- DL manuals
- Jeep
- Automobile
- 2002 WJ
- Service Manual
Jeep 2002 WJ Service Manual
Summary of 2002 WJ
Page 1
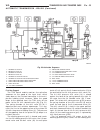
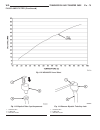
Group tab locator 0a lubrication & maintenance 7a cooling 8ea electronic control modules 8fa engine systems 8ia ignition control 9a engine 11a exhaust system 14a fuel system 19a steering - 2.7l - diesel 21a transmission and transfer case 25a emissions control - 2.7l diesel service manual comment for...
Page 2: Lubrication & Maintenance
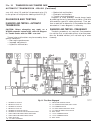
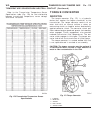
Lubrication & maintenance table of contents page page lubrication & maintenance specifications - fluid capacities . . . . . . . 1 international symbols description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 parts & lubricant recommendation standard procedure - parts & lubricant recommenda...
Page 3: International Symbols
Description specification rear axle ± 0.3 l (1 oz.) 198 rbi (model 35) 1.66 l (3.5 pts.)* 226 rba (model 44) 2.24 l (4.75 pts.)** * with trac-lok add 0.07 l (2.5 oz.) of friction modifier. ** with trac-lok or vari-lok, add 0.07 l (2.5 oz.) of friction modifier. *** includes 0.9l (1.0 qts.) for coola...
Page 4
Use of 100 percent ethylene-glycol will cause for- mation of additive deposits in the system, as the cor- rosion inhibitive additives in ethylene-glycol require the presence of water to dissolve. The deposits act as insulation, causing temperatures to rise to as high as 149 deg. C (300) deg. F). Thi...
Page 5
Tion against freezing is provided with a 68 percent antifreeze concentration, which prevents freezing down to -67.7°c (-90°f). A higher percentage will freeze at a warmer temperature. Also, a higher per- centage of antifreeze can cause the engine to over- heat because specific heat of antifreeze is ...
Page 6
Description - engine oil warning: new or used engine oil can be irritating to the skin. Avoid prolonged or repeated skin contact with engine oil. Contaminants in used engine oil, caused by internal combustion, can be hazardous to your health. Thoroughly wash exposed skin with soap and water. Do not ...
Page 7: Fluid Fill/check
Condition. As the vehicle is driven, the atf will begin to look darker in color and may eventually become brown. This is normal. Atf+4 also has a unique odor that may change with age. Consequently, odor and color cannot be used to indicate the fluid condi- tion or the need for a fluid change. Fluid ...
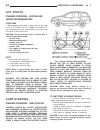
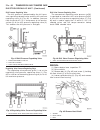
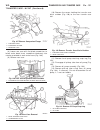
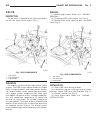
Page 8: Lift Points
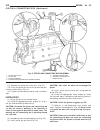
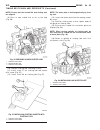
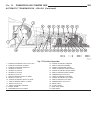
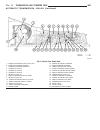
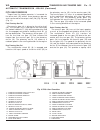
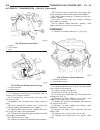
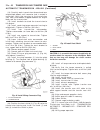
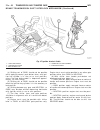
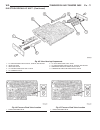
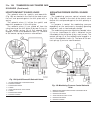
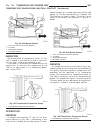
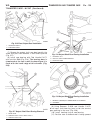
Lift points standard procedure - hoisting and jacking recommendations floor jack when properly positioned, a floor jack can be used to lift a wj vehicle (fig. 7). Support the vehicle in the raised position with jack stands at the front and rear ends of the frame rails. Caution: do not attempt to lif...
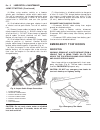
Page 9: Emergency Tow Hooks
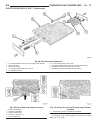
(2) when using another vehicle as a booster source, park the booster vehicle within cable reach. Turn off all accessories, set the parking brake, place the automatic transmission in park or the manual transmission in neutral and turn the ignition off. (3) on disabled vehicle, place gear selector in ...
Page 10: Towing
Towing standard procedure - towing recommendations a vehicle equipped with sae approved wheel lift- type towing equipment can be used to tow wj vehi- cles. When towing a 4wd vehicle using a wheel-lift towing device, use tow dollies under the opposite end of the vehicle. A vehicle with flatbed device...
Page 11
(6) turn the ignition switch to the off position to unlock the steering wheel. (7) secure steering wheel in straight ahead posi- tion with a clamp device designed for towing. (8) place transmission in park. Four-wheel-drive vehicle towing daimlerchrysler corporation recommends that a 4wd vehicle be ...
Page 12: Cooling - 2.7L Diesel
Cooling - 2.7l diesel table of contents page page cooling - 2.7l diesel operation—cooling system . . . . . . . . . . . 1 diagnosis and testing diagnosis and testing - preliminary checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 diagnosis and testing - cooling system . . . . . . . ....
Page 13
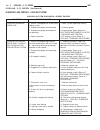
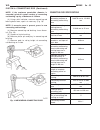
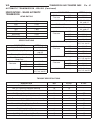
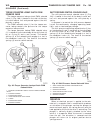
Diagnosis and testing - cooling system cooling system diagnosis—diesel engine condition possible causes correction temperaturegauge reads low 1. Vehicle is equipped with a heavy duty cooling system. 1. None. System operating normaly. 2. Temperature gauge not connected 2. Connect gauge. 3. Temperatur...
Page 14
Condition possible causes correction temperature gauge reading inconsistent ( erratic, cycles or fluctuates) 1. Heavy duty cooling system, extream cold ambient (outside) temperature or heater blower motor in high position. 1. None. System operating normaly. 2. Temperature gauge or gauge sensor defec...
Page 15
Condition possible causes correction inadequate heater performance. Guage may or may not read low. 1. Heavy duty cooling system, and cooler ambient temperatures. 1. None. Normal condition. 2. Obstruction in heater hoses. 2. Remove hoses, remove obstruction. 3. Water pump damaged. 3. Replace water pu...
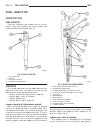
Page 16: Accessory Drive
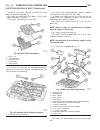
Accessory drive table of contents page page drive belts diagnosis and testing - accessory drive belt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 belt tensi...
Page 17
Accessory drive belt diagnosis chart condition possible causes correction rib chunking (one or more ribs has separated from belt body) 1. Foreign objects imbedded in pulley grooves. 1. Remove foreign objects from pulley grooves. Replace belt. 2. Installation damage 2. Replace belt rib or belt wear 1...
Page 18
Condition possible causes correction noise (objectional squeal, squeek, or rumble is heard or felt while drive belt is in operation) 1. Incorrect belt tension 1. Inspect/replace tensioner if necessary 2. Bearing noise 2. Locate and repair 3. Belt misalignment 3. Align belt/pulley(s) 4. Belt to pulle...
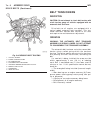
Page 19: Belt Tensioners
Belt tensioners description caution: do not attempt to check belt tension with a belt tension gauge on vehicles equipped with an automatic belt tensioner. Drive belts on all engines are equipped with a spring loaded automatic belt tensioner. This ten- sioner maintains constant belt tension at all ti...
Page 20: Engine
Engine table of contents page page coolant description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 diagnosis and testing - cooling system leaks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 standard procedure standard procedure - adding additional coolant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 21
Glycol is 125 deg. C (257 deg. F ) at 96.5 kpa (14 psi), compared to 128 deg. C (263 deg. F) for ethylene-gly- col. Use of propylene-glycol can result in boil-over or freeze-up in chrysler vehicles, which are designed for ethylene-glycol. Propylene glycol also has poorer heat transfer characteristic...
Page 22
Leaks are not visible, inspect for internal leakage. Large radiator leak holes should be repaired by a reputable radiator repair shop. Internal leakage inspection remove engine oil pan drain plug and drain a small amount of engine oil. If coolant is present in the pan, it will drain first because it...
Page 23: Coolant Recovery
Year/100,000 mile formula (glycol base coolant with corrosion inhibitors called hoat, for hybrid organic additive technology) is recommended. This coolant offers the best engine cooling without corrosion when mixed with 50% distilled water to obtain to obtain a freeze point of -37°c (-35°f). If it l...
Page 24: Engine Coolant Temp
- cooling/engine/radiator pressure cap - description) removal warning: do not open cooling system unless coolant temperature is below 90c (194°f). Open container slowly and release pressure. Store coolant in proper con- tainers only. Wear protective gloves, clothing and eye wear. Risk of injury to s...
Page 25: Engine Coolant
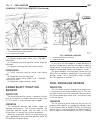
Warning: use extreme caution when engine is operating. Do not stand in a direct line with fan. Do not put your hands near pul- leys, belts or fan. Do not wear loose clothes. (6) start engine and inspect for leaks. Engine coolant thermostat removal warning: risk of injury to skin and eyes from scaldi...
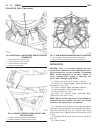
Page 26: Radiator Fan
(2) remove engine cover (refer to 9 - engine - removal). (3) drain engine coolant (refer to 7 - cooling/ engine/coolant - standard procedure). (4) remove accessory drive belt (refer to 7 - cooling/accessory drive/drive belts - removal). (5) disconnect coolant hoses at water pump. (6) remove idler pu...
Page 27
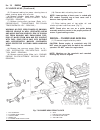
• steering flow control valve • fan control valve • two stage g-rotor hydraulic drive the hydraulic fan and drive are not serviceable. Any failure of the fan blade, hydraulic fan drive or fan shroud requires replacement of the fan module. The fan blade and hydraulic fan drive are matched and balance...
Page 28
Note: there is a steering flow control valve located in the fan drive motor. Because of the design of the valve, steering assist can not be effected by the radiator cooling fan even during fan drive failure. Removal (1) raise vehicle on hoist. (2) drain cooling system.(refer to 7 - cooling - standar...
Page 29
Installation caution: there is an external ground wire con- nected to the hydraulic fan drive located at the elec- trical connector on the fan assembly. This ground must remain connected at all times. Failure to ensure ground before engine is operating can cause severe damage to the ecm. (1) positio...
Page 30: Radiator Pressure Cap
(10) install radiator upper hose. (11) connect electrical connector for hydraulic fan control solenoid and assure ecm ground to fan assembly. (12) tighten fan shroud upper mounting bolts to 6 n·m (50 in. Lbs.). (13) refill cooling system (refer to 7 - cooling - standard procedure). Caution: do not r...
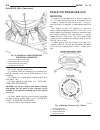
Page 31: Radiator
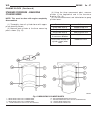
Operation a vent valve in the center of the cap will remain shut as long as the cooling system is pressurized. As the coolant cools, it contracts and creates a vacuum in cooling system. This causes the vacuum valve to open and coolant in reserve/overflow tank to be drawn through connecting hose into...
Page 32
Removal warning: risk of injury to skin and eyes from scalding coolant. Do not open cool- ing system unless temperature is below 90°c (194°f). Open cap slowly to release pressure. Store coolant in approved and appropriately marked container. Wear protective gloves, clothing and eye wear. Note: const...
