- DL manuals
- Lada
- Automobile
- Niva 4x4
- Service Manual
Lada Niva 4x4 Service Manual
http://www.lada.co.uk
Lada Niva 4x4
Service Manual
Fuel Injection
You can do anything you like with this manual except sell it or
otherwise make money from it.
You use the information contained with this manual at your own risk.
If you're not sure how to do something either don't do it or ask
someone who knows about such things. The font of all Lada
knowledge can be found at:
http://www.lada.co.uk/forum
For Lada parts, advice and general all round Lada wonderfulness
these blokes aren't bad:
Contact
Tom
G
realey
tom@lada.co.uk
Summary of Niva 4x4
Page 1
Http://www.Lada.Co.Uk lada niva 4x4 service manual fuel injection you can do anything you like with this manual except sell it or otherwise make money from it. You use the information contained with this manual at your own risk. If you're not sure how to do something either don't do it or ask someon...
Page 2: Chapter 3. Power Train
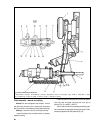
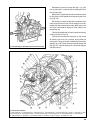
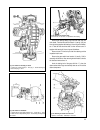
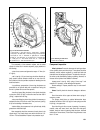
The design of the clutch is shown on fig. 3-1. The clutch release fork 11 (fig. 3-1) can be of two types: with a leaf or wire spring. Chapter 3. Power train clutch 57 fig. 3-1. Clutch assembly: 1 - bleeder; 2 - central diaphragm spring; 3 - diaphragm spring rivet; 4 - pressure plate; 5 - clutch disc...
Page 3
Fault diagnosis diagnosis remedy incomplete clutch release (clutch spin) 1. Excessive gaps in clutch release drive 2. Buckling of clutch disc (camming action more than 0.5 mm) 3. Roughness on clutch disc friction linings 4. Jammed rivets or broken clutch disc friction linings 5. Jammed clutch disc h...
Page 4
Bleeding the clutch hydraulic system air in the clutch hydraulic system is indicated by incomplete clutch release, and also by "sponginess" and "failure" of clutch pedal. To expel air from the hydraulic drive: - clean the tank and the bleeder from dust and dirt; - check the liquid level in the hydra...
Page 5
Clutch assembly - removal and refitting removal. First remove the gearbox (see "gearbox"). Undo the bolts and remove the clutch cover in assembly with the pressure plate. Do not lift this unit by holding the pressure plate thrust flange. Refitting is a reversal of removal, providing the following: -...
Page 6
Clutch inspection the inspection of the clutch is carried out on a bench, which simulates the engine flywheel and has a metal intermediate ring 4 (fig. 3-5) with thickness of 8.2 mm simulating the clutch disc. Having fixed the clutch cover, make four release strokes equal to 8-9 mm. The release stro...
Page 7
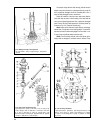
62 fig. 3-8. Master cylinder components: 1 - body; 2 - sealing; 3 - plug; 4 - gasket; 5 - union; 6 - retaining washer;7 - cap; 8 - circlip; 9 - pushrod piston; 10 - sealing ring; 11 - master cylinder piston; 12 - spring fig. 3-7. Straightening the clutch disc fig. 3-9. Slave cylinder components: 1 -...
Page 8
Master and slave cylinders - dismantling, inspection, repair and reassembly master cylinder. Turn out plug 3 (fig. 3-8), remove protective rubber cap 7 and circlip 8. This will allow to withdraw from the cylinder body piston 9, sealing ring 10, floating piston 11 with sealing ring and piston return ...
Page 9
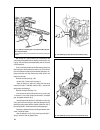
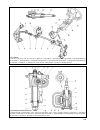
Gearbox the design of the gearbox is shown on fig. 3-12, 3-26, 3-34. Fault diagnosis diagnosis remedy noise in gearbox 1. Noise in bearings 2. Worn teeth on gears and syn- chro units 3. Low oil level in gearbox 4. Axial shaft movement difficulty in engaging gears 1. Incomplete clutch release 2. Jamm...
