- DL manuals
- Icom
- Transceiver
- iC-7850
- Instruction Manual
Icom iC-7850 Instruction Manual
Summary of iC-7850
Page 1
The transceivers i7850 i7851 instruction manual a7205h-1ex-3 printed in japan © 2015–2018 icom inc..
Page 2: Disposal
I preface thank you for choosing the ic-7850/ic-7851. The ic-7850/ic-7851 has many built-in high technology circuitry and unique functions, such as the dualwatch on the main and sub bands, a high speed spectrum scope scan, a high-reso- lution waterfall screen, and many other outstanding features. Th...
Page 3
Ii important read this instruction manual carefully before at- tempting to operate the transceiver. Save this instruction manual. This manual contains important safety and operating instructions for the transceiver. Explicit definitions word definition r danger! Personal death, serious injury or an ...
Page 4
Iii precautions r danger high rf voltage! Never attach an antenna or internal antenna connector during transmission. This may result in an electrical shock or burn. R warning! Never operate the transceiver with a headset or other audio accessories at high volume levels. The continuous high volume op...
Page 5
Iv this equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class b digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interfer- ence in a residential installation. This equipment gen- erates, uses and can ...
Page 6
V functions and features of adobe ® acrobat ® reader the following functions and features can be used with adobe® reader®. • keyword search click “find” (ctrl+f) or “advanced search” (shift+ctrl+f) in the edit menu to open the search screen. This is convenient when search- ing for a particular word ...
Page 7: Band Edge Warning Beep
Vi description information this instruction manual is described based on the following manner. “ ” (quotation marks): used to indicate icons, setting items, and screen titles displayed on the screen. [ ] (brackets): used to indicate keys, dials, and knobs. Routes to the set mode and setting screen d...
Page 8
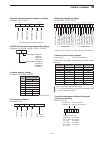
Vii q ac power cable † .................................................. 1 w rack mounting handles ................................ 1 pair e screws for rack mounting handles ................... 1 set r sd card ................................................................. 1 t feet .................
Page 9
Viii table of contents panel description section 1 ■ front panel ……………………………………………………………… 1-2 ■ rear panel ……………………………………………………………… 1-12 ■ display …………………………………………………………………… 1-14 ■ screen menu arrangement …………………………………………… 1-16 set mode items section 2 ■ about the setting screen configuration ………………...
Page 10
Ix table of contents ■ microphones (optional products) ……………………………………… 3-9 d sm-50 ………………………………………………………………… 3-9 d sm-30 ………………………………………………………………… 3-9 d hm-36 ………………………………………………………………… 3-10 ■ connecting the rc-28 (optional product) …………………………… 3-10 basic operation section 4 ■ when first applying pow...
Page 11
X table of contents ■ ■ electronic keyer functions ……………………………………………… 5-9 d memory keyer screen ……………………………………………… 5-10 d editing a keyer memory …………………………………………… 5-11 d contest number set mode ………………………………………… 5-12 d keyer set mode ……………………………………………………… 5-13 ■ ■ operating rtty (fsk) ………………………………………...
Page 12
Xi table of contents functions for receive section 7 ■ preamplifier ……………………………………………………………… 7-2 ■ attenuator ……………………………………………………………… 7-2 ■ rit function ……………………………………………………………… 7-3 ï rit monitor function ………………………………………………… 7-3 ■ agc function control …………………………………………………… 7-4 ï selecting the preset...
Page 13
Xii table of contents ■ playing back the recorded audio (qso) ……………………………… 9-4 ■ operating while playing back ………………………………………… 9-5 ■ deleting a recorded audio file ………………………………………… 9-6 ■ deleting a recorded audio folder ……………………………………… 9-6 ■ instant replay function ………………………………………………… 9-7 ■ recordin...
Page 14
Xiii table of contents d editing (programming) memory names …………………………… 11-6 ■ ■ memory clearing………………………………………………………… 11-6 ■ ■ memo pads ……………………………………………………………… 11-7 d entering frequencies and operating modes into memo pads …… 11-7 d calling up a frequency and operating mode from memo pads … 11-8 ...
Page 15
Xiv set mode section 15 ■ ■ set mode description …………………………………………………… 15-2 d set mode operation ………………………………………………… 15-2 d screen arrangement ………………………………………………… 15-3 ■ ■ level set screen ………………………………………………………… 15-4 ■ ■ acc set screen ………………………………………………………… 15-6 ■ ■ display set screen ……………………………………...
Page 16
Xv table of contents specifications and options section 19 ■ specifications …………………………………………………………… 19-2 d general ……………………………………………………………… 19-2 d transmitter …………………………………………………………… 19-2 d receiver ……………………………………………………………… 19-3 d antenna tuner ………………………………………………………… 19-3 ■ options ……………………………………………...
Page 17: Panel Description Section
1-1 panel description section 1 ■ front panel ……………………………………………………………… 1-2 ■ rear panel ……………………………………………………………… 1-12 ■ display …………………………………………………………………… 1-14 ■ screen menu arrangement …………………………………………… 1-16.
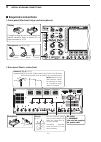
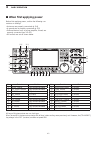
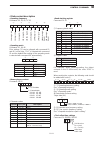
Page 18: Front Panel
1-2 1 panel description q power key [power] (pp. 4-3, 14-6) first, turn on the internal power supply. The internal power supply switch is located on the rear panel. (p. 1-12) ➥ push to turn on the transceiver power. • the [power] indicator above this key lights blue. ➥ hold down for 1 second to turn...
Page 19
1-3 1 panel description u microphone connector [mic] connect an optional microphone. • see page 3-4 for appropriate microphones. • see page 20-3 for microphone connector information. I sd card slot [sd card] (pp. 3-5, 10-2) insert the supplied sd card for both reading and stor- ing a wide variety of...
Page 20
1-4 1 panel description @3 agc control [agc] (p. 7-4) ■ ■ rotate to adjust the continuously-variable agc cir- cuit time constant. • to use the [agc] control, push the appropriate band’s [agc vr] (the [agc vr] indicator lights white). @4 agc volume key [agc vr] (p. 7-4) ➥ push to toggle the [agc] con...
Page 21
1-5 1 panel description #0 multi-function keys push to select the functions indicated in the display to the right of these keys. • functions vary, depending on the operating mode. ➥ push to select the ant1, ant2, ant3 or ant4 antenna connector. (p. 13-2) ➥ hold down for 1 second to display the anten...
Page 22
1-6 1 panel description #1 squelch control [sql] (p. 4-4) rotate to adjust the squelch threshold level. The squelch removes noise output from the speaker (closed condition) when no signal is received. • the squelch is particularly effective for fm. It is also available for other modes. • 11 to 12 o’...
Page 23
1-7 1 panel description #8 mini spectrum scope key [m.Scope] (p. 6-2) ➥ push to turn the mini spectrum scope screen on or off. • you can simultaneously display the mini spectrum scope screen with other screens, such as the memo- ry or set mode screens. ➥ hold down for 1 second to turn on the regular...
Page 24
1-8 1 panel description %1 automatic tuning key [auto tune] push to turn on the automatic tuning function in the cw or am mode. Important! When receiving a weak signal, or receiving a signal with interference, the automatic tuning function may tune the receiver to an undesired signal. %2 sub dial ch...
Page 25
1-9 1 panel description %6 notch key [notch] (p. 7-13) ➥ push to select the notch function between auto, manual, or off in the ssb or am mode. ➥ push to turn the manual notch function on or off in the cw, rtty, or psk mode. ➥ push to turn the auto notch function on or off in the fm mode. • “ mn ” is...
Page 26
1-10 1 panel description ^5 lock key [lock] (p. 4-12) push to turn the dial lock function on or off. ^6 quick tuning key [ts] ➥ push to turn the quick tuning step function on or off. (p. 4-7) • while the quick tuning icon, “ z ,” is displayed above the frequency readout, the frequency can be changed...
Page 27
1-11 1 panel description &3 digital rf selector key [digi-sel] (p. 7-12) push to turn the digital rf preselector on or off. • the [digi-sel] indicator lights white when the preselec- tor is in use. &4 passband tuning controls [twin pbt] (p. 7-5) adjusts the receiver’s if filter ‘passband width’ usin...
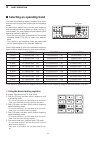
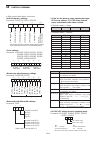
Page 28: Rear Panel
1-12 1 panel description q antenna connector [ant 1–4] (p. 3-4) connects to a 50 Ω antenna with a pl-259 plug connector. W ground terminal [gnd] (p. 3-2) connect this terminal to ground to prevent electrical shocks, tvi, bci and other problems. E circuit breaker cuts off the ac input if excessive cu...
Page 29
1-13 1 panel description !3 usb port [usb b] usb b type port connects to a pc. • a usb a-usb b cable is required. !4 accessory socket [a acc1] accessory socket [a acc2] accessory socket [b acc1] accessory socket [b acc2] connects to external equipment such as a linear amplifier, an automatic antenna...
Page 30: Display
1-14 1 panel description q band width indicator (p. 7-5) displays the passband width of the if filter. W mode indicator displays the selected mode. E shift frequency indicator (p. 7-5) displays the shift frequency of the if filter. R passband width indicator (p. 7-5) graphically displays the passban...
Page 31
1-15 1 panel description ■ display (continued) !4 lan indicator displays when the remote station accesses the transceiver through the lan connector. (an optional rs-ba1 is required.) !5 multi-function screen display screen for the digital multi-function me- ter, spectrum scope, audio scope, voice re...
Page 32: Screen Menu Arrangement
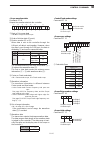
1-16 1 panel description f-1 f-2 f-3 f-4 f-5 f-6 f-7 f-3 f-4 f-5 f-2 f-5 f-3 f-6 f-3 f-7 ■ screen menu arrangement the following screens can be selected from the start up screen . Choose the desired screen using the fol- lowing guide. Pushing [exit/set] several times returns to the start up screen ....
Page 33: Set Mode Items Section
2-1 set mode items section 2 ■ ■ about the setting screen configuration ……………………………… 2-2 ■ ■ scope set …………………………………………………………… 2-3 ■ ■ voice set ……………………………………………………………… 2-4 ■ ■ keyer 001 ……………………………………………………………… 2-4 ■ ■ keyer cw-key ……………………………………………………… 2-5 ■ ■ rtty log set ………………………………………………………… ...
Page 34
2-2 2 set mode items ■ about the setting screen configuration the transceiver setting consists of the following items. Setting screen ref. Spectrum scope scope set pp. 2-3, 6-10 voice memory voice set pp. 2-4, 9-13 memory keyer keyer 001 pp. 2-4, 5-12 keyer cw-key pp. 2-5, 5-13 rtty decode rtty log ...
