- DL manuals
- Icom
- Receiver
- IC-R10
- Instruction Manual
Icom IC-R10 Instruction Manual
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
iR10
COMMUNICATIONS RECEIVER
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is sub-
ject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Summary of IC-R10
Page 1
Instruction manual ir10 communications receiver this device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is sub- ject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may c...
Page 2
R warning! Never connect the receiver to an ac outlet. This may pose a fire hazard or result in an electric shock. R warning! Never operate the receiver with a headset or other audio accessories at high volume levels. Hearing experts advise against continuous high volume op- eration. If you experien...
Page 3
Ii unpacking accessories included with the receiver: qty. 1q antenna ............................................................................1 1w handstrap.........................................................................1 1e belt clip (with 2 screws).........................................
Page 4
Table of contents iii important ..................................................................................... I explicit definitions .................................................................. I cautions ....................................................................................
Page 5
Table of contents iv operating theory electromagnetic radiation which has frequencies of 20,000 hz (20 khz*) and above is called radio frequency (rf) energy because it is useful in radio transmissions. The ic-r10 re- ceives rf energy from 0.5 mhz to 1300 mhz* and converts it into audio frequency (af...
Page 6: Panel Description
1 1 panel description ■ front and side panels function switch (pgs. 5, 6) while pushing [func], the sec- ondary functions of switches and controls can be accessed. Function display (p. 3) indicates the operating condition. Keypad (pgs. 5, 6) numeral and other function keys for tuning and activating ...
Page 7: Top Panel
1 panel description 2 ■ top panel antenna connector (p. 9) connects the supplied flexible antenna. Be careful when con- necting an external antenna (see operating notes, p. Iv). Volume control [vol] (p. 10) adjusts the audio output level. Squelch control [sql] (p. 11) ➥ varies the squelch threshold ...
Page 8: At T
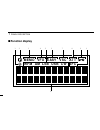
1 panel description 3 at t vsc easy vfo memo af c c w usb lsb a m wfm 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 7 9 0 a ■ function display.
Page 9
1 4 panel description q sleep timer indicator appears while the sleep timer is activated (p. 66). W function indicator appears while the function ([func]) switch is pushed. E memory mode indicator appears while in memory mode (p. 23). R vfo mode indicator appears while in vfo mode (p. 11). T receive...
Page 10: Keypad
1 panel description 5 ■ keypad key primary function secondary function (while pushing [func]) push for 1 sec. To toggle power on and off. Opening mes- sage appears for 1 sec. After power on (p. 10). Not available push and hold this switch to force the squelch open (p. 64). Not available selects a re...
Page 11
1 panel description 6 key primary function secondary function (while pushing [func]) when fm receive mode is selected in vfo mode: toggles the band scope function (p. 17). Toggles the vsc function on and off (p. 38). Selects the sleep timer conditions (p. 66). In vfo mode: sets program scan edge fre...
Page 12: Charging Ni-Cd Batteries
Ni-cd batteries and accessories 2 7 ■ charging ni-cd batteries the supplied ni-cd batteries are rechargeable and can be charged approx. 300 times. Charge the batteries before first operating the receiver or when the batteries become ex- hausted. If you want to be able to charge the batteries more th...
Page 13: Battery Installation
2 ni-cd batteries and accessories 8 ■ battery installation install 4 aa (r6) size batteries as illustrated below. Remove the cover from the receiver. Install 4 aa (r6) size dry cell, alkaline or the supplied ni-cd batteries into the receiver. Caution: make sure the polarity of the batteries is cor- ...
Page 14: Accessory Attachment
2 ni-cd batteries and accessories 9 ■ accessory attachment antenna insert the supplied antenna into the antenna connector and rotate the an- tenna as shown in the diagram below. Keep the jack cover attached when jacks are not in use to avoid bad contacts. Belt clip attach the belt clip using the sup...
Page 15: Basic Operation
1. Turn power on push [power] for 1 sec. To turn power on. • opening message is displayed for 1 sec. Basic operation 3 10 ■ general operating the ic-r10 is easy. However, in order to get the most out of its oper- ating potential, please go through the following procedures, step-by-step. Then, try th...
