Kurzweil KDFX V2 - MUSICIANS REFERENCE REV B Reference
K
DFX
V2
M
usician’s Reference
© Young Chang Co., Ltd. 2002. All rights reserved. Permission is granted to reprint up to two copies of this manual for personal use.
Kurzweil ® is a product line of Young Chang Co., Ltd. Young Chang®, Kurzweil ® , V. A. S. T. ®, KDFX®, Pitcher®, and LaserVerb®, KSP8 ™,
K2600™, K2500™, and K2000™ are trademarks of Young Chang Co., Ltd. SmartMedia™ is a trademark of Toshiba Corporation. ADAT® is a
registered trademark of Alesis Corporation. All other products and brand names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies. Product features and specifications are subject to change without notice.
Part Number: 910379, Rev. B
Summary of KDFX V2 - MUSICIANS REFERENCE REV B
Page 1
K dfx v2 m usician’s reference © young chang co., ltd. 2002. All rights reserved. Permission is granted to reprint up to two copies of this manual for personal use. Kurzweil ® is a product line of young chang co., ltd. Young chang®, kurzweil ® , v. A. S. T. ®, kdfx®, pitcher®, and laserverb®, ksp8 ™...
Page 2: World Wide Web Home Page
Ii young chang international contacts contact the nearest young chang office listed below to locate your local young chang/ kurzweil representative. Young chang america, inc. P.O. Box 99995 lakewood, wa 98499-0995 tel: 1-253-589-3200 fax: 1-253-984-0245 young chang co., ltd. 178-55 gajwa-dong seo-ku...
Page 3: Table of Contents
Table of contents-1 table of contents young chang international contacts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ii introducing kdfx version 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1 overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 4
Table of contents-2 auxfx bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8 outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9 chaining effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 5: Chapter 1
Chapter 1 introducing kdfx version 2 overview kdfx v2 gives you more control than ever over the effects in each studio, through several enhancements: • you can assemble chains of up to four fx presets on an fxbus. • you have access to 26 new kdfx algorithms (29 for k2500). • you can mute or bypass e...
Page 6
1-2 introducing kdfx version 2 additions and changes to effects mode pages additions and changes to effects mode pages prior to v2, there was a single effects mode page, which was responsible primarily for setting the fx mode and fx chan parameters. This pair of parameters affected how the k2600/k25...
Page 7: Main Page
enable ...
Page 8: Soft Buttons In Effects Mode
1-4 introducing kdfx version 2 main page soft buttons in effects mode the main button takes you to the kdfxmode:main page, where you can view the current studio and the fx presets assigned to the five kdfx buses. The ctrl button takes you to the kdfxmode:ctrl page, which contains parameters that det...
Page 9: Effects Bus Editor
...
Page 11: The Ctrl Page
Introducing kdfx version 2 the ctrl page 1-7 the ctrl page the ctrl page is where you set a variety of important parameters for kdfx, including the effects control mode (fxctrl) for the current studio; this parameter was known as fx mode in kdfx v1, and its function is the same in kdfx v2. As in kdf...
Page 12: Bypass and Mute Pages
1-8 introducing kdfx version 2 bypass and mute pages bypass and mute pages in kdfx v1, you could perform a global bypass by pressing the effects button while inside an editor. You could not bypass effects outside of an editor. With kdfx v2, you can bypass effects buses, inside or outside of an edito...
Page 16
1-12 introducing kdfx version 2 chaining effects use the left and right cursor buttons to select each block. When a block is selected, move the alpha wheel or press the + or - buttons to select a different fx preset (you can also change the preset by cursoring to the full name of the preset after th...
Page 17: Kdfx V2 Objects
Introducing kdfx version 2 kdfx v2 objects 1-13 kdfx v2 objects listed below are the new kdfx objects added with version 5.Xx (k2500) or 3.Xx (k2600) of the base objects file. These include new fx algorithms, presets, and studios added to the k2500/k2600 with the new object files. Objects marked “ad...