Page 33
Installation caution: constant tension hose clamps are used on most cooling systems hoses. Use only the tools that are designed for this type of service. A number or letter is stamped on the clamp. If replacement is required, use only an original equipment clamp with the matching number or let- ter....
Page 34: Electronic Control Modules
Electronic control modules table of contents page page engine control module description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 standard procedure - ecm/skim programming - diesel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 remova...
Page 35
Normal driving modes engine idle, warm-up, acceleration, deceleration and wide open throttle modes are controlled based on all of the sensor inputs to the ecm. The ecm uses these sensor inputs to adjust fuel quantity and fuel injector timing. Limp-in mode if there is a fault detected with the accele...
Page 36
Standard procedure - ecm/skim programming - diesel note: before replacing the ecm for a failed driver, control circuit or ground circuit, be sure to check the related component/circuit integrity for failures not detected due to a double fault in the circuit. Most ecm driver/control circuit failures ...
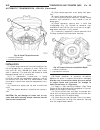
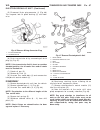
Page 37: Transmission Control
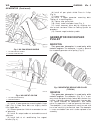
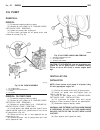
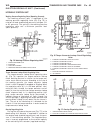
Installation (1) install ecm on bracket (fig. 2). (2) position ecm and bracket assembly in vehicle (fig. 2). (3) install ecm bracket to inner fender retaining nuts (fig. 2). (4) connect ecm electrical connectors (fig. 2). (5) connect negative battery cable. Transmission control module description th...
Page 38
Trol circuit. The brake/transmission shift interlock (btsi) solenoid and the park lockout solenoid (also part of the slsa) are controlled by the tcm. The pcm and abs broadcast messages over the controller area network (can c) bus for use by the tcm. The tcm uses this information, with other inputs, ...
Page 39
To confirm switch status. The pcm receives this information and allows operation of the starter cir- cuit. N2 and n3 speed sensors the n2 and n3 input speed sensors are two hall- effect speed sensors that are used by the tcm to cal- culate the transmissions input speed. Since the input speed cannot ...
Page 40
• lateral acceleration (calculated by the tcm). • gear change frequency (how often the shift occurs). Based on how aggressive the driver is, the tcm moves up the shift so that the present gear is held a little longer before the next upshift. If the driving style is still aggressive, the shift point ...
Page 41
Controlled limp-in mode when a failure does not require the tcm to shut down the solenoid supply, but the failure is severe enough that the tcm places the transmission into a predefined gear, there are several shift performance concerns. For instance, if the transmission is slip- ping, the controlle...
Page 42: Engine Systems
Engine systems table of contents page page charging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 starting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 charging table of contents page page charging description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
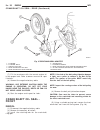
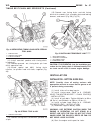
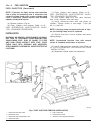
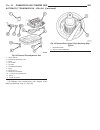
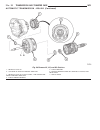
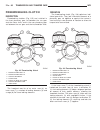
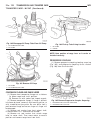
Page 43: Generator
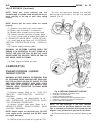
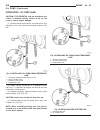
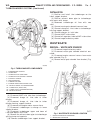
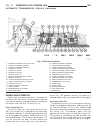
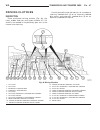
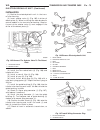
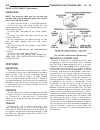
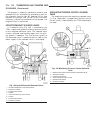
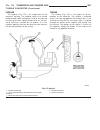
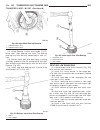
Generator description the generator is belt-driven by the engine. It is serviced only as a complete assembly. If the genera- tor fails for any reason, the entire assembly must be replaced. On certain generators, a decoupler is used. Refer to generator decoupler for additional informa- tion. As the e...
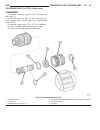
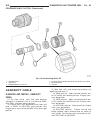
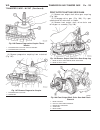
Page 44: Generator Decoupler
(2) install 2 lower generator mounting bolts finger tight (fig. 2). Note lower bolts are slightly shorter than upper bolts. (3) connect generator field wire connector to rear of generator. (4) install b+ output cable nut and cable to rear of generator. (5) install bolt at air conditioning line suppo...
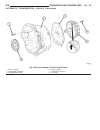
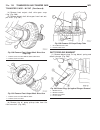
Page 45
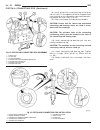
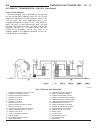
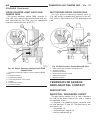
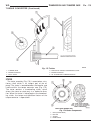
Diagnosis and testing - generator decoupler condition possible causes correction does not drive generator (generator not charging) internal failure replace decoupler noise coming from decoupler internal failure replace decoupler removal the generator decoupler is used only with certain engines. Two ...
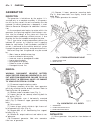
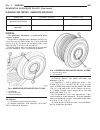
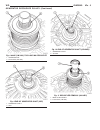
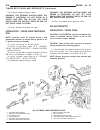
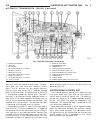
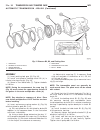
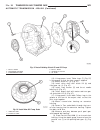
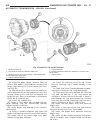
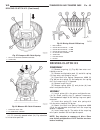
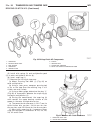
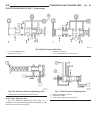
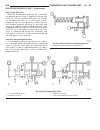
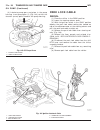
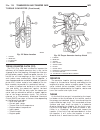
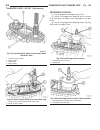
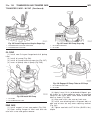
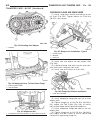
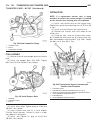
Page 46
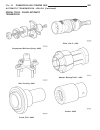
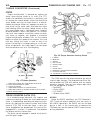
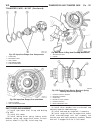
Fig. 8 #8823 (vm.1048) tool and ina decoupler 1 - ina decoupler 2 - tool #8823 (vm.1048) fig. 9 end of generator shaft (hex) 1 - generator shaft 2 - hex fig. 10 end of generator shaft (splined) 1 - generator shaft 2 - splines fig. 11 decoupler removal (ina-hex) 1 - deep 10 mm socket 2 - tool #8823 (...
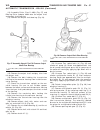
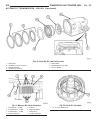
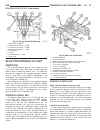
Page 47
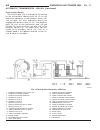
Litens decoupler (1) disconnect negative battery cable. (2) remove generator and accessory drive belt. Refer to generator removal. (3) position special tool #8433 (fig. 13) into decoupler. Align to hex end of generator shaft. (4) the generator shaft uses conventional right- hand threads to attach de...
Page 48
(4) do not use an adjustable, ratcheting “click type” torque wrench. Most “click type” wrenches will only allow torque to be applied in a clockwise rotation. Use a dial-type or beam-type wrench. Tighten in counter-clockwise rotation (fig. 15) or, (fig. 16). Refer to torque speci- fications. (5) inst...
Page 49: Starting
Starting table of contents page page starting specifications starter motor - diesel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 starter motor removal - 2.7l diesel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 installation - 2.7l diesel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 starting specifications starter motor - diesel starte...
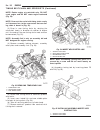
Page 50: Starter Motor
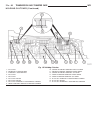
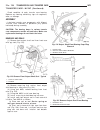
Starter motor removal - 2.7l diesel (1) disconnect and isolate negative battery cable. (2) raise and support vehicle. (3) remove battery cable mounting nut and cable eyelet at starter solenoid battery terminal. (4) remove 2 starter mounting bolts (fig. 1). (5) partially lower starter to gain access ...
Page 52: Ignition Control
Ignition control table of contents page page glow plug description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 53: Glow Plug Relay
Warning: no sparks, open flames or smok- ing. Risk of poisoning from inhaling or swallowing fuel. Risk of injury to skin and eyes exposed to fuel. Pour fuels only into suitable and appropriately marked containers. Wear protective clothing. Note: press in on fuel line locking tab to release fuel line...
Page 54: Engine
Engine table of contents page page engine - 2.7l diesel description description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 description - engine cover . . . . . . . . . . 3 standard procedure standard procedure - compression testing engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 inspecti...
Page 55: Engine - 2.7L Diesel
Oil pan removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 oil pump removal removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 removal- oil pump chain . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 installation installatio...
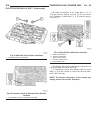
Page 56
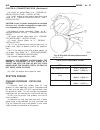
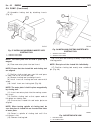
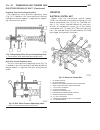
Description - engine cover the engine cover is a black plastic cover used to cover the top of the engine (fig. 2). Standard procedure standard procedure - compression testing engine (1) warm up engine to operating temperature (approx. 80 °c ). (2) shut off engine. (3) remove engine cover (refer to 9...
Page 57
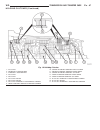
(10) at normal operating temperature the oil pres- sure must not drop below 3 bar (44 psi.). When engine speed is raised, oil pressure must rise with out delay and be no less than 3 bar (44 psi.) at 3000 rpm. (11) if oil pressure is out of range, determine cause. Removal removal - 2.7l diesel engine...
Page 58
Removal - engine cover (1) firmly grasp front of cover and lift straight up to release cover from mounting ball studs (fig. 3). (2) pull cover out of rear mounts and remove from vehicle (fig. 4). Installation installation - 2.7l diesel engine caution: when installing engine, care must be taken not t...
Page 59
(25) install turbocharger outlet to charge air cooler. (26) install junction block bracket to compressor. (27) install air conditioning lines to compressor. (28) install air tube at turbocharger. (29) install air cleaner housing. (30) install coolant module (refer to 7 - cool- ing/engine/radiator - ...
Page 60
Specifications - torque specifications 2.7l diesel description n·m ft. Lbs. In. Lbs. Crankcase ventilation screw-air charge distribution pipe to air charge distribution panel 11 - 97 cylinder head 8m-bolt- cylinder head to timing case cover 20 15 - bolt-front cover to cylinder head 14 - 124 12m-bolt...
Page 61
Description n·m ft. Lbs. In. Lbs. Connection-flange of exhaust manifold to turbo charger 30 22 - connection-turbo charger to front catalytic converter 30 22 - charge air pipe/charge air cooling bolt-charge air distribution pipe 16 - 141 bolt-inlet port shut off positioning motor to air charge distri...