Page 35: Scope Set
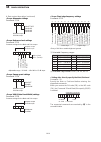
2-3 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Scope during tx (center type) transmit signal spectrum indication setting. Off, on p. 6-10 max hold peak level holding function setting. Off, 10s hold, on center type display center frequency setting when using the center type scope. Filter...
Page 36: Voice Set
2-4 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Voice 1st menu root screen selection that displays first after [voice](f) is pushed. Voice-root, voice-tx p. 9-13 voice tx auto monitor automatic monitor function setting when transmitting a voice memory recording. Off, on voice tx repeat t...
Page 37: Keyer Cw-Key
2-5 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Keyer repeat time interval setting for the memory keyer trans- mission repeat. 1 ~ 60 seconds (in 1 second steps) p. 5-13 dot/dash ratio dot/dash ratio setting for ele-key. 1:1:2.8 ~ 1:1:4.5 (in 0.1 steps) rise time rise time of the transmi...
Page 38: Psk Decode Set
2-6 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Psk fft scope averaging psk fft scope averaging function setting. Off, 2, 3, 4 p. 5-34 psk fft scope waveform color psk fft scope waveform color setting. 0~255 (in 1 digit steps) psk afc range psk afc (automatic frequency control) function'...
Page 39: Level Set
2-7 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Ssb rx hpf/lpf hpf (high-pass filter)/lpf (low-pass fil- ter) cut-off frequency setting for the received audio in ssb mode. Hpf 100hz ~ 2000hz lpf 500hz ~ 2400hz p. 15-4 ssb rx tone (bass) rx tone level setting for ssb. Bass –5~+5 (in 1 dig...
Page 40: Acc Set
2-8 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Acc-a af/sql output select [a acc1] band selection for the af/sql signal output. Main, sub p. 15-6 acc-b af/sql output select [b acc1] acc-a output select [a acc1] output signal setting. Af, if acc-a af/if xfc output (split on) band selecti...
Page 41
2-9 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Usb output select [usb b] output signal setting. Af, if p. 15-7 usb af/if xfc output (split on) band selection for the af/if signal output while holding down [xfc] dur- ing split operation. Main, sub usb af output level af output level sett...
Page 42: Display Set
2-10 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Lcd unit bright lcd unit brightness setting. 0 (dark) to 100% (bright) range (in 1% steps) p. 15-10 backlight (switches) switch illumination brightness setting. Display type screen image type setting. A, b, 50th anniversary (only ic-7850) ...
Page 43: Time Set
2-11 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Date date setting. Year 2000~2099, month/day 1- 1~12-31 p. 15-12 time (now) clock setting. 0:00~23:59 ntp function ntp server client function setting. Off, on ntp server address ntp server address setting. Utc offset offset time setting fr...
Page 44
2-12 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Transverter function transverter function setting. On, auto p. 15-14 transverter offset offset frequency setting for the transverter operation. 0.000 to 99.999 mhz (in 1 khz steps) rtty mark frequency rtty mark frequency setting. 1275, 161...
Page 45
2-13 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Cw normal side carrier point setting for the cw mode op- eration. Lsb, usb p. 15-16 apf type audio filter shape setting for apf. Soft, sharp mic af out band selection for audio output from [mic] (pin 8). Main+sub, sub mic input dc bias bia...
Page 46
2-14 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Ci-v output (for ant) antenna controller status data output set- ting. Off, on p. 15-18 ci-v usb port link setting for ci-v signal line between [usb b] and [remote]. Link to [remote], unlink from [remote] ci-v usb baud rate ci-v data trans...
Page 47
2-15 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Primary dns server (valid after reboot) primary dns (domain name system) serv- er address setting for the ip remote control. P. 15-20 2nd dns server (valid after re- boot) secondary dns (domain name system) server address setting for the i...
Page 48: Load Set
2-16 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Load contents loading contents setting. All, select p. 10-4 ant memory antenna memory load setting. Yes, no ref in/out, ref adjust, filter cal reference frequency signal, reference fre- quency adjustment value, and 1.2 khz filter calibrati...
Page 49: Filter Shape Set
2-17 2 set mode items items descriptions range or value ref. Hf ssb (600hz – ) hf bands ssb mode filter shape setting when 600 hz or narrower width is set. Sharp, soft p. 7-9 hf ssb-d (600hz – ) ssb-d mode hf cw ( – 500hz) cw mode filter shape setting when 500 hz or narrower width is set. Hf cw (600...
Page 50
3-1 installation and connections section 3 caution: the transceiver weights approximately 23.5 kg (52 lb). Always have two people available to carry, lift or turn over the transceiver. ■ unpacking ……………………………………………………………… 3-2 ■ selecting a location …………………………………………………… 3-2 ■ grounding ……………………………………...
Page 51: Unpacking
3-2 3 installation and connections ■ unpacking after unpacking, immediately report any damage to the delivering carrier or dealer. Keep the shipping car- tons. For a description and a diagram of accessory equip- ment included with the transceiver, see ‘supplied ac- cessories’ on page vii of this man...
Page 52: Connecting Antenna
3-3 3 installation and connections ■ connecting antenna for radio communications, the antenna is of critical importance, along with the output power and receiver sensitivity. Select antennas, such as a well-matched 50 Ω antenna, and feedline. If you use only one antenna, connect it to the [ant1] con...
Page 53: Required Connections
3-4 3 installation and connections ■ required connections d front panel (electronic keyer and microphone) d rear panel (basic connection) microphones (pp. 3-9, 3-10) cw key a straight or bug key can be used when the internal electronic keyer is turned off in keyer set mode. (p. 5-13) optional hm-36 ...
Page 54: Advanced Connections
3-5 3 installation and connections ■ advanced connections d front panel (microphone, headphones and sd card) d rear panel (optional products and external equipment) headphones mic external equipment for afsk opera- tion (p. 3-8), or an external keypad (p. 20-3) can also be connected to [mic]. Sd car...
Page 55
3-6 3 installation and connections ■ advanced connections (continued) d rear panel (optional products and external equipment) l b external display connects to a pc-style monitor display. (dvi-i) connects to a usb device such as keyboard, mouse, hub, memory (usb flash drive), or optional rc-28. • tur...
Page 56: Linear Amplifier Connections
3-7 3 installation and connections ■ linear amplifier connections d connecting the ic-pw1/euro d connecting a non-icom linear amplifier r warning! Set the transceiver output power and linear ampli- fier alc output level referring to the linear amplifier instruction manual. The alc input level must b...
Page 57
3-8 3 installation and connections ■ fsk and afsk (sstv) connections the transceiver has a modem function for rtty and psk. However, if you want to use a pc to operate these digital modes, it is necessary to prepare the fol- lowing interface circuit, or use a similar 3rd party de- vice. Refer to the...
Page 58
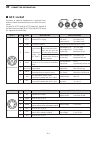
3-9 3 installation and connections ■ microphones (optional products) d sm-50 d sm-30 q r w e q w t mic gain on off low cut y r mic gain y top view top view bottom view bottom view q ptt switch hold down to transmit, release to receive. W ptt lock switch push to lock the ptt switch in the transmit mo...
Page 59
3-10 3 installation and connections ■ microphones (optional products) (continued) d hm-36 q ptt switch hold down to transmit, release to receive. W up/down switches [up]/[dn] change the selected readout frequency or memory channel. • holding down continuously changes the frequency or memory channel....
Page 60: Basic Operation Section
4-1 basic operation section 4 ■ when first applying power …………………………………………… 4-2 ■ power on ……………………………………………………………… 4-3 d resetting the cpu (initial setup) …………………………………… 4-3 ■ adjusting the audio level ……………………………………………… 4-4 ■ adjusting the squelch level …………………………………………… 4-4 ■ adjusting the rf gai...
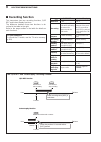
Page 61: When First Applying Power
4-2 4 basic operation w e r t y u o q i !0 !1 !2 !3 !4 !5 !6 !7 !8 !9 @0 no. Control position no. Control position q delay control fully counterclockwise !1 moni gain control 12 o'clock w key speed control fully counterclockwise !2 comp control 12 o'clock e rf pwr control fully clockwise !3 drive co...
Page 62: Power On
4-3 4 basic operation ■ power on q push [i/o] on the rear panel to turn on the main power. • the transceiver power is still off but the [power] indi- cator lights orange. • when first applying power, refer to the ‘resetting the cpu (initial setup).’ w push [power] on the front panel. • the transceiv...
Page 63: Adjusting The Audio Level
4-4 4 basic operation ■ adjusting the audio level ➥ rotate the [af] control to adjust the audio output level. • set a suitable audio level. Independently adjust the main and sub bands. ■ adjusting the rf gain the [rf] control adjusts the receiver sensitivity. This is usually set for maximum sensitiv...
Page 64
4-5 4 basic operation ■ selecting the main and sub bands ■ selecting the vfo or memory mode [main] [sub] vfo indicator memory channel number [v/m] this transceiver has 2 identical receivers, main and sub. The main band is displayed on the left hand side, and the sub band is displayed on the right ha...
Page 65: Selecting An Operating Band
4-6 4 basic operation ■ selecting an operating band the triple band stacking register provides three mem- ories for each band to store frequencies and operating modes. If a band key is pushed once, the last used frequency and operating mode are called up. When the key is pushed again, the next previ...
Page 66: Setting The Frequency
4-7 4 basic operation ■ setting the frequency the transceiver has several setting methods for conve- nient frequency setting. D tuning with [dial] q select the desired band with the band keys. W rotate [main dial] to set the desired frequency in the main band. Rotate [sub dial] to set the desired fr...
Page 67
4-8 4 basic operation ■ setting the frequency (continued) d selecting the fine tuning function the minimum tuning step of 1 hz can be used for fine tuning. With the quick tuning function off. Q hold down [ts] for 1 second. • the 1 hz digit is displayed. W rotate [main dial] to tune the frequency. • ...
Page 68
4-9 4 basic operation [example] 7.00000 mhz 21.24000 mhz 21.24000 mhz 21.36000 mhz push push push f-inp ent push keypad key entries d entering the frequency with the keypad the transceiver has a keypad for direct frequency en- try, as described below. Q push [f-inp]. • the “ f-inp ” indicator is dis...
Page 69: Selecting The Operating Mode
4-10 4 basic operation the following modes are selectable. • ssb (usb/lsb) and ssb data (usb data/lsb data) modes • cw and cw reverse (cw-r) modes • rtty and rtty reverse (rtty-r) modes • psk and psk reverse (psk-r) modes • am and am data modes • fm and fm data modes select the desired operating mod...
