- DL manuals
- Lancair
- Tools
- ES-P
- Pilot Operating Handbook
Lancair ES-P Pilot Operating Handbook
Summary of ES-P
Page 1
Pilot's operating handbook and airplane flight manual ® es-p manufacturer: heizer ij serial no: 001 model: esp lancair kit no: 120 this aircraft is faa approved in the experimental category based on far 23. This document must be carried in the aircraft..
Page 2: Originally Published By
Originally published by lancair international inc. 2244 airport way redmond, oregon 97756 adapted for heizer ij esp serial number 001 by isaac heizer woodinville, washington 98072 warning this is an experimental aircraft having experimental documentation. No aspect of this documentation can be assum...
Page 3: Introduction
Introduction this pilot’s operating handbook is in the format and contains most data recommended in the gama (general aviation manufacturers association) handbook specification number 1. Use of the terms warning, caution and note the following conventions will be used for the terms, warning, caution...
Page 4: Lancair Es-P
Lancair es-p handbook section 2 general section 3 limitations section 4 emergency procedures section 5 normal procedures section 6 weight & balance section 7 systems descriptions section 8 handling, servicing & maintenance section 9 supplements section 10 safety information section 11 addendum.
Page 5: Section 2 General
Section 2 general table of contents important notice...................................................................... 2 descriptive data........................................................................ 4 general airspeed terminology and symbols ........ 7 meteorological terminology ........
Page 6: Important Notice
This is a state-of-the-art, high performance general aviation aircraft. Its performance is spectacular and its life almost beyond measure when given reasonable care. You must become familiar with this handbook as well as the fars that are applicable to its operation. The combination will provide you...
Page 7: Warning
The owner/operator should frequently refer to all supplements, whether stcs (supplemental type certificate) or lancair supplements direct from lancair, for appropriate placards, limitations, normal, emergency and other operational procedures for proper operation of their lancair with any optional eq...
Page 8: Descriptive Data
Descriptive data engine this aircraft is fitted with a continental tsio-550e (3) six cylinder fuel injected twin-turbocharged engine. Propeller this aircraft is equipped with an mt mtv-9-d/198-58a 3 blade hydraulic constant speed propeller with a mccauley c290d3-r/t43 propeller governor. The propell...
Page 9
Specific loading (max take-off weight) wing area 140 ft 2 wing loading 25.7 lb./ft 2 power loading (350 hp) 10.3 lb./h.P..
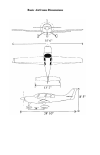
Page 10: Basic Airframe Dimensions
Basic airframe dimensions.
Page 11: General Airspeed Terminology
General airspeed terminology and symbols cas calibrated airspeed is the indicated speed of an airplane, corrected for position error and instrument error. Calibrated airspeed is equal to true airspeed in standard atmosphere at sea level. Gs ground speed is the speed of an airplane relative to the gr...
Page 12: Meteorological Terminology
V x best ange-of-cimb speed is the airspeed that delivers the greatest gain of altitude in the shortest possible horizontal distance. V y best rate-of-climb speed is the airspeed that delivers the greatest gain in altitude in the shortest possible time. M mo maximum mach number. Meteorological termi...
Page 13: Pressure Altitude
Pressure altitude altitude measured from standard sea- level pressure (29.92 in hg) by a pressure or barometric altimeter. It is the indicated pressure altitude corrected for position and instrument error. In this handbook altimeter instrument errors are assumed to be zero. Position errors may be ob...
Page 14: Cht (Cylinder
Cht (cylinder head temperature) the indicator used to identify the operating temperature of the engines' cylinder(s). Tit the temperature of the exhaust gases as they enter the respective turbocharger. Tachometer indicates the rpm of the engine/propeller. Propeller governor regulates the rpm of the ...
Page 15: Reference Datum
Weight and balance terminology reference datum an imaginary vertical plane from which all horizontal distances are measured for balance purposes. Station a location along the airplane fuselage usually given in terms of distance from the reference plane. Arm the horizontal distance from the reference...
Page 16: Payload Weight
Payload weight weight of occupants, cargo and baggage. Useful load difference between take-off weight or ramp weight (if applicable) and basic empty weight. Maximum ramp weight maximum weight approved for ground maneuvering. (it includes weight of start, taxi and run up fuel). Maximum take- off weig...
Page 17: Section 3 Limitations
Section 3 limitations table of contents aircraft operating speeds................................................. 2 altitude limitation ............................................................... 3 powerplant operating limitations .............................. 3 oil specification ................
Page 18: Aircraft Operating Speeds
Aircraft operating speeds the airspeed is shown on both the pfd and backup airspeed indicator. The airspeed on the pfd is indicated with an airspeed tape and colored bands. The backup airspeed indicator has four colored arcs on the outer circumference. Speed symbol kias caution, smooth air only yell...
