- DL manuals
- Kantronics
- Radio Modems
- KAM Plus
- Reference Manual
Kantronics KAM Plus Reference Manual
Summary of KAM Plus
Page 1
Kam plus reference manual version 7.0 – march 21, 1994 version 7.1 – august 29, 1994 version 8.0 – may 1995 version 8.2 – may 1995.
Page 2
2 table of contents introduction to commands some abbreviations .......................................................................... 3 entry ................................................................................................ 3 format ..................................................
Page 3
3 introduction to commands some abbreviations x >: this represents a single control character sent from your terminal program to the kam plus. To send this character, press and hold the control key and type the second key ( x ) while hold- ing the control key down. If another letter follows this (i....
Page 6
6 ascbaud n ( n = 20 – 500) default 110 this command sets the default baud rate used when entering ascii mode with no baud rate speci- fied. See also: ascii ascii [ n ] ( n = 20 – 500) immediate command this command places the kam plus in ascii mode. If you specify the optional value n , the kam plu...
Page 7
7 axhang n ( n = 0 – 255) default 0 when operating through a voice repeater, this command should be set to the hang time of the re- peater. If the kam plus has detected activity within this time interval, it will not use the axdelay setting, since the repeater should still be transmitting. Each unit...
Page 9
9 cd internal l external l software default internal/internal when set to internal, the kam plus will detect a signal when any energy is present on the audio input to the kam plus. When set to external, the signal detection is supplied by an external de- vice, connected to the xcd pin of the radio p...
Page 12
12 cw [ n ] ( n = 5 – 99) default 20 this command places the kam plus in the cw mode. If n is not specified, the speed set in cwspeed will be used for transmit and receive. Specifying n will allow you to enter the cw mode at the desired speed. The kam plus will automatically adjust to copy stations ...
Page 13
13 cwspeed n ( n = 5 – 99) default 20 this command sets the cw speed used when entering the cw mode. If this value is less than cwfarns, the kam plus will transmit cw using farnsworth spacing. See also: cw cwtone n ( n = 50 – 2000) default 750 this command sets the center frequency of the cw filter ...
Page 14
14 daytime yymmddhhmm[ss] default 01/01/93 00:00:00 this command sets or reads the real-time clock and software clock in the kam plus. The clock de- termines date and time display in conjunction with the cstamp, mheard, mstamp and pbbs/node messages. When entering the daytime digits to set the clock...
Page 15
15 disconne immediate command this command will initiate an immediate command disconnect request on the current i/o stream. When an acknowledgment is received, your kam plus will display the message *** discon- nected . If you issue a second disconnect command before receiving the acknowledgment, yo...
Page 17
17 frack n ( n = 1 – 15) default 4/4 after transmitting a packet requiring acknowledgment, the kam plus waits frack seconds before incrementing the retry counter and sending the packet again. If the retry count is exceeded, the current operation is aborted. If the packet address includes relay-reque...
Page 18
18 gscan r,m,s,f v7.0 immediate command gscan is a general scan function that will sample the audio signal applied at the hf port of the kam plus. The signal is sampled r times per second, and the resulting binary data is sent to the computer through the serial port. The first sample will be in the ...
Page 19
19 hbaud n ( n = 50 – 300 for hf; 300, 400, 600 or 1200 for vhf) default 300/1200 this command sets the baud rate used by the kam plus for transmission of data over the radio link. It is not related to the terminal baud rate (set by abaud). Hf packet is normally operated at 300 baud, and vhf packet ...
Page 22
22 lt n text ( n = 1 – 4) ( text up to 128 characters) v8.0 default blank this command fills the specified locate text (lt) buffer with text. N specifies which buffer to use (1 – 4). If gpshead is set for this buffer and if the intface command is set to gps, the buffer contents will be updated autom...
Page 23
23 maxusers n ( n = 0 – 26) default 10/10 this command sets the maximum number of streams (channels) available for packet connections. Each stream is designated by a stream letter beginning with "a". With the default value of 10, streams are lettered a – j for each port (hf and vhf). In order to cha...
