- DL manuals
- Keithley
- Measuring Instruments
- SourceMeter 2400
- User Manual
Keithley SourceMeter 2400 User Manual - Measure Only
3-20
Basic Source-Measure Operation
2400 Series SourceMeter
®
User’s Manual
Measure only
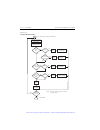
Front panel measure only
In addition to being used for conventional source-measure operations, the SourceMeter
can also be used to measure only voltage or current. Perform the following steps to use the
SourceMeter to measure voltage or current:
1.
Select source-measure functions.
Measure voltage only (voltmeter) — Press SOURCE I to select the I-Source, and
press MEAS V to select the voltage measurement function.
Measure current only (ammeter) — Press SOURCE V to select the V-Source, and
press MEAS I to select the current measurement function.
2.
Set source and compliance levels.
Use the editing procedure provided in step 2 of the Basic source-measure proce-
dure to edit the source and compliance levels as follows:
a.
Select the lowest source range and set the source level to zero (0.00000µA or
000.000mV).
b.
Set compliance to a level that is higher than the expected measurement.
CAUTION
When using the SourceMeter as a voltmeter, V-Compliance must be set
higher than the voltage that is being measured. Failure to do this could
result in instrument damage due to excessive current that will flow into
the SourceMeter.
3.
Select range.
Use the RANGE
and
keys to select a fixed measurement range that will
accommodate the expected reading. Use the lowest possible range for best
accuracy.
When measuring current, AUTO range can be used instead. The SourceMeter will
automatically go to the most sensitive range. When measuring voltage, DO NOT
use AUTO range (see the following CAUTION).
CAUTION
When using the SourceMeter as a voltmeter only, DO NOT use AUTO
range and NEVER select a measurement range that is below the
applied signal level. For these conditions, high current will be drawn
from the external source. This high current could damage the external
source or test circuit.
4.
Connect voltage or current to be measured. Connect the DUT to the SourceMeter
using 2-wire connections. (
Figure 2-2
).
5.
Turn output on. Press the ON/OFF key to turn the output on.
6.
Take reading from display.
7.
When finished, turn output off.
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com
Summary of SourceMeter 2400
Page 1
Artisan technology group is your source for quality new and certified-used/pre-owned equipment • fast shipping and delivery • tens of thousands of in-stock items • equipment demos • hundreds of manufacturers supported • leasing/monthly rentals • itar certified secure asset solutions service center r...
Page 3
Warranty keithley instruments, inc. Warrants this product to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of 1 year from date of shipment. Keithley instruments, inc. Warrants the following items for 90 days from the date of shipment: probes, cables, rechargeable batteries, diskettes...
Page 5
Manual print history the print history shown below lists the printing dates of all revisions and addenda created for this manual. The revision level letter increases alphabetically as the manual undergoes sub- sequent updates. Addenda, which are released between revisions, contain important change i...
Page 6: Afety Precautions
The following safety precautions should be observed before using this product and any associated instrumentation. Although some instruments and accessories would normally be used with non-hazardous voltages, there are situations where hazardous conditions may be present. This product is intended for...
Page 7
Bles or jumpers, installing or removing switching cards, or making internal changes, such as installing or removing jumpers. Do not touch any object that could provide a current path to the common side of the circuit under test or power line (earth) ground. Al- ways make measurements with dry hands ...
Page 8
Table of contents 1 getting started general information ................................................................... 1-2 warranty information .......................................................... 1-2 contact information ............................................................ 1-2 man...
Page 9
Menus ....................................................................................... 1-20 main menu ......................................................................... 1-20 rules to navigate menus .................................................... 1-24 editing source and compliance ...
Page 10
Nplc caching ................................................................... 3-10 nplc cache setup ...................................................... 3-10 typical nplc cache test times .................................. 3-11 v-source protection ..................................................
Page 11
5 pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) overview .................................................................................... 5-2 pulse characteristics .................................................................... 5-3 pulse width .........................................................
Page 12
Pulse-measure considerations .................................................. 5-16 measurement speed ........................................................... 5-16 filter .................................................................................. 5-17 auto range .............................
Page 13
I-source operating boundaries .......................................... 6-21 voltage compliance boundaries .................................. 6-24 v-source operating boundaries ......................................... 6-26 current compliance boundaries ................................. 6-28 source...
Page 14
Filters ......................................................................................... 7-9 response time considerations ...................................... 7-9 front panel filter control ................................................... 7-10 configuring filter ..........................
Page 15
Buffer statistics .................................................................... 9-3 minimum and maximum .............................................. 9-3 peak-to-peak ................................................................. 9-3 average ..................................................
Page 16
Sweep branching program example ....................................... 10-27 pulse mode sweeps (model 2430 only) ................................. 10-32 front panel pulse mode sweep procedure ...................... 10-33 remote pulse mode sweep operation ............................. 10-34 11 trigg...
Page 17
Pulse mode triggering (model 2430) ..................................... 11-30 trigger models ................................................................ 11-30 idle ........................................................................... 11-33 source event detector .............................
Page 18
Configuring and performing limit tests .................................. 12-19 configuring limit tests ..................................................... 12-19 performing front panel limit tests ................................... 12-21 step 1: configure test system. ...............................
Page 19
14 remote operations differences: remote vs. Local operation .................................... 14-2 operation enhancements (remote operation) .................... 14-2 math expressions ........................................................ 14-2 concurrent measurements .............................
Page 20
Response messages ......................................................... 14-17 sending a response message .................................... 14-17 multiple response messages .................................... 14-17 response message terminator (rmt) ..................... 14-17 message exchange...
Page 21
Queues .................................................................................... 15-18 output queue ................................................................... 15-18 error queue ...................................................................... 15-19 programming example — read...
Page 22
Define math expression ................................................... 18-30 [:expression] 18-30 enable and read math expression result .......................... 18-33 :state .............................................................. 18-33 :data? ...............................................
Page 23
Read display .................................................................... 18-47 data? ...................................................................... 18-47 define :text messages .................................................. 18-48 data ................................................
Page 24
Set compliance parameters ............................................. 18-68 [:level] ............................................................ 18-68 rsynhronize ................................................... 18-69 tripped? ................................................................. 1...
Page 25
Configure list ................................................................... 18-91 current ................................................. 18-91 voltage ................................................ 18-91 append .................................................. 18-92 points? ...............
Page 26
Error queue .................................................................... 18-105 [:next]? ............................................................... 18-105 clear ..................................................................... 18-105 enable .............................................
Page 27
Auto range change mode ............................................... 18-117 rcmode ................................................... 18-117 trace subsystem ................................................................ 18-117 read and clear buffer .................................................
Page 28
C data flow introduction ............................................................................... C-2 fetch? .............................................................................. C-3 calculate[1]:data? ....................................................... C-4 calculate2:data? ........
Page 29
Sweep limitations ............................................................... F-6 staircase and custom sweeps ...................................... F-6 source memory sweeps ............................................... F-6 limit test sequence .....................................................
Page 30
List of illustrations 1 getting started figure 1-1 sourcemeter front panel ........................................................ 1-7 figure 1-2 sourcemeter rear panel .......................................................... 1-9 figure 1-3 main menu tree ............................................
Page 31
Figure 6-13 v-source limit lines .............................................................. 6-28 figure 6-14 v-source operating examples ............................................... 6-29 figure 6-15 source i ................................................................................ 6-31...
Page 32
Figure 11-11 operation model for triggering example ........................... 11-27 figure 11-12 trigger model for remote trigger example ......................... 11-29 figure 11-13 2430 pulse mode trigger model (front panel operation) .... 11-31 figure 11-14 2430 pulse mode trigger model (remote...
Page 33
18 scpi command reference figure 18-1 ascii data format .............................................................. 18-49 figure 18-2 ieee-754 single precision data format (32 data bits) ........ 18-50 figure 18-3 key-press codes ................................................................ 18...
Page 34
List of tables 1 getting started table 1-1 line frequency remote commands ....................................... 1-12 table 1-2 power line fuse ..................................................................... 1-13 table 1-3 basic display commands ..................................................
Page 35
7 range, digits, speed, and filters table 7-1 range and digits commands ................................................... 7-6 table 7-2 range and digits programming example ................................ 7-6 table 7-3 speed commands ..................................................................
Page 36
13 digital i/o port, safety interlock, and output configuration table 13-1 digital output line settings ................................................... 13-5 table 13-2 output configuration commands ........................................ 13-11 table 13-3 output configuration programming example...
Page 37
Table 18-10 trace command summary ............................................... 18-21 table 18-11 trigger command summary ............................................. 18-22 b status and error messages table b-1 status and error messages ..................................................... B-3 d ...
Page 38
1 getting started • general information — covers general information that includes warranty infor- mation, contact information, safety symbols and terms, inspection, and available options and accessories. • product overview — summarizes the features of the sourcemeter. • front and rear panel familia...
Page 39: General Information
1-2 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual general information warranty information warranty information is located at the front of this manual. Should your sourcemeter require warranty service, contact the keithley representative or authorized repair facility in your area for furth...
Page 40
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-3 inspection the sourcemeter was carefully inspected electrically and mechanically before shipment. After unpacking all items from the shipping carton, check for any obvious signs of physi- cal damage that may have occurred during transit. (t...
Page 41
1-4 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual model 5806 kelvin clip lead set —includes two kelvin clip test leads (0.9m) with banana plug termination. Designed for instruments that measure four-terminal resistance. A set of replacement rubber bands is available (keithley p/n ga-22). M...
Page 42: Product Overview
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-5 rack mount kits model 4288-1 single fixed rack mount kit —mounts a single sourcemeter in a standard 19-inch rack. Model 4288-2 side-by-side rack mount kit —mounts two instruments (models 182, 428, 486, 487, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2010, 2015, 240...
Page 43
1-6 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual model 2420: • source voltage from 5µv to 63v; measure voltage from 1µv to 63.3v. • source current from 500pa to 3.15a; measure current from 100pa to 3.165a. • measure resistance from 10µ Ω ( Ω in manual ohms) to 21.1m Ω . • maximum source p...
Page 44
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-7 • math expressions — five built-in, up to five user-defined (bus only). • reading and setup storage — up to 2500 readings and seven setups (five user defaults, factory default, *rst default) can be stored and recalled. • closed-cover calibr...
Page 45
1-8 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual operation keys: edit select source or compliance reading for editing. Toggle toggle display positions of source and measure readings, or display v and i measurements. Local cancel remote operation. Rel enable/disable relative reading on pre...
Page 46
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-9 rear panel summary the rear panel of the model 2400 sourcemeter is shown in figure 1-2 . (the models 2410, 2420, 2425, 2430, and 2440 are similar.) the following abbreviated information should be reviewed before operating the instrument. Fi...
Page 47: Power-Up
1-10 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual rs-232 connector: rs-232 connector for rs-232 remote operation. Use a straight through (not null modem) db-9 cable. Gpib connector: ieee-488 connector for gpib remote operation. Use a shielded cable (model interface 7007-1 or 7007-2). Powe...
Page 48
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-11 warning the power cord supplied with the sourcemeter contains a separate ground for use with grounded outlets. When proper connections are made, instrument chassis is connected to power line ground through the ground wire in the power cord...
Page 49
1-12 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual line frequency setting at the factory, the sourcemeter is configured to sense the power line frequency and auto- matically select the frequency setting. If, however, the line power source is noisy, the sourcemeter may select the wrong sett...
Page 50: Cooling Fan
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-13 fuse replacement a rear panel fuse protects the power line input of the sourcemeter. If the line fuse needs to be replaced, perform the following steps: caution for continued protection against fire or instrument damage, replace the fuse o...
Page 51: Display
1-14 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual when the output is turned off, the fan will either run at the low speed or stay at the speed it was at when the output was on (current range dependent). This speed option is set from the fan selection of the general menu. (see “ main menu ...
Page 52
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-15 toggle key note for the model 2430 pulse mode, the toggle key is disabled. With the output on, the toggle key manipulates readings on the top display and on the bottom-left display. It has no effect on the compliance reading (cmpl), which ...
Page 53: Default Settings
1-16 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual front panel tests use the test/front-panel-tests selection of the main menu to test various aspects of the front panel. Test selections include: • keys — front panel keys are tested. Pressing a key displays a message that iden- tifies that...
Page 54
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-17 power-on configuration you can also define which of the stored setups (factory default or user) the instrument assumes as the power-on configuration as follows: 1. Press the menu key, select savesetup, then press enter. 2. From the saveset...
Page 55
1-18 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual setting bench or gpib default guard cable limit tests: digout: size 4-bit mode: grading binning control immediate auto clear: disabled delay 0.00001 sec clear pattern 15 h/w limits: control disabled fail mode: in compliance cmpl pattern 15...
Page 56
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-19 setting bench or gpib default pulse mode (2430 only): pulse delay 0.0s pulse width 0.20ms ranging (measure): auto range enabled rel off value 0.0 rs-232 no effect sense mode 2-wire source delay 1ms auto-delay enabled source shape (2430 onl...
Page 57: Menus
1-20 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote setups you can also save and recall setups via remote using the following scpi commands: • save and recall user setups using *sav and *rcl ( section 16 ). • restore gpib defaults using *rst ( section 16 ). • restore bench defaults u...
Page 58
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-21 menu item 1 description parameters communication 2 gpib rs-232 baud bits parity terminator flow ctrl cal 3 unlock execute view dates save lock change password test display tests 4 keys display patterns char set select and configure remote ...
Page 59
1-22 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual menu item 1 description parameters a/d ctrl auto zero 5 disable enable once line freq nplc cache disable enable refresh reset general digout serial# timestamp fan (2420, 2425, 2430, and 2440) numbers beeper control auto-zero, line frequenc...
Page 60
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-23 figure 1-3 main menu tree press menu key (use and to select item, then press enter). ▲ ▲ savesetup global save restore poweron bench gpib user-setup-number reset source memory save restore communication gpib rs-232 bits parity terminator f...
Page 61
1-24 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual rules to navigate menus many source-measure functions and operations are configured from the front panel menus. Use the following rules to navigate through these configuration menus: note complete rules to edit source and compliance values...
Page 62
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-25 • source or — increments or decrements the source or compliance value. Note that pressing either of these keys will automatically enable the source edit mode. • range or — selects the source or compliance range. • numeric keys (0-9) — allo...
Page 63
1-26 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual front panel control front panel display circuitry is controlled from the disable display configuration menu, which is accessed by pressing config and then edit (or toggle). To select an option (now, never, sweep, or store), use the edit cu...
Page 64
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-27 these various configuration menus are covered in detail in the pertinent sections of this manual. Table 1-6 measurement configuration menus configuration menu item description config meas v sense mode 2-wire 4-wire cmpl-range-sync config m...
Page 65
1-28 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual table 1-7 source and range configuration menus configuration menu item description config source v configure v source protection sense mode 2-wire 4-wire guard ohms cable delay auto delay disable enable trig control scale factor shape dc p...
Page 66
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-29 configuration menu item description config range config range config auto range auto range type single src mtr multiple program upper range limit. Program lower range limit. Select auto range type. Select single sourcemeter operation. Sele...
Page 67
1-30 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual configuration menu item description config limit configure limits menu digout size 3-bit 4-bit mode grading immediate end sorting auto clear disable enable h/w limits control disable enable fail mode in out s/w limits control disable enabl...
Page 68
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-31 table 1-9 trigger configuration menu configuration menu item description config trig configure trigger arm layer arm in immediate gpib timer manual tlink once never ↓ stest once never ↑ stest once never ↑↓ stest once never arm out line eve...
Page 69
1-32 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual table 1-10 sweep, digits, speed, and data store configuration menus configuration menu item description config sweep configure sweeps type stair log custom # points adjust points init src memory start # points sweep count finite infinite s...
Page 70
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-33 table 1-11 output and display configuration menus configuration menu item description config on/off output configure output interlock disable enable off state high impedance normal zero guard auto off disable enable config edit or toggle d...
Page 71
1-34 getting started 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual table 1-12 sweep, digits, speed, and output configuration menus configuration menu item description config sweep configure sweeps type stair log custom # points adjust points init src memory start # points sweep count finite infinite sourc...
Page 72
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual getting started 1-35 configuration menu item description config on/off output configure output interlock disable enable off state high impedance normal zero guard auto off disable enable configure output. Enable/disable interlock. Disable interlock. Enable int...
Page 74
2 connections • connection overview — discusses front/rear terminal selection and using a test fixture interlock. • connections to dut — covers various methods for making connections to the dut, including 4-wire remote sensing, 2-wire local sensing, cable and ohms guard, as well as sense and guard s...