Page 16
3-1. Adjust the rf gain rotate [sql] maximum counter- clockwise, to adjust rf gain to opti- mum level. What is rf gain? Rf gain controls receive sensitivity gain—reduce the gain when you don’t want to receive very weak sig- nals or when excessively strong in- terfering signals are being received, et...
Page 17: Selecting A Receive Mode
3 basic operation 12 ■ selecting a receive mode what are receive modes? Radio signals can be propagated in a variety of ways (or modes). Each mode has its own physical properties that de- termine to some degree its uses. The ic-r10 receives the 6 most common modes: am, fm, wfm, usb, lsb and cw. When...
Page 18: Selecting A Tuning Step
3 basic operation 13 what are tuning steps? Tuning steps are the frequency change increments when you rotate the tuning control or operate a scan. The following steps are available: 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 6.25, 8, 9, 10, 12.5, 15, 20, 25, 30, 50, 100 khz and user programmable tuning steps (p. 66). It is im...
Page 19
3 basic operation 14 when you know the exact frequency you want to listen to, the quickest way to tune it is by direct keypad entry. Remember that the frequency must be between 0.5 mhz and 1300 mhz. The diagram below shows the correla- tion between the function display fre- quency digits and the fre...
Page 20
3 basic operation 15 ■ tuning a frequency (via the dial) when you want to listen to frequencies near the displayed frequency, the easi- est way to tune them is with the tuning dial. All signals have what is called an “oc- cupied bandwidth.” they will be re- ceived as long as the receiver is tuned an...
Page 21: Dial Select Steps
3 basic operation 16 ■ dial select steps what are dial select steps? When tuning with the dial, if you want to change the fre- quency faster than the selected tuning step can, use the dial select function. A dial select step is an increment of frequency change much like a tuning step is. Unlike a tu...
Page 22: Band Scope Function
3 basic operation 17 ■ band scope function what is the band scope function? The band scope detects signal availability in the range of ±5 channels (up to ±100 khz) from the displayed frequency, and displays the result on the multi function dot-matrix display. This gives you a visual reference of cur...
Page 23
3 basic operation 18 set band scope function q while pushing [func], push [ (1) bscope]. Repeat the above step or push [clr] to turn off the band scope function. Vfo fm 144.0000 higher freq. Displayed freq. Lower freq. Signal strength.
Page 24
3 basic operation 19 ■ listening example 1 — television broadcast in wfm mode 1. Turn power on push [power] for 1 sec. To turn power on. 2. Select vfo push [clr] or [v/m] to select vfo mode. 3. Adjust volume rotate [vol] to obtain the desired level of audio output. 4. Adjust squelch rotate [sql] ful...
Page 25: (Example 59.75 Mhz)
8. Use the tuning dial rotate [dial] to search for nearby stations above and below the tuned frequency. 3 basic operation 20 7. Tune the station use the keypad to enter the fre- quency — (example 59.75 mhz). [example] (example 59.75 mhz) 7-1. Tune the station enter the frequency from the 100 khz dig...
Page 26
Basic operation 3 21 1. Turn power on push [power] for 1 sec. To turn power on. 2. Select vfo push [clr] or [v/m] to select vfo mode. 3. Adjust volume rotate [vol] to obtain the desired level of audio output. 4. Adjust squelch rotate [sql] fully counterclockwise, then clockwise until the audio noise...
Page 27: (Example 118.00 Mhz)
3 basic operation 22 (example 118.00 mhz) 7. Tune the station enter a frequency of 118.0000 mhz* using the keypad (p. 14). *check listings for your area. 7-1. Tune the station enter the frequency from the 100 khz digit when you want to change below the 1 mhz digit only — (example from 118 mhz to 118...
Page 28: Memory Mode
Memory mode 4 23 ■ general what is memory mode? Memory mode is the second operating mode—the first being vfo mode. Memory mode is used to store often- used frequencies, their receive modes, attenuator settings (p. 65), as well as skip information for scanning (p. 56). This provides convenient recall...
Page 29
4 memory mode 24 ■ selecting a bank and memory channel selecting a bank channel when your desired memory channel is not stored or you do not want to store a frequency in the displayed bank, you must change the bank number. While pushing [func], rotate [dial]. Selecting a memory channel—1 if you want...
