Kurzweil K2600 - MUSICIANS GUIDE REV A PART NUMBER 910331 CHAP 10 Manual
KDFX Reference
In This Chapter
10-1
Chapter 10
KDFX Reference
In This Chapter
¥
KDFX Algorithms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-2
¥
KDFX Presets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-3
¥
KDFX Studios . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-5
¥
KDFX Algorithm SpeciÞcations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-8
Summary of K2600 - MUSICIANS GUIDE REV A PART NUMBER 910331 CHAP 10
Page 1
Kdfx reference in this chapter 10-1 chapter 10 kdfx reference in this chapter ¥ kdfx algorithms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-2 ¥ kdfx presets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-3 ¥ kdfx studios . . . . . . . ...
Page 2: Kdfx Algorithms
10-2 kdfx reference kdfx algorithms kdfx algorithms reverb algorithms delay algorithms chorus / flange / phaser algorithms id name 1 miniverb 2 dual miniverb 3 gated miniverb 4 classic place 5 classic verb 6 tq place 7 tq verb 8 diffuse place 9 diffuse verb 10 omniplace 11 omniverb 12 panaural room ...
Page 3: Kdfx Presets
Kdfx reference kdfx presets 10-3 kdfx presets id preset name kdfx alg 1 nicelittlebooth 1 2 small wood booth 4 3 natural room 5 4 prettysmallplace 4 5 sun room 5 6 soundboard 7 7 add more air 10 8 standard booth 8 9 a distance away 6 10 live place 8 15 brightsmallroom 1 16 bassy room 1 17 percussive...
Page 4
10-4 kdfx reference kdfx presets 721 chorusmedchamber 704 722 vanilla chorrvb 704 723 chorus slow hall 704 724 softchorus hall 704 725 chorbigbrtplate 704 726 chorus air 704 727 chorus hiceiling 704 728 chorus minihall 704 729 cathedralchorus 704 730 psilochorushall 704 731 guitarchorlsrdly 705 732 ...
Page 5: Kdfx Studios
Kdfx reference kdfx studios 10-5 kdfx studios id name bus1 fx preset bus2 fx preset bus3 fx preset bus4 fx preset aux bus fx preset 1 roomchordly hall 16 156 714 0 78 2 rmchorchrv hall 17 154 722 0 69 3 roomchorcdr hall 16 156 714 0 76 4 roomchor hall 23 157 0 0 78 5 roomchrch4t hall 22 156 706 0 72...
Page 6
10-6 kdfx reference kdfx studios 61 compeqmphch room 952 912 153 0 4 62 bthqflg4tap hall 2 737 133 0 76 63 chmbtremcdr room 42 973 715 0 29 64 chmbcmpflrv hall 41 952 744 0 69 65 chamdstecho room 41 764 131 0 28 66 chamflg4tap hall 41 173 136 0 75 67 chmbenv4tap gtrv 42 903 134 0 112 68 cmbrshaplsr ...
Page 7
Kdfx reference kdfx studios 10-7 121 auxmpflglasr plt 0 760 923 0 103 122 auxshap4md plate 0 917 756 0 31 123 flgenv4tap plate 173 904 133 0 31 124 enhrflgcdr plate 969 170 712 0 96 125 auxringpfd plate 0 913 762 0 97 126 gtrvshapmdl room 112 916 754 0 29 127 gtdenhcstim room 112 969 976 0 17 128 gt...
Page 8
10-8 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications kdfx algorithm specifications algorithms 1 and 2: miniverbs 1 miniverb 2 dual miniverb versatile, small stereo and dual mono reverbs paus: 1 for miniverb 2 for dual miniverb miniverb is a versatile stereo reverb is found in many combination algorithm...
Page 9
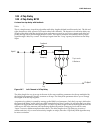
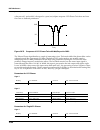
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-9 seamless. Density controls how tightly the early reßections are packed in time. Low density settings have the early reßections grouped close together, and higher values spread the reßections for a smoother reverb. Figure 10-2 simplified block diagram...
Page 10
10-10 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications dual miniverb parameters page 1 page 2 page 3 wet / dry a simple mix of the reverb sound with the dry sound. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Rvrb time the reverb time displayed is accurate for normal settings of t...
Page 11
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-11 diff scale a multiplier which affects the diffusion of the reverb. At 1.00x, the diffusion will be the normal, carefully adjusted amount for the current room type. Altering this parameter will change the diffusion from the preset amount. Size scale ...
Page 12
10-12 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 3 gated miniverb a reverb and compressor in series. Paus: 2 this algorithm is a small reverb followed by a gate. The main control for the reverb is the room type parameter. The main control for the reverb is the room type parameter. Room type change...
Page 13
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-13 if gate duck is turned on, then the behaviour of the gate is reversed. The gate is open while the side chain signal is below threshold, and it closes when the signal rises above thresold. If the gate opened and closed instantaneously, you would hear...
Page 14
10-14 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications if delayed, and thus you can get by with a dryer mix while maintaining the same subjective wet/dry level. Room type the conÞguration of the reverb algorithm to simulate a wide array of carefully designed room types and sizes. This parameter effectiv...
Page 15
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-15 algorithms 4–11: classic / tq / diffuse / omni reverbs 4 classic place 5 classic verb 6 tq place 7 tq verb 8 diffuse place 9 diffuse verb 10 omniplace 11 omniverb parameters absorption this controls the amount of reßective material that is in the sp...
Page 16
10-16 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications elements are accurately representing their preset values determined by the current room type. Room types with similar names in different reverb algorithms do not sound the same. For example, hall1 in diffuse verb does not sound the same as hall1 in ...
Page 17
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-17 modeling real spaces. High depth settings can create chorusing qualities, which wonÕt be unsuitable for real acoustic spaces, but can nonetheless create interesting effects. Instruments that have little if no inherent pitch ßuctuation (like piano) a...
Page 18
10-18 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 12 panaural room room reverberation algorithm paus: 3 the panaural room reverberation is implemented using a special network arrangement of many delay lines that guarantees colorless sound. The reverberator is inherently stereo with each input injec...