Page 75: Connection Overview
2-2 connections 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual connection overview warning to prevent electric shock, test connections must be configured such that the user cannot come in contact with conductors or any dut that is in contact with the conductors. Safe installation requires proper shields, b...
Page 76: Connections to Dut
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual connections 2-3 remote command terminals selection use the :route:terminals ( section 18 ) command to select the front or rear panel termi- nals via remote. For example, send the following command to select the rear terminals: :rout:term rear conversely, send ...
Page 77
2-4 connections 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual warning to prevent electric shock and/or damage to the sourcemeter, common mode voltage must be externally limited as follows: models 2400 and 2410 — limit common mode voltage to 250vdc, 1.05a maximum models 2420 and 2425 — limit common mode vo...
Page 78
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual connections 2-5 note to avoid redundancy, generic sourcemeter drawings will be used in this section. A generic drawing excludes the labeling for the terminal voltage differentials. Sensing methods basic source-measure operations are performed using either 2-wi...
Page 79
2-6 connections 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 2-3 four-wire connections (remote sense) note connections alone do not determine sense mode. For local sensing ( figure 2-2 ), 2-wire sensing must be selected from the sense mode option of the configure v-source menu. For remote sensing ...
Page 80
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual connections 2-7 warning when sourcing voltage in remote sense, make sure the sense leads are connected to the dut. If a sense lead becomes disconnected, 0v will be sensed, and the sourcemeter will increase the output voltage (to possi- bly hazardous levels) to...
Page 81
2-8 connections 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual guarding methods cable guard use the high-impedance (cable) guard connection scheme shown in figure 2-4 for the fol- lowing source-measure condition: • test circuit impedance is >1g Ω . Note that cable guard must be selected for this connection...
Page 82
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual connections 2-9 ohms guard use the guarded ohms connection schemes shown in figure 2-5 for the following source- measure operation: • in-circuit resistance measurements on the dut where other parasitic leakage devices are present. Note that ohms guard must be ...
Page 83
2-10 connections 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 2-5 guarded ohms measurements (ohms guard) warning: no internal operator servica caution: for continued protection against fir hi lo ieee-488 (enter ieee address with front panel warning: no internal operator servica caution: for contin...
Page 84
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual connections 2-11 sense and guard selections note when sense or guard settings are changed, the output will turn off. Sense selection when using the sense hi and lo terminals of the sourcemeter, 4-wire remote sensing must be selected. When not using these termi...
Page 85
2-12 connections 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual guard selection cable guard is used for high-impedance guarding for cables (i.E., coax and triax) and test fixtures. Ohms guard provides a high-current guard output, which allows in-circuit guarded ohms measurements. On power-up, cable guard i...
Page 86
3 basic source-measure operation • operation overview — discusses source-measure capabilities, compliance limit, and fundamental source-measure configuration. • operation considerations —covers warm-up, auto zero, v-source protection, and source delay. • basic source-measure procedure — describes th...
Page 87: Warning - Caution
3-2 basic source-measure operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual warning - caution the sourcemeter uses a heat sink to dissipate heat. Also, the models 2410, 2420, 2430, and 2440 have a cooling fan. The left side of the case is cut out to expose the black, finned heat sink. This heat sink ...
Page 88: Operation Overview
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic source-measure operation 3-3 operation overview source-measure capabilities from the front panel, the sourcemeter can be configured to perform the following operations: • source voltage — display current and/or voltage measurement • source current — disp...
Page 89
3-4 basic source-measure operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual the full range of operation is explained in section 6 , “ overheating protection ” and “ oper- ating boundaries .” note output transient recovery — the time required for the v-source to recover to its original value (within 0...
Page 90
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic source-measure operation 3-5 2420 2425/2430 range source measure range source measure 200mv 2v 20v 60v 10µa 100µa 1ma 10ma 100ma 1a 3a ±210mv ±2.1v ±21v ±63v ±10.5µa ±105µa ±1.05ma ±10.5ma ±105ma ±1.05a ±3.15a ±211mv ±2.11v ±21.1v ±63.3v ±10.55µa ±105.5µ...
Page 91
3-6 basic source-measure operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual compliance limit when sourcing voltage, the sourcemeter can be set to limit current. Conversely, when sourcing current, the sourcemeter can be set to limit voltage. The sourcemeter output will not exceed the compliance limit....
Page 92
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic source-measure operation 3-7 setting the compliance limit front panel compliance limit set the compliance limit from the front panel as follows: 1. Select the desired source and measure functions using the meas and source keys. 2. Press the edit key unti...
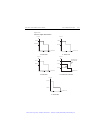
Page 93
3-8 basic source-measure operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic circuit configurations the fundamental source-measure configurations for the sourcemeter are shown in figure 3-1 . When sourcing voltage, you can measure current or voltage (configuration a). When sourcing current, you ...
Page 94: Operation Considerations
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic source-measure operation 3-9 operation considerations the following paragraphs discuss warm-up period, auto zero, v-source protection, and source delay. Warm-up the sourcemeter must be turned on and allowed to warm up for at least one hour to achieve rat...
Page 95
3-10 basic source-measure operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual nplc caching nplc caching speeds up source memory sweeps by caching a/d reference and zero val- ues. When nplc caching is enabled (using the nplc-cache/enable menu selec- tion), the a/d reference and zero values will be save...
Page 96
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic source-measure operation 3-11 typical nplc cache test times typically, nplc caching will decrease source memory sweep times by a factor of three. The table below shows typical averaged times for a test consisting of 10 sweeps of four source memory locati...
Page 97
3-12 basic source-measure operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual warning even with the voltage protection limit set to the lowest value, never touch anything connected to the terminals of the sourcemeter when the output is on. Always assume that a hazardous voltage (>30v rms) is present w...
Page 98
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic source-measure operation 3-13 front panel source delay to set the manual source delay from the front panel: 1. Press config then source v. 2. Select delay from the displayed choices, then press enter. 3. Enter the desired delay value, then press enter. 4...
Page 99
3-14 basic source-measure operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic source-measure procedure output control use the on/off output key to turn the sourcemeter output on or off for basic source- measure situations. You can also control the output off state (high impedance, normal, zero, ...
Page 100
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic source-measure operation 3-15 note that compliance can also be determined by the measurement range. Depending on which value is lower, compliance occurs at the programmed value (real compliance) or at the maximum compliance value for the present fixed me...
Page 101
3-16 basic source-measure operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual note to clear the source value to 0v or 0a, press the menu key while in the edit source field. • value adjust — to adjust the value, use the edit cursor keys to place the cur- sor at the appropriate position, and use the sou...
Page 102
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic source-measure operation 3-17 note 2400 — with the 200v v-source range selected, the highest current measure- ment range is 100ma. With the 1a i-source range selected, the highest voltage measurement range is 20v. 2410 — with the 1kv v-source range selec...
Page 103
3-18 basic source-measure operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual step 6: turn output off. When finished, turn the output off by pressing the on/off output key. The output indicator light will turn off. Remote command source-measure procedure basic source-measurement procedures can also be...
Page 104
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic source-measure operation 3-19 source-measure programming example table 3-6 summarizes the command sequence for a basic source-measure procedure. Note that the steps correspond to those listed previously in “ front panel source-measure proce- dure .” thes...
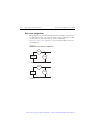
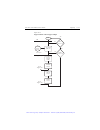
Page 105: Measure Only
3-20 basic source-measure operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual measure only front panel measure only in addition to being used for conventional source-measure operations, the sourcemeter can also be used to measure only voltage or current. Perform the following steps to use the sourceme...
Page 106
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic source-measure operation 3-21 remote command measure only table 3-7 summarizes the basic command sequence for measure only. The steps outlined correspond to those in the “ front panel measure only ” sequence above. These commands set up the sourcemeter f...
Page 107: Sink Operation
3-22 basic source-measure operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sink operation when operating as a sink (v and i have opposite polarity), the sourcemeter is dissipating power rather than sourcing it. An external source (i.E., battery) or an energy storage device (i.E., capacitor) can for...
Page 108
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic source-measure operation 3-23 do not attempt to charge or discharge batteries exceeding the current or voltage requirements listed below: model 2400: 21v @ 1.05a or 210v @ 105ma model 2410: 21v @ 1.05a or 1100v @ 21ma model 2420: 21v @ 3.15a or 63v @ 1.0...
Page 109
3-24 basic source-measure operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual caution if using the i-source to charge and/or discharge batteries, the following precautions must be observed. Failure to observe these precautions could result in damage to the sourcemeter that is not covered by the warran...
Page 110
4 ohms measurements • ohms configuration menu — outlines the ohms configuration menu that allows you to set up various ohms measurement aspects. • ohms measurement methods — discusses auto and manual ohms measurement methods and how to select them. • ohms sensing — covers 2-wire and 4-wire ohms sens...
Page 111: Ohms Configuration Menu
4-2 ohms measurements 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ohms configuration menu note for the model 2430 pulse mode, offset-compensated ohms cannot be enabled from the ohms configuration menu. However, offset-compensated ohms is avail- able as a math function ( section 8 , “ math operations ”)....
Page 112: Ohms Measurement Methods
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ohms measurements 4-3 ohms measurement methods note for the model 2430, the following ohms measurement procedures assume that the dc mode of operation is selected (“vsrc” or “isrc” displayed in the source field). If in the pulse mode (“vpls” or “ipls” displaye...
Page 113
4-4 ohms measurements 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual selecting ohms measurement method on power-up, auto ohms is the default method for the ohms function. Perform the follow- ing steps to check and/or change the ohms measurement method: 1. Press config and then Ω to display the ohms configu...
Page 114
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ohms measurements 4-5 3. Select measurement range. Use the range and keys to select a range appropriate for the expected ohms reading, or use autorange by pressing auto. When using manual ranging, select- ing the most sensitive (lowest) range provides the best...
Page 115
4-6 ohms measurements 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual note use the v-source for manual ohms measurements when high-speed settling is required (i.E., production testing). 4. Select measurement range. Using the range and keys, select the lowest possible fixed range or use auto range. Note that...
Page 116: Ohms Sensing
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ohms measurements 4-7 ohms sensing ohms measurements can be made using either 2-wire or 4-wire sensing. (see section 2 for information on connections and sensing methods.) note that resistance measurement accuracy specifications are based on using 4-wire sensi...
Page 117
4-8 ohms measurements 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 4-3 4-wire resistance sensing sense selection use the following procedure to select 2-wire or 4-wire sense operation: 1. Press config then Ω to display the ohms configuration menu. 2. Select sense mode, then press enter. 3. Select ...
Page 118: Offset-Compensated Ohms
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ohms measurements 4-9 offset-compensated ohms note for the model 2430, the following offset-compensated ohms method is not valid in the pulse mode. However, offset compensated ohms is available as a math function ( section 8 , “ math operations ”). The presenc...
Page 119
4-10 ohms measurements 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual offset-compensated ohms procedure note the following procedure assumes that the desired ohms measurement method (auto or manual) is already selected and the sourcemeter is connected to the dut as explained in section 2 . Refer to “ selec...
Page 120: Ohms Source Readback
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ohms measurements 4-11 ohms source readback note for the model 2430 pulse mode, ohms source readback cannot be enabled. With ohms source readback enabled, the instrument measures the actual source value instead of the programmed value used for ohms measurement...
Page 121: Remote Ohms Programming
4-12 ohms measurements 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual 6. Press exit to return to normal display. 7. Press meas then Ω to select the ohms measurement function. 8. Select the appropriate measurement range, or use autoranging if desired. 9. Turn on the output by pressing the on/off output key....
Page 122
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ohms measurements 4-13 ohms programming example table 4-3 summarizes the command sequence for a typical auto ohms measurement. These commands set up the sourcemeter as follows: • ohms mode and range: auto, 20k Ω • offset compensation: off • sense mode: 4-wire ...
Page 124
5 pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) • overview — provides a summary of pulse mode operation. • pulse characteristics — describes the timing characteristics that make up the pulse width and output off-time of the pulse period. Explains how to achieve the fastest pulse output. • pulse energy limi...
Page 125: Overview
5-2 pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual overview note the pulse mode is only available for the model 2430. The documentation in this section does not apply to the models 2400, 2410, 2425, and 2440. While in the pulse mode, the model 2430 can output one or m...
Page 126: Pulse Characteristics
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 5-3 pulse characteristics note for the purpose of discussion, positive polarity pulses are shown in the follow- ing illustrations. Keep in mind that the model 2430 can output negative pulses. As shown in figure 5-1 , a pu...
Page 127
5-4 pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse width the pulse width can be set from 0.15msec to 5.00msec. However, depending on how the sourcemeter is configured, the pulse width setting may not be achievable. For example, if it takes 1.667msec to perform t...
Page 128
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 5-5 pulse width delay when the pulse width setting is greater than the sum of the signal measurement and over- head times, a delay is used to achieve the desired pulse width. The pulse width delay can be calculated as fol...
Page 129
5-6 pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse delay the pulse delay (pd) is set by the user. It can be set from 0 to 9999.999sec. Pulse duty cycle duty cycle is the percentage of time during the pulse period that the output is on. It is cal- culated as foll...
Page 130
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 5-7 auto zero the output off-time can be reduced by disabling auto zero. With auto zero disabled, only the signal is measured. As shown in figure 5-3 , the reference and zero measurements (which normally are part of the o...
Page 131
5-8 pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse-only the fastest pulses are achieved by disabling measurements altogether. With the signal not measured, as shown in figure 5-4 , the pulse width can be as short as the 150µsec over- head. With reference and zer...
Page 132
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 5-9 pulse energy limitations (10a range) energy for pulses are provided by an internal bank of capacitors. Each pulse consumes energy from the capacitors. After a pulse is generated, the capacitors begin to recharge. The ...
Page 133: Pulse Mode Configuration
5-10 pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse mode configuration front panel pulse mode configuration select pulse mode, and set pulse width and pulse delay 1. Press config then source v or i. 2. Select shape from the displayed choices, then press enter. 3...
Page 134
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 5-11 4. For continuous pulse output, select infinite, press enter and proceed to step 6. Otherwise, select finite, press enter and proceed to the next step to set the arm count. 5. Enter the desired arm count value and pr...
Page 135: Basic Pulse Mode Operation
5-12 pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic pulse mode operation note the following procedure assumes that the model 2430 is already connected to the dut as explained in section 2 . Warning hazardous voltages (>30v rms) can appear on the selected input/ ...
Page 136
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 5-13 step 4: select source. Press source v to source voltage pulses or press source i to source current pulses. The presently programmed pulse value (vpls or ipls) and compliance level (cmpl) are displayed. Step 5: set pu...
Page 137
5-14 pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual step 7: turn output on. Turn the output on by pressing the trig key or the on/off output key. The output indicator will be on whenever a pulse is being sourced. During each pulse off-time, the output will be off (ind...
Page 138
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 5-15 remote command pulse-measure operation basic pulse commands table 5-1 summarizes the commands to perform pulse-measure operations. See section 18 for more information on using these commands. Ignored settings and inv...
Page 139: Pulse-Measure Considerations
5-16 pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse-measure programming example table 5-2 summarizes the command sequence to output and measure pulses. Note that the steps correspond to those listed in the “front panel pulse-measure procedure,” page 5-12 . Pulse...
Page 140
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 5-17 filter filtering cannot be used while the model 2430 is in the pulse mode. You can configure the filter, but you cannot enable it. Pressing the filter key displays the “invalid in pulse mode!” message. For remote ope...
Page 141
5-18 pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual offset-compensated ohms from the front panel there are two methods to perform offset-compensated ohms measure- ments. For one method, which is enabled from the config ohms menu, the 2-point measurement process is per...
Page 142
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 5-19 input triggers in the dc mode, you can enable the source, delay and/or measure input event detectors. See section 11 for details on triggering. In the pulse mode, only the source detector is used. You can enable the ...
Page 143
5-20 pulse mode operation (model 2430 only) 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual turning source on for remote pulse mode operation, an :initiate command is used to start the pulse output process. The :read? Command will send :initiate to start the pulse process, and it will also acquire the pulse...
Page 144
6 source-measure concepts • compliance limit — discusses compliance limit including real and range compli- ances, maximum compliance values, and how to determine compliance limit. • overheating protection — provides information on preventing sourcemeter over- heating, including power equations. • so...
Page 145: Compliance Limit
6-2 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual compliance limit when sourcing voltage, the sourcemeter can be set to limit current. Conversely, when sourcing current, the sourcemeter can be set to limit voltage. The sourcemeter output will not exceed the compliance limit. 2400 —...