Page 62
Description n·m ft. Lbs. In. Lbs. Bolt-oil-water heat exchanger to timing cover case 15 - 133 oil level pressure bolt-dip stick guide tube to cylinder head 14 - 123 bolt-oil level sensor to oil pan 14 - 123 coolant pre- heater coolant pre-heater in engine block 35 26 - engine cooling general bolt-be...
Page 63
Description n·m ft. Lbs. In. Lbs. Timing chain tensioner to timing case cover 80 59 - camshaft bolt-camshaft bearing cap to cylinder head 9 - 80 bolt-driver to inlet camshaft 50 37 - common rail diesel injection bolt-bango bolt of leak oil line to rail 20 - 177 bolt-bracket to high pressure pump 9 -...
Page 64
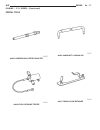
Special tools #8927 compression tester adapter #8928 fuel pressure tester #8929 camshaft locking pin #8931 timing chain retainer wg engine 9a - 11 engine - 2.7l diesel (continued).
Page 65
#8932 crankshaft lock #8936 front crankshaft seal installer #8937 slide hammer #8938 injector remover 9a - 12 engine wg engine - 2.7l diesel (continued).
Page 66
#8940 vibration damper remover #8942 oil jet installer #8944 rear main seal installer #8945 adapter cable wg engine 9a - 13 engine - 2.7l diesel (continued).
Page 67
#8946 valve service tools #8947 rivet opener #8948 chain separator tool #8949 thrust piece 9a - 14 engine wg engine - 2.7l diesel (continued).
Page 68
#8950 pressing screw #8951 assembly links #8952 assembly inserts wg engine 9a - 15 engine - 2.7l diesel (continued).
Page 69: Cylinder Head
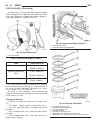
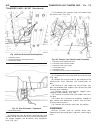
Cylinder head standard procedure standard procedure - cylinder head bolt inspection (1) measure cylinder head bolts between points shown (fig. 5). Cylinder head bolts thread diameter 12 m length when new 102 mm maximum length 104 mm (2) if the cylinder head bolt length is greater than the maximum al...
Page 70
Removal removal - cylinder head (1) disconnect negative battery cable. (2) raise and support vehicle. Warning: risk of injury to skin and eyes from scalding coolant. Do not open cool- ing system unless temperature is below 90°c (194°f). Open cap slowly to release pressure. Store coolant in approved ...
Page 71
(5) disconnect cooling fan power steering hose at power steering pump and set aside. (6) remove cylinder head cover (refer to 9 - engine/cylinder head/cylinder head cover(s) - removal). (7) remove timing chain tensioner (refer to 9 - engine/valve timing/tmng belt/chain tensioner&pulley - removal). W...
Page 72
(2) position piston of number 1 cylinder to ignition tdc. (3) remove engine cover. (refer to 9 - engine/ cylinder head/cylinder head cover(s) - removal). (4) remove timing chain tensioner (refer to 9 - engine/valve timing/timing belt/chain and sprockets - removal). (5) carefully raise locking pawl o...
Page 73
Belt/chain and sprockets - installation) tighten to 80n·m (59 lbs.Ft.). (18) remove retaining lock for crankshaft/starter ring gear. (19) install cylinder head cover (refer to 9 - engine/cylinder head/cylinder head cover(s) - installation). (20) install and properly route fuel injector and glow plug...
Page 74: Cylinder Head Cover(S)
Warning: us extreme caution when the engine is operating. Do not stand in a direct line with the fan. Do not put your hands near the pulleys, belts or fan. Do not wear loose clothes. (8) start engine and inspect for leaks. Cylinder head cover(s) removal (1) disconnect negative battery cable. (2) det...
Page 75
Warning: suitably mark the valve and the position in the cylinder head before removal. Failure to do so will result in improperly seated valves and pos- sible engine damage after reassembly. Note: using tool, screw retaining fork into threaded edge of cylinder head and position thrust piece vertical...
Page 76: Camshaft(S)
Note: using tool, screw retaining fork into threaded edge of cylinder head and position thrust piece vertically at the top of each valve spring retainer. Note: ensure that the valve collets are seated properly. (7) compress valve and install valve keepers. (8) repeat steps 3 through 7 as necessary. ...
Page 77
(7) install cylinder head cover (refer to 9 - engine/cylinder head/cylinder head cover(s) - installation). (8) install injectors (refer to 14 - fuel system/ fuel injection/fuel injector - installa- tion). Warning: use extreme caution when the engine is operating. Do not stand in a direct line with t...
Page 78
(10) mark camshaft sprocket relative to timing chain. (11) unbolt camshaft sprocket from exhaust cam- shaft. Note: note the position of dowel pin for camshaft sprocket alignment during reassembly. (12) remove camshaft sprocket. Caution: camshaft bearing caps must remain in proper order and position....
Page 79: Engine Block
(10) inspect/set basic position of camshafts (refer to 9 - engine/cylinder head/camshaft(s) - standard procedure). (11) install cylinder head cover (refer to 9 - engine/cylinder head/cylinder head cover(s) - installation). Note: refer to the appropriate injector servicing procedures for cleaning of ...
Page 80
Standard procedure - measuring cylinder bores note: this must be done with engine completely disassembled. (1) thoroughly clean all cylinder bores with appro- priate cleaning solvent. (2) measure each cylinder at the three measuring points shown (fig. 13). (3) using the three measurment point, measu...
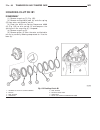
Page 81: Crankshaft
Crankshaft standard procedure - measure crankshaft and block journals note: after any bearing damage occurred, remove all debris which is present in the main oil gallery, connecting rod bores, and in the crankshaft and oil galleries. Include removal of the inserting steel ball of the main oil galler...
Page 82: Crankshaft Oil Seal -
Caution: oil grooves in the thrust washers must point toward the thrust collars of the crankshaft. Caution: thrust washers in the bearing cap each have two retaining lugs as a anti-twist lock. Caution: oil thread and head contact surfaces of bolts that retain the crankshaft bearing caps; tighten bol...
Page 83: Crankshaft Oil Seal -
(7) fill the crankcase with the correct engine oil, to the proper level. Refer to owners manual for spec- ifications. (8) connect the negative battery cable. Warning: use extreme caution when the engine is operating. Do not put your hands near the pulleys, belts or fan. Do not wear loose clothes. (9...
Page 84: Flywheel
Installation note: thoroughly clean all mating surfaces with the appropriate solvents to assure that no grease or oil is present during reassembly. Note: carefully position the front crankshaft seal evenly onto the timing cover. (1) install the front crankshaft seal. (2) install the belt pulley/vibr...
Page 85: Piston & Connecting Rod
Installation note: a flex rod torque wrench must not be used in order to avoid angle errors when tightening to degrees. (1) align flywheel and inner and outer washers with straight pin. Tighten bolts in two stages. 45n·m (33 lbs. Ft.) then 90°. (2) remove the retaining lock from the crankshaft/ star...
Page 86
Note: if the maximum permissible diameter is exceeded, grind off contact surface of connecting rod bearing cap by a maximum of 0.02mm. (3) using a dial indicator, measure connecting rod bearing basic bore, repair as necessary (fig. 19). Note: if excessive wear is present, press in new connecting rod...
Page 87
Standard procedure - measuring piston protrusion after replacing the pistons/connecting rods or machining the engine block contact surface, it is then necessary to measure the piston protrusion. Measure protrusion between piston crown and cyl- inder head contact surface without the head gasket insta...
Page 88
(11) remove the piston pin circle clip. (fig. 21). (12) press the piston pin out of the piston and con- necting rod bushing. (fig. 21). (13) inspect the connecting rod for wear and dam- age. Installation (1) assign piston to the cylinder bore. (2) using the appropriate clean engine oil, oil pis- ton...
Page 89
(8) install piston with arrow pointing in the direc- tion of travel (in the opposite direction to power flow) (the marking on the connecting rod should be point- ing toward the inlet side). (fig. 23). (9) clean and inspect the connecting rod bolts. Caution: assure that the correct top and bottom con...
Page 90: Piston Rings
(13) install oil pump (refer to 9 - engine/lu- brication/oil pump - installation). (14) install engine oil pan and oil pan drain plug (refer to 9 - engine/lubrication/oil pan - installation). Caution: install a cylinder head gasket of standard thickness or a cylinder head gasket of repair thick- nes...
Page 91
(4) place ring in the cylinder bore and push down with inverted piston to position near lower end of the ring travel. Measure ring gap with a feeler gauge fit- ting snugly between ring ends (fig. 25). Ring gap measurement chart item specification top compression ring 0.229 - 0.610 mm (0.0090 - 0.024...
Page 92: Vibration Damper
Vibration damper removal (1) disconnect negative battery cable. (2) remove accessory drive belt (refer to 7 - cooling/accessory drive/drive belts - removal). (3) install retaining lock for crankshaft/ring gear (fig. 28). (4) remove crankshaft center bolt and washer (fig. 28). Note: if hub of belt pu...
Page 93: Oil
Operation vacuum pump output is transmitted to the heater, electronic, vacuum, air conditioner (hevac) and speed control, systems through a supply hose. The hose is connected to an outlet port on the pump hous- ing and uses an in-line check valve to retain system vacuum when vehicle is not running. ...
Page 94: Oil Jet
Oil jet description there are five oil jets installed in the engine block (fig. 30). These oil jets are used to cool and lubricate the piston assemblies. Removal the engine must be removed from the vehicle and completely dissassembled to replace the oil jets. (1) remove engine from vehicle. (2) comp...
Page 95: Oil Pump
Oil pump removal removal (1) disconnect negative battery cable. (2) remove oil pan (refer to 9 - engine/lubri- cation/oil pan - removal). (3) unbolt oil pump from crankcase. (4) press chain tensioner off oil pump chain and remove oil pump (fig. 32). Removal- oil pump chain (1) disconnect negative ba...
Page 96
Installation - oil pump chain caution: it is essential that the installation pro- cedure is followed exactly. Failure to do so will result in severe engine damage. (1) connect old oil pump chain and new chain with temporary link, outer plate and locking element (fig. 34). (2) slowly rotate crankshaf...
Page 97
(5) assemble riveting tool by attaching inserts. (fig. 37). Note: the outer plate will be held in place by a magnet. (6) place new outer plate into tool insert. Note: ensure that the riveted link and riveting tool are aligned. (7) position riveting tool over new link and press in new rivet as far as...
Page 98: Oil Cooler & Lines
(18) tighten riveting tool spindle until it stops. (19) remove riveting tool, inspect riveting, rerivet if necessary (fig. 40). (20) repeat procedure for both rivets. (21) install oil pump (refer to 9 - engine/lu- brication/oil pump - installation). (22) install oil pan (refer to 9 - engine/lubri- c...
Page 99: Intake Manifold
(13) start engine and inspect for leaks. (14) inspect engine oil level 2 minutes after turn- ing engine off. Refill as necessary. Intake manifold description - inlet port shut off a swirl and a charge air inlet port each are pro- vided in the intake manifold for each cylinder (fig. 41). The charge a...
Page 100
(12) position piston of cylinder 1 to ignition tdc. Markings on the camshaft bearing cap must be aligned. (13) install retaining lock for crankshaft/starter ring gear. (14) remove timing chain tensioner (refer to 9 - engine/valve timing/timing belt/chain and sprockets - removal) (15) release rail on...