Page 18
1-14 introducing kdfx version 2 kdfx v2 objects additional fx studios new to k2500 167 auxchorenvf hall 182 auxflgchdl hall 168 auxchrvencr chor 183 auxdstlsr cdr 169 auxchrdsteq room 184 cpdlenfltcmpgtrv 170 aux chdlsrs hall 185 rotoorgfx2 hall 171 aux eqflng dsteq 186 chdlflptlzvb plt 172 auxflngp...
Page 19: New Fx Presets
Introducing kdfx version 2 kdfx v2 objects 1-15 new fx presets 104 cool dark place 793 very nazty rotor 105 gunshot verb 794 80's funk guitar 106 rvrb compression 795 mean 70'sfunkgtr 107 snappy drum room 796 crunch guitar 108 roomitizer 797 classic gtr dist 109 live to tape 798 saturatedgtrdist 123...
Page 20
1-16 introducing kdfx version 2 kdfx v2 objects additional fx presets new to k2500 11 viewing booth 817 non-linear 846 flange echo 122 reverse reverb 2 818 slapverb 847 rotary club 196 static phaser 819 full bass 848 rotary hall 782 vibrchrdstrotor1 820 room + delay 849 chorus 783 vibrchrdstrotor2 8...
Page 21: Chapter 2
Chapter 2 a tour of kdfx v2 let’s take a tour through several kdfx v2 studios. After you do this, you should have a pretty good idea of what it’s like to work with effects mode. Note: if you have a k2600, the information in this chapter replaces the information on 9-12 through 9-26 in the rev. A k26...
Page 22: A Simple Studio
2-2 a tour of kdfx v2 a simple studio a simple studio call up program #199 on your k2600/k2500. In program mode, either scroll the alpha wheel to program 199 default program, or press 1-9-9-enter on the alphanumeric pad. Now go into effects mode by pressing the effects button, and you’ll see this pa...
Page 23
A tour of kdfx v2 a simple studio 2-3 delays. These parameters are called “bus overrides,” because they override parameters which are actually inside the fx preset itself—these parameters can be adjusted from inside the fx preset, or they can be set from out here, where they are much more convenient...
Page 24
2-4 a tour of kdfx v2 a simple studio the s at the upper left says that the input a is being handled as a stereo feed; this can be changed to two mono feeds. The p means that the stereo feed has a pan control; you can choose to make this a balance control instead, by setting this parameter to sb. If...
Page 25
A tour of kdfx v2 a simple studio 2-5 the auxfx page press the auxfx soft button. This page appears: this is the global auxfx page, and shows us what is happening on the auxiliary effects bus. The aux bus is a second processor, which follows the four insert fxbuses. It has its own fx preset, with bu...
Page 26: A More Complex Studio
2-6 a tour of kdfx v2 a more complex studio here’s a diagram of what this studio looks like: figure 2-1 structure of studio 200* a more complex studio press exit as many times as necessary to get to program mode. Call up program 200 elecpno/flute. This is a split keyboard program: on layer 1, which ...
Page 27
A tour of kdfx v2 a more complex studio 2-7 these overrides (that is, which parameters are available, and their values) are stored as part of the studio, not as part of the fx preset, and therefore you don’t have to create new fx presets just because you want to change a couple of parameters. There ...
Page 28
2-8 a tour of kdfx v2 a more complex studio this input is configured to be stereo. It has a large bass boost: 12.0 db of everything at 370 hz and below, which adds a strong low-frequency emphasis to the signal being ring-modulated. Its signal is being sent only to the first fxbus. The stereo separat...
Page 29
A tour of kdfx v2 a more complex studio 2-9 outputs finally, press the output soft button to get to the output page. Here we see that the four physical output pairs are each passing different parts of the studio. If the outputs are connected to an external mixer, you can treat each of them separatel...
Page 30: Chaining Effects
2-10 a tour of kdfx v2 chaining effects chaining effects now we’ll see how you can employ multiple effects on a single bus using the new chaining feature in kdfx v2. Start in program mode by highlighting program 199 default program, then pressing the effects button. From the kdfxmode:main page, sele...