Page 19
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-19 parameters page 1 page 2 wet/dry the amount of the stereo reverberator (wet) signal relative to the original input (dry) signal to be output. The dry signal is not affected by the bass gain control. The wet signal is affected by the bass gain contro...
Page 20
10-20 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications an almost reverse reverberation, set build env to 100%. You can think of build env as setting the position of a see-saw. The left end of the see-saw represents the driving of the reverberation at the earliest time, the pivot point as driving the rev...
Page 21
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-21 13 stereo hall a stereo hall reverberation algorithm. Paus: 3 the stereo hall reverberation is implemented using a special arrangement of all pass networks and delay lines which reduces coloration and increases density. The reverberator is inherentl...
Page 22
10-22 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications varies the injection length over a range of 0 to 500ms. At a build time of 0ms, there is no extension of the build time. In this case, the build env control adjusts the density of the reverberation, with maximum density at a setting of 50%. In addit...
Page 23
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-23 pre dly introducing predelay creates a gap of silence between that allows the dry signal to stand out with greater clarity and intelligibility against the reverberant background. This is especially helpful with vocal or classical music. Build time s...
Page 24
10-24 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 14 grand plate a plate reverberation algorithm. Paus: 3 this algorithm emulates an emt 140 steel plate reverberator. Plate reverberators were manufactured during the 1950's, 1960's, 1970's, and perhaps into the 1980's. By the end of the 1980's, they...
Page 25
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-25 parameters page 1 page 2 wet/dry the amount of the stereo reverberator (wet) signal relative to the original input (dry) signal sent to the output. The dry signal is not affected by the lowpass or bass gain controls. The wet signal is affected by th...
Page 26
10-26 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 15 finite verb reverse reverberation algorithm. Paus: 3 the left and right sources are summed before being fed into a tapped delay line which directly simulates the impulse response of a reverberator. The taps are placed in sequence from zero delay ...
Page 27
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-27 page 3 wet/dry wet/dry sets the relative amount of wet signal and dry signal. The wet signal consistts of the reverb itself (stereo) and the delayed mono signal arriving after the reverb has ended (simulating the dry source in the reverse reverb seq...
Page 28
10-28 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 130 complex echo multitap delay line effect consisting of 6 independent output taps and 4 independent feedback taps paus: 1 complex echo is an elaborate delay line with 3 independent output taps per channel, 2 independent feedback taps per channel, ...
Page 29
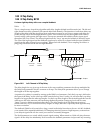
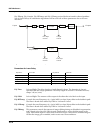
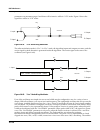
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-29 also at the input to the delays are 1 pole (6db/oct) lopass Þlters controlled by the hf damping parameter. Figure 10-6 signal flow of complex echo parameters page 1 page 2 wet/dry 0 to 100 %wet out gain off, -79.0 to 24.0 db feedback 0 to 100 % l di...
Page 30
10-30 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications page 3 page 4 wet/dry the relative amount of input signal and effected signal that is to appear in the Þnal effect output mix. When set to 0%, the output is taken only from the input (dry). When set to 100%, the output is all wet. Out gain the overa...
Page 31
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-31 131 4-tap delay 132 4-tap delay bpm a stereo four tap delay with feedback paus: 1 this is a simple stereo 4 tap delay algorithm with delay lengths deÞned in milliseconds (ms). The left and right channels are fully symetric (all controls affect both ...
Page 32
10-32 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications the feedback (fdbk level) controls how long a sound in the delay line takes to die out. At 100% feedback, your sound will be repeated indeÞnitely. Hf damping selectively removes high frequency content from your delayed signal and will also cause you...
Page 33
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-33 dry bal the left-right balance of the dry signal. A setting of -100% allows only the left dry signal to pass to the left output, while a setting of 100% lets only the right dry signal pass to the right output. At 0%, equal amounts of the left and ri...
Page 34
10-34 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications parameters page 1 page 2 page 3 tempo basis for the delay lengths, as referenced to a musical tempo in bpm (beats per minute). When this parameter is set to ÒsystemÓ, the tempo is locked to the internal sequencer tempo or to incoming midi clocks. Wh...
Page 35
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-35 133 8-tap delay 134 8-tap delay bpm a stereo eight tap delay with cross-coupled feedback paus: 2 this is a simple stereo 8 tap delay algorithm with delay lengths deÞned in milliseconds (ms). The left and right channels are fully symmetric (all contr...
Page 36
10-36 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications signal from entering the delay. You may have to practice using the hold parameter. Each time your sound goes through the delay, it is reduced by the feedback amount. If feedback is fairly low and you turn on hold at the wrong moment, you can get a d...
Page 37
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-37 fdbk level the percentage of the delayed signal to feed back or return to the delay input. Turning up the feedback will cause the effect to repeatedly echo or act as a crude reverb. Xcouple 8 tap delay is a stereo effect. The cross coupling control ...
Page 38
10-38 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications the measure with interesting rhythmical patterns. Setting tap levels allows some ÒbeatsÓ to receive different emphasis than others. Parameters page 1 page 2 page 3 page 4 tempo basis for the delay lengths, as referenced to a musical tempo in bpm (be...
Page 39
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-39 135 spectral 4-tap 136 spectral 6-tap tempo based 4 and 6 tap delays with added shapers and resonant comb filters on each tap paus: 2 for spectral 4-tap 3 for spectral 6-tap spectral 4 tap and spectral 6 tap are respectively 2 and 3 processing alloc...
Page 40
10-40 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications when temp is set to 60 bpm, each 1/24th of a beat is equivalent to 1/24th of a second. When tempo is set to 250 bpm, each 1/24th of a beat is equivalent to 10ms of delay. Figure 10-9 spectral 6 tap r input r output r dry delay imaging (individual sh...
Page 41
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-41 figure 10-10 various shaper curves used in the spectral multi-taps parameters for spectral 4-tap page 1 page 2 wet/dry 0 to 100 % out gain off, -79.0 to 24.0 db fdbk level 0 to 100 % tempo system, 0 to 255 bpm hf damping 16 to 25088 hz diff delay 0 ...