Page 10
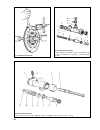
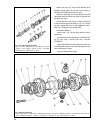
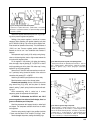
65 fig. 3-12. Gearbox: 1 - input shaft; 2 - front cover with guide sleeve; 3 - input shaft oil seal; 4 - spring washer; 5 - bearing set collar; 6 - gearbox housing; 7 - breather; 8 - output shaft needle bearing; 9 - synchro spring thrust washer; 10 - 4th speed synchro unit crown; 11 - 3rd/4th synchr...
Page 11
Dismantling and reassembly dismantling. Wash the gearbox and place it on a bench. Drain oil and remove the bottom cover with the lining. Remove the clutch release fork, and the coupling in assem- bly with the bearing and the spring from the guide sleeve in the gearbox front cover. Remove the clutch ...
Page 12
Turn out the 3rd/4th gearshift fork fastening bolt. Install lock 41.7816. 4068 on the input shaft or simultaneously engage both gears. This will prevent the turning of the input, output and inter- mediate shafts and will allow to do the subsequent operations on dismantling. Attention. Since 1997, on...
Page 13
68 fig. 3-24. Removing the 5th synchro unit hub/reverse driven gear: 1 - intermediate shaft; 2 - reverse driven gear; 3 - reverse idler gear shaft; 4 - 5th synchro unit hub; 5 - output shaft; 6 - 1st/2nd selector rod; 7 - 3rd/4th selector rod fig. 3-22. Removing the 5th speed/reverse selector rod: 1...
Page 14
Simultaneously remove the reverse idler gear 1 (fig. 3-23) from the shaft, gear 3 in assembly with the coupling and fork 4 from the output shaft. With the help of a special mandrel (like a screwdriver) remove the 5th synchro unit hub together with reverse driven gear 2 from key 4 (fig. 3-24). With t...
Page 15
With the help of a special mandrel (like a screwdriver) take out the input shaft together with the bearing and the synchro unit ring (fig. 3-28) and remove the needle bearing from the front end of the output shaft. Punch out the output shaft from the idler bearing, take out the idler bearing and, ha...
Page 16
- note visually the location of parts relative to risk a (fig. 3-34), made on the directing plate, so that to reassemble the parts in the same order; - having undone the nuts from the fastening bolts, separate the parts of the gear selector mechanism and remove lever 9, ball socket 4 and rubber seal...
Page 17
On surfaces mating with the clutch housing, with the rear and bottom covers there should be no damages that may cause oil leak. Insignificant damages should be smoothed with a file. If parts are badly damaged or worn, renew them. Check the condition of the front cover and ensure that the input shaft...
Page 18
Should be no roughness or scuffings on the rolling surfaces of the shaft front end. Check the condition of needle rolling surface in the opening of the primary shaft. Examine the intermediate shaft, no chipping or excessive wear of teeth is allowed. The surface of the reverse gear shaft should be ab...
Page 19
Spontaneous gear or differential lock disengagement 1. Worn teeth on gears and cou- plings 2. Weak detent spring or detent component wear 3. Incomplete gear engagement and differential lock due to drive system component damage or due to dents on gears, clutches or splines oil leak 1. Damaged sealing...
Page 20
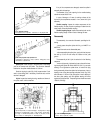
- refit and tighten the flange fastening bolts on the transfer box and the layshaft; if the bolts fit perfectly in the apertures of the flanges, the centering is carried out correctly, otherwise the flanges should be re-aligned. Dismantle and reassembly dismantle. Wash the transfer box and drain oil...
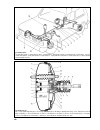
Page 21
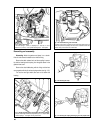
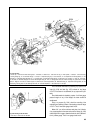
76 fig. 3-36. Transfer box operating system: 1 - differential locking clutch yoke; 2 - differential locking clutch; 3 - yoke stop bolt; 4 - boot; 5 - lever spring; 6 - differential locking fork rod; 7 - front axle case cover; 8 - lock washer; 9 - lever shaft bush; 10 - lever shaft; 11 - differential...
Page 22
Remove the bearing setting rings from the front and rear drive shafts. Take the front axle drive shaft 11 (see fig. 3-35) out from the casing together with bearing 8, thrust ring and oil deflec- tor 9. Take the rear axle drive shaft out from the rear cover 31 together with bearing 36, thrust ring an...
