- DL manuals
- Kantronics
- Modem
- KAM
- Operation Manual
Kantronics KAM Operation Manual
Summary of KAM
Page 1
Kam kpc-4 kpc-2400 kpc-2 kpc-1 operations manual version 3.0 – aug. 13, 1990 rf data communications specialists 1202 e. 23rd street, lawrence, kansas 66046 order number (913) 842-7745 service number (913) 842-4476 9 am - noon, 2 pm - 5 pm central time, monday-friday.
Page 2
The kam , kpc-4 , kpc-2400 , kpc-2 and kpc-1 are kantronics hardware and software designs incor- porating the ax.25 version 2 level 2 packet protocol as adopted by the american radio relay league. This manual contains information from earlier kpc-1 , kpc-2 , kpc-2400 , kpc-4 and kam manuals and adde...
Page 3
Operations manual table of contents page preface ..................................................................................................... 1 some abbreviations .......................................................................... 1 intro/getting started ................................
Page 4
Kantronics host mode operation ............................................................ 28 communication format host computer to tnc ............................................................ 28 kam hf modes ....................................................................... 29 tnc to host...
Page 5: Preface
Preface 1 preface this manual will introduce you to the various modes of operation available with your new kan- tronics tnc. It assumes that you have read the installation manual and have successful completed connecting your tnc to your computer and radios. First, we start with the modes common to a...
Page 6: Intro / Getting Started
Intro 2 intro / getting started now that you have your new kantronics unit connected to your radio and computer, let's take a moment to see what it is and how to make it understand what you want to do. A terminal node controller (tnc) is very similar to a telephone modem because it receives digital ...
Page 7
Intro 3 again, the changes will not be remembered unless you have used the perm command, or using a battery backup or smartwatch. All commands are listed alphabetically in the commands manual and many are discussed by mode in this operations manual. The command manual also has an introduction that g...
Page 8
Intro 4 corresponds to a setting of full duplex for the computer. If you set your computer for half duplex, you will need to turn echo off or you will see two of everything you type. When using a split screen program, you may want to set echo off in the tnc because the program will be handling what ...
Page 9
Intro 5 pmode ( kam only). When set to none as default, the kam will be in the packet mode. This com- mand allows you to have your kam come on in the mode you select. Optional parameters are: ascii, amtor, cw, fec, rtty, navtex and none (packet). Starting the kam in the kiss or host mode is accompli...
Page 10: Front Panels
Front panels 6 front panels kam the front panel has two switches, eight leds and a ten segment led bargraph. There are seven leds used as operating status indicators. The front panel is divided into two sections. The left three leds are the indicators associated with hf operation, and the four right...
Page 11
Front panels 7 ten segment led bargraph the bargraph provides a visual indication of the received hf signal. The end segments, labeled mark and space, blink alternately on a properly tuned rtty/ascii/amtor or packet signal. In cw mode the left end (mark) of the bargraph illuminates when no signal is...
Page 12
Front panels 8 monitor mail – this led will illuminate when there is a station connected to your pbbs. In addition, whenever the pbbs is holding mail addressed to you and no connection to the pbbs exists, this led will blink continuously. Rpt – this led will illuminate whenever the kpc-4 gateway or ...
Page 13
Front panels 9 kpc-2400 the front panel has five led indicators which provide information as follows: power – this led illuminates when power is applied. The power on/off switch is located on the rear panel. Xmit – this led illuminates when the tnc keys the ptt line of your radio to send data. Rcv –...
Page 14: Packet Mode
Packet 10 packet mode packet-radio is the communication of digital data via radio. A packet is a group of characters with a flag and header at the beginning and a checksum and flag at the end. A flag is a specific charac- ter used to signify the beginning and ending of a packet. The header is inform...
Page 15
Packet 11 monitoring and calling cq if you turn the monitor command on, you will begin to see other people's packets on your screen. You will notice two callsigns at the beginning of each packet separated by a > . The first callsign is the station the packet is from. And the second callsign is the s...