Page 70: Selecting The Meter Readout
4-11 4 basic operation ■ selecting the meter readout the s/rf meter readout during transmit can be se- lected from the following items. ➥ push the multi-function [meter]( ) key several times to select the desired meter item. • the selectable meters are: p o swr alc comp v d i d in that order. D digi...
Page 71: Dial Lock Function
4-12 4 basic operation ■ selecting the meter readout (continued) d selecting the meter type a total of 3 meter types are selectable. The meter types are standard, edgewise and bar me- ters. Follow the instructions to select the meter type. Q select the “meter type (normal screen)” item in the displa...
Page 72: Basic Transmit Operation
4-13 4 basic operation ■ basic transmit operation d transmitting q push [transmit] or [ptt] (microphone) to trans- mit. • the main band’s [tx] indicator lights red. • when split operation is selected, the sub band’s [tx] indicator lights. W push [transmit] again or release [ptt] (micro- phone) to re...
Page 73
4-14 4 basic operation ■ basic transmit operation (continued) d adjusting the drive gain the drive gain is active for all modes except ssb with- out speech compressor. The [drive] control adjusts the amplifying gain at the driver stage. Q push the multi-function [meter]( ) key to select the alc mete...
Page 74: Band Edge Warning Beep
4-15 4 basic operation see the next page for details of entering a frequency range on the band edge screen. ■ band edge warning beep this function allows you to hear a beep tone when you tune in or out of an amateur band’s frequency range. A regular beep sounds when you tune into a range, and a lowe...
Page 75
4-16 4 basic operation ■ band edge warning beep (continued) d entering the user band edge up to 30 frequency ranges can be set. • in the default setting, all frequency ranges that can be used, are entered. When new band edge is entered, change or delete the band edge that includes the duplicate freq...
Page 76
4-17 4 basic operation • the multi-function keys for entering the frequen- cy range: when inserting a blank line, push [ p ](f) or [ q ](f) to select the line below the one where you want to insert a new line. And then push [ins]( ). • if 30 band edges are already entered, a new line cannot be inser...
Page 77
4-18 4 basic operation ■ about the 5 mhz frequency band operation (usa version only) operation on the 5 mhz frequency band is allowed on 5 discrete frequencies and must adhere to the follow- ing: • the usb, usb data, cw, and psk modes. • maximum of 100 watts erp (effective radiated power) • 2.8 khz ...
Page 78
5-1 receive and transmit section 5 ■ ■ convenient functions for receive …………………………………… 5-2 ■ ■ convenient functions for transmit …………………………………… 5-3 ■ ■ operating ssb ………………………………………………………… 5-4 ■ ■ operating cw …………………………………………………………… 5-5 d about the cw pitch control ………………………………………… 5-6 d apf (audio...
Page 79
5-2 5 receive and transmit this section, describes particular operations for each operating mode, such as operating the memory keyer in the cw mode, or operating the encoder or decoder in the rtty or psk mode. If you use functions that are described in section 6: scope operation, section 7: function...
Page 80
5-3 5 receive and transmit ssb/am/fm modes vox function (p. 8-2) the vox (voice-operated transmission) function switches between transmit and receive with your voice. This function provides hands-free operation. ➥ push [vox/bk-in] to turn the vox function on or off. • “vox” is displayed when the vox...
Page 81: Operating Ssb
5-4 5 receive and transmit ■ operating ssb before transmitting, monitor your selected operating frequency to make sure you don’t cause interference to other stations on the same frequency. Q push a band key to select desired band. W push the mode key [ssb] to select the ssb mode. • “usb” or “lsb” is...
Page 82: Operating Cw
5-5 5 receive and transmit ■ operating cw before transmitting, monitor your selected operating frequency to make sure you don’t cause interference to other stations on the same frequency. Q push a band key to select the desired band. W push the mode key [cw] to select the cw mode. • “cw” or “cw-r” i...
Page 83
5-6 5 receive and transmit • filter screen cw pitch display (example: 700 hz) [cw pitch] ■ operating cw (continued) d about the cw pitch control the received cw audio pitch and cw side tone can be adjusted to suit your preference. This does not change the operating frequency. Q rotate [cw pitch] to ...
Page 84
5-7 5 receive and transmit d adjusting the key speed when using the internal electric keyer, you can adjust the key speed. ➥ rotate [key speed]. • the key speed popup appears. You can confirm the ad- justed speed by numeral. • selectable speed: 6 ~ 48 wpm (word per minutes). D about the cw reverse m...
Page 85
5-8 5 receive and transmit ■ operating cw (continued) d about 137 khz band operation (europe version only) the 137 khz band, between the 135.7 khz to 137.8 khz, operation in the cw mode is optionally available. The rf signal from [x-verter] is used for the 137 khz band operation, and an external amp...
Page 86: Electronic Keyer Functions
5-9 5 receive and transmit ■ electronic keyer functions this transceiver has a number of convenient functions for the built-in electronic keyer. The multi-function screens are off: q push the mode key [cw]. W push [keyer](f). • the memory keyer screen is displayed. E push [exit/set]. • the memory ke...
Page 87
5-10 5 receive and transmit ■ electronic keyer functions (continued) d memory keyer screen preset characters can be sent using the memory keyer screen. Contents of the memory keyer are entered in the keyer edit screen. • transmitting the multi-function screens are off: q push the mode key [cw]. W pu...
Page 88
5-11 5 receive and transmit d editing a keyer memory the contents of the memory keyer memories can be set in the keyer edit screen . The memory keyer can memorize and retransmit eight cw key codes for of- ten-used cw sentences, contest serial numbers, and so on. The capacity of the memory keyer is 7...
Page 89
5-12 5 receive and transmit ■ electronic keyer functions (continued) d contest number set mode this mode is used to set the number style, count up trigger and present number. • setting contents the multi-function screens are off: q push [keyer](f). • the memory keyer screen is displayed. W display t...
Page 90
5-13 5 receive and transmit d keyer set mode this set mode is used to set the memory keyer repeat time, dash weight, paddle specifications, keyer type, and so on. • setting contents the multi-function screens are off: q push [keyer](f). • the memory keyer screen is displayed. W display the memory ke...
Page 91: Operating Rtty (Fsk)
5-14 5 receive and transmit ■ operating rtty (fsk) a dsp-based high-quality baudot rtty encoder/de- coder is built-in to the transceiver. When connecting a pc keyboard, you can operates rtty without an ex- ternal rtty terminal or pc. If you would rather use your rtty terminal, consult the equipment ...
Page 92
5-15 5 receive and transmit d about the rtty reverse mode received characters are occasionally garbled when the received signal has the mark and space tones reversed. This reversal can be caused by incorrect tnc connections, setting, or commands. To receive reversed rtty signals correctly, select th...
Page 93
5-16 5 receive and transmit ■ operating rtty (fsk) (continued) d functions for the rtty decoder display q push the mode key [rtty/psk] to select the rtty mode. • after the rtty mode is selected, hold down [rtty/psk] for 1 second to toggle between the rtty and rtty-r modes. • “rtty” or “rtty-r” appea...
Page 94
5-17 5 receive and transmit • rtty threshold setting screen d setting the decoder threshold level adjust the rtty decoder threshold level if some characters are displayed, even though no signal is re- ceived. Q display the rtty decode screen, then push [adj] (f). Decode [f-3] adj [f-5] • the rtty th...
Page 95
5-18 5 receive and transmit q display the rtty decode screen, then push [tx mem](f). Decode [f-3] tx mem [f-4] • the rtty memory screen is displayed. W push [edit](f). • the rtty memory edit screen is displayed. E push [rt1..Rt8](f) several times. • push [rt1..Rt8] to select the tx memory. (rt1 rt2 ...
Page 96
5-19 5 receive and transmit d editing the rtty memory the contents of the rtty memories can be set us- ing the memory edit menu. The memory can store and retransmit 8 rtty message for often-used rtty con- tent. The capacity of the memory is 70 characters per memory channel. • programming contents q ...
Page 97
5-20 5 receive and transmit ■ operating rtty (fsk) (continued) d turning on the rtty log turn on the rtty log to store your rtty operating record, both tx and rx, onto an sd card or usb flash drive. Be sure to insert an sd card or usb flash drive, other- wise this function does not work. Q display t...
Page 98
5-21 5 receive and transmit d confirm the rtty log contents you can confirm the rtty log contents on the trans- ceiver display. Q display the rtty decode screen, then push [](f). Decode [f-3] [f-1] displays • the function menu changes to menu 2. W push [log view](f). • the rtty log list screen is di...
Page 99
5-22 5 receive and transmit ■ operating rtty (fsk) (continued) d rtty decode set mode this set mode is used to set the decode usos func- tion, time stamp setting, and other rtty settings. Q display the rtty decode screen, then push [](f). Decode [f-3] [f-1] displays • the function menu changes to me...
Page 100
5-23 5 receive and transmit rtty auto cr+lf by tx (default: on) selects sending a new line code (cr+lf) once when transmitting. • on: transmits the cr+lf code once. • off: does not transmit the cr+lf code. Rtty time stamp (default: on) turns the time stamp (date, transmission or reception time) disp...
Page 101: Operating Psk
5-24 5 receive and transmit ■ operating psk a high-quality dsp-based psk encoder/decoder is built into the transceiver. You can connect a keyboard to the transceiver and operate psk without a pc. (p. 3-6) this transceiver can be used in the psk31 and psk63 modes. If you would rather use your psk sof...
Page 102
5-25 5 receive and transmit • indication example tuned bpsk signal bpsk/qpsk idle signal unmodulated signal tuned qpsk signal d vector indicator and waterfall display you can fine tune the psk signal using the vector tun- ing indicator and waterfall display. Q slowly rotate the [main dial]. • when a...
Page 103
5-26 5 receive and transmit ■ operating psk (continued) d functions for the psk decoder display q push the mode key [rtty/psk] to select the psk mode. • after the psk mode is selected, hold down [rtty/psk] for 1 second to toggle between the psk and psk-r modes. • “psk” or “psk-r” appears. W push [de...
Page 104
5-27 5 receive and transmit d about the bpsk and qpsk modes the bpsk and qpsk modes are selectable in the psk31 mode. • the bpsk (binary phase shift keying) mode is the most commonly used mode. • the qpsk (quadrature phase shift keying) mode has error correction capability to provide better de- codi...
Page 105
5-28 5 receive and transmit ■ operating psk (continued) d setting the decoder threshold level adjust the psk decoder threshold level if some charac- ters are displayed even, though no signal is received. Q display the psk decode screen, then push [adj](f). Decode [f-3] adj [f-5] • the threshold sett...