Page 25
25 morse code tx rx morse code tx rx **-- ---* ***-* **-*- *-*** *-*-* *--** *---* -**-- -*-*- -*--- --*-* ---*- *-***- $00 $00 $21 (!) $00 $25 (%) $2b (+) $00 $00 $00 $26 (&) $00 $00 $00 $00 $00 $00 $534e (sn) $00 $4253 (as) $4152 (ar) $00 $00 $00 $4b41 (ka) $00 $00 $00 $00 *-*- ----- **-** **--* *...
Page 34
34 persist n ( n = 0 – 255) default 192/63 this command sets the value used to determine the probability of transmitting a packet after slottime expires. This method of determining access to the radio channel has proven more effi- cient in sharing the frequency than using the dwait method. The highe...
Page 37
37 rbaud n ( n = 20 – 500) default 45 this command sets the default baud rate used when entering rtty mode. It also sets the baud rate used for rtty operation if pmode is rtty. When operating in the rtty mode, typing the [ ctrl-c ][ 0 ] directive will also switch to the rbaud rate. See also: pmode, ...
Page 38
38 restore defaults immediate command this command will completely restore your kam plus to factory defaults. The kam plus will return all parameters to factory values, and will run the autobaud routine, asking you to press (*) to set baud rate . Any messages in the mailbox will be deleted. See also...
Page 39
39 screenl n ( n = 0 – 255) default 0 this value is used to format data sent to your terminal. A carriage return sequence is sent to the terminal at the end of a line when n characters have been printed. A value of 0 inhibits this action. See also: autolf sendpac n ( n = $00 – $ff) default $0d (ø) t...
Page 42
42 trans immediate command this command places the kam in transparent mode. The current link state is not affected. If par- ity is set to none, you may send all 8 bits from the computer in this mode. There are no special editing characters, all characters are sent over the radio as received. To get ...
Page 44
44 version immediate command displays the current firmware version number installed in your kam plus. Wefax n this command permits the reception of weather facsimile. The audio input to the vhf port of the kam plus is sampled n times per second, and a black/white decision is made on each sample. Eac...
Page 45
45 xon n ( n = $00 – $ff) default $11 [ctrl-q] this command selects the character sent by the kam plus to the terminal to restart input from the terminal. See also: xflow, xoff.
Page 46
46 operation of the kam plus this section of the manual describes kam plus operation. Each operational mode of the kam plus is described including an example of that mode. You will benefit most from this section if you read from it while you are at your station with your kam plus connected to your c...
Page 47
47 amtor operation with your kam plus, several modes of amtor operation are possible. Each amtor station is iden- tified by a selcal (selective call) which is derived from your amateur callsign. The accepted prac- tice in amtor is to use the first letter of your callsign and the last three letters o...
Page 48
48 tion, the other station will "turn it over" to you so you can send data to him, normally the other station will make some kind of statement in the message to indicate that he is going to let you talk. For instance, he might say so how copy? . The other station then types a +? Which is trans- mitt...
Page 49
49 mode b (selfec) operation receiving mode b selfec if you want to receive only messages specifically addressed to you, you can set up your kam plus for mode b selfec receive. To do this, set the autostrt command on in your kam plus and then enter the amtor standby mode or the fec mode as described...
Page 50
50 amtor directives while operating your kam plus in the amtor modes, several directives are available to perform various functions without returning to the command mode ( cmd: ) the directives and their pur- poses are: [ ctrl-c ][ a ] abort link [ ctrl-c ][ d ] break link and remain in amtor standb...
Page 51
51 ascii operation to operate ascii mode with your kam plus, you must first have the command prompt ( cmd: ). Type ascii and press return. This places the kam plus in the ascii mode and the ascbaud com- mand controls the baud rate of the transmitted data. If you want to operate ascii at a different ...
Page 52
52 cw operation type cw and press return to place the kam plus in the cw mode of operation from the command prompt ( cmd: ) by typing cw and pressing return. The kam plus will enter the cw code, ready to receive morse code at the speed set in the cwspeed command. The kam plus will automatically adju...