Page 146
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-3 maximum compliance values the maximum compliance values for the measurement ranges are summarized in table 6-1 . Table 6-1 compliance limits 2400 2410 2420 measure range maximum compliance value measure range maximum compliance valu...
Page 147
6-4 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual compliance examples when the sourcemeter goes into real compliance, the cmpl label for the compliance dis- play will flash. When the sourcemeter goes into range compliance, the units label (“ma”) will flash instead. For the followin...
Page 148
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-5 note when in compliance, the source output may exceed the programmed value in order to maintain the compliance limit. Determining compliance limit the relationships to determine which compliance is in effect are summarized as follow...
Page 149: Overheating Protection
6-6 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual when sourcing current, use the following commands to acquire the measurement range and the compliance setting: voltage:range? Query voltage measurement range. Voltage:protection? Query voltage compliance limit. When sourcing voltage...
Page 150
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-7 above 30˚c, for both source and sink operation, the sourcemeter will not overheat if the high power range(s) is not used. For the models 2400 and 2410, the high power range is 1a. For the model 2420, the high power ranges are 20v, 3...
Page 151
6-8 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual model 2410 sourcemeter when using the 1a range, you can use the two equations below to determine if the sourcemeter will overheat. Both of the equations must be true to ensure that the sourcemeter will not overheat. The result of th...
Page 152
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-9 models 2425 and 2430 sourcemeters there are two equations for each of the high power ranges (20v, 3a and 100v, 1a). Both of the equations for the selected voltage range must be true to ensure that the sourcemeter will not overheat. ...
Page 153: Source-Delay-Measure Cycle
6-10 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-delay-measure cycle in addition to static source and/or measure operation, sourcemeter operation can consist of a series of source-delay-measure (sdm) cycles ( figure 6-1 ). During each sdm cycle, the following occurs: 1. Se...
Page 154
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-11 the manually set delay (up to 9999.999 sec) is available to compensate for longer settling required by external circuitry. The more capacitance seen at the output, the more settling time is required for the source. The actual delay...
Page 155
6-12 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep waveforms there are four basic sweep types to select from: linear staircase, logarithmic staircase, custom, and source memory. Three of the sweeps are shown in figure 6-3 . The linear stair- case sweep goes from the start lev...
Page 156
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-13 figure 6-3 three basic sweep waveform types bias start stop bias start stop 0.1 1 10 100 bias first point last point a. Linear staircase sweep b. Logarithmic staircase sweep logarithmic scale shown for staircase steps. C. Custom sw...
Page 157: Operating Boundaries
6-14 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual operating boundaries source or sink depending on how it is programmed and what is connected to the output (load or source), the sourcemeter can operate in any of the four quadrants. The four quadrants of operation for the sourcemet...
Page 158
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-15 model 2400 sourcemeter the general operating boundaries for the model 2400 are shown in figure 6-4 . In this drawing, the 1a, 20v and 100ma, 200v magnitudes are nominal values. The actual max- imum output magnitudes of the sourceme...
Page 159
6-16 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual model 2410 sourcemeter the general operating boundaries for the model 2410 are shown in figure 6-5 . In this drawing, the 1a, 20v and 20ma, 1kv magnitudes are nominal values. The actual maxi- mum output magnitudes of the sourcemete...
Page 160
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-17 model 2420 sourcemeter the general operating boundaries for the model 2420 are shown in figure 6-6 . In this drawing, the 3a, 20v and 1a, 60v magnitudes are nominal values. The actual maximum output magnitudes of the sourcemeter ar...
Page 161
6-18 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual models 2425 and 2430 sourcemeters the general operating boundaries for the models 2425 and 2430 are shown in figure 6-7 . The boundaries for the model 2425 and model 2430 dc mode are shown in figure 6-7a , and the boundaries for th...
Page 162
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-19 figure 6-7 model 2425/2430 operating boundaries (t amb ≤ 30°c) –i = 100% duty cycle = ≤ 60% duty cycle (iii) source –v +v +i (iv) sink (ii) sink (i) source -20v 20v -3a -2a -1a 1a 3a 2a 0.5a -0.5a -100v 100v 10a 6a -6a -10a -100v 1...
Page 163
6-20 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual model 2440 sourcemeter the general operating boundaries for the model 2440 are shown in figure 6-8 . In this drawing, the 5a, 10v and 1a, 40v magnitudes are nominal values. The actual maximum output magnitudes of the sourcemeter ar...
Page 164
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-21 i-source operating boundaries figure 6-9 and figure 6-10 show the operating boundaries for the i-source. Only the first quadrant of operation is covered. Operation in the other three quadrants is similar. 2400 — figure 6-9a shows t...
Page 165
6-22 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 6-9 i-source output characteristics source i limit v 210v 21v 105ma 1.05a a. Model 2400 source i limit v 1100v 21v 21ma 1.05a b. Model 2410 source i limit v 63v 21v 1.05a 3.15a c. Model 2420 source i limit v 21v 1.05a 3.15a ...
Page 166
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-23 figure 6-10 shows the limit lines for the i-source. The current source limit line represents the maximum source value possible for the presently selected current source range. For example, if on the 100ma current source range, the ...
Page 167
6-24 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual voltage compliance boundaries where within the boundaries the sourcemeter operates depends on the load (dut) that is connected to its output. Figure 6-11 shows operation examples for resistive loads that are 200 Ω and 800 Ω , respe...
Page 168
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-25 figure 6-11 i-source operating examples voltage limit load line operating point current source load line i-source (i s ) v-meter (vm) 20v 40v 100ma 200 Ω dut load line (r) v m = i s · r = (100ma) (200 Ω ) = 20v a. Normal i-source o...
Page 169
6-26 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual v-source operating boundaries figure 6-12 and figure 6-13 show the operating boundaries for the v-source. Only the first quadrant of operation is covered. Operation in the other three quadrants is similar. 2400 — figure 6-12a shows...
Page 170
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-27 figure 6-12 v-source output characteristics 210v 21v 105ma 1.05a a. Model 2400 1100v 21v 21ma 1.05a b. Model 2410 63v 21v 1.05a 3.15a c. Model 2420 21v 1.05a 3.15a d. Models 2425 and 2430 10.5a model 2430 pulse mode dc mode 105v li...
Page 171
6-28 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 6-13 shows the limit lines for the v-source. The voltage source limit line represents the maximum source value possible for the presently selected voltage source range. For example, if on the 20v source range, the voltage so...
Page 172
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-29 figure 6-14 v-source operating examples current limit load line operating point voltage source load line v-source (v s ) i-meter (i m ) 25ma 50ma 50v 2k Ω dut load line (r) i m = v s / r = 50v/2k Ω = 25ma a. Normal v-source operati...
Page 173
6-30 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source i measure i and source v measure v the sourcemeter can measure the function it is sourcing. When sourcing a voltage, you can measure voltage. Conversely, if you are sourcing current, you can measure the output current. For t...
Page 174: Basic Circuit Configurations
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-31 basic circuit configurations source i when configured to source current (i-source) as shown in figure 6-15 , the sourcemeter functions as a high-impedance current source with voltage limit capability and can mea- sure current (i-me...
Page 175
6-32 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source v when configured to source voltage (v-source) as shown in figure 6-16 , the sourcemeter functions as a low-impedance voltage source with current limit capability and can measure current (i-meter) or voltage (v-meter). Sense...
Page 176
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-33 measure only (v or i) figure 6-17 shows the configurations for using the sourcemeter exclusively as a voltmeter or ammeter. As shown in figure 6-17a , the sourcemeter is configured to measure voltage only by setting it to source 0a...
Page 177: Guard
6-34 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual guard warning guard is at the same potential as output hi. Thus, if hazardous volt- ages are present at output hi, they are also present at the guard terminal. Note see section 2 , “ guarding methods ,” for details on guarded test ...
Page 178
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-35 inside the test fixture, a triaxial cable can be used to extend guard to the dut. The center conductor of the cable is used for in/out hi, the inner shield is used for guard, and the outer shield is used for in/out lo and is connec...
Page 179
6-36 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 6-18 high-impedance measurements insulator i d dut metal mounting plate i l r l1 r l2 insulator i m = i d + i l i m = measured current i d = dut current i l = leakage current in/out hi i-meter in/out lo v-source a. Unguarded...
Page 180
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-37 figure 6-19 in-circuit ohms measurements in/out lo in/out hi a. Unguarded sourcemeter r 3 10k Ω v-meter i-source b. Guarded x1 i g i g = v m r 3 r 2 10k Ω r 1 20k Ω resistor network in/out lo in/out hi note: ohms guard selected r 3...
Page 181
6-38 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual guard sense when the guard-to-lo resistance path is less than 1k Ω , remote guard sensing should be used to compensate for ir drop in the guard test lead and/or switch contacts on a switching card. Figure 6-19 was modified to creat...
Page 182
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-39 figure 6-20 in-circuit ohms measurements using guard sense guard (ohms mode) b. Remote guard sense a. Local guard sense r tl sourcemeter 1 Ω test lead resistance i g in/out lo in/out hi r 3 100 Ω r 2 10k Ω r 1 20k Ω i l guard (ohms...
Page 183: Data Flow
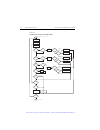
6-40 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual data flow data flow for front panel operation is summarized by the block diagrams provided in fig- ure 6-21 . Note that if rel is enabled, the result of the rel operation is sent to the other blocks. Note see appendix c for remote ...
Page 184
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-41 figure 6-21 data flow front panel measurement conversions data store v, i, Ω display buffer and statistics readings display readings a. Math (fctn) and limit tests disabled measurement conversions data store v, i, Ω display buffer ...
Page 185
6-42 source-measure concepts 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual buffer considerations when the sourcemeter is in the process of storing readings, configuration changes affect what gets stored in the buffer. These storage considerations and restrictions are summa- rized in table 6-3 . The first ...
Page 186
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-measure concepts 6-43 changing math function • if you started with only a basic measurement function selected, you can enable a math function, but only the voltage, current, or resistance component of the cal- culation will be stored in the buffer. The ...
Page 188
7 range, digits, speed, and filters • range and digits — discusses maximum readings, ranging limitations, manual and autoranging, and display resolution. • speed — discusses speed settings, which are used to control the integration period of the a/d converter. • filters — provides information on the...
Page 189: Range and Digits
7-2 range, digits, speed, and filters 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual range and digits range the selected measurement range affects the accuracy of the measurements as well as the maximum signal that can be measured. Note that with the output off, dashed lines are dis- played (i.E., --.---- ...
Page 190
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual range, digits, speed, and filters 7-3 2425 and 2430 — range limitations are source mode dependent: 2425 and 2430 dc mode — with the 100v v-source range selected, the highest current measurement range is 1a. With the 20v v-source range selected, the highest cur...
Page 191
7-4 range, digits, speed, and filters 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual note that source settling time can affect the time it takes the instrument to auto range. When the instrument auto ranges, both the source and sense circuits monitor each other, so if one takes longer to settle, the other ...
Page 192
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual range, digits, speed, and filters 7-5 limits evaluation neither the high limit nor the low limit are evaluated until the unit has switched to the autorange mode. This means that if the unit is already on a range higher than the upper limit, or lower than the l...
Page 193
7-6 range, digits, speed, and filters 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual range and digits commands range and digits programming example table 7-2 shows a programming example for controlling range and digits. The sourcemeter is set up as follows: • source function: volts • source level: 10v • me...
Page 194: Speed
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual range, digits, speed, and filters 7-7 speed the speed/accuracy menu is used to set the integration time of the a/d converter (period of time the input signal is measured). The integration time affects the usable digits, the amount of reading noise, and the ult...
Page 195
7-8 range, digits, speed, and filters 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse speed (nplc) – model 2430 pulse mode press speed or config speed to display the speed choices: 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.10 note display resolution for the model 2430 pulse mode is not affected b...
Page 196: Filters
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual range, digits, speed, and filters 7-9 speed programming example use any nplc command to set the speed. For example, send the following command to set the amps speed to 10 plc: :sens:curr:nplc 10 filters note for the pulse mode of the model 2430, filtering is n...
Page 197
7-10 range, digits, speed, and filters 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual front panel filter control configuring filter filter type and count is configured from the configure filtering menu and is struc- tured as shown in figure 7-3 . Use section 1 , “ rules to navigate menus ,” to check and/or...
Page 198
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual range, digits, speed, and filters 7-11 figure 7-2 moving average and repeating filters response time the filter parameters have speed and accuracy trade-offs for the time needed to display, store, or output a filtered reading. These affect the number of readin...
Page 199
7-12 range, digits, speed, and filters 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 7-3 filter configuration menu tree remote filter programming filter commands table 7-4 summarizes filter commands. See section 18 , “ sense1 subsystem ,” “ configure and control filter ,” for more details. Table 7-...
Page 200
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual range, digits, speed, and filters 7-13 filter programming example table 7-5 summarizes the command sequence to program filter aspects as follows: • filter type: moving • filter count: 20 • filter state: on table 7-5 filter programming example command descripti...
Page 202
8 relative and math • relative — discusses the relative (rel) mode that can be used to null offsets or subtract a baseline value from readings. • math operations — provides detailed information on the following math (fctn) operations: power, offset-compensated ohms, varistor, alpha, voltage coeffici...
Page 203: Relative
8-2 relative and math 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual relative the rel (relative) feature can be used to null offsets or subtract a baseline reading from present and future readings. With rel enabled, subsequent readings will be the difference between the actual input value and the rel value...
Page 204
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual relative and math 8-3 remote rel programming rel commands table 8-1 summarizes rel commands. See section 18 , “ calculate2 ” subsystem, for addi- tional information. Rel programming example table 8-2 lists commands for setting up and enabling rel. These comman...
Page 205: Math Operations
8-4 relative and math 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual math operations built-in math functions the sourcemeter has built-in math functions to calculate the following: • power • offset compensated Ω • varistor alpha • voltage coefficient • percent deviation the power and percent deviation math...
Page 206
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual relative and math 8-5 this two-point measurement method is mathematically expressed as: offset-compensated Ω = ∆ v / ∆ i where ∆ v = v2 – v1 and ∆ i = i2 – i1. • v1 is the voltage measurement with the i-source set to a specific level. • v2 is the voltage measu...
Page 207
8-6 relative and math 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual percent deviation this calculation provides the percent deviation between the normal display reading and the user set reference value: where: x is the normal display measurement reading (v, i, or Ω ). Y is the reference value. When prompt...
Page 208
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual relative and math 8-7 • for percent deviation, you will be prompted to set the reference value. The following methods are available: • user-specified reference value — enter the desired reference value and press enter. • acquire reference value — with the outp...
Page 209
8-8 relative and math 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual math programming example table 8-4 summarizes the basic command sequence for voltage coefficient testing, which is a change in resistance of resistive elements with applied voltage. Although such changes in resistance with voltage are pre...
Page 210
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual relative and math 8-9 figure 8-2 connections for voltage coefficient tests user-defined math functions in addition to the pre-defined math functions, you can also define your own functions by using appropriate remote commands (user-defined math functions are n...
Page 211
8-10 relative and math 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual user-defined math function programming example table 8-6 shows the command sequence for a typical user-defined math function. This example defines a percent deviation math function. Table 8-5 commands for user-defined math functions comm...
Page 212
9 data store • data store overview — outlines basic data store (buffer) capabilities. • storing readings — discusses the procedure for storing readings in the internal buffer. • recalling readings — provides detailed information for recalling readings stored in the buffer. • buffer statistics — disc...
Page 213: Data Store Overview
9-2 data store 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual data store overview the sourcemeter has a data store (buffer) to store from 1 to 2500 source-measure read- ings. The instrument stores the source-measure readings that are displayed during the stor- age process. Each source-measure reading also ...
Page 214
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual data store 9-3 timestamp the first source-measure reading stored in the buffer (#0000) is timestamped at 0000000.000 seconds. Subsequent readings can be recalled in absolute or delta timestamp format. For the absolute format, the timestamp references readings ...
Page 215
9-4 data store 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual average the average mode displays the mean (average) of all measured readings stored in the buffer. The following equation is used to calculate mean: where: y is the average. X i is a stored reading. N is the number of stored readings. Standard ...
Page 216
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual data store 9-5 timestamp accuracy because of internal timing methods, the timestamp value is only approximate. The method in which the timestamp is implemented limits its use in time-critical applications. If accu- rate test timing is crucial, it is recommende...
