- DL manuals
- Kawasaki
- Other
- FJ151V
- Service Manual
Kawasaki FJ151V Service Manual
Summary of FJ151V
Page 1
Fj151v fj180v 4-stroke air-cooled gasoline engine service manual.
Page 3: Quick Reference Guide
This quick reference guide will assist you in locating a desired topic or pro- cedure. •bend the pages back to match the black tab of the desired chapter num- ber with the black tab on the edge at each table of contents page. •refer to the sectional table of contents for the exact pages to locate th...
Page 5: Fj151V
Fj151v fj180v 4-stroke air-cooled gasoline engine service manual all rights reserved. No parts of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic mechanical photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permis...
Page 6
List of abbreviations a ampere(s) lb pound(s) abdc after bottom dead center m meter(s) ac alternating current min minute(s) atdc after top dead center n newton(s) bbdc before bottom dead center pa pascal(s) bdc bottom dead center ps horsepower btdc before top dead center psi pound(s) per square inch...
Page 7
Emission control information to protect the environment in which we all live, kawasaki has incorporated crankcase emission (1) and exhaust emission (2) control systems (em) in compliance with applicable regulations of the united states environmental protection agency and california air resources boa...
Page 8: Foreword
Foreword this manual is designed primarily for use by trained mechanics in a properly equipped shop. However, it contains enough detail and basic in- formation to make it useful to the owner who de- sires to perform his own basic maintenance and repair work. A basic knowledge of mechanics, the prope...
Page 9: General Information
General information 1-1 1 general information table of contents before servicing ..................................................................................................................... 1-2 model identification................................................................................
Page 10
1-2 general information before servicing before starting to service the engine, carefully read the applicable section to eliminate unnecessary work. Photographs, diagrams, notes, cautions, warnings, and detailed descriptions have been in- cluded wherever necessary. Nevertheless, even a detailed acco...
Page 11
General information 1-3 before servicing (12)seal guide a seal guide is required for certain oil or grease seals during installation to avoid damage to the seal lips. Before a shaft passes through a seal, apply a little oil, preferably high-temperature grease on the lips to reduce rubber to metal fr...
Page 12
1-4 general information model identification fj180v (recoil starter model) fj180v (electric starter model).
Page 13
General information 1-5 general specifications fj151v, fj180v item recoil starter model electric starter model type forced air-cooled, vertical shaft, ohv, 4-stroke gasoline engine bore × stroke 65 mm × 54 mm (2.56 in. × 2.13 in.) displacement 179 cm³ (10.9 cu in.) direction of rotation counterclock...
Page 14
1-6 general information unit conversion table prefixes for units: prefix symbol power mega m × 1 000 000 kilo k × 1 000 centi c × 0.01 milli m × 0.001 micro µ × 0.000001 units of mass: kg × 2.205 = lb g × 0.03527 = oz units of volume: l × 0.2642 = gal (us) l × 0.2200 = gal (imp) l × 1.057 = qt (us) ...
Page 15: Periodic Maintenance
Periodic maintenance 2-1 2 periodic maintenance table of contents periodic maintenance chart ................................................................................................... 2-2 torque and locking agent..................................................................................
Page 16
2-2 periodic maintenance periodic maintenance chart to ensure satisfactory operation over an extended period of time, any engine requires normal main- tenance regular intervals. The periodic maintenance chart shows periodic inspection and mainte- nance items and suitable intervals. The bullet mark (...
Page 17
Periodic maintenance 2-3 torque and locking agent the following tables list the tightening torque for the major fasteners, and the parts requiring use of a non-permanent locking agent or silicone sealant etc. Letters used in the "remarks" column mean: l : apply a non-permanent locking agent. O : app...
Page 18
2-4 periodic maintenance torque and locking agent torque fastener n·m kgf·m ft·lb remarks starter motor mounting bolts 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb fuel tank cover bolts 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb electrical system flywheel bolt 42 4.3 31 spark plug 22 2.2 16 kill switch bolt 1.5 0.15 13 in·lb the table below, relating...
Page 19
Periodic maintenance 2-5 specifications item standard fuel system idle speed (1) : low idle speed: choke start model 1 550 r/min(rpm) priming start model not specified high idle speed: choke start model 3 300 r/min (rpm) priming start model 3 200 r/min (rpm) fj151v model 2 950 r/min (rpm) air cleane...
