- DL manuals
- Keithley
- Multimeter
- 2002
- Getting Started Manual
Keithley 2002 Getting Started Manual
Summary of 2002
Page 1
Model 2002 multimeter getting started manual a g r e a t e r m e a s u r e o f c o n f i d e n c e.
Page 2: Warranty
Warranty keithley instruments, inc. Warrants this product to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of 3 years from date of shipment. Keithley instruments, inc. Warrants the following items for 90 days from the date of shipment: probes, cables, rechargeable batteries, diskette...
Page 3
Model 2002 multimeter getting started manual ©1994, keithley instruments, inc. All rights reserved. Cleveland, ohio, u.S.A. First printing may 1994 document number: 2002-903-01 rev. A.
Page 4: Manual Print History
Manual print history the print history shown below lists the printing dates of all revisions and addenda created for this manual. The revision level letter increases alphabetically as the manual undergoes sub- sequent updates. Addenda, which are released between revisions, contain important change i...
Page 5: Safety Precautions
Safety precautions the following safety precautions should be observed before using this product and any asso- ciated instrumentation. Although some instruments and accessories would normally be used with non-hazardous voltages, there are situations where hazardous conditions may be present. This pr...
Page 6
If a screw is present, connect it to safety earth ground using #18 awg or larger wire. The symbol on an instrument or accessory indicates that 1000v or more may be present on the terminals. Refer to the product manual for detailed operating information. Instrumentation and accessories should not be ...
Page 7: Table of Contents
Table of contents 1 front panel operation product overview................................................................................. 1-2 display ................................................................................................ 1-8 power-up..........................................
Page 8
1 front panel operation.
Page 9: Product Overview
Product overview if you have any questions after reviewing this information, please contact your local keithley representative, or call one of our applications engineers at 1-800-348-3735 (u.S. And canada only). Worldwide phone numbers are listed on the back cover. The model 2002 is an 8 ½ -digit mu...
Page 10
Some additional capabilities of the model 2002 include: • data storage with burst mode capability • scan (measure) channels of an external scanner (e.G., model 7001 or 7002) • single button zeroing (rel) • built-in math functions • digital ltering • remote operation using the ieee-488 bus by install...
Page 11
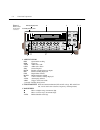
Next prev power display 2002 multimeter dcv acv dci aci Ω 2 Ω 4 freq temp rel trig info local exit enter range range err rem talk lstn srq rear rel filt math 4w auto arm trig smpl ! F r 500v peak front/rear 2a 250v amps cal store recall chan scan filter math config menu hi input lo sense Ω 4 wire in...
Page 12
4 handle (not shown) pull out and rotate to desired position 5 display keys prev/next scroll through multiple displays of a function 6 operation keys rel enables/disables relative reading trig triggers unit store enables data storage recall displays reading data (reading, number, time). Use prev/nex...
Page 13
Warning: no internal operator servicable parts,service by qualified personnel only. Warning: no internal operator servicable parts,service by qualified personnel only. Caution: for continued protection against fire hazard,replace fuse with same type and rating. Caution: for continued protection agai...
Page 14
1 input connections input hi and lo used for dc volts, ac volts, and 2-wire resistance measure- ments amps used with input lo to make dc current and ac current measurements sense Ω 4 wire hi and lo used with input hi and lo to make 4-wire resistance measurements 2 fan keep filter clean to ensure pro...
Page 15: Display
Display as shown in the model 2002 front panel overview (figure 2), the front panel has three lines of display information: the primary display line, the secondary display line, and annunciators. • primary display line: the top line displays readings along with units. It can also display measurement...
Page 16: Bench Defaults
Bench defaults the model 2002 can save one, v e, or ten user setups in non-volatile memory, depending on the installed memory option. You can select one of the user setups as the power-on default, or have the instrument power up to either of the two factory defaults (optimized for “bench” or “gpib” ...
Page 17: Voltage Measurements
Voltage measurements assuming “bench” reset conditions, the basic procedure is as follows: 1. Connect test leads to the input hi and lo terminals. Either the front or rear inputs can be used; place the inputs button in the appropriate position. 2. Select the measurement function by pressing dcv or a...