Page 106
5-29 5 receive and transmit d psk memory transmission preset characters can be sent using the psk memory. Contents of the memory are entered in the psk memory edit screen. The multi-function screens are off: q push [decode](f). • the psk decode screen is displayed. W push [tx mem](f) to select the p...
Page 107
5-30 5 receive and transmit q display the psk decode screen, then push [tx mem](f). Decode [f-3] tx mem [f-4] • the psk memory screen is displayed. W push [edit](f). • the psk memory edit screen is displayed. E push [pt1..Pt8](f) several times. • push [pt1..Pt8] to select the tx memory. (pt1 pt2 pt3...
Page 108
5-31 5 receive and transmit • preset contents ch name contents pt1 mycallx2 ↵ de icom icom k ↵ pt2 mycallx3 ↵ de icom icom icom k ↵ pt3 qslur599 ↵ qsl ur 599 599 bk ↵ pt4 de+ur599 ↵ qsl de icom icom ur 599 599 bk ↵ pt5 73 gl sk ↵ 73 gl sk ↵ pt6 cq cq cq ↵ cq cq cq de icom icom icom k ↵ pt7 rig&ant ↵...
Page 109
5-32 5 receive and transmit ■ operating psk (continued) d turning on the psk log turn on the psk log to store your psk operating re- cord, both tx and rx, onto an sd card or usb flash drive. Be sure to insert an sd card or usb flash drive, other- wise this function does not work. Q display the psk d...
Page 110
5-33 5 receive and transmit d confirm the psk log contents you can confirm the psk log contents on the trans- ceiver display. Q display the psk decode screen, then push [](f). Decode [f-3] [f-1] displays • the function menu changes to menu 2. W push [log view](f). • the psk log list screen is displa...
Page 111
5-34 5 receive and transmit psk fft scope averaging (default: off) sets the fft scope waveform averaging function from 2 to 4 or off. Recommendation! Use the default or smaller number fft scope wave- form setting for tuning. Psk fft scope waveform color (default: (r) 51 (g) 153 (b) 255) sets the col...
Page 112
5-35 5 receive and transmit psk font color (recieve) (default: (r) 128 (g) 255 (b) 128) sets the text color for received characters. • the color is set in the rgb format. • push [ t u ]( f ) to select r (red), g (green) and b (blue). Rotate [main dial] to adjust the ratio from 0 to 255. • the color ...
Page 113: Operating Am Or Fm
5-36 5 receive and transmit ■ operating am or fm before transmitting, monitor the operating frequency to make sure transmitting won’t cause interference to other stations on the same frequency. Q push a band key to select the desired band. W push the mode key [am/fm] to select the am or fm mode. • “...
Page 114: Repeater Operation
5-37 5 receive and transmit ■ repeater operation a repeater amplifies received signals and retransmits them on a different frequency. When using a repeater, the transmit frequency is shifted from the receive fre- quency by an offset amount. A repeater can be ac- cessed using split frequency operatio...
Page 115
5-38 5 receive and transmit d repeater tone frequency setting some repeaters require subaudible tones to be ac- cessed. Subaudible tones are superimposed on your normal signal, and must be set in advance. The trans- ceiver has 50 tones from 67.0 hz to 254.1 hz. Q hold down the multi-function [tone](...
Page 116: Tone Squelch Operation
5-39 5 receive and transmit ■ tone squelch operation the tone squelch opens only when you receive a sig- nal containing a matching subaudible tone in the fm mode. You can silently wait for calls from others using the same tone. When you transmit, the tone frequency is superim- posed on your own sign...
Page 117: Data Mode (Afsk) Operation
5-40 5 receive and transmit ■ data mode (afsk) operation when operating amtor or packet with a pc appli- cation software, consult the manual that comes with the software. Before transmitting, monitor the operating frequency to make sure transmitting won’t cause interference to other stations on the ...
Page 118: Scope Operation Section
6-1 scope operation section 6 ■ ■ spectrum scope screen ……………………………………………… 6-2 d operating the spectrum scope …………………………………… 6-3 d center mode ………………………………………………………… 6-4 d fixed mode …………………………………………………………… 6-5 d dual scope screen …………………………………………………… 6-6 d mini scope screen …………………………………………………… 6-6...
Page 119: Spectrum Scope Screen
6-2 6 scope operation • center mode screen • fixed mode screen ■ spectrum scope screen this dsp-based spectrum scope allows you to display the activity on the selected band, as well as the relative strengths of various signals. This transceiver has two spectrum scope modes. One is the center mode, a...
Page 120
6-3 6 scope operation d operating the spectrum scope the multi-function screens are off: q push [scope](f). • the spectrum scope screen is displayed. Function action selects the function menu. Span when the center mode is selected, selects the scope span. • selectable spans: ±2.5, 5.0, 10, 25, 50, 1...
Page 121
6-4 6 scope operation ■ spectrum scope screen (continued) d center mode displays signals around the operating frequency within the selected span. The operating frequency is always displayed in the center of the screen. The multi-function screens are off: q push [scope](f). • the spectrum scope scree...
Page 122
6-5 6 scope operation the marker display in the fixed mode in the fixed mode, the marker displays the operat- ing frequency. So, the transceiver always displays the main marker on the main scope, or the sub marker on the sub scope. • marker types : main marker displays the operating frequency for ma...
Page 123
6-6 6 scope operation ■ spectrum scope screen (continued) d dual scope screen this transceiver has a dual scope mode that simul- taneously displays the main and sub scopes during dualwatch operation. You can select the “over/under” or “side by side” lay- out in the scope set screen. The multi-functi...
Page 124
6-7 6 scope operation d scope attenuator while operating in the band with a high noise floor, set the scope attenuator to reduce the noise level. • even if the scope attenuator is on, it does not affect the receiver sensitivity. The multi-function screens are off: q push [scope](f). • the spectrum s...
Page 125
6-8 6 scope operation • function menu (menu2) • reference level (±0.0 db) • difference spectrum (+20.0 db, ±0.0 db, –20.0 db) • display example (+20.0 db) • display example (–20.0 db) reference level (+20.0 db) ±0.0 db –20.0 db +20.0 db all signal levels appear stronger. All signal levels appear wea...
Page 126
6-9 6 scope operation d sweep speed select the sweep speed to change the fft (fast fou- rier transform) scope renew speed and the waterfall speed. • if you want to change only the waterfall speed, you can select “slow,” “mid,” or “fast” in the scope set screen. Q display the spectrum scope screen, t...
Page 127
6-10 6 scope operation ■ spectrum scope screen (continued) d scope set screen this set screen is used to set the waveform color, scope range for the fixed mode, and so on. Q display the spectrum scope screen, then hold down [expd/set](f) for 1 second. Scope [f-1] expd/set [f-7] • the scope set scree...
Page 128
6-11 6 scope operation waterfall speed (default: mid) select the waterfall speed. • slow: sets the waterfall speed to slow. • mid: sets the waterfall speed to mid. • fast: sets the waterfall speed to fast. Waterfall size (expand scope) (default: mid) select the waterfall height in the expand scope s...
Page 129
6-12 6 scope operation ■ spectrum scope screen (continued) dual scope auto select (default: on) when the dual scope is selected, the band selection keys, [main] and [sub] simultaneously select the main or sub scope. • off: push [m/s dual](f) or click the mouse button to select the main or sub scope....
Page 130
6-13 6 scope operation fixed edges (20.00 – 22.00) (default: 21.000–21.450 mhz) (default: 21.000–21.150 mhz) (default: 21.150–21.450 mhz) set the upper and lower edge frequencies for the fixed mode. Three edges are assigned to each band. Push [edge](f) to select the edge. • selectable range: 20.000 ...
Page 131
6-14 6 scope operation ■ spectrum scope screen (continued) d usb mouse operation if you connect a usb mouse to the transceiver, a mouse pointer appears on the spectrum scope screen. Now, you can change the frequency or settings by us- ing the mouse. • clicking while holding down [xfc] changes the tr...
Page 132: Audio Scope Screen
6-15 6 scope operation • audio scope screen ■ audio scope screen this audio scope allows you to display the received signal’s frequency component on the fft scope, and its waveform components on the oscilloscope. The fft scope has an waterfall. Note: when the monitor function is on, you can see the ...
Page 133
6-16 6 scope operation ■ audio scope screen (continued) d audio scope set mode this set mode is used to set the fft scope waveform type, color, waterfall display and oscilloscope wave- form color. Q display the audio scope screen, then hold down [set](f) for 1 second. Audio [f-6] set [f-7] • the aud...
Page 134
7-1 functions for receive section 7 ■ preamplifier ……………………………………………………………… 7-2 ■ attenuator ……………………………………………………………… 7-2 ■ rit function ……………………………………………………………… 7-3 ï rit monitor function ………………………………………………… 7-3 ■ agc function control …………………………………………………… 7-4 ï selecting the preset value …………………………...
Page 135: Preamplifier
7-2 7 functions for receive ■ preamplifier the preamp amplifies received signals in the receiver front end to improve the signal-to-noise ratio and sen- sitivity. Set this to p.Amp 1 or p.Amp 2 when receiving weak signals. ➥ push the multi-function [p.Amp]( ) key several times to turn on preamp 1 or...
Page 136: Rit Function
7-3 7 functions for receive ■ rit function the rit (receive increment tuning) function compen- sates for differences in frequencies of other stations. The function shifts the receive frequency up to ±9.99 khz in 10 hz steps, without moving the transmit frequency. Q push [rit] to turn on the rit func...
Page 137: Agc Function Control
7-4 7 functions for receive mode default selectable agc time constant 0.3 (fast) 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6, 2.0, ssb 2.0 (mid) 2.5, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0 6.0 (slow) 0.1 (fast) 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6, 2.0, cw 0.5 (mid) 2.5, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0 1.2 (slow) rtty 0.1 (fast) 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, ...
Page 138: Twin Pbt Operation
7-5 7 functions for receive ■ twin pbt operation in general, the pbt (passband tuning) electronically narrows the if passband width by shifting the if fre- quency to slightly outside of the if filter passband, to reject interference. The transceiver uses dsp for the pbt function. You can watch the n...
Page 139: If Filter Selection
7-6 7 functions for receive [exit/set] (f) function keys [main dial] [filter] main, sub • when selecting “fil1” (wide) • when selecting “fil2” (mid) • when selecting “fil3” (narrow) • while adjusting the passband width • when selecting the passband width (500 hz or less) blinks mode if filter adjust...