Page 20
2-6 periodic maintenance special tools valve seat cutter, 45° - 27.5: 57001-1114 valve seat cutter, 32° - 25: 57001-1118 valve seat cutter, 32° - 28: 57001-1119 valve seat cutter holder bar: 57001-1128 valve seat cutter holder, 6: 57001-1360
Page 21
Periodic maintenance 2-7 periodic maintenance procedures fuel system idle speed adjustment (choke start model) caution do not adjust idle speed with the air cleaner re- moved. High idle speed adjustment • start and warm up the engine without load. • tighten the control panel mounting bolts [a] tempo...
Page 22
2-8 periodic maintenance periodic maintenance procedures choke adjustment • stop the engine. • move the throttle lever [a] at a dash to the high idle po- sition, align bend part of throttle lever with hole of control panel [b] and insert the 6 mm (0.24 in.) diameter pin or bolt [c] through hole. Whe...
Page 23
Periodic maintenance 2-9 periodic maintenance procedures choke start model • place a suitable container [b] under the bolt [a] of the carburetor. • loosen the bolt to drain the carburetor and check to see if water or dirt has accumulated in the carburetor. • tighten the bolt. Torque - float chamber ...
Page 24
2-10 periodic maintenance periodic maintenance procedures • visually inspect the fuel filter [b] of the fuel tap [a]. If the filter is clear with no signs of dirt or other contami- nation, the replacement of the filter is not necessary. If the filter is dark or looks dirty, replace it with a new one...
Page 25
Periodic maintenance 2-11 periodic maintenance procedures air cleaner element installation • install: foam element paper element • install the hollow [a] of the air cleaner case to fit the pro- jection [b] of the air cleaner body. • move the holders [a]. Air cleaner element cleaning and inspection n...
Page 26
2-12 periodic maintenance periodic maintenance procedures air cleaner housing (case and body) inspection • clean the housing with detergent and water and dry it thoroughly. • check the housing for deformation or other damage. Seal the housing well and permit only filtered air to reach the carburetor...
Page 27
Periodic maintenance 2-13 periodic maintenance procedures valve clearance inspection note ○ valve clearance must be checked when the engine is cold (at room temperature). • remove the rocker cover (see cylinder head assembly removal in the engine top end chapter). • place the piston at the top dead ...
Page 28
2-14 periodic maintenance periodic maintenance procedures valve seat inspection • remove the valve (see valve mechanism removal/instal- lation in the engine top end chapter). • inspect the valve seats for damage. If the seats are warped or distorted beyond recondition- ing, replace the cylinder head...
Page 29
Periodic maintenance 2-15 periodic maintenance procedures if the manufacturer’s instructions are not available, use the following procedure. Seat cutter operating cares: 1. This valve seat cutter is designed only for valve seat re- pair. Do not use the valve seat cutter for other purposes. 2. Do not...
Page 30
2-16 periodic maintenance periodic maintenance procedures • coat the seat with machinist’s dye. • fit a 45° seat cutter [a] to the holder and slide it into the valve guide. ○ resurface the valve seat with a 45° cutter, removing only enough material to produce a smooth and concentric seat. Caution do...
Page 31
Periodic maintenance 2-17 periodic maintenance procedures • when lapping is completed, wash all parts in solvent to remove lapping compound. Dry the parts thoroughly. • note the position of the lapping mark on the valve face. The lapping mark should appear on or near the center of the valve face. • ...
Page 32
2-18 periodic maintenance periodic maintenance procedures • remove the oil filler cap and pour in the specified type and amount of oil. Engine oil type: sf, sg, sh or sj class viscosity: sae30, sae10w-30 capacity: 0.65 l (0.69 us qt) electrical system spark plug cleaning and inspection • remove the ...
Page 33: Fuel System
Fuel system 3-1 3 fuel system table of contents exploded view................................... 3-2 specifications .................................... 3-6 governor link mechanism (choke start model) .................................... 3-7 control panel assembly removal 3-7 control panel assembly ...
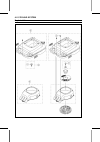
Page 34
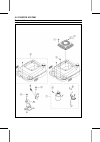
3-2 fuel system exploded view.
Page 35
Fuel system 3-3 exploded view torque no. Fastener n·m kgf·m ft·lb remarks 1 governor arm clamp nut 7.8 0.80 69 in·lb 2 fuel tank cover bolts 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb 3 tank drain bolt 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb 4. Modified model 5. Priming start model 6. Choke start model r: replacement parts.
Page 36
3-4 fuel system exploded view.
