- DL manuals
- Keithley
- Measuring Instruments
- 2182
- Service Manual
Keithley 2182 Service Manual
www.keithley.com
Model 2182/2182A Nanovoltmeter
2182A-902-01 Rev. A / July 2004
A G R E A T E R M E A S U R E O F C O N F I D E N C E
Summary of 2182
Page 1
Www.Keithley.Com model 2182/2182a nanovoltmeter service manual 2182a-902-01 rev. A / july 2004 a g r e a t e r m e a s u r e o f c o n f i d e n c e.
Page 2: Warranty
Warranty keithley instruments, inc. Warrants this product to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of one (1) year from date of shipment. Keithley instruments, inc. Warrants the following items for 90 days from the date of shipment: probes, cables, software, rechargeable batt...
Page 3
Model 2182/2182a nanovoltmeter service manual ©2004, keithley instruments, inc. All rights reserved. Cleveland, ohio, u.S.A. First printing, july 2004 document number: 2182a-902-01 rev. A this service manual supports both the models 2182 and2182a. References to the model 2182 also apply to the model...
Page 4: Manual Print History
Manual print history the print history shown below lists the printing dates of all revisions and addenda created for this manual. The revision level letter increases alphabetically as the manual undergoes sub- sequent updates. Addenda, which are released between revisions, contain important change i...
Page 5: Safety Precautions
Safety precautions 11/07 the following safety precautions should be observed before using this product and any associated instrumentation. Although some instruments and accessories would normally be used with non-hazardous voltages, there are situations where hazardous conditions may be present. Thi...
Page 6
For maximum safety, do not touch the product, test cables, or any other instruments while power is applied to the circuit under test. Always remove power from the entire test system and discharge any capacitors before: connecting or disconnecting cables or jumpers, installing or removing switching c...
Page 7: Table of Contents
Table of contents 1 performance verification introduction ................................................................................ 1-2 verification test requirements .................................................... 1-2 environmental conditions ...............................................
Page 8: Troubleshooting
4 troubleshooting introduction ................................................................................ 4-2 repair considerations ................................................................. 4-2 power-on self-test ....................................................................... 4...
Page 9: Replaceable Parts
6 replaceable parts introduction ................................................................................ 6-2 parts lists .................................................................................... 6-2 ordering information ...............................................................
Page 11: List of Illustrations
List of illustrations 1 performance verification figure 1-1 connections for 100mv-100v range accuracy ..................... 1-6 figure 1-2 connections for 10mv range accuracy .................................. 1-7 figure 1-3 connections for temperature accuracy verification .............. 1-9 figure...
Page 12: List of Tables
List of tables 1 performance verification table 1-1 recommended verification equipment .................................. 1-3 table 1-2 input cable color codes .......................................................... 1-6 table 1-3 dc voltage measurement accuracy limits ...............................
Page 13: Replaceable Parts
6 replaceable parts table 6-1 motherboard parts list ............................................................ 6-3 table 6-2 motherboard parts list (continued) ......................................... 6-4 table 6-3 motherboard parts list (continued) ......................................... 6-6 ...
Page 14: Performance
1 performance verification performance verification.
Page 15: Introduction
Introduction use the procedures in this section to verify that model 2182 accuracy is within the limits stated in the instrument’s one-year accuracy specifications. You can perform these verification procedures: • when you first receive the instrument to make sure that it was not damaged during ship...
Page 16: Warm-Up Period
Warm-up period allow the model 2182 to warm up for at least 2-1/2 hours before conducting the verification procedures. If the instrument has been subjected to temperature extremes (those outside the ranges stated above), allow additional time for the instrument’s internal temperature to stabilize. T...
Page 17: Verification Reading Limits
Verification reading limits the verification limits stated in this section have been calculated using only the model 2182 one-year accuracy specifications, and they do not include test equipment uncertainty. If a particular measurement falls outside the allowable range, recalculate new limits based ...
Page 18: Test Summary
4. Using either range key, select full, then press enter. The unit will then remind you to disconnect the input cable: remove input 5. Make sure the input cable is disconnected, then press enter. The unit will then perform auto-calibration, a process that will take several minutes to complete. Durin...
