- DL manuals
- Icom
- Transceiver
- IC-7410
- Instruction Manual
Icom IC-7410 Instruction Manual
Summary of IC-7410
Page 1
Instruction manual hf/50 mhz transceiver i7410
Page 2
I foreword thank you for making the ic-7410 your radio of choice. We hope you agree with icom’s philosophy of “technology first.” many hours of research and devel- opment went into the design of your ic-7410. Features ❍ high receiver performance: third-order intercept point (ip3) of +30 dbm (hf band...
Page 3
Precautions r danger high rf voltage! Never attach an antenna or internal antenna connector during transmission. This may result in an electrical shock or burn. R warning! Never operate the transceiver with a headset or other audio accessories at high volume levels. Hearing experts advise against co...
Page 4
Iii table of contents foreword .............................................................. I important ............................................................... I explicit definitions ............................................ I supplied accessories....................................... ...
Page 5
Table of contents iv 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 4 receive and transmit .......................... 35 – 52 ■ operating ssb ................................................ 35 ■ operating cw ................................................. 36 d about the cw reverse mode ......
Page 6
V table of contents 7 memory operation ................................ 69 – 74 ■ general description ......................................... 69 d memory channel contents ........................... 69 ■ memory channel selection .............................. 69 d selection in the vfo mode ..........
Page 7
Table of contents vi 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 14 control command ............................ 101 – 108 ■ remote jack (ci-v) information ..................... 101 d ci-v connection example .......................... 101 d data format ........................................
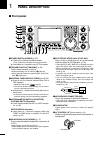
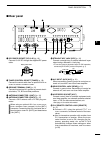
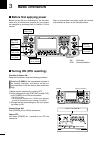
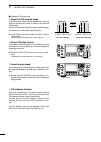
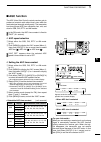
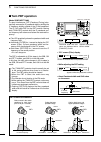
Page 8: Front Panel
Q power switch [power] (p. 23) ➥ push to turn on the transceiver power. • first, confirm the dc power source is turned on. ➥ hold down for 1 second to turn off the power. W transmit switch [transmit] (p. 34) push to select transmit or receive. • while transmitting, the tx indicator ( @1 ) lights red...
Page 9
!0 rf gain control/squelch control [rf/sql] (outer control; p. 32) rotate to adjust the rf gain and squelch threshold level. The squelch removes noise output to the speaker when no signal is received (closed condition). • the squelch is particularly effective in fm, but also works in other modes. • ...
Page 10
!7 noise blanker switch [nb] (p. 60) ➥ push to turn the noise blanker on or off. The noise blanker reduces pulse-type noise such as that generated by vehicle ignition systems. The noise blanker cannot be used in the fm mode, and is not effective for non-pulse-type noise. • “nb” appears when the nois...
Page 11
[rtty] push to alternately select the rtty and rtty-r (rtty reverse) modes. • “rtty” or “rtty-r” appears. [am/fm] ➥ push to alternately select the am or fm modes. • “am” or “fm” appears. ➥ hold down for 1 second to select the am or fm data mode (am-d/fm-d). • “ d ” appears in addition to “am” or “fm...
Page 12
#3 transmit frequency check switch [xfc] ➥ during split frequency or repeater operation, hold down to listen to the transmit frequency. (pp. 52, 56) • while holding down this switch, the transmit fre - quency can be changed with [dial], keypad or memo pad. • when the split lock function is turned on...
Page 13
✔ what is the pbt control? The pbt function electronically modifies the if passband width to reject interference. This transceiver uses the dsp circuit for the pbt function. $1 notch switch [notch] (p. 61) (mode = auto notch : ssb/am/fm manual notch : ssb/cw/rtty/am) ➥ in the ssb and am modes, push ...
Page 14
$8 memo pad-write switch [mp-w] (p. 74) push to write the displayed data into a memo pad. • the five most recent entries remain in the memo pads. • the memo pad capacity can be extended from 5 to 10 in the “memopad numbers” item in the set mode. (p. 87) $9 vfo/memory switch [vfo/memo] ➥ push to swit...
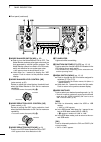
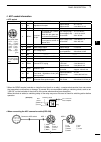
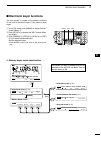
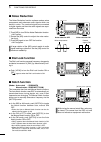
Page 15: Rear Panel
8 1 panel description 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ rear panel q dc power socket [dc 13.8v] (p. 19) connect 13.8 v dc through the supplied dc power cable. Rear panel view w tuner control socket [tuner] (p. 18) connect the control cable from an optional ah-4 hf/ 50 mh z auto...