Page 32
2-12 a tour of kdfx v2 chaining effects chain, since you have now maximized your pau usage. If you’d like to have four effects on the chain, you’ll have to select only effects that use a single pau. (you’ll also have to remove the empty effects block from fxbus 3 so that it will be available for fxb...
Page 33
A tour of kdfx v2 a complex studio with real-time control 2-13 a complex studio with real-time control the final studio we’ll look at is a bit more complex, not least because it’s under real-time control. Getting real-time control of a studio requires doing some advance work. Most noticeably, you ha...
Page 34
2-14 a tour of kdfx v2 a complex studio with real-time control looking at the studio starting from setupmode, press edit, then more> three times. Now press the kdfx soft button to view the studio. The name of the studio associated with this setup, 202*complex, appears. Highlight the studio’s name an...
Page 35
A tour of kdfx v2 a complex studio with real-time control 2-15 setting up fxmods how do you set up fxmods? That’s back on the kdfx page in the setup editor. Exit the studio editor (if you have made any changes, don’t save them—that will only confuse things!), then press the kdfx soft button. Listed ...
Page 36
2-16 a tour of kdfx v2 a complex studio with real-time control if you now go inside the fx preset (by pressing edit), you’ll see that the left and right feedback levels (“fdbk lvl”) are under fxmod control: press param2, you’ll see that the left and right lfo rates are also under fxmod control. Go b...
Page 37
...
Page 38
2-18 a tour of kdfx v2 a complex studio with real-time control and in conclusion... Here’s a summary of the fxmods in our complex studio with real-time control: • soft pedal puts compression on the bass and drums. • slider f controls the feedback on the chorus on the piano/string pad. Slider e contr...
Page 39
A tour of kdfx v2 a note about effects in setups 2-19 a note about effects in setups this applies primarily to k2600r/k2500r users who are playing their units with a conventional midi keyboard. In order to play setups, which normally require a multi-zoned/multichannel keyboard like the k2600 or pc2,...
Page 40: Building Your Own
2-20 a tour of kdfx v2 building your own building your own now that we’ve walked you through a complex studio, here are some hints on how to go about building your own. First, you want to decide whether you want the studio to be static, or to be dynamic under fxmod control from the k2600/k2500 keybo...
Page 41: Chapter 3
Algorithm reference 3-1 chapter 3 algorithm reference this chapter provides complete reference information for the new algorithms included in kdfx v2. This information is in addition to the algorithm information provided in chapter 10 of your k2600 musician’s reference or your k2500 kdfx algorithm r...
Page 42
3-2 algorithm reference degen regen bpm 138 degen regen bpm long delay allowing loop instability paus: 4 each degen regen bpm starts as a simple mono delay line with feedback. However with the fdbk gain and dist drive parameters, the algorithm can be pushed hard into instability. When degen regen bp...
Page 43
Algorithm reference degen regen bpm 3-3 figure 1 degen regen bpm parameters: page 1 page 2 wet/dry -100 to 100%wet out gain off, -79.0 to 24.0 db loop gain off, -79.0 to 24.0 db tempo system, 1 to 255 bpm loop lvl -100 to 100% send gain off, -79.0 to 24.0 db hf damping 8 to 25088 hz lf damping 8 to ...
Page 44
3-4 algorithm reference degen regen bpm page 3 page 4 wet/dry the relative amount of input signal and delay signal that is to appear in the final effect output mix. When set to 0%, the output is taken only from the input (dry). When set to 100%, the output is all wet. Out gain the overall gain or am...
Page 45
Algorithm reference degen regen bpm 3-5 looplength the delay length of the feedback tap. If feedback is turned up from 0%, this parameter sets the repeating delay loop length. In degen regen bpm, the loop length is specified as a fraction or multiple of the tempo, in “beats.” the length of a delay l...
