- DL manuals
- Kurzweil
- Music Equipment
- ALGORITHMS2
- Algorithm Manual
Kurzweil ALGORITHMS2 Algorithm Manual
FXAlgs #724-6, 728: Distortion
Algorithm Reference-94
FXAlgs #724-6, 728: Distortion
FXAlg #724 Ñ Mono Distortion
FXAlg #725 Ñ MonoDistort + Cab
FXAlg #726 Ñ MonoDistort + EQ
FXAlg #728 Ñ StereoDistort+EQ
Small distortion algorithms
Allocation Units:
1 for Mono Distortion; 2 for MonoDistort + Cab; 2 for MonoDistort + EQ;
3 for StereoDistort + EQ
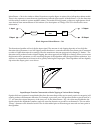
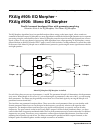
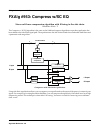
Mono Distortion sums its stereo input to mono, performs distortion followed by a hipass filter and sends the result
as centered stereo.
Block diagram of Mono Distortion
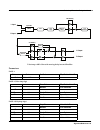
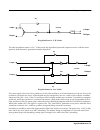
MonoDistort + EQ is similar to Mono Distortion except the single hipass filter is replaced with a pair of second-order
hipass/lowpass filters to provide rudimentary speaker cabinet modeling. The hipass and lowpass filters are then
followed by an EQ section with bass and treble shelf filters and two parametric mid filters.
Block diagram of MonoDistort + EQ
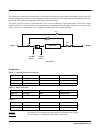
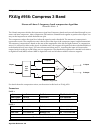
StereoDistort + EQ processes the left and right channels separately, though there is only one set of parameters for
both channels. The stereo distortion has only one parametric mid filter.
Block diagram of StereoDistort+EQ
Distortion
L Output
R Output
L Input
R Input
R Input
L Input
Distortion
R Output
L Output
EQ
Cabinet
Distortion
EQ
Distortion
EQ
R Output
L Output
L Input
R Input
Summary of ALGORITHMS2
Page 1
Fxalgs #724-6, 728: distortion algorithm reference-94 fxalgs #724-6, 728: distortion fxalg #724 Ñ mono distortion fxalg #725 Ñ monodistort + cab fxalg #726 Ñ monodistort + eq fxalg #728 Ñ stereodistort+eq small distortion algorithms allocation units: 1 for mono distortion; 2 for monodistort + cab; 2...
Page 2
Fxalgs #724-6, 728: distortion algorithm reference-95 monodistort + cab is also similar to mono distortion except the hipass is replaced by a full speaker cabinet model. There is also a panner to route the mono signal between left and right outputs. In monodistort + cab, the distortion is followed b...
Page 3
Fxalgs #724-6, 728: distortion algorithm reference-96 parameters - mono distortion: page 1 monodistort + cab: page 1 monodistort + eq: page 1 page 2 stereodistort+eq: page 1 wet/dry 0 to 100%wet out gain off, -79.0 to 24.0 db dist drive 0 to 96 db warmth 16 to 25088 hz highpass 16 to 25088 hz wet/dr...
Page 4
Fxalgs #724-6, 728: distortion algorithm reference-97 page 2 wet/dry the amount of distorted (wet) signal relative to unaffected (dry) signal. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. For distortion, it is often necessary to turn the output gain down as the distortion driv...
Page 5
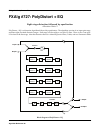
Fxalg #727: polydistort + eq algorithm reference-98 fxalg #727: polydistort + eq eight-stage distortion followed by equalization allocation units: 2 polydistort + eq is a distortion algorithm followed by equalization. The algorithm consists of an input gain stage, and then eight cascaded distortion ...
Page 6
Fxalg #727: polydistort + eq algorithm reference-99 polydistort is an unusual distortion algorithm which provides a great number of parameters to build a distortion sound from the ground up. The eight distortion stages each add a small amount of distortion to the sound. Taken together, they can prod...
Page 7
Fxalg #727: polydistort + eq algorithm reference-100 page 4 wet/dry this is a simple mix of the distorted signal relative to the dry undistorted input signal. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. For distortion, it is often necessary to turn the output gain down as the...