Page 16
!1 usb (universal serial bus) connector [usb] using a usb cable, connect a pc to do the follow- ing: - input modulation (p. 89) - remotely control the transceiver using ci-v com- mands (p. 101) - send the received audio to the pc - send the decoded characters to the pc (p. 89) about the usb driver: ...
Page 17
10 1 panel description 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 d acc socket information • acc socket acc pin no. Name description specifications 1 2 3 4 8 7 6 5 9 10 11 12 13 rear panel view color refers to the cable strands of the supplied cable. Q brown w red e orange r yellow t gree...
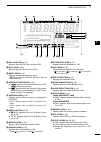
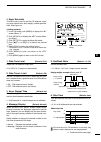
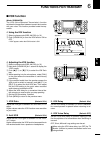
Page 18: Lcd Display
11 1 panel description ■ lcd display q power down transmission icon (p. 98) appears when the output power is decreased by the reduced power transmission function. W tx icon indicates the transmit frequency is displayed. ➥ “ ” appears while the operating frequency is in an amateur band. ➥ “ ” appears...
Page 19
12 1 panel description 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 !6 dial lock icon (p. 61) appears when the dial lock function is on. !7 split icon (p. 66) appears when the split function is on. !8 mode icons (p. 31) displays the selected operating mode. • “ d ” appears when the ssb data...
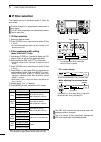
Page 20: Function Display
13 1 panel description d m1 (menu 1) (mode: ssb) agc tbw scp (mode: ssb-d) agc 1 ⁄ 4 scp (mode: cw) agc 1 ⁄ 4 key scp (mode: rtty) agc 1 ⁄ 4 rtty scp (mode: am) agc scp (mode: fm) agc ton scp d function keys on m1 (menu 1) agc key [agc](f-1) (p. 56) (mode: ssb/cw/rtty/am/fm) ➥ push to select the tim...
Page 21
14 1 panel description 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 d m2 (menu 2) scan mem swr tcon vsc d function keys on m2 (menu 2) scan key [scan](f-1) (p. 75) (mode: ssb/cw/rtty/am/fm) push to display the “scan” screen. Memory name key [mem](f-2) (p. 73) (mode: ssb/cw/rtty/am/fm) push ...
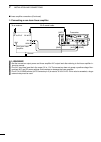
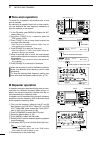
Page 22: Installation and Connections
2 15 installation and connections ■ selecting a location select a location for the transceiver that allows ade- quate air circulation, free from extreme heat, cold, or vibrations, and away from tv sets, tv antenna ele- ments, radios and other electromagnetic sources. The base of the transceiver has ...
Page 23: Required Connections
16 2 installation and connections 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ required connections d front panel + _ dc power supply (p. 19) ps-126 use the heaviest possible gauge wire or strap and make the connection as short as possible. Grounding prevents elec- trical shocks, tvi and ...
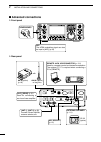
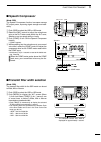
Page 24: Advanced Connections
17 2 installation and connections d rear panel ■ advanced connections d front panel headphones mic the afsk modulation signal can also be input to [mic]. (p. 92) ah-4 (option) (p. 18) ah-2b (option) or long wire with acc socket (p. 10) remote jack , usb connector (p. 101) used for computer control a...
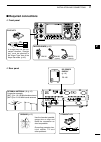
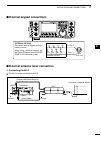
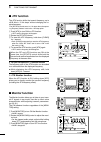
Page 25: External Keypad Connections
18 2 installation and connections 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ external keypad connections to pin e to pin y 1.5 k ø ±5% 1.5 k ø ±5% 2.2 k ø ±5% 4.7 k ø ±5% s1 (m1) s2 (m2) s3 (m3) s4 (m4) external keypad 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 (front view) [mic] external keypad connect an extern...
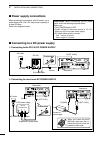
Page 26: Power Supply Connections
19 2 installation and connections ■ power supply connections when operating the transceiver with ac power, use a power supply with 13.8 v dc output and a capacity of at least 23 amps. Refer to the diagrams below. Caution: before connecting the dc power cable, check the following important items. Mak...
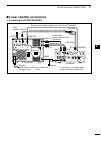
Page 27: Linear Amplifier Connections
20 2 installation and connections 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ linear amplifier connections d connecting the ic-pw1/pw1euro exciter 1 1&2 remote control cable (supplied with the ic-pw1/pw1euro) acc cable (supplied with the ic-pw1/pw1euro) to an antenna [acc1] [remote] [ant...
Page 28
21 2 installation and connections ■ linear amplifier connections (continued) d connecting a non-icom linear amplifier r warning! • set the transceiver output power and linear amplifier alc output level after referring to the linear amplifier in - struction manual. • the alc input level must be in th...