Page 46
3-6 algorithm reference degen regen bpm tnlfodepth the output delay taps (1 and 2) will have their positions modulated by an lfo (internal to the fx processor) if the tnlfodepth parameter is non-zero. A moving tap on a delay line will result in a pitch shift, and tnlfodepth sets the maximum pitch sh...
Page 47
Algorithm reference switch loops 3-7 139 switch loops looped delay lines with input switching paus: 2 switch loops allows you to run up to four parallel recirculating delay lines of different lengths, switching which delay line(s) are receiving the input signal at a given moment. The stereo input is...
Page 48
3-8 algorithm reference switch loops parameters: page 1 page 2 page 3 out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Dry in/out if set to in, dry in/out allows the dry input signal to be added to the final algorithm output. Dry gain if dry in/out is in, then dry gain controls th...
Page 49
Algorithm reference switch loops 3-9 dlyselectn you select which delay lines (a, b, c, or d) receive the mono input signal with the dlyselect (1, 2, 3, or 4) parameters. Since there are four delay lines, you can turn on none, 1, 2, 3, or 4 of the delay lines. All four of the dlyselect parameters are...
Page 50
3-10 algorithm reference moving delay 140 moving delay generic stereo moving delay lines paus: 1 moving delay is identical to dual movdelay except that the algorithm now has stereo controls rather than dual mono. This means all the controls except l pan and r pan are no longer dual left and right bu...
Page 51
Algorithm reference allpass phaser 3 3-11 161 allpass phaser 3 allpass filter phasers paus: 3 the allpass phasers are algorithms that use allpass filters to achieve a phaser effect. These algorithms do not have built in lfos, so like manual phaser, any motion must be supplied with an fxmod. Unlike t...
Page 52
3-12 algorithm reference allpass phaser 3 by adding the phaser output to the dry input using, for example, a wet/dry parameter, you can produced peaks and notches in the frequency response. At frequencies where the phaser is “in phase” with the dry signal, the signal level doubles (or there is a 6 d...
Page 53: Rotary Effects
Algorithm reference vc+dist+1rotor 2 3-13 rotary effects 738 vc+dist+1rotor 2 739 vc+dist+hilorotr 740 vc+tube+rotor 4 741 rotor 1 742 vc+dist+hilorot2 rotating speaker algorithms paus: 1 for rotor 1 2 each for vc+dist+1rotor 2, vc+dist+hilorotr, and vc+dist+hilorot2 4 for vc+tube+rotor 4 the rotary...
Page 54
3-14 algorithm reference vc+dist+hilorot2 for the rotating speakers, you can control the crossover frequency of the high and low frequency bands (the frequency where the high and low frequencies get separated). The rotating speakers for the high and low frequencies have their own controls. For both,...
Page 55
Algorithm reference vc+dist+hilorot2 3-15 parameters (vc+dist+1rotor 2): page 1 page 2 page 3 page 4 vc+dist+hilorotr gives you a model of the hammond vibrato/chorus, distortion and the band splitting for high and low frequency drivers. To pack all this into a two-pau algorithm, a few sacrifices had...
Page 56
3-16 algorithm reference vc+dist+hilorot2 figure 7 vc+dist+hilorotr and vc+dist+hilorot2 parameters (vc+dist+hilorotr and vc+dist+hilorot2): page 1 (vc+dist+hilorotr) page 1 (vc+dist+hilorot2) in gain off, -79.0 to 24.0 db in/out in or out out gain off, -79.0 to 24.0 db vibchinout in or out dist dri...
Page 57
Algorithm reference vc+dist+hilorot2 3-17 page 2 page 3 page 4 rotor 1 is a rotating speaker model on a budget. Its most attractive feature is its small size (one pau). Obviously a few things had to be scaled back. There is no vibrato/chorus model and no distortion control. There is only a single ro...
Page 58
3-18 algorithm reference vc+dist+hilorot2 figure 8 rotor 1 parameters (rotor 1): page 1 page 2 page 3 page 4 in/out in or out in gain off, -79.0 to 24.0 db out gain off, -79.0 to 24.0 db cabinet lp 8 to 25088 hz gain off, -79.0 to 24.0 db rate -10 to 10 hz size 0 to 250 mm trem 0 to 100% beam w 45.0...