Page 8: Fxalg #729: Tubeampmd>Chor
Tube amp/distortion/delay combinations algorithm reference-101 tube amp/distortion/delay combinations fxalg #729: tubeampmd>chor fxalg #730: tubeampmd>flan fxalg #731: polyampmd>chor fxalg #732: polyampmd>flan mono distortion circuits in combination with moving delays, and a stereo chorus or stereo ...
Page 9
Tube amp/distortion/delay combinations algorithm reference-102 the cabinet can by switched on or off with the cab in/out parameter. The cab pan parameter adjusts the final pan position of the cabinet at the output of the algorithm, but this does not affect the cabinet signal fed into the final stere...
Page 10
Tube amp/distortion/delay combinations algorithm reference-103 tubeampmd>chor with moving delay inserted postdist parameters: page 1 page 2 (tubeamp algs) page 2 (polyamp algs) in/out in or out out gain off; -79.0 to 24.0 db input bal -100 to 100% tube drive off; -79.0 to 60.0 db warmth 16 to 25088 ...
Page 11
Tube amp/distortion/delay combinations algorithm reference-104 page 3 page 4 (chorus algs) page 4 (flange algs) in/out toggles the entire effect on or off. When off, the input signal is passed. Input bal adjusts the ratio of left and right algorithm inputs to be summed into the monaural signal that ...
Page 12
Tube amp/distortion/delay combinations algorithm reference-105 md delay adjusts the delay time for the moving delay circuit, which is the center of lfo excursion. Md lfomode adjusts the lfo excursion type. In flange mode, the lfo is optimized for ßange effects and lfo dpth adjusts the excursion amou...
Page 13: Fxalg #734: Vibchor+Rotor 4
Fxalg #733: vibchor+rotor 2 ¥ fxalg #734: vibchor+rotor 4 algorithm reference-106 fxalg #733: vibchor+rotor 2 ¥ fxalg #734: vibchor+rotor 4 vibrato/chorus, through optional distortion, into rotating speaker allocation units: 2 for vibchor+rotor 2; 4 for vibchor+rotor 4 the vibchor+rotor algorithms c...
Page 14
Fxalg #733: vibchor+rotor 2 ¥ fxalg #734: vibchor+rotor 4 algorithm reference-107 rotating speaker with virtual microphones for the rotating speakers, you can control the crossover frequency of the high and low frequency bands (the frequency where the high and low frequencies get separated). The rot...
Page 15
Fxalg #733: vibchor+rotor 2 ¥ fxalg #734: vibchor+rotor 4 algorithm reference-108 parameters: page 1 page 2 page 3 page 4 in/out when set to ÒinÓ, the algorithm is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the algorithm is bypassed. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. For distortion,...
Page 16
Fxalg #733: vibchor+rotor 2 ¥ fxalg #734: vibchor+rotor 4 algorithm reference-109 distwarmth a lowpass Þlter in the distortion control path. This Þlter may be used to reduce some of the harshness of some distortion settings without reducing the bandwidth of the signal. [vibchor+rotor 4 only] cabinet...
Page 17
Fxalg #733: vibchor+rotor 2 ¥ fxalg #734: vibchor+rotor 4 algorithm reference-110 loresonate a simulation of cabinet resonant modes express as a percentage. For realism, you should use very low settings. This is for the low frequency signal path. Lo res dly the number of samples of delay in the reso...
Page 18
Fxalg #734: distort + rotary algorithm reference-111 fxalg #734: distort + rotary small distortion followed by rotary speaker effect allocation units: 2 distort + rotary models an amplifier distortion followed by a rotating speaker. The rotating speaker has separately controllable tweeter and woofer...
Page 19
Fxalg #734: distort + rotary algorithm reference-112 in/out when set to ÒinÓ, the algorithm is active; when set to ÒoffÓ the algorithm is bypassed. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. For distortion, it is often necessary to turn the output gain down as the distortion...
Page 20: Fxalg #735/6: Kb3 Fx
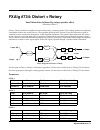
Fxalg #735/6: kb3 fx algorithm reference-113 fxalg #735/6: kb3 fx vibrato/chorus into distortion into rotating speaker into cabinet allocation units: 7 for full working effect (4 for kb3 fxbus, 3 for kb3 auxfx) the kb3 fxbus and kb3 auxfx algorithms contain multiple effects designed for the hammond ...