Page 29: Microphones
22 2 installation and connections 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ microphone connector information (front panel view) y gnd (ptt ground) t ptt r squelch switch q microphone input w +8 v dc output e frequency up/down i af output (varies with [af]) gnd (microphone ground) u [mi...
Page 30: Before First Applying Power
[rf/sql] : 12 o’clock [mic] : 12 o’clock [nr] : max. Ccw [cw pitch] : 12 o’clock [rf pwr] : max. Cw [af] : max. Ccw ■ before first applying power before turning on your transceiver for the first time, make sure all connections required for your system are complete by reviewing them in section 2 of t...
Page 31: Vfo Description
24 3 basic operation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ vfo description the ic-7410 has two vfos; “a” and “b,” that are con- venient for quickly selecting two frequencies, or split frequency operation. You can use either vfo to call up a frequency and operating mode. Vfo is an a...
Page 32: Selecting A Frequency Band
25 3 basic operation d using the band stacking registers. Q push a band key ([1.8 1] to [50 0] or [gene •]). • the previously selected frequency and operating mode are called up as the first band stacking register of that frequency band. W select a frequency and an operating mode, and then push the ...
Page 33: Frequency Setting
26 3 basic operation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ frequency setting you can select the transceiver’s frequency by using [dial], or you can enter it using the keypad. D tuning with [dial] q select the desired frequency band. • push a band key 1–3 times. Three different freq...
Page 34
27 3 basic operation ■ frequency setting (continued) d quick tuning function the operating frequency can be changed in “khz” steps for quick tuning. You can set a tuning step in each operating mode. Q push [ts] to turn on the quick tuning function. • “ z ” appears above the 1 khz digit. W hold down ...
Page 35
28 3 basic operation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 d auto tuning step function when you rotate [dial] rapidly, the tuning speed can automatically accelerate, depending on the “main dial auto ts” setting in the set mode. Q hold down [menu] for 1 second to enter the set mode. W...
Page 36
29 3 basic operation ■ frequency setting (continued) d band edge warning beep you can hear a beep tone when you tune in or out of an amateur band’s frequency range. A regular beep sounds when you tune into a range, and an lower tone error beep sounds when you tune out of a range. Also, the tx icon a...
Page 37
30 3 basic operation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 d programming the user band edge when “on (user)” or “on (user) & tx” is selected in the “band edge beep” item, the “user band edge” item appears in the set mode. A total of 30 band edge frequencies can be pro- grammed in the...
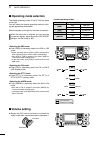
Page 38: Operating Mode Selection
■ operating mode selection the usable operating modes in the ic-7410 are listed to the right. You can select the desired operating mode by push- ing the appropriate mode switch. See the diagram to the right for the order of selection. When the data mode is selected, you can mute the microphone signa...
Page 39
32 3 basic operation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ squelch and receive (rf) sensitivity adjusts the rf gain and squelch threshold level. The squelch removes noise output to the speaker when no signal is received (closed position). • the squelch is particularly effective for...
Page 40: Voice Synthesizer Operation
33 3 basic operation ■ voice synthesizer operation the ic-7410 has a built-in voice synthesizer to an- nounce the operating frequency, mode and s-meter level in clear, electronically-generated voice, in eng- lish (or japanese). First, select the desired parameters to be announced in the set mode. (p...
Page 41: Basic Transmit Operation
34 3 basic operation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ basic transmit operation before transmitting, monitor the operating fre- quency to make sure transmitting won’t cause interference to other stations on the same fre- quency. It’s good amateur practice to listen first, and t...
Page 42: Receive And Transmit
4 35 receive and transmit a g c t b w s c p m1 [dial] [ssb] [af] [mic] [transmit] tx indicator “lsb” or “usb” appears ■ operating ssb q select the desired band. (p. 25) w push [ssb] to select the lsb or usb mode. • when operating above 10 mhz, usb is selected first; when operating below 10 mhz, lsb ...
Page 43: Operating Cw
36 4 receive and transmit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ operating cw q select the desired band. (p. 25) w push [cw] to select the cw mode. • pushing [cw] alternately selects cw or cw reverse mode. E rotate [dial] to tune a desired signal. • the s-meter indicates the receive...
Page 44
37 bfo cw-r mode (usb side) bfo desired signal cw mode (lsb side) interference desired signal interference ■ operating cw (continued) d about the cw reverse mode the cw reverse mode receives signals with a reverse side cw carrier point similar to voice of the lsb and usb modes. Use when interfering ...
Page 45: Electronic Keyer Functions
38 4 receive and transmit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ electronic keyer functions you can access a number of convenient functions of the built-in electronic keyer in the memory keyer menu. Q in the cw mode, push [menu] to display the “m1” screen (menu 1). W push [key](f-4)...