Page 59
Algorithm reference vc+dist+hilorot2 3-19 vc+tube+rotor 4 faithfully models the response and smooth distortion caused by overloading a vacuum tube circuit. Parameters (vc+tube+rotor 4): page 1 (vc+tube+rotor 4) page 2 page 3 page 4 in/out when set to in, the algorithm is active; when set to out the ...
Page 60
3-20 algorithm reference vc+dist+hilorot2 roto inout when set to in the rotary speaker is active; when set to out the rotary speaker is bypassed. Dist curve controls the curvature of the distortion. 0% is no curvature (no distortion at all). At 100%, the curve bends over smoothly and becomes perfect...
Page 61
Algorithm reference vc+dist+hilorot2 3-21 lo size the effective size (radius of rotation) of the rotating woofer in millimeters. Affects the amount of doppler shift or vibrato of the low frequency signal. Lo trem controls the depth of tremolo of the low frequency signal. Expressed as a percentage of...
Page 62
3-22 algorithm reference subtle distort 743 subtle distort adds small amount of distortion to signal. Paus: 1 use subtle distort to apply small amounts of distortion to a signal. The distortion characteristic is set with the curvature and evenorders parameters. Increasing curvature increases the dis...
Page 63
Algorithm reference quantize+alias 3-23 744 quantize+alias digital quantization followed by simulated aliasing. Paus: 1 the quantize+alias algorithm offers some of the worst artifacts that digital has to offer! Digital audio engineers will go to great lengths to remove, or at least hide the effects ...
Page 64
3-24 algorithm reference quantize+alias clearly a one-bit word gives a very crude approximation to the original signal while four bits is beginning to do a good job of reproducing the original decaying sine wave. When a good strong signal is being quantized (its word length is being shortened), quan...
Page 65
Algorithm reference quantize+alias 3-25 in the quantize+alias algorithms, we do not actually sample the incoming signal at a lower rate. Instead we use a special modulation algorithm to simulate the effect of pitches falling when they should be rising. The pitch (coarse and fine) parameters roughly ...
Page 66
3-26 algorithm reference pitcher+miniverb 745 pitcher+miniverb combination algorithm of pitcher followed by miniverb paus: 2 pitcher+miniverbis pitcher followed by miniverb. Pitcher applies a filter to the signal, the filter having a regular series of peaks in its frequency response which generally ...
Page 67
Algorithm reference pitcher+miniverb 3-27 page 3 wet/dry the relative amount of input signal and effected signal that is to appear in the final effect output mix. When set to 0%, the output is taken only from the input (dry). When set to 100%, the output is all wet. Out gain the overall gain or ampl...
Page 68
3-28 algorithm reference pitcher+miniverb rv hfdamp reduces high frequency components of the reverb above the displayed cutoff frequency. Removing higher reverb frequencies can often make rooms sound more natural. Rv predlyl/r the delay between the start of a sound and the output of the first reverb...
Page 69
Algorithm reference reverb+compress 3-29 746 reverb+compress a reverb and compressor in series. Paus: 2 reverb+compress is configured as a reverb followed by a compressor. The reverbs used are the same as miniverb. The compressor is a soft-knee compressor and can be configured as a feed-forward or f...
Page 70
3-30 algorithm reference reverb+compress time controls how long it takes the compressor to respond to a reduction in signal levels. At long release times, the signal may stay compressed well after the signal falls below threshold. At short release times, the compressor will open up almost as soon as...
Page 71
Algorithm reference reverb+compress 3-31 in/out when set to in the overall algorithm is active; when set to out the algorithm is bypassed. Reverbw/d this is a simple mix of the reverb input (dry) with the reverb output (wet) to produce the final reverb output. Reverbgain an overall level control of ...