Page 140
7-7 7 functions for receive d dsp filter shape the dsp filter shape for ssb, ssb data and cw can be independently set to soft or sharp. Q hold down [filter] for 1 second. • the filter screen is displayed. W select the ssb, ssb-d1 or cw mode. E push [filter] several times to set the desired if filter...
Page 141
7-8 7 functions for receive • when selecting “1.2 k” roofing filter • in the filter calibration mode (automatic adjustment) blinks ■ if filter selection (continued) d 1.2 khz filter calibration this transceiver has the 1.2 khz optimum roofing filter operating at 64 mhz. The characteristic of this ro...
Page 142
7-9 7 functions for receive ■ if filter selection (continued) hf ssb (600hz – ) (default: sharp) select the filter shape for the ssb mode in the hf bands. Options: sharp or soft the set filter shape is automatically used only when the if filter is set to 600 hz or wider. Hf ssb-d (600hz – ) (default...
Page 143: Dualwatch Operation
7-10 7 functions for receive ■ dualwatch operation dualwatch simultaneously monitors two frequencies. This transceiver has 2 independent receiver circuits, the main and sub bands, so that you can use dual- watch with no compromises, even on different bands and modes. Q set the desired mode in the ma...
Page 144: Noise Blanker
7-11 7 functions for receive ■ noise blanker the noise blanker eliminates pulse-type noise such as the noise from car ignitions. The noise blanker cannot be used in the fm mode. Q push [nb] to turn on the noise blanker function. • [nb] indicator lights. • pushing [nb] toggles the noise blanker funct...
Page 145: Noise Reduction
7-12 7 functions for receive ■ noise reduction the noise reduction function reduces random noise components and enhances desired signals that are buried in noise. The noise reduction function uses the dsp circuit. Q push [nr] to turn on the noise reduction. • [nr] indicator lights. • pushing [nr] to...
Page 146: Notch Function
7-13 7 functions for receive ■ notch function the transceiver has auto and manual notch functions. • auto notch: used in the ssb, am, or fm mode • manual notch: used in the ssb, cw, rtty, psk, or am mode d auto notch function the auto notch function uses dsp to automatically at- tenuates beat tones,...
Page 147: Auto Tuning Function
7-14 7 functions for receive ■ auto tuning function when an off-frequency signal is received, the auto tuning function tunes the desired signal within a ±500 hz range in the cw mode, or a ±5 khz range in the am mode. This function is usable only in the cw and am modes. ➥ push [auto tune] to turn on ...
Page 148
8-1 functions for transmit section 8 ■ ■ about the vox function ………………………………………………… 8-2 d turning on the vox function ……………………………………… 8-2 d adjusting the vox function ………………………………………… 8-2 d vox set mode ……………………………………………………… 8-3 ■ ■ about the break-in function …………………………………………… 8-4 d semi break-in o...
Page 149: About The Vox Function
8-2 8 functions for transmit ■ about the vox function the vox (voice-operated transmission) function switches between transmit and receive with your voice. This function provides hands-free operation. D turning on the vox function q push the mode key to select a phone mode (ssb, am, fm). W push [vox...
Page 150
8-3 8 functions for transmit d vox set mode q hold down [vox/bk-in] for 1 second. • the vox set screen is displayed. W select the desired item using by pushing [ p ](f) or [ q ](f). E rotate [main dial] to the desired value or level. • hold down [def](f) for 1 second to select a default value. R pus...
Page 151: About The Break-In Function
8-4 8 functions for transmit ■ about the break-in function the break-in function is used in the cw mode to auto- matically toggle the transceiver between transmit and receive when keying. The transceiver is capable of full break-in or semi break-in. D semi break-in operation in the semi break-in mod...
Page 152: About The
8-5 8 functions for transmit ■ about the ∂ tx function the ∂ tx function shifts the transmit frequency up to ±9.999 khz in 1 hz steps (10 hz steps when the 1 hz step readout is not visible) without shifting the receive frequency. Q push [ ∂ tx]. • “ ∂ tx ” is displayed. W rotate [rit/ ∂ tx]. E to re...
Page 153
8-6 8 functions for transmit ■ setting the transmit filter width (ssb/ssb-d only) ■ setting the speech compressor (ssb only) the transmit filter width for the ssb and ssb-d modes can be set. Only the ssb mode can be set to wide, mid and narrow. Q push the mode key [ssb] to select the usb or lsb mode...
Page 154: Split Frequency Operation
8-7 8 functions for transmit split frequency operation allows you to transmit and receive in the same mode on two different frequencies. Split frequency operation uses one frequency on the main band and another on the sub band. The following is an example of using 21.290 mhz for receiving and 21.310...
Page 155
8-8 8 functions for transmit when you find a dx station, an important consider- ation is how to set the split frequency. When you hold down [split] for 1 second, the split frequency function is turned on, the sub band fre- quency is equalized to the main band frequency, and it becomes the initial tr...
Page 156
9-1 voice recorder functions section 9 ■ recording function ……………………………………………………… 9-2 ■ recording a qso ……………………………………………………… 9-3 quick recording ……………………………………………………… 9-3 basic recording ……………………………………………………… 9-3 ■ playing back the recorded audio (qso) ……………………………… 9-4 ■ operating while playing bac...
Page 157: Recording Function
9-2 9 voice recorder functions 15 seconds (default) present present past future push to record the audio contents rec past future hold down to start recording rec hold down to stop recording rec qso rec function instant replay function starts recording when [rec] is held down. Stores the previous 15...
Page 158: Recording A Qso
9-3 9 voice recorder functions d basic recording you can record both received and transmitted audio. ❍ the multi-function screens are off. Q push [voice](f). • the voice memory screen is displayed. W hold down [qso rec](f) for 1 second to start voice recording. • “ ” appears while recording. • “ ” a...
Page 159
9-4 9 voice recorder functions total time shows the file’s total playback time. Playback mark appears while the audio is playing back. • the mark disappears while pausing. You can playback the recorded qso audio. ❍ the multi-function screens are off. Q push [voice](f). • the voice memory screen is d...
Page 160: Operating While Playing Back
9-5 9 voice recorder functions for your reference: • holding down a key repeats the action until it is re- leased (other than the [ ](f) key). Example: hold down [ ](f) to repeat skipping 10 seconds until you release the [ ](f) key. (default: 10 seconds) • you can fast forward or rewind the file tha...
Page 161
9-6 9 voice recorder functions you can delete the recorded audio file. ❍ the multi-function screens are off. Q push [voice](f). • the voice memory screen is displayed. W push [qso play](f). • the voice qso player screen is displayed. • the folder list is displayed. • the folder name is formatted yyy...
Page 162: Instant Replay Function
9-7 9 voice recorder functions ■ instant replay function the instant replay function records the previous 15 seconds. This function is convenient for checking mis- heard audio. The audio is recorded into the built-in memory when [rec] is pushed. Only one record can be stored , and it is overwritten ...
Page 163: Recording The
9-8 9 voice recorder functions you can playback the recorded audio. ➥ hold down [play] for 1 second. • starts to playback all of the recorded audio. (default: 15 second) ➥ push [play]. • starts to playback the recorded audio for preset time period (default: 5 seconds). (p. 9-14) voice [f-2] set [f-7...
Page 164
9-9 9 voice recorder functions to transmit a message using the voice memory , first record the desired message as described below. You can record up to 8 digital voice messages of up to 200 seconds each, for transmission. D recording ❍ the multi-function screens are off. Q push [voice](f). • the voi...
Page 165
9-10 9 voice recorder functions d programming a tx message name you can enter alphanumeric names of up to 30 char- acters each for the recorded message . Example: entering a tx message name ‘cq ja3yua’ to the voice memory channel t1. ❍ the multi-function screens are off. Q push [voice](f). • the voi...
Page 166
9-11 9 voice recorder functions for your reference: when an external keypad (pp. 3-6, 20-4) or pc keyboard is connected (p. 15-16) , you can transmit the recorded messages. • when pushing one of [s1] to [s8] on the external keypad, the recorded message in t1 to t8 is transmitted once. When holding d...
Page 167
9-12 9 voice recorder functions ■ transmitting a recorded message (continued) d setting the transmit level ❍ the multi-function screens are off. Q push [voice](f). • the voice memory screen is displayed. W push [send](f). • the voice tx screen is displayed. E push [tx lev.](f). • opens the “tx level...
Page 168: Voice Set Mode
9-13 9 voice recorder functions ■ voice set mode sets the automatic monitor function, short play and normal recording times for the voice recorder. ❍ the multi-function screens are off. Q push [voice](f). • the voice memory screen is displayed. W push [set](f). • the voice set screen is displayed. E...
Page 169
9-14 9 voice recorder functions ptt auto rec (default: off) turn the ptt automatic recording function on or off. • off: the recording does not start even if a signal is transmitted. • on: the recording automatically starts when a sig- nal is transmitted. The recording will stop when: • 10 seconds ha...
Page 170: Section
10-1 using an sd card or usb flash drive section 10 ■ about the sd card ……………………………………………………… 10-2 ï inserting the sd card ……………………………………………… 10-2 ï removing the sd card ……………………………………………… 10-2 ■ sd/usb-memory menu screen ……………………………………… 10-3 ï save set screen ……………………………………………………… 10-4 ï load set s...
Page 171: About The Sd Card
10-2 10 using an sd card or usb flash drive an sdhc card is supplied. You can also use third party cards. An sd card of up to 2 gb, or an sdhc of up to 32 gb, can be used. Icom has checked the compatibility with the following sd and sdhc cards. (as of july 2018) brand type memory size sandisk® sd 2 ...
Page 172: Sd/usb-Memory Menu Screen
10-3 10 using an sd card or usb flash drive ■ sd/usb-memory menu screen • setting save screen (p. 10-5) • save set screen (p. 10-4) • load set screen (p. 10-4) • format screen (p. 10-8) • capture list screen (p. 10-10) • sd/usb-memory menu screen • unmount screen (p. 10-9) • firmware update screen (...
Page 173
10-4 10 using an sd card or usb flash drive load contents (default: select) select the contents to be loaded from the sd card or usb flash drive to the transceiver. • all: all memories and settings of the file are load- ed into the transceiver. • select: the specified memories and settings of the fi...
Page 174
10-5 10 using an sd card or usb flash drive ■ saving the setting data onto an sd card or usb flash drive memory channels and transceiver’s settings can be saved on a card or flash drive. Saving data settings on a card or flash drive allows you to easily restore the transceiver to its previous set- t...
Page 175
10-6 10 using an sd card or usb flash drive ■ loading the saved data files onto an sd card or usb flash drive memory channels and transceiver’s settings on the card or flash drive can be copied to the transceiver. This function is convenient when: • copying the saved data to another ic-7850/ic-7851 ...