Page 53
53 character(s) displayed on your terminal when that code is received. (see the morse command for details) note: if the cwptt command is off, the kam plus front panel will not indicate that you have en- tered the transmit mode, or that you have returned to receive. If it is on, the bargraph will go ...
Page 54
54 g-tor mode g-tor, short for golay-tor, is an innovation of kantronics, g-tor was implemented in the kam plus and enhancement board for the kam in early 1994 and establishes a completely now hybrid- arq hf digital communications system for the amateur service. Golay error correction coding forms t...
Page 55
55 the keyboard. It is very important that you include in your cq the fact that you are asking for a g- tor contact. For instance, you might send: cq cq cq de w0xi w0xi w0xi - gtor cq cq cq de w0xi w0xi w0xi - gtor cq cq cq de w0xi w0xi w0xi - gtor pse arq in gtor mode only kkk be sure you include y...
Page 56
56 once you have concluded your conversation, you may break the link by typing the [ ctrl-c ][ d ] di- rective. This will send the proper qrt frame to the other station and return your kam plus to g- tor standby mode. Alternatively you may use the [ ctrl-c ][ x ] directive which will also break the ...
Page 57
57 hints for g-tor operation if you choose to use the fsk mode of your transceiver, you must connect the fsk output from the kam plus (pin 5) to the fsk input of your radio. The actual tones transmitted are controlled by your radio in this mode. Most radios use a mark frequency of 2125 hz and a spac...
Page 58
58 summary of g-tor directives [ ctrl-c ][ a ] abort a link or abort an attempt to link after the first invalid response code [ ctrl-c ][ b ] enter data transparency mode (for binary file transfer) [ ctrl-c ][ d ] disconnect from the station you are linked to. A changeover will be performed if requi...
Page 59
59 navtex operation navtex/amtex theory navtex transmissions are, in reality, mode b amtor (fec). What makes navtex unique however, is the actual message format. Navtex stations always transmit on 518 khz lsb and are typically located on the coast lines. The same format is now being used by the amer...
Page 60
60 for arrl amtex bulletins, the defined b1 codes are: a arrl issued bulletins c crrl issued bulletins (canadian) i iaru issued bulletins j jarl issued bulletins s amsat issued bulletins x miscellaneous and the currently assigned message classes are: a emergency bulletins b priority bulletins d rese...
Page 61
61 packet operation when you first turn your kam plus on, it sends you a sign on message and then a command prompt ( cmd: ). Anytime you see this command prompt, your kam plus is in the packet mode of operation. After you first turn on your kam plus it will monitor packet data received on hf and on ...
Page 63
63 pactor operation pactor operation is possible in two modes. The first mode, normally referred to as arq mode, is a "connected" or linked mode where two stations are in conversation with each other. Complete er- ror checking occurs in this mode and the receiving station will request retransmission...
Page 64
64 pactor, precede the callsign of the station with an exclamation point (!) when starting the con- nection (e.G. Pactor !Dc7xj ). Monitor only mode the kam plus provides you with a method to monitor pactor without allowing another station to link to you. To enter this mode, you must first have the ...
Page 65
65 rtty operation to operate rtty mode with your kam plus, you must first have the command prompt ( cmd: ). Type rtty and press return. This places the kam plus in the rtty mode and the baud rate of the transmitted data is controlled by the rbaud command. If you want to operate rtty at a different s...
Page 66
66 mars feature when you set code rtty mars in your kam several special functions are enabled for rtty opera- tion. A. Typing [ ctrl-g ] on the keyboard automatically sends (figs)jjjjjsssss(ltrs) over the radio. This is an attention signal. B. When you first enter the transmit mode (with [ ctrl-c ][...
Page 67
67 kantronics pbbs your kantronics tnc includes a personal bulletin board system (pbbs) which is capable of storing and forwarding messages for you and other users. This pbbs provides the same message facilities as a computer based bbs (normally referred to as a full-service bbs), including the forw...