Page 16
Packet 12 when you have finished your conversation you need to end the connection. To do this, you go into the command mode and type a d for disconnect. Remember to press the return or enter key after any command to the tnc. Once your station has received the acknowledgment for the the discon- nect ...
Page 17
Packet 13 gateway in the kam and kpc-4 a gateway is also available. This is similar to digipeating except that the re- transmission of the packets takes place on the other radio port of the tnc from where it was re- ceived. In other words, if you are on vhf and send a packet via a gateway callsign o...
Page 18
Packet 14 people use the unproto mode and are aware that a collision may occur once in a while. You can usually tell by the conversation if something was missed; if you don't get an answer to a question it's probably not that he is ignoring you, but either the question or the answer got collided wit...
Page 19
Packet 15 frack frame acknowledgment time. If the tnc expects an acknowledgment of a packet it has sent, it will wait frack seconds for the acknowledgment. If the acknowledgment is not received it will either send a poll or retransmit the packet, depending on the setting of ax25l2v2. When digis are ...
Page 20
Packet 16 packet of information. This is the major difference between version 1 and version 2. The connect attempts would then continue for the number of retries set in the tnc and if no response was re- ceived from station b after all of the above, station a would disconnect and dump the packet un-...
Page 21
Packet 17 hardware flow control hardware flow control monitors the voltages on the rts and cts pins of the rs-232 cable. There- fore these two wired must be in the cable between your tnc and computer. The tnc holds cts high as long as it can receive data. Once its buffer gets full, it pulls this lin...
Page 22
Packet 18 getting out of transparent getting into transparent mode is easy, just type a t in command mode. But since transparent mode allows the sending of all characters you can not get out of transparent mode by just typing a ctrl-c (comannd character) as in convers mode. In order to get out of tr...
Page 23: Pbbs
Pbbs 19 pbbs general your tnc contains the kantronics personal mailbox system which will allow you to leave messages for others which may be retrieved later. The personal mailbox is compatible with the large com- munity bulletin board systems (rli, mbl, etc.) and will allow them to forward mail for ...
Page 24
Pbbs 20 using the pbbs is therefore the same, whether you are using your own pbbs or another persons pbbs. At this point, you are ready to send a message to another user, or issue any other mailbox command. Let's assume i want to send a message to ka5ztx. I would now use the send command: s ka5ztk a...
Page 25
Pbbs 21 reverse forwarding messages from your mailbox the kantronics tnc mailbox will allow you to enter messages which will be forwarded by full-ser- vice bbss (rli, mbl, etc.). These messages have a special format and can only be entered in your own personal mailbox. Let's suppose i want to send a...
Page 26: Ka-Node
Ka-node 22 ka-node general the kantronics ka-node is part of your tnc, which provides users with local acknowledgments of packets, rather than the "old" style end-to-end acknowledgment previously required when connect- ing to distant stations. This feature is useful when connecting to distant statio...
Page 27
Ka-node 23 using a ka-node to use the ka-node as a means of connecting to some other node or end-user, you must first connect to the ka-node. At the cmd: prompt on your tnc, issue a connect request to the callsign of the ka-node, let's say law. When you make connection, you will see the following me...
Page 28
Ka-node 24 ample, if you connected to law with w0xi, law connected (via your request) to kc with wx0xi- 15. This is automatic. At this point, you could connect to another ka-node, some other network node using ax.25 as an uplink or downlink protocol, or to an end-user. Let's assume that you de- sire...
Page 29
Ka-node 25 using the xconnect command ( kam and kpc-4 only) the cross-connect (xconnect) command is a unique feature of the ka-node. This command al- lows cross linking between two frequencies through the node in much the same manner as the kantronics unique gateway command, but with local acknowled...
Page 30
Ka-node 26 ka-node commands for remote use when accessed by radio, the ka-node has several commands which may be given to it. These commands are listed here for reference, with a description of each command. In these descrip- tions, the upper case characters of the command are requires. Lower case c...
