [ ➀ moni]. ➥ to prevent howling and sensitivity rejection, avoid set- ting the 430(440) mhz band frequency near a multiple of ...
Page 31: Crossband Full Duplex
4 basic operation 26 the microphone can select the desired output power directly. Ä push [band] to select the desired band, if nec- essary. Å push [ ➃ high] for high output power; [ ➄ mid] for middle output power; and [ ➅ low] for low out- put power. • the output power cannot be changed while trans-...
Page 32: Repeater Operation
Repeater operation 5 27 ■ operation ➀ push the desired band’s tuning dial. ➁ set the receive frequency (repeater output frequency). (pgs. 15–19) ➂ push and hold [dup] to select – duplex or push it for 1 sec. Again for + duplex. • “dup –” or “dup” appears to indicate the transmit frequency for minus ...
Page 33
5 repeater operation 28 Ä push [band] to select the desired band, if nec- essary. Å set the receive frequency (repeater output fre- quency). (pgs. 15–19) Ç push [ ➆ dup–] to select – duplex; push [ ➇ dup+] for + duplex. É push [func] then [ ➆ tone] to turn on the sub- audible tone encoder according ...
Page 34: Subaudible Tones
5 repeater operation 29 ■ subaudible tones ➀ push the desired band’s tuning dial. ➁ select the mode/channel you wish to set the subaudible tone frequency to, such as vfo mode or memory/call channel. ➂ push [set] one or more times until “t” appears and flashes as shown above. • push [moni] to reverse...
Page 35: Offset Frequency
5 repeater operation 30 ■ offset frequency ➀ push the desired band’s tuning dial. ➁ select the mode/channel you wish to set the offset fre- quency to, such as vfo mode or memory/call channel. • the offset frequency can be independently programmed into each mode or channel. ➂ push [set] one or more t...
Page 36: Auto Repeater
5 repeater operation 31 ■ auto repeater (u.S.A. Version only) the u.S.A. Version automatically activates the repeater set- tings (dup or dup– and tone encoder on/off) when the operating frequency falls within the general repeater output frequency range and deactivates them when outside of the range....
Page 37: Memory Operation
Memory operation 6 32 ■ general description the transceiver has 99 regular memory channels plus 6 scan edge memory channels (3 pairs) on each band; each of these can be individually programmed with the following data. • operating frequency (pgs. 15–19) • duplex direction (dup or dup–) and its offset...
Page 38: Programming A Memory Channel
6 memory operation 33 ■ programming a memory channel vfo mode settings, including the set mode contents such as subaudible tone frequency, etc., are programmed into a mem- ory channel. ➀ set the desired frequency in vfo mode: ➥ push the desired band’s [v/mhz] to select vfo mode. ➥ set the frequency ...
Page 39
6 memory operation 34 ■ programming a memory channel via the microphone memory channel programming can be performed via the microphone. Ä push [band] to select the desired band, if necessary. Å set the desired frequency in vfo mode: ➥ push [vfo] to select vfo mode. ➥ set the frequency using the keyp...
Page 40: Transferring Memory
6 memory operation 35 ■ transferring memory contents this function transfers a memory channel’s contents into a vfo (or another memory/call channel). This is useful when search- ing for signals around a memory channel frequency and for re- calling the offset frequency, subaudible tone frequency, etc...
Page 41: Memory Clearing
■ memory clearing contents of programmed memories can be cleared (blanked), if desired. ➀ push [s.Mw] momentarily. ➁ select the memory channel to be cleared with the tuning dial. ➂ push [s.Mw] briefly, then a second time for 1 sec. • 3 beeps sound, then the frequency is cleared. • “ ! ” flashes cont...
Page 42: Call Channel Operation
Call channel operation 7 37 ■ calling up a call channel each band has an independent call channel to store a most- often-used frequency for quick recall. ➀ push the desired band’s [m/call] once or twice to display a large “c” in the memory channel readout. • to transmit on the call channel, select t...
Page 43: Programming A Call Channel
7 call channel operation 38 ■ programming a call channel in addition to an operating frequency, duplex information and subaudible tone information (tone encoder or tone squelch* on/off and its frequency) can be programmed into the call channel. *an optional ut-104 is necessary. ➀ push the desired ba...
Page 44: Scratch Pad Memory
Scratch pad memory 8 39 ■ what is a scratch pad memory? During vfo operation, the transceiver automatically memo- rizes operating frequency information, separate from regular memory channels, when transmitting on a new frequency. The 3 previously operated frequencies for each band can be recalled. N...