Page 18: Current Measurements
Current measurements assuming “bench” reset conditions, the basic procedure is as follows: 1. Connect test leads to the amps and input lo terminals. Either the front or rear inputs can be used; place the inputs button in the appropriate position. 2. Select the measurement function by pressing dci or...
Page 19
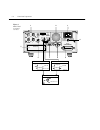
Two and four-wire resistance measurements assuming “bench” reset conditions, the basic procedure is as follows: 1. Connect test leads to the model 2002 as follows: a. For 2-wire, connect the test leads to input hi and lo. B. For 4-wire, connect the test leads to input hi and lo, and sense Ω 4 wire h...
Page 20
2001 multimeter 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 edit err rem talk lstn srq rear rel filt math 4w auto arm trig smpl model 2002 resistance under test shielded cable optional shield note: source current flows from the input hi to input lo terminals. Figure 6 two and four- wire resistance mea...
Page 21: Frequency Measurements
Frequency measurements the model 2002 can make frequency measurements from 1hz to 15mhz through its input hi and input lo terminals, and from 1hz to 1mhz through its amps and input lo termi- nals. Assuming “bench” reset conditions, the basic procedure is as follows: 1. Connect test leads to the inpu...
Page 22
Trigger level an appropriate trigger level is needed for the frequency counter to operate properly. The in- strument only counts cycles with peak amplitudes that reach the trigger level. For example, if the trigger level is set for 5v, cycles with peak amplitudes less than 5v are not counted. Use th...
Page 23: Temperature Measurements
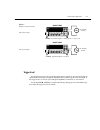
Temperature measurements the model 2002 measures temperature with two different sensor types: rtds and thermo- couples. With rtds, the model 2002 can measure temperature between -200 ° c and +630 ° c. Rtds can be connected to the input terminals or the optional model 2001-scan scanner card. With the...
Page 24
Figure 8 four-wire rtd temperature measurements connections to banana jacks connections to circular jack connections to terminal block 2001 multimeter 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 edit err rem talk lstn srq rear rel filt math 4w auto arm trig smpl model 2002 sense Ω 4-wire hi platinum r...
Page 25
1-18 front panel operation.
Page 26
2 measurement options.
Page 27: Multiple Displays
This section describes the details of making measurements. Configuration options, triggers, reading storage, and scanning are just a few of the topics discussed. You will find this informa- tion useful whether operating the model 2002 from the front panel or ieee-488 bus. Multiple displays each meas...
Page 28
Table 1 multiple displays by function function next display all dc voltage ac voltage dc current ac current 2-wire resistance 4-wire resistance frequency temperature data storage buffer bar graph zero-centered bar graph maximum and minimum values relative and actual values calculated and actual valu...
Page 29
Bar graph — the bar graph is a graphical represen- tation of the reading with zero at the left end. Each full segment of the bar represents approximately 4% of the range limit. 2002 multimeter filt 4w arm zero-centered bar graph — the zero-centered bar graph is a graphical representation of the read...
Page 30
Calculated and actual — this display is used with a math calculation. While the top line provides the re- sult of the math calculation, the bottom line provides the raw reading. 2002 multimeter buffer — these bottom line displays are used when recalling readings from the data store buffer. They pro-...
Page 31: Menus
Menus there are two basic menu structures used by the model 2002: the main menu and the con- figure menus. The main menu accesses items for which there are no dedicated keys; the con- figure menus configure measurement functions and other instrument operations. Table 2 summarizes main menu selection...
Page 32
Table 3 configuration settings for each measurement function function speed filter reso- lution coupling max. Signal level units (v, db, dbm) ac type offset comp. Max. Auto range senso r dc voltage ac voltage 2-wire resistance 4-wire resistance dc current ac current frequency/period temperature • • ...
Page 33
Navigating menus use the following rules to navigate through the menu structures. Table 5 summarizes the front panel keys used for navigation. 1. From the instrument’s normal state of displaying readings, you can: • view a configuration menu by pressing config and then the desired function or op- er...
Page 34
Table 5 menu summary action description config-(function) menu or range ▲ range ▼ enter exit info press the config key, then a function key (e.G., dcv) to view the top level of a function configuration menu. Press the menu key to view the top level of the main menu. The operations that have no corre...