Page 37
Fuel system 3-5 exploded view torque no. Fastener n·m kgf·m ft·lb remarks 1 priming nut 1.2 0.12 11 in·lb 2 throttle valve screw 0.70 0.07 6 in·lb l 3 main jet 1.1 0.11 9.7 in·lb 4 drain screw 5.4 0.55 48 in·lb 5 float chamber mounting bolt 5.4 0.55 48 in·lb 6 float chamber mounting bolt (choke star...
Page 38
3-6 fuel system specifications standard item fj151v, fj180v carburetor make/type walbro lmj-16a (choke start model) walbro lmj-17a (priming start model) walbro lmj-17b (modified model) throttle bore diameter 20 mm (0.79 in.) venturi diameter 14 mm (0.55 in.) main jet (mj) #76 (priming start model) #...
Page 39
Fuel system 3-7 governor link mechanism (choke start model) control panel assembly removal • remove: air cleaner elements (see air cleaner element re- moval) recoil starter (see recoil starter removal in the starter system chapter) fuel tank (see fuel tank removal) control panel mounting bolts [a] •...
Page 40
3-8 fuel system governor link mechanism (priming start model) control panel assembly removal • remove: air cleaner elements (see air cleaner element re- moval) recoil starter (see recoil starter removal in the starter system chapter) fuel tank (see fuel tank removal) control panel mounting bolts [a]...
Page 41
Fuel system 3-9 governor link mechanism governor arm installation • install the governor arm [a] onto the governor shaft [b] temporarily. • be sure the link spring [c] around the throttle link rod [d] is in place and that it pulls the governor arm and the throttle lever [e] toward each other. • loos...
Page 42
3-10 fuel system governor link mechanism • when removing the governor gear assembly [a] for re- placing, use two screw drivers [b] of an appropriate size. Caution protect the gasket-mount surface of the crankcase cover when removing the governor assembly with the screw drivers. Governor assembly ins...
Page 43
Fuel system 3-11 governor link mechanism governor shaft installation • apply engine oil to the governor shaft. • install: washer [a] governor shaft [b] snap pin [c] • check that the governor shaft moves freely in its operating range..
Page 44
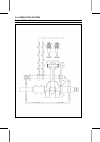
3-12 fuel system carburetor fuel and air flow (choke start model) the main system of the carburetor consists of the main jet [a], the main nozzle [b], and the main air passage [c] (main air jet [d]). The main system meters fuel to the en- gine during moderate to high load conditions. Fuel flows thro...
Page 45
Fuel system 3-13 carburetor fuel and air flow (priming start model) the main system of the carburetor consists of the main jet [a], the main nozzle [b], and the main air passage [c] (main air jet [d]). The main system meters fuel to the en- gine during moderate to high load conditions. Fuel flows th...
Page 46
3-14 fuel system carburetor high altitude operation at high altitude, the standard carburetor air-fuel mixture will be excessively rich. Performance will decrease, and fuel consumption will increase. High altitude performance can be improved by installing a smaller diameter main jet in the carbureto...
Page 47
Fuel system 3-15 carburetor • install the primer pipe [a] and the drain screw as shown in the figure. 90° ∼ 100° [b] • for choke start model; note the following. • place the engine on a level surface. • drain the fuel in the carburetor completely by unscrewing the bolt [a] at the bottom of the float...
Page 48
3-16 fuel system carburetor • install the pipe [a] of the float chamber as shown in the figure. 90° ∼ 100° [b] • for modified model; note the following. • using a properly sized blade screw driver, carefully re- place the main jet [a] with a new one for expected altitude. • tighten the main jet to t...
Page 49
Fuel system 3-17 carburetor carburetor removal warning gasoline is extremely flammable and can be ex- plosive under certain conditions. Turn the engine switch stop position. Do not smoke. Make sure the area is well-ventilated and free from any source of flame or sparks, this includes any appliance w...
Page 50
3-18 fuel system carburetor carburetor disassembly/assembly • refer to the illustration shown for disassembly and as- sembly. • there are several passage plugs (ball plugs) in the car- buretor body. Do not remove them. • before disassembly, mark the outside of throttle valve for assembling them. • r...
Page 51
Fuel system 3-19 carburetor • for choke start model 1. Throttle valve screw 2. Throttle valve 3. Throttle shaft 4. Seal 5. Screw 6. Spring 7. Limiter 8. Pilot screw 9. Spring 10. Choke valve 11. Choke shaft 12. Seal 13. Main nozzle 14. Main jet 15. Float 16. Needle jet 17. Float pin 18. Gasket 19. F...
Page 52
3-20 fuel system carburetor • for priming start model 1. Throttle valve screw 2. Throttle valve 3. Throttle shaft 4. Seal 5. Screw 6. Spring 7. Limiter 8. Pilot screw 9. Spring 10. Main nozzle 11. Main jet 12. Float 13. Needle jet 14. Float pin 15. Gasket 16. Float chamber 17. Gasket 18. Drain screw.