Page 217: Remote Command Data Store
9-6 data store 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote command data store data store commands table 9-1 summarizes commands associated with data store operation. See section 18 , “ trace subsystem ” and “ calculate3 ,” for more detailed information on these commands. Table 9-1 data store comm...
Page 218
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual data store 9-7 data store programming example table 9-2 summarizes the commands for basic data store operation. These commands set up the sourcemeter as follows: • reading source: raw readings. • number of points: 10. • acquired data: buffer readings, mean (av...
Page 220
10 sweep operation • sweep types —describes the four basic sweep types: linear staircase, logarithmic staircase, custom, and source memory sweep. • configuring and running a sweep — discusses the procedure for setting up and performing sweeps including selecting and configuring a sweep, setting the ...
Page 221: Sweep Types
10-2 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep types sweeps allow you to program the instrument to step through specific voltage and current values and perform measurements at each source value. The four basic sweep types, which are described in the following paragraphs, include:...
Page 223
10-4 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual logarithmic staircase sweep this sweep is similar to the linear staircase sweep. The steps, however, are done on a loga- rithmic scale as shown in the example sweep in figure 10-2 . This is a 5-point log sweep from 1 to 10v. As with the st...
Page 224
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-5 the programmable parameters for a log sweep include the start and stop levels and the number of measurement points for the sweep. The specified start, stop, and point parame- ters determine the logarithmic step size for the sweep. Step siz...
Page 225
10-6 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual custom sweep examples the custom sweep can be configured to provide a 50% duty cycle pulse sweep. Figure 10-3 shows a pulse sweep that provides three 1v pulses on a 0v bias level. This pulse sweep is configured by specifying six points for...
Page 226
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-7 source memory sweep for a source memory sweep, up to 100 setup configurations can be saved in memory. When the sweep is performed, the setup at each memory point is recalled. This allows multiple functions and math expressions to be used i...
Page 227
10-8 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual saving source memory setups perform the following steps to save source memory setups: 1. Configure the sourcemeter for the desired source, measure, and/or math expres- sion operation. 2. Press menu to display the main menu: • select savese...
Page 228
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-9 table 10-2 source memory saved configurations mode remote command current integration rate resistance integration rate voltage integration rate concurrent functions enable functions disable functions manual/auto ohms offset-compensated ohm...
Page 229
10-10 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep branching when using a source memory sweep while performing limit tests, the normal sequence of sweep memory points can be changed. This is useful when, based on the results of an ini- tial test, a different set of tests are needed....
Page 230
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-11 caution must be used when branching since infinite memory loops can inadvertently be created. Also, a single source memory sweep will always sweep the number of points specified, regardless of how many branches were taken. Memory sweep br...
Page 231
10-12 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual diode test example limit testing and a source memory sweep can be used to test a diode. Three tests that are typically performed on a diode include the forward voltage test (v f ), reverse break- down voltage test (v r) and leakage curren...
Page 232
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-13 sml 001 — compliance test • limit 1 test – fail if in compliance, branch to source memory location 005 for “pass” condition. • summary – limit 1 test is configured such that if the diode is installed correctly in the test fixture, it will...
Page 233
10-14 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sml 007 — leakage current test • source +v, measure i. • limit 2 test – min/max limits for current reading. • summary – this test is the same as the test at memory location 004, except the source voltage is reversed to properly bias the d...
Page 234
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-15 • sweep count — use this menu item to specify how many sweeps to perform: – finite — use this option to enter a discrete number of sweeps to perform with the results stored in the data store buffer. The maximum number of finite sweeps tha...
Page 235
10-16 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual setting delay generally, the time duration spent at each step (or point) of a sweep consists of the source delay and the time it takes to perform the measurement (nplc setting). Note for the model 2430 pulse mode, source delay is not used...
Page 236
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-17 warning hazardous voltages (>30v rms) can appear on the selected input/ output lo terminal when performing fast pulse sweep operations. To eliminate this shock hazard, connect the lo terminal to earth ground. If using the front panel term...
Page 237
10-18 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual step 3: set delay. Set the source delay as follows: 1. Press config then source v or source i depending on the selected source function. 2. Select delay, then press enter. 3. Set the delay to the desired value, then press enter. 4. Press ...
Page 238
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-19 6. Again from the configure sweeps menu, choose source ranging, press enter, then select best fixed, auto range, or fixed as appropriate. 7. Press exit to return to normal display. Step 3: set delay. Set the source delay as follows: 1. Pr...
Page 239
10-20 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual 4. Use the displayed menu selections to enter the desired # points, individual point values (adjust points), and init (initial) value. 5. From the configure sweeps menu, select sweep count, press enter, then choose finite or infinite as d...
Page 240
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-21 performing a source memory sweep step 1: store setups in source memory. Store instrument setups in source memory as follows: 1. Configure the sourcemeter for various desired operating modes such as source, measure, delay, and/or math expr...
Page 241
10-22 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote sweep operation staircase sweep commands table 10-3 summarizes remote commands used for linear and log staircase sweep opera- tion. See section 18 , “ configure voltage and current sweeps ,” for more details on these commands. Stai...
Page 242
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-23 for the purposes of this test, assume the following basic sweep parameters: source function: current sense function: volts source mode: sweep start current: 1ma stop current: 10ma step current: 1ma voltage compliance: 1v source delay: 100...
Page 243
10-24 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual table 10-4 lists the command sequence for the diode programming example. Custom sweep commands table 10-5 summarizes remote commands used for custom sweep operation. See section 18 , “ configure list ,” for more details on these commands....
Page 244
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-25 custom sweep programming example as an example of custom sweep operation, assume a five-point sweep with the following parameters: source function: volts sense function: current voltage sweep mode: list (custom sweep) sweep voltage points...
Page 245
10-26 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source memory sweep programming example as an example of source memory sweep operation, assume a three-point sweep with the following operating modes: source memory location #1: source voltage, measure current, 10v source value source mem...
Page 246
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-27 sweep branching program example the code fragment below is a visual basic sweep branching subroutine. This example sets up source memory locations 1-3 as indicated in code comments. Location 100 is used as a dummy location. Failure at any...
Page 247
10-28 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual call outputcmd(intgpib, “:calc2:lim1:stat on”) 'set limit1 on call outputcmd(intgpib, “:calc2:lim1:comp:fail in”)'set fail mode to in compliance call outputcmd(intgpib, “:calc2:lim1:comp:sour2 8”)'set digital output pattern for compliance...
Page 248
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-29 call outputcmd(intgpib, “:calc2:lim2:stat on”) 'set limit2 on call outputcmd(intgpib, “:calc2:lim2:upp 3e-2”) 'set upper limit to 30ma call outputcmd(intgpib, “:calc2:lim2:low 2e-2”) 'set lower limit to 20ma call outputcmd(intgpib, “:calc...
Page 249
10-30 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual call outputcmd(intgpib, “:calc2:lim2:stat on”) 'set limit2 on call outputcmd(intgpib, “:calc2:lim2:upp 4e-2”) 'set upper limit to 40ma call outputcmd(intgpib, “:calc2:lim2:low 3e-3”) 'set lower limit to 30ma call outputcmd(intgpib, “:calc...
Page 250
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-31 call outputcmd(intgpib, “*rst”) 'restore gpib default conditions. Call outputcmd(intgpib, “:calc2:clim:bcon end”) call outputcmd(intgpib, “:sense:func:conc off”) 'turn off concurrent functions. Call outputcmd(intgpib, “trig:coun 3”) 'trig...
Page 251
10-32 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse mode sweeps (model 2430 only) when performing a sweep with the model 2430 in the pulse mode, each step or point of the sweep is made up of a pulse period. In general, a pulse period consists of the pulse width (output on-time) and t...
Page 252
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sweep operation 10-33 front panel pulse mode sweep procedure the procedure to perform a pulse mode sweep is summarized as follows: note the following procedure assumes that the model 2430 is already connected to the dut as explained in section 2 . Warning haza...
Page 253
10-34 sweep operation 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote pulse mode sweep operation the commands for pulse mode operation are provided in table 5-1 in section 5 , while the staircase sweep commands are provided in table 10-3 . Table 10-9 provides a typical remote command sequence for per...
Page 254
11 triggering • front panel trigger operation — discusses front panel triggering including the trigger model, various layers, event detection, delay, and device action, and front panel trigger configuration. • remote trigger operation — details the remote trigger model and summarizes trigger command...
Page 255
11-2 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual front panel trigger operation front panel trigger model note for the model 2430, the following discussion on the trigger model pertains explicitly to the dc mode of operation. The trigger model operates a little dif- ferently for the pulse mode...
Page 256
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-3 figure 11-1 front panel trigger model never arm-in event immediate gpib timer manual tlink ↓ stest ↑ stest ↑↓ stest once never idle bypass arm event detector ? Arm event detector once source event detector trigger delay source action delay even...
Page 257
11-4 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual arm layer event detector bypass — as shown in figure 11-1 , there is a bypass for the arm event detector. This bypass can only be used if tlink or stest is the selected arm-in event. The bypass serves to “jump-start” operation. With the event d...
Page 258
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-5 trigger layer the trigger layer uses three event detectors; one for each action (source, delay, and measure). Each of these event detectors can be turned on or off individually. Event detector bypass — as shown in figure 11-1 , there is a bypas...
Page 259
11-6 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual measure action — during this phase of the sdm cycle, the measurement process takes place. If the repeat filter is enabled, as shown in the blow-up drawing for measure action, the instrument samples the specified number of reading conversions to...
Page 260
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-7 bench defaults the bench defaults are listed as follows. They are also denoted in figure 11-1 by the “ ✛ ” symbol. • arm-in event = immediate • trigger-in source = immediate • arm count = 1 • trigger count = 1 • trigger delay = 0.0 sec • delay ...
Page 261
11-8 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual configuring triggering trigger configuration menu press config and then trig to display the trigger configuration menu, which is outlined below and shown in figure 11-2 . Note that bullets indicate the primary items of the menu, while dashes an...
Page 262
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-9 – arm out — use to configure the arm layer output trigger: / line — select the trigger link line for the output trigger: line #1, #2, #3, or #4. / events — enable (on) or disable (off) the arm layer output triggers. Trig layer exit on enables a...
Page 263
11-10 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual note for the model 2430 pulse mode, an output trigger can only occur after the mea- sure action. Therefore, the output trigger settings for the source and delay actions are ignored. – delay — specify the time delay (in seconds) for the trigger...
Page 264: Remote Trigger Operation
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-11 remote trigger operation note for the model 2430, the following discussion on the remote triggering pertains explicitly to the dc mode of operation. The trigger model operates a little dif- ferent for the pulse mode. These differences are cove...
Page 265
11-12 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 11-3 remote trigger model arm-in event immediate bus timer manual tlink nstest pstest bstest arm event detector source event detector trigger delay source action delay event detector delay** action measure event detector measure action ...
Page 266
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-13 while operating within the trigger model (arm indicator on), most commands will not be executed until the sourcemeter completes all of its programmed source-measure opera- tions and returns to the idle state. The ifc (interface clear), sdc (se...
Page 267
11-14 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual tlink — event detection occurs when an input trigger via the trigger link input line is received. See “trigger link,” page 11-19 , for more information. With tlink selected, you can loop around the arm event detector by setting the event detec...
Page 268
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-15 trigger delay a programmable delay is available before the source action. The trigger delay can be manually set from 0.00000 to 999.99990 seconds. Note that this delay is separate from the delay action of the sdm cycle. The delay action is dis...
Page 269
11-16 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual counters programmable counters are used to repeat operations within the trigger model layers. For example, if performing a 10-point sweep, the trigger counter would be set to 10 (trigger:count 10). Operation will stay in the trigger layer unti...
Page 270
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-17 gpib defaults the gpib defaults are listed as follows. They are also denoted in figure 11-3 by the “ ✛ ” symbol. • arm-in event = immediate • trigger-in source = immediate • arm count = 1 • trigger count = 1 • trigger delay = 0.0 sec • delay a...
Page 271
11-18 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote trigger commands table 11-1 summarizes remote trigger commands. These commands are covered in more detail in section 18 except for *trg, a common command covered in section 16 . Table 11-1 remote trigger commands command description :in...
Page 272: Trigger Link
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-19 trigger link input and output triggers are received and sent via the rear panel trigger link connec- tor. The trigger link has four lines. At the factory, line #2 is selected for output triggers, and line #1 is selected for input triggers. The...
Page 273: Triggering Examples
11-20 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual output trigger specifications the sourcemeter can be programmed to output a trigger after various trigger model actions. (see “trigger models,” page 11-30 .) the output trigger provides a ttl- compatible output pulse that can be used to trigge...
Page 274
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-21 to program the sourcemeter for the trigger parameters above, perform the following steps: 1. Press config then trig. 2. Select arm-layer, then press enter. 3. Choose arm-in, then press enter. 4. Select manual, then press enter. 5. Select count...
Page 275
11-22 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 11-8 trigger model for front panel trigger example 0.1 sec trigger delay idle source action delay action measure action manual arm-in event arm count = 2? Trigger count = 10? Arm event detector idle yes no yes no arm layer trigger layer...
Page 276
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-23 external trigger example in a simple test system, you may want to close a switching channel and then measure the resistance of the dut connected to that channel. This test system is shown in figure 11-9 , which uses a sourcemeter to measure 10...
Page 277
11-24 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual trigger link connections the trigger link connections for this test system are shown in figure 11-10 . Trigger link of the sourcemeter is connected to trigger link (in or out) of the switching mainframe. Note that with the default trigger sett...
Page 278
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-25 instrument configurations for this example, the sourcemeter and switching mainframe are configured as shown below. Sourcemeter setup 1. Restore bench defaults: press the menu key, select savesetup, then press the enter key. From the savesetup ...
Page 279
11-26 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual switching mainframe setup 1. Restore bench defaults: press the menu key, select savesetup, and then press enter. From the savesetup menu, select reset, then press enter. Press enter to confirm the action. Press enter to return to the setup men...
Page 280
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-27 figure 11-11 operation model for triggering example a) turning the sourcemeter output on places it at point a in the flowchart, where it waits for an external trigger. B) pressing step takes the model 7001/2 out of the idle state and places op...
Page 281
11-28 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual the trigger applied to the model 7001/2 from the sourcemeter closes the next channel in the scan, which then triggers the sourcemeter to measure that dut. This process contin- ues until all 10 channels are scanned and measured. Remote trigger ...
Page 282
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-29 figure 11-12 trigger model for remote trigger example 0.1 sec trigger delay idle source action delay action sense action *trg arm-in event arm count = 2? Trigger count = 10? Arm event detector idle yes no yes no arm layer trigger layer tlink t...
Page 283
11-30 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pulse mode triggering (model 2430) triggering for the model 2430 is similar to triggering for the dc mode. However, in order to accomplish fast pulse output, triggering is simplified for the pulse mode. The following information covers the tri...
Page 284
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-31 figure 11-13 2430 pulse mode trigger model (front panel operation) never arm-in event immediate gpib timer manual tlink ⇓ stest ⇑⇓ stest ⇑⇓ stest once never idle bypass arm event detector ? Arm event detector once source event detector source ...
Page 285
11-32 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 11-14 2430 pulse mode trigger model (remote operation) arm-in event immediate bus timer manual tlink nstest pstest bstest arm event detector source event detector no yes idle another arm ? Another trigger ? Yes no arm layer trigger laye...
Page 286
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual triggering 11-33 idle as with dc mode front panel operation, the sourcemeter is taken out of idle by pressing the on/off output key. For dc mode remote operation, the output must be on and then an initiate command must be sent to take the instrument out of idl...
Page 287
11-34 triggering 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual output triggers all three output triggers are available in the trigger layer for the pulse mode. If enabled, the output triggers occur where indicated in the trigger model. Invalid trigger settings front panel operation for front panel operati...
Page 288
12 limit testing • types of limits — discusses the three types of limits: compliance, coarse limits, and fine limits. Also summarizes the two operating modes: grading and sorting. • operation overview — covers binning control and pass/fail condition for the grading and sorting modes. • binning syste...
Page 289: Types of Limits
12-2 limit testing 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual types of limits as shown in figure 12-1 , there are 11 limit tests that can be performed on a dut. These limits include: • limit 1: compliance test • limit 2: course limits • limits 3, 5-12: fine limits note limit 4 is reserved for the conta...
Page 290
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit testing 12-3 pass/fail information pass/fail information for limit tests can be obtained as follows: • a pass or fail indication on the front panel display. • by programming the unit to output specific pass/fail bit patterns on the digital i/o port, whic...