Page 45: Transferring Scratch Pad
8 scratch pad memory 40 ➀ push the desired band’s tuning dial. ➁ select the call channel by pushing the selected band’s [m/call] once or twice. • a large “c” appears. ➂ rotate the selected band’s tuning dial to select the desired scratch pad memory. • one of “l1”–“l3” appears. ➃ push [ (s.Mw) mw] mo...
Page 46: Scan Operation
Scan operation 9 41 full scan (p. 42) repeatedly scans all fre- quencies over the entire band. Used as the sim- plest scan without any pre- liminary settings neces- sary. Programmed scan (p. 42) repeatedly scans bet- ween two user- programmed frequencies. Used for checking for fre- quencies within a...
Page 47: Scan Start/stop
■ scan start/stop d pre-operation • common setting: scan resume condition. (p. 46) • for programmed scan: program the scan edges. (p. 43) • for memory scan: program 2 or more memory chan- nels; set memory skip settings, if de- sired. (p. 45) d operation ➀ push the desired band’s tuning dial. ➁ selec...
Page 48: Programming Scan Edges
9 scan operation 43 ■ programming scan edges scan edges can be programmed in the same manner as memory channels. Scan edges are programmed into pairs of scan edge channels, 1a/1b to 3a/3b, in memory channels. ➀ push the desired band’s tuning dial. ➁ set the desired frequency in vfo mode: ➥ push the ...
Page 49: Programming Scan Edges Via
9 scan operation 44 ■ programming scan edges via the microphone Ä push [band] to select the desired band, if nec- essary. Å set the desired frequency in vfo mode: ➥ push [vfo] to select vfo mode. ➥ set the frequency using the keypad. Ç push [func] then [ e mw] momentarily. É push [ y ] or [ z ] to s...
Page 50: Skip Channel Setting
9 scan operation 45 ■ skip channel setting the memory skip function speeds up scanning by checking only desired memory channels. Set the memory channels to be skipped or scanned as follows. ➀ push the desired band’s tuning dial. ➁ select the memory channel to program or to cancel the skip function o...
Page 51: Scan Resume
9 scan operation 46 ■ scan resume condition the scan resume condition can be selected as timer, pause or empty pause scan. The empty pause scan is useful for finding unused frequencies. The resume condition is also used for priority watch. (p. 47) ➀ push the desired band’s tuning dial. ➁ push [set] ...
Page 52: Priority Watch
Priority watch 10 47 ■ priority watch types priority watch checks for signals on a memory or call chan- nel every 5 sec. While operating on a vfo frequency. The transceiver has 3 priority watch types to suit your needs. You can transmit on the vfo frequency while the priority watch operates. The wat...
Page 53: Priority Watch Operation
10 priority watch 48 ■ priority watch operation ➀ push the desired band’s tuning dial. ➁ select vfo mode; then, set an operating frequency. ➂ set the watching channel(s). For memory channel watch: select the desired memory channel. For memory scan watch: select memory mode; then, push [ (v/mhz) scan...
Page 54: Dtmf Memory Encoder
Dtmf memory encoder 11 49 ■ programming a dtmf code dtmf codes are used for autopatching, accessing repeaters, controlling other equipment, etc. The transceiver has 8 dtmf memory channels (d1– d8) for storage of often-used dtmf codes of up to 16 digits. Note: dtmf memory channels are commonly used f...
Page 55
11 dtmf memory encoder 50 ■ programming a dtmf code via the microphone [example]: programming “5428ab453” into dtmf memory channel “d4.” dtmf codes can be directly programmed via the keypad on the microphone. The contents can be overwritten, but cannot be cleared via the micro- phone. See the page a...
Page 56: Transmitting A Dtmf Code
11 dtmf memory encoder 51 ■ transmitting a dtmf code d using the dtmf memory function (automatic transmission) the selected dtmf code is transmitted at each push of the ptt switch when the dtmf memory encoder is turned on. ➀ push [dtmf] to turn the dtmf memory encoder on. • “d” appears in place of t...
Page 57: Dtmf Speed
11 dtmf memory encoder 52 ■ dtmf speed the rate at which dtmf memories send individual dtmf characters can be set to accommodate operating needs. This setting does not affect an optional pager or code squelch op- eration. ➀ push [power] to turn power off. ➁ while pushing [ (vol) set l] (left side), ...
Page 58: Pocket Beep and Tone Squelch
Pocket beep and tone squelch 12 53 Ä push [band] to select the desired band, if nec- essary. Å set the operating frequency. Ç program the subaudible tone frequency in set mode. • see p. 29 for programming details. É push [func] then [ ➇ t sql s ] to turn the pocket beep on. • turn off the pager or c...