Page 101: Timing Belt/chain And
(14) install the ac compressor and reconnect elec- trical connector. (15) install belt pulley onto power steering pump. (16) apply sealant to lower portain of, and install, front cover to cylinder block. Tighten bolts to 20n·m (177 lbs in) (refer to 9 - engine/cylinder head - installation). (17) ins...
Page 102
Removal - intermediate gear (1) disconnect negative battery cable. (2) remove engine cover (refer to 9 - engine - removal). Warning: no fire, flames or smoking. Risk of poisoning from inhaling or swallowing fuel. Risk of injury to eyes and skin from contact with fuel. Pour fuels only into suitable a...
Page 103
(3) remove low pressure fuel pump and drive (refer to 14 - fuel system/fuel delivery/ fuel injection pump - removal). (4) remove guide rail in cylinder head (refer to 9 - engine/valve timing/timing belt/chain and sprockets - removal). (5) remove timing chain tensioner (refer to 9 - engine/valve timi...
Page 104
(11) install camshaft sprocket with timing chain, to camshaft. (12) remove pressed - out timing chain pin from chain separation tool. (13) attach special tool 8931, timing chain retainer, to cylinder head with bolts supplied (fig. 49). (14) remove timing chain to camshaft sprocket tie straps. (15) c...
Page 105
Installation - intermediate gear note: refer to appropriate injector servicing proce- dures for cleaning of injectors and recesses. (1) install intermediate gear and bushing. Tighten bolt to 40n·m (30 lbs.Ft.) (2) install camshaft sprocket, noting dowel pin alignment. Tighten bolt to 18 n·m (159 lbs...
Page 106
(12) connect negative battery cable. Warning: use extreme caution when the engine is operating. Do not stand in a direct line with fan. Do not put your hands near the pulleys, belts or fan. Do not wear loose clothing. (13) start engine and inspect for leaks. Installation - timing chain tensioning ra...
Page 107
Note: rotate engine at crankshaft only. Do not crank engine and do not rotate engine backward (fig. 52). Note: draw out the end of old timing chain evenly as it becomes free, to the same extent that new tim- ing chain is drawn in (fig. 52). (2) draw in new timing chain by rotating the crankshaft slo...
Page 108
Note: ensure that the riveted link and riveting tool are aligned. (9) press in new riveted link as far as the stop (fig. 56). (10) remove riveting tool to change inserts. (11) install insert f1 on riveting tool and secure with screw (fig. 57). (12) install insert d8 on riveting tool (fig. 57). Note:...
Page 109
(17) remove riveting tool. (18) turn over moving assembly insert (d8) to the riveting profile. (19) position riveting tool exactly over middle of pin. (20) tighten riveting tool spindle to end of travel. (21) repeat procedure for both riveting pins (fig. 59). (22) inspect riveting, rerivet if requir...
Page 110: Timing Chain Tensioner
Timing chain tensioner removal (1) disconnect negative battery cable. Caution: rotate engine at crankshaft only. Do not rotate the engine with the bolt of the camshaft sprocket. Do not rotate the engine counter clock- wise. Note: markings on the camshaft and camshaft bearing cap must be aligned. (2)...
Page 112: Exhaust System And
Exhaust system and turbocharger - 2.7l diesel table of contents page page exhaust system and turbocharger - 2.7l diesel description - 2.7l diesel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 diagnosis and testing - diesel engine . . 1 turbocharger system description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 113: Turbocharger System
Turbocharger system description caution: the turbocharger is a performance part and must not be tampered with. The wastegate bracket is an integral part of the turbocharger. Tam- pering with the wastegate components can reduce durability by increasing cylinder pressure and ther- mal loading due to i...
Page 114: Wastegate
(3) disconnect maf inlet tube from turbocharger. (4) disconnect charge air inlet tube at turbo- charger. (5) disconnect charge air inlet tube to turbo- charger housing support bracket. (6) disconnect wastegate motor vacuum hose. (7) disconnect turbocharger to charge air lower support bracket. (8) di...
Page 115: Charge Air Cooler And
Installation (1) position and install waste gate solenoid onto bracket. (2) connect engine vacuum harness to waste gate solenoid (3) connect waste gate solenoid electrical connec- tor. (4) connect negative battery cable. Charge air cooler and plumbing description the charge air system consists of th...
Page 116
(6) rinse the cooler with hot soapy water to remove any remaining solvent. (7) rinse thoroughly with clean water and blow dry with compressed air. Inspection visually inspect the charge air cooler for cracks, holes, or damage. Inspect the tubes, fins, and welds for tears, breaks, or other damage. Re...
Page 118: Fuel System
Fuel system table of contents page page fuel injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 fuel delivery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 fuel injection table of contents page page camshaft position sensor description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 119: Crankshaft Position
(2) remove engine cover (refer to 9 - engine - removal). (3) disconnect camshaft position sensor electrical connector. (4) remove retaining bolt and remove sensor. Installation (1) install camshaft position sensor and tighten bolt. (2) reconnect electrical connector. (3) install engine cover (refer ...
Page 120
Removal warning: no sparks, open flames or smok- ing. Risk of poisoning from inhaling and swallowing fuel. Risk of injury to eyes and skin from contact with fuel. Pour fuels only into suitable and appropri- ately marked containers. Wear protective clothing. Note: to avoid leakage problems, the rail ...
Page 121: Fuel Injector
Fuel injector description fuel injector there are individual fuel injectors for all five cyl- inders. These fuel injectors are used to spray fuel into the combustion chamber (fig. 4). Operation the injector operation can be subdivided into four operating states with the engine running and the high-p...
Page 122
The force exerted by the triggered solenoid now exceeds that of the valve spring and the armature opens the bleed orifice. Almost immediately, the high- level pick-up current is reduced to the lower holding current required for the electromagnet. This is possi- ble due to the magnetic circuit’s air ...
Page 123
Note: if injectors are tight, remove with extraction claw in place of tensioning claw. If extraction claw contacts cylinder head cover, remove cylinder head cover. If necessary, remove injectors with threaded adaptor and discard injector. (8) remove injectors (fig. 6). (9) clean injectors and recess...
Page 124: Fuel Rail
(7) if injectors four and five were replaced raise engine back in position and install engine mount through bolts. (8) install engine cover (refer to 9 - engine - installation). (9) connect negative battery cable. Warning: use extreme caution when the engine is operating. Do not put your hands near ...
Page 125: Manifold Air Flow (Maf)
Installation warning: no fire, flames or smoking. Risk of poisoning from inhaling or swallowing fuel. Risk of injury to eyes and skin from contact with fuel. Pour fuels only into suitable and appropriately marked con- tainers. Wear protective clothing. (1) position and loosely install fuel return li...
Page 126: Fuel Pressure Solenoid
Fuel pressure solenoid description the fuel pressure solenoid is attached to the rear of the fuel rail. The solenoid controls and maintains the rail pressure constant along with a control cur- rent transmitted by the engine control module (ecm) (fig. 10). Operation high pressure which is present in ...
Page 127: Boost Pressure Sensor
(3) remove fuel rail (refer to 14 - fuel system/ fuel injection/fuel injector - removal). (4) clamp fuel rail securely in vise with protective jaws. Note: once removed, the pressure solenoid must always be replaced. (5) remove fuel pressure solenoid retaining screws and remove solenoid (fig. 12). In...
Page 128: Intake Air Temperature
Operation when the intake manifold pressure is low (high vacuum) sensor voltage output is 0.25-1.8 volts at the ecm. When the intake manifold pressure is high due to turbo boost, sensor voltage output is 2.0-4.7 volts. The sensor receives a 5-volts reference from the ecm. Sensor ground is also provi...
Page 129: Fuel Delivery
Fuel delivery table of contents page page fuel delivery standard procedure - bleeding air from fuel system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 fuel filter / water separator description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 130: Fuel Pump
(1) disconnect negative battery cable. (2) insert a suitable hose into the fuel drain port in rear of filter, turn drain port counterclockwise and drain fuel into a suitable and appropriately marked container. (3) disconnect fuel feed and return lines at fuel fil- ter and set aside. (4) disconnect f...
Page 131
High pressure side a. Filling the piston: the piston is moved down as a result of the piston spring. The fuel supplied by the fuel delivery pump flows along the ring passage, the valve disk and the valve spring into the cylinder. The ball valve prevents the fuel from being able to flow back from the...
Page 132
Removal - low pressure pump warning: no sparks, open flames or smok- ing. Risk of poisoning from inhaling and swallowing fuel. Risk of injury to eyes and skin from contact with fuel. Pour fuels only into suitable and appropri- ately marked containers. Wear protective clothing. (1) disconnect negativ...
Page 133: Fuel Lines
(1) position and secure the high pressure pump to cylinder head (fig. 3). Tighten bolts to 14 n·m (124 lbs. In.). Caution: never slacken the thread connection. Use a wrench to counterhold at threaded connec- tion when slackening and tightening torque in order to avoid also slackening the threaded co...
Page 134
Caution: do not crimp or bend lines. Note: after removing injection lines, seal connec- tions and ensure cleanliness. (3) unscrew union nuts of injection lines. (4) remove injection lines (fig. 5). Installation - high pressure lines warning: no sparks, open flames or smok- ing. Risk of poisoning fro...
Page 136: Steering - 2.7L - Diesel
Steering - 2.7l - diesel table of contents page pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 pump table of contents page page pump removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 rese...
Page 137: Reservoir
Installation caution: power steering system fluid may be con- taminated with metal shavings, overheated or improper fluid. All fluid should be drained from the system. After any component replacement, system should be flushed and filled with mopar power steering fluid, or equivalent. (1) position th...
Page 138: Pulley
(5) install the intercooler outlet hose to the vehi- cle. (6) fill the reservoir and check the power steering system for leaks. Pulley removal (1) open the hood and disconnect the negative bat- tery cable. (2) remove the intercooler outlet hose from the vehicle. (3) remove the accessory drive belt f...
Page 139
(6) disconnect the high pressure hose from the power steering gear. (7) remove the hose from the clipped position on the fan shroud. (8) raise and support the vehicle. (9) remove the metal skid plate. (10) disconnect the high pressure hose from the hydraulic fan motor. (11) remove the hose from the ...
Page 140
Installation - return hose - reservoir to the hydraulic fan module (1) install the hose to the vehicle. (2) reconnect the rubber return hose to the hydraulic fan motor. Tighten the hose. (3) install the metal skid plate. (4) reconnect the rubber return hose to the power steering reservoir. Tighten t...
Page 142
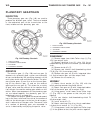
Transmission and transfer case table of contents page page automatic transmission - w5j400 description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 diagnosis and testing diagnosis and testing - automatic transmission . . . ...
Page 143: Automatic Transmission -
Planetary geartrain description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101 operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101 disassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101 assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101 shift mechanism des...
Page 144
Gear sets which are coupled to each other. The plan- etary gear sets each have four planetary pinion gears. The oil pressure for the torque converter lock-up clutch and clutch k2 is supplied through bores in the drive shaft. The oil pressure to clutch k3 is transmitted through the output shaft. The ...