Page 46
39 4 receive and transmit ■ electronic keyer functions (continued) d memory keyer send menu pre-set characters can be sent using the keyer send menu. Contents of the memory keyer are set in the edit menu. • transmitting q in the cw mode, push [menu] to display the “m1” screen (menu 1). W push [key](...
Page 47
40 4 receive and transmit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 d editing a memory keyer the contents of the memory keyer memories can be set using the memory keyer edit menu. The memory keyer can memorize and re-transmit 4 cw key codes for often-used cw sentences, contest serial num...
Page 48
41 4 receive and transmit ■ electronic keyer functions (continued) d contest number set mode this mode is used to set the contest number and count up trigger, etc. • setting contents q in the cw mode, push [menu] to display the “m1” screen (menu 1). W push [key](f-4) to display the “key” screen (mem...
Page 49
42 4 receive and transmit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 d keyer set mode this set mode is used to set the cw sidetone, mem- ory keyer repeat time, dash weight, paddle specifica- tions, keyer type, etc. • setting contents q in the cw mode, push [menu] to display the “m1” scree...
Page 50
43 4 receive and transmit d keyer set mode (continued) paddle polarity 7. (default: normal) set the paddle polarity. • normal or reverse polarity can be selected. Keyer type 8. (default: elec-key) select the keyer type for the [elec-key] connector on the front panel. • straight key, bug-key or elec-...
Page 51: Operating Rtty (Fsk)
44 4 receive and transmit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ operating rtty (fsk) when using your rtty terminal or tnc, consult the manual that comes with the equipment. Q select the desired band. (p. 25) w push [rtty] to select the rtty mode. • pushing [rtty] alternately select...
Page 52: Rtty Functions
45 4 receive and transmit ■ rtty functions the rtty menu has a number of convenient functions for rtty operation. Q push [rtty] to select the rtty mode. • pushing [rtty] alternately selects the rtty or rtty reverse mode. W push [menu] to display the “m1” screen (menu 1). E push [rtty](f-4) to displa...
Page 53
46 4 receive and transmit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 d about the rtty reverse mode received characters are occasionally garbled when the mark and space signals are reversed. This rever- sal can be caused by incorrect tnc connections, set- ting or commands. To receive rever...
Page 54
47 4 receive and transmit ■ rtty functions (continued) d twin peak filter the twin peak filter changes the receive frequency response by boosting 2125 and 2295 hz for better copying of rtty signals. Q in the rtty mode, push [menu] to display the “m1” screen (menu 1). W push [rtty](f-4) to display th...
Page 55
48 4 receive and transmit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 d rtty set mode the rtty set mode is used to set the mark and shift frequencies, keying type, decode usos function, rtty decoder new line code and the number of de- code screen display lines. • setting contents q in the ...
Page 56: Operating Am/fm
49 4 receive and transmit a g c t b w s c p m1 [dial] [am/fm] [af] [mic] band keys [transmit] tx indicator appears ■ operating am/fm q select the desired band. (p. 25) w push [am/fm] to select the am or fm mode. • if desired, after am or fm is selected, hold down [am/ fm] for 1 second to select the ...
Page 57: Tone Squelch Operation
50 4 receive and transmit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 tone squelch operation the tone squelch opens only when you receive a sig- nal containing a matching subaudible tone. You can silently wait for calls from others using the same tone. Q push [am/fm] once or twice to selec...
Page 58: Tone Scan Operation
51 4 receive and transmit to search for a repeater’s sub-audible tone, a tone scan is available. By monitoring a repeater signal with a tone squelch, you can determine the tone frequency necessary to open the repeater or the squelch. Q in the fm mode, push [menu] to display the “m1” screen (menu 1)....
Page 59
52 4 receive and transmit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 d repeater access tone frequency setting some repeaters require a subaudible tone to be ac- cessed. Subaudible tones are superimposed on your normal signal and must be set first. You can select 50 tones from 67.0 hz to 2...
Page 60: Functions For Receive
5 53 functions for receive ■ rit function the rit (receive increment tuning) function com- pensates for off-frequency operation of the received station. The function shifts the receive frequency up to ±9.99 khz in 10 hz steps*, without changing the trans- mit frequency. * the [rit/ ∂ tx] control tun...
Page 61: Simple Band Scope
54 5 functions for receive 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ simple band scope the band scope function allows you to visually check the location and strength of signals around a specified frequency. The ic-7410’s band scope function can be used in any operating mode and any fre...
Page 62: Preamplifier
55 5 functions for receive ■ preamplifier the preamplifier amplifies weak signals in the receiver front end, to improve the s/n ratio and sensitivity. Turn this function on when receiving weak signals. ➥ push [p.Amp•att] one or more times to set the preamp off, preamp 1 on or preamp 2 on. • either “...