Page 42
10-42 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications page 3 parameters for spectral 6-tap page 1 page 2 page 3 page 4 tap3 delay 0 to 32 bts tap4 delay 0 to 32 bts tap3 shapr 0.10 to 6.00 x tap4 shapr 0.10 to 6.00 x tap3 pitch c-1 to c8 tap4 pitch c-1 to c8 tap3 ptamt 0 to 100% tap4 ptamt 0 to 100% ta...
Page 43
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-43 wet/dry the relative amount of input signal and effected signal that is to appear in the Þnal effect output mix. When set to 0%, the output is taken only from the input (dry). When set to 100%, the output is all wet. Negative values polarity invert ...
Page 44
10-44 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications algorithms 150–153: choruses 150 chorus 1 151 chorus 2 152 dual chorus 1 153 dual chorus 2 one and three tap dual mono choruses paus: 1 for chorus 1 (both) 2 for chorus 2 (both) chorus is an effect that gives the illusion of multiple voices playing ...
Page 45
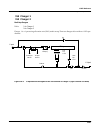
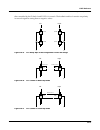
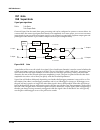
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-45 chorus 2 is a 2 unit allocation multi-tapped delay (3 taps) based chorus effect with cross-coupling and individual output tap panning. Figure 10-11 is a simpliÞed block diagram of the left channel of chorus 2. Figure 10-12 block diagram of left chan...
Page 46
10-46 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications chorus 1 uses just 1 unit allocation and has one delay tap. Figure 10-13 is a simpliÞed block diagram of the left channel of chorus 1. Figure 10-14 block diagram of left channel of dual chorus 1 (right channel is similar) the left and right channels...
Page 47
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-47 in the stereo chorus 1 and chorus 2, the relative phases of the lfos modulating the left and right channels may be adjusted. Figure 10-15 delay for a single lfo the settings of the lfo rates and the lfo depths determine how far the lfos will sweep a...
Page 48
10-48 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications page 2 parameters for chorus 2 page 1 page 2 page 3 parameters for dual chorus 1 page 1 page 2 tap lvl -100 to 100% lfo rate 0.01 to 10.00 hz tap dly 0.0 to 1000.0 ms lfo depth 0.0 to 50.0 ct l/r phase 0.0 to 360.0 deg wet/dry -100 to 100%wet out ga...
Page 49
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-49 page 3 parameters for dual chorus 2 page 1 page 2 page 3 page 4 wet/dry the relative amount of input (dry) signal and chorus (wet) signal that is to appear in the Þnal effect output mix. When set to 0%, the output is taken only from the input. When ...
Page 50
10-50 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications xcouple controls how much of the left channel input and feedback signals are sent to the right channel delay line and vice versa. At 50%, equal amounts from both channels are sent to both delay lines. At 100%, the left feeds the right delay and vice...
Page 51
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-51 154 flanger 1 155 flanger 2 multi-tap flangers paus: 1 for flanger 1 2 for flanger 2 flanger 1 is a 1 processing allocation unit (pau) multi-sweep thru-zero ßanger effect with two lfos per channel. Figure 10-17 simplified block diagram of the left c...
Page 52
10-52 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications flanger 2 is a 2 processing allocation unit (pau) multi-sweep thru-zero ßanger effect with two lfos per channel. Figure 10-18 simplified block diagram of the left channel of flanger 2 (right channel is similar) flanging was originally created by sum...
Page 53
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-53 the realm of chorusing, where the ear begins to perceive the audio output as nearly two distinct signals, but with a variable time displacement. Figure 10-19 comb filters : solid line for addition; dashed line for subtraction the heart of the ßanger...
Page 54
10-54 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications occur smoothly. You can assign the static delay tap to a continuous controller and use the controller to do manual ßanging. Figure 4 shows the delay line for a single lfo. Figure 10-20 delay for a single lfo consider a simple example where you have ...
Page 55
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-55 be added to the input of the ßanger signal (flanger 2 only). White noise has a lot of high frequency content and may sound too bright. The noise may be tamed with a Þrst order lowpass Þlter. Parameters for flanger 1 page 1 page 2 page 3 parameters f...
Page 56
10-56 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications page 3 page 4 wet/dry the relative amount of input signal and ßanger signal that is to appear in the Þnal effect output mix. When set to 0%, the output is taken only from the input (dry). When set to 100%, the output is all wet. Negative values pola...
Page 57
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-57 vast function to smoothly vary the delay length. The range for all delays and excursions is 0 to 230 ms, but for ßanging the range 0 to 5 ms is most effective. Statdlyfin a Þne adjustment to the static delay tap length. The resolution is one sample....
Page 58
10-58 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications algorithms 156–160: phasers 156 lfo phaser 157 lfo phaser twin 158 manual phaser 159 vibrato phaser 160 singlelfo phaser a variety of single notch/bandpass phasers paus: 1 each a simple phaser is an algorithm which produces an vague swishing or phas...
Page 59
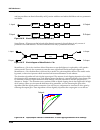
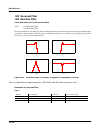
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-59 instead of addition by setting wet/dry to -50%, then the notches become peaks and the peaks become notches. Figure 10-21 response of typical phaser with (i) wet/dry = 50% and (ii) wetdry = -50%. Some of the phaser algorithms have feedback. When feed...
Page 60
10-60 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications when set to 0% and at 200%, the signal is a pure (wet) allpass response. Lfo phaser twin does not have out gain or feedback parameters. Figure 10-22 response of lfo phaser twin with wet/dry set to 100%. The vibrato phaser algorithm has a couple of i...
Page 61
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-61 page 2 wet/dry the amount of phaser (wet) signal relative to unaffected (dry) signal as a percent. Out gain the output gain in decibels (db) to be applied to the combined wet and dry signals. Fdbk level the phaser output can be added back to its inp...
Page 62
10-62 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications notch/bp the amount of notch depth or bandpass. At -100% there is a complete notch at the center frequency. At 100% the Þlter response is a peak at the center frequency. 0% is the dry unaffected signal. Out gain the output gain in decibels (db) to b...