Page 145
Shift groups the hydraulic control components (including actua- tors) which are responsible for the pressure distribu- tion before, during, and after a gear change are described as a shift group. Each shift group contains a command valve, a holding pressure shift valve, a shift pressure shift valve,...
Page 146
First gear powerflow torque from the torque converter is increased via the drive shaft (25) and all three planetary gearsets and transferred to the output shaft (26) (fig. 2) and (fig. 3). Front planetary gear set the annulus gear (8) is driven by the drive shaft (25). The sun gear (21) is held agai...
Page 147
Second gear powerflow torque from the torque converter is increased via the drive shaft (25) and the center and rear plane- tary gearset and transferred to the output shaft (26) (fig. 4) and (fig. 5). Front planetary gear set the planetary carrier (13) and sun gear (21) are connected via the engaged...
Page 148
Center planetary gear set the annulus gear (10) is driven at the same speed as the rear planetary carrier (15) as a result of a mechanical connection. The sun gear (22) is held against the housing by the multiple-disc holding clutch b2 (6). The planetary pinion gears (18) turn on the fixed sun gear ...
Page 149
Third gear powerflow torque from the torque converter is increased via the drive shaft (25) and the center planetary gearset and transferred to the output shaft (26) (fig. 6) and (fig. 7). Front planetary gear set the planetary carrier (13) and sun gear (21) are connected via the engaged multiple-di...
Page 150
Multiple-disc holding clutch b2 (6). The planetary pinion gears (18) turn on the fixed sun gear (22) and increase the torque from the annulus gear (10) to the planetary carrier (14). The output shaft (26) con- nected to the planetary carrier (14) turns at a reduced speed in the running direction of ...
Page 151
Fig. 7 third gear powerflow 1 - torque converter lock-up clutch 14 - center planetary carrier 2 - torque converter turbine 15 - rear planetary carrier 3 - torque converter impeller 16 - torque converter stator 4 - holding clutch b1 17 - front planetary pinion gears 5 - holding clutch b3 18 - center ...
Page 152
Fourth gear powerflow speed and torque are not converted by the direct gear ratio of the 4th gear. Power is transferred from the drive shaft (25) to the output shaft (26) via three locked planetary gearsets (fig. 8) and (fig. 9). Front planetary gear set the planetary carrier (13) and sun gear (21) ...
Page 153
Fig. 9 fourth gear powerflow 1 - torque converter lock-up clutch 14 - center planetary carrier 2 - torque converter turbine 15 - rear planetary carrier 3 - torque converter impeller 16 - torque converter stator 4 - holding clutch b1 17 - front planetary pinion gears 5 - holding clutch b3 18 - center...
Page 154
Fifth gear powerflow torque from the torque converter is increased via the drive shaft (25) and all three planetary gearsets and transferred to the output shaft (26) (fig. 10) and (fig. 11). Front planetary gear set the annulus gear (8) is driven by the drive shaft (25). The sun gear (21) is held ag...
Page 155
Reverse gear powerflow torque from the torque converter is increased via the drive shaft (25) and all three planetary gearsets and transferred with reversed direction of rotation to the output shaft (26) (fig. 12) and (fig. 13). Front planetary gear set the annulus gear (8) is driven by the drive sh...
Page 156
Center planetary gear set the annulus gear (10) is held against the housing by the multiple-disc holding clutch b3 (5) via the mechanical connection to the planetary carrier (15). The sun gear (22) turns backwards due to the engaged multiple-disc clutch k3 (12). The planetary gears (18) turn on the ...
Page 157
Reverse gear powerflow (4wd low) torque from the torque converter is increased via the drive shaft (25) and all three planetary gearsets and transferred with reversed direction of rotation to the output shaft (26) (fig. 14) and (fig. 15). Front planetary gear set the clutch k1 (7) is shifted. The pl...
Page 158
Center planetary gear set the annulus gear (10) is held against the housing by the multiple-disc holding clutch b3 (5) via the mechanical connection to the planetary carrier (15). The sun gear (22) turns backwards due to the engaged multiple-disc clutch k3 (12). The planetary gears (18) turn on the ...
Page 159
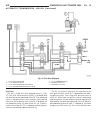
Shift groups/ shift sequence 1-2 shift - first gear engaged the end face of the command valve (5) (fig. 16) is kept unpressurized via the solenoid valve for 1-2 and 4-5 shift (1). Via the holding pressure shift valve (4), the working pressure (p-a) is present at the multiple- disc holding clutch b1 ...
Page 160
Shift phase via the 1-2 and 4-5 shift solenoid valve (1) (fig. 17), the shift valve pressure (p-sv) is directed onto the end face of the command valve (5). The command valve is moved and the shift pressure (p-s) coming from the shift pressure shift valve (3) is directed via the command valve (5) ont...
Page 161
Second gear engaged after the gearchange is complete, the pressure on the end face of the command valve (5) (fig. 18) is reduced via the 1-2 and 4-5 shift solenoid valve (1), and the command valve (5) is pushed back to its basic position. Via the holding pressure shift valve (4) the working pressure...
Page 162
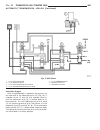
Gear shift n to d (1st gear) - engine started with the engine started (fig. 19) and the gearshift lever in the neutral or park positions, holding clutch b1 (1) and driving clutch k3 (4) are applied and the various valves in the 1-2/4-5 shift group are positioned to apply pressure to the holding clut...
Page 163
Activation sequence the selector valve (fig. 20) opens the shift pres- sure (p-s) feed connection from the ball valve (19) with the shift valve b2 (9). With the shift valve b2 (9) in the upper position, shift pressure (p-s) travels behind the piston b2 (5) and simultaneously to the opposing face of ...
Page 164
First gear engaged the tcm control module monitors the activation sequence via the speed of the input shaft, which slows down as the frictional connection in the multi- ple-disc holding clutch increases. When the speed drops to the specified level, the tcm shuts off the power to the 3-4 shift soleno...
Page 165
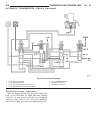
Sure shift valve (12) and the 3-4 command valve (13) to the piston of multiple-disc holding clutch b2 (5). Diagnosis and testing diagnosis and testing - automatic transmission caution: before attempting any repair on a w5j400 automatic transmission, check for diagnos- tic trouble codes with the drb ...
Page 166
Vehicle is drivable (1) check for transmission fault codes using drb t scan tool. (2) check fluid level and condition. (3) adjust gearshift cable if complaint was based on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts. (4) road test and note how transmission upshifts, downshifts, and engages. Vehicle is disable...
Page 167
Condition possible causes correction lever in 9 p 9 position blocked (brake activated) 1. No vacuum brake booster after long immobilization, brake pedal not fully applied/hard pedal. 1. Check vacuum/ tightness of brake booster. 2. No stoplamp switch signal (no dtc in ecm). 2. Check contact to stopla...
Page 168
Condition possible causes correction no upshift into 5th gear when full throttle or kick down activation 1. The upshift 4-5 at full throttle or kick down never occurs until reaching cut off speed. Under these conditions, the high powered vehicle will never shift into 5th gear below 250 km/h. 1. Inst...
Page 169
Condition possible causes correction leakage at the area of the electrical plug to the conductor plate 1. Deformation o-rings. 1. Replace o-rings. 2. Deformation adapter. 2.Replace adaptor. 3. The conductor plate is not fitted surface to surface on the valve body in one corner, the plug is not cente...
Page 170
(17) disconnect transmission fluid cooler lines at transmission fittings and clips. (18) disconnect the transmission vent hose from the transmission. (19) support rear of engine with safety stand or jack. (20) raise transmission slightly with service jack to relieve load on crossmember and supports....
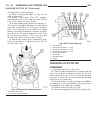
Page 171
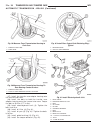
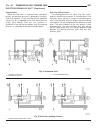
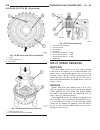
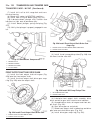
(12) remove the transmission rear output shaft bearing retaining ring (1) (fig. 26). Fig. 25 remove electrohydraulic unit 1 - heat shield 2 - electrohydraulic unit 3 - bolt 4 - oil filter 5 - oil pan 6 - clamping element 7 - bolt 8 - drain plug 9 - drain plug gasket 10 - 13-pin plug connector 11 - b...
Page 172
(13) assemble puller, size 5, 8903 (fig. 27) and bearing puller adapter 8904 onto the output shaft and output shaft bearing. (14) remove the output shaft bearing (fig. 28). (15) remove the output shaft end-play shim from the output shaft. (16) remove the bolts holding the transmission housing to the...
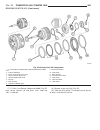
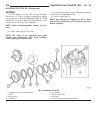
Page 173
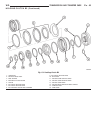
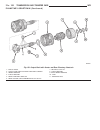
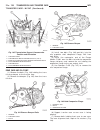
Fig. 29 remove k1, k2, and k3 clutches 1 - driving clutch k1 5 - thrust washer 2 - sun gear of front planetary gear set 6 - front planetary gear set, driving clutch k2, and drive shaft 3 - driving clutch k3, output shaft , and center and rear planetary gear sets 7 - teflon rings 4 - thrust needle be...
Page 174
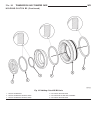
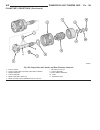
Fig. 30 remove holding clutch b1 and oil pump 1 - bolts - m6x32 4 - bolts - m8x35 2 - converter housing 5 - holding clutch b1 3 - intermediate plate 6 - oil pump wg transmission and transfer case 21a - 33 automatic transmission - w5j400 (continued).
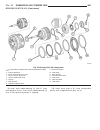
Page 175
Assembly (1) insert parking lock gear (5) (fig. 32). (2) install multiple-disc holding clutch b2 (4) in transmission housing (6) (fig. 32). (3) screw in torx socket bolts (7). Tighten the bolts to 16 n·m. Note: during the measurement the snap ring (7) (fig. 33) must contact the upper bearing surface...
Page 176
Fig. 32 install b2, b3, and parking gear 1 - snap-ring 5 - park gear 2 - holding clutch b3 discs 6 - transmission housing 3 - spring washer 7 - bolts - m8x60 4 - holding clutch b2 fig. 33 measure b3 clutch clearance 1 - outer disc - 6.5 mm 5 - piston 2 - outer discs - 1.8 mm 6 - friction discs 3 - o...
Page 177
(12) using grease, insert teflon rings (7) (fig. 37) in the groove so that the joint remains together (13) mount clutch k1 (1) (fig. 37). (14) install drive shaft with clutch k2 (6) and front gear set (1) (fig. 37). (15) install front washer (5) and thrust needle bearing (4) (fig. 37). (16) install ...
Page 178
(b) using the depth gauge, measure from the parallel rest 8906 (1) to the contact surface of the output shaft bearing (2) in the transmission hous- ing (fig. 39). (c) subtract the first figure from the second fig- ure to determine the current end-play of the trans- mission. Select a shim such that t...