Page 176
10-7 10 using an sd card or usb flash drive ■ saving with a different file name • setting save screen • when entering “ja3yua” • when changing a file name to “ja3yua” • confirmation window you can change the file name when saving onto a card or flash drive. The file name can be up to 15 characters. ...
Page 177: Deleting A Data File
10-8 10 using an sd card or usb flash drive ■ deleting a data file note: formatting a card or flash drive erases all its data. Before formatting any used card, back up its data onto your pc. If you use a brand new sd card, format it by doing the following steps. Q display the sd/usb-memory set scree...
Page 178
10-9 10 using an sd card or usb flash drive ■ unmounting an sd card or usb flash drive • when unmounting the sd card • unmount screen • when unmounting the usb flash drive • sd/usb-memory set screen electrically unmounts the card or flash drive when the power is on. Note: if you remove a card or fla...
Page 179: Screen Capture Function
10-10 10 using an sd card or usb flash drive d viewing the captured screen ■ screen capture function you can capture the transceiver display onto the sd card or usb flash drive. Most of the screens described in this manual were captured using this function. Note: some screens cannot be captured. Q d...
Page 180: Memory Operation Section
11-1 memory operation section 11 ■ ■ memory channels ……………………………………………………… 11-2 ■ ■ memory channel selection …………………………………………… 11-2 d using the m-ch [ p ] or [ q ] keys …………………………………… 11-2 d using the keypad …………………………………………………… 11-2 ■ ■ memory list screen ……………………………………………………… 11-3 d selecting a me...
Page 181: Memory Channels
11-2 11 memory operation memory memory transfer over- channel channel capability to vfo writing clear number regular memory 1–99 one frequency and one mode yes yes yes channels in each memory channel. Scan edge one frequency and one mode in memory p1, p2 each memory channel as scan yes yes no channe...
Page 182: Memory List Screen
11-3 11 memory operation ■ memory list screen the memory list screen simultaneously shows 9 memory channels and their programmed contents. 15 memory channels can be displayed in the expanded memory list screen . You can select a desired memory channel from the memory list screen . D selecting a memo...
Page 183
11-4 11 memory operation or hold down for 1 second. Beep beep beep [example]: programming 7.088 mhz/lsb into memory channel 12. Or then hold down for 1 second. Beep beep beep [example]: programming 21.288 mhz/usb into memory channel 18. ■ entering memory channel contents d entering in the memory mod...
Page 184: Copying Memory Contents
11-5 11 memory operation ■ copying memory contents the frequency and operating mode in a memory chan- nel can be copied to the vfo. Copying can be performed in either the vfo or mem- ory mode. D copying in the vfo mode this is useful for copying memory contents to the vfo mode. Q push [v/m] to selec...
Page 185: Memory Names
11-6 11 memory operation ■ memory names all memory channels (including scan edges) can be assigned alphanumeric names of up to 10 characters. Upper case letters, lower case letters, numerals, some symbols and spaces can be used. D editing (programming) memory names the multi-function screens are off...
Page 186: Memo Pads
11-7 11 memory operation ■ memo pads the transceiver has a memo pad function to store fre- quency and operating mode for easy write and recall. The memo pads are separate from memory channels. The default quantity of memo pads is 5. However, this can be increased to 10 in the others set mode, if de-...
Page 187
11-8 11 memory operation • memo pad list screen memo pads mp-r temporary pad oldest content newest content mp-r ■ memo pads (continued) d calling up a frequency and operating mode from memo pads d using the memo pad list screen you can easily call up the desired frequency and oper- ating mode of mem...
Page 188: Scans Section
12-1 scans section 12 ■ ■ scan types ……………………………………………………………… 12-2 ■ ■ preparing for a scan …………………………………………………… 12-3 ■ ■ scan set mode ………………………………………………………… 12-4 ■ ■ programmed scan ……………………………………………………… 12-5 ■ ■ fine programmed scan ………………………………………………… 12-6 ■ ■ memory scan ……………………………………………………………...
Page 189: Scan Types
12-2 12 scans ■ scan types • the scan functions can be used on the main band only. • you can scan while operating on a frequency using the dualwatch or split functions. Programmed scan repeatedly scans between two scan edge frequencies (scan edge memory channels p1 and p2). This scan works in the vf...
Page 190: Preparing For A Scan
12-3 12 scans ■ preparing for a scan for a programmed scan: enter scan edge frequencies into the scan edge memory channels p1 and p2. For a ∂ f scan: set the ∂ f span ( ∂ f scan range) in the scan screen. For a memory scan: enter frequencies in two or more memory channels, except scan edge memory ch...
Page 191: Scan Set Mode
12-4 12 scans ■ scan set mode when the squelch is open, the scan continues until it is manually stopped — it does not pause on detected sig- nals. When the squelch is closed, the scan stops when a signal is detected, then resumes according to the scan resume setting. The scan speed and the scan resu...
Page 192: Programmed Scan
12-5 12 scans ■ programmed scan a programmed scan searches for signals between scan edge memory channels “p1” and “p2.” before starting the programmed scan, you must enter scan edge frequencies into these channels. If the same frequencies are entered into scan edge memory channels p1 and p2, the pro...
Page 193: Fine Programmed Scan
12-6 12 scans • while scanning blinks blinks ■ fine programmed scan in the fine programmed scan, the scan speed de- creases when the squelch opens, but the transceiver keeps scanning. The scanning tuning step changes to 10 hz when the squelch opens. The multi-function screens are off. Q push [scan](...
Page 194: Memory Scan
12-7 12 scans ■ memory scan the multi-function screens are off. Q push [v/m]. • selects the memory mode. • pushing [v/m] toggles between the vfo and memory modes. W push [scan](f). • the scan screen is displayed. E push [memo](f). • the memory scan starts. • “ memory scan ” and decimal points blink ...
Page 195
12-8 12 scans d setting in the scan screen the multi-function screens are off. Q push [v/m]. • selects the memory mode. • pushing [v/m] toggles between the vfo and memory modes. E push [scan](f). • the scan screen is displayed. R select the desired memory channel to set as a se- lect memory channel....
Page 196: F Scan
12-9 12 scans ■ ∂ f scan the multi-function screens are off. Q select the vfo mode or a memory channel. W select the desired operating mode. • the operating mode can also be changed while scan- ning. E push [scan](f) . • the scan screen is displayed. R push [ ∂ f span](f) to set the ∂ f span. • sele...
Page 197: Tone Scan
12-10 12 scans ■ tone scan by monitoring a signal on an hf/6 m repeater input frequency, the transceiver can determine the tone fre- quency required to access the repeater. Q set the frequency or memory channel to be checked for a tone frequency. W push the mode key [am/fm] several times to select t...
Page 198
13-1 antenna tuner operation section 13 ■ ■ antenna connection and selection …………………………………… 13-2 ■ ■ receive antenna-i/o selection ……………………………………… 13-2 ■ ■ antenna memory settings ……………………………………………… 13-3 d selecting the antenna type ………………………………………… 13-4 d antenna selection mode …………………………………………… 13...
Page 199
13-2 13 antenna tuner operation ■ antenna connection and selection 3.5/7 mhz bands 21/28 mhz bands rx only 50 mhz bands ant4 ant3 ant2 ant1 ( ) multi-function keys [rx-ant b] out out in in [rx-ant a] • antenna connection example the transceiver has four antenna connectors for the hf/50 mhz bands, [a...
Page 200: Antenna Memory Settings
13-3 13 antenna tuner operation ■ antenna memory settings this function stores the antenna connector number for each frequency band. You can assign an antenna connected to [ant1] to [ant4] and the two [rx-i/o] and an operating band. Note: [ant1] is set as the default for all operating bands and no [...
Page 201
13-4 13 antenna tuner operation ■ antenna memory settings (continued) d selecting the antenna type when no antenna is connected to [ant2], [ant3], and/or [ant4], these antenna connectors can be de- activated— by deleting the antenna number from se- lection. This prevent the transceiver from accident...
Page 202
13-5 13 antenna tuner operation push [[ant] sw](f) to select the antenna selection mode. • antenna selection mode • options of the antenna selection mode d temporary memory the antenna temporary memory memorizes the man- ually selected antenna. The selected antenna will be recalled even if frequency...
Page 203
13-6 13 antenna tuner operation [rx-ant b] out out in in [rx-ant a] • when the rx-i/o is selected. Off rx-i/o a rx-i/o b • when the rx-i/o is selected (1) the setting is displayed set to rx-i/o a set to [rx-i/o] off • when the rx-i/o is selected (2) when a common antenna is selected on the main and ...
Page 204: About The Antenna Tuner
13-7 13 antenna tuner operation ■ about the antenna tuner the internal automatic antenna tuner automatically matches the transceiver to the connected antenna. After the tuner matches an antenna, the variable ca- pacitor angles are memorized as a preset point for each frequency range (100 khz steps)....
Page 205
13-8 13 antenna tuner operation ■ antenna tuner operation (continued) • ptt tuner start the tuner is always activated when ptt is pushed after the frequency is changed (more than 1% from last-tuned frequency). This function removes the “hold down [tuner],” and activates the tuner for the first trans...
Page 206: Clock And Timers Section
14-1 clock and timers section 14 ■ ■ time set mode ………………………………………………………… 14-2 d setting the date ……………………………………………………… 14-2 d setting the current time …………………………………………… 14-2 d setting the utc offset ……………………………………………… 14-2 d selecting the clock2 function …………………………………… 14-3 d setting the clock2 utc...
Page 207: Time Set Mode
14-2 14 clock and timers ■ time set mode this transceiver has a built-in calendar and 24-hour clock (accuracy of ±75 seconds per month) with daily power on/off timer functions. Before operating these timers, set the current date and time. The multi-function screens are off: q push set [f-7] then tim...
Page 208
14-3 14 clock and timers • when the “clock2 function” item is selected d selecting the clock2 function turn the clock 2 display on or off. (default: on) clock 2 is convenient to display the utc or other coun- try’s local time. In the time set screen: q push [ p ](f) or [ q ](f) to select the “clock2...
Page 209
14-4 14 clock and timers [main dial] [exit/set] (f) function keys • when the “ntp function” item is selected • when the “ntp server address” item is selected • when editing the “ntp server address” item a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w...
Page 210: Setting The Daily Timer
14-5 14 clock and timers ■ setting the daily timer the transceiver automatically turns power on and/or off on the specified day and time, with the specified frequency settings in both the main and sub bands. The multi-function screen is off: q hold down [timer] for 1 second. • the timer set screen i...