Page 68
68 r:9310i2/1107 27268@wk5m.#neks.Ks.Usa.Noam r:931012/1025 16433@nolly.#neks.Ks.Us.A.Noam r:931011/2021 928@n0oer.#neks.Ks.Usa.Na r:931008/1814 2072@n0obm.#ncks.Ks.Usa.Na r:931008/2003 19520@nx0r.#nks.Ks.Usa.Na r:931008/1153 30798@ag0n.#wne.Ne.Usa.Na r:931007/1147 35850@n7mmc.#sewy.Wy.Usa.Na r:9310...
Page 69
69 your pbbs, the message number, your mycall ( urcall ) and the htext you have set. For in- stance, your r: line might be: r:931008/1255 23@urcall.#wtx.Tx.Usa.Noam some bbs operator groups are insisting that your system is not a bbs, and therefore should not include r: lines. Their reasoning is tha...
Page 70
70 setting up other functions of your kam plus pbbs your kam plus automatically configures your personal mailbox when your first sign on to it. The pbbs is initially set with a callsign including your call and an ssid of -1 (e.G. W0xj-1) and a size of 100 kbytes. To change the callsign, use the mypb...
Page 71
71 tion to which you are connecting (i.E. Pbbs is w0xj-1, your station must be w0xj-n). Once con- nected to the pbbs, the very first command you enter must be sysop. The kam plus pbbs will then respond with three lines of six numbers each. Choose one of these three lines and decode the rtext using t...
Page 72
72 the edit command will also permit you to edit the text of a message. The format to edit text is: e # "string1" "string2" specify the message number in place of #. The kam plus will then replace the first occurrence of string1 with string2. You may use either double quotes ( " ) or single quotes (...
Page 73
73 connect to the myremote and start the password sequence but then disconnect, the penalty tim- er is in effect for 15 minutes. Be careful when using the remote access feature. You can change any command in the kam plus without restriction, but this can lead to problems. For instance, if you change...
Page 74
74 hardware information precautions the kam plus is grounded through its connections to your transceiver. Make sure your transceiver is properly grounded and your computer has equal ground potential. Follow the grounding instruc- tions in your transceiver manual. Cables provided with your kam plus a...
Page 75
75 the purpose of the pins (by name) is: fg – frame ground: this pin is attached to the chassis of the equipment as a safety ground. Txd – transmit data; this line carries the data from your computer to the kam plus. Rxd – receive data: this line carries the data from the kam plus to your computer. ...
Page 76
76 pin 1: connects to your mic input of your radio, providing the audio signal to be transmitted. Pin 2: when a ground is applied to this pin and the kam plus cd command is set to software, the kam will not transmit packet. This is normally used as an external means of supplying carrier detect to th...
Page 77
77 afsk output level vhf the afsk output level from the kam plus to your vhf transceiver may be adjusted using potenti- ometer r-10 and jumper k2. When the k2 jumper is placed on one post only, the output level may be adjusted from 2 mv pp to 60 mv pp . Placing the jumper on both posts allows adjust...
Page 78
78 hard reset a hard reset process is provided, although you will rarely need to perform this step. A hard reset will completely erase the memory of your kam plus, test some internal hardware, and re-initialize all parameters to the factory default values. When performing a hard reset, you should co...
Page 79
79 (n1 × 100) / (n1+n2) where n1 is the number to the left of the displayed slash, and n2 is to the right of the slash. For instance, if the kam plus displays 1400/1800, the ratio can be determined by: (1400 × 100) / (1400 + 1800) or 140000/3200 = 44 since the total is 100, the ratio is then 44/56 a...
Page 80
80 specifications size: 1-¾" × 6" × 9" (4.5 cm x 15.3 cm x 23 cm) weight: 2.5 lbs (1.1 kg) input voltage requirements: 9 vdc – 15 vdc current requirements: 260 ma (max), 160 ma (idle) power plug polarity: center pin positive watchdog timer: 2.5 minutes external carrier detect: pulldown to ground ptt...
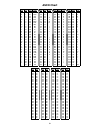
Page 81: Ascii Chart
81 ascii chart ctrl dec hex code dec hex char dec hex char dec hex char @ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z [ / ] ^ _ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 ...