Page 31
Ka-node 27 the long (jheard l) version of this command will also show the destination field and digipeaters used. This list would look like: (kam) lawkan/h* >w0xi 01/09/88 08:25:15 via ksku, top*, ksku n66046/v >beacon 01/10/88 00:03:10 wk5m-3/h* >wd0emr 01/10/88 00:03:19 via w0xi, top* wd0emr/v >kc...
Page 32
Host 28 kantronics host mode operation to operate in the host mode with a kantronics tnc you must first set the intface command to host. After this is set, it will necessary to perform a soft reset to enter the host mode. This may be accomplished by typing reset at the cmd: prompt. If you want the t...
Page 33
Host 29 kam hf modes when operating non-packet modes (i.E. Rtty, ascii, amtor or cw) with the kam , a few additio- nal host to tnc frames are required. First, select the mode with standard command structures as described above (e.G. Fend c2artty 75 fend). Data that you wish to transmit to the other ...
Page 34
Host 30 hf mode operation when using a non-packet mode on the hf port of the kam , received hf data will be sent to the host with status byte 'd', ort byte '2' and stream byte '0'. Each received character is sent from the kam to the host in a separate block. When operating amtor mode a, another kam ...
Page 35: Wefax Mode
Wefax 31 wefax mode general facsimile reception (wefax) is available with your tnc since the weather facsimile broadcast are using an 800 hz fsk shift which is compatible with the kantronics 1200 baud modem. In order to receive wefax, you must have a program for your computer which will receive 8 bi...
Page 36
Wefax 32 location frequencies (mhz) halifax, ns norfolk, va san diego, ca mobile, al san fran, ca washington, dc 4.275, 6.630, 9.890, 13.510 8.080, 10.865, 16.410 8.646, 17.410 9.158 4.346, 8.682, 12.730, 17.151 4.795, 10.185, 12.205, 14.672 in addition, many of the frequency guides for sale by vari...
Page 37
Wefax 33 the wefax command to cause your tnc to enter the wefax mode, you use the wefax command. Kpc-4 and kam owners must remember to set maxusers 0/1 before issuing the wefax command. Wefax n this command will cause the tnc to sample the audio input at n samples per second. The value of n is deter...
Page 38
Wefax 34 some considerations for the rs-232 port. When the tnc is set in wefax mode, it will send pixel by pixel bytes to your computer continually until you send it a ctrl-c or turn it off! When in wefax mode, the tnc will do nothing else; it is simply too busy handling all that data. The bytes sen...
Page 39: Kiss Mode
Kiss 35 kiss mode the kiss mode allows the tnc to act as a modem and packet assembler/disassembler (pad). The heart of the work to be done concerning what happens to data, must reside in your computer in order to use this mode of operation. The kiss code, as designed by phil karn, is implemented to ...
Page 40
Kiss 36 let's look at data from the tnc to the computer. First, all information flowing in this direction is da- ta. No special messages are sent from the tnc to the computer in kiss mode. The only data flow- ing in this direction is that received through the radio link. Every "frame" of data sent f...
Page 41
Kiss 37 one final sequence of value (particularly for pc compatible users) is the "leave kiss mode" se- quence: c0 ff c0 if for some reason, you have intface kiss and permed, when you turn the unit off and then on again, you will be in kiss mode. The only way to leave this, would be to perform a har...
Page 42: Rtty And Ascii Modes
Rtty / ascii 38 rtty and ascii modes kam only rtty theory rtty is a 5 level (5 bit) baudot code, which limits the number of possible characters to 32. This obviously does not provide enough combinations for all 26 letters of the alphabet and the numer- als and punctuation. Therefore, in order to all...
Page 43
Rtty / ascii 39 rtty and ascii operation rtty and ascii operation with the kam is accomplished through the hf radio port. Several com- mands and special directives are used to control the operation of the kam in rtty or ascii opera- tion. The following commands (from the cmd: prompt) will set the de...
Page 44
Rtty / ascii 40 now that you've entered the desired mode (let's assume rtty), we'll walk through a sample of rtty operation. The same procedures will apply to ascii operation. First, let's see how we can call cq in rtty. Since we entered the rtty mode without any other parameters, we are operating a...