Page 21
Fxalg #735/6: kb3 fx algorithm reference-114 highest frequency. The crossover filters for the lower and upper drivers may be set independently. A small amount of overlap seems to work well. The gains of the high and low band signals may also be separately controlled. At this point kb3 fxbus has fini...
Page 22
Fxalg #735/6: kb3 fx algorithm reference-115 parameters (kb3 auxfx): page 1 page 2 page 3 page 4 in/out when set to ÒinÓ, the algorithm is active; when set to ÒoffÓ the algorithm is bypassed. For the entire algorithm to be active, kb3 fxbus must also be active with its roto inout parameter set to Òi...
Page 23: Fxalg #900: Env Follow Filt
Fxalg #900: env follow filt algorithm reference-116 fxalg #900: env follow filt envelope-following stereo 2-pole resonant filter allocation units: 2 the envelope-following filter is a stereo resonant filter with the resonant frequency controlled by the envelope of the input signal (the maximum of le...
Page 24
Fxalg #900: env follow filt algorithm reference-117 the attack and release rates of the envelope follower are adjustable. The rates are expressed in decibels per second (db/s). The envelope may be smoothed by a lopass filter which can extend the attack and release times of the envelope follower. A l...
Page 25
Fxalg #901: trigenvelopefilt algorithm reference-118 fxalg #901: trigenvelopefilt triggered envelope-following stereo 2-pole resonant filter allocation units: 2 the triggered envelope-following filter is used to produce a filter sweep when the input rises above a trigger level. The triggered envelop...
Page 26
Fxalg #901: trigenvelopefilt algorithm reference-119 page 2 wet/dry the amount of modulated (wet) signal relative to unaffected (dry) signal as a percent. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Filtertype the type of resonant Þlter to be used. May be one of ÒlowpassÓ, Òh...
Page 27
Fxalg #902: lfo sweep filter algorithm reference-120 fxalg #902: lfo sweep filter lfo-following stereo 2-pole resonant filter allocation units: 2 the lfo following filter is a stereo resonant filter with the resonant frequency controlled by an lfo (low-frequency oscillator). The filter type is selec...
Page 28
Fxalg #902: lfo sweep filter algorithm reference-121 page 2 wet/dry the amount of modulated (wet) signal relative to unaffected (dry) signal as a percent. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Lfo tempo basis for the rates of the lfo, as referenced to a musical tempo in...
Page 29: Fxalg #904 Dual Res Filter
Fxalg #903 resonant filter ¥ fxalg #904 dual res filter algorithm reference-122 fxalg #903 resonant filter ¥ fxalg #904 dual res filter stereo and dual-mono 2-pole resonant filters allocation units: 1 (each) the resonant filter is available as a stereo (linked parameters for left and right) or dual ...
Page 30: Fxalg #905: Eq Morpher ¥
Fxalg #905: eq morpher ¥ fxalg #906: mono eq morpher algorithm reference-123 fxalg #905: eq morpher ¥ fxalg #906: mono eq morpher parallel resonant bandpass filters with parameter morphing allocation units: 4 for eq morpher, 2 for mono eq morpher the eq morpher algorithms have four parallel bandpass...
Page 31
Fxalg #905: eq morpher ¥ fxalg #906: mono eq morpher algorithm reference-124 frequency response of (i) a single bandpass filter, and (ii) the sum of two bandpass filters now that weÕve gone through what the algorithm does, the question becomes Òwhy are we doing this?Ó with careful thought to paramet...
Page 32
Fxalg #905: eq morpher ¥ fxalg #906: mono eq morpher algorithm reference-125 page 3 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the algorithm is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the algorithm is bypassed. Out gain an overall level control of the eq morpher output. Out pan provides panning of the output signal between left and...
Page 33: Fxalg #907: Ring Modulator
Fxalg #907: ring modulator algorithm reference-126 fxalg #907: ring modulator a configurable ring modulator allocation units: 1 ring modulation is a simple effect in which two signals are multiplied together. Typically, an input signal is modulated with a simple carrier waveform such as a sine wave ...