Page 19: Verification Procedures
Warning the maximum voltage between any terminals to chassis ground is 350v peak. Exceeding this value may cause a breakdown in insulation, creating a shock hazard. Caution the maximum voltage between channel 1 hi and lo is 120v. The maximum voltage between channel 2 hi and lo is 12v. Exceeding thes...
Page 20
2. Turn on the power, and allow a 2-1/2 hour warm-up period. 3. Restore factory defaults, and do a full auto-calibration, as previously described. 4. Select the model 2182 dcv1 measurement function, and select the 100mv range. 5. Set the calibrator output to 0.00000mv, and allow the reading to settl...
Page 21
7. Set the dc calibrator output voltage to 1.000000v. 8. Verify voltage reading accuracy for the 10mv range listed in table 1-3 . 9. Repeat steps 7 and 8 for a negative 10mv source voltage by setting the calibrator voltage to –1.00000v. Temperature measurement accuracy follow the steps below to veri...
Page 22
Figure 1-3 connections for temperature accuracy verification 2. Turn on the power, and allow a 2-1/2 hour warm-up period. 3. Press shift then tcoupl, then use the range and left and right arrow keys to select the following: • units: c • junc: sim, set to 0°c • type: j • sens: tcouple 4. Select the m...
Page 23: Analog Output Accuracy
5. Verify temperature measurement accuracy for each of the temperature settings listed in table 1-4 . For each measurement: • set the model 2182 for the appropriate thermocouple type. • set the temperature calibrator to the correct thermocouple type and temperature setting. • verify that the model 2...
Page 24
Figure 1-4 connections for analog output accuracy 2. Select the model 2182 dcv1 measurement function, and choose the 10v range. 3. Press shift then aout, then use the range and left and right arrow keys to set the following: • state: on • m: +1.0000000 • b: +00.000000 4. Set the calibrator voltage t...
Page 25
1-12 performance verification.
Page 26: Calibration
2 calibration calibration.
Page 27: Introduction
Introduction use the procedures in this section to calibrate the model 2182. These procedures require accurate test equipment to supply precise dc voltages. Calibration can be performed either from the front panel, or by sending scpi calibration commands over the ieee-488 bus or rs-232 port with the...
Page 28: Calibration Considerations
Calibration considerations when performing the calibration procedures: • make sure that the test equipment is properly warmed up and connected to the appropriate model 2182 jack. • always allow the source signal to settle before calibrating each point. • use only copper-to-copper connections to mini...
Page 29
Calibration dates choose the dates selection in the calibration menu to display the date the model 2182 was calibrated and the date calibration is due. The unit will display these dates as in the examples below: date:12/07/97 ndue:12/08/98 calibration count choose the count selection in the calibrat...
Page 30: Calibration Errors
5. Use the up and down range keys to toggle between y (yes) and n (no). Choose n if you do not want to change the code. Choose y if you want to change the code. The unit then prompts you to enter a new code. Enter the code, and press enter. Remote code to unlock calibration via remote, send the foll...
Page 31: Aborting Calibration
Aborting calibration you can abort the front panel calibration process at any time by pressing exit. The instrument will then ask you to confirm your decision to abort with the following message: abort cal? Press exit to abort calibration at this point, or press any other key to return to the calibr...
Page 32
Preparing the model 2182 for calibration 1. Turn on the model 2182, and allow it to warm up for at least 2-1/2 hours before performing the calibration procedure. 2. Start the calibration process as follows: a. Access the calibration menu by pressing shift then cal. B. Use the up and down range keys ...
Page 33
4. When the unit is done calibrating, it will display the following prompt: remove input 5. Remove the low-thermal short, and press enter. During this phase, the calibrating message will be displayed. Dc volts calibration 1. After the front panel short and open procedure, the unit will prompt you fo...
Page 34
3. Set the calibrator to output dc volts, and turn external sense off. 4. Perform the steps listed in table 2-4 to complete dc volts calibration. For each calibration step: • set the calibrator to the indicated value, and make sure it is in operate. • wait for the signal voltage to settle. • press t...