Page 59: Tone Squelch Operation
12 pocket beep and tone squelch 54 ■ tone squelch operation the tone squelch opens only when receiving a signal with the same pre-programmed subaudible tone. This function can be activated on both bands with separate tone frequencies si- multaneously. To operate the tone squelch function, an op- tio...
Page 60: Tone Scan
12 pocket beep and tone squelch 55 Ä push [band] to select the desired band, if nec- essary. Å set the desired frequency to be checked for a tone frequency e.G. Repeater input frequency. Ç push [func] then [ ➈ t sql] to turn the tone squelch on. É push [ ➁ scan] to start the tone scan. Ñ when the to...
Page 61: Pager and Code Squelch
Pager and code squelch 13 56 ■ pager function the pager functions can be used only when an optional ut-49 is installed. This function uses dtmf codes for paging and can be used as a “message pager” to inform you of a caller’s identity even if you leave the transceiver temporarily unattended. Persona...
Page 62: Code Channels
13 pager and code squelch 57 ■ code channels d before programming the pager and code squelch functions require id codes and a group code. These codes are 3-digit dtmf codes and must be written in the code channels before operation. The trans- ceiver has separate code channels for each band. D code c...
Page 63: Code Programming
13 pager and code squelch 58 ■ code programming ➀ push the desired band’s tuning dial. • each band has separate code channels. ➁ push [dtmf] 2 times to turn the pager function on. • “p” appears in place of the 100 mhz digit. ➂ push [ (vol) set] to select the code channel setting display. ➃ rotate th...
Page 64: Pager Operation
13 pager and code squelch 59 ■ pager operation d calling a specific station ➀ push the desired band’s tuning dial. ➁ set the operating frequency. ➂ push [dtmf] 2 times to turn the pager function on. • “p” appears in place of the 100 mhz digit. • an optional tone squelch can be used together with the...
Page 65
13 pager and code squelch 60 d waiting for a call from a specific station ➀ push the desired band’s tuning dial. ➁ set the operating frequency. ➂ push [dtmf] to turn the pager function on. • “p” appears in place of the 100 mhz digit. • an optional tone squelch can be used together with the pager fun...
Page 66: Code Squelch Function
13 pager and code squelch 61 ■ code squelch function the code squelch function can be used only when an optional ut-49 is installed. Code squelch operation provides communication with silent standby since you only receive calls from stations which know your id or group code. To use the code squelch ...
Page 67: Code Squelch Operation
13 pager and code squelch 62 Ä push [band] to select the desired band, if nec- essary. Å set the operating frequency. Ç push [func] then [ ➄ c sql] to turn the code squelch on. • “c” appears in place of the 100 mhz digit. • an optional tone squelch can be used together with the code squelch. (p. 54)...
Page 68: External Dtmf Remote
External dtmf remote (u.S.A. Version only) 14 63 when installing the optional ut-49 dtmf decoder unit , the u.S.A. Version can be remotely controlled using dtmf sig- nals on the sub band. To operate external dtmf remote, a 144 mhz or 430(440) mhz transceiver with a dtmf encoder is required. ➀ set th...
Page 69
14 external dtmf remote 64 [ent] 100 mhz 10 mhz 1 mhz 100 khz 10 khz 3 d 1 4 4 vfo mode 144.750 mhz call mr vfo clr [ent] 2 digits 2 d 1 5 memory mode memory channel 15 scratch pad memory 2 7 1 2 3 a high 4 5 6 b low1 7 8 9 c up ent down m 0 # d 5 [example] dtmf keypad [down] [down] 1 call channel m...
Page 70: Optional Unit Installation
Optional unit installation 15 65 ■ optional unit installation there are 2 optional internal units available. Ut-49 dtmf decoder unit the following functions are added when the ut-49 is in- stalled: • pager function • code squelch • external dtmf remote function (u.S.A. Version only) ut-104 tone sque...
Page 71: Wireless Operation
Wireless operation 16 66 ■ connection wireless remote control is available when the following op- tions are used: • hm-90 wireless microphone • ex-1759 infrared receiver the bc-96 microphone holder is additionally recommended for use with the hm-90, since the hm-90’s internal battery re- quires char...
Page 72: Ex-1759 Installation
16 wireless operation 67 ■ ex-1759 installation the ex-1759 infrared receiver can be installed for 2 differ- ent purposes depending on the hm-90 charger. This is be- cause the ex-1759 has both an infrared receiver and a microphone connector which contains microphone charging capabilities. • when usi...
Page 73: Hm-90 Switches
16 wireless operation 68 ■ hm-90 switches ➊ ptt switch ➥ push and hold to transmit; release to receive. ➥ toggles between transmitting and receiving while the one-touch ptt function is in use. ➋ band switches [band select y , z ] ➥ select the desired band as the main band. ➥ activate the para-watch ...