Page 291
12-4 limit testing 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit 2, limit 3, and limit 5-12 tests these software (s/w) tests are used to determine if a dut is within specified high and low limits. Typically, the limit 2 test is used to test for coarse tolerance limits, and the limit 3 and limit 5-12...
Page 292: Operation Overview
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit testing 12-5 operation overview grading mode grading mode limits operation is detailed by the flowchart in figure 12-2 . A test is only performed if it is enabled. If disabled, operation proceeds to the next test. The following assumes the first three li...
Page 293
12-6 limit testing 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 12-2 grading mode limit testing perform limit 1 test ? Yes no pass ? No yes display “fail” perform limit 2 test ? Yes no pass ? No yes perform limit 3, 5-12 tests ? Yes no pass ? No yes another test cycle ? No yes start turn output on...
Page 294
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit testing 12-7 immediate binning — use immediate binning when you want to stop all testing after the first failure occurs. Any pending tests will be cancelled, and the dut will be placed in the bin assigned to that test failure. If no failures occur, all e...
Page 295
12-8 limit testing 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual pass condition for this discussion, assume that all grading mode limit tests pass. After the three limit tests pass, the “pass” message is displayed, and operation drops down to the binning control decision block. (note that the pass conditi...
Page 296
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit testing 12-9 sorting mode sorting mode limits operation is detailed by the flowchart in figure 12-5 . A test is only performed if it is enabled. If disabled, operation proceeds to the next test. The following assumes the digital output of the sourcemeter...
Page 297
12-10 limit testing 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 12-5 sorting mode limit testing perform limit 1 test ? Yes no pass ? No yes display “fail” perform limit 2 test ? Yes no pass ? No yes perform limit 3, 5-12 tests ? Yes no pass ? No yes start turn output on and press limit key. Outpu...
Page 298: Binning Systems
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit testing 12-11 binning systems the sourcemeter can be used with a component handler to perform binning operations on dut packages. With this system, you can test single-element devices (i.E., resistor). Add- ing a scanner to the system allows binning oper...
Page 299
12-12 limit testing 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual digital output lines the four output lines output a specific bit pattern based on the pass/fail results of the vari- ous limit tests. (see “types of limits,” page 12-2 .) in the 3-bit output mode, line 4 can also be used either as an end-of...
Page 300
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit testing 12-13 category pulse component handler when using this type of handler, the sourcemeter pulses one of the four handler lines when a pass or fail condition occurs. The handler then places the dut in the bin assigned to that pulsed line. When inter...
Page 301
12-14 limit testing 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual basic binning systems two basic binning systems are shown in figure 12-7 and figure 12-8 . Both systems require a handler to physically place the device packages in the appropriate bins. The han- dler is controlled by the sourcemeter via th...
Page 302
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit testing 12-15 multiple-element device binning figure 12-8 shows a basic binning system to test three-element resistor networks. Note that this system requires a scanner card that is installed in a switching mainframe. Scanner card switching is controlled...
Page 303
12-16 limit testing 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 12-8 binning system multiple-element devices switching mainframe handler trigger link scanner card ch 1 ch 2 ch 3 dig in multi-element device package r1 r2 r3 in/out hi lo trigger link* dig i/o sourcemeter *trigger layer configured t...
Page 304
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit testing 12-17 digital output clear pattern after every binning operation, the digital output needs to be reset to a clear pattern, which serves as a no action condition for the component handler. The sourcemeter can be programmed to automatically clear t...
Page 305
12-18 limit testing 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual auto-clear timing the following timing diagram example ( figure 12-9 ) and discussion explain the relation- ship between the digital output lines for auto-clear. Figure 12-9 digital output auto-clear timing example initially, the four digit...
Page 306
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit testing 12-19 configuring and performing limit tests configuring limit tests press config and then limit to display the config limits menu. The limits con- figuration menu is structured shown below and in figure 12-10 . Note that bullets indicate the pri...
Page 307
12-20 limit testing 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual • h/w limits — use this menu item to control and set the fail mode for the limit 1 (compliance) test: – control — use to enable or disable the test. – fail mode — use to select the fail mode for limit 1 test. With in selected, the test will...
Page 308
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit testing 12-21 figure 12-10 limits configuration menu tree performing front panel limit tests perform the basic steps below to run limit tests from the front panel. See “remote limit testing,” page 12-23 , for remote commands and a programming example. St...
Page 309
12-22 limit testing 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual step 3: configure limit tests. Select and configure the following limit tests parameters as explained in “configuring limit tests,” page 12-19 : • use digout to configure the digital i/o port for size, mode, and auto clear. • set your h/w l...
Page 310: Remote Limit Testing
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit testing 12-23 remote limit testing limit commands table 12-1 summarizes remote commands to control limit testing parameters, while table 12-2 summarizes commands to control the digital i/o port bit parameters for limit testing. See section 18 , “ calcula...
Page 311
12-24 limit testing 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit test programming example diode breakdown voltage test is an example that readily lends itself to pass/fail analysis. This test verifies the reverse and often the forward voltage at which the device begins to show a large deviation in ...
Page 312
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual limit testing 12-25 test parameters for this test include: • source function: current • sense function: voltage • source current: 100ma • source delay: 100ms • limit 2 upper value: 0.85v • limit 2 lower value: 0.75v • limit 3 upper value: 0.82v • limit 3 lower...
Page 313
12-26 limit testing 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual table 12-3 limits test programming example command description *rst :sens:func:conc off :sour:func curr :sens:func 'volt:dc' :sour:curr:trig 0.1 :sour:del 0.1 :calc2:feed volt :calc2:lim2:upp 0.85 :calc2:lim2:low 0.75 :calc2:lim3:upp 0.82 :...
Page 314
13 digital i/o port, safety interlock, and output configuration • digital i/o port — discusses the various input/output lines on the digital i/o port as well as the +5v line that can be used to power external logic circuits. • safety interlock — describes how to use the digital i/o port as a safety ...
Page 315: Digital I/o Port
13-2 digital i/o port, safety interlock, and output configuration 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual digital i/o port the sourcemeter has a digital input/output port that can be used to control external digital circuitry, such as a handler that is used to perform binning operations when testing...
Page 316
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual digital i/o port, safety interlock, and output configuration 13-3 sot line the input line (sot) is used by the handler to start limit testing. With the ↓ stest arm event selected ( section 11 , “ configuring triggering ”), the handler must pulse sot low in ord...
Page 317
13-4 digital i/o port, safety interlock, and output configuration 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source operation figure 13-3 shows the basic output configuration for source operation. In this case, the external relay coil is connected between the digital output line (pins 1 to 4) and groun...
Page 318: Safety Interlock
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual digital i/o port, safety interlock, and output configuration 13-5 remote digital output control use the :source2:ttl command to control the digital output line logic levels, where is the decimal value shown in table 13-1 . For example, send the following comma...
Page 319
13-6 digital i/o port, safety interlock, and output configuration 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual when the interlock is enabled (see “front panel output configuration,” page 13-7 ), the out- put of the sourcemeter cannot be turned on unless the interlock line is pulled low through a switch t...
Page 320
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual digital i/o port, safety interlock, and output configuration 13-7 front panel output configuration the output is configured from the configure output menu and is structured as fol- lows. Note that bullets indicate the primary items of the sweep menu, while das...
Page 321
13-8 digital i/o port, safety interlock, and output configuration 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 13-5 output configuration menu tree output-off states note for the model 2430 pulse mode, output-off is always set to normal. High impedance with this output-off state, the output relay o...
Page 322
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual digital i/o port, safety interlock, and output configuration 13-9 zero when in this output-off state, the zer message is displayed (instead of off), and the sourcemeter is configured as follows: when the v-source is the selected source: • the programmed v-sour...
Page 323
13-10 digital i/o port, safety interlock, and output configuration 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual note when changing the output-off state with the output off, the selected output-off state will be entered immediately. On power-up, the sourcemeter will momentarily be in the high impedance ou...
Page 324: Remote Output Configuration
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual digital i/o port, safety interlock, and output configuration 13-11 remote output configuration output configuration commands table 13-2 summarizes output configuration commands. These commands include those to enable and disable the interlock as well as comman...
Page 325
13-12 digital i/o port, safety interlock, and output configuration 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual output configuration programming example table 13-3 lists the command sequence for output configuration. These commands set up the sourcemeter as follows: • interlock: enabled • output-off mode...
Page 326
14 remote operations • differences: remote vs. Local operation — summarizes remote operation enhancements and local-to-remote and remote-to-local transitions. • selecting an interface — describes how to select between the gpib and rs-232 interfaces. • gpib operation — covers gpib bus standards, bus ...
Page 327
14-2 remote operations 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual differences: remote vs. Local operation operation enhancements (remote operation) there are some source-measure operations you can do over the ieee-488 bus and rs-232 interface that you cannot do from the front panel; these are summarize...
Page 328: Selecting An Interface
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote operations 14-3 remote-to-local transition when changing from remote to local operation, the following actions occur. • the sourcemeter stops performing source-measure operations and returns to the idle state (arm annunciator off). • all sweep operation...
Page 329: Gpib Operation
14-4 remote operations 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual gpib operation this section contains information about gpib standards, bus connections, and primary address selection. Gpib standards the gpib is the ieee-488 instrumentation data bus with hardware and programming standards originally ad...
Page 330
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote operations 14-5 to allow many parallel connections to one instrument, stack the connectors. Two screws are located on each connector to ensure that connections remain secure. Present standards call for metric threads, which are identified with dark-colo...
Page 331
14-6 remote operations 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual to connect the sourcemeter to the ieee-488 bus, follow these steps: 1. Line up the cable connector with the connector located on the rear panel. The con- nector is designed so it will fit only one way. Figure 14-3 shows the location of t...
Page 332: General Bus Commands
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote operations 14-7 general bus commands general commands are those commands, such as dcl, that have the same general mean- ing regardless of the instrument. Table 14-1 lists the general bus commands. Ren (remote enable) the remote enable command is sent to...
Page 333
14-8 remote operations 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual with auto output off enabled (:source1:clear:auto on), the output will remain on if operation is terminated before the output has a chance to automatically turn off. To send the ifc command, the controller need only set the ifc line true...
Page 334: Front Panel Gpib Operation
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote operations 14-9 note with :arm:source bus selected and an :initiate command sent, do not send any commands (except get, dcl, sdc, ifc, *trg, and :abort) while per- forming source-measure operations (arm annunciator on). If you do, erratic operation will...
Page 335
14-10 remote operations 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual talk this indicator is on when the instrument is in the talker active state. Place the unit in the talk state by addressing it to talk with the correct mta (my talk address) command. Talk is off when the unit is in the talker idle state...
Page 336: Programming Syntax
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote operations 14-11 programming syntax the information in this section covers syntax for both common commands and scpi com- mands. For information not covered here, see the ieee-488.2 and scpi standards. See section 16 and section 18 for more details on co...
Page 337
14-12 remote operations 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual name parameter — select a parameter name from a listed group. Example: = never = next :trace:feed:control next numeric representation format — this parameter is a number that can be expressed as an integer (e.G., 8), a real number (e.G....
Page 338
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote operations 14-13 angle brackets — angle brackets () are used to denote a parameter type. Do not include the brackets in the program message. For example: :output the indicates a boolean-type parameter is required. Therefore, to enable the selected sourc...
Page 339
14-14 remote operations 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual long-form and short-form versions a scpi command word can be sent in its long-form or short-form version. The command subsystem tables in section 18 provide the long-form version. However, the short-form version is indicated by upper ca...
Page 340
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote operations 14-15 program messages a program message is made up of one or more command words sent by the computer to the instrument. Each common command is a three letter acronym preceded by an asterisk (*). Scpi commands are categorized in the :status s...
Page 341
14-16 remote operations 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual after the first command (:enab) is executed, the path pointer is at the third command level in the structure. Since :enab? Is also on the third level, it can be typed in without repeating the entire path name. Notice that the leading co...
Page 342
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote operations 14-17 response messages a response message is the message sent by the instrument to the computer in response to a query command program message. Sending a response message after sending a query command, the response message is placed in the o...
Page 343: Rs-232 Interface Operation
14-18 remote operations 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual rs-232 interface operation note the programmable aspects of rs-232 operation (baud rate, data bits, parity, and terminator are configured from the communication option of the main menu. (see section 1 , “ main menu .”) sending and recei...
Page 344
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote operations 14-19 terminator the sourcemeter can be configured to terminate each program message that it transmits to the controller with any of the following combinations of and : carriage return carriage return and line feed line feed line feed and car...
Page 345
14-20 remote operations 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 14-4 rs-232 interface connector table 14-3 provides pinout identification for the 9-pin (db-9) or 25-pin (db-25) serial port connector on the computer (pc). Table 14-2 rs-232 connector pinout pin number description 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ...
Page 346
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote operations 14-21 error messages see appendix b for rs-232 error messages. Programming example the following quickbasic 4.5 programming example will control the sourcemeter via the rs-232 com2 port. Place the sourcemeter into the rs-232 mode from the fro...
Page 348
15 status structure • overview — provides an operational overview of the status structure for the sourcemeter. • clearing registers and queues — covers the actions that clear (reset) registers and queues. • programming and reading registers — explains how to program enable registers and read any reg...
Page 349: Overview
15-2 status structure 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual overview the sourcemeter provides a series of status registers and queues allowing the operator to monitor and manipulate the various instrument events. The status structure is shown in figure 15-1 . The heart of the status structure is t...
Page 350
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status structure 15-3 figure 15-1 sourcemeter status register structure 3 5 6 cal 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 condition register (always zero) 3 5 6 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 event register 3 5 6 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 event enable register & & & & & & & & & & & & & & & & logi...
Page 351
15-4 status structure 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual clearing registers and queues when the sourcemeter is turned on, the bits of all registers in the status structure are cleared (reset to 0), and the two queues are empty. Commands to reset the event and event enable registers, and the err...
Page 352
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status structure 15-5 programming and reading registers programming enable registers the only registers that can be programmed by the user are the enable registers. All other registers in the status structure are read-only registers. The following explains how...
Page 353
15-6 status structure 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual the (non-decimal numeric) parameter type is used to send non-decimal values. These values require a header (#b, #h or #q) to identify the data format being sent. The letter in the header can be upper or lower case. The (numeric representa...
Page 354
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status structure 15-7 status byte and service request (srq) service request is controlled by two 8-bit registers; the status byte register and the ser- vice request enable register. Figure 15-3 shows the structure of these registers. Figure 15-3 status byte an...
Page 355
15-8 status structure 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status byte register the summary messages from the status registers and queues are used to set or clear the appropriate bits (b0, b2, b3, b4, b5, and b7) of the status byte register. These summary bits do not latch, and their states (0 or...
Page 356
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status structure 15-9 service request enable register the generation of a service request is controlled by the service request enable register. This register is programmed by you and is used to enable or disable the setting of bit b6 (rqs/mss) by the status su...
Page 357
15-10 status structure 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status byte and service request commands the commands to program and read the status byte register and service request enable register are listed in table 15-3 . For details on programming and reading registers, see “programming enable r...
Page 358: Status Register Sets
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status structure 15-11 status register sets as shown in figure 15-1 , there are four status register sets in the status structure of the sourcemeter; standard event status, operation event status, measurement event status, and questionable event status. Note s...
Page 359
15-12 status structure 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure 15-4 standard event status operation event register the used bits of the operation event register (shown in figure 15-5 ) are described as follows: • bit b0, calibrating (cal) — set bit indicates that the sourcemeter is calibratin...
Page 360
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status structure 15-13 figure 15-5 operation event status measurement event register the used bits of the measurement event register (shown in figure 15-6 ) are described as follows: • bit b0, limit 1 fail (l1) — set bit indicates that the limit 1 test has fai...
Page 361
15-14 status structure 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual • bit b7, reading overflow (rof) — set bit indicates that the volts or amps read- ing exceeds the selected measurement range of the sourcemeter. • bit b8, buffer available (bav) — set bit indicates that there are at least two read- ings ...
Page 362
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status structure 15-15 questionable event register the used bits of the questionable event register (shown in figure 15-7 ) are described as follows: • bits b0 through b7 — not used. • bit b8, calibration summary (cal) — set bit indicates that an invalid calib...
Page 363
15-16 status structure 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual condition registers as figure 15-1 shows, each status register set (except the standard event register set) has a condition register. A condition register is a real-time, read-only register that constantly updates to reflect the present ...