Page 63
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-63 wet/dry the amount of phaser (wet) signal relative to unaffected (dry) signal as a percent. When set to 50% you get a complete notch. When set to -50%, the response is a bandpass Þlter. 100% is a pure allpass Þlter (no amplitude changes, but a stron...
Page 64: Combination Algorithms
10-64 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications combination algorithms 700 chorus+delay 701 chorus+4tap 703 chor+dly+reverb 706 flange+delay 707 flange+4tap 709 flan+dly+reverb 722 pitcher+chor+dly 723 pitcher+flan+dly a family of combination effect algorithms (“+”) paus: 1 or 2 signal routing (2...
Page 65
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-65 parameters for two-effect routing page 1 mix effect adjusts the amount of each effect that is mixed together as the algorithm wet signal. Negative values polarity invert that particular signal. A/dry->b this parameter controls how much of the a effe...
Page 66
10-66 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications page 2 mix effect left and right. Adjusts the amount of each effect that is mixed together as the algorithm wet signal. Separate left and right controls are provided. Negative values polarity invert that particular signal. A/dry>b this parameter con...
Page 67
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-67 flange the ßangers are basic 1 tap dual ßangers. Separate lfo controls are provided for each channel. Slight variations between algorithms may exist. Some algorithms offer separate left and right feedback controls, while some offer only one for both...
Page 68
10-68 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications maximum possible time. Because of this, when you slow down the tempo, you may Þnd the delays lose their sync. Delay regeneration is controlled by dly fdbk. Separate left and right feedback control is generally provided, but due to resource allocatio...
Page 69
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-69 page 2 reverb the reverbs offered in these combination effects is miniverb. Information about it can be found in the miniverb documentation. Parameters associated with this reverb begin with rv. Miniverb tap1 delay 0 to 8 bts tap3 delay 0 to 8 bts t...
Page 70
10-70 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications configurable combination algorithms 702 chorus4tap 704 chorusreverb 705 choruslasrdly 708 flange4tap 710 flangereverb 711 flangelasrdly 712 flangepitcher 713 flangeshaper 714 lasrdlyreverb 715 shaperreverb a family of combination effect algorithms p...
Page 71
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-71 of both effects determined by the mix parameters, and the input dry signal. Negative wet/dry values polarity invert the summed wet signal relative to dry. Figure 10-24 chor4tap with a->b cfg set to ch->4t and 4t->ch bi-directional routing mix effect...
Page 72
10-72 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications since these effects have 2 taps per channel, control over 4 lfos is necessary with a minimum number of user parameters (figure 2). This is accomplished by offering 2 sets of lfo controls with three user interface modes: dual1tap, link1tap, or link2t...
Page 73
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-73 then controlled by the fl statlvl and fl lfo lvl controls. The feedback and level controls can polarity invert each signal be setting them to negative values. Figure 10-25 lfo delay taps in the configurable chorus and flange figure 10-26 lfo control...
Page 74
10-74 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications figure 10-28 lfo control in link2tap mode parameters for chorus page 1 parameters for flange page 1 page 2 ch lfo cfg dual1tap... Ch lrphase 0 to 360 deg ch rate 1 0.01 to 10.00 hz ch rate 2 0.01 to 10.00 hz ch depth 1 0.0 to 100 ct ch depth 2 0.0 t...
Page 75
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-75 ch lfo cfg sets the user interface mode for controlling each of the 4 chorus lfos. Ch lrphase controls the relative phase between left channel lfos and right channel lfos. In dual1tap mode, however, this parameter is accurate only when ch rate 1 and...
Page 76
10-76 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications dly fbimag, dly xcouple, dly hfdamp, and dly lfdamp are just like those found in other algorithms. Not all laser delays in combination algorithms will have all four of these parameters due to resource allocation. Figure 10-29 laser delay (left chann...
Page 77
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-77 dly xcple this parameter controls the amount of signal that is swapped between the left and right channels through each feedback generation when dly fdbk is used. A setting of 0% has no affect. 50% causes equal amounts of signal to be present in bot...
Page 78
10-78 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications causing the image to collapse into a center point source. A setting of 100% causes the left and right channels to swap each regeneration, which is also referred to as Òping-pongingÓ. All other parameters refer to 4-tap delay bpm documentation. Rever...
Page 79
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-79 shp inp lp adjusts the cutoff frequency of the 1 pole (6db/oct) lopass Þlter at the input of the shaper. Shp out lp adjusts the cutoff frequency of the 1 pole (6db/oct) lopass Þlter at the output of the shaper. Shp amount adjusts the shaper intensit...
Page 80
10-80 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 714 quantize+flange digital quantization followed by flanger paus: 1 digital audio engineers will go to great lengths to remove, or at least hide the effects of digital quantization distortion. In quantize+flange we do quite the opposite, making qua...
Page 81
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-81 quantized (its word length is being shortened), quantization usually sounds like additive noise. But notice that as the signal decays in the above Þgures, fewer and fewer quantization levels are being exercised until, like the one bit example, there...
Page 82
10-82 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications page 2 page 3 in/out when set to ÒinÓ, the quantizer and ßanger are active; when set to ÒoutÓ, the quantizer and ßanger are bypassed. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Quant w/d the relative amount of quantized (wet...
Page 83
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-83 the tempo. At Ò0Ó, the lfos stop oscillating and their phase is undetermined (wherever they stopped). Fl fdbk the level of the ßanger feedback signal into the ßanger delay line. The feedback signal is taken from the lfo delay tap. Negative values po...
Page 84
10-84 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 715 dual movdelay 716 quad movdelay generic dual mono moving delay lines paus: 1 for dual 2 for quad each of these algorithms offers generic moving delay lines in a dual mono conÞguration. Each separate moving delay can be used as a ßanger, chorus, ...
Page 85
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-85 720 monopitcher+chor 721 monopitcher+flan mono pitcher algorithm (filter with harmonically related resonant peaks) with a chorus or flanger paus: 2 each the mono pitcher algorithm applies a Þlter which has a series of peaks in the frequency response...