Page 35: Relative
Relative rel subtracts a reference value from actual readings. When rel is enabled, the instrument uses the present reading as a relative value. Subsequent readings will be the difference between the actual input value and the rel value. Actual input – reference = displayed reading thus, when you pe...
Page 36: Trigger
Trigger the following overview is intended to acquaint you with basic triggering. For a complete ex- planation, see the model 2002 user’s manual. The simplified model for triggering is shown in figure 9. It is known as the trigger model. Idle the instrument is in idle whenever it is not within one o...
Page 37
Trigger model layers the trigger model has three layers: the arm layer, scan layer and measure layer. For ieee- 488 bus operation, these layers are known as arm layer 1, arm layer 2 and the trigger layer. Once the model 2002 is taken out of idle, operation proceeds through the layers of the trigger ...
Page 38
Device action the primary device action is a measurement. However, the device action could include a function change and a channel scan (if scanner is enabled). A channel is scanned (closed) before a measurement is made. When scanning internal channels, the previous channel opens and the next channe...
Page 39: Speed
Speed speed sets the integration time of the a/d converter, the period of time the input signal is measured. The speed can be set for each measurement function except freq. The integration time is specified in parameters based on a number of power line cycles (nplc), where one plc for 60hz is 16.67m...
Page 40: Resolution
Resolution except for freq, temp and some special cases for acv, all functions can operate from 3.5 to 8.5 digits of resolution. Each function can have its own unique resolution setting. Configure resolution perform the following steps to set resolution for a measurement function: 1. Press the confi...
Page 41: Filter
Filter filtering stabilizes noisy measurements. The model 2002 uses a digital filter, which is based on reading conversions. The displayed, stored, or transmitted reading is an average of a number of reading conversions. When a filter is enabled by pressing filter (filt annunciator turns on), the se...
Page 42
Configuring filters each measurement function, except freq, has its own filter configuration. The procedure to configure a filter is summarized as follows: 1. Select the measurement function. 2. Press config and then filter to display the following filter menu options: auto: selects auto filtering. ...
Page 43: Buffer (Data Store)
Buffer (data store) the model 2002 has a buffer to store readings at two different rates: normal and burst modes. The maximum number of readings that can be stored depends on the installed memory option (standard, mem1 or mem2) and the user-programmable data group (full or compact). Storage capacity...
Page 44
4. Press enter to start storing readings. The asterisk (*) annunciator turns on to indicate a data storage operation. 5. To recall stored readings, press recall. Use the range keys to scroll through the buffer. Burst mode the burst data acquisition mode maximizes the reading rate of the model 2002. ...
Page 45: Math
Math the math key lets you perform math operations on single readings and display the result. The three math calculations that are configured from the configure math menu structure are: polynomial: where: x is the normal display reading a2, a1, and a0 are user entered constants y is the displayed re...
Page 46
Enabling math the selected math calculation is enabled by simply pressing the math key. When enabled, the math annunciator turns on and the calculation type (none, poly, %, or % dev) is dis- played. Also, one of the following messages is briefly displayed: math enabled display = none (reading) math ...
Page 47: Internal Scanning
Internal scanning the model 2002 can be used with a scanner card (such as the model 2001-scan or 2001- tcscan) installed in the option slot of the instrument. This section provides basic information for scanning internal channels. If the scanner card is not already installed, refer to the scanner ca...
Page 48
Configure internal channels a unique measurement function can be assigned to each of the internal scanner card channels. For example, dcv can be assigned to channels 1 and 2, and Ω 2 can be assigned to channels 3 and 4. Also, scanner card channels can be skipped during the scan by designating them a...
Page 49
Close/open channels the chan key is used to close an internal channel or channel pair (for 4-wire functions), or open any internal closed channel or channel pair. Perform the following steps to close or open channels: 1. Press chan to display the following channel selection options: close-channel: u...
Page 50
Ratio and delta calculations with ratio or delta selected from the scan operation menu, the model 2002 can measure two specified internal scanner channels (reference channel and measure channel) and then compute the ratio or difference (delta) between them. Valid measurement functions for ratio and ...
Page 51: External Scanning
External scanning the model 2002 can be used with a scanner card (such as the model 7011 multiplexer card) installed in an external scanning mainframe (model 7001 or 7002 switch system). With the use of external triggering, the model 2002 can measure and store each scanned channel. Note for complete...