Page 53
Fuel system 3-21 carburetor carburetor cleaning warning clean the carburetor in a well ventilated area, and take care that there is no sparks or flame anywhere near the working area, this includes any appliance with a pilot light. Because of the danger of highly flammable liquids, do not use gasolin...
Page 54
3-22 fuel system carburetor carburetor inspection warning gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explo- sive under certain. Turn the engine switch stop position. Do not smoke. Make sure the area is well ventilated and free from any source of flame or sparks this includes any appliance with a pil...
Page 55
Fuel system 3-23 carburetor • inspect the float valve for excessive wear or damage. The tip should be smooth, without any grooves, scratches, or tears. The rod at the other end of the needle should move smoothly when pushed in and released. Good [a] bad [b] if either the needle or the seat is worn o...
Page 56
3-24 fuel system priming pump priming pump removal • remove the tube [a] from the priming pump. • remove the nut [b] and washer [c]. • remove the priming pump from the inlet manifold. • inspect the priming pump for damages. If the priming pump is damaged, replace it with a new one. Priming pump inst...
Page 57
Fuel system 3-25 inlet manifold (choke start model) inlet manifold removal • unscrew the inlet manifold mounting bolts [a]. • remove the breather pipe [b] from the inlet manifold. Inlet manifold installation • replace the o-ring [a] with a new one. • clean the mating surface of the carburetor and th...
Page 58
3-26 fuel system inlet manifold (priming start model) inlet manifold removal • unscrew the inlet manifold mounting bolts [a]. • remove the breather pipe [b] from the inlet manifold. Inlet manifold installation • replace the o-ring [a] with a new one. • clean the mating surface of the carburetor and ...
Page 59
Fuel system 3-27 inlet manifold inlet manifold inspection • inspect the inlet manifold for cracks. • cracks not visible to the eye may be detected by using a metal crack detection system (visual color check: com- monly found at automotive parts store). If a crack is present in the inlet manifold, re...
Page 60
3-28 fuel system fuel tank fuel tank removal • remove: air cleaner elements (see air cleaner element re- moval) recoil starter (see recoil starter removal in the starter system chapter) oil gauge fuel tank cover bolts [a] • for modified model; note the following. • remove: air cleaner elements (see ...
Page 61
Fuel system 3-29 fuel tank fuel tank cleaning warning clean the fuel tank in a well ventilated area, and take care that there is no sparks or flame anywhere near the working area. Because of the danger of highly flammable liquids, do not use gasoline or low-flash point solvent to clean the tank. • r...
Page 62
3-30 fuel system fuel filter fuel filter inspection • refer to the fuel filter inspection in the peri- odic maintenance chapter..
Page 63
Fuel system 3-31 air cleaner air cleaner element removal • refer to the air cleaner element removal in the periodic maintenance chapter. Air cleaner element installation • refer to the air cleaner element installation in the peri- odic maintenance chapter. Air cleaner element cleaning and inspection...
Page 65: Cooling System
Cooling system 4-1 4 cooling system table of contents exploded view........................................................................................................................ 4-2 cooling fan ...................................................................................................
Page 66
4-2 cooling system exploded view.
Page 67
Cooling system 4-3 exploded view torque no. Fastener n·m kgf·m ft·lb remarks 1 flywheel bolt 42 4.3 31 2 fuel tank cover bolts 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb 3. Modified model.
Page 68
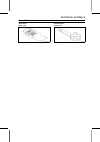
4-4 cooling system cooling fan cooling fan removal • refer to the flywheel removal in the electrical system chapter. Cooling fan installation • refer to the flywheel installation in the electrical system chapter. Cooling fan inspection • visually inspect the blades [a] in the cooling fan [b]. If the...
Page 69: Engine Top End
Engine top end 5-1 5 engine top end table of contents exploded view........................................................................................................................ 5-2 specifications ................................................................................................
Page 70
5-2 engine top end exploded view.
Page 71
Engine top end 5-3 exploded view torque no. Fastener n·m kgf·m ft·lb remarks 1 cylinder head bolts (7t) 22 2.2 16 s cylinder head bolts (7n) 25 2.5 18 s cylinder head bolts (9n) 26 2.6 19 s 2 valve clearance lock screws 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb 3 connecting rod big end cap bolts 5.9 0.60 52 in·lb o 4 rocke...