Page 63: Agc Function
56 5 functions for receive 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ agc function the agc (auto gain control) controls receiver gain to produce a constant audio output level, even when the received signal strength varies greatly. The transceiver has three pre-set agc time constants; fa...
Page 64: If Filter Selection
57 5 functions for receive ■ if filter selection the transceiver has 3 passband width if filters for each mode. The filter selection is automatically memorized in each mode. The pbt shift frequencies are automatically memo- rized in each filter. D if filter selection q select the desired mode. W pus...
Page 65
58 5 functions for receive 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 d 1st if filter selection (mode: ssb/cw/rtty/am) the ic-7410 has a 15 khz filter passband width at the 1st if frequency. The 1st if filters reduce interference from strong nearby signals. If the optional fl-430 1 st if ...
Page 66: Twin Pbt Operation
59 5 functions for receive ■ twin pbt operation (mode: ssb/cw/rtty/am) to reject interference, pbt (passband tuning) elec- tronically narrows the if passband width by shifting the if frequency slightly outside of the if filter passband. The ic-7410 uses dsp for the pbt function. Moving both [twin-pb...
Page 67: Noise Blanker
60 5 functions for receive 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ noise blanker (mode: ssb/cw/rtty/am) the noise blanker eliminates pulse-type noise such as noise from car ignitions. Q push [nb] to turn on the noise blanker function. • “nb” appears. W rotate the [nb] control to adju...
Page 68: Noise Reduction
61 5 functions for receive ■ noise reduction the noise reduction function reduces random noise components and enhances audio signals which are buried in noise. The received signals are converted to digital signals and then the audio signals are sepa- rated from the noise. Q push [nr] to turn on the ...
Page 69: Functions For Transmit
6 62 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 functions for transmit 5 ■ vox function (mode: ssb/am/fm) the vox (voice-operated transmission) function switches the transceiver between transmit and receive with your voice. This function provides hands-free op- eration. D using the vox func...
Page 70: Break-In Function
63 6 functions for transmit ■ break-in function (mode: cw) the break-in function is used in the cw mode to auto- matically toggle the transceiver between transmit and receive when keying. The ic-7410 is capable of full break-in or semi break-in. D semi break-in operation during semi break-in operati...
Page 71: Speech Compressor
64 6 functions for transmit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ speech compressor (mode: ssb) the speech compressor function increases average rf output power, improving signal strength and read- ability. Q push [ssb] to select the usb or lsb mode. W rotate the [mic] control to a...
Page 72: Tx Function
65 6 functions for transmit ■ ∂ tx function the ∂ tx function shifts the transmit frequency up to ±9.99 khz in 10 hz steps* without changing the re- ceive frequency. * the [rit/ ∂ tx] control tunes in 1 hz steps when the operat- ing frequency readout is set to the 1 hz step option. Q push [ ∂ tx] to...
Page 73: Split Frequency Operation
66 6 functions for transmit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ split frequency operation split frequency operation allows you to transmit and receive on two different frequencies. Split frequency operation is performed using frequencies in vfo a and vfo b. The following is an ex...
Page 74: Quick Split Function
67 6 functions for transmit ■ quick split function when you hold down [split] for 1 second, the split frequency operation is turned on. The undisplayed vfo is automatically changed according to the plus/ minus frequency shift programmed in the set mode, or equalized when 0 khz (default setting) is p...
Page 75: Measuring Swr
68 6 functions for transmit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ measuring swr the ic-7410 has a built-in circuit for measuring an- tenna swr— no external equipment or special adjust- ments are necessary. The ic-7410 can measure swr two ways— spot mea- surement and plot measuremen...
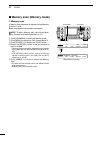
Page 76: Memory Operation
69 memory operation 7 ■ general description the transceiver has 101 memory channels (99 regular, and 2 scan edges). The memory mode is very useful to quickly change to often-used frequencies. While in the memory mode, all 101 memory channels are tunable, which means the programmed frequency can be t...
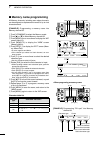
Page 77: Memory Channel Programming
70 memory operation 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 7 10 7 memory channels can be programmed in either the vfo mode or the memory mode. D programming in the vfo mode q push [vfo/memo] to select the vfo mode. W set the frequency, operating mode, and other data into both vfo a and vfo...
Page 78: Memory Clearing
71 memory operation 7 hold down ■ memory clearing any no-longer-used regular memory channel can be cleared, and then become a blank channel. Q push [vfo/memo] to select the memory mode. W push [ y ] or [ z ] to select a regular memory channel to be cleared. E hold down [m-clr] for 1 second to clear ...
Page 79: Memory Contents Copying
72 memory operation 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 7 10 7 the memory channel contents (frequency, operating mode, etc.) can be copied to the vfo. The copy can be performed in either the vfo mode or the memory mode. D copying in the vfo mode this is useful for copying programmed con...