Page 35: Remote Calibration
Remote calibration follow the steps in this section to perform calibration via remote. See appendix b for a detailed list and description of scpi calibration commands. When sending calibration commands, be sure that the model 2182 completes each step before sending the next command. You can do so ei...
Page 36
Note keep drafts away from low-thermal connections to avoid thermal drift, which could affect calibration accuracy. 2. Send the following command: :cal:prot:dc:step1 3. After the model 2182 completes this step, remove the low-thermal short, and send this command: :cal:prot:dc:step2 dc volts calibrat...
Page 37: Factory Calibration
Saving calibration constants after completing the calibration procedure, send the following command to save the new calibration constants: :cal:prot:save note calibration constants will not be saved unless the :save command is sent. Calibration constants can be returned using the :cal:prot:data? Com...
Page 38: Remote Factory Calibration
Remote factory calibration follow the steps in this section to perform factory calibration via remote. See appendix b for a detailed list and description of scpi calibration commands. When sending calibration commands, be sure that the model 2182 completes each step before sending the next command. ...
Page 39
Precalibration 1. Connect the calibrator to channel 1 of the model 2182 input jack using the low- thermal cable, as shown in figure 2-3 . Wait two minutes to allow for thermal equilibrium before proceeding. (see table 2-3 for model 2107 cable connections.) 2. Set the calibrator to output dc volts, a...
Page 40
Short and open calibration 1. Connect the model 2188 low-thermal shorting plug to the instrument input jack, as shown in figure 2-4 . Wait at least three minutes before proceeding to allow for thermal equilibrium. 2. Send the following command: :cal:prot:dc:step1 3. After the model 2182 completes th...
Page 41
Analog output calibration 1. Connect the model 2182 analog output to channel 1 of the front panel input jack, as shown in figure 2-5 . 2. Send the following command to calibrate the analog output: :cal:prot:dc:step5 figure 2-5 connections for analog output calibration programming calibration dates p...
Page 42
Saving calibration constants after completing the calibration procedure, send the following command to save the new calibration constants: :cal:prot:save note calibration constants will not be saved unless the :save command is sent. Calibration constants can be returned using the :cal:prot:data? Com...
Page 43
2-18 calibration.
Page 44: Routine Main-
3 routine maintenance routine main- tenance.
Page 45: Introduction
Introduction the information in this section deals with routine type maintenance that can be performed by the operator. Line fuse replacement warning disconnect the line cord at the rear panel, and remove all test leads and cables connected to the instrument (front and rear) before replacing the lin...
Page 46: Line Voltage Selection
Perform the following steps to replace the line fuse: 1. Carefully pry the locking tab that secures the fuse carrier to the power module. 2. Pull out the fuse carrier, and replace the fuse with the type specified in table 3-1 . Caution to prevent instrument damage, use only the fuse type specified i...
Page 47
3-4 routine maintenance.
Page 48: Troubleshoot-
4 troubleshooting troubleshoot- ing.
Page 49: Introduction
4-2 troubleshooting introduction this section of the manual will assist you in troubleshooting and repairing the model 2182. Included are self-tests, test procedures, troubleshooting tables, and circuit descriptions. Note that disassembly instructions are located in section 5 , while component layou...
Page 50: Power-On Self-Test
Troubleshooting 4-3 power-on self-test during the power-on sequence, the model 2182 will perform a checksum test on its eprom and test its ram. If one of these tests fails, the instrument will lock up. Front panel tests there are two front panel tests: one to test the functionality of the front pane...
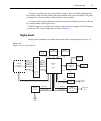
Page 51: Principles of Operation
4-4 troubleshooting principles of operation the following information is provided to support the troubleshooting tests and procedures covered in this section of the manual. Refer to the following block diagrams: figure 4-1 — power supply block diagram figure 4-2 — digital circuitry block diagram fig...
Page 52: Display Board
Troubleshooting 4-5 ac power is applied to the ac power module receptacle. Power is routed through the line fuse and line voltage selection switch of the power module to the power transformer. The power transformer has several secondary windings for the various supplies. Ac voltage for the display f...