Page 72
3-32 algorithm reference st chorus+delay 781 st chorus+delay 784 st flange+delay combination effect algorithms using time/frequency units instead of tempo paus: 1 or 2 the algorithms listed here are identical in most respects to combination effects elsewhere documented. For example, st chorus+delay ...
Page 73
Algorithm reference gate+cmp[eq]+vrb 3-33 790 gate+cmp[eq]+vrb combination algorithm designed for vocal processing. Paus: 4 each this algorithm is provided with vocal processing in mind. It includes a gate followed by a compressor and a reverb. Equalization is included as part of the compressor’s si...
Page 74
3-34 algorithm reference gate+cmp[eq]+vrb page 3 page 4 page 5 out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the entire algorithm. Gatein/out when set to in the gate is active; when set to out the gate is bypassed. Gatescinp select the input source channel for gate side-chain processing—le...
Page 75
Algorithm reference gate+cmp[eq]+vrb 3-35 gate atk the time for the gate to ramp from closed to open (reverse if gate duck is on) after the signal rises above threshold. Gate rel the time for the gate to ramp from open to closed (reverse if gate duck is on) after the gate timer has elapsed. Gatesigd...
Page 76
3-36 algorithm reference gate+cmp[eq]+vrb specified frequency. Negative values cut the signal at the specified frequency. Cmpscmidf, mid freq the center frequency of the parametric mid filter in intervals of one semitone. The boost or cut will be at a maximum at this frequency. Cmpscmidw, mid width ...
Page 77
Algorithm reference gate+tubeamp 3-37 792 gate+tubeamp combination algorithm designed for guitar processing. Paus: 3 this algorithm is provided with guitar processing in mind. It sends the signal through a gate, tone controls, tube distortion and cabinet simulation or eq section. Also depending on t...
Page 78
3-38 algorithm reference gate+tubeamp basic flat response from 100 hz to 4 khz with 24db/oct rolloffs on each end lead 12 open back hard american type with one 12” driver 2x12 closed back classic american type with two 12” drivers open 12 open back classic american type with one 12” driver open 10 o...
Page 79
Algorithm reference gate+tubeamp 3-39 gate duck when set to off, the gate opens when the signal rises above threshold and closes when the gate time expires. When set to on, the gate closes when the signal rises above threshold and opens when the gate time expires. Gate time the time in seconds that ...
Page 80
3-40 algorithm reference revrse laserverb 914 revrse laserverb a bizarre reverb which runs backwards in time. Paus: 4 revrse laserverb is a mono effect that simulates the effect of running the laserverb in reverse. When you play a sound through the algorithm, it starts out relatively diffuse then bu...
Page 81
Algorithm reference revrse laserverb 3-41 figure 18 revrse laserverb parameters: page 1 page 2 wet/dry the amount of reverbed (wet) signal relative to unaffected (dry) signal. Rvrs w/d a special wet/dry control in which the “dry” signal is in fact delayed so that it is the last sound to be sent to t...
Page 82
3-42 algorithm reference revrse laserverb contour controls the overall envelope shape of the reverb. When set to a high value, sounds start at a high level and build slowly to the final “hit.” as the control value is reduced, sounds start lower and build rapidly to the final “hit.”.
Page 83
Algorithm reference gated laserverb 3-43 915 gated laserverb the laserverb algorithm with a gate on the output. Paus: 3 gated laserverb is laserverb lite with a gate on the output. For a detailed explanation of laserverb see the section for laserverb lite. The gate controls are covered under gate. S...
Page 84
3-44 algorithm reference gated laserverb page 3 wet/dry the amount of reverbed and gated (wet) signal relative to unaffected (dry) signal. The gate is on the wet signal path. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. Fdbk lvl the percentage of the reverb output to feed back...
Page 85
Algorithm reference gated laserverb 3-45 gate thresh the signal level in db required to open the gate (or close the gate if ducking is on). Gate duck when set to off, the gate opens when the signal rises above threshold and closes when the gate time expires. When set to on, the gate closes when the ...