Page 179
(27) install the transfer case adapter housing onto the transmission case. (28) install the bolts to hold the transfer case adapter housing onto the transmission case. Torque the bolt to 20 n·m (177 in.Lbs.). (29) install electrohydraulic unit (2). Tighten the bolts to 8 n·m. (30) install oil filter...
Page 180
Installation (1) check torque converter hub and hub drive flats for sharp edges burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and flats with 320/400 grit paper and crocus cloth if necessary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging pump seal at installation. (2) if a replacement transmission is being i...
Page 181
(14) carefully work transmission forward and over engine block dowels until converter hub is seated in crankshaft. Verify that no wires, or the transmission vent hose, have become trapped between the engine block and the transmission. (15) install two bolts to attach the transmission to the engine. ...
Page 182
Specifications - w5j400 automatic transmission gear ratios 1st 3.59:1 2nd 2.19:1 3rd 1.41:1 4th 1.00:1 5th 0.83:1 reverse 3.16:1 reverse (4wd low) 1.93:1 specifications component metric (mm) output shaft end-play 0.3-0.5 output shaft end-play snap-rings 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5 rear planetary gear set...
Page 183
Special tools - w5j400 automatic transmission compressor, multi-use spring - 8900 tool, pressing - 8901 punch, drift - 8902 puller, size 5 - 8903 adapter, bearing puller - 8904 socket - 8905 21a - 42 transmission and transfer case wg automatic transmission - w5j400 (continued).
Page 184
Parallel rest - 8906 pliers - 8907 funnel - 8908 tube, filler - 8909 pump - 8910 wg transmission and transfer case 21a - 43 automatic transmission - w5j400 (continued).
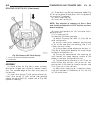
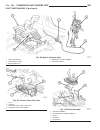
Page 185: Brake Transmission Shift
Brake transmission shift interlock mechanism description the brake transmission shifter/ignition interlock (btsi), is a cable and solenoid operated system. It interconnects the automatic transmission floor mounted shifter to the steering column ignition switch (fig. 46). Operation the system locks t...
Page 186
Diagnostic chart condition possible cause correction key will not rotate to the off/lock position. 1. Misadjusted park lock cable. 1. Adjust park lock cable. (refer to 21 - transmission and transfer case/automatic transmission/brake transmission shift interlock system - adjustments) 2. Misadjusted g...
Page 187
(4) shifting out of park should not be possible while applying normal push-button force, and igni- tion key cylinder is in the run or start positions, unless the foot brake pedal is depressed approxi- mately 1/2 inch (12mm). (5) shifting out of park should not be possible when the ignition key cylin...
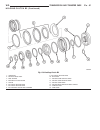
Page 188: Driving Clutches
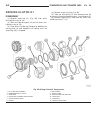
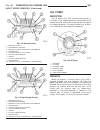
Driving clutches description three multi-plate driving clutches (fig. 48), the front, middle and rear multi-plate clutches k1, k2 and k3, are located in the planetary gear sets in the transmission housing. A multi-plate driving clutch consists of a number of internally toothed discs (4) on an intern...
Page 189
Operation the driving clutches (fig. 49) produce a non-posi- tive locking connection between two elements of a planetary gear set or between one element from each of two planetary gear sets in order to transmit the drive torque. If the piston (20) on multi-plate clutch k1 (1) is subjected to oil pre...
Page 190: Driving Clutch K1
Driving clutch k1 disassembly (1) remove snap-ring (11) (fig. 50) from outer multiple-disc carrier (6). (2) take multiple-disc pack (12) out of outer mul- tiple-disc carrier (6). (3) place multi-use spring compressor 8900 on the spring plate (8) and compress the spring until the snap-ring (10) is ex...
Page 191
Assembly (1) install piston (6) (fig. 51) in the outer multi- ple-disc carrier (1). Check sealing rings (4 and 5), replace if necessary. The rounded off edges of the sealing rings must point outwards. (2) insert disc spring (7) (fig. 51). Insert disc spring with the curvature towards the piston. (3)...
Page 192: Driving Clutch K2
(8) measure the k1 clutch pack clearance. (a) mount pressing tool 8901 (1) (fig. 52) on outer multiple disc. (b) using a lever press, compress pressing tool as far as the stop (then the marking ring is still visible, see small arrow). (c) using a feeler gauge, determine the play 9l9 (fig. 53) at thr...
Page 193
(7) fit multi-use spring compressor 8900 (fig. 55) onto spring retainer (9) and press until snap-ring (10) is released. (8) remove snap-ring (10) (fig. 54). (9) take out disc spring (7) and pull piston (6) out of outer multiple-disc carrier. Fig. 54 driving clutch k2 components 1 - k1 inner disc car...
Page 194
Assembly (1) install piston (6) (fig. 56) in outer multiple- disc carrier. Inspect seals (4 and 5), replace if neces- sary. The rounded edges of the seals must point to the outside. (2) insert disk spring (7) and spring retainer (9). Insert disk spring (7) with curved side pointing toward spring ret...
Page 195
(9) insert axial needle bearing (2) into k1 inner multiple-disk carrier. Insert axial needle bearing (2) with a little grease to prevent it slipping. (10) install drive shaft in k1 inner multiple-disc carrier with integrated front gear set (3). Fig. 56 driving clutch k2 components 1 - k1 inner disc ...
Page 196: Driving Clutch K3
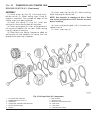
(11) fit internally-geared wheel (14). Pay attention to installation position. Driving clutch k3 disassembly (1) remove snap-ring (1) (fig. 60) from outer mul- tiple-disc carrier. (2) remove multiple-disc pack (2) and disk spring (3) from outer multiple-disc carrier. (3) place multi-use spring compr...
Page 197
(5) install disk spring (3) and multiple-disc pack (2) in outer multiple-disc carrier (8). (6) insert snap-ring (1). (7) measure the k3 clutch clearance. (a) mount pressing tool 8901 (1) (fig. 61) on outer multiple disc. (b) using a lever press, compress pressing tool as far as the stop (then the ma...
Page 198: Electrohydraulic Unit
Electrohydraulic unit description the electrohydraulic control unit comprises the shift plate made from light alloy for the hydraulic control and an electrical control unit. The electrical control unit comprises of a supporting body made of plastic, into which the electrical components are assembled...
Page 199
Shift pressure (p-s) the shift pressure is determined by the shift pres- sure regulating solenoid valve and the shift pressure regulating valve. The shift pressure: • regulates the pressure in the activating shift element during the shift phase. • determines together with the modulating pres- sure t...
Page 200
Torque converter lockup clutch regulating valve the torque converter lock-up clutch regulating valve (fig. 65) is located in the valve housing of the electrohydraulic control module. The valve is respon- sible for the hydraulic control of the torque converter lockup clutch and distribution of the lu...
Page 201
Shift pressure shift valve each shift group possesses one shift pressure shift valve (fig. 69). The 1-2 / 4-5 and 2-3 shift pressure shift valves are installed in the shift valve housing; the 3-4 shift pressure shift valve is installed in the valve housing. It assigns the shift pressure (p-s) to the...
Page 202
Shift pressure regulating valve the shift pressure regulating valve (fig. 71) is located in the valve housing of the shift plate. It reg- ulates the shift pressure (p-s). Fig. 69 shift pressure shift valve 1 - 1-2/4-5 command valve 2 - driving clutch k1 3 - holding clutch b1 4 - 1-2/4-5 shift pressu...
Page 203
Regulating valve pressure regulating valve the regulating valve pressure regulating valve (fig. 72) is located in the valve housing of the elec- trohydraulic control module. It regulates the regulat- ing valve pressure (p-rv). Shift valve pressure regulating valve the shift valve pressure regulating...
Page 204
Hydraulic control unit working pressure regulating valve (operating pressure) the working pressure (p-a) is regulated at the working pressure regulating valve (22) (fig. 75) in relation to load (modulating pressure) and gear (k1 or k2 pressure). The spring in the working pressure regulating valve se...
Page 205
Command valve when the end face is unpressurized (stationary phase), the working pressure is directed to the actu- ated shift element. If the end face of the command valve (fig. 78) is subjected to the shift valve pressure (p-sv) (shift phase), then the shift pressure is switched to the activating e...
Page 206
Shift pressure shift valve when the multiple-disc brake b1 (3) is activated, the working pressure (pa) is applied to the end face of the 1-2 / 4-5 shift pressure shift valve (4) (fig. 80) via the command valve (1). Its shift state is main- tained during the shift phase by substituting the shift elem...
Page 207
Shift pressure regulating valve the shift pressure is determined by the shift pres- sure regulating solenoid valve and the shift pressure regulating valve (3) (fig. 82). In addition, pressure from the clutch k2 (1) is also present at the annular surface (2) of the shift pressure regulating valve (3)...
Page 208
(5) disconnect 13-pin plug connector (1) (fig. 86). Turn bayonet lock of guide bushing (2) anti-clock- wise. (6) drain transmission oil by unscrewing oil drain plug (8) (fig. 87). Note: if the transmission fluid is burnt or contains abraded particles, the oil cooler lines and oil cooler must be flus...
Page 209
(9) unbolt leaf spring (5) (fig. 90). (10) unscrew torx bolts (1) (fig. 90). (11) remove valve housing (2) from valve body (4) (fig. 90). (12) remove the strainers for the modulating pres- sure and shift pressure control solenoid valves (fig. 91) from the valve housing. (13) remove the strainer (1) ...
Page 210
(15) note the location of all check balls (1, 3, 4) (fig. 93) and the central strainer (2) for re-installa- tion. Remove all check balls (1, 3, 4) and the central strainer (2). (16) remove the screws holding the side covers to the valve body and valve housing. (17) remove all valves and springs from...
Page 211
(18) remove all valves and springs from the valve housing (2) (fig. 95). Check all valves for ease of movement and shavings. (19) remove the pressure supply valve (1) (fig. 96) from the valve body. Assembly note: pay great attention to cleanliness for all work on the shift plate. Fluffy cloths must ...
Page 212
Fig. 95 valve housing components 1 - 2-3 overlap regulating valve, sleeve, and piston 6 - 3-4 shift pressure shift valve 2 - valve housing 7 - 3-4 overlap regulating valve, sleeve, and piston 3 - selector valve 8 - operating pressure regulating valve 4 - 3-4 holding pressure shift valve 9 - lubricat...
Page 213
(2) install all valves and springs from the valve body (1) (fig. 98). Check all valves for ease of move- ment and shavings. Note: the sleeves and pistons of the overlap reg- ulating valves must not be mixed up. (3) install all valves and springs into the valve housing (2) (fig. 99). Check all valves...
Page 214
(7) position the sealing plate (3) onto the valve body (4) (fig. 102). Fig. 99 valve housing components 1 - 2-3 overlap regulating valve, sleeve, and piston 6 - 3-4 shift pressure shift valve 2 - valve housing 7 - 3-4 overlap regulating valve, sleeve, and piston 3 - selector valve 8 - operating pres...
Page 215
(8) install the valve housing (2) onto the valve body (4) and sealing plate (3). (9) install the shift plate torx bolts (1) (fig. 102). Tighten the bolts to 8 n·m. (10) install leaf spring (5) (fig. 102). (11) install the strainers for the modulating pres- sure and shift pressure control solenoid va...