Page 53: Digital Circuitry
4-6 troubleshooting microcontroller u401 is the display board microcontroller that controls the display and interprets key data. The microcontroller uses three internal peripheral i/o ports for the various control and read functions. Display data is serially transmitted to the microcontroller from t...
Page 54: Analog Circuitry
Troubleshooting 4-7 memory circuits roms u102 and u103 store the firmware code for instrument operation. U103 stores the d0-d7 bits of each data word, and u103 stores the d8-d15 bits. Rams u104 and u105 provide temporary operating storage. U104 stores the d0-d7 bits of each data word, and u105 store...
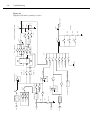
Page 55
4-8 troubleshooting figure 4-3 simplified schematic of analog circuitry protection ch2_hi ch 2 q671 + - bootstrap amp u638 acal u643 7v_ref 1v_ref 0.1v_ref lo q663 pa th a q61 1, 612 q613, 614 pa th b +v -v q624 flip_upper_b u61 1 flip_upper_a q622(p a th a) q623(p a th b) protection q627, 630 + - u...
Page 56
Troubleshooting 4-9 input signal conditioning protection circuits the ch1 hi, ch2 hi, and ch2 lo inputs have protection circuits designed to prevent circuit damage from over-voltage signal conditions. Q666 and q667 provide protection for ch1 hi, while q661 and q662 provide similar protection for ch2...
Page 57: Troubleshooting
4-10 troubleshooting circuit gain table 4-1 summarizes the circuit gain factors for the various ranges. Troubleshooting troubleshooting information for the various circuits is summarized below. Use the “principles of operation” on page 4-4 and the component layouts at the end of section 6 as aids in...
Page 58: Power Supply Checks
Troubleshooting 4-11 power supply checks power supply problems can be checked out using table 4-3 . Table 4-3 power supply checks step item/component required condition remarks 1 line fuse check continuity. Remove to check. 2 line voltage 120v/240v as required. Check power module position. 3 line po...
Page 59: Digital Circuit Checks
4-12 troubleshooting digital circuit checks digital circuit problems can be checked out using table 4-4 . Table 4-4 digital circuit checks step item/component required condition remarks 1 power-on test ram ok, rom ok. Verify that ram and rom are functional. 2 tp301 digital common. All signals refere...
Page 60: Analog Circuit Checks
Troubleshooting 4-13 analog circuit checks table 4-5 summarizes checks for the analog circuits. These tests involve applying specific test voltages to the channel 1 input terminals and measuring voltages at the indicated test points. See figure 1-1 in section 1 for dc voltage input test connection. ...
Page 61
4-14 troubleshooting analog signal switching states table 4-6 and table 4-7 provide switching states of the various ics and transistors for the basic measurement functions and ranges. These tables can be used to assist in tracing an analog signal from the channel 1 and channel 2 inputs to the a/d mu...
Page 62
Troubleshooting 4-15 table 4-7 input protection and low-noise preamplifier analog switching states function and range q666 q667 q664 q665 q672 q673 q674 u645 pin 1, 16 u645 pin 8 u645 pin 9 dcv1: 10mv on on on on off off off on off off 100mv on on on on off off off off off on 1v on on on on off off ...
Page 63: No Comm Link Error
4-16 troubleshooting no comm link error a “no comm link” error indicates that the front panel processor has stopped communicating with the main processor, which is located on the motherboard. This error indicates that one of the main processor roms may require re-seating in its socket. Roms may be r...
Page 64: Disassembly
5 disassembly disassembly.
Page 65: Introduction
Introduction this section explains how to handle, clean, and disassemble the model 2182. Disassembly drawings are located at the end of this section. Handling and cleaning to avoid contaminating pc board traces with body oil or other foreign matter, avoid touching the pc board traces while you are r...
Page 66: Static Sensitive Devices
Static sensitive devices cmos devices operate at very high impedance levels. Therefore, any static that builds up on you or your clothing may be sufficient to destroy these devices if they are not handled properly. Use the following precautions to avoid damaging them: caution many cmos devices are i...