Page 30
1. Bank and memory channel setting q select memory mode (p. 23). W set the bank and memory chan- nel number (p. 24) you want to program to. 2. Setting other information q select vfo mode (p. 11). W set the frequency and receive mode (p. 12) you want in vfo mode. 4 memory mode 25 ■ programming a memo...
Page 31
1. Setting receive conditions q select vfo mode (p. 11). W set the frequency and receive mode (p. 12). 2. Bank and memory channel setting while pushing [func], push [ (v/m) mw]. 4 memory mode 26 ■ programming a memory channel — 2 this is the simplest method to memo- rize the received frequency along...
Page 32
1. Set up q set the frequency you want to program in vfo mode. W while pushing [func], push [ (v/m) mw] to enter mem- ory write mode. 2. Bank and memory channel setting q while pushing [func], rotate [dial] to select the bank you want to program (p. 24). W rotate [dial] or push 2 digit keys to selec...
Page 33
4 memory mode 28 3. Programming details — cont. 3 push [edit], then rotate [dial] to select receive mode. 4 push [edit], then rotate [dial] to select the skip scan condition. T push [edit], then rotate [dial] to select the attenuator condition. Y push [edit], then rotate [dial] or enter alphanumeric...
Page 34: Programming Example 1 —
4 memory mode 29 ■ programming example 1 — (118.0250 mhz; am to channel b07) 1. Bank and memory channel setting q push [v/m] to select memory mode. W while pushing [func], rotate [dial] to select bank “b”. E push [0] and [7] to enter the mem- ory channel number. 2. Data setting q push [v/m] to selec...
Page 35: Programming Example 2 —
4 memory mode 30 ■ programming example 2 — (59.75 mhz; wfm to channel a45) 1. Setting the frequency q push [v/m] to select vfo mode. W push [mode] one or more times to select wfm mode. E push numeral keys or rotate [dial] to set the frequency to 59.75 mhz. 2. Set the bank and memory channel 1 while ...
Page 36: Programming Example 3 —
4 memory mode 31 ■ programming example 3 — (121.5 mhz, emer.,am, skip: off, att: off, aviation to channel f01) 1. Setting the frequency q push [v/m] to select vfo mode. W rotate [dial] or push numeral keys to enter 121.5 mhz. 2. Bank and memory channel setting q while pushing [func], push [ (v/m) mw...
Page 37
4 memory mode 32 3. Programming details — cont. T push [edit] to change the re- ceive mode item. Y rotate [dial] to select am mode, then push [edit] to change the item. U rotate [dial] to select the off position for skip setting, then push [edit]. 3. Programming details — cont. I rotate [dial] to se...
Page 38: Memory Copy
4 memory mode 33 ■ memory copy what is the memory copy function? The memory copy function copies the contents (minus bank names) of the selected memory channel to vfo or to another memory channel. This is quite useful when you want to search for signals around the displayed frequency or when you wan...
Page 39: Copying Example 1
4 memory mode 34 ■ copying example 1 (59.7500 mhz, wfm, a45 to vfo) 1 push [v/m] to select memory mode (p. 23). 2 select the memory channel a45 (p. 24). 3 while pushing [func], push [ (v/m) mw] for 2 sec. To copy the contents of memory a45 to vfo. • vfo mode is automatically selected. ■ copying exam...
Page 40: Scanning Operation
Memory scan repeatedly scans all programmed memory channels ex- cept blank channels. Full scan repeatedly scans operatable frequency range. Scanning operation 5 35 0.5 mhz 1300 mhz a01 a02 a03 a04 a05 a49 b00 b01–r99 blank ■ general scan types the ic-r10 has 2 major scan types: programmed scan and m...
Page 41
5 scanning operation 36 program scan repeatedly scans between two user-programmed fre- quencies (scan edges). Bank scan repeatedly scans all memory channels in the selected bank except blank channels. Auto-memory write scan same as programmed scan except that paused fre- quencies are automatically s...
Page 42: Before Scanning
5 scanning operation 37 ■ before scanning set the following conditions before scanning. Information what happens when you rotate the tun- ing dial during scanning? While scanning— scanning direction is changed. Example: if you rotate [dial] counterclockwise while scanning up (frequency/memory channe...
Page 43
5 scanning operation 38 set the vsc set the vsc on if necessary. While pushing [func], push [ (2) vsc] (vsc indicator ap- pears). While pushing [func], push [(2)vsc) to turn off the vsc (vsc indicator disappears). What is vsc? The vsc (voice scanning control) pauses a scan only when modulated signal...