Page 52
Configure external channels a unique measurement function can be assigned to each of the external scanner card chan- nels. For example, dcv can be assigned to channels 1 and 2, and Ω 2 can be assigned to channels 3 and 4. Also, scanner card channels can be skipped during the scan by designating them...
Page 53
E. Use the exit key to back out of the menu structure. Configure scan perform the following steps to configure the model 2002 for an external scan: 1. Press config and then scan to display the scan operation menu options. 2. Use the cursor keys ( and ) to select external and press enter. Perform the...
Page 54
6. Switch system – set channel spacing as follows. Note that the message on the model 2002 tells you which channel spacing option to select. • select channel-spacing • select triglink or external use the exit key to back out of the menu structure. 7. Model 2002 – press enter. The display will prompt...
Page 55
3 ieee-488 bus operation.
Page 56: Software Support
Software support several support alternatives are available for the model 2002. Contact your local keithley representative for more detailed information. Keithley software subroutines in basic, c, and pascal to help users develop software faster, microsoft quickbasic, microsoft basic, microsoft quic...
Page 57: Ieee-488 Bus Standards
Ieee-488 bus standards for remote operation, the model 2002 uses the ieee-488 bus for communication between in- strumentation and the controller (computer). The ieee-488 bus is also known as the gpib (gen- eral purpose interface bus). In addition to conforming to the ieee-488-1978 and ieee-488.1-198...
Page 58: Primary Address Selection
Primary address selection the model 2002 is shipped from the factory with a programmed primary address of 16. The address is displayed on power-up. Programming examples in this manual assume a primary ad- dress of 16. Perform the following steps to check and/or change the primary address: 1. Press m...
Page 59: Common Commands
Common commands common commands are common to all ieee-488 devices on the bus. The following infor- mation summarizes the common commands that are used most often. For complete details, refer to section 3 in the user’s manual. *cls (clear status) clears all event registers and error queue. After cle...
Page 60: Scpi Commands
Scpi commands in the model 2002 multimeter, you are given access to control settings that are hidden on oth- er instruments. The increased capability does, however, produce increased complexity. To ac- commodate this, the multimeter incorporates the standard commands for programmable instruments (sc...
Page 61: Scpi Command Syntax
Scpi command syntax tree structure scpi commands are organized in a tree structure, similar to disk directories in computer op- erating systems. Each subdirectory is called a subsystem. For example, part of the sense1 sub- system is listed below and shown in figure 16. [sense[1]] :data? :function ""...
Page 62
A command summary table is a way of documenting scpi commands, but it does not show complete command names. A complete command is formed by joining the components. For ex- ample, the complete :state command in the example is: sense1:voltage:dc:reference:state note that square brackets are not part o...
Page 63
Query commands with few exceptions, every scpi command has a corresponding query. A command sets a control point in the instrument; a query determines the present setting of the control point. The query is simply the command name with a "?" attached. Some commands are actions rather than control poi...
Page 64
Command syntax notice in the preceding examples that there is no colon character at the beginning of the com- mands. A leading colon instructs the model 2002 to interpret the command starting at the root (highest level) of the command tree. Since the model 2002 also starts at the root each time you ...
Page 65
Scpi signal oriented commands signal oriented commands are used to acquire readings using a set of high-level instructions to control the measurement process. The two most commonly used commands are :fetch? And :measure? . Details on all signal oriented commands are covered in section 3 in the user’...
Page 66: Scpi Subsystem Commands
Scpi subsystem commands detailed information an all scpi commands are covered in the user’s manual. In this section, only the command used for basic operation are summarized. Defaults :system system subsystem :preset set the 2002 to the system present defaults. Some of the selected defaults include:...
Page 67
:voltage:dc path to configure dcv: :nplc set speed: 0.01 to 10 plc. :auto enable or disable auto nplc. :range path to configure measurement range: [:upper] specify expected reading to select range. :auto enable or disable auto range. :reference specify reference (rel): -1100 to +1100. :state enable ...