Page 67: Disassembly
Disassembly case cover removal follow the steps below to remove the case cover to gain access to internal parts. Warning before removing the case cover, disconnect the line cord and any test cables from the instrument. 1. Remove handle — the handle serves as an adjustable tilt-bail. Adjust its posit...
Page 68: Motherboard Removal
Motherboard removal perform the following steps to remove the motherboard. This procedure assumes that the case cover is already removed. 1. Remove the ieee-488, rs-232 and bnc jack fasteners. The ieee-488 and the rs-232 connectors each have two nuts that secure the connectors to the rear panel, whi...
Page 69
Main cpu firmware replacement changing the firmware may be necessary as upgrades become available. The firmware revision levels for the main and front panel cpus are displayed during the power-on sequence. (the main firmware revision level is displayed on the left; the front panel firmware revision ...
Page 70: Changing Trigger Link Lines
Changing trigger link lines the model 2182 uses two lines of the trigger link rear panel connector as external trigger (ext trig) input and voltmeter complete (vmc) output. At the factory, line 1 is configured as vmc and line 2 as ext trig. Line 1, 3 or 5 of the trigger link can be configured as vmc...
Page 71: Removing Power Components
Removing power components the following procedures to remove the power transformer and/or power module require that the case cover and motherboard be removed, as previously explained. Warning disconnect the line cord and input connector before removing the case cover. Power transformer removal perfo...
Page 72: Instrument Reassembly
Instrument reassembly reassemble the instrument by reversing the previous disassembly procedures. Make sure that all parts are properly seated and secured, and that all connections are properly made. Warning to ensure continued protection against electrical shock, verify that power line ground (gree...
Page 73
5-10 disassembly.
Page 79: Replaceable
6 replaceable parts replaceable parts.
Page 80: Introduction
6-2 replacement parts introduction this section contains replacement parts information and component layout drawings for the model 2182. Parts lists the electrical parts lists for the model 2182 are shown in tables at the end of this section. For part numbers to the various mechanical parts and asse...
Page 81
Replacement parts 6-3 table 6-1 motherboard parts list circuit designation description keithley part no. C101-113,130-132,136-141,150,152,501- 505 cap, .1uf, 10%, 25v, ceramic c-495-.1 c114,c116,c117,c323 cap, .1uf, 10%, 25v, ceramic c-495-.1 c118,134,515,520,751,758,761,763,765 cap, 47p, 5%, 100v, ...
Page 82
6-4 replacement parts table 6-1 motherboard parts list (continued) circuit designation description keithley part no. Cn701 modified potting box 2182-321a cn702 shield cn-68 cn703 shield cn-70 cr101,102,316,317,654 diode, dual switching, bav99l rf-82 cr301-309,311-314 diode, switching, mmsd914t19 rf-...
Page 83
Replacement parts 6-5 circuit designation description keithley part no. Q619,q652 trans, npn pair, lm394 tg-142 q620,q621 trans, n channel jfet, sst4118 tg-347 q624,u651 selected transistor 2010-600a q627,q630 trans,n channel jfet tg-225 q633,q634,q638,q670,q639,q507 trans, n channel jfet, snj132199...
Page 84
6-6 replacement parts table 6-1 motherboard parts list (continued) circuit designation description keithley part no. R501 res, 1.28m, .1%, 1/8w metal film r-176-1.28m r505 res, 5.11k, 1%, 100mw, thick film r-418-5.11k r506,r691 res, 470,5%, 125mw, metal film r-375-470 r508,r625 res, 24.9k, 1%, 100mw...
Page 85
Replacement parts 6-7 table 6-1 motherboard parts list (continued) circuit designation description keithley part no. R670,r673,r687,r688 res, 2.49k, 1%, 125mw, metal film r-391-2.49k r671,672,689,690,694,695 res, 1m, 5%, 125mw, metal film r-375-1m r681 res, 20k,1%,125mw, metal film r-391-20k r692 re...
Page 86
6-8 replacement parts table 6-1 motherboard parts list (continued) circuit designation description keithley part no. U151,u613,u629,u307,u308 ic,op-amp,ad707, ic-712 u301 ic,+5v regulator,500ma,7805 ic-93 u302 ic,pos voltage reg +15v,500ma,78m15 ic-194 u303 ic,neg voltage reg -15v,500ma,79m15 ic-195...