Page 216
Installation (1) position the electrohydraulic unit in the trans- mission housing. (2) insert selector valve (1) (fig. 105) in driver of detent plate (2). When installing the electrohydraulic control module in the transmission housing, the plas- tic part of the selector valve (1) must engage in the ...
Page 217: Fluid And Filter
Fluid and filter description the oil level control (fig. 109) is located on the electrohydraulic unit and consists of the float (5) which is integrated into the electrohydraulic unit. The float is positioned to plug the opening between the oil gallery and gearset chamber so that the rotat- ing gears...
Page 218
Diagnosis and testing - causes of burnt fluid burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating which has three primary causes. (1) internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or clutch seal failure. (2) a result of restricted fluid flow through ...
Page 219
Standard procedure standard procedure - check oil level (1) verify that the vehicle is parked on a level sur- face. (2) remove locking pin (1) (fig. 111). Remove the plate of the locking pin with a suitable tool and press out the pin remaining in the cap downwards. (3) remove cap (2). Warning: risk ...
Page 220
Fig. 112 w5j400 fill level chart fig. 113 dipstick tube cap components 1 - locking pin 2 - tube cap 3 - dipstick tube fig. 114 remove dipstick tube cap lock 1 - locking pin 2 - tube cap 3 - dipstick tube wg transmission and transfer case 21a - 79 fluid and filter (continued).
Page 221: Freewheeling Clutch
Freewheeling clutch description freewheeling clutches (fig. 115) are installed in the front planetary gear set between the sun gear and the stator shaft, and in the rear planetary gear set between the sun gear and the intermediate shaft. The freewheel consists of an outer race (4), an inner race (7)...
Page 222
Disassembly (1) remove retaining ring (5) (fig. 117) from hol- low shaft (1). (2) remove rear sun gear (4) with the k3 inter- nally toothed disk carrier and rear freewheeling clutch f2 (3). (3) remove snap-ring (2) (fig. 117) for freewheel. (4) press freewheeling clutch out of sun gear. (5) check o-...
Page 223
(6) check the anti-friction bearing (fig. 118) in the rear planetary sun gear for damage. Replace as nec- essary. Assembly (1) press freewheeling clutch f2 (3) (fig. 119) into sun gear (4). (2) install snap-ring (2) for freewheeling clutch. (3) check o-rings (6) (fig. 119) on hollow shaft, replace i...
Page 224: Gearshift Cable
Gearshift cable diagnosis and testing - gearshift cable (1) the floor shifter lever and gate positions should be in alignment with all transmission park, neutral, and gear detent positions. (2) engine starts must be possible with floor shift lever in park or neutral gate positions only. Engine start...
Page 225
Removal (1) shift transmission into park. (2) raise vehicle. (3) remove the shift cable eyelet from the trans- mission manual shift lever. (4) remove shift cable from the cable support bracket. (5) lower vehicle. (6) remove necessary console parts for access to shift lever assembly and shift cable. ...
Page 226: Holding Clutches
(13) verify that the shift lever is in the park posi- tion. (14) push and hold forward on the shifter handle with at least 10-15 n·m of force to take up any move- ment of the shifter and gearshift cable adjuster. (15) tighten the adjustment screw to 7 n·m (65 in.Lbs.). (16) verify correct shifter op...
Page 227
Fig. 123 holding clutches 1 - b1 clutch 10 - center planetary gearset annulus gear 2 - externally toothed disc 11 - center planetary gearset pinion gears 3 - internally toothed disc 12 - center planetary gearset sun gear 4 - b3 clutch 13 - front planetary gearset pinion gears 5 - b2 clutch 14 - fron...
Page 228
Fig. 124 holding clutches 1 - b1 clutch 10 - center planetary gearset annulus gear 2 - externally toothed disc 11 - center planetary gearset pinion gears 3 - internally toothed disc 12 - center planetary gearset sun gear 4 - b3 clutch 13 - front planetary gearset pinion gears 5 - b2 clutch 14 - fron...
Page 229: Holding Clutch B1
Holding clutch b1 disassembly (1) remove snap-ring (7) (fig. 125). (2) remove multiple-disc pack (6) and disc spring (5) from outer multiple-disc carrier. (3) place the multi-use spring compressor 8900 (8) (fig. 125) on disc spring (3) and compress the spring until the snap-ring (4) is exposed. (4) ...
Page 230
Assembly (1) install piston (2) (fig. 126) in outer multiple- disc carrier (1). Press in piston using the disc spring (3) and multi-use spring compressor 8900 (8). Place compressor (8) on disc spring (3) and compress until the groove of the snap-ring is exposed note: check vulcanized gasket, replace...
Page 231: Holding Clutch B2
(5) measure b1 clutch clearance. (a) mount pressing tool 8901 (1) (fig. 127) on outer multiple disc. (b) using a lever press (fig. 127), compress pressing tool as far as the stop (then the marking ring is still visible, see small arrow). (c) using a feeler gauge, determine the play 9l9 (fig. 128) at...
Page 232
Fig. 129 holding clutch b2 1 - snap-ring 9 - b3 piston sealing ring 2 - multiple disc pack 10 - b2 piston 3 - disc spring 11 - piston guide sealing ring 4 - b2 and b3 piston guide 12 - piston guide sealing ring 5 - o-ring 13 - piston guide ring 6 - b3 piston sealing ring 14 - piston back pressure di...
Page 233
(6) separate piston guide ring (13) and the b2 pis- ton (10) from the b3 piston (8) by blowing com- pressed air into the bore (d) (fig. 130). (7) press piston guide ring (13) out of the b2 pis- ton (10). (8) separate piston guide (4) from the b3 piston (8) by blowing compressed air into the bore (a)...
Page 234
Fig. 131 holding clutch b2 1 - snap-ring 9 - b3 piston sealing ring 2 - multiple disc pack 10 - b2 piston 3 - disc spring 11 - piston guide sealing ring 4 - b2 and b3 piston guide 12 - piston guide sealing ring 5 - o-ring 13 - piston guide ring 6 - b3 piston sealing ring 14 - piston back pressure di...
Page 235
Fig. 132 holding clutch b2/b3 seals 1 - piston guide ring 4 - b3 piston sealing ring 2 - piston guide ring sealing ring 5 - b3 piston/b2 outer disc carrier 3 - piston guide ring sealing ring 6 - b3 piston sealing ring 21a - 94 transmission and transfer case wg holding clutch b2 (continued).
Page 236: Input Speed Sensors
Input speed sensors description the input speed sensors (6, 8) (fig. 136) are fixed to the shell of the control unit via contact blades. The speed sensors are pressed against the transmission housing (2) by a spring (7) which is held against the valve housing of the shift plate (5). This ensures a d...
Page 237: Oil Pump
Oil pump description the oil pump (fig. 138) (crescent-type pump) is installed in the torque converter casing behind the torque converter and is driven by the drive flange of the torque converter. The pump creates the oil pres- sure required for the hydraulic procedures. Operation when the engine is...
Page 238
Disassembly (1) remove pump gears (1 and 2) (fig. 140) from pump housing. (2) remove the inner oil pump seal (1) (fig. 141). (3) replace the outer oil pump o-ring (2) (fig. 141). Assembly (1) install new inner oil pump seal (1) (fig. 142). (2) replace o-ring (2) (fig. 142). Fig. 139 oil pump 1 - cre...
Page 239: Park Lock Cable
(3) lubricate pump gears and place in the pump housing. Insert pump gear (1) (fig. 143) so that the chamfer (arrow) points towards the pump housing. Park lock cable removal (1) place the shifter in the park position. (2) lower the steering column cover. (3) with the ignition switch in the “run” posi...
Page 240: Pistons
Installation note: the gearshift cable must be secured into position and properly adjusted before the installa- tion of the park lock cable. (1) verify that the shifter is in the park position. (2) push the park lock cable straight into the square mounting hole in the steering column until cable sna...
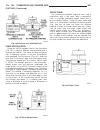
Page 241
Force multiplication using the 10 psi example used in the illustration (fig. 147), a force of 1000 lbs. Can be moved with a force of only 100 lbs. The secret of force multiplica- tion in hydraulic systems is the total fluid contact area employed. The illustration, (fig. 147), shows an area that is t...
Page 242: Planetary Geartrain
Planetary geartrain description three planetary gear sets (fig. 149) are used to produce the different gear ratios. These are located in the mechanical part of the transmission as the front, middle and rear planetary gear sets. Operation the annulus gear (1) (fig. 150) and sun gear (3) elements of a...
Page 243
Fig. 151 output shaft with center and rear planetary geartrain 1 - teflon rings 7 - driving clutch k3 2 - output shaft with center planetary carrier 8 - thrust washer 3 - needle bearing 9 - axial needle bearing 4 - thrust washer 10 - shim 5 - rear planetary gear set 11 - retaining ring 6 - rear holl...
Page 244
Fig. 152 output shaft with center and rear planetary geartrain 1 - teflon rings 7 - driving clutch k3 2 - output shaft with center planetary carrier 8 - thrust washer 3 - needle bearing 9 - axial needle bearing 4 - thrust washer 10 - shim 5 - rear planetary gear set 11 - retaining ring 6 - rear holl...
Page 245: Shift Mechanism
(8) inspect axial play (fig. 153) between shim (10) and retaining ring (11). Check axial play 9s9 between shim (10) and retaining ring (1) using a feeler gauge. Clearance should be 0.15-0.6 mm. Shims are avail- able in thicknesses of 3.0, 3.4, and 3.7 mm. Adjust as necessary note: during the test, a...
Page 246
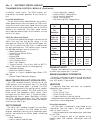
Slsa grey code table c1 c2 c3 c4 c5 park h h h l l t1 l h h l h reverse l h h h l t2 l l h h h neutral h l h h l t3 h l l h h d l l h l l 4 l l l h l 3 l h l l l 2 h l l l l 1 h h l h l park lockout solenoid the slsa contains a park lockout solenoid. The park lockout solenoid is energized by the tcm...
Page 247
Fig. 155 ignition interlock cable 1 - shift mechanism 4 - steering column assembly 2 - shifter btsi lever 5 - interlock cable 3 - adjustment clip fig. 156 transfer case shift cable 1 - clip 2 - shifter 3 - transfer case shift lever pin 4 - transfer case shift cable fig. 157 shifter assembly 1 - shif...
Page 248: Solenoid
Installation (1) install shifter assembly onto the shifter assem- bly studs on the floor pan. (2) install the nuts to hold the shifter assembly onto the floor pan. Tighten nuts to 28 n·m (250 in.Lbs.). (3) place the floor shifter lever in park position. (4) loosen the adjustment screw on the shift c...
Page 249
Upshift/downshift solenoid valves the solenoid valves for upshifts and downshifts (fig. 158) are located in the shell of the electric con- trol unit and pressed against the shift plate with a spring. The solenoid valves (1) initiate the upshift and downshift procedures in the shift plate. The soleno...