Page 74
16 wireless operation 69 d keypad key function secondary function (after ) func other functions calls up a call channel. No secondary function. • after : input the appropriate digit for frequency or memory channel selection. • after : transmit the appropriate dtmf code. • after : transmit the approp...
Page 75
16 wireless operation 70 key function secondary function (after ) func other functions clears a digit before entry. Cancels the scan, priority watch, pager, code squelch or dtmf memory function. Writes the vfo contents into the memory channel or call channel. Advances the memory channel number when ...
Page 76: Microphone
16 wireless operation 71 ■ microphone address the transceiver has 8 possible microphone addresses to help prevent interference from other hm-90 wireless micro - phones . Set both the microphone address and microphone dip switch to the same value as follows. Note: when the supplied microphone is conn...
Page 77: Other Functions
Other functions 17 72 ■ beep tones on/off you can select silent operation by turning beep tones off or you can select to have confirmation beeps sound at the push of a switch by turning beep tones on. ➀ push power to turn power off. ➁ while pushing [ (vol) set l], turn power on to enter initial set ...
Page 78: Auto Power-Off
17 other functions 73 ■ auto power-off the auto power-off function conveniently turns the transceiver power off after a preset time in which no operations are per- formed. In this way, when you forget to turn the power off, the transceiver automatically turns itself off, thereby con- serving battery...
Page 79: Microphone [F-1]/[F-2] Keys
17 other functions 74 ■ microphone [f-1]/[f-2] keys switches on the transceiver’s front panel can be assigned to the microphone’s [f-1] and [f-2] keys. ➀ turn power off. ➁ while pushing the desired switch on the transceiver and [f-1] or [f-2] on the microphone, turn power on. • the switches’ functio...
Page 80: Maintenance
Maintenance 18 75 ■ troubleshooting if your transceiver seems to be malfunctioning, please check the following points before sending it to a service center. Problem possible cause solution ref. No power comes on. • power connector has a poor contact. • polarity of the power connection is reversed. •...
Page 81
18 maintenance 76 problem possible cause solution ref. Frequency cannot be set via microphone. • the frequency lock function is activated. • the microphone keypad lock function is acti- vated. • priority watch is paused on the watching fre- quency. • push and hold [ (vfo) lock] to deactivate the fre...
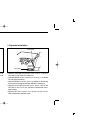
Page 82: Fuse Replacement
18 maintenance 77 ■ fuse replacement if the fuse blows or the transceiver stops functioning, find the source of the problem if possible, and replace the damaged fuse with a new, rated one (fgb 20 a) as shown in the dia- gram below. ■ partial resetting if you want to initialize the operating conditio...
Page 83: Specifications
Specifications 19 78 general • frequency coverage version vhf uhf 144–148 mhz 440–450 mhz asia 144–148 mhz 430–440 mhz europe 144–146 mhz 430–440 mhz italy 144–146 mhz 430–440 mhz tx rx 136–174 mhz* 2 tx rx 136–174 mhz* 2 400–479 mhz* 3 * 1 118–136 mhz is usable in the vhf display only; guaranteed f...
Page 84: Options
Options 20 79 some of the following options may not be available due to variations in local electrical standards, etc. If you have any questions regarding options please consult your icom dealer. D antenna ah-32 144/430(440) mhz dual band antenna dual band mobile antenna. Frequency range: 144–148 mh...
Page 85
20 options 80 d wireless microphone accessories hm-90 wireless microphone infrared, full remote control microphone. Wired remote con- trol is also possible. Ex-1759 infrared receiver used to receive control signals from the hm-90. Ex-1513 infrared sub receiver used with the ex-1759 to increase remot...
Page 86: Mode Arrangement
Mode arrangement 21 81 memory mode (p. 32) vfo mode (p. 15) call channel (p. 37) scratch pad memory (p. 39) see p. 49 for details. Dtmf memory code channel used for programming the code channel for pager and code squelch (p. 57). M/call v/mhz scan v/mhz scan set l or no operation for 30 sec. Sel l *...
Page 87
Y channel r programming e channel for d code squelch initial set mode set mode moni sel l sel l sub band mute (p. 23) skip skip channel* 2 setting (p. 45) beep tone on/off (p. 72) turn power on while pushing [set l]. Time-out timer (p. 72) auto power-off (p. 73) dup t auto repeater* (p. 31) * u.S.A....
Page 88
1-1-32 kamiminami, hirano-ku, osaka 547-0003 japan a-5382h-1ex printed in japan copyright © 1996 by icom inc. Count on us! Ic-2710h.Qxd 02.2.8 16:55 page 83 (1,1).