Page 80: Memory Name Programming
73 memory operation 7 ■ memory name programming all memory channels, including scan edges channels, can be assigned an alphanumeric names of up to nine characters each. [example]: programming a memory name into memory channel 99. Q push [vfo/memo] to select the memory mode. W push [ y ] or [ z ] to ...
Page 81: Memo Pad Function
74 memory operation 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 7 10 7 you can call up a memo pad by pushing [mp-r] while in either the vfo or memory mode. • the memo pad data is called up, starting from the most recently written. When you call up a memo pad, the previously dis- played data is ...
Page 82: Scans
75 scans 8 scan – ∂ f frequency + ∂ f frequency center frequency (start frequency) jump mch 1 mch 5 mch 2 mch 3 mch 4 mch 6 mch 7 mch 99 sel sel sel sel sel mch 1 mch 5 mch 2 mch 3 mch 4 mch 6 mch 7 mch 99 sel sel sel sel sel scan p1 or p2 jump scan edge p2 or p1 scan edge ■ scan types scanning auto...
Page 83: Preparation
76 scans 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 11 8 8 ■ preparation for a programmed scan: program scan edge frequencies into program scan edge channels “p1” and “p2,” in the same manner as programming memory channels (p. 70) for a memory scan: program two or more memory channels. (progra...
Page 84: Scan Set Mode
77 scans 8 ■ scan set mode the scan speed and the scan resume function can be set in the scan set mode. Q push [menu] one or more times to display the “m2” screen (menu 2). W push [scan](f-1) to display the “scan” screen. E push [set](f-5) to enter the scan set mode. R push [ y ](f-1) or [ z ](f-2) ...
Page 85
78 scans 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 11 8 8 a programmed scan searches for signals between program scan edge channels “p1” and “p2.” before starting the programmed scan, scan edges must be programmed into these channels. Refer to “ ■ memory channel programming” to pro- gram prog...
Page 86: Memory Scan (Memory Mode)
79 scans 8 d memory scan a memory scan searches for signals through memory channels 1 to 99. Blank (unprogrammed) channels are skipped. Note: to start a memory scan, two or more mem- ory channels must be programmed. (p. 70) q push [vfo/memo] to select the memory mode. W push [menu] to display the “m...
Page 87
80 scans 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 11 8 8 d select memory scan select memory scan searches for signals through memory channels programmed as “sel” (select). Note: to start a select memory scan, two or more memory channels must be designated as select memory channels. Q start a...
Page 88: F Scan and Fine
81 scans 8 ∂ f (delta frequency) scan searches for signals within the specified range with the displayed vfo frequency or memory channel frequency as the center frequency. The frequency range is specified by the width of the selected span. Q push [vfo/memo] once or twice to select the vfo mode or me...
Page 89: Antenna Tuner Operation
82 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 10 11 12 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 8 antenna tuner operation 9 13 9 [ant•meter] the ic-7410 has 2 antenna connectors for the hf/50 mhz bands, [ant1] and [ant2]. You can memorize the antenna for each operating band the ic-7410 covers. When you change the operating band, the previously ...
Page 90: Antenna Tuner Operation
83 antenna tuner operation 9 ❍ if the tuner cannot tune the antenna, check the following and try again: • the correct antenna connector selection. • the antenna connection and feedline. • the untuned antenna swr. (less than 3:1 for the hf bands; less than 2.5:1 for the 50 mhz band) • the transmit po...
Page 91
84 antenna tuner operation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 10 11 12 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 13 9 9 • ah-4 hf/50 mhz automatic antenna tuner the optional ah-4 matches the ic-7410 to a long wire antenna more than 7 m/23 ft long (3.5 mhz and above). • see page 18 for the transceiver and ah-4 connec - tion. • see the a...
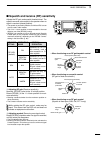
Page 92: Set Mode
85 set mode 10 ■ set mode description the set mode is used for programming infrequently changed values or functions. D the set mode settings q hold down [menu] for 1 second to enter the set mode. W push [ y ](f-1) or [ z ](f-2) to select the desired item. E rotate [dial] to select the desired option...
Page 93
86 set mode 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 10 10 14 user band edge 7. This “user band edge” item appears only when “on (user)” or “user (on) & tx” is selected in the “band edge beep” item. (p. 85) when you select “on (user)” or “on (user) & tx” in the “band edge beep” item, you can ...
Page 94
87 set mode 10 tuner (ptt start) 17. (default: off) whenever you push [ptt], the internal or external an- tenna tuner automatically starts tuning if the operating frequency is changed by more than 1% from the last- tuned frequency. • off : tuning starts only when [tuner] is pushed. • on : (internal ...