Page 87
Replacement parts 6-9 table 6-1 motherboard parts list (continued) circuit designation description keithley part no. Vr151,152,303,602,608,650,603 diode,zener 5.1v, bzx84c5v1 dz-88 vr301,vr302,vr655,vr656 diode, zener 11v,mmsz11t1 dz-103 vr304 diode zener dz-121 vr601,vr604,vr613,vr614 diode, zener ...
Page 88
6-10 replacement parts table 6-3 connector board parts list circuit designation description keithley part no. Connector cs-236 connector, housing cs-638-3 connector cs-933 c670 cap,.1uf, 20%,50v,ceramic c-418-.1 u644 ic, centigrade temp sensor lm35dm ic-906 table 6-4 mechanical parts list toy. Descr...
Page 92: Specifica-
A specifications specifica- tions.
Page 93: Drn.
Keithley instruments, inc. Cleveland, ohio 44139 drn. Ckd. App. Date date date part number ltr revisions app. Date form 28777a-sbg bruning 40-21 62198-sbg specifications spec-2182a a released 29844 sz 6/11/04 hw 6/11/04 sk 6/11/04 rkn 6/08/04 rev a page 1 of 3 2182a nanovoltmeter specifications volt...
Page 94: Drn.
Keithley instruments, inc. Cleveland, ohio 44139 drn. Ckd. App. Date date date part number ltr revisions app. Date form 28777a-sbg bruning 40-21 62198-sbg specifications ⌠ spec-2182a a released 29844 sz 6/11/04 hw 6/11/04 sk 6/11/04 rkn 6/08/04 rev a page 2 of 3 2182a nanovoltmeter specifications te...
Page 95: Drn.
Keithley instruments, inc. Cleveland, ohio 44139 drn. Ckd. App. Date date date part number ltr revisions app. Date form 28777a-sbg bruning 40-21 62198-sbg specifications ⌠ spec-2182a a released 29844 sz 6/11/04 hw 6/11/04 sk 6/11/04 rkn 6/08/04 rev a page 3 of 3 2182a nanovoltmeter specifications an...
Page 96: Calibration
B calibration reference calibration reference.
Page 97: Introduction
Introduction this appendix contains detailed information on the various model 2182 remote calibration commands, calibration error messages, and methods to detect the end of each calibration step. Section 2 of this manual covers detailed calibration procedures. B-2 calibration reference.
Page 98: Command Summary
Command summary table b-1 summarizes model 2182 calibration commands. These commands are covered in detail in the following paragraphs. Table b-1 remote calibration command summary command description :calibration :protected :code send the code to unlock calibration. Default: 'ki002182'. :initiate r...
Page 99
Default calibration constants and tolerances default calibration constants and tolerances for the model 2182 are listed in table b-2 . The tolerances for user-entered values are expressed as a percentage (10%). For example, for the +10v calibration, the calibration signal can be +9v to +11v. The res...
Page 100
Table b-2 default calibration constants and tolerances cal constant name default cal constant cal constant tolerance typical constants description usr_10vfs usr_m10vfs usr_100vfs aper_corr_1plc aper_corr_5plc c10mvz c1vz c10vz c100vz c10vratz_ch2hi c10vratz c10vratz_low_q c10vfs cm10vfs cfe_b_0_div1...
Page 101: Miscellaneous Commands
Miscellaneous commands miscellaneous commands are those commands that perform such functions as saving calibration constants, locking out calibration, and programming date parameters. :code (:calibration:protected:code) purpose to unlock calibration so that you can perform the calibration procedures...
Page 102: :lock
:lock (:calibration:protected:lock) purpose to lock out calibration. Format :cal:prot:lock query :cal:prot:lock? Response 0 calibration unlocked 1 calibration locked description the :lock command allows you to lock out calibration after completing those procedures. Thus, :lock performs the opposite ...
Page 103: :date
:date (:calibration:protected:date) purpose to program the calibration date. Format :cal:prot:date , , parameters = 1997 to 2096 = 1 to 12 = 1 to 31 query :cal:prot:date? Response , , description the :date command allows you to store the calibration date in instrument eerom for future reference. You...