Page 34
Fxalg #907: ring modulator algorithm reference-127 ring modulator in Òl*rÓ mode the other modulation mode is ÒoscÓ. In this mode, the algorithm inputs and outputs are stereo, and the carrier signal for both channels is generated inside the algorithm. Ring modulator in ÒoscÓ mode the carrier signal i...
Page 35
Fxalg #907: ring modulator algorithm reference-128 configurable wave shapes (osc1 only) parameters: page 1 page 2 page 3 wet/dry the amount of modulated (wet) signal relative to unaffected (dry) signal as a percent. When in Òl*rÓ mode, the left input will be used as the dry signal. Out gain the over...
Page 36
Fxalg #907: ring modulator algorithm reference-129 osc1plswid when the conÞgurable oscillator is set to pulse, the plswid parameter sets the pulse width as a percentage of the waveform period. The pulse is a square wave when the width is set to 50%. This parameter is active only in ÒoscÓ mode and wh...
Page 37: Fxalg #908: Pitcher
Fxalg #908: pitcher algorithm reference-130 fxalg #908: pitcher creates pitch from pitched or non-pitched signal allocation units: 1 this algorithm applies a filter which has a series of peaks in the frequency response to the input signal. The peaks may be adjusted so that their frequencies are all ...
Page 38
Fxalg #908: pitcher algorithm reference-131 [opqh=100, 0, 0, 0] deeper notches between wider peaks [opqh= -100, 0, 0, 0] peaks on odd harmonic multiples and notches on even harmonic multiples of a frequency one octave down from the pitch setting. [opqh=0, 100, 100, 100] like [100,100,100,100], excep...
Page 39
Fxalg #908: pitcher algorithm reference-132 [opqh= -50,100,100,100] halfway between [0,100,100,100] and [-100,100,100,100]. If the "odd" parameter is modulated with an fxmod, then one can morph smoothly between the [100,100,100,100] and [-100,100,100,100] curves. [opqh=100, -100, 100, 100] [opqh=100...
Page 40
Fxalg #908: pitcher algorithm reference-133 parameters: page 1 wet/dry the relative amount of input signal and effected signal that is to appear in the Þnal effect output mix. When set to 0%, the output is taken only from the input (dry). When set to 100%, the output is all wet. Out gain the overall...
Page 41: Fxalg #909: Super Shaper
Fxalg #909: super shaper algorithm reference-134 fxalg #909: super shaper ridiculous shaper allocation units: 1 the super shaper algorithm packs two and a half times the number of shaping loops, and 8 times the gain of the shaper found in vast. Refer to the section on shapers in the k2500 performanc...
Page 42: Fxalg #910: 3 Band Shaper
Fxalg #910: 3 band shaper algorithm reference-135 fxalg #910: 3 band shaper 3-band shaper allocation units: 2 the 3 band shaper non-destructively splits the input signal into 3 separate bands using 1 pole (6db/oct) filters, and applies a vast-type shaper to each band separately. Refer to the k2500 p...
Page 43: Fxalg #913: Laserverb
Fxalg #911: mono laserverb ¥ fxalg #912: laserverb lite ¥ fxalg #913: laserverb algorithm reference-136 fxalg #911: mono laserverb ¥ fxalg #912: laserverb lite ¥ fxalg #913: laserverb a bizarre reverb with a falling buzz allocation units: 1 for mono laserverb; 2 for laserverb lite; 3 for laserverb l...
Page 44
Fxalg #911: mono laserverb ¥ fxalg #912: laserverb lite ¥ fxalg #913: laserverb algorithm reference-137 the output from laserverb can be fed back to the input. By turning up the feedback, the duration of the laserverb sound can be greatly extended. Cross-coupling may also be used to move the signal ...
Page 45
Fxalg #911: mono laserverb ¥ fxalg #912: laserverb lite ¥ fxalg #913: laserverb algorithm reference-138 fdbk lvl the percentage of the reverb output to feed back or return to the reverb input. Turning up the feedback is a way to stretch out the duration of the reverb, or, if the reverb is set to beh...