Page 86
3-46 algorithm reference poly pitcher 916 poly pitcher creates pitch from pitched or non-pitched signal—twice. Paus: 2 poly pitcher is closely based on pitcher, and most of the features of poly pitcher are covered in the section on pitcher. Poly pitcher is really just a pair of pitcher algorithms (a...
Page 87
Algorithm reference poly pitcher 3-47 pitch a, b the fundamental pitch imposed upon the input expressed in semitone scale intervals. Pitcher a and pitcher b may be set independently. Pchoff al pchoff ar pchoff bl pchoff br an offset from the pitch frequency in semitones. Not only are the a and b pit...
Page 88
3-48 algorithm reference frequency offset 917 frequency offset 918 mutualfreqoffset single side band modulation paus: 2 frequency offset and mutualfreqoffset perform single side band (ssb) modulation. Essentially what this means is that every frequency component of your input sound will be offset (i...
Page 89
Algorithm reference mutualfreqoffset 3-49 mutualfreqoffset modulates the two input signals (left and right) with each other. If one of the signals is a sine wave, the algorithm behaves like frequency offset. Now imagine that one of the input signals is the sum of two sine waves. Both of the two sine...
Page 90
3-50 algorithm reference mutualfreqoffset page 2 parameters (mutualfreqoffset): page 1 page 2 wet/dry the amount of modulated (wet) signal relative to the unaffected (dry) signal as a percent. Out gain the overall gain or amplitude at the output of the effect. In lowpass a first-order lowpass filter...
Page 91
Algorithm reference mutualfreqoffset 3-51 dwnoffspan the down modulated signal may be panned to the left or right algorithm outputs. -100% sends the signal to the left output and 100% sends the signal to the right output. Upoffspan the up modulated signal may be panned to the left or right algorithm...
Page 92
3-52 algorithm reference wackedpitchlfo 919 wackedpitchlfo an lfo based pitch shifter. Paus: 3 okay, it ain’t pretty, but wackedpitchlfo uses lfo modulated delay lines with cross fades to produce a shift of signal pitch. You can set the amount of shift in coarse steps of semitones or fine steps of c...
Page 93
Algorithm reference wackedpitchlfo 3-53 lfo rate the frequency of the lfos that drive the pitch shifter. The pitch shifter produces a certain amount of tremolo that will oscillate based on this rate. However reducing the rate will increase the delay lengths needed by the pitch shifter. Shift crs a c...
Page 94
3-54 algorithm reference chaos! 920 chaos! Fun with chaos and instability paus: 2 the moment you scroll to the chaos! Algorithm, you will discover it is wildly unstable. Chaos! Is a delay feedback algorithm which includes lots of gain with distortion plus plenty of filters tweaking the sound. Modify...
Page 95
Algorithm reference chaos! 3-55 figure 24 resonating frequencies with fb invert set to (i) out and set to (ii) in. In addition to the distortion warmth filter, there are six filters built into the delay line loop: a highpass, a lowpass, a treble and a bass shelf, and two parametric midrange filters....
Page 96
3-56 algorithm reference chaos! Drive cut reduces the signal level after the distortion. By reducing the signal level after the distortion, chaos! Can be returned to stability while still producing a lot of distortion. Drive cut is also inside the feedback loop. Warmth warmth affects the character o...
Page 97
Algorithm reference band compress 3-57 948 band compress stereo algorithm to compress a single frequency band paus: 3 band compress is in most respects identical to softkneecompress. However, band compress compresses only on a single band of frequencies. Frequency band selection is based on a parame...
Page 98
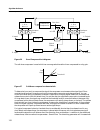
3-58 algorithm reference band compress figure 26 band compress block diagram the soft-knee compressor is used which has a more gradual transition from compressed to unity gain. Figure 27 soft-knee compression characteristic to determine how much to compress the signal, the compressor must measure th...
Page 99
Algorithm reference band compress 3-59 the attack and release times, although the effect is significant only when its time is longer than the attack or release time. Generally the smoothing time should be kept at or shorter than the attack time. You have the choice of using the compressors configure...