Page 86
10-86 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications the Þgures below show pt pkshape of -1.0 and 1.0, for a pitch of c6 and a pksplit of 0%. Figure 10-33 response of pitcher with different pkshape settings. Applying pitcher to sounds such as a single sawtooth wave will tend to not produce much output...
Page 87
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-87 page 2 page 3 parameters for monopitcher + flan page 1 page 2 page 3 wet/dry this is a simple mix of the pitched and chorused or ßanged signal relative to the dry input signal. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Mix ...
Page 88
10-88 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications mix chorus, mix flange the amount of the ßanger or chorus signal to send to the output as a percent. Pt/dry->ch, pt/dry->fl the relative amount of pitcher signal to dry signal to send to the chorus or ßanger. At 0% the dry input signal is routed to ...
Page 89: Distortion Algorithms
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-89 distortion algorithms 724 mono distortion 725 monodistort + cab 726 monodistort + eq 728 stereodistort+eq small distortion algorithms paus: 1 for mono distortion 2 for monodistort + cab 2 for monodistort + eq 3 for stereodistort + eq figure 10-34 bl...
Page 90
10-90 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications and lowpass Þlters are then followed by an eq section with bass and treble shelf Þlters and two parametric mid Þlters. Figure 10-36 block diagram of stereodistort+eq stereodistort + eq processes the left and right channels separately, though there i...
Page 91
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-91 signals that are symmetric in amplitude (they have the same shape if they are inverted, positive for negative) will usually produce odd harmonic distortion. For example, a pure sine wave will produce smaller copies of itself at 3, 5, 7, etc. Times t...
Page 92
10-92 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications page 2 wet/dry the amount of distorted (wet) signal relative to unaffected (dry) signal. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. For distortion, it is often necessary to turn the output gain down as the distortion drive i...
Page 93
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-93 mid gain the amount of boost or cut that the mid parametric Þlter should apply in db. Every increase of 6 db approximately doubles the amplitude of the signal. Positive values boost the signal at the speciÞed frequency. Negative values cut the signa...
Page 94
10-94 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 727 polydistort + eq eight stage distortion followed by equalization paus: 2 polydistort + eq is a distortion algorithm followed by equalization. The algorithm consists of an input gain stage, and then eight cascaded distortion stages. Each stage is...
Page 95
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-95 polydistort is an unusual distortion algorithm which provides a great number of parameters to build a distortion sound from the ground up. The eight distortion stages each add a small amount of distortion to your sound. Taken together, you can get a...
Page 96
10-96 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications page 4 wet/dry this is a simple mix of the distorted signal relative to the dry undistorted input signal. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. For distortion, it is often necessary to turn the output gain down as the d...
Page 97
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-97 733 vibchor+rotor 2 737 vibchor+rotor 4 vibrato/chorus into optional distortion into rotating speaker paus: 2 for vibchor+rotor 2 4 for vibchor+rotor 4 the vibchor+rotor algorithms contain multiple effects designed for the hammond b3 ¨ emulation (kb...
Page 98
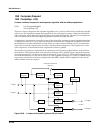
10-98 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications microphone. The signal is then passed through a Þnal lowpass Þlter to simulate the band-limiting effect of the speaker cabinet. Figure 10-41 rotating speaker with virtual microphones for the rotating speakers, you can control the cross-over frequenc...
Page 99
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-99 parameters page 1 page 2 page 3 page 4 in/out when set to ÒinÓ, the algorithm is active; when set to ÒoffÓ the algorithm is bypassed. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. For distortion, it is often necessary to turn t...
Page 100
10-100 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications dist drive applies a boost to the input signal to overdrive the distortion algorithm. When overdriven, the distortion algorithm will soft-clip the signal. Since distortion drive will make your signal very loud, you may have to reduce the out gain a...
Page 101
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-101 large sample skips (audible as clicks when signal is passing through the effect). There are four of these parameters to include 2 pairs (a and b) for high and low frequency drivers. Mic lvl the level of the virtual microphone signal being sent to t...
Page 102
10-102 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 734 distort + rotary small distortion followed by rotary speaker effect paus: 2 distort + rotary models an ampliÞer distortion followed by a rotating speaker. The rotating speaker has separately controllable tweeter and woofer drivers. The algorith...
Page 103
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-103 for the rotating speakers, you can control the cross-over frequency of the high and low frequency bands (the frequency where the high and low frequencies get separated). The rotating speakers for the high and low frequencies have their own controls...
Page 104
10-104 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications cabinet hp a highpass Þlter to simulate the band-limiting of a speaker cabinet. The Þlter controls the lower frequency limit of the output. Cabinet lp a lowpass Þlter to simulate the band-limiting of a speaker cabinet. The Þlter controls the upper ...
Page 105
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-105 hiresxcurs the number of samples of delay to sweep through the resonator at the rotation rate of the rotating speaker. This is for the high frequency signal path. Resh/lphs this parameter sets the relative phases of the high and low resonators. The...
Page 106: Kb3 Fx Algorithms
10-106 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications kb3 fx algorithms 735 kb3 fxbus 736 kb3 auxfx vibrato/chorus into distortion into rotating speaker into cabinet paus: 7 for full working effect 4 for kb3 fxbus 3 for kb3 auxfx the kb3 fxbus and kb3 auxfx algorithms contain multiple effects designed...
Page 107
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-107 c2, c3) settings. The vibrato chorus has been carefully modelled after the electro-mechanical vibrato/ chorus in the b3. An ampliÞer distortion algorithm follows the vibrato/chorus. The distortion algorithm will soft clip the input signal. The amou...
Page 108
10-108 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications rotation before you hear changes to tremolo when parameter values are changed. Negative microphone angles take a longer time to respond to tremolo changes than positive microphone angles. Figure 10-48 acoustic beams for (i) low frequency driver and...
Page 109
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-109 dist drive applies a boost to the input signal to overdrive the distortion algorithm. When overdriven, the distortion algorithm will soft-clip the signal. Since distortion drive will make your signal very loud, you may have to reduce the out gain a...