Page 68
:frequency path to configure freq: :coupling specify input coupling: ac or dc . :reference specify reference (rel): 0 to 15e6. :state enable or disable reference (rel). :acquire use input signal as reference (rel). :digits specify measurement resolution: 4 or 5. :source select source: current or vol...
Page 69
Measurement units (acv and temp) :unit unit subsystem :temperature select units for temp: c , f , or k . :voltage path to configure units for acv: :ac select units for acv: v , db , or dbm . :db path to set db reference voltage: :reference specify reference (volts): 0.001 to 750. :dbm path to set db...
Page 70
Trigger model performing a system preset (:system:preset) configures the trigger model for typical in- strument operation. After a system preset, many advanced operations can be accomplished using the initiate commands, :abort, and the trigger (measure) layer commands. All of the following commands ...
Page 71
Status register the status register structure of the model 2002 lets you monitor and act upon numerous events that occur. Many programming decisions can be made by monitoring the measurement event register and the operation event register. See the user’s manual for details of the status registers. :...
Page 72: Program Examples
Program examples all examples presume quickbasic version 4.5 or higher and a cec ieee-488 interface card with cec driver version 2.11 or higher, with the model 2002 at address 16 on the ieee- 488 bus. Changing function and range the model 2002 has independent controls for each of its measurement fun...
Page 73
'example program to demonstrate changing function and range, 'taking readings on various functions 'for quickbasic 4.5 and cec pc488 interface card 'edit the following line to where the quickbasic 'libraries are on your computer '$include: 'c:\qb45\ieeeqb.Bi' 'initialize the cec interface as address...
Page 74
One-shot triggering our older dmms generally have two types of triggering: one-shot and continuous. In one- shot, each activation of the selected trigger source causes one reading. In continuous, the dmm is idle until the trigger source is activated, at which time it begins taking readings at a spec...
Page 75
Continuous triggering #1 the following example program sets up the model 2002 to take readings as fast as it can once it receives an external trigger. The actual reading rate will depend upon other factors, such as a/d integration time, autozero mode, autorange on/off, etc. 'example program to demon...
Page 76
Continuous triggering #2 the following example program sets up the model 2002 to take readings continuously after an external trigger is received. The trigger rate is set to one reading every 50ms. 'example program to demonstrate continuous triggering 'at a specified rate 'for quickbasic 4.5 and cec...
Page 77
Generating srq on buffer full when your program must wait until the model 2002 has completed an operation, it is more efficient to program the 2002 to assert the ieee-488 srq line when it is finished, rather than repeatedly serial polling the instrument. An ieee-488 controller will typically address...
Page 78
Storing readings in buffer the reading buffer in the model 2002 is flexible and capable. It has four controls, which are found in the trace susbsystem. There are commands to control: • the size of the buffer (in readings). Trace:points • whether or not extra data is stored with each reading (e.G., c...
Page 79
'example program to demonstrate the reading buffer 'for quickbasic 4.5 and cec pc488 interface card 'edit the following line to where the quickbasic 'libraries are on your computer '$include: 'c:\qb45\ieeeqb.Bi' 'initialize the cec interface as address 21 call initialize(21, 0) 'reset controls in in...
Page 80
Taking readings with the scanner card the model 2001-scan is an optional 10-channel scanner card for the model 2002 multim- eter. Only one channel can be closed at a time. If you close a channel while another is already closed, the first one opens with break-before-make operation. You can use the sc...
Page 81
'example program to demonstrate taking readings on different 'scanner channels 'for quickbasic 4.5 and cec pc488 interface card 'edit the following line to where the quickbasic 'libraries are on your computer '$include: 'c:\qb45\ieeeqb.Bi' 'initialize the cec interface as address 21 call initialize(...
Page 82
The following example program sets up the model 2002 using a scan list to measure dc volt- age on channel 1, ac voltage on channel 2, and 2-wire resistance on channel 3. The meter takes ten sets of readings, with each set spaced 15 seconds apart, and each of the three readings in each group taken as...
Page 83
'*rst sets trig:sour to imm call send(16, "trig:coun 3", status%) call send(16, "arm:lay2:sour tim;tim 15", status%) call send(16, "arm:lay2:coun 10", status%) 'trace subsystem is not affected by *rst call send(16, "trac:poin 30;egr full", status%) call send(16, "trac:feed sens1;feed:coun next", sta...