Page 23
Remove front cover 4 (fig. 3-40) with the differential, fit the differential bearing setting ring and take out the bearing in assembly with the differential from the front cover. Remove the setting rings from the bearings of the drive- and intermediate shafts and remove both input- and layshafts fro...
Page 24
- remove circlips 8 (see fig. 3-42) and spring washer 14, then press out the differential pinion shaft and remove the differential pinions and the drive shaft gears with support washers. Press out worn or damaged oil seals from the front axle case, from the front bearing cover and from the rear cove...
Page 25
After reassembly, top-up oil in the transfer box to the lower edge of the filler neck. Inspection prior to inspection, all parts of the transfer box should be carefully cleaned with a brush and a scraper, and then washed. Blow the parts with a jet of compressed air. Especially carefully wash and blo...
Page 26
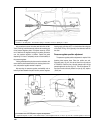
Noise and vibration of propeller shafts 1. Deformation of front or rear pro- peller shaft 2. Propeller shafts out-of-balance 3. Worn or damaged centering bush on layshaft flexible coupling flange 4. Worn u-joint 5. Loose grease seal retainer on spline joint of front or rear pro- peller shaft 6. Insu...
Page 27
Spline joint. Check the gap in the spline joint of the sliding yoke of the forward and rear shafts. The maximum allowable backlash on the spline middle diameter is 0.30 mm. Check for the plug in yoke 5 (fig. 3-48), inspect retainer 7 and seal 6 of the sliding yoke. If necessary, renew the seal, and ...
Page 28
Using two feeler gauges 2, with 4 and 3 blades of different thickness accordingly, determine which will tightly fit in the clear- ance h between the base of the bearing and the yoke groove end face, and install a circlip of the same thickness. Note. One feeler gauge has blades with thickness of 1.45...
Page 29
Rear axle the design of the rear axle is shown on fig. 3-54. Fault diagnosis diagnosis remedy excessive noise from the rear wheels 1. Loose wheel fastening 2. Worn or failed axle shaft ball bearing constant excessive noise at rear axle operation 1. Deformed rear axle beam, damaged axle shaft bearing...
Page 30
Check the beam deformation by attaching a try square to the outer (fig. 3-56) and side (fig. 3-57) surfaces of the flange a.70172; if the beam is not deformed, the try square will fit per- fectly. Size of deformation is checked by a probe. If a 0.2 mm gauge passes through on any of the flanges, the ...
Page 31
If deformation exceeds this size, straighten the beam, follow- ing the procedure given below. After straightening, carefully wash the beam, clean the mag- netic plug, put it in place and check the following: - quality of weld seams and leak-proofness of the beam; - the beam breather and the beam sho...
Page 32
Graphite greasing or ãëñ-15. After refitting, check the operation of axle shafts during an actual road test. Inspection inspect the parts composing a complete set, and make sure that: - bearing is not worn and is not damaged; if the axial gap exceeds 0.7 mm, renew the bearing; - stop ring and bearin...
Page 33
After press-fitting, ensure, that the ring does not shift under the axial load of 19.6 kn (2000 kgf). To do this, place the axle shaft assembly on a special fixture (fig. 3-63), and grip the stop ring in special vice. Attach the leg of indicator 1 with scale interval of 0.01 mm to the axle shaft fla...
Page 34
Test 2. Accelerate the vehicle approximately up to 100 km/h, place the gear shift lever in neutral, switch off ignition and let the vehicle to roll on to a stop; listen to the noise character at various speeds during deceleration. Attention. With the ignition switched off, be attentive and careful. ...
Page 35
- turn the differential side gears and differential pinions so that the last ones will roll out from the differential openings, then take them out; - remove the differential side gears with support washers. Inspection of reduction gear components before inspection carefully wash all parts. It will h...
Page 36
Fails to be achieved even by increasing the washer thickness, renew the gears due to their excessive wear. Fix the gear on the differential box. Using tool a.70152 press-fit the roller bearing inner rings on the differential box. Drive gear - refitting and adjustment the correct location of the driv...
Page 37
In this case fit an adjusting ring with thickness of 3.05 mm. Fit an adjusting ring of the necessary thickness on the driving gear and press fit using tool a.70152 (fig. 3-74) the rear bearing inner ring which was taken from tool a.70184. Fit the distance sleeve. Attention. When repairing the rear a...