Page 44: Full Scan
5 scanning operation 39 ■ full scan this is the simplest scanning operation, searching the full fre- quency range (0.5–1300 mhz) in the selected receive mode and tuning step. Start and stop the scan 1 push [v/m] to select vfo mode. (p. 11) 2 push [scan] to start scanning. To change the direction of ...
Page 45: Program Scan
5 scanning operation 40 ■ program scan this is the most useful basic scan for searching over a spec- ified frequency range. 1. Select program scan channel q push [v/m] to select vfo mode (p. 11). W while pushing [func], push [ (4) prog-s]. Rotate [dial] to se- lect the program scan channel. Displays...
Page 46: Auto Memory Write Scan
■ auto memory write scan this scan is useful for searching a specified frequency range and automatically storing busy frequencies into memory channels. The same frequency ranges used for program scan are used for auto memory write scan. 5 scanning operation 41 1. Select program scan channel q push [...
Page 47
5 scanning operation 42 during auto-memory write scanning: 1 busy (paused) frequencies are automatically stored into bank q memory channels. 2 the scan is automatically cancelled when bank q becomes full. 3 unmodulated or beat signals may not be stored into mem- ory channels when the vsc function is...
Page 48: Bank Scan
5 scanning operation 43 2. Start and stop scanning push [scan] to start scanning. To change the scan direction, rotate [dial] during scan- ning. When the memory skip function is on (p. 61), specified memory chan- nels (p. 56) are skipped. Also, “ skip ” is dis- played. Push [clr] or [scan] to stop s...
Page 49: Mode Select Scan
5 scanning operation 44 2. Start and stop scanning push [scan] to start scanning. To change the scan direction, rotate [dial] during scan- ning. When the memory skip func- tion is on (p. 61), specified memory channels (p. 56) are skipped. Also, “ skip ” is displayed. Push [clr] or [scan] to stop sca...
Page 50: Skip Function
5 scanning operation 45 2. Program skip setting — cont. When bank r becomes full, an error beep sounds when trying to set more skip frequencies. When you want to cancel the skip function, turn off the skip setting in the memory channel (p. 56). T after set up, push [scan] or [clr] to stop scanning. ...
Page 51: Signavi Function
5 scanning operation 46 2. Select scan type and start scanning 1 while pushing [func], push [ (4) prog-s] for program scan or [ (5) amws] for auto-memory write scan, then rotate [dial] to select scanning frequency band. • confirm that the receive mode of the selected scan band is fm and also that th...
Page 52: Priority Watch
Priority watch 6 47 memory channel watch while listening to a selected memory channel, priority watch checks for signals on the priority frequency every 5 sec. • when the selected memory channel is masked (blank), the the watch does not start. • skip memory channels can be selected. Vfo frequency wa...
Page 53
6 priority watch 48 memory scan/bank scan/mode select scan watch while scanning all or selected memory channels, priority watch checks for signals on the priority frequency every 5 sec. • when the skip function is on, skips specified memory channels. • when the selected bank or receive mode is not m...
Page 54
6 priority watch 49 2. Set main frequency set the frequency in vfo mode (pgs. 14, 15) or select the memory channel (p. 24) you want to listen to with the prior- ity channel, or start scanning (p. 35). While pushing [func], push [ (9) prio], or push [clr] only to stop priority watch. 1. Program a pri...
Page 55: Easy Mode
Easy mode 7 50 2. Select frequency range and start scanning 1 push a numeral key to select a fre- quency range to search. 2 push [scan] to start scanning. 3 push [scan] or [clr] to stop scanning. Easy fm 0: 0.5000 scan flashes while scanning ■ easy mode operation 1. Select easy mode push [easy] to s...
Page 56: Edit Function
Edit function 8 51 ■ memory channel edit you can store the following items into a memory channel: 1. Frequency settings: ( set freq ) memorized frequencies can be edited or erased. 2. Channel names: ( set ch name ) alphanumeric names can be input or edited. (up to 8 characters per name.) 3. Receive ...