Page 110
10-110 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications page 4 in/out when set to ÒinÓ, the algorithm is active; when set to ÒoffÓ the algorithm is bypassed. For the entire algorithm to be active, kb3 fxbus must also be active with its roto inout parameter set to ÒinÓ. To completely bypass the rotary, o...
Page 111
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-111 mic pos the angle of the virtual microphones in degrees from the ÒfrontÓ of the rotating speaker. This parameter is not well suited to modulation because adjustments to it will result in large sample skips (audible as clicks when signal is passing ...
Page 112
10-112 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 900 env follow filt envelope following stereo 2 pole resonant filter paus: 2 the envelope following Þlter is a stereo resonant Þlter with the resonant frequency controlled by the envelope of the input signal (the maximum of left or right). The Þlte...
Page 113
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-113 figure 10-50 block diagram of envelope following filter parameters page 1 page 2 wet/dry the amount of modulated (wet) signal relative to unaffected (dry) signal as a percent. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Filt...
Page 114
10-114 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 901 trigenvelopefilt triggered envelope following stereo 2 pole resonant filter paus: 2 the triggered envelope following Þlter is used to produce a Þlter sweep when the input rises above a trigger level. The triggered envelope following Þlter is a ...
Page 115
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-115 figure 10-52 block diagram of triggered envelope filter the time constant of the envelope follower may be set (env rate) as well as the decay rate of the generated envelope (rel rate). After the detected envelope rises above the trigger level, a tr...
Page 116
10-116 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications retrigger the threshold at which the envelope detector resets such that it can trigger again in fractions of full scale where 0db is full scale. This value is only useful when it is below the value of trigger. Env rate the envelope detector decay r...
Page 117
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-117 902 lfo sweep filter lfo following stereo 2 pole resonant filter paus: 2 the lfo following Þlter is a stereo resonant Þlter with the resonant frequency controlled by an lfo (low- frequency oscillator). The Þlter type is selectable and may be one of...
Page 118
10-118 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications a sine wave when set to 100% smoothing. The sudden change in amplitude of the sawtooths develops a more gradual slope with smoothing, ending up as triangle waves when set to 100% smoothing. Figure 10-54 configurable wave shapes parameters page 1 pa...
Page 119
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-119 lfo plswid when the lfo shape is set to pulse, the plswid parameter sets the pulse width as a percentage of the waveform period. The pulse is a square wave when the width is set to 50%. This parameter is active only when the pulse waveform is selec...
Page 120
10-120 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 903 resonant filter 904 dual res filter stereo and dual mono 2 pole resonant filters paus: 1 for resonant filter 1 for dual res filter the resonant Þlter is available as a stereo (linked parameters for left and right) or dual mono (independent cont...
Page 121
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-121 parameters for dual res filter page 1 page 2 wet/dry the amount of Þltered (wet) signal relative to unaffected (dry) signal. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the Þlter. Filtertype the type of resonant Þlter to be used. May be...
Page 122
10-122 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 905 eq morpher/ 906 mono eq morpher parallel resonant bandpass filters with parameter morphing paus: 4 for eq morpher 2 for mono eq morpher the eq morpher algorithms have four parallel bandpass Þlters acting on the input signal and the Þlter result...
Page 123
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-123 arranged in parallel and their outputs summed, so the bandpass peaks are added together and the multiple resonances are audible. Figure 10-57 frequency response of (i) a single bandpass filter; (ii) the sum of two bandpass filters now that weÕve go...
Page 124
10-124 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications page 2 page 3 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the algorithm is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the algorithm is bypassed. Out gain an overall level control of the eq morpher output. Out pan provides panning of the output signal between left and right output chan...
Page 125
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-125 907 ring modulator a configurable ring modulator paus: 1 ring modulation is a simple effect in which two signals are multiplied together. Typically, an input signal is modulated with a simple carrier waveform such as a sine wave or a sawtooth. Sinc...
Page 126
10-126 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications parameters on parameter pages 2 and three will be inactive while in Òl*rÓ mode. Figure 2 shows the signal ßow when in Òl*rÓ mode: figure 10-59 “l*r” mode ring modulator the other modulation mode is ÒoscÓ. In ÒoscÓ mode, the algorithm inputs and out...
Page 127
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-127 change in amplitude of the sawtooths develops a more gradual slope with smoothing, ending up as triangle waves when set to 100% smoothing. Figure 10-61 configurable wave shapes parameters page 1 page 2 page 3 wet/dry the amount of modulated (wet) s...
Page 128
10-128 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications osc1 freq the fundamental frequency of the conÞgurable oscillator. The oscillators can be set through the audible frequencies 16-25088 hz with 1 semitone resolution. This parameter is active only in ÒoscÓ mode. Osc1shape shape selects the waveform ...
Page 129
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-129 908 pitcher creates pitch from pitched or non-pitched signal paus: 1 this algorithm applies a Þlter which has a series of peaks in the frequency response to the input signal. The peaks may be adjusted so that their frequencies are all multiples of ...
Page 130
10-130 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications in figure 10-63, peaks are odd multiples of a frequency one octave down from the pitch setting. This gives a hollow, square-wavey sound to the output. Figure 10-64 [100, 0, 0, 0] in figure 10-64, there are deeper notches between wider peaks figure ...
Page 131
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-131 figure 10-66 is like [100,100,100,100], except that all the peaks are at (all) multiples of half the pitch frequency. Figure 10-67 [50,100,100,100] figure 10-67 is halfway between [0,100,100,100] and [100,100,100,100]. Figure 10-68 [-50,100,100,100...
Page 132
10-132 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications figure 10-68 is halfway between [0,100,100,100] and [-100,100,100,100]. If the odd parameter is modulated with an fxmod, then one can morph smoothly between the [100,100,100,100] and [-100,100,100,100] curves. Figure 10-69 [100, -100, 100, 100] fig...
Page 133
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-133 wet/dry the relative amount of input signal and effected signal that is to appear in the Þnal effect output mix. When set to 0%, the output is taken only from the input (dry). When set to 100%, the output is all wet. Out gain the overall gain or am...