Page 38
Differential housing bearings preload and adjustment of the side gap in final drive gears mesh these operations are carried out simultaneously using tool a.95688/r and key a.55085. Fix the tool on the reduction gear casing (see fig. 3-77) with screws 1 and 6, having screwed them in the bolt aperture...
Page 39
After moving the driven gear, check the side gap by indicator 2 (see fig. 3-78). Repeat the adjustment if the clearance does not correspond to the rated value. Remove tool a.95688/r, fit the adjusting nut lock plates and fix them by bolts with spring washers. In spare parts the lock plates are deliv...
Page 40
Driven gear teeth the contact pattern is located in regular intervals closer to the narrow end of the tooth, occupying two thirds of length and without covering the top and the base of the tooth, as shown on fig. 3-80, e. The examples of wrong location of contact pattern on the tooth working surface...
Page 41
Front axle the design of the front axle is shown on fig. 3-81. A number "13" is painted on the reduction gear casing for distinction. Fault diagnosis diagnosis remedy constant excessive noise at front axle operation 1. Worn or badly adjusted differ- ential bearings 2. Wrong adjustment, damage or wea...
Page 42
Ing the guidelines given in subsection "rear axle", distance "d" (see fig. 3-79) should increase by 0.08 - 0.11 mm. For adjustment use bracket 67.8701.9508 with a measuring end piece and key 67.7812.9520. Place cover 12 with sealing 8 on the inner joint bearing cas- ing 9 (see fig. 3-81), then press...
Page 43
State this ring should pass free through the spline opening in race 11, what allows to connect and to separate the joint and shaft 4. The joint is protected by boot 6 from dirt and moisture, which in its turn is protected from mechanical damages by shroud 5. On the shaft 4 and on the joint case the ...
Page 44
- using a knock-out and a hammer, beat the inner joint race from shaft 4; - after removing the thrust ring, move the shroud from the shaft; - wash the inner cavities of the joint housings and other com- ponents. The most difficult and crucial are the operations on disman- tling and reassembling the ...
Page 45: Chapter 4
Chapter 4 wheel suspensions fault diagnosis noise and knock in suspension at vehicle movement 1. Faulty shock-absorbers 2. Loose anti-roll bar fastening bolts 3. Worn arm silent blocks 4. Loose shock-absorber fastening or worn shock absorber eye rubber bushes 5. Worn arm balljoints 6. Excessive gap ...
Page 46
Un-even tyre tread wear 1. Excessive speed at cornering 2. Excessive wear of suspension joints and bushes 3. Wheels out of balance (stains in regular intervals on tread outer path and on central path when driving with a disbalanced wheel for a long time) 4. Uneven wheel braking 5. Shock-absorbers do...
Page 47
Excessive wear of tyre tread 1. High driving speed 2. Heavy vehicle acceleration 3. Often braking 4. Wrong wheel alignment angles 5. Excessive clearance in front wheel hub bearings 6. Vehicle overload 7. Recommended rearrangement of wheels was not carried out tyres squeal at cornering 1. Abnormal ty...
Page 48
Front wheel alignment angle - checking and adjustment the check and adjustment of the front wheel alignment angle is carried out on special test-benches according to the instruc- tions. Attention. It is necessary to check the wheel align- ment angle after replacement or repair of suspension com- pon...
Page 49
104 before adjusting the wheel alignment angles check the fol- lowing: - pressure in tyres; - axial gap in front wheel hub bearings; - serviceability of shock-absorbers (absence of rod jamming); - radial and axial runout of tyres; - gap in suspension balljoints; - free play of steering wheel. Rectif...
Page 50
105 after adjustment, refit the fastening clamps with the slot fac- ing back with allowable deviation downward by 60° to the hori- zontal plane of the vehicle. With the nuts tightened the clamp slot edges should not contact. After toe-in adjustment, ensure that wheels and steering mechanism componen...
Page 51
- remove old greasing and wash with kerosine the inner cav- ity of the steering knuckle, the outer and inner cavities of the hub, the cv-join case tail and bearings; - fill 40 gr of fresh ãàíéã-24 in bearing cages, spread even- ly in the cavity of the steering knuckle between the bearings, grease th...