Page 211: Setting The Sleep Timer
14-6 14 clock and timers ■ setting the sleep timer the sleep timer automatically turns off the transceiv- er power after the set period ends. The timer can be set to between 5 and 120 minutes, in 5 minute steps. The multi-function screens are off: q hold down [timer] for 1 second. • the timer set sc...
Page 212: Set Mode Section
15-1 set mode section 15 set mode description …………………………………………………… 15-2 d set mode operation ………………………………………………… 15-2 d screen arrangement ………………………………………………… 15-3 level set screen ………………………………………………………… 15-4 acc set screen ………………………………………………………… 15-6 display set screen …………………………………………………… 15-10 ti...
Page 213: Set Mode Description
15-2 15 set mode ■ set mode description the set mode is used to make the infrequently changed settings. The transceiver has the level set mode, acc set mode, display set mode, time set mode, others set mode and sd/usb set mode (see section 10 for de- tails) . D set mode operation the multi-function ...
Page 214
15-3 15 set mode f-7 the following screens can be selected from the start up screen. Choose the desired screen using the fol- lowing guide. Pushing [exit/set] several times returns to the start up screen. • start up screen • display set screen (p. 15-10) • time set screen (p. 15-12) • others set scr...
Page 215: Level Set Screen
15-4 ■ level set screen 15 set mode ssb rx hpf/lpf (default: – – – – – – –) sets the receive audio high-pass filter and low-pass filter cut-off frequency in 100 hz steps. Selectable ranges: • hpf: between 100 hz and 2000 hz • lpf: between 500 hz and 2400 hz if this item is set, the [ssb rx tone (bas...
Page 216
15-5 ■ level set screen (continued) 15 set mode fm tx tone (bass) (default: 0) sets the bass level of the transmit audio tone in the fm mode from –5 to +5. Fm tx tone (treble) (default: 0) sets the treble level of the transmit audio tone in the fm mode from –5 to +5. Ssb tbw (wide) (default: 100 – 2...
Page 217: Acc Set Screen
15-6 15 set mode acc-a af/sql output select (default: main) selects the audio and squelch signals to output from [a acc1] (audio: pin 5, squelch: pin 6) between the main and sub bands. • main: main band’s af and squelch signals are out- put from [a acc1]. • sub: sub band’s af and squelch signals are...
Page 218
15-7 15 set mode acc-b af beep/speech... Output (default: off) select "on" to output the beep and speech audio from [b acc1]. • off: beep and speech audio are not output from [b acc1]. • on: beep and speech audio are output from [b acc1]. • setting the [acc-b af sql output select] item is neces- sar...
Page 219
15-8 15 set mode usb if output level (default: 50%) sets the [usb b] output level. • range: 0%–100% (in 1% steps) lan output select (default: af) selects the signal output from [lan]. • af: af signal is output from [lan]. • if: if signal is output from [lan]. Lan af sql (default: on) select the sque...
Page 220
15-9 15 set mode data2 mod (default: acc-b) selects the connector(s) to input the modulation signal when data 2 mode (d2) is on. • mic: use the signal from [mic]. • acc-a: use the signal from [a acc1] (pin 4). • acc-b: use the signal from [b acc1] (pin 4). • mic,acc-a: use the signal from [mic] and ...
Page 221: Display Set Screen
15-10 15 set mode lcd unit bright (default: 50% ) adjusts the lcd brightness. • range: 0 (dark) to 100% (bright) (in 1% steps) backlight (switches) (default: 80 ) adjusts the key backlight brightness. • range: 1 (dark) to 100 (bright) (in 1 steps) display type (default for ic-7850: 50th anniversary)...
Page 222
15-11 15 set mode apf-width popup (apf off ➡ on) (default: on) turns the apf filter width display on or off. Mn-q popup (mn off ➡ on) (default: on ) turns the notch filter bandwidth display on or off. Screen saver function (default: 60 min ) turns the screen saver function on (timer: 15, 30 or 60 mi...
Page 223: Time Set Screen
15-12 15 set mode date (default: 2000) set the date (year/month/day). (the day of the week is automatically set.) • range: year 2000–2099, month/day 1-1 to 12-31 time (now) (default: 0:00) set the current time. (the time is displayed in the 24 hours format.) • sets the current time. Ntp function (de...
Page 224: Others Set Screen
15-13 15 set mode calibration marker (default: off) turns the reference frequency calibration marker on or off. • off: turns off the marker. • on: turns on the marker. Beep (confirmation) (default: on) turns the confirmation beep on or off. • off: turns off the beep. • on: sounds the beep when a key...
Page 225
15-14 15 set mode ■ others set screen (continued) fm split offset (hf) (default: –0.100mhz) sets the offset frequency for the split function in the fm mode on the hf bands. • range: –9.999mhz to +9.999mhz (in 1 khz steps) fm split offset (50mhz) (default: –0.500mhz) sets the offset frequency for the...
Page 226
15-15 15 set mode ■ others set screen (continued) speech [mode] switch (default: off) turns the operating mode announcement on or off. • off: the operating mode is announced. • on: the operating mode is announcer when the mode is changed. Memo pad quantity (default: 5) sets the number of memo pad ch...
Page 227
15-16 15 set mode ■ others set screen (continued) filter screen main/sub select (default: auto (by filter,pbt operation)) selects the filter setting display. • fix: (always) the selected band's filter setting is always dis- played. • auto (by filter,pbt operation): (relative) the displayed filter se...
Page 228
15-17 15 set mode ■ others set screen (continued) keyboard [f1]–[f8] (voice) (default: off) enables the voice memory transmission using a key- board connected to [usb a]. • off: turn off the function. • on: pushing one of [f1] to [f8] on the keyboard, transmits the programmed voice memory (t1– t8). ...
Page 229
15-18 15 set mode ■ others set screen (continued) ci-v address (default: 8eh) selects the ci-v address. • range: 02h–8eh–dfh "8eh" is the default address of ic-7850/ic-7851. Ci-v transceive (default: on) turns the transceive function on or off. • off: turn the function off. • on: turn the function o...
Page 230
15-19 15 set mode ■ others set screen (continued) usb keying (cw) (default: off) you can control to transmit, receive and keying from the pc, through the usb port. Select the control port to be used for communication between the transceiver and pc, according to the op- erating condition. • off: turn...
Page 231
15-20 15 set mode mouse pointer speed (default: mid) selects the mouse pointer speed. • options: slow, mid, fast mouse pointer acceleration (default: on) turns the mouse pointer acceleration on or off. • off: turn off the function. • on: turn on the function. Usb dial select (default: sub only) sele...
Page 232
15-21 15 set mode network name when you remotely control the transceiver using the optional rs-ba1, enter a network name of up to 15 characters. Usable characters: characters (a–z, a–z, 0–9) and symbols (! # $ %& " ` ^ + – . , ; = ( ) [ ] { } _ ~ @) • push [edit](f) to enter the edit mode. • push [a...
Page 234: Maintenance Section
16-1 maintenance section 16 ■ adjusting the main dial brake ………………………………………… 16-2 ■ using the voice synthesizer operation ……………………………… 16-2 ■ swr reading …………………………………………………………… 16-3 ■ calibration the frequency (approximate) …………………………… 16-4 ■ setting my call sign …………………………………………………… 16-5 ■ cleanin...
Page 235
16-2 16 maintenance ■ adjusting the main dial brake the tension of [main dial] may be adjusted to suit your preference. The brake adjustment is located on the bottom side of the front panel. See the figure to the right. Slide the brake adjustment for a comfortable tension level while turning the dia...
Page 236: Swr Reading
16-3 16 maintenance • screen image example— type b ■ swr reading the transceiver has a high-performance swr meter. The meter displays a stable measurement in real time, even if the transmit output power varies frequently, such as during ssb mode operation. You can measure the swr of an antenna itsel...
Page 237
16-4 16 maintenance a very accurate frequency counter is required to cal- ibrate the frequency of the transceiver. However, a rough check may be performed by receiving radio sta- tion wwv, wwvh, or other standard frequency sig- nals. Caution: the transceiver has been thoroughly adjusted and tested a...
Page 238: Setting My Call Sign
16-5 16 maintenance ■ setting my call sign your own call sign can be displayed at power on. [example] set the call sign ja3yua. Q select the “my call” item in the display set screen. Set [f-7] display [f-3] my call w push [edit](f). • a cursor blinks. E push [abc]( ) or [123]( ). • pushing [123]( ) ...
Page 239: Screen Saver Function
16-6 16 maintenance ■ screen saver function the transceiver has a screen saver function to protect the lcd from the “burn-in” effect. The screen saver functions when no operation is per- formed for the set time period. Q select the “screen saver function” item in the dis- play set screen. Set [f-7] ...
Page 240: Resetting The Cpu
16-7 16 maintenance ■ resetting the cpu note: resetting clears all programmed con- tents in memory channels and returns programmed values in the set mode to default values. Recommendation: save memory channel content, setting status, and so on, onto an sd card or a usb flash drive before resetting t...
Page 241: About Protection Indications
16-8 16 maintenance ■ about protection indications the transceiver has a 2 step protection function to pro- tect the final power amplifiers. The function detects the power amplifier temperature and activates when the temperature becomes ex- tremely high. • power down transmission reduces the transmi...
Page 242: Fuse Replacement
16-9 16 maintenance ■ fuse replacement when no external dc output is available from [ext dc] and acc connectors, the internal fuse may be open. Replace the fuse in this case. R warning! Disconnect the ac power cable from the ac outlet before removing the transceiv- er’s cover. Caution: the transceiv...
Page 243: Troubleshooting
16-10 16 maintenance ■ troubleshooting the following chart is designed to help you correct problems which are not equipment malfunctions. If you are unable to locate the cause of a problem or solve it through the use of this chart, contact your nearest icom dealer or service center. D transceiver po...
Page 244
16-11 16 maintenance problem possible cause solution ref. Programmed scan does not stop. Programmed scan does not start. Memory scan does not start select memory scan does not start • squelch is open. • the same frequencies have been programmed in scan edge memory channels p1 and p2. • 2 or more mem...
Page 245
17-1 updating the firmware section 17 ■ general ………………………………………………………………… 17-2 d checking the firmware version …………………………………… 17-2 ■ preparation ……………………………………………………………… 17-3 d file downloading …………………………………………………… 17-3 ■ firmware update— using an sd card/usb flash drive …………… 17-4.
Page 246: General
17-2 17 updating the firmware ■ general the ic-7850/ ic-7851 ’s firmware can be updated, if de- sired. By updating the firmware, new function(s) can be added and the improvement of performance pa- rameters can be made. Ask your dealer or distributor about how to update the firmware if you have no pc...