Page 364
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status structure 15-17 event enable registers as figure 15-1 shows, each status register set has an enable register. Each event register bit is logically anded (&) to a corresponding enable bit of an enable register. Therefore, when an event bit is set and the...
Page 365: Queues
15-18 status structure 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual programming example — program and read register set the command sequence in table 15-8 programs and reads the measurement register set. Registers are read using the binary format (which directly indicates which bits are set). The command...
Page 366
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status structure 15-19 error queue the error queue holds error and status messages. When an error or status event occurs, a message that defines the error/status is placed in the error queue. When a message is placed in the error queue, the error available (ea...
Page 367
15-20 status structure 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual programming example — read error queue the following command reads the error queue: stat:que? Table 15-9 error queue commands command description default status :queue [:next]? :enable :enable? :disable :disable? :clear system :error [:n...
Page 368
16 common commands • command summary — lists the ieee-488.2 common commands used by the sourcemeter. • command reference — provides a detailed reference for all common commands except for those associated with the status structure, discussed in section 15 . Artisan technology group - quality instrum...
Page 369: Command Summary
16-2 common commands 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual command summary common commands (summarized in table 16-1 ) are device commands that are common to all devices on the bus. These commands are designated and defined by the ieee-488.2 standard. Most of these commands are described in detail...
Page 370: Command Reference
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual common commands 16-3 command reference *idn? — identification query the identification code includes the manufacturer, model number, serial number, and firm- ware revision levels and is sent in the following format: keithley instruments inc., model nnnn, xxxxx...
Page 371
16-4 common commands 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual *opc programming example the command sequence in table 16-2 will perform 10 measurements. After the measure- ments are completed (in approximately 10 seconds), an ascii “1” will be placed in the output queue and displayed on the computer c...
Page 372
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual common commands 16-5 *sav, *rcl programming example table 16-3 summarizes the basic command sequence for saving and recalling a setup. The present setup is stored in memory location 2, gpib defaults are restored, and the memory location 2 setup is recalled. *r...
Page 373
16-6 common commands 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual *trg programming example the command sequence in table 16-4 configures the sourcemeter to be controlled by bus triggers. The last command, which sends a bus trigger, triggers one measurement. Each subsequent bus trigger will also trigger a...
Page 374
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual common commands 16-7 *wai — wait-to-continue effectively, the *wai command is a no-op (no operation) for the sourcemeter and thus, does not need to be used. Two types of device commands exist: • sequential commands — a command whose operations are allowed to f...
Page 376
17 scpi signal oriented measurement commands • command summary — summarizes those commands used to configure and acquire readings. • configuring measurement function — provides detailed information on com- mands to configure the measurement function. • acquiring readings — describes commands to acqu...
Page 377: Command Summary
17-2 scpi signal oriented measurement commands 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual command summary the signal oriented measurement commands are used to acquire readings. You can use these high-level instructions to control the measurement process. These commands are summarized in table 17-1 . Co...
Page 378: Acquiring Readings
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi signal oriented measurement commands 17-3 • the count values of the trigger model are set to one. • the delay of the trigger model is set to zero. • all math calculations are disabled. • buffer operation is disabled. • autozero is enabled. • the source ou...
Page 379
17-4 scpi signal oriented measurement commands 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual if the sourcemeter is instead programmed to source v and measure v, the voltage reading will be the v-measure reading (not the programmed v-source value). Both current and resistance readings will be nans (current...
Page 380
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi signal oriented measurement commands 17-5 note for the model 2430 pulse mode, the output will turn on when the :read? Com- mand is sent. See appendix c , “ data flow ,” for a detailed explanation on how data flows through the various operation blocks of t...
Page 383: Reference Tables
18-2 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual reference tables table 18-1 through table 18-11 summarize the commands for each scpi subsystem. The following list includes the scpi subsystem, table number where each command is summa- rized, and the page number where detailed refe...
Page 384
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-3 table 18-1 calculate command summary command description default parameter scpi source memory :calculate[1] subsystem to control calc1: ✓ :math path to configure and control math expressions: ✓ [:expression] define math expression u...
Page 388
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-7 :calculate2 :clear clear test results: [:immediate] clear latest limit test result and reset digital i/o port back to :source2:ttl settings. :auto enable or disable clearing of test results when :initiate command is sent. On :auto? ...
Page 389
18-8 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual table 18-2 display command summary command description default parameter scpi :display :enable :enable? :cndisplay [:window[1]] :text :data :data? :state :state? :data? :attributes? :window2 :text :data :data? :state :state? :data? ...
Page 390
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-9 table 18-3 format command summary command description default parameter scpi :format :sregister :sregister? [:data] [] [:data]? :border :border? :elements [:sense[1]] [:sense[1]]? :calculate :calculate? :source2 :source2? Select dat...
Page 391
18-10 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual table 18-5 route command summary command description default parameter scpi source memory :route :terminals :terminals? Select in/out terminals: (front or rear). Query in/out terminals. Front ✓ ✓ table 18-6 sense command summary co...
Page 393
18-12 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual [:sense[1]] :voltage[:dc] :protection [:level]? Query voltage compliance limit. ✓ :tripped? In voltage compliance?: 1 (yes), 0 (no). ✓ :rsynchronize enable or disable measure and compliance range synchronization. Off :rsynchronize?...
Page 394
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-13 table 18-7 source command summary command description default parameter scpi source memory [:source[1]] path to control sourcing: ✓ :clear path to clear source: [:immediate] turn selected source off. :auto enable or disable auto cl...
Page 395
18-14 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual [:source[1]] :current [:level] :triggered set level when triggered: ✓ [:amplitude] specify current level. 1 0 ✓ [:amplitude]? Query current level. ✓ :sfactor set current scaling factor (-999.9999e+18 to +999.999e+18). 1.0 ✓ 2 :stat...
Page 396
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-15 [:source[1]] :voltage [:level] set v-source level (in volts): ✓ [:immediate] set specified level immediately: ✓ [:amplitude] specify voltage level. 1 0 ✓ ✓ 3 [:amplitude]? Query voltage level. ✓ :triggered set specified level when ...
Page 397
18-16 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual [:source[1]] :sweep configure sweep source mode: ✓ :spacing select sweep spacing type (linear or logarithmic). Linear ✓ :spacing? Query sweep spacing. ✓ :points specify number of sweep points (2 to 2500). 2500 ✓ :points? Query numb...
Page 398
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-17 :source2 path to control digital output lines: :bsize set digital i/o bit size (3 or 4). 1 4 :bsize? Query digital i/o bit size. :ttl [:level] [:default] , specify digital output pattern. 2 15 [:level] [:default]? Query default out...
Page 399
18-18 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual table 18-8 status command summary command description default parameter scpi :status :measurement [:event]? :enable or :enable? :condition? :operation [:event]? :enable or :enable? :condition? :questionable [:event]? :enable or :en...
Page 400
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-19 table 18-9 system command summary command description default parameter scpi source memory :system :preset return to :system:preset defaults. ✓ :posetup select power-on setup (rst, preset or sav 0-4). :posetup? Query power-on setup...
Page 401
18-20 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual :system :azero control auto zero and nplc caching. ✓ [:state] control auto zero (off = disabled; on = enabled; once = force immediate update of auto zero.) on ✓ [:state]? Query auto zero state. ✓ :caching control nplc caching. [:st...
Page 403
18-22 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual table 18-11 trigger command summary command description default parameter scpi :initiate[:immediate] :abort :arm [:sequence[1]] [:layer[1]] :count :count? :source :source? :timer :timer? [:tconfigure] :direction :direction? [:async...
Page 404
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-23 command description default parameter scpi :trigger [:sequence[1]] [:tconfigure] :direction :direction [:asynchronous] :iline :iline? :input :input? :oline :oline? :output :output? Enable (source) or disable (acceptor) bypass. Quer...
Page 405: Calculate Subsystems
18-24 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual calculate subsystems there are three calculate subsystems. The calc1 subsystem is used for math expres- sions, calc2 is used for limit tests, and calc3 provides statistical data on readings stored in the buffer. The commands in the...
Page 406
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-25 description this command can be used to select a math expression that already exists (built-in or user-defined). Math expression names that already exist can be listed using the :catalog? Command. The actual math expression can be ...
Page 407
18-26 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual +814 “mismatched brackets” — improper use of brackets for vectored math expression indices. For example, calc1:math:expr (volt[0*curr[0]) generates this error. +815 “too many parenthesis” — too many closed parentheses were detected...
Page 408
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-27 offset compensated ohms: *rst :sens:func:off:all :sens:func “volt”,“curr” :sour:func volt or curr if :sour:func volt then :sour:volt:star ; stop ; mode swe if :sour:func curr then :sour:curr:star ; stop ; mode swe :sour:swe:poin 2 ...
Page 409
18-28 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual varistor alpha *rst :sens:func:off:all :sens:func:on “volt”,“curr” :sour:func:mode curr :sour:curr:star ;stop ;mode swe :sour:curr:step :trig:coun 2 :calc:math:expr:name “varalpha” :calc:stat on :output on :init :calc:data? Percent...
Page 410
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-29 :delete[:selected] :calculate[1]:math[:expression]:delete[:selected] delete user-defined math expression parameters = “user-name” name of user-defined math expression description this command is used to remove (delete) the specifie...
Page 411
18-30 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual define math expression [:expression] or [:define] :calculate[1]:math[:expression] define math formula :calculate[1]:math[:expression][:define] define math formula parameters and standard math operator symbols. See “description” for...
Page 412
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-31 the readings used for the calculation depend on how the sourcemeter is configured. If configured to source v measure i, the voltage reading for the calculation will be the source value, and the current reading will be the current m...
Page 413
18-32 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual arrays will be created. The calculation will now yield two results, one for each array. The first result, as before, is based on the fourth and 10th readings of the first array. The second result is based on the 14th and 20th readi...
Page 414
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-33 enable and read math expression result :state :calculate[1]:state control calc1 parameters = 0 or off disable calc1 calculation 1 or on enable calc1 calculation query :state? Query state (on or off) of calc1 description this comman...
Page 415: Calculate2
18-34 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual :latest? :calculate[1]:data:latest? Read latest calc1 result description this command works exactly like calc1:data? Except that it returns only the latest calc1 result. Calculate2 the following commands are used to configure and c...
Page 416
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-35 null feed reading offset :calculate2:null:offset specify null offset (rel) for feed parameters = -9.999999e20 to specify null offset value 9.999999e20 query :offset? Query null offset value description this command lets you establi...
Page 417
18-36 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual note see appendix c , “ data flow ,” for a detailed explanation on how data flows through the various operation blocks of the sourcemeter. It clarifies the type of readings that are acquired by the various commands to read data. La...
Page 418
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-37 description these commands are used to set the upper and lower limits for limit 2, limit 3, and limit 5 through limit 12 tests. The actual limit depends on which measurement function is currently selected. For example, a limit valu...
Page 419
18-38 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual use the following table to determine the parameter value for the desired decimal digital output pattern. For non-decimal parameters, convert the decimal value to its binary, octal, or hexadecimal equivalent. The sourcemeter can be ...
Page 421
18-40 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual fail? :calculate2:limit[1]:fail? Read limit 1 test result :calculate2:limitx:fail? Read limit x test result (x = 2, 3, 5-12) description these commands are used to read the results of limit 1, limit 2, limit 3, and limit 5 to limit...
Page 422
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-41 description this command is used to define the 3-bit or 4-bit output pattern for the digital i/o port when there are no failures. Note that the output value can be specified in binary, octal, decimal, or hexadecimal format. Use the...
Page 424
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-43 bcontrol :calculate2:climits:bcontrol control digital i/o port pass/fail update parameters = immediate update output when first failure occurs end update output after sweep is completed query :bcontrol? Query when digital output wi...
Page 425: Calculate3
18-44 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual clear test results [:immediate] :calculate2:climits:clear[:immediate] clears test results and resets digital i/o port description this command clears the test results (pass or fail) of the limit tests and resets the output lines of...
Page 426
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-45 acquire statistic :data? :calculate3:data? Read calc3 result description this query command is used to perform the selected statistic operation and read the result(s). The result(s) is always returned in ascii format. If the buffer...
Page 427: Display Subsystem
18-46 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual display subsystem the display subsystem controls the display of the sourcemeter and is summarized in table 18-2 . Control display digits :display:digits set display resolution parameters = 4 3.5 digit resolution 5 4.5 digit resolut...
Page 428
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-47 attributes? :display[:window[1]]:attributes? Query attributes; top display :display:window2:attributes? Query attributes; bottom display description this query command is used to determine which characters on the dis- play are blin...
Page 429
18-48 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual define :text messages data :display[:window[1]]:text:data define message; top display :display:window2:text:data define message; bottom display parameters = ascii characters for message types: string ‘aa...A’ or “aa...A” indefinite...
Page 430: Format Subsystem
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-49 format subsystem the commands for this subsystem are used to select the data format for transferring instru- ment readings over the bus. These commands are summarized in table 18-3 . Data format [:data] [,length] :format[:data] [,]...
Page 431
18-50 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ieee-754 single precision format real,32, or sreal will select the binary ieee-754 single precision data format. Figure 18-2 shows the normal byte order format for each data element. For example, if three valid elements are specifi...
Page 432
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-51 data elements elements :format:elements [sense[1]] specify data elements for data string parameters = voltage includes voltage reading current includes current reading resistance includes resistance reading time includes timestamp ...
Page 433
18-52 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual timestamp is reset (:system:time:reset). The timestamp for each reading sent over the bus is referenced, in seconds, to the start time. After 99,999.999 seconds, the timer resets to zero and starts over. Note timestamp values are a...
Page 434
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-53 sorting mode status bit values: result 1 bit #: 21 20 19 9 8 meas. Event status 2 limit 1 and 4 pass and 2, 3, and 5-12 disabled 0 0 0 0 0 bit 5 (lp) limit test 1 fail 0 0 0 0 1 bit 0 (l1) limit test 2 pass 0 0 0 1 0 bit 5 (lp) lim...
Page 435
18-54 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual grading mode status bit values: result 1 bit #: 21 20 19 9 8 meas. Event status 2 all limits pass 0 0 0 0 0 bit 5 (lp) limit test 1 fail 0 0 0 0 1 bit 0 (l1) hi limit test 2 fail 1 0 0 1 0 bit 2 (hl2) lo limit test 2 fail 0 0 0 1 0...
Page 436
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-55 example reading string the example ascii reading string shown in figure 18-1 shows a mea- surement of a 10k Ω resistor, with the sourcemeter configured to source i measure v. The voltage reading is the voltage measurement (1.000236...
Page 437
18-56 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual byte order border :format:border specify binary byte order parameters = normal normal byte order for binary formats swapped reverse byte order for binary formats query :border? Query byte order description this command is used to c...
Page 438: Output Subsystem
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-57 when a status register is queried, the response message is a value that indicates which bits in the register are set. For example, if bits b5, b4, b2, b1, and b0 of a register are set (110111), the following values will be returned...
Page 439
18-58 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual interlock control state :output[1]:interlock:state control hardware interlock parameters = 0 or off disable interlock 1 or on enable interlock query :state? Query state of interlock description this command is used to enable or dis...
Page 440: Route Subsystem
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-59 note to prevent excessive wear on the output relay, do not use the himpedance mode for tests that turn the output on and off frequently. With normal selected, the v-source is selected and set to 0v when the output is turned off. Co...
Page 441: Sense1 Subsystem
18-60 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual sense1 subsystem the sense1 subsystem is used to configure and control the measurement functions of the sourcemeter. Many of the commands are global, where a single command affects all func- tions. Some commands are unique to a spe...
Page 442
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-61 [:on] off [:sense[1]]:function[:on] specify functions to be enabled [:sense[1]]:function:off specify functions to be disabled parameters = “current[:dc]” amps measurement function “voltage[:dc]” volts measurement function “resistan...
Page 443
18-62 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual all [:sense[1]]:function[:on]:all enable all measurement functions [:sense[1]]:function:off:all disable all measurement functions description this command is used to enable or disable all measurement functions. When enabled (:on:al...
Page 444
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-63 resistance:mode [:sense[1]]:resistance:mode select ohms measurement mode parameters = manual manual ohms mode auto auto ohms mode query :mode? Query ohms mode description this command is used to select the ohms measurement mode. Wi...
Page 445
18-64 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual select measurement range notes: 1. You cannot select a current measurement range if sourcing current. Conversely, you cannot select a voltage measurement range if sourcing voltage. Also, autorange cannot be enabled for those source...