Page 72
5-4 engine top end specifications item service limit cylinder head cylinder compression 196 kpa (2.0 kgf/cm², 28.4 psi) (min) cylinder head warp 0.03 mm (0.001 in.) valves valve head thickness: exhaust 0.36 mm (0.014 in.) inlet 0.35 mm (0.014 in.) valve stem runout: exhaust 0.05 mm (0.002 in.) inlet...
Page 73
Engine top end 5-5 specifications item standard valves valve clearance: exhaust 0.10 ∼ 0.15 mm (0.004 ∼ 0.006 in.) inlet 0.10 ∼ 0.15 mm (0.004 ∼ 0.006 in.) valve seating surface angle: exhaust 45° inlet 45° valve seating surface width: exhaust 0.6 ∼ 0.9 mm (0.024 ∼ 0.035 in.) inlet 0.6 ∼ 0.9 mm (0.0...
Page 74
5-6 engine top end special tools compression gauge: 57001-221 piston ring compression: 57001-1095 piston ring compression belt, 55 ∼ 67: 57001-1096 compression gauge adapter m14 × 1.25: 57001-1159.
Page 75
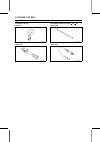
Engine top end 5-7 cylinder head compression measurement • before measuring compression, do the following. ○ thoroughly warm up the engine so that engine oil be- tween the piston and cylinder wall will help seal compres- sion as it does during normal running. ○ stop the engine. • disconnect the spar...
Page 76
5-8 engine top end cylinder head cylinder head assembly removal • remove: air cleaner elements (see air cleaner element in the fuel system chapter) recoil starter (see recoil starter removal in the starter system chapter) fuel tank (see fuel tank removal in the fuel system chapter) muffler (see muff...
Page 77
Engine top end 5-9 cylinder head • tighten the cylinder head bolts following the tightening sequence as shown in the figure. Torque - cylinder head bolts: 7t: 22 n·m (2.2 kgf·m, 16 ft·lb) 7n: 25 n·m (2.5 kgf·m, 18 ft·lb) 9n: 26 n·m (2.6 kgf·m, 19 ft·lb) caution a torque wrench must be used to assure...
Page 78
5-10 engine top end cylinder head push rod inspection • place the push rod in v blocks that are as far apart as possible, and set a dial gauge [a] on the rod at the halfway point between the blocks. Turn the rod to measure the runout. The difference between highest and the lowest dial readings is th...
Page 79
Engine top end 5-11 cylinder head • apply engine oil to the valve stem. • install the valve. • check to see that the valve moves smoothly up and down in the guide. • install the spring and the valve retainer. • to install the collets, push down the valve retainer with thumbs and install the collets....
Page 80
5-12 engine top end valves valve clearance inspection • refer to the valve clearance inspection in the periodic maintenance chapter. Valve clearance adjustment • refer to the valve clearance adjustment in the periodic maintenance chapter. Valve seat inspection • refer to the valve seat inspection in...
Page 81
Engine top end 5-13 valves valve guide inside diameter • use a small bore gauge or a micrometer to measure the inside diameter [a] of the valve guides [b] at three posi- tions down the guide length. If the measurement is more than the service limit, replace the cylinder head with a new one. Valve gu...
Page 82
5-14 engine top end cylinder, piston piston removal • remove: air cleaner elements (see air cleaner element in the fuel system chapter) recoil starter (see recoil starter removal in the starter system chapter) fuel tank (see fuel tank removal in the fuel system chapter) flywheel (see flywheel remova...
Page 83
Engine top end 5-15 cylinder, piston • carefully spread the ring opening with your thumbs then push up to the opposite side of the ring [a] to remove it. • remove the 3-piece oil ring with your thumbs in the same manner. Piston installation • install the expander [a] in the piston oil ring groove so...
Page 84
5-16 engine top end cylinder, piston • install the snap ring [a] in the piston [b] as shown in the figure. Caution do not reuse the snap rings, as removal weakens and deforms them. They could fall out and score the cylinder wall. • apply engine oil to the piston skirt and the cylinder bore. Using th...
Page 85
Engine top end 5-17 cylinder, piston piston cleaning • remove the piston and piston rings (see piston re- moval). Caution never clean the piston head assembled. Carbon particles will fall between the piston and cylinder, and damage the piston and cylinder. • scrape the carbon off [a] the piston head...
Page 86
5-18 engine top end cylinder, piston • measure the piston ring thickness [a]. ○ use a micrometer to measure the ring thickness at several points around the rings. If any of the measurement is less than the service limit, replace the entire set of rings with new ones. Piston ring thickness service li...