Page 46
Fxalg #950: hardkneecompress ¥ fxalg #951: softkneecompress algorithm reference-139 fxalg #950: hardkneecompress ¥ fxalg #951: softkneecompress stereo hard- and soft-knee signal-compression algorithms allocation units: 1 the stereo hard- and soft-knee compressors are very similar algorithms and prov...
Page 47
Fxalg #950: hardkneecompress ¥ fxalg #951: softkneecompress algorithm reference-140 to determine how much to compress the signal, the compressor must measure the signal level. Since musical signal levels will change over time, the compression amounts must change as well. You can control the rate at ...
Page 48
Fxalg #950: hardkneecompress ¥ fxalg #951: softkneecompress algorithm reference-141 fdbkcomprs a switch to set whether the compressor side chain is conÞgured for feed-forward (out) or feedback (in). Atk time the time for the compressor to start to cut in when there is an increase in signal level (at...
Page 49: Fxalg #952: Expander
Fxalg #952: expander algorithm reference-142 fxalg #952: expander a stereo expansion algorithm allocation units: 1 this algorithm expands the signal (reduces the signalÕs gain) when the signal falls below the expansion threshold. The amount of expansion is based on the larger magnitude of the left a...
Page 50
Fxalg #952: expander algorithm reference-143 the signal being expanded may be delayed relative to the side chain processing. The delay allows the signal to stop being expanded just before an attack transient arrives. Since the side chain processing ÒknowsÓ what the input signal is going to be before...
Page 51
Fxalg #953: compress w/sc eq algorithm reference-144 fxalg #953: compress w/sc eq stereo soft-knee compression algorithm with filtering in the side chain allocation units: 2 the compress w/sc eq algorithm is the same as the softkneecompress algorithm except that equalization has been added to the si...
Page 52
Fxalg #953: compress w/sc eq algorithm reference-145 parameters: page 1 page 2 page 3 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the compressor is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the compressor is bypassed. Out gain compressing the signal causes a reduction in signal level. To compensate, the output gain parameter may be us...
Page 53
Fxalg #953: compress w/sc eq algorithm reference-146 scbassgain the amount of boost or cut that the side chain bass shelving Þlter should apply to the low frequency signals in db. Every increase of 6 db approximately doubles the amplitude of the signal. Positive values boost the bass signal below th...
Page 54: Fxalg #955: Comp/exp + Eq
Fxalg #954: compress/expand ¥ fxalg #955: comp/exp + eq algorithm reference-147 fxalg #954: compress/expand ¥ fxalg #955: comp/exp + eq a stereo soft-knee compression and expansion algorithm with and without equalization allocation units: 2 for compress/expand; 3 for cmp/exp + eq these are stereo co...
Page 55
Fxalg #954: compress/expand ¥ fxalg #955: comp/exp + eq algorithm reference-148 to determine how much to compress or expand the signal, the compressor/expander must measure the signal level. Since musical signal levels will change over time, the compression and expansion amounts must change as well....
Page 56
Fxalg #954: compress/expand ¥ fxalg #955: comp/exp + eq algorithm reference-149 threshold. The expander release time may be set quite long. An expander may be used to suppress background noise in the absence of signal, thus typical expander settings use a fast attack (to avoid losing real signal), s...
Page 57
Fxalg #954: compress/expand ¥ fxalg #955: comp/exp + eq algorithm reference-150 page 4 (comp/exp + eq only) in/out when set to ÒinÓ the compressor/expander is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the compressor/expander is bypassed. Out gain compressing the signal causes a reduction in signal level. To compens...
Page 58
Fxalg #954: compress/expand ¥ fxalg #955: comp/exp + eq algorithm reference-151 comp/exp + eq: bass gain the amount of boost or cut that the bass shelving Þlter should apply to the low frequency signals in db. Every increase of 6 db approximately doubles the amplitude of the signal. Positive values ...
Page 59: Fxalg #956: Compress 3 Band
Fxalg #956: compress 3 band algorithm reference-152 fxalg #956: compress 3 band stereo soft-knee 3-frequency band compression algorithm allocation units: 4 the 3-band compressor divides the input stereo signal into 3 frequency bands and runs each band through its own stereo soft-knee compressor. Aft...