Page 447
18-66 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual 2430 pulse mode = -10.5 to 10.5 expected reading in amps -105 to 105 expected reading in volts 0 to 2.1e7 expected reading in ohms default 1.05e-4 (amps), 21 (volts), 2.1e5 (ohms) minimum -10.5 (amps), -105 (volts), 0 (ohms) maximu...
Page 448
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-67 select auto range auto [:sense[1]]:current[:dc]:range:auto control auto ranging for amps [:sense[1]]:voltage[:dc]:range:auto control auto ranging for volts [:sense[1]]:resistance:range:auto control auto ranging for ohms parameters ...
Page 449
18-68 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ulimit [:sense[1]]:current[:dc]:range:auto:ulimit? Query auto ranging upper limit for amps [:sense[1]]:voltage[:dc]:range:auto:ulimit? Query auto ranging upper limit for volts [:sense[1]]:resistance:range:auto:ulimit set auto rangi...
Page 450
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-69 2425 and 2430 dc mode = -3.15 to 3.15 current compliance limit -105 to 105 voltage compliance limit default 105ua, 21v minimum -3.15a, -105v maximum 3.15a, 105v 2430 pulse mode = -10.5 to 10.5 current compliance limit -105 to 105 v...
Page 451
18-70 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual tripped? [:sense[1]]:current[:dc]:protection:tripped? Query current compliance state [:sense[1]]:voltage[:dc]:protection:tripped? Query voltage compliance state description this command is used to determine if the source is in comp...
Page 452
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-71 configure and control filter note for the model 2430 pulse mode, filtering is not used. Therefore, the following filter commands are not valid for the model 2430 pulse mode. Tcontrol [:sense[1]]:average:tcontrol select filter type ...
Page 453: Source Subsystem
18-72 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual [:state] [:sense[1]]:average[:state] enable or disable filter parameters = 0 or off disable digital filter 1 or on enable digital filter query :state? Query state of digital filter description these commands are used to enable or d...
Page 454
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-73 auto :source[1]:clear:auto parameters = 1 or on enable auto output-off = 0 or off disable auto output-off query :auto? Query state of auto output-off description this command is used to control auto output-off for the source. With ...
Page 455
18-74 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual [:mode] :source[1]:function[:mode] select source mode parameters = voltage select voltage mode current select current mode memory select memory mode query [:mode]? Query selected source description this command is used to select th...
Page 456
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-75 select range range :source[1]:current:range select range for i-source :source[1]:voltage:range select range for v-source parameters 2400 = -1.05 to 1.05 specify i-source level (amps) -210 to 210 specify v-source level (volts) defau...
Page 457
18-76 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual 2425 and 2430 dc mode = -3.15 to 3.15 specify i-source level (amps) -105 to 105 specify v-source level (volts) default 100µa range (i-source) 20v range (v-source) minimum 10µa range (i-source) 200mv range (v-source) maximum 3a rang...
Page 458
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-77 the above command will select the 20v range for the v-source. As listed in the “parameters,” you can also use the minimum, maximum and default parameters to manually select the source range. The up parameter selects the next higher...
Page 459
18-78 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual 2420 = -3.15 to 3.15 set i-source amplitude (amps) -63 to 63 set v-source amplitude (volts) default 0a or 0v minimum -3.15a or -63v maximum +3.15a or +63v 2425 and 2430 dc mode = -3.15 to 3.15 set i-source amplitude (amps) -105 to ...
Page 460
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-79 the minimum and maximum parameters are only valid if the highest source range is presently selected. Sending the minimum or maxi- mum parameters on a lower source range will generate error -221 (set- ting conflict). Triggered[:ampl...
Page 461
18-80 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual query :triggered? Query triggered amplitude for fixed source :triggered? Default query *rst default amplitude :triggered? Minimum query lowest allowable amplitude :triggered? Maximum query highest allowable amplitude description th...
Page 462
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-81 2410 = -1100 to 1100 specify v-source limit 20 set limit to 20v 40 set limit to 40v 100 set limit to 100v 200 set limit to 200v 300 set limit to 300v 400 set limit to 400v 500 set limit to 500v 501 to 1100 set limit to none none se...
Page 463
18-82 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual 2440 = -42 to 42 specify v-source limit 4 set limit to 4v 8 set limit to 8v 12 set limit to 12v 16 set limit to 16v 20 set limit to 20v 24 set limit to 24v 32 set limit to 32v 33 to 42 set limit to none none set limit to 42v defaul...
Page 464
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-83 set delay note for the model 2430 pulse mode, source delay is not used. Therefore, the follow- ing commands for source delay are ignored. Delay :source[1]:delay manually set source delay parameters = 0 to 999.9999 specify delay in ...
Page 465
18-84 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual configure voltage and current sweeps there are two methods to configure the start and stop levels of a sweep. You can use either the :start and :stop commands or you can use the :center and :span commands. Note in order to run a sw...
Page 466
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-85 spacing :source[1]:sweep:spacing select scale for sweep parameters = linear linear scale logarithmic logarithmic scale query :spacing? Query scale for sweep description this command is used to select the scale for the sweep. With l...
Page 467
18-86 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual 2430 pulse mode = -10.5 to 10.5 set i-source level (amps) -105 to 105 set v-source level (volts) default 0a or 0v minimum -10.5a or -105v maximum +10.5a or +105v 2440 = -5.25 to 5.25 set i-source level (amps) -42 to 42 set v-source...
Page 468
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-87 center span :source[1]:current:center specify center point of current sweep :source[1]:voltage:center specify center point of voltage sweep :source[1]:current:span specify span of the current sweep :source[1]:voltage:span specify s...
Page 469
18-88 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual query :center? Query center point for sweep :center? Default query *rst default level :center? Minimum query lowest allowable level :center? Maximum query highest allowable level :span? Query span for sweep :span? Default query *rs...
Page 470
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-89 2420 = -6.3 to 6.3 set i-source level (amps) -128 to 128 set v-source level (volts) default 0a or 0v minimum -6.3a or -128v maximum +6.3a or +128v 2425 and 2430 dc mode = -6.3 to 6.3 set i-source level (amps) -210 to 210 set v-sour...
Page 471
18-90 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual an alternate way to set the source-measure points in a linear sweep is to simply specify the number of source-measure points in the sweep using the :points command. Note that the :step and :points commands are coupled. Changing the...
Page 472
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-91 direction :source[1]:sweep:direction set direction of sweep parameters = up run sweep from start to stop down run sweep from stop to start query :direction? Query direction of sweep description normally, a sweep is run from the sta...
Page 473
18-92 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual description these commands are used to define a list of source values (up to 100) for the list sourcing mode of operation. When operation is started, the instrument will sequentially source each current or voltage value in the list...
Page 474
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-93 description this command is used to add one or more values (up to 100) to a source list that already exists. The source values are appended to the end of the list. (by using multiple appended lists, up to 2500 points can be in a li...
Page 475
18-94 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual of the sourcemeter with calc1 disabled. User-defined math expressions are replaced with the power math expression. Error 809 (source memory location revised) occurs when a memory sweep ref- erences an expression that no longer exis...
Page 476
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-95 route:terminals calculate1:state calculate1:math[:expression]:name calculate2:feed calculate2:null:offset calculate2:null:state calculate2:limit[1]:state calculate2:limit[1]:compliance:fail calculate2:limit[1]:compliance:source2 ca...
Page 477
18-96 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual recall :source:memory:recall return to specified setup parameters = 1 to 100 specify memory location description this command is used to return the sourcemeter to the setup stored at the specified memory location. Set scaling facto...
Page 478
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-97 sour:volt:star 1.0 sour:volt:stop 10.0 sour:volt:step 1.0 sour:swe:poin? (returns 10) trig:coun 10 sour:volt:mode swe outp on init voltage list the previous linear voltage sweep can instead be performed using a voltage list as foll...
Page 479
18-98 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual now add the logstep value to log 10 (start) and to each subsequent result. This will create a list of log 10 values. Next take the anti-log of each log 10 value to get the actual sweep values: value# log 10 value sweep value 1 -3.0...
Page 480
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-99 soak time soak :source[1]:soak set multiple mode soak time parameters = soak time (s) 0.000 to 9999.999s query :soak? Query multiple mode soak time description with syst:rcmode set to multiple, sour:soak specifies the amount of tim...
Page 481
18-100 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual delay :source[1]:pulse:delay specify pulse delay parameters = 0 to 9999.99900 specify pulse delay in seconds minimum 0 seconds maximum 9999.999 seconds default 0 seconds query :delay? Query pulse width :delay? Default query *rst d...
Page 482
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-101 use the following table to determine the parameter value for the desired decimal digital output pattern: mode :source2:ttl4:mode control digital i/o port line 4 mode parameters = eotest use line 4 as eot signal busy use line 4 as ...
Page 483
18-102 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual bstate :source2:ttl4:bstate control busy and eot polarity parameters = 1 set eot/busypolarity high 0 set eot/busy polarity low query :bstate? Query eot/busy polarity description this command sets the polarity of the eot or busy si...
Page 484
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-103 auto :source2:clear:auto control auto-clear for digital output parameters = 0 or off disable auto-clear 1 or on enable auto-clear query :auto? Query auto-clear description this command is used to enable or disable auto-clear for t...
Page 485: Status Subsystem
18-104 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status subsystem the status subsystem is used to control the status registers of the sourcemeter. The com- mands in this subsystem are summarized in table 18-8 . Note these registers and the overall status structure are fully expl...
Page 486
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-105 select default conditions preset :status:preset return registers to default conditions description when this command is sent, the following scpi event registers are cleared to zero (0): 1. Operation event enable register. 2. Event...
Page 487: System Subsystem
18-106 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual disable :status:queue:disable disable messages for error queue parameters = (numlist) where numlist is a specified list of messages that you wish to disable for the error queue. Query :disable? Query list of disabled messages desc...
Page 488
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-107 query :posetup? Query power-on setup description this command is used to select the power-on defaults. With rst selected, the instrument powers up to the *rst default conditions. With pres selected, the instrument powers up to the...
Page 489
18-108 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual select guard mode guard :system:guard select guard mode parameters = ohms ohms guard mode cable cable guard mode query :guard? Query guard mode description this command is used to select the guard mode. Ohms guard is a low- impeda...
Page 490
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-109 control beeper [:immediate] :system:beeper[:immediate] parameters freq = 65 to 2e6 specify frequency in hz time = 0 to 7.9 specify time duration note the frequency and time values must be separated by a comma (i.E., :syst:beep 100...
Page 491
18-110 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual control auto zero state :system:azero:state control auto zero parameters = on enable auto zero off disable auto zero once force immediate auto zero update query :state? Query state of auto zero description this command is used to ...
Page 492
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-111 follow these general steps to program and use nplc caching: 1. Send this command to disable auto zero: syst:azer off. 2. Enable nplc caching by sending: syst:azer:cach on. 3. Set up and run your source memory sweep with the :sour:...
Page 493
18-112 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual error queue note see section 15 for details on the error queue. [:next]? :system:error[:next]? Read oldest error (code and message) description as error and status messages occur, they are placed in the error queue. The error queu...
Page 494
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-113 simulate key presses key :system:key simulate key-press parameters = 1 range up arrow key 2 source down arrow key 3 left arrow key 4 menu key 5 fctn key 6 filter key 7 speed key 8 edit key 9 auto key 10 right arrow key 11 exit key...
Page 495
18-114 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual the parameter listing provides the key-press code in numeric order. Fig- ure 18-3 also illustrates the key-press codes. The queue for the :key? Query command can only hold one key-press. When :key? Is sent over the bus, and the so...
Page 496
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-115 read version of scpi standard version? :system:version? Read scpi version description this query command is used to read the version of the scpi standard being used by the sourcemeter. Example code: 1996.0 the above response messa...
Page 497
18-116 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual query timestamp time? :system:time? Query timestamp query :time? Query timestamp description this query returns the current timestamp value. Reset timestamp reset :system:time:reset reset timestamp description this action command ...
Page 498: Trace Subsystem
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-117 auto range change mode rcmode :system:rcmode control auto range change mode parameters = single single mode multiple multiple mode query :rcmode? Query auto range change mode description this command controls the auto range change...
Page 499
18-118 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual note see appendix c , “ data flow ,” for a detailed explanation on how data flows through the various operation blocks of the sourcemeter. It clarifies the types of readings that are acquired by the various commands to read data. ...
Page 500
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-119 feed :trace:feed specify readings source parameters = sense[1] put raw readings in buffer calculate[1] put calc1 readings in buffer calculate2 put calc2 readings in buffer query :feed? Query buffer feed description this command is...
Page 501: Trigger Subsystem
18-120 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual trigger subsystem the trigger subsystem is made up of a series of commands and subsystems to configure the trigger model. These commands and subsystems are summarized in table 18-11 . Note see section 11 , “ triggering ,” for more...
Page 502
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-121 warning with auto output-off disabled, the source output will remain on after all programmed source-measure operations are completed. Beware of hazardous voltage ( ≥ 30vdc, 42.4 peak-to-peak) that may be present on the output term...
Page 503
18-122 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual for example, assume the arm count is set to 2 and the trigger counter is set to 10, the sourcemeter is configured to perform 10 source-measure operations twice for a total of 20 source-measure operations. The product of the arm co...
Page 504
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-123 source :arm[:sequence[1]][layer[1]]:source specify arm event control source :trigger[:sequence[1]]:source specify trigger event control source parameters = immediate pass operation through immediately tlink select trigger link tri...
Page 505
18-124 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual timer :arm[:sequence[1]][:layer[1]]:timer set interval for arm layer timer parameters = 0.001 to 9999.999 specify timer interval in seconds 10000.00 to 99999.99 specify timer interval in seconds query :timer? Query programmed time...
Page 506
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual scpi command reference 18-125 description when tlink is the selected trigger layer control source, and an event detector in the trigger layer is enabled, operation will hold up at that detector until an input trigger is received via the trigger link. When the ...
Page 507
18-126 scpi command reference 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual output :arm[:sequence[1]][layer[1]][:tconfigure]:output arm layer events :trigger[:sequence[1]][:tconfigure]:output trigger layer events parameters arm layer triggers : tenter trigger on entering trigger layer texit trigger on exi...
Page 509: Sourcemeter
Sourcemeter ® line specifications 2400, 2400-c, 2410, 2410-c, 2420, 2420-c, 2425, 2425-c, 2430, 2430-c, 2440, 2440-c additional source specifications transient response time: 30µs minimum for the output to recover to its spec. Following a step change in load. Command processing time: maximum time re...
Page 510: Sourcemeter
Sourcemeter ® line specifications resistance measurement accuracy (local or remote sense) default default normal enhanced test test current accuracy (23°c ±5°c) accuracy (23°c ±5°c) 5 default current 2420, 2425, 1 year, ±(% rdg. + ohms) 1 year, ±(% rdg. + ohms) range resolution 2400, 2410 2430, 2440...
Page 511: Sourcemeter
Sourcemeter ® line specifications system speeds 1 reading rates applicable for voltage or current measurements. Auto zero off, autorange off, filter off, display off, trigger delay = 0, and binary reading format. 2 purely resistive lead. 1µa and 10µa ranges 3 1000 point sweep was characterized with ...
Page 512: Accuracy Calculations
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual specifications a-5 accuracy calculations the information below discusses how to calculate accuracy for both sense and source functions. Measure accuracy measurement accuracy is calculated as follows: accuracy = ±(% of reading + offset) as an example of how to ...
Page 513
A-6 specifications 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source-delay-measure (sdm) cycle timing the following timing information assumes that the sourcemeter is being triggered exter- nally via the trigger link. For cases i through iv, it is assumed that the output auto-off feature is enabled (:s...
Page 514
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual specifications a-7 a/d conversion this is the time it takes to measure the specified a/d converter phase. In general, there are three a/d phases required to generate a voltage or current reading. These phases are often referred to as the signal, reference, and...
Page 515
A-8 specifications 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual source on time ≅ source configuration + source delay + (3 × a/d conversion) + firm- ware overhead example: source delay = 0µsec nplc setting = 0.01 plc power line frequency = 60hz source on time ≅ 50µsec + 0 + [(3 × 0.01 × 1/60) + 185µsec] +...
Page 516
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual specifications a-9 case iii: auto-zero disabled and measuring one function figure a -3 case iii timing diagram trigger latency: 225µsec max source configuration: 50µsec max a/d conversion: [nplc setting × (1 / power line frequency)] + 185µsec firmware overhead...
Page 517
A-10 specifications 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual case iv: auto-zero disabled and all measurements disabled figure a -4 case iv timing diagram trigger latency: 225µsec max source configuration: 50µsec max firmware overhead: 310µsec for source v 590µsec for source i source on time ≅ source ...