Page 45
Rtty / ascii 41 autolf on causes the kam to insert a line feed after every carriage return which is received from the distance station. If received rtty or ascii signal appear double-spaced on your screen, you want to turn this command off. The autostrt command is useful if you wish to leave your st...
Page 46
Rtty / ascii 42 amtor mode by using the invert directive ( ctrl-c i ). (see fskinv for inverting for inverting signals that you are transmitting.) the lcrtty command can be used to send and receive lower case rtty. When on, lower case characters may be sent and receive in rtty and amtor modes of ope...
Page 47
Rtty / ascii 43 once you have entered either the rtty or ascii mode, the shift may be changed by using the ctrl-c s directive. This will sequentially step through the available shifts – 170, 425, 850 and mo- dem. Initially, the kam will enter the rtty or ascii mode using the shift set in the shift c...
Page 48: Amtor Mode
Amtor 44 amtor mode kam only amtor theory information transmitted by amtor is specially encoded to provide a scheme of error detection. This coding takes the form of each character containing 4 space signals and 3 mark signals. The receiving station can use this 4/3 ratio to determine if the charact...
Page 49
Amtor 45 if you want to initiate a call to another station using the 625 form of amtor, simply use the amtor command with appropriate selcal: amtor xdbuxas or amtor 123456789 amtor arq (mode a) operation requires that both station transmit alternately. First the informa- tion sending station (the st...
Page 50
Amtor 46 empty, allowing you to respond to an arq call answering your cq. For instance, to enter amtor and call cq, the sequence would be: cmd: amtor ctrl-c t cq cq cq de wk5, wk5m wk5m selcal wwkm wwkm wwkm cq cq cq de wk5, wk5m wk5m selcal wwkm wwkm wwkm cq cq cq de wk5, wk5m wk5m selcal wwkm wwkm...
Page 51
Amtor 47 summary of amtor directives ctrl-c e return to receive mode when transmit buffer is empty ctrl-c i invert received mark/space signals ctrl-c r return to receive mode immediately ctrl-c s select next mark/space shift ctrl-c t enter transmit mode – seize iss status ctrl-c x exit amtor mode ba...
Page 52: Navtex / Amtex Mode
Navtex / amtex 48 navtex / amtex mode kam only navtex / amtex theory navtex transmissions are, in reality, mode b amtor (fec). What makes navtex unique how- ever, is the actual message format. Navtex stations always transmit on 518 khz lsb and are typi- cally located on the coast lines. The same for...
Page 53
Navtex / amtex 49 once a message has been received from a particular station with less than a specified amount of errors, it will not been printed again, as the receiving system keeps track of the message numbers it has received. If it then sees the same message class and number from the same transm...
Page 54: Cw Mode
Cw 50 cw mode kam only several parameters can be set for the default values you would like to use when entering the cw mode operation. These parameters and their factory default are listed here for your reference: cwband 200 cwspeed 25 cwtone 750 prosign $5c if you want to change any of these, simpl...
Page 55
Cw 51 once you have selected your desired transmit speed, either by the above ctrl-c n directive, the cw nn command, or by locking to a received station with the ctrl-c l command, you can enter the transmit mode by using the ctrl-c t directive. At this point, the transmitter turns on and charac- ter...
Page 56
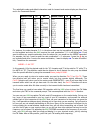
Cw 52 the redefinable codes and default characters used for transmit and receive display are listen here and in the commands manual. Morse code tx rx morse code tx rx **-- --* ***-* **-*- *-*** *-*-* *--** *---* -**-- -*-*- -*--- --*-* ---*- *-***- $00 $00 $21(!) $00 $25(%) $2b(+) $00 $00 $00 $26(&)...
Page 57
Cw 53 you can also use the kam to send cw to you by storing a file on the disk and then connecting the kam green wire (cw key) to your key input of your hf transceiver. Again, set the transceiver so that it will generate sidetone, but will not transmit. Place the kam in the cw mode, out it in trans-...