Page 87
Engine top end 5-19 cylinder, piston • measure the inside diameter [a] of the connecting rod small end at several points. Use a dial bore gauge. If the inside diameter is greater than the service limit, re- place the connecting rod with a new one. Connecting rod small end inside diameter service lim...
Page 88
5-20 engine top end muffler muffler removal • remove: muffler cover bolt [c] muffler cover nuts [a] muffler cover [b] muffler • remove the gasket. • do not use unnecessary force on the muffler when remov- ing the muffler assembly, or they could become damaged or distorted. Muffler installation • cle...
Page 89: Lubrication System
Lubrication system 6-1 6 lubrication system table of contents exploded view........................................................................................................................ 6-2 engine oil flow chart..................................................................................
Page 90
6-2 lubrication system exploded view.
Page 91
Lubrication system 6-3 exploded view torque no. Fastener n·m kgf·m ft·lb remarks 1 oil drain plug 22 2.2 16 2 oil filter cover bolt 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb o: apply engine oil. R: replacement parts.
Page 92
6-4 lubrication system engine oil flow chart.
Page 93
Lubrication system 6-5 specifications item standard engine oil type sf, sg, sh or sj class viscosity sae30, sae10w-30 capacity 0.65 l (0.69 us qt) level operating range (grid area) on dipstick item service limit oil pump inner and outer rotor clearance 0.14 mm (0.006 in.) outer rotor outside diamete...
Page 94
6-6 lubrication system engine oil caution engine operation with insufficient, deteriorated, or contaminated engine oil will cause accelerated wear and may result in engine seizure and accident. Before starting the engine for the first time, add oil: the engine is shipped dry. Preoil the engine to fo...
Page 95
Lubrication system 6-7 lubrication system the oil pump on the camshaft top discharges the oil. The oil passes the crankcase oil passage, the discharge hole on the crankcase flywheel side, and the camshaft gear side edge. Finally, the oil mist lubricates the connecting rod big end, the small end, the...
Page 96
6-8 lubrication system oil pump oil pump removal • remove: air cleaner elements (see air cleaner element removal in the fuel system chapter) recoil starter (see recoil stater removal in the starter system chapter) fuel tank (see fuel tank removal in the fuel system chapter) flywheel (see flywheel re...
Page 97
Lubrication system 6-9 oil pump • measure the outside diameter [a] of the outer rotor with a micrometer at several points. If the rotor diameter is less than the service limit, replace both the inner and outer rotor with new ones. Outer rotor outside diameter service limit: 22.940 mm (0.9031 in.) • ...
Page 99: Camshaft/crankshaft
Camshaft/crankshaft 7-1 7 camshaft/crankshaft table of contents exploded view........................................................................................................................ 7-2 specifications ......................................................................................
Page 100
7-2 camshaft/crankshaft exploded view.
Page 101
Camshaft/crankshaft 7-3 exploded view torque no. Fastener n·m kgf·m ft·lb remarks 1 crankcase cover bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb s 2 connecting rod big end cap bolts 5.9 0.60 52 in·lb o 3 valve clearance lock screws 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb 4 rocker arm bolts 28 2.8 20 hg: apply high-temperature grease. O: appl...
Page 102
7-4 camshaft/crankshaft specifications item service limit camshaft, tappet cam lobe height: exhaust 22.060 mm (0.8685 in.) inlet 22.060 mm (0.8685 in.) camshaft journal diameter: pto side 7.77 mm (0.3059 in.) flywheel side 13.927 mm (0.5483 in.) camshaft hole inside diameter: crankcase cover 11.060 ...
Page 103
Camshaft/crankshaft 7-5 crankcase crankcase cover removal • drain the oil (see oil change in the lubrication system chapter). • remove: air cleaner elements (see air cleaner element removal in the fuel system chapter) recoil starter (see recoil starter removal in the starter system chapter) fuel tan...
Page 104
7-6 camshaft/crankshaft crankcase • be sure to replace any oil seal with a new one. ○ install the oil seal so that the marks [a] face out. ○ thoroughly pack high-temperature grease [b] into the space between the seal lip [c] and the dust lip [d]. Press in the new oil seal using a press or suitable t...
Page 105
Camshaft/crankshaft 7-7 crankcase • measure the inside diameter [a] of the crankshaft journal metal on the crankcase at several points. Replace the crankcase with a new one if the inside diameter is greater than the service limit. Crankshaft journal metal inside diameter service limit: 27.98 mm (1.1...