Page 518
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual specifications a-11 cases v and vi: measure one function, output auto-off disabled, and no source setting changes figure a -5 case v timing diagram auto-zero: enabled trigger latency: 500µsec max figure a -6 case vi timing diagram auto zero: disabled trigger l...
Page 521: Introduction
B-2 status and error messages 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual introduction this appendix contains a summary of status and error messages, which status register bits are set when messages occur, and methods to avoid or eliminate most common scpi errors. Status and error messages table b-1 sum...
Page 522
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status and error messages b-3 table b-1 status and error messages number error message event 1 status register 2 bit -440 -430 -420 -410 -363 -362 -361 -360 -350 query unterminated after indefinite response query deadlocked query unterminated query interrupted...
Page 523
B-4 status and error messages 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual number error message event 1 status register 2 bit -178 -171 -170 -168 -161 -160 -158 -154 -151 -150 -148 expression data not allowed invalid expression expression error block data not allowed invalid block data block data error s...
Page 524
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status and error messages b-5 number error message event 1 status register 2 bit +100 +101 +102 +103 +104 +105 +106 +107 +108 +109 +110 +111 +112 +113 +114 measurement events: limit 1 failed low limit 2 failed high limit 2 failed low limit 3 failed high limit ...
Page 525
B-6 status and error messages 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual number error message event 1 status register 2 bit +500 +501 +502 +503 +504 +505 +506 +507 +508 +509 +510 calibration errors: date of calibration not set next date of calibration not set calibration data invalid dac calibration ov...
Page 526
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status and error messages b-7 number error message event 1 status register 2 bit +811 +812 +813 +814 +815 +816 +817 +818 +819 +820 +821 +822 +823 +824 +825 +826 +827 +828 +829 +830 +831 +900 not an operator or number mismatched parenthesis not a number of data...
Page 527
B-8 status and error messages 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual eliminating common scpi errors there are three scpi errors that occur more often than any others: • -113, “undefined header” • -410, “query interrupted” • -420, “query unterminated” the following paragraphs discuss the most likely...
Page 528
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual status and error messages b-9 • incorrectly configured ieee-488 driver. The driver must be configured so that when talking on the bus it sends line-feed with eoi as the terminator, and when lis- tening on the bus it expects line-feed with eoi as the terminator...
Page 531: Introduction
C-2 data flow 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual introduction data flow for remote operation is summarized by the block diagram shown in figure c-1 . Refer to this block diagram for the following discussion. Figure c-1 data flow block diagram sense (measurements) volts, amps, ohms, timestamp, f...
Page 532
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual data flow c-3 the sense block represents the basic measured readings of voltage, current, and resis- tance. If filter is enabled, the readings will be filtered. The sense block also measures time for the timestamp. When the initiate command is sent, the progra...
Page 533
C-4 data flow 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual calculate[1]:data? If calculate1 is enabled, sample buffer data is fed to the calc1 block where the results for the selected math expression are calculated. The calc1:data? Command will read the results of the math expression. If, for example, 20...
Page 535: Introduction
D-2 ieee-488 bus overview 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual introduction basically, the ieee-488 bus is a communication system between two or more electronic devices. A device can be either an instrument or a computer. When a computer is used on the bus, it serves to supervise the communicatio...
Page 536: Bus Description
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview d-3 bus description the ieee-488 bus, which is also frequently referred to as the gpib (general purpose interface bus), was designed as a parallel transfer medium to optimize data transfer with- out using an excessive number of bus lines....
Page 537
D-4 ieee-488 bus overview 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure d-1 ieee-488 bus configuration device 1 able to talk, listen and control (computer) device 2 able to talk and listen sourcemeter device 3 only able to listen (printer) device 4 only able to talk dav nrfd ndac ifc atn srq ren eo...
Page 538: Bus Lines
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview d-5 bus lines the signal lines on the ieee-488 bus are grouped into three different categories: data lines, management lines, and handshake lines. The data lines handle bus data and com- mands, while the management and handshake lines ens...
Page 539
D-6 ieee-488 bus overview 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual nrfd (not ready for data) — the acceptor controls the state of nrfd. It is used to signal to the transmitting device to hold off the byte transfer sequence until the accepting device is ready. Ndac (not data accepted) — ndac is also c...
Page 540: Bus Commands
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview d-7 bus commands the instrument may be given a number of special bus commands through the ieee-488 interface. This section briefly describes the purpose of the bus commands which are grouped into the following four categories. 1. Uniline ...
Page 541
D-8 ieee-488 bus overview 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual uniline commands atn, ifc and ren are asserted only by the controller. Srq is asserted by an external device. Eoi may be asserted either by the controller or other devices depending on the direction of data transfer. The following is ...
Page 542
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview d-9 addressed multiline commands addressed commands are multiline commands that must be preceded by the device listen address before that instrument will respond to the command in question. Note that only the addressed device will respond...
Page 543
D-10 ieee-488 bus overview 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual common commands common commands are commands that are common to all devices on the bus. These com- mands are designated and defined by the ieee-488.2 standard. Generally, these commands are sent as one or more ascii characters that t...
Page 544
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview d-11 figure d-3 command codes d 7 d 6 d 5 d 4 x 0 0 0 command x 0 0 1 command x 0 1 0 primary address x 0 1 1 primary address x 1 0 0 primary address x 1 0 1 primary address x 1 1 0 x 1 1 1 bits d 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 d 2 0 0...
Page 545
D-12 ieee-488 bus overview 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual typical command sequences for the various multiline commands, a specific bus sequence must take place to properly send the command. In particular, the correct listen address must be sent to the instrument before it will respond to ad...
Page 546
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview d-13 ieee command groups command groups supported by the sourcemeter are listed in table d-5 . Common com- mands and scpi commands are not included in this list. Table d-5 ieee command groups handshake command group ndac = not data accept...
Page 547: Interface Function Codes
D-14 ieee-488 bus overview 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual interface function codes the interface function codes, which are part of the ieee-488 standards, define an instru- ment’s ability to support various interface functions and should not be confused with pro- gramming commands found els...
Page 548
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview d-15 pp (parallel poll function) —the instrument does not have parallel polling capabilities (pp0). Dc (device clear function) —dc1 defines the ability of the instrument to be cleared (initialized). Dt (device trigger function) —dt1 defin...
Page 551: Introduction
E-2 ieee-488 and scpi conformance information 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual introduction the ieee-488.2 standard requires specific information about how the sourcemeter imple- ments the standard. Paragraph 4.9 of the ieee-488.2 standard (std 488.2-1987) lists the documentation requirements...
Page 552
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual ieee-488 and scpi conformance information e-3 table e-1 ieee-488 documentation requirements requirements description or reference (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (6) (7) (8) (9) (10) (11) (12) (13) (14) (15) (16) (17) (18) (19) (20) (21) (22) (23) ieee...
Page 553
E-4 ieee-488 and scpi conformance information 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual table e-2 coupled commands command also changes :sense...:range:upper :sense...:nplc :source...:range :source...:start :source...:stop :source...:step :source...:points :source...:center :source...:span ren, gtl :s...
Page 555: Introduction
F-2 contact check function 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual introduction this appendix contains information on the contact check function available with the mod- els 2400-c, 2410-c, 2420-c, 2425-c, 2430-c, and 2440-c sourcemeters. Overview description the contact check function detects measur...
Page 556
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual contact check function f-3 block diagram a block diagram of the contact check circuitry is shown in figure f-2 . The microproces- sor sends a contact check pulse that is amplified to drive the primaries of four transform- ers. The secondaries of transformers t...
Page 557: Operation
F-4 contact check function 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual operation dut connections the contact check function can be used to verify satisfactory contact resistance to the dut at both the front and rear panels. If you do not wish to perform contact check using the guard/guard sense jacks (o...
Page 558
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual contact check function f-5 contact check threshold resistances there are three different threshold resistances available for contact check: 2 Ω , 15 Ω , and 50 Ω . (the factory default is 50 Ω .) these threshold values were chosen to ensure that reli- able con...
Page 559
F-6 contact check function 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual trigger model operation in relation to the standard trigger models ( figure 11-1 and figure 11-8 ), the contact check test is performed just before the source action block in the trigger layer. Note for the model 2430 pulse mode, the...
Page 560
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual contact check function f-7 limit test sequence when enabled, the contact check limit test (limit 4) is performed before all other limit tests, as shown in figure f-4 . Figure f-5 shows a flowchart for grading mode limit testing with contact check limit testing...
Page 561
F-8 contact check function 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual figure f-5 grading mode contact check limit testing perform limit 1 test ? Yes no pass ? No yes display “fail” perform limit 2,3,5-12 tests ? Yes no pass ? No yes another test cycle ? No yes start turn output on and press limit key. ...
Page 562
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual contact check function f-9 figure f-6 sorting mode contact check limit testing perform limit 1 test ? Yes no pass ? No yes display “fail” perform limit 2,3,5-12 tests ? Yes no pass ? No yes start turn output on and press limit key. Output fail pattern test ano...
Page 563
F-10 contact check function 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual binning failure indications (grading mode) as previously discussed, it is possible to place a fail pattern on the digital i/o port when contact check fails. It is important to note that, depending on whether source auto clear is ena...
Page 564
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual contact check function f-11 auto clear off, immediate binning bin control at end of each point is sweep: :calc2:clim:bcon imm the output will remain on between each sweep point if no contact check failure occurs. If a contact check failure occurs before the ex...
Page 565
F-12 contact check function 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual using contact check 1. Make connections to the dut ( figure f-3 ). 2. Press the menu key, select a/d ctrl, then choose cont chk, and press enter. 3. Select enable, then press enter. 4. At the cont-chk resistance prompt, select the d...
Page 566
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual contact check function f-13 7. Select 4 wire, then press enter. 8. Press exit to return to normal display. 9. Select the Ω function and set range, then turn on the output. 10. Observe the display for an “open lead” message when the contact check fails. Using e...
Page 567
F-14 contact check function 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual remote contact check operation contact check remote commands table f-3 summarizes contact check remote commands. Commands specific to contact check operation are covered in detail later in this appendix, while remaining commands are...
Page 568
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual contact check function f-15 command description :format:elements:calculate status bit 18 (262144) of the status word returned by read?, fetch?, measure?, measure:voltage?, mea- sure:current?, measure:resistance?, trace:data?, calculatel :data?, or :calculate2:...
Page 569
F-16 contact check function 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual contact check programming example table f-4 summarizes a basic contact check programming example. This example sets up the sourcemeter as follows: • contact check: enabled • contact check threshold resistance: 2 Ω • limit 4 test: en...
Page 570
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual contact check function f-17 contact check command reference configure and control contact check ccheck :system:ccheck enable or disable contact check. Parameters = 0 or off disable contact check 1 or on enable contact check query :ccheck? Query state of contac...
Page 571
F-18 contact check function 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual fail? :calculate2:limit4:fail? Read limit 4 test result description this command is used to read the results of the limit 4 test: 0 = limit 4 test passed 1 = limit 4 test failed reading the results of the limit test does not clear t...
Page 572
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual contact check function f-19 use the following table to determine the parameter value for the desired decimal digital output pattern. For non-decimal parameters, convert the decimal value to its binary, octal, or hexadecimal equivalent. Configure and control co...
Page 573: Contact Check Defaults
F-20 contact check function 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual tout :trigger:sequence2:tout specify contact check timeout parameters = 0.00000 to 999.99990(sec) contact check timeout query :tout? Query contact check timeout description this command programs the contact check timeout interval. W...
Page 575: Introduction
G-2 gpib 488.1 protocol 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual introduction the sourcemeter supports two gpib protocols: scpi and 488.1. The 488.1 protocol is included to significantly increase speed over the gpib. When using the 488.1 protocol, throughput is enhanced up to 10 times for data sent t...
Page 576: Protocol Differences
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual gpib 488.1 protocol g-3 protocol differences the following information covers the differences between the 488.1 protocol and the scpi protocol. Message exchange protocol (mep) when the 488.1 protocol is selected, the mep is disabled to speed up gpib operation....
Page 577
G-4 gpib 488.1 protocol 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual nrfd hold-off *opc, *opc?, and *wai are still functional but are not needed for the 488.1 protocol. When sending commands, the gpib is automatically held off when it detects a terminator. The hold-off is released when all the commands h...
Page 578
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual gpib 488.1 protocol g-5 trigger-on-talk trigger-on-talk functionality has been added for the 488.1 protocol. If a query has not been received by the instrument, the sourcemeter will automatically assume a read? Command has been sent when it is addressed to tal...
Page 579
G-6 gpib 488.1 protocol 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual gpib reading speed comparisons the tables that follow compare the differences in reading speed for the scpi and 488.1 protocols. Included in all tables is the percentage improvement achieved with the 488.1 protocol compared to the scpi ...
Page 580
2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual gpib 488.1 protocol g-7 table g-3 scpi/488.1 reading speed comparisons for source-measure-limit test sweep operation (rdgs/sec) speed nplc/trig. Origin scpi 488.1 improvement fast 0.01/internal 809.5 981.1 21.19% 0.01/external 756.2 886.9 17.28% medium 0.10/in...
Page 581
G-8 gpib 488.1 protocol 2400 series sourcemeter ® user’s manual single-shot operation table g-5 through table g-7 show reading rates for measure-only, source-measure, and source-measure-limit test single-shot operation respectively. Note that the reading rate can be increased by >100%. Table g-5 scp...
Page 582
Index numerics 2-wire local sensing 2-7 4-wire remote sensing 2-6 6-wire ohms measurements 4-11 a accessories 1-3 acquiring readings 17-3 adapters 1-4 auto ohms measurements 4-4 auto ranging 7-3 auto zero 3-9 disable/enable 5-11 front panel 3-9 remote command 3-9 auto-clear 12-17 b basic circuit con...
Page 583
Compliance determining limit 6-5 examples 6-4 maximum values 6-3 principles 6-4 setting front panel compliance limit 3-7 setting remote compliance limit 3-7 types 6-2 compliance limit 6-2 setting 3-7 configuration measurement function 17-2 configure output menu 13-7 conformance information ieee-488 ...
Page 584
F factory default settings 1-17 filter 7-9 front panel control 7-10 programming example 7-13 remote programming 7-12 front panel operation auto zero 3-9 compliance limit 3-7 contact check function f-11 data store 9-2 digital output control 13-4 filter 7-10 gpib 14-9 guard selection 2-12 limit testin...
Page 585
M manual ranging 7-3 math 8-4 built-in functions 8-4 front panel operation 8-6 programming example 8-8 remote operation 8-7 user-defined functions 8-9 measure only front panel operation 3-20 programming example 3-21 remote operation 3-21 measure voltage or current 3-20 menus 1-20 configuration 1-26 ...
Page 586
Pulse characteristics 5-3 fast pulse output 5-6 output off-time 5-5 pulse duty cycle 5-6 pulse jitter 5-8 pulse width 5-4 pulse energy limitations 5-9 pulse mode basic operation 5-12 overview 5-2 sweeps 10-32 triggering 11-30 pulse mode configuration front panel operation 5-10 remote operation 5-11 ...
Page 587
Remote programming data store 9-6 display 1-15 filter 7-12 math 8-7 ohms 4-12 range and digits 7-5 relative 8-3 speed 7-8 sweeps 10-22 ren (remote enable) 14-7 response messages 14-17 rs-232 interface baud rate 14-18 connections 14-19 data bits and parity 14-18 flow control (signal handshaking) 14-1...
Page 588
T toggle key 1-15 toggling the source and measure display fields 1-25 trigger link 11-19 input requirements 11-19 output specifications 11-20 triggering 11-1 examples 11-20 external example 11-23 front panel configuration 11-8 front panel example 11-20 front panel model 11-2 front panel operation 11...
Page 590
Service form model no. _______________ serial no. __________________ date _________________ name and telephone no. ____________________________________________________ company _______________________________________________________________________ list all control settings, describe problem and chec...
Page 593
Specifications are subject to change without notice. All keithley trademarks and trade names are the property of keithley instruments, inc. All other trademarks and trade names are the property of their respective companies. Keithley instruments, inc. 28775 aurora road • cleveland, ohio 44139 • 440-...
Page 594
Artisan technology group is your source for quality new and certified-used/pre-owned equipment • fast shipping and delivery • tens of thousands of in-stock items • equipment demos • hundreds of manufacturers supported • leasing/monthly rentals • itar certified secure asset solutions service center r...