Page 60
Fxalg #956: compress 3 band algorithm reference-153 page 3 page 4 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the compressor is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the compressor is bypassed. Out gain compressing the signal causes a reduction in signal level. To compensate, the output gain parameter may be used to increase the g...
Page 61: Fxalg #957: Gate ¥
Fxalg #957: gate ¥ fxalg #958: super gate algorithm reference-154 fxalg #957: gate ¥ fxalg #958: super gate signal gate algorithms allocation units: 1 for gate; 2 for super gate gate and super gate do stand-alone gate processing and can be configured as a stereo or mono effects. As a stereo effect, ...
Page 62
Fxalg #957: gate ¥ fxalg #958: super gate algorithm reference-155 signal envelope for gate and super gate when retrigger is ÒonÓ if retrigger is off (super gate only), then the gate will open when the side chain signal rises above threshold as before. The gate will then close as soon as the gate tim...
Page 63
Fxalg #957: gate ¥ fxalg #958: super gate algorithm reference-156 gate closes or opens after the gate timer has elapsed. The signal dly parameter delays the signal being gated, but does not delay the side chain signal. By delaying the main signal relative to the side chain signal, you can open the g...
Page 64
Fxalg #957: gate ¥ fxalg #958: super gate algorithm reference-157 threshold the signal level in db required to open the gate (or close the gate if ducking is on). Ducking when set to ÒoffÓ, the gate opens when the signal rises above threshold and closes when the gate time expires. When set to ÒonÓ, ...
Page 65: Fxalg #959: 2 Band Enhancer
Fxalg #959: 2 band enhancer algorithm reference-158 fxalg #959: 2 band enhancer 2-band spectral modifier allocation units: 1 the 2 band enhancer modifies the spectral content of the input signal primarily by brightening signals with little or no high frequency content, and boosting pre-existing bass...
Page 66
Fxalg #959: 2 band enhancer algorithm reference-159 hi shelf g the boost or cut of the high shelving Þlter. Hi delay adjusts the number of samples the hipass signal is delayed. Hi mix adjusts the output gain of the hipass signal. Lo delay adjusts the number of samples the lopass signal is delayed. L...
Page 67: Fxalg #960: 3 Band Enhancer
Fxalg #960: 3 band enhancer algorithm reference-160 fxalg #960: 3 band enhancer 3-band spectral modifier allocation units: 2 the 3 band enhancer modifies the spectral content of the input signal by boosting existing spectral content, or stimulating new content. First, the input is non-destructively ...
Page 68
Fxalg #960: 3 band enhancer algorithm reference-161 page 2 page 3 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the effect is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the effect is bypassed. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Crossover1 adjusts one of the -6db crossover points at which the input signal ...
Page 69
Fxalgs #961/962: tremolo and tremolo bpm algorithm reference-162 fxalgs #961/962: tremolo and tremolo bpm a stereo tremolo or auto-balance effect. Allocation units: 1 tremolo and tremolo bpm are 1-pau stereo tremolo effects. In the classical sense, a tremolo is the rapid repetition of a single note ...
Page 70
Fxalgs #961/962: tremolo and tremolo bpm algorithm reference-163 parameters (tremolo): page 1 page 2 parameters (tremolo bpm): page 1 page 2 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the effect is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the effect is bypassed. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Tem...
Page 71
Fxalgs #961/962: tremolo and tremolo bpm algorithm reference-164 pulsewidth when the lfo shape is set to pulse, this parameter sets the pulse width as a percentage of the waveform period. The pulse is a square wave when the width is set to 50%. This parameter is active only when the pulse waveform i...
Page 72: Fxalg #963: Autopanner
Fxalg #963: autopanner algorithm reference-165 fxalg #963: autopanner a stereo auto-panner allocation units: 1 "autopanner" is a 1-pau stereo auto pan effect. The process of panning a stereo image consists of shrinking the image width of the input program then cyclically moving this smaller image fr...
Page 73
Fxalg #963: autopanner algorithm reference-166 parameters: page 1 page 2 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the auto-panner is active; when set to ÒoutÓ auto-panner is bypassed. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Lfo rate the speed of the panning motion. Rate scale this multipl...