Page 247: Preparation
17-3 17 updating the firmware ■ preparation d file downloading q access the following url. Http://www.Icom.Co.Jp/world/index.Html w click the [support] button. E click the “firmware updates/software downloads” link. R click the desired firmware file link in the ic-7850/ ic-7851 group. T read “regard...
Page 248
17-4 17 updating the firmware ■ firmware update— using an sd card/usb flash drive when updating the firmware using a memory device, no ip address as well as subnet mask settings are necessary. Q copy the downloaded firmware data onto an sd card or a usb flash drive (“ic-7850_7851” folder). • the mem...
Page 249
17-5 17 updating the firmware ■ firmware update— using an sd card/usb flash drive (continued) • downloads the firmware update data from the sd card or the flash drive, and then automatically loads the data onto the main cpu. • downloading and loading status is displayed in the “file loading” dialog....
Page 250: Control Command
18-1 ■ remote control (ci-v) information …………………………………… 18-2 d ci-v connection …………………………………………………… 18-2 d preparing …………………………………………………………… 18-2 d data format …………………………………………………………… 18-2 d data content description ………………………………………… 18-11 control command section 18.
Page 251
18-2 ■ remote control (ci-v) information 18 control command d ci-v connection the transceiver's operating frequency, mode, vfo and memory selection, can be remotely controlled when connecting to a pc. Choose the connection method from the following: • a usb cable (a-b type, user supplied) the requir...
Page 252: Command Table
18-3 d command table 18 control command cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 00 see p. 18-11 send frequency data (transceive) 01 see p. 18-11 send mode data (transceive) 02 see p. 18-13 read band edge frequencies 03 see p. 18-11 read operating frequency 04 see p. 18-11 read operating mode 05 see p. 18-11 ...
Page 253
18-4 d command table (continued) 18 control command cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 15 01 @9 00 read noise or s-meter squelch status (squelch close) 01 read noise or s-meter squelch status (squelch open) 02 @9 0000 to 0255 read s-meter level (0000=s0, 0120=s9, 0241=s9+60 db) 05 @9 00 read various squ...
Page 254
18-5 d command table (continued) 18 control command cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 1a † 05 0023 0000 to 0255 send/read cw side tone gain (0000=0% to 0255=100%) 0024 00 or 01 send/read cw side tone gain limit (00=off, 01=on) 0025 00 to 06 send/read audio output level at apf on (00=0 db, 06=+6 db) 002...
Page 255
18-6 d command table (continued) 18 control command cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 1a † 05 0078 00 to 02 send/read screen image type ( 00=a, 01=b, 02=50th anniversary for only ic-7850) 0079 00 to 08 send/read frequency readout font ( 00=basic (1), 01=basic (2), 02=basic (3), 03=italic (1), 04=italic...
Page 256
18-7 d command table (continued) 18 control command cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 1a † 05 0147 00 or 01 send/read the memory keyer transmission set for [f1] to [f8] on the keyboard (00=off, 01=on) 0148 00 or 01 send/read external keypad set for voice memory (00=off, 01=on) 0149 00 or 01 send/read e...
Page 257
D command table (continued) 18-8 18 control command cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 1a † 05 0195 00 to 09 send/read peak color level set for waterfall of the spectrum scope ( 00=grid 1, 01=grid 2, 02=grid 3, 03=grid 4, 04=grid 5, 05=grid 6, 06=grid 7, 07=grid 8, 08=grid 9, 09=grid 10) 0196 00 or 01 s...
Page 258
D command table (continued) 18-9 18 control command cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 1a † 05 0256 00 to 03 send/read averaging function for rtty fft scope ( 00=off, 01=averaging the two observations, 02=averaging the three observations, 03=averaging the four observations) 0257 see p. 18-12 send/read r...
Page 259
18-10 18 control command d command table (continued) cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 1a † 0a see p. 18-13 send/read limited tx output power level for the tx power limit function 0b 00 or 01 send/read ntp server access (00=stop, 01=start) 0c 00 to 02 read ntp server access result ( 00=accessing, or ha...
Page 260
18-11 18 control command d data content description • operating frequency command: 00, 03, 05, 1c 03 q x x x x x w e x r t x x 0 0 10 hz digit: 0–9 1 hz digit: 0–9 1 khz digit: 0–9 100 hz digit: 0–9 100 khz digit: 0–9 10 khz digit: 0–9 10 mhz digit: 0–6 1 mhz digit: 0–9 1000 mhz digit: 0 (fix ed) 10...
Page 261
18-12 18 control command d data content description (continued) • offset frequency settings command: 1a 050114, 050115, 050120 1 khz digit: 0–9 100 hz digit: 0 (fix ed) 100 khz digit: 0–9 10 khz digit: 0–9 10 mhz digit: 0–9 † 1 mhz digit: 0–9 direction: 00=+ direction 01=– direction q 0 x x x x xx w...
Page 262
18-13 18 control command • repeater tone/tone squelch frequency settings command: 1b 00, 1b 01 100hz digit: 0–2 10 hz digit: 0–9 1 hz digit: 0–9 0.1 hz digit: 0–9 fixed digit: 0* fixed digit: 0* q * 0 0 x x x w e x *not necessary when setting a frequency. • ssb/ssb-d transmission passband width sett...
Page 263
18-14 18 control command d data content description (continued) • memory content setting command: 1a 00 x e r −i o , !0 !1 !2 −!4 !5 −!7 x x x ... ... X x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x q , w !8 −@7 q , w memory channel numbers 0001–0099: memory channel 1 to 99 0100: programmed ...
Page 264
18-15 18 control command • scope waveform data command: 27 00 outputs the waveform data to the controller x x x x x x x x x x x x x x ...... X x q w e r t y u q main or sub scope data • 00=main scope, 01=sub scope w order of division data (current) e division number (01 or 15) when data is sent to t...
Page 265
18-16 18 panel description d data content description (continued) • scope attenuator settings command: 27 18 x x x x 00=att off 10=10 db 20=20 db 30=30 db 00=main scope 01=sub scope • scope reference level settings command: 27 19 common settings for the main and sub scopes x x x x x 0 x x 00= + (plu...
Page 266
19-1 specifications and options section 19 ■ specifications …………………………………………………………… 19-2 d general ……………………………………………………………… 19-2 d transmitter …………………………………………………………… 19-2 d receiver ……………………………………………………………… 19-3 d antenna tuner ………………………………………………………… 19-3 ■ options ………………………………………………………………… 19-4.
Page 267: Specifications
19-2 19 specifications and options ■ specifications d general • frequency coverage (unit: mhz): receiver 0.030000–60.000000* 1 transmitter 0.135700–0.137800* 2 , 1.800000–1.999999* 2 , 3.500000–3.999999* 2 , 5.255000 – 5.405000* 1, * 2 , 7.000000–7.300000* 2 , 10.100000–10.150000* 2 , 14.000000–14.3...
Page 268
19-3 19 specifications and options d receiver • receive system: double conversion superheterodyne system • intermediate frequencies: 1st 64.455 mhz ( main band ) 64.555 mhz ( sub band ) 2nd 36 khz • sensitivity for all versions: ssb, cw, rtty, psk (bw=2.4 khz, 10 db s/n, typical) 0.100– 1.799999 mhz...
Page 269: Options
19-4 19 specifications and options ■ options ic-pw1/euro hf /50 mh z all band 1 k w linear amplifier full-duty-cycle 1 kw linear amplifier including an automatic antenna tuner. Has automatic tuning and band selection ca- pability when used with an icom transceiver. Full break-in (qsk) operation. The...
Page 270: Connector Information
20-1 connector information section 20 ■ ■ acc socket ……………………………………………………………… 20-2 ■ ■ microphone connector ………………………………………………… 20-3 ■ ■ [elec-key] jack ……………………………………………………… 20-3 ■ ■ [key] jack ……………………………………………………………… 20-3 ■ ■ [ext keypad] jack …………………………………………………… 20-4 ■ ■ [ref i/o] connector ………...
Page 271: Acc Socket
20-2 20 connector information ■ acc socket 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 acc 1 pin no. Name description specifications 1 rtty controls rtty keying “high level”: “low level”: output current: more than 2.4 v less than 0.6 v less than 2 ma 2 gnd connects to ground. Connected in parallel with acc 2 pin 2. 3 send* inp...
Page 272: Microphone Connector
20-3 20 connector information 8 v dc is applied to pin 1 for microphone operation. You can turned off if it is not necessary in the “mic input dc bias” item of the others set screen. (p. 15- 16) the circuit is used to output memory information in 4-channel memories. You can output desired memory inf...
Page 273: [Ext Keypad] Jack
20-4 20 connector information ■ [ext keypad] jack the circuit is used to output memory content in 8 chan- nel memories. You can output desired memory content such as cw memory keyer, voice memory, rtty/psk memory to be transmitted. Push a switch to send the memory information. Hold down the switch f...
Page 274: [Meter] Jack
20-5 20 connector information ■ [meter] jack connects to an external meter. • output impedance: 4.7 k Ω • output voltage can be adjusted to 5 v maximum you can adjust the output voltage with the “external meter level (m)” for the main band and “external me- ter level (s)” item for the sub band in th...
Page 275: Index
I-1 index symbol ∂ f scan ................................................................ 12-9 ∂ tx function ........................................................... 8-5 monitor function ................................................. 8-5 number 1⁄4 tuning step function ..........................
Page 276
I-2 index cw mode operating cw .................................................... 5-5 cw pitch control ..................................................... 5-6 cw reverse mode ................................................... 5-7 cw side tone function ..............................................
Page 277
I-3 index l level set screen .............................................2-7, 15-4 linear amplifier connections ................................... 3-7 loading the saved data files onto an sd card .............................................. 10-6 onto a usb flash drive ..............................
Page 278
I-4 index bpsk and qpsk modes ................................. 5-27 bpsk31 and bpsk63 modes ......................... 5-27 operating ......................................................... 5-24 psk decode set ........................................... 2-6 psk decode set mode .......................
Page 279
I-5 index screen menu arrangement ................................... 1-16 screen saver function ........................................... 16-6 screen type and font selections ........................... 16-3 sd card ................................................................. 10-2 deleting a...
Page 280
I-6 index user band edge .................................................... 4-15 utc offset ............................................................ 14-2 v vbw ................................................................... 6-10 vector tuning indicator ........................................
Page 281
For amateur base station installations it is recom- mended that the forwards clearance in front of the an- tenna array is calculated relative to the eirp (effective isotropic radiated power). The clearance height below the antenna array can be determined in most cases from the rf power at the antenn...
Page 282
Please record the serial number of your transceiver below for future servicing reference: serial number : date of purchase : place where purchased :.
Page 283
1-1-32 kamiminami, hirano-ku, osaka 547-0003, japan.