Page 250
Torque converter lockup clutch pwm solenoid valve the torque converter lockup clutch pwm solenoid valve (1) (fig. 160) is located in the shell of the elec- tric valve control unit and pressed against the shift plate by a spring. The pwm solenoid valve (1) for the torque con- verter lockup controls t...
Page 251
The plunger is made of a conductive material and accomplishes this movement by providing a path for the magnetic field to flow. By keeping the air gap between the plunger and the coil to the minimum necessary to allow free movement of the plunger, the magnetic field is maximized. Upshift/downshift s...
Page 252: Temperature Sensor/
Torque converter lockup clutch pwm solenoid valve the torque converter lockup pwm solenoid (1) (fig. 164) valve converts pulse-wave-modulated cur- rent controlled by the tcm into the appropriate hydraulic control pressure (p-s/tcc). Shift pressure control solenoid valve the shift pressure regulating...
Page 253
Description the transmission oil temperature sensor (1) (fig. 167) is located in the shell of the electric valve con- trol unit and is fixed to the conductor tracks. Its purpose is to measure the temperature of the transmission oil and pass the temperature to the tcm as an input signal. It is a temp...
Page 254: Torque Converter
Refer to the transmission temperature sensor specifications table (fig. 170) for the relationship between transmission temperature, sensor voltage, and sensor resistance. Torque converter description the torque converter (fig. 171) is a hydraulic device that couples the engine crankshaft to the tran...
Page 255
Impeller the impeller (fig. 172) is an integral part of the converter housing. The impeller consists of curved blades placed radially along the inside of the housing on the transmission side of the converter. As the con- verter housing is rotated by the engine, so is the impeller, because they are o...
Page 256
Stator the stator assembly (fig. 174) is mounted on a sta- tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil pump. The stator is located between the impeller and turbine within the torque converter case (fig. 175). The stator contains a freewheeling clutch, which allows the stator to rotate only in...
Page 257
Torque converter clutch (tcc) the tcc (fig. 176) was installed to improve the efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou- pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impelle...
Page 258
Stator torque multiplication is achieved by locking the stator’s over-running clutch to its shaft (fig. 177). Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter- clockwise direction. When ...
Page 259: Transfer Case - Nv247
Partial emcc partial emcc operation modulates the tcc sole- noid (duty cycle) to obtain partial torque converter clutch application. Partial emcc operation is main- tained until full emcc is called for and actuated. During partial emcc some slip does occur. Partial emcc will usually occur at low spe...
Page 260
(6) remove the rear driveshaft retaining bolts and remove the driveshaft from the transfer case compan- ion flange. Support the driveshaft with mechanics wire (fig. 181). (7) disconnect the transfer case shift cable from the shifter arm (fig. 182). (8) disconnect the vent tube from the transfer case...
Page 261
Rear case and oil pump (1) remove the bolts (fig. 184) holding the trans- fer case damper to the transfer case. (2) remove the damper (fig. 185) from the trans- fer case. (3) install two bolts (fig. 186) partially into the rear propellor shaft companion flange, 180° from each other. (4) install the ...
Page 262
(8) loosen rear case with flat blade screwdriver to break sealer bead. Insert screwdriver blade only into notches provided at each end of case (fig. 189). (9) remove rear case. (10) remove the screws holding the transfer case chain snubber (fig. 190) to the rear transfer case half. (11) remove the o...
Page 263
Companion flange and range lever (1) remove front companion flange nut as follows: (a) move range lever to 4l position. (b) remove nut with socket and impact wrench. (2) remove companion flange. If flange is difficult to remove by hand, remove it with bearing splitter, or with standard two jaw pulle...
Page 264
(2) remove progressive coupling from mainshaft (fig. 197). Front output shaft and drive chain (1) remove rear output shaft drive gear snap-ring (fig. 198). (2) disengage drive gear (fig. 199). Pry gear upward and off mainshaft as shown. (3) remove front output shaft, drive chain and drive gear as as...
Page 265
(4) remove front output shaft drive gear snap- ring. (fig. 200) (5) remove output shaft drive gear from front out- put shaft. (fig. 201) (6) remove the oil pump pickup tube from the front case half. (fig. 202) shift forks and mainshaft (1) remove detent plug, o-ring, detent spring and detent plunger...
Page 266
(2) remove shift rail from shift fork and transfer case housing. (3) rotate range shift fork until it disengages from shift sector. (4) remove mainshaft and shift fork from input gear pilot bearing. Note: loose needle bearings are used to support the drive sprocket hub on the mainshaft. Do not lift ...
Page 267
Input and low range gear (1) remove snap-ring that retains input gear in low range gear (fig. 207). (2) remove retainer (fig. 208). (3) remove front tabbed thrust washer (fig. 209). (4) remove input gear (fig. 210). (5) remove rear tabbed thrust washer from low range gear (fig. 211). Inspection main...
Page 268
Examine the input gear carefully. Be sure the gear teeth and bearing surfaces are in good condition. Replace the gear if wear or damage is evident. Check the input gear pilot bearing. Rotate the bearing and check for roughness or noise. Also check bearing position in the bore. The bearing should be ...
Page 269
Check condition of each transfer case bearing. Replace any bearing exhibiting signs of roughness, wear, or damage. Assembly lubricate transfer case components with mopar t transfer case lubricant or petroleum jelly (where indicated) during assembly. Caution: the bearing bores in various transfer cas...
Page 270
(7) remove the output shaft rear bearing with the screw and jaws from remover l-4454 and cup 8148 (fig. 217). (8) install new bearing with tool handle c-4171 and installer 5066 (fig. 218). The bearing bore is chamfered at the top. Install the bearing so it is flush with the lower edge of this chamfe...
Page 271
(12) using remover c-4210 and handle c-4171, drive input shaft bearing into case. The bearing locating ring must be fully seated against case sur- face. (13) remove input gear pilot bearing by inserting a suitably sized drift into the splined end of the input gear and driving the bearing out with th...
Page 272
Shift forks and mainshaft (1) install new sector shaft o-ring and bushing (fig. 225). (2) install shift sector. (3) install locking clutch spring, locking clutch, blockout spring, and range clutch sleeve, to main- shaft as shown in (fig. 226). Install snap ring. (4) install drive sprocket hub to mai...
Page 273
(7) install shift rail to shift range fork and trans- fer case housing. (8) rotate shift sector to neutral position. (9) install new o-ring on detent plug (fig. 227). (10) lubricate detent plunger with transfer case lubricant or light coat of petroleum jelly. (11) install detent plunger, spring and ...
Page 274
Progressive coupling (1) install progressive coupling (fig. 233). (2) install the progressive coupling thrust washer (fig. 234) over the output shaft and against the cou- pling. (3) install the progressive coupling snap-ring (fig. 235) onto the output shaft. Fig. 231 installing drive chain, front ou...
Page 275
Oil pump (1) install new o-ring on flanged end of oil pickup tube. (2) install oil pump (fig. 236). (3) install oil pump retaining snap-ring (fig. 237). (4) insert oil pickup tube in pump (fig. 238). Rear case (1) install magnet in front case pocket (fig. 239). (2) clean sealing flanges of front cas...
Page 276
Companion flange and range lever (1) install range lever, washer and locknut on sec- tor shaft (fig. 242). Tighten locknut to 27-34 n·m (20-25 ft. Lbs.) torque. (2) install new seal washer on front output shaft (fig. 243). (3) lubricate flange hub with transfer case lubri- cant and install flange on...
Page 277
Final assembly (1) position transfer case damper onto the transfer case. (2) install the damper bolts (fig. 245). Tighten bolts to 41-54 n·m (30-40 ft. Lbs.) torque. (3) install drain plug. Tighten plug to 41-54 n·m (30-40 ft. Lbs.) torque. (4) level transfer case and fill it with mopar t transfer c...
Page 278
(5) install the rear driveshaft. Torque the bolts to 32 n·m (24 ft. Lbs.). Be certain to install the drive- shaft in the same position as before removal. (6) install the front driveshaft. Torque the bolts to 32 n·m (24 ft. Lbs.) (fig. 247). Be certain to install the driveshaft in the same position a...
Page 279
Special tools transfer case - nv247 handle - c-4171 installer, seal - 7884 installer, bearing - 5066 installer, seal - 6952-a installer, bearing - 6953 installer, seal - c-3995-a remover, bearing - c-4210 remover, bearing - l-4454 cup, installer - 8148 installer, bearing - 8128 21a - 138 transmissio...
Page 280: Emissions Control - 2.7L
Emissions control - 2.7l diesel table of contents page page emissions control - 2.7l diesel description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 exhaust gas recirculation . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 on-board diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 emissions control - 2.7l diesel d...
Page 281: Exhaust Gas Recirculation
Exhaust gas recirculation table of contents page page exhaust gas recirculation description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 valve description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 operation . . ...
Page 282: Valve
Valve description the egr valve is mounted to the intake manifold at the left rear corner of the engine (fig. 1). Operation the engines use exhaust gas recirculation (egr) systems. The egr system reduces oxides of nitrogen (nox) in engine exhaust and helps prevent detona- tion (engine knock). Under ...
Page 283: Solenoid
Solenoid description the egr solenoid is mounted in the left-rear of the engine compartment (fig. 3). The egr solenoid serves two different functions. One is to control vac- uum bleed-off of the egr valve. The other is to con- trol the “on time” of the egr valve. Removal (1) disconnect negative batt...
Page 284: On-Board Diagnostics
On-board diagnostics table of contents page on-board diagnostics description - diagnostic trouble codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 on-board diagnostics description - diagnostic trouble codes on the following pages, a list of dtc’s is provided for the 2.7l diesel en...
Page 285
Engine control module (ecm) - drbiii t codes generic scan tool code drb iii t scan tool display p0070 ambient air temperature circuit signal voltage too high ambient air temperature circuit signal voltage too low p0100 mass air flow sensor signal voltage too high mass air flow sensor signal voltage ...
Page 286
Generic scan tool code drb iii t scan tool display p0235 boost pressure sensor plausibility boost pressure sensor signal voltage too low boost pressure sensor signal voltage too high boost pressure sensor signal voltage too high or low p0243 boost pressure evm short circuit boost pressure evm open c...
Page 287
Generic scan tool code drb iii t scan tool display p0579 speed control switch signal too high speed control switch signal too low speed control switch plausibility error p0606 ecm recovery flag ecm redundant monitoring ecm gate array monitoring p0615 starter relay circuit short circuit p0620 generat...
Page 288
Generic scan tool code drb iii t scan tool display p0703 brake switch signal plausibility brake switch signal plausibility after initialization p0836 4 wheel drive switch signal too low 4 wheel drive switch signal too high 4 wheel drive switch plausibility error 2 4 wheel drive switch plausibility e...
Page 289
Generic scan tool code drb iii t scan tool display p1608 a to d monitoring, ram test failure a to d monitoring, ground connection to pps failure a to d monitoring, test voltage failure p1610 5 voltage supply too high 5 voltage supply too low p1643 cabin heater relay short circuit cabin heater relay ...
Page 290: Service Manual Comments
Service manual comments what errors(s) have you found? ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________...
Page 291
Daimlerchrysler corporation attn. Publications dept. Cims 486-02-70 800 chrysler drive auburn hills, mi 48326-2757 8.