Page 84
4 specs and accessories.
Page 85: Specifications
Specifications the following pages contain the condensed specifications for the 2002. Every effort has been made to make these specifications complete by characterizing its performance under the variety of conditions often encountered in production, engineering, and research. The 2002 provides trans...
Page 86
Dc volts dcv input characteristics and accuracy enhanced accuracy 1 - 10plc, dfilt 10 relative accuracy temp. Full reso- input ±(ppm of reading + ppm of range) coeffi- range scale lution resistance transfer 5 24 hours 2 90 days 3 1 year 3 2 years 3 cient* 200 mv 4 ±210.000000 1 nv >100 g Ω 0.4 + 1.5...
Page 87
Ohms enhanced accuracy 1 - 10plc, offset comp. On, dfilt 10 temperature coefficient relative accuracy ± (ppm of reading + ± (ppm of reading + ppm of range) ppm of range) / °c range transfer 5 24 hours 3 90 days 4 1 year 4 2 years 4 outside t cal ±5°c 20 Ω 2.5 + 3 5 + 4.5 15 + 6 17 + 6 20 + 6 2.5 + 0...
Page 88
Dc current uncertainty = ± [ (ppm reading) × (measured value) + (ppm of range) × (range used) ] / 1,000,000. % accuracy = (ppm accuracy) / 10,000. 5ppm of range = 10 counts at 6 ½ digits. Dc in-circuit current the dc in-circuit current measurement function allows a user to measure the current throug...
Page 89
Temperature (rtd) reso- 4-wire accuracy 3 range lution 24 hours 1 90 days 2 1 year 2 2 years 2 –100° to +100°c 0.001°c ±0.016°c ±0.020°c ±0.021°c ±0.022°c –200° to +630°c 0.001°c ±0.061°c ±0.066°c ±0.068°c ±0.070°c –148° to +212°f 0.001°f ±0.029°f ±0.036°f ±0.038°f ±0.040°f –328° to +1166°f 0.001°f ...
Page 90
General specifications and standards compliance power voltage: 90–134v and 180–250v, universal self-selecting. Frequency: 50hz, 60hz, or 400hz, self-identifying at power-up. Consumption: environmental operating temperature: 0°c to 50°c. Storage temperature: –40°c to 70°c. Humidity: 80% r.H., 0°c to ...
Page 91: Accessories Available
Accessories available rack kits 4288-1 single fixed rack mount kit: allows mounting on the right or left of a standard rack opening, 4288-2 side-by-side rack mount kit: allows two of the following instruments to be mounted side-by-side: 2001, 2002, 182, 428, 486, 487, 7001. 4288-3 side-by-side rack ...
Page 92
Additional cables 8530 gpib to printer cable, 2m (6.6 ft) 7007-1 shielded gpib cable, 1m (3.3 ft) 7007-2 shielded gpib cable, 2m (6.6 ft) 7051-2 bnc trigger interconnect cable, 0.6m (2 ft) 7051-5 bnc trigger interconnect cable, 1.5m (5 ft) 7051-10 bnc trigger interconnect cable, 3m (10 ft) service p...
Page 93: Index
Index a accessories 4-8 accuracy 4-2 amps fuse 1-7 annunciators 1-4 auto filter 2-16 b bench default 1-9, 2-13 buffer 3-23, 3-24 buffer (data store) 2-18 burst mode 2-19 c cables 4-9 channels 2-23, 2-24, 2-27, 3-15, 3-26, 3-28 command syntax 3-10 common commands 3-5 configuration settings 2-7 config...
Page 94
S scpi signal oriented commands 3-11 scpi subsystem commands 3-12 sense1 3-7 shielding 1-12 short form 3-8 software support 3-2 specifications 4-2 speed 2-14 srq 3-23 status register 3-17 t temperature measurements 1-16 thermocouples 1-16 trigger 2-11 trigger level 1-15 trigger link 1-7, 4-8 trigger...
Page 95
Specifications are subject to change without notice. All keithley trademarks and trade names are the property of keithley instruments, inc. All other trademarks and trade names are the property of their respective companies. Keithley instruments, inc. 28775 aurora road • cleveland, ohio 44139 • 440-...