Page 95
88 set mode 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 10 10 14 mic up/down speed 27. (default: high) set the rate at which frequencies are scanned while holding down the microphone [up] / [dn] switches. • low : low speed (25 tuning steps/second) • high : high speed (50 tuning steps/second) qui...
Page 96
89 set mode 10 usb audio sql 38. (default: off(open)) select whether or not to output the audio from the [usb] connector on the rear panel, according to the squelch state. The same audio signals are sent from the [usb] con- nector and the [acc] sockets. - the beep tones and the voice synthesizer ann...
Page 97
90 set mode 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 10 10 14 d the tone control set mode settings q push [menu] one or more times to display the “m2” screen (menu 2). W push [tcon](f-4) to enter the tone control set mode. E push a mode switch to select the desired operating mode. R push [ y ...
Page 98
91 set mode 10 tbw(mid) l 9. (default: 300) (mode: ssb) set the lower cut-off frequency of the transmission passband width for your mid setting to 100, 200, 300 or 500 hz. Tbw(mid) h 10. (default: 2700) (mode: ssb) set the higher cut-off frequency of the transmission passband width for your mid sett...
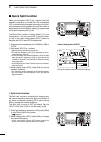
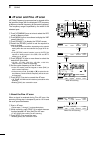
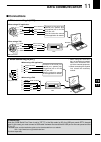
Page 99: Data Communication
92 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 12 13 14 16 17 18 19 20 21 data communication 15 11 10 11 ■ connections • when using a tnc • when using a pc application tnc pc rs-232c rear panel view 4 8 12 1 2 3 7 6 5 9 10 11 13 rtty output audio input ptt gnd fskk af send gnd 4 8 12 1 2 3 7 6 5 9 10 11 13 rtty output audio ...
Page 100: Packet (Afsk) Operation
93 data communication 11 ■ packet (afsk) operation before operating packet (afsk), be sure to consult the operating manual that came with your tnc. Q connect the tnc and pc. (p. 92) w select the desired band. (p. 25) e push [ssb] or [am/fm] to select the desired oper- ating mode. R hold down the sam...
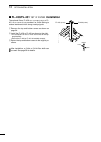
Page 101: Option Installation
94 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 14 15 17 18 19 20 21 option installation 11 16 12 13 12 ■ opening the transceiver’s case icom strongly suggests that the customer have their dealer or icom distributor, for a reasonable fee, in- stall icom options at the time of the order. Icom un- derstands that even the sim...
Page 102: Fl-430/fl-431
95 option installation 12 ■ fl-430/fl-431 1 st if filter installation the optional filters, fl-430 1 st if filter (6 k h z ) or fl- 431 1 st if filter (3 k h z ) provides 6 or 3 khz filtering to reduce interference from strong nearby signals. Q remove the top and bottom covers as shown on page 94. W...
Page 103: Maintenance
96 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 14 15 16 18 19 20 21 maintenance 17 13 12 13 d transceiver power problem possible cause solution ref. Power does not turn on when the [power] switch is pushed. • the power cable is improperly connected. • a fuse is blown. • re-connect the dc power cable correctly. • correc...
Page 104
97 13 maintenance ■ troubleshooting (continued) d scanning problem possible cause solution ref. A programmed scan does not stop. • squelch is open. • set the [rf/sql] control to the threshold point. P. 32 a programmed scan does not start. • the same frequencies are programmed into the scan edge memo...
Page 105: Frequency Calibration
98 13 maintenance 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ frequency calibration (approximate) [pbt-clr] [ af ] [ rf/sql ] [ ∂tx ] [ rit ] [ menu ] [ ssb ] [p.Amp÷att] [ √ ] [ ∫ ] [dial] Ù 47 Ú o f f set c a l i b r a t i o n m a r k e r Ù 48 Ú 5 0 % set r e f a d j u s t • calibratio...
Page 106: Fuse Replacement
99 13 maintenance d circuitry fuse replacement except for the power amplifier, the 13.8 v dc from the dc power cable is applied to all units in the ic-7410, through the circuitry fuse. This fuse is located in the pa unit. Q remove the top cover. (p. 94) w remove the 22 screws, then remove the pa shi...
Page 107: Resetting The Cpu
100 13 maintenance 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ■ resetting the cpu d partial reset if you want to reset the operating parameters to their default values (vfo frequency, vfo settings, menu group’s contents) without clearing certain data as de- scribed below, a partial reset ...
Page 108: Control Command
101 control command 14 ■ remote jack (ci-v) information controller to ic-7410 fe fe 80 e0 cn sc data area fd preamb le code (fix ed) tr ansceiv er’ s def ault address controller’ s def ault address command number (see the command tab le) sub command number (see the command tab le) bcd code data such...