Page 104: :data?
:data? (:calibration:protected:data?) purpose to request the calibration constants for the active range. Format :cal:prot:data? Response comma-separated ascii floating-point constants description the :cal:prot:data? Query requests the calibration constants for the active range. The returned constant...
Page 105: Precalibration Commands
Precalibration commands :pcal :calibrate:protected:pcal:stepn note precal :step commands are intended to be one-time manufacturing calibration steps, and are only allowed if the step key was held in at power-up. Purpose to perform various precal steps. Format :cal:prot:pcal:stepn parameters see tabl...
Page 106: Detecting Calibration Errors
Detecting calibration errors if an error occurs during any calibration step, the model 2182 will generate an appropriate error message. Several methods to detect calibration errors are discussed below. Reading the error queue as with other model 2182 errors, any calibration errors will be reported i...
Page 107: Generating An Srq On Error
Status byte eav (error available) bit whenever an error is available in the error queue, the eav (error available) bit (bit 2) of the status byte will be set. Use the *stb? Query to obtain the status byte, then test bit 2 to see if it is set. If the eav bit is set, an error has occurred, and you can...
Page 108: Using The *opc Command
Detecting calibration step completion when sending remote calibration commands, you must wait until the instrument completes the current operation before sending another command. You can use either *opc? Or *opc to help determine when each calibration step is completed. Using the *opc command the *o...
Page 109
B-14 calibration reference.
Page 110: Calibration
C calibration program calibration program.
Page 111: Introduction
Introduction this appendix includes a calibration program written in basic to help you to field calibrate the model 2182. Refer to section 2 for more details on calibration procedures, equipment, and connections. Appendix b covers calibration commands in detail. Computer hardware requirements the fo...
Page 112: General Program Instructions
General program instructions 1. With the power off, connect the model 2182 and the calibrator to the ieee-488 interface of the computer. Be sure to use shielded ieee-488 cables for bus connections. 2. Turn on the computer, the model 2182, and the calibrator. Allow the model 2182 and the multimeter t...
Page 113
Case 3 print "connect calibrator to channel 1 input." print "wait 2 minutes." gosub keycheck print #1, "output 4;extsense off" print #1, "output 4;"; msg$ print #1, "output 4;oper" case 4, 5 print #1, "output 4;"; msg$ print #1, "output 4;oper" end select if i > 2 then gosub settle print #1, "output...
Page 114
Errcheck: ' error check routine. Print #1, "output 7;:syst:err?" ' query error queue. Print #1, "enter 7" input #2, e, err$ if e 0 then beep: print err$: goto errcheck ' display error. Return ' settle: ' calibrator settling routine. Do: print #1, "output 4;isr?" ' query status register. Print #1, "e...
Page 115
C-6 calibration program.
Page 116: Index
Index code b-6 count? B-6 date b-8 dc b-9 lock b-7 ndue b-8 pcal b-10 save b-7 a aborting calibration 2-6 analog circuit checks 4-13 analog circuitry 4-7 analog output accuracy 1-10 analog signal switching states 4-14 assembly drawings 5-3 auto-calibration (acal) 1-4 b board installation 5-9 c calib...
Page 117
P parts lists 6-2 performance verification 1-1 performing the verification test procedures 1-5 power module connections 5-9 power module removal 5-8 power supply 4-4 power supply checks 4-11 power transformer removal 5-8 power-on self-test 4-3 precalibration commands b-10 principles of operation 4-4...
Page 118: Service Form
Service form model no. Serial no. Date name and telephone no. Company list all control settings, describe problem and check boxes that apply to problem. ❏ intermittent ❏ analog output follows display ❏ particular range or function bad; specify ❏ ieee failure ❏ obvious problem on power-up ❏ batteries...
Page 120
Specifications are subject to change without notice. All keithley trademarks and trade names are the property of keithley instruments, inc. All other trademarks and trade names are the property of their respective companies. A g r e a t e r m e a s u r e o f c o n f i d e n c e keithley instruments,...