Page 57
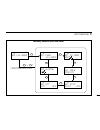
8 edit function 52 memory channel edit flow chart memo fm set freq 144.0000 memo fm set ch name a00 memo fm set mode mode:fm memo fm set skip skip: off memo fm set att att: off memo fm set b-name a: memo fm or a00 144.0000 clr edit edit edit edit edit edit edit edit * 1 * 2 * 1 push for 2 sec. * 2 f...
Page 58: Memory Channel Edit
8 edit function 53 ■ memory channel edit 1. Enter memory edit mode q push [v/m] to select memory mode, then select the memory channel (pgs. 23, 24). W push [edit] to enter memory edit mode. 3. Set channel names q enter channel names via the keypad or by ro- tating [dial]. • when you enter channel na...
Page 59
8 edit function 54 4. Set receive mode and skip condition q rotate [dial] to select receive mode. W push [edit] to change the item. E rotate [dial] to select skip condi- tion. R push [edit] to change the item. 5. Set attenuator condition q rotate [dial] to select attenuator condition. W push [edit] ...
Page 60: Program Scan Channel Edit
8 edit function 55 ■ program scan channel edit arrange memorized contents into program scan channels 00 to 19. You can edit the following items: 1. Channel names: ( set ch name ) set channel names for programmed frequency range; up to 8 characters per name. 2. Scan band edge 1: ( start freq ) set th...
Page 61
8 edit function 56 program/auto-memory write scan and easy mode channel edit flow chart start freq easy vfo fm 144.0000 end freq easy vfo fm 146.0000 easy vfo fm set ch name easy vfo fm set mode mode:fm easy vfo fm scan delay 5sec easy vfo fm set ts ts 5.00khz vfo fm s: 144.0000 e: 146.0000 easy fm ...
Page 62
8 edit function 57 ■ program scan or easy mode channel edit 1. Enter edit mode q push [v/m] or [edit] to select vfo or easy mode (p. 11 or 50). W while pushing [func], push [ (4) prog-s] or [ (5) amws] to se- lect program or auto-memory write scan mode; then select the scan channel (pgs. 40, 41) whe...
Page 63
8 edit mode 58 4. Set end frequency q enter the start frequency via the keypad or [dial]. W push [edit] to change the item. 5. Set receive mode and tuning step q rotate [dial] to select receive mode. W push [edit] to change the item. E rotate [dial] to select skip condi- tion. R push [edit] to chang...
Page 64: Set Mode
Set mode 9 59 message on beep on contrast low hi light auto 5sec program skip off memory skip on power save 1:4 scan delay 5sec 52 ci-v address ci-v baud 9600 ci-v trn on vfo fm 144.0000 memo fm a00 144.0000 clr set func + clr easy fm 0: 0.5000 set mode flow chart ■ general what is set mode? Set mod...
Page 65
Set mode 9 60 entering set mode while pushing [func], push [ (clr) set] to enter set mode. Push [edit] to select next item. Opening message rotate [dial] to toggle opening message on or off. Off message message on beep audio rotate [dial] to set beep audio on or off. Beep off beep on display contras...
Page 66
9 set mode 61 memory skip condition rotate [dial] to toggle the memory skip scan condi- tion on or off. Memory skip off memory skip on power save condition rotate [dial] to select the power save ratio or turn the function off. Power save 1:4 power save 1:16 power save off backlight condition rotate ...
Page 67
9 set mode 62 scan delay condition rotate [dial] to set the scan pausing time. Scan delay 5sec scan delay 10sec scan delay pause ci-v address rotate [dial] to select the ci-v address from 01 to 7f. 52 ci-v address 01 ci-v address 7f ci-v address ci-v baud rotate [dial] to select ci- v baud from 300,...
Page 68: Other Functions
Other functions 10 63 setting afc while pushing [func], push [ (.) afc] to toggle the afc function on and off. ■ afc function the afc (automatic frequency control) function tunes the displayed frequency automatically when an off-center fre- quency is received. It activates in fm modes only. Vfo af c...
Page 69: Monitor Function
10 other functions 64 set monitor while pushing [moni], squelch mute is released; when the vsc function is on, both squelch and vsc mute are re- leased. ■ monitor function the monitor function releases the squelch or vsc mute mo- mentarily when very weak signals are received without having to re-adj...
Page 70: Att Function
10 other functions 65 set att while pushing [func], push [ (0) att] to toggle the att function on and off. ■ att function the att (attenuator) function protects desired signals from distorting when excessively strong signals, such as broad- cast, pager signals, etc. Are nearby. This setting can be m...