Page 52
Note. When removing the upper arm shaft, note the amount and arrangement of washers between the upper arm shaft and the crossmember, and also the number of shims between the crossmember and car body chassis arm, so that at refitting all washers and shims will be properly replaced. Disconnect the eng...
Page 53
- remove the front wheel hub in assembly with the brake disc, using pusher 67.7823.9516; - remove the front brake splash guard; - remove the front suspension shock-absorber; - lower the suspension lower arm on a support and compress the suspension spring to fully unload the lower arm; - disconnect t...
Page 54
The front suspension, it is permissible to install the a class springs on the front suspension. But you can not install the b class springs on the front suspension, if the a class springs are installed on the rear suspension. Inspect the gaskets and renew, if they have damages. Anti-roll bar, suspen...
Page 55
The lower arm. The pressing-out and press-fitting of the joint can be carried out on a press, using tool 67.7823.9526, and also with tool 67.7823.9517 (fig. 4-12), which is installed on the arm so that the head of the tool screw was directed inside. Tighten the tool screw to press out the joint. For...
Page 56
For the rear suspension, it is permissible to install the b class springs (with black marking). If on the front suspension the springs of b class are installed, the rear suspension should be fit- ted with b class springs only. To avoid damage and excessive tightening of control arm rubber bushes and...
Page 57
112 fig. 4-18. Front and rear suspension shock absorbers: 1 - lower eye; 2 - compression valve body; 3 - compression valve discs; 4 - compression valve throttling disc; 5 - compression valve spring; 6 - compression valve holder; 7 - compression valve cap; 8 - recoil valve nut; 9 - recoil valve sprin...
Page 58
Speed of 60 min -1 , rod stroke length of 80 mm for the front shock- absorber, and 100 mm - for the rear one. The curve of the diagram (fig. 4-19) should be smooth, and in points of transition (from the recoil stroke to the compression stroke) - without areas parallel to zero line. Evaluation of dia...
Page 59: Chapter 5. Steering
Chapter 5. Steering the steering mechanism design is shown on fig. 5-1, 5-2. Since november, 1998, vehicles are fitted with a telescopic intermediate shaft instead of a cylindrical intermediate shaft 17 (see fig. 5-1) and the steering wheel 19 is fastened by a self-lock- ing nut. There are two varia...
Page 60
115 fig. 5-2. Steering mechanism, sectional view: 1 - adjuster screw plate; 2 - adjuster screw; 3 - cap; 4 - screw nut; 5 - oil filler plug; 6 - cover; 7 - worm; 8 - housing; 9 - drop arm; 10 - securing nut; 11 - spring washer; 12 - oil seal; 13 - bronze bush; 14 - drop arm shaft; 15 - drop arm shaf...
Page 61
Steering - inspection, check and adjustment general inspection the steering system should be examined at any signs of mal- function (rattle, excessive free play of the steering wheel or, on the contrary, its hard rotation, and so on). The inspection is car- ried out on the trestles or an inspection ...
Page 62
Inspect the tie-rod balljoint protective caps. If the protective caps are in good condition and provide inside cleanness, their service life is practically unlimited. Moisture, dust and other foreign particles inside the joint will result in premature wear of components. The cap should be replaced i...
Page 63
Tening nut and fix it in three points. Move the combination switch case fully towards the steering wheel, and tighten the switch fas- tening clip. Reconnect the wires of the ignition switch and fix the switch on the steering column bracket with screws. Reconnect the combination switch plugs to the v...
Page 64
6). Undo the fastening bolt, take off cover 12 (see fig. 5-5) of the steering box together with cap, adjusting screw 8, adjusting plate 9, lock washer 10 and jam nut. Take out from the steering box 1 the pitman arm shaft 7 in assembly with the roller. Undo the fastening bolt, remove cover 3 from the...
Page 65
After press-fitting in the steering box, finally process the bushes with a reamer a.90336 up to the size of 28.698-28.720 mm. The mounting gap between the pitman arm shaft and the bushes should be within 0.008-0.051 mm. Check for easy rotation of the pitman arm roller on the ball bearing. The ball b...