Page 134
10-134 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 909 super shaper ridiculous shaper paus: 1 the super shaper algorithm packs 2-1/2 times the number of shaping loops, and 8 times the gain of the vast shaper. Refer to the section on shapers in the musicianÕs guide for an overview of vast shaper. Se...
Page 135
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-135 910 3 band shaper 3 band shaper paus: 2 the 3 band shaper non-destructively splits the input signal into 3 separate bands using 1 pole (6db/oct) Þlters, and applies a vast-type shaper to each band separately. Refer to the musicians guide for an ove...
Page 136
10-136 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 911 mono laserverb 912 laserverb lite 913 laserverb a bizarre reverb with a falling buzz paus: 1 for mono laserverb 2 for laserverb lite 3 for laserverb laserverb is a new kind of reverb sound that has to be heard to be believed! When it is fed an ...
Page 137
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-137 the output from laserverb can be fed back to the input. By turning up the feedback, the duration of the laserverb sound can be greatly extended. Cross-coupling may also be used to move the signal between left and right channels, producing a left/ri...
Page 138
10-138 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Fdbk lvl the percentage of the reverb output to feed back or return to the reverb input. Turning up the feedback is a way to stretch out the duration of the reverb, or, if the reve...
Page 139
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-139 950 hardknee compress 951 softkneecompress stereo hard- and soft-knee signal compression algorithms paus: 1 the stereo hard- and soft-knee compressors are very similar algorithms and provide identical parameters and user interface. Both algorithms ...
Page 140
10-140 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications in the hard-knee compressor, there is a sudden transition from uncompressed to compressed at the compression threshold. In the soft-knee compressor there is a more gradual transition from compressed to unity gain. Figure 10-76 hard- and soft-knee c...
Page 141
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-141 so is of limited usefulness. In compressors which use more than 1 pau, the delay affects the main signal only, regardless of the side chain conÞguration. A meter is provided to display the amount of gain reduction that is applied to the signal as a...
Page 142
10-142 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 952 expander a stereo expansion algorithm paus: 1 this is a stereo expander algorithm. The algorithms expands the signal (reduced the signalÕs gain) when the signal falls below the expansion threshold. The amount of expansion is based on the larger...
Page 143
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-143 noise), and the threshold set just above the noise level. You can set just how far to drop the noise with the expansion ratio. Figure 10-78 expansion transfer characteristic the signal being expanded may be delayed relative to the side chain proces...
Page 144
10-144 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications signal dly the time in ms by which the input signal should be delayed with respect to expander side chain processing (i.E. Side chain pre-delay). This allows the expansion to appear to turn off just before the signal actually rises. Ratio the expan...
Page 145
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-145 953 compress w/sc eq stereo soft-knee compression algorithm with filtering in the side chain paus: 2 the compress w/sc eq algorithm is the same as the softkneecompress algorithm except that equalization has been added to the side chain signal path....
Page 146
10-146 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications page 2 page 3 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the compressor is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the compressor is bypassed. Out gain compressing the signal causes a reduction in signal level. To compensate, the output gain parameter may be used to increase the g...
Page 147
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-147 sctrebgain the amount of boost or cut that the side chain treble shelving Þlter should apply to the high frequency signals in db. Every increase of 6 db approximately doubles the amplitude of the signal. Positive values boost the treble signal abov...
Page 148
10-148 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 954 compress/expand 955 comp/exp + eq a stereo soft-knee compression and expansion algorithm with and without equalization paus: 2 for compress/expand 3 for cmp/exp + eq these are a stereo compressor and expander algorithms. One version is followed...
Page 149
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-149 to determine how much to compress or expand the signal, the compressor/expander must measure the signal level. Since musical signal levels will change over time, the compression and expansion amounts must change as well. You can control how fast th...
Page 150
10-150 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications expander may be used to suppress background noise in the absence of signal, thus typical expander settings use a fast attack (to avoid losing real signal), slow release (to gradually fade out the noise), and the threshold set just above the noise l...
Page 151
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-151 page 4 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the compressor/expander is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the compressor/ expander is bypassed. Out gain compressing the signal causes a reduction in signal level. To compensate, the output gain parameter may be used to in...
Page 152
10-152 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications makeupgain provides an additional control of the output gain. The out gain and makeupgain controls are additive (in decibels) and together may provide a maximum of 24 db boost to offset gain reduction due to compression or expansion. Bass gain the ...
Page 153
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-153 956 compress 3 band stereo soft-knee 3 frequency band compression algorithm paus: 4 the 3 band compressor divides the input stereo signal into 3 frequency bands and runs each band through its own stereo soft-knee compressor. After compression, the ...
Page 154
10-154 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications times, the signal may stay compressed well after the signal falls below threshold. At short release times, the compressor will open up almost as soon as the signal drops. For typical compressor behaviour, the attack time is considerably shorter tha...
Page 155
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-155 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the compressor is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the compressor is bypassed. Out gain compressing the signal causes a reduction in signal level. To compensate, the output gain parameter may be used to increase the gain by as much...
Page 156
10-156 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 957 gate 958 super gate signal gate algorithms paus: 1 for gate 2 for super gate gate and super gate do stand alone gate processing and can be conÞgured as a stereo or mono effects. As a stereo effect, the stereo signal gates itself based on its am...
Page 157
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-157 figure 10-86 signal envelope for gate and super gate when retrigger is “on” if retrigger is off (super gate only), then the gate will open when the side chain signal rises above threshold as before. The gate will then close as soon as the gate time...
Page 158
10-158 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications if ducking is turned on, then the behaviour of the gate is reversed. The gate is open while the side chain signal is below threshold, and it closes when the signal rises above thresold. If the gate opened and closed instantaneously, you would hear ...
Page 159
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-159 hear one of the input channels, but you want your mono output panned to stereo. -100% is panned to the left, and 100% is panned to the right. Sc input the side chain input may be the amplitude of the left l input channel, the right r input channel,...