Page 100
3-60 algorithm reference band compress comprschan select which input channel will receive compression processing—left, right or both. If you select left or right, the opposite channel will pass through unaffected. Fdbkcomprs a switch to set whether the compressor side chain is configured for feed-fo...
Page 101
Algorithm reference compressdualtime 3-61 949 compressdualtime compression with 2 release time constants paus: 2 compressdualtime is a basic compressor with two different release rates, which change from one rate to another as the compression gain reduction crosses a threshold set by the rel thres (...
Page 102
3-62 algorithm reference compressdualtime figure 28 opto compress the soft-knee compressor is used which has a more gradual transition from compressed to unity gain. Figure 29 soft-knee compression characteristic for typical compressor behavior, the attack time is considerably shorter than the relea...
Page 103
Algorithm reference compressdualtime 3-63 parameters: page 1 page 2 in/out when set to in the compressor is active; when set to out the compressor is bypassed. Out gain the output gain parameter may be used to increase the gain by as much as 24 db, or reduce the gain to nothing. Note that the out ga...
Page 104
3-64 algorithm reference compressdualtime ratio the compression ratio in effect above the compression threshold. High ratios are highly compressed; low ratios are moderately compressed. Comp thres the compression threshold level in dbfs (decibels relative to full scale) above which the signal begins...
Page 105
Algorithm reference 3 band eq 3-65 971 3 band eq bass and treble shelving filter and parametric eqs paus: 1 this algorithm is a multi-band equalizers with parametric eq and bass and treble tone controls. You can control the gain, frequency and bandwidth of each band of parametric eq and control of t...
Page 106
3-66 algorithm reference hf stimulate 1 972 hf stimulate 1 high-frequency stimulator paus: 1 the high-frequency stimulator algorithm is closely based on the v.A.S.T. High frequency stimulator dsp function, and the manual description is repeated here (edited for kdfx specifics). The overall effect of...
Page 107
Algorithm reference harmonicsuppress 3-67 975 harmonicsuppress stereo algorithm to expand a single frequency band or harmonic bands. Paus: 2 harmonicsuppress is a special expander algorithm. In most respects it is identical to expander. However, harmonicsuppress expands on only harmonically related ...
Page 108
3-68 algorithm reference harmonicsuppress figure 32 band suppression to determine how much to expand the signal, the expander must measure the signal level. Since musical signal levels will change over time, the expansion amounts must change as well. You can control how fast the expansion changes in...
Page 109
Algorithm reference harmonicsuppress 3-69 a meter is provided to display the amount of gain reduction that is applied to the signal as a result of expansion. Parameters: page 1 (harmonicsuppress) page 2 in/out when set to in the expander is active; when set to out the band suppressor is bypassed. Ou...
Page 110
3-70 algorithm reference harmonicsuppress smoothtime a lowpass filter in the control signal path. It is intended to smooth the output of the expander’s envelope detector. Smoothing will affect the attack or release times when the smoothing time is longer than one of the other times. Signal dly the t...
Page 111
Index-1 numerics 3 band eq, 3-65 a allocation parameter, 2-3 allpass phaser 3, 3-11 audio levels, 2-4 auxfx bus, 2-8 auxfx page (studio editor), 2-5 b band compress, 3-57 bypass, 1-8 c chan/bank button for bypassing, 1-4 chaos!, 3-54 compressdualtime, 3-61 d degen regen bpm, 3-2 e embedded editors w...
Page 112
Index-2 st flange+delay, 3-32 studio tutorial example, 2-2 studio editor auxfx page, 2-5 input page, 2-3 subtle distort, 3-22 switch loops, 3-7 t tempo control, 2-2 tutorial, 2-1 v vc+dist+1rotor 2, 3-13 vc+dist+hilorot2, 3-13 vc+dist+hilorotr, 3-13 vc+tube+rotor 4, 3-13 w wackedpitchlfo, 3-52 websi...