Page 106
7-8 camshaft/crankshaft breather the function of the breather is to create a negative pressure in the crankcase which prevents oil from being forced out of the engine through the piston rings, oil seals or gaskets. Valve controls direction of air flow caused by piston movement so that air flow from ...
Page 107
Camshaft/crankshaft 7-9 breather breather chamber cover removal • remove the bolts [a] and the breather chamber cover [b]. Breather chamber cover installation • install a new gasket and the breather chamber cover, and tighten the bolts. Breather valve inspection • remove the breather valve [a]. • in...
Page 108
7-10 camshaft/crankshaft camshaft, tappet camshaft, tappet removal • drain the oil (see oil change in the lubrication system chapter). • remove: air cleaner elements (see air cleaner element removal in the fuel system chapter) recoil starter (see recoil starter removal in the starter system chapter)...
Page 109
Camshaft/crankshaft 7-11 camshaft, tappet camshaft, tappet installation • apply engine oil to the following. Tappet journal camshaft journal cam lobe surface camshaft gear • install the tappets in those old positions. • align the punch marks [a] on the crankshaft gear and on the camshaft gear. • ins...
Page 110
7-12 camshaft/crankshaft camshaft, tappet • inspect the camshaft to make sure that its acr (automatic compression reduction) function operates smoothly and does not have any damage or abnormal wear. If acr parts are worn, replace the acr with a new one. When the weight [a] is closed, if the top of t...
Page 111
Camshaft/crankshaft 7-13 crankshaft, connecting rod connecting rod removal • remove: piston (see piston removal in the engine top end chap- ter) connecting rod installation • install: piston (see piston installation in the engine top end chapter) crankshaft removal • drain the oil (see oil change in...
Page 112
7-14 camshaft/crankshaft crankshaft, connecting rod connecting rod bend/twist • measure the connecting rod bend. ○ select an arbor of the same diameter of the connecting rod big end, and insert the arbor through the connecting rod big end. ○ select an arbor of the same diameter of the piston pin and...
Page 113
Camshaft/crankshaft 7-15 crankshaft, connecting rod • measure the crankpin width [a] with a dial caliper. If the crankpin width is greater than the service limit, re- place the crankshaft with a new one. Crankpin width service limit: 24.17 mm (0.95 in.) connecting rod big end bearing/crankpin wear •...
Page 114
7-16 camshaft/crankshaft crankshaft, connecting rod crankshaft main journal/wear • measure both journals at several points around the jour- nal circumference. If the journal diameter is less than the service limit, re- place the crankshaft with a new one. Crankshaft journal diameter service limit: p...
Page 115: Starter System
Starter system 8-1 8 starter system table of contents exploded view........................................................................................................................ 8-2 electric starter system .......................................................................................
Page 116
8-2 starter system exploded view.
Page 117
Starter system 8-3 exploded view torque no. Fastener n·m kgf·m ft·lb remarks 1 recoil starter mounting bolts 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb 2 brake arm mounting bolt 9.3 0.95 82 in·lb 3 brake lever assembly mounting bolt 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb 4 starter motor mounting bolts 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb 5 fuel tank cover bolts 6...
Page 118
8-4 starter system electric starter system starter motor removal • remove: air cleaner elements (see air cleaner element in the fuel system chapter) recoil starter (see recoil starter removal) fuel tank (see fuel tank removal in the fuel system chapter) • remove the starter motor mounting bolts [a] ...
Page 119
Starter system 8-5 recoil starter system recoil starter removal • remove: recoil starter mounting bolts [a] recoil starter [b] recoil starter installation • install the recoil starter and tighten the mounting bolts. Torque - recoil starter mounting bolts: 6.9 n·m (0.70 kgf·m, 61 in·lb) rope guide re...
Page 120
8-6 starter system recoil starter system rope guide installation • set the guide so that the thick side [a] faces the outside [b], and press it with a suitable tool [c]. • clamp the rope with the clip [a] so it can not wind back. • untie the rope from the case and push it through the guide. • instal...
Page 121
Starter system 8-7 pad brake pad brake assembly removal • remove: air cleaner elements (see air cleaner element removal in the fuel system chapter) recoil starter (see recoil starter removal) fuel tank (see fuel tank removal in the fuel system chapter) pulley (see flywheel removal in the electrical ...
Page 122
8-8 starter system pad brake • tighten the bolt [a]. • install the lever assembly [b]. • tighten the brake lever assembly mounting bolt [c]. Torque - brake lever assembly mounting bolt: 6.9 n·m (0.70 kgf·m, 61 in·lb) ○ check the lever assembly moves smoothly after installa- tion. • install the sprin...