Page 66: Chapter 6
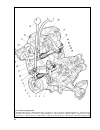
Chapter 6 braking system the design of the braking system is shown on fig. 6-1. Fault diagnosis diagnosis remedy insufficient efficiency of braking 1. Leak of brake liquid from wheel cylinders of front or rear brakes 2. Air in brake system 3. Damaged rubber sealings in master brake cylinder 4. Damag...
Page 67
122 fig. 6-1. Braking system: 1 - rear brake wheel cylinder; 2 - parking brake rear cable; 3 - rear brake guide; 4 - parking brake front cable; 5 - parking brake lever; 6 - brake pedal; 7 - servo unit; 8 - second circuit pipeline; 9 - primary circuit pipeline; 10 - master cylinder; 11 - wheel cylind...
Page 68
Renew the components in the slightest doubt in serviceability. Flexible hoses, irrespective their condition, should be renewed after 100000 km or after 5 years of vehicle operation to prevent sudden breaks due to aging. After five years of operation it is recommended to renew the brake liquid. Servo...
Page 69
Ask an assistant to press the brake pedal with effort of 686- 784 n (70-80 kgf) and simultaneously observe the outcoming part of the pressure regulator piston. If the piston moves by 0.5-0.9 mm in relation to the regulator housing, thus twisting the torsion arm, the pressure regulator is efficient. ...
Page 70
Raise the protective rubber cap 6 (see fig. 6-5) and, by turn- ing the pressure regulator on the bolts, get a slight contact between the arm and piston 2. Keep the regulator in this position, fully tighten bolts 1 and 7, then apply a thin layer of greasing Ñí-1 on shaft 5 and the work- ing part of p...
Page 71
Clutch and brake pedal bracket removal and refitting. To remove the pedal bracket: - remove the steering shaft bracket, as mentioned in section "steering"; - disconnect the servo unit push rod from the brake pedal, having removed lock shackle 26 (fig. 6-8) and taken out pin 24; - disconnect the wire...
Page 72
Check and repair. At hard pedal movement examine the working surfaces of pedals, bushes and shaft. If there will be small risks or traces of oxidation on surfaces of metal parts, grind them slightly with sandpaper; renew worn outer plastic bushes on pedals. Check the spring tension. The length of th...
Page 73
Inspection of components . Before reassembly, wash all components with isopropyl alcohol; dry by a jet of compressed air or wipe with a clean cloth, but do not allow their contact with min- eral oil, kerosine or diesel fuel, which can damage the sealings. Note. Time of washing the sealing rings in i...
Page 74
Forcing a jet of compressed air through the aperture for brake liquid, push out pistons 14 from the cylinder block and take out sealing rings 4. The reassembly of the front brake is carried out in sequence reverse to dismantle. When assembling, lubricate the sealing rings, pistons and cylinder mirro...
Page 75
Assembly and take out the worn pads from the carrier grooves (fig. 6-16); - carefully depress the pistons in cylinders to a stop, paying attention not to splash the liquid from the master cylinder reser- voir, and place new brake pads in carrier grooves; - move the lower directing splay on the calip...
Page 76
The reassembly of the automatic adjuster and the wheel cylinder is carried out in reverse sequence, paying attention to the following: - piston thrust screws are tightened to torque 4-7 n•m (0.4- 0.7 kgf•m); - slot a (see fig. 6-19) on thrust rings should be directed ver- tically upward; vertical de...
Page 77
Brake drums. Examine the brake drums. If the working sur- faces have deep risks or excessive ovality, chisel the drums. Then grind on a machine tool with abrasive fine stones. This will help to increase the lining durability, and improve the uniformity and efficiency of braking. The maximum allowabl...
Page 78
Remove the regulator and disconnect the arm. Plug all open- ings of the pressure regulator and pipelines. Refitting of the pressure regulator is carried out in reverse sequence. Before tightening the regulator fastening bolt place tool 67.7820.9519 (see fig. 6-6) on the end of the regulator arm. Dir...
Page 79
Handbrake removal and refitting . Place the handbrake lever in the lowest position, disconnect the cable ends from the brake shoe levers (see "rear brake"). Slacken locknut 5 (see fig. 6-4) and adjusting nut 6, remove return spring 9 (fig. 6-24), then completely undo the locknut and nut. Take out th...
Page 80
135.
Page 81
136.