Page 19: Altitude Limitation
Altitude limitation the maximum flight altitude is 25,000 msl with a working oxygen system and 14,000 msl without oxygen available. This is to ensure backup oxygen is available in the event of pressurization system failure. Powerplant operating limitations operating limitations for the tsio-550e eng...
Page 20: Oil Specification
Oil specification lubricating oil used must conform to teledyne continental motors’ specification mhs24. All temperatures 15w50 or 20w50 below 40°f ambient (sea level) sae30 or 10w30 above 40°f ambient (sea level) sae50 or 20w60 powerplant instrument markings the engine instrumentation area of the g...
Page 21: Flight Load Factor Limits
The aft cg limit must be considered a firm limit. Loads that place the cg further aft are dangerous and must not be accepted. A “weight and balance" sheet must be completed and carried in the aircraft at all times. Reference datum the datum is located at fs “0.” this can be located by measuring 51.2...
Page 23: Section 4 Emergency
Section 4 emergency procedures table of contents emergency airspeeds ............................................................. 2 engine failure ............................................................................ 3 engine failure during take-off (not ariborne)..... 3 engine failure immed...
Page 24: Note
Note all airspeeds quoted in this section are indicated airspeeds (kias) and assume zero instrument error. Emergency airspeeds emergency descent idle power, flaps up, speed brakes deployed 165 kias best glide – flaps up flaps down speed brakes retracted 100 kias 90 kias aoa 2 green landing approach ...
Page 25: Engine Failure
Engine failure engine failure during take-off (not ariborne) sufficient runway remaining: throttle idle brakes apply as necessary flaps up boost pump off mixture cutoff fuel selector off ignition off master switches off engine failure immediately after takeoff (below 400 feet agl) airspeed 95 with f...
Page 26: In-Flight Restart
In-flight restart caution actual shutdown of an engine for practice or training purposes should not be done. Engine failure simulation should be done by reducing power. 1 master switch on 2 mixture ¾ full rich 3 fuel selector fullest tank 4 fuel boost pump high 5 magnetos both 6 throttle normal star...
Page 27: Caution
Observe engine for visible damage or evidence of smoke or flame. Extreme roughness may be indicative of propeller blade problem. Mixture adjust as appropriate to power setting being used. Do not arbitrarily go to full rich as the roughness may be caused by an over rich mixture magnetos on low boost ...
Page 28: Warning
Develop manifold pressure above ambient pressure. The engine will revert to "normally aspirated" and can be operated, but will produce less than its rated horsepower. If turbocharger failure occurs before takeoff, do not fly the aircraft. If a failure occurs in flight, readjust mixture as necessary ...
Page 29: Are Recommended:
Turbocharger failure. If a power loss is experienced followed by surging of rpm, fuel flow, and manifold pressure, the following steps are recommended: 1 mixture idle cutoff 2 fuel selector fullest tank 3 fuel pump low boost 4 throttle cruise position 5 propeller cruise rpm 6 mixture enrich slowly f...
Page 30: Caution
Gauge or thermocouple. If the oil pressure drops as temperature increases, proceed as follows: oil door push to open airspeed increase power reduce if previous steps do not lower oil temperature. Land as soon as possible if oil temperature cannot be reduced. Caution if these steps do not restore oil...
Page 31: Engine Fire During Start
Propeller pull to lowest rpm land immediately and exit the aircraft engine fire during start starter continue cranking mixture idle cut-off fuel selector off boost pump off throttle full open emergency descent rpm 2700 to maintain pressurization throttle appropriate to keep engine warm and maintain ...
Page 32: Warning
Fuel selector off ignition off flaps as required when landing is assured speedbrakes retracted master switches off door seal deflated attempt to fly the aircraft and keep the wings level through the approach and landing until the aircraft comes to rest. Exit the aircraft and remain clear until assur...
Page 33: Warning
Leads for the ammeter shunts. Electrical system overcharging there are two alternators and two separate electrical systems. The main system is driven from the main alternator on the front of the engine and the auxiliary system is driven from a smaller alternator on the back of the engine. The main s...
Page 34: Note
If there is an electrical demand above what can be produced by either alternator, the corresponding battery temporarily satisfies the increased requirement and a battery discharging condition exists. As the battery charge is expended, the voltage to the system will read something less than the optim...
Page 35: Carbon Monoxide Alert
Multi-function display if the mfd should malfunction or perform improperly, you may continue to utilize those portions of the mfd data that are not in question. Moving map errors may be associated with a raim alarm indicating the loss of adequate gps position accuracy. Data or functions that have fa...
Page 36: Caution
Airspeed reduce until propeller rpm control is