Page 71: Sleep Timer Function*
10 other functions 66 set sleep timer q while pushing [func], push [ (3) sleep] one or more times to set the sleep timer condition. W release [func] to set the selected condition. E when the specified time elapses, the receiver emits 5 beeps then powers off. *when you want to use the sleep timer fun...
Page 72: Memory Search Function
10 other functions 67 enter memory channel names enter memory channel names via the keypad or [dial]. • when you enter channel names with [dial] or a character as- signed to the same key, push [ent] before you enter the next character to change the digit (see page 72 for alphanumeric key assignments...
Page 73
10 other functions 68 searching push [scan] to start memory channel search. • only the first one or two characters are needed to start a search. Smaller channel numbers are displayed first in cases where two or more channels start with the same characters. • push [scan] again to display the next can...
Page 74: Auto Mode and Ts Function
10 other functions 69 set auto mode push [mode] one or more times, in vfo mode, until “ auto mode ” appears, then push [clr] to return to vfo mode. ■ auto mode and ts function the auto receive mode select and auto tuning step select functions are optionally available. This function can be set up and...
Page 75: Resetting The Cpu
10 other functions 70 ■ resetting the cpu there are 2 ways to reset the cpu as follows: partial reset: when you want to initialize the operat- ing conditions (vfo frequency, vfo settings, set mode contents) without clearing the memory, program scan, easy mode and auto ts/mode set- tings, a partial r...
Page 76: Data Cloning
10 other functions 71 ■ data cloning the ic-r10 has receiver-to-receiver data cloning capability. This function is useful when you want to copy all of the programmed contents from one ic-r10 to another. An optional opc-474 cloning cable is required. In addition, the optional cs-r10 cloning software ...
Page 77: Alphanumeric Key Assignment
Alphanumeric key assignment 11 72 keypad input corresponding alphanumeric character no modifier key while pushing [func] q (q), z (z), 1 (1) q (q), z (z), 1 (1) a (a), b (b), c (c), 2 (2) a (a), b (b), c (c) 2 (2) d (d), e (e), f (f), 3 (3) d (d), e (e), f (f), 3 (3) g (g), h (h), i (i), 4 (4) g (g)...
Page 78: Control Commands
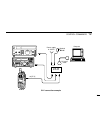
Control commands 12 73 ■ general the ic-r10 can be connected to a pc via the pc’s rs-232c port using an optional ct-17 ci-v level convertor . This allows you to control the receiver from the pc and/or transfer data from the receiver to the pc. Control is provided via icom’s ci-v communication interf...
Page 79
12 control commands 74 ct-17 power supply 9–15vdc rs-232c cable ic-r10 to [ci-v] computer optional bc-25 ci-v connection example.
Page 80: Troubleshooting
13 troubleshooting 75 if your receiver seems to be malfunctioning, please check the following points before sending it to a service center. Problem possible cause solution ref. No power comes on. • the installed batteries are exhausted. (a slight current flows in the circuits even when the power is ...
Page 81
13 troubleshooting 76 problem possible cause solution ref. Cannot start scanning. • [sql] is rotated too far clockwise. • incorrect receive mode (lsb, usb or cw) is se- lected. • scan edges are set to the same frequencies. • 2 or more memory channels have not been pro- grammed. • no channels have be...
Page 82: Specifications
Specifications 14 77 general frequency coverage : (unit: mhz) tuning steps : 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 6.25, 8, 9, 10, 12.5, 15, 20, 25, 30, 50 and 100 khz or user programmable (0.1–999.99 khz/0.1 khz steps) number of mem. Channels : 1000 receive modes : fm, am, wfm, usb, lsb, cw antenna connector : bnc (50 Ω...
Page 83: Options
Options 15 78 • cs-r10 cloning software + opc-478 cloning cable allows you to transfer data from memories, etc., quickly and easily edit and store data via an ibm compatible pc. • lc-140 carrying case protects the receiver from everyday wear and tear. • ct-17 ci - v level convertor for receiver remo...
Page 84
A-5410h-1ex- t printed in japan copyright 1996 by icom inc. 6-9-16 kamihigashi, hirano-ku, osaka 547 japan.