Page 109
102 control command 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 15 16 17 19 20 21 14 18 14 d command table cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 00 see p. 106 send operating frequency for transceive 01 see p. 106 send operating mode for transceive 02 see p. 106 read band edge frequencies 03 see p. 106 read operating fre...
Page 110
103 control command 14 d command table (continued) cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 16 42 00 send/read repeater tone off 01 send/read repeater tone on 43 00 send/read tone squelch off 01 send/read tone squelch on 44 00 send/read speech compressor off 01 send/read speech compressor on 45 00 send/read m...
Page 111
104 control command 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 15 16 17 19 20 21 14 18 14 cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 1a 05 0030 00 send/read bw popup (pbt) setting off 01 send/read bw popup (pbt) setting on 0031 00 send/read bw popup (fil) setting off 01 send/read bw popup (fil) setting on 0032 00 send/read ...
Page 112
105 control command 14 d command table (continued) cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 1a 05 0074 00 send/read normal selection for paddle po- larity 01 send/read reverse selection for paddle polarity 0075 00 send/read straight selection for keyer type 01 send/read bug-key selection for keyer type 02 sen...
Page 113
106 control command 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 15 16 17 19 20 21 14 18 14 • character code setting command : 1a 00 character ascii code character ascii code a–z 41–5a a–z 61–7a 0–9 30–39 space 20 ! 21 # 23 $ 24 % 25 & 26 \ 5c ? 3f " 22 ’ 27 ` 60 ^ 5e + 2b – 2d ✱ 2a ⁄ 2f . 2e , 2c : 3a ; 3b = 3d 3...
Page 114
107 control command 14 • memory keyer contents command : 1a 02 x q : channel data w – &1 : text data x x x …… x x 01 : m1 02 : m2 03 : m3 04 : m4 • character’s code character ascii code description 0–9 30–39 number a–z 41–5a alphabetical characters a–z 61–7a alphabetical characters space 20 word spa...
Page 115
108 control command 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 15 16 17 19 20 21 14 18 14 13 • data mode with filter width setting command : 1a 06 x x x x q w 00: data mode off 01: fil1 02: fil2 03: fil3 00: data mode off 01: data mode on • repeater tone/tone squelch frequency setting command : 1b 00, 1b 01 q * e w...
Page 116: Specifications
109 specifications 15 ■ general • frequency coverage : (unit: mhz) receive 0.030–60.000* 1 * 2 transmit 1.800–1.999* 2 , 3.500–3.999* 2 , 5.33050* 3 , 5.34650* 3 , 5.36650* 3 , 5.37150* 3 , 5.40350* 3 , 7.000–7.300* 2 , 10.100–10.150* 2 , 14.000–14.350* 2 , 18.068–18.168* 2 , 21.000–21.450* 2 , 24.8...
Page 117: Receiver
110 specifications 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 16 17 18 20 21 19 15 14 15 ■ receiver • receive system : double superheterodyne system • intermediate frequencies 1st : 64.455 mhz 2nd : 36 khz • sensitivity ssb, cw : 0.16 µv (1.80–29.99 mhz) * 4 (10 db s/n) bw=2.4 khz 0.13 µv (50.0–54.0 mhz) * 5 am ...
Page 118: Options
111 options 16 ah-4 hf automatic antenna tuner specially designed to tune a long wire antenna for hf/50 mhz bands. The “ptt tune” function provides simple operation. • input power rating: 120 w ah-2b antenna element a 2.5 m long antenna ele- ment for mobile operation with the ah-4. • frequency cover...
Page 119
112 options 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 17 18 19 21 20 16 15 16 • opc-599 adapter cable 13-pin, acc connector to 7-pin + 8-pin acc connector. • mb-123 carrying handle convenient when carrying the transceiver. The same as that supplied with the transceiver. • opc-420 shield control cable for the...
Page 120: Installation Notes
113 ce 17 installation notes for amateur base station installations it is recom- mended that the forward clearance in front of the an- tenna array is calculated relative to the eirp (effective isotropic radiated power). The clearance height below the antenna array can be determined in most cases fro...
Page 121: Declaration
114 ce 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 19 20 21 17 17 declaration of conformity we icom inc. Japan 1-1-32, kamiminami, hirano-ku osaka 547-0003, japan kind of equipment: type-designation: signature authorized representative name place and date of issue version (where applicable): y. Furuka...
Page 122
Memo.
Page 123
Memo 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21.
Page 124
1-1-32 kamiminami, hirano-ku, osaka 547-0003, japan a-6904h-1ex- q printed in japan © 2011 icom inc. At fi it pl gb ro be fr lv pt is tr cy de lt sk li hr cz gr lu si no dk hu mt es ch ee ie nl se bg at fi it pl gb ro be fr lv pt is tr cy de lt sk li hr cz gr lu si no dk hu mt es ch ee ie nl se bg a...