Page 74: Fxalg #964: Dual Autopanner
Fxalg #964: dual autopanner algorithm reference-167 fxalg #964: dual autopanner a dual mono auto-panner allocation units: 2 "dual autopanner" is a 2-pau dual mono auto-pan effect. Left and right inputs are treated as two mono signals which can each be independently auto-panned. Parameters beginning ...
Page 75
Fxalg #964: dual autopanner algorithm reference-168 parameters: page 1 page 2 page 3 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the auto-panner is active; when set to ÒoutÓ auto-panner is bypassed. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Lfo rate the speed of the panning motion. Origin the ...
Page 76: Fxalg #965: Srs
Fxalg #965: srs algorithm reference-169 fxalg #965: srs licensed Òsound retrieval system¨Ó or srs tm effect allocation units: 1 the srs tm algorithm has been licensed from srs labs, inc. The following is from an srs labs press release: srs, the sound retrieval system, is based on the human hearing s...
Page 77: Fxalg #966: Stereo Image
Fxalg #966: stereo image algorithm reference-170 fxalg #966: stereo image stereo enhancement with stereo channel correlation metering allocation units: 1 stereo image is a stereo enhancement algorithm with metering for stereo channel correlation. The stereo enhancement performs simple manipulations ...
Page 78
Fxalg #966: stereo image algorithm reference-171 parameters: page 1 page 2 l in gain the input gain of the left channel in decibels (db). R in gain the input gain of the right channel in decibels (db). Centergain the level of the sum of left and right channels in decibels (db). The summed stereo sig...
Page 79: Fxalg #967: Mono -> Stereo
Fxalg #967: mono -> stereo algorithm reference-172 fxalg #967: mono -> stereo stereo simulation from a mono input signal allocation units: 1 mono -> stereo is an algorithm which creates a stereo signal from a mono input signal. The algorithm works by combining a number of band-splitting, panning and...
Page 80
Fxalg #967: mono -> stereo algorithm reference-173 page 2 in/out the algorithm is functioning when in/out is set to ÒinÓ. If set to Òout, whatever is on the input channels gets passed to the output unaltered. Out gain the output gain of the pseudo-stereo signal in decibels (db). Centergain the level...
Page 81: Fxalg #968: Graphic Eq ¥
Fxalg #968: graphic eq ¥ fxalg #969: dual graphic eq algorithm reference-174 fxalg #968: graphic eq ¥ fxalg #969: dual graphic eq dual mono 10-band graphic equalizers allocation units: 3 the graphic equalizer is available as stereo (linked parameters for left and right) or dual mono (independent con...
Page 82
Fxalg #968: graphic eq ¥ fxalg #969: dual graphic eq algorithm reference-175 parameters (graphic eq): page 1 page 2 parameters (dual graphic eq): page 1 page 2 page 3 in/out in graphic eq, when set to ÒinÓ the equalizer is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the equalizer is bypassed. L in/out, r in/out in du...
Page 83: Fxalg #970: 5 Band Eq
Fxalg #970: 5 band eq algorithm reference-176 fxalg #970: 5 band eq stereo bass and treble shelving filters and 3 parametric eqs allocation units: 3 this algorithm is a stereo 5 -band equalizer with 3 bands of parametric eq and with bass and treble tone controls. The user has control over the gain, ...
Page 84
Fxalg #998: fxmod diagnostic algorithm reference-177 fxalg #998: fxmod diagnostic fxmod source-metering utility algorithm allocation units: 1 the fxmod diagnostic algorithm is used to obtain a metered display of fxmod sources. This algorithm allows you to view the current levels of any data sliders,...
Page 85: Fxalg #999: Stereo Analyze
Fxalg #999: stereo analyze algorithm reference-178 fxalg #999: stereo analyze signal metering and channel summation utility algorithm allocation units: 1 stereo analyze is a utility algorithm which provides metering of stereo signals as its primary function. In addition to metering, the gains of the...
Page 86
Fxalg #999: stereo analyze algorithm reference-179 by inverting one channel with respect to the other, you can hear what is characterized as Òphasey-nessÓ. Usually in stereo recordings, you can localize the phantom image of sound sources somewhere between the two loudspeakers. With a phasey signal, ...
Page 87
Fxalg #999: stereo analyze algorithm reference-180