Page 123: Electrical System
Electrical system 9-1 9 electrical system table of contents exploded view........................................................................................................................ 9-2 specifications ..........................................................................................
Page 124
9-2 electrical system exploded view.
Page 125
Electrical system 9-3 exploded view torque no. Fastener n·m kgf·m ft·lb remarks 1 flywheel bolt 42 4.3 31 2 spark plug 22 2.2 16 3 kill switch bolt 1.5 0.15 13 in·lb 4. Modified model do: degrease the taper..
Page 126
9-4 electrical system specifications item standard service limit ignition system ignition coil: primary winding resistance in the text – – – secondary winding resistance in the text – – – spark plug: type ngk bpr5es – – – gap 0.75 mm (0.030 in.) – – –.
Page 127
Electrical system 9-5 special tools hand tester: 57001–1394 bracket holder: 57001–1536.
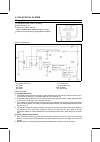
Page 128
9-6 electrical system wiring diagram recoil starter model.
Page 129
Electrical system 9-7 wiring diagram electric starter model.
Page 130
9-8 electrical system precautions there are a number of important precautions that you must follow when servicing electrical systems. Learn and observe all the rules below. ○ do not hit the electric parts with a hammer or do not drop the electric parts. These may result in the electric parts damage ...
Page 131
Electrical system 9-9 charging system flywheel removal • remove: air cleaner elements (see air cleaner element removal in the fuel system chapter) recoil starter (see recoil starter removal in the starter system chapter) fuel tank (see fuel tank removal in the fuel system chapter) • hold the pulley ...
Page 132
9-10 electrical system charging system • using a suitable flywheel puller [a], remove the flywheel [b]. Caution always use flywheel puller. • for electric starter model; note the following. • remove: ignition coil with charging coil (see ignition coil re- moval) • remove the pad brake assembly (see ...
Page 133
Electrical system 9-11 charging system • for electric starter model; as shown in the figure. • for recoil starter model; note the following. • install: ignition coil (see ignition coil installation) pad brake assembly (see pad brake assembly instal- lation in the starter system chapter) • install th...
Page 134
9-12 electrical system charging system • for modified model; note the following. • install the pulley [a]. • tighten the flywheel bolt [b]. Torque - flywheel bolt: 42 n·m (4.3 kgf·m, 31 ft·lb) • install the removed parts (see appropriate chapters). Circuit composition c: condenser co: ignition coil ...
Page 135
Electrical system 9-13 charging system (3) spark delay characteristic 1. The trigger position of the thyristor (scr) changes and spark delay by decreasing the voltage wave form applied to the thyristor (scr) in the revolutions number set up in the spark delay characteristic control circuit in the fi...
Page 136
9-14 electrical system ignition system ignition coil removal • for recoil starter model; note the following. • remove: fan (see flywheel removal) spark plug cap ground lead [a] bolts [b] ignition coil [c] • for electric starter model; note the following. • remove: fan (see flywheel removal) spark pl...
Page 137
Electrical system 9-15 ignition system • for recoil starter model; note the following. • install: ignition coil [a] bolts [b] ground lead [c] • when installing the ground lead, put ground lead between second and third fin. • for electric starter model; note the following. • install: ignition coil wi...
Page 138
9-16 electrical system ignition system spark plug installation • insert the spark plug vertically into the plug hole with the plug installed in the plug wrench. • tighten the plug. Torque - spark plug: 22 n·m (2.2 kgf·m, 16 ft·lb) • fit the plug cap securely. • pull up the spark plug cap lightly to ...
Page 139: Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting 10-1 10 troubleshooting table of contents engine troubleshooting guide ............................................................................................... 10-2 starter motor troubleshooting guide ...............................................................................
Page 140
10-2 troubleshooting engine troubleshooting guide if the engine malfunctions, check if the way the engine is used is correct. If engine malfunctions even if engine is used correctly, systematically carry out troubleshooting starting with simple points. This chart describes typical troubleshooting pr...
Page 141
Troubleshooting 10-3 engine troubleshooting guide.
Page 142
10-4 troubleshooting engine troubleshooting guide.
Page 143
Troubleshooting 10-5 engine troubleshooting guide.
Page 144
10-6 troubleshooting starter motor troubleshooting guide 1. Disconnect spark plug cap, and ground the cap terminal. 2. Turn engine switch to "start" position and check condition. Warning engine may be cranked in this test. Do not touch any rotating parts of engine and equip- ment during test. Cautio...
Page 145
Part no.99924-2063-04 printed in japan.