Page 160
10-160 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications sctrebfreq the center frequency of the side chain treble shelving Þlters in intervals of one semitone. Scmidgain the amount of boost or cut that the side chain parametric mid Þlter should apply in db to the speciÞed frequency band. Every increase o...
Page 161
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-161 959 2 band enhancer 2 band spectral modifier paus: 1 the 2 band enhancer modiÞes the spectral content of the input signal primarily by brightening signals with little or no high frequency content, and boosting pre-existing bass energy. First, the i...
Page 162
10-162 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications hi shelf g the boost or cut of the high shelving Þlter. Hi delay adjusts the number of samples the hipass signal is delayed. Hi mix adjusts the output gain of the hipass signal. Lo delay adjusts the number of samples the lopass signal is delayed. L...
Page 163
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-163 960 3 band enhancer 3 band spectral modifier paus: 2 the 3 band enhancer modiÞes the spectral content of the input signal by boosting existing spectral content, or stimulating new ones. First, the input is non-destructively split into 3 frequency b...
Page 164
10-164 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications page 2 page 3 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the effect is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the effect is bypassed. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Crossover1 adjusts one of the -6db crossover points at which the input signal ...
Page 165
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-165 961 tremolo 962 tremolo bpm a stereo tremolo or auto-balance effect paus: 1 tremolo and tremolo bpm are 1 processing allocation unit (pau) stereo tremolo effects. In the classical sense, a tremolo is the rapid repetition of a single note created by...
Page 166
10-166 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications parameters for tremolo bpm page 1 page 2 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the effect is active; when set to ÒoutÓ the effect is bypassed. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Tempo for tremolo bpm. Basis for the rate of the lf...
Page 167
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-167 963 autopanner a stereo auto-panner paus: 1 autopanner is a 1 processing allocation unit (pau) stereo auto pan effect. The process of panning a stereo image consists of shrinking the image width of the input program then cyclically moving this smal...
Page 168
10-168 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications parameters page 1 page 2 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the auto-panner is active; when set to ÒoutÓ auto-panner is bypassed. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Lfo rate the speed of the panning motion. Rate scale multipli...
Page 169
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-169 964 dual autopanner a dual mono auto-panner paus: 2 dual autopanner is a 2 processing allocation unit (pau) dual mono auto pan effect. Left and right inputs are treated as two mono signals which can each be independently auto-panned. Parameters beg...
Page 170
10-170 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications figure 10-93 lfo shapes available for dual autopanner parameters page 1 page 2 page 3 in/out when set to ÒinÓ the auto-panner is active; when set to ÒoutÓ auto-panner is bypassed. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. ...
Page 171
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-171 -3db. Values above -3db will cause somewhat of a bump in level as an image passes through the center. Values below -3db will cause a dip in level at the center. Lfo shape the waveform type for the lfo. Choices are sine, saw+, saw-, pulse, tri, and ...
Page 172
10-172 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 965 srs licenced sound retrieval system ® or srs tm effect paus: 1 the srs tm algorithm has been licenced from srs labs, inc. The following is from an srs labs press release: srs, the sound retrieval system, is based on the human hearing system. It...
Page 173
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-173 966 stereo image stereo enhancement with stereo channel correlation metering paus: 1 stereo image is a stereo enhancement algorithm with metering for stereo channel correlation. The stereo enhancement performs simple manipulations of the sum and di...
Page 174
10-174 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications parameters page 1 page 2 l in gain the input gain of the left channel in decibels (db). R in gain the input gain of the right channel in decibels (db). Centergain the level of the sum of left and right channels in decibels (db). The summed stereo s...
Page 175
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-175 967 mono -> stereo stereo simulation from a mono input signal paus: 1 mono -> stereo is an algorithms which creates a stereo signal from a mono input signal. The algorithm works by combining a number of band-splitting, panning and delay tricks. The...
Page 176
10-176 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications page 2 in/out the algorithm is functioning when in/out is set to ÒinÓ. If set to Òout, whatever is on the input channels gets passed to the output unaltered. Out gain the output gain of the pseudo-stereo signal in decibels (db). Centergain the leve...
Page 177
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-177 968 graphic eq 969 dual graphic eq dual mono 10 band graphic equalizer paus: 3 the graphic equalizer is available as stereo (linked parameters for left and right) or dual mono (independent controls for left and right). The graphic equalizer has ten...
Page 178
10-178 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications figure 10-97 overall response with all gains set to +12 db, 0 db and -6 db parameters for graphic eq page 1 page 2 parameters for dual graphic eq page 1 page 2 in/out in or out 31hz g -12.0 to 24.0db 1000hz g -12.0 to 24.0db 62hz g -12.0 to 24.0db ...
Page 179
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-179 page 3 in/out when set to in the left channel equalizer is active; when set to out the left channel equalizer is bypassed. 31hz g gain of the left 31 hz band in db. 62hz g gain of the left 62 hz band in db. 125hz g gain of the left 125 hz band in d...
Page 180
10-180 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 970 5 band eq stereo bass and treble shelving filters and 3 parametric eqs paus: 3 this algorithm is a stereo 5 band equalizer with 3 bands of parametric eq and with bass and treble tone controls. The user has control over the gain, frequency and b...
Page 181
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-181 midn freq the center frequency of the eq in intervals of one semitone. The boost or cut will be at a maximum at this frequency. Midn width the bandwidth of the eq may be adjusted. You specify the bandwidth in octaves. Small values result in a very ...
Page 182
10-182 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 998 fxmod diagnostic fxmod source metering utility algorithm paus: 1 the fxmod diagnostic algorithm is used to obtain a metered display of fxmod sources. This algorithm allows you to view the current levels of any data sliders, midi controls, switc...
Page 183
Kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications 10-183 999 stereo analyze signal metering and channel summation utility algorithm paus: 1 stereo analyze is a utility algorithm which provides metering of stereo signals as its primary function. In addition to metering, the gains of the two channels are s...
Page 184
10-184 kdfx reference kdfx algorithm specifications parameter to attempt to correct the problem. Positive delays are delaying the left channel, while negative delays are delaying the right channel. By inverting one channel with respect to the other, you can hear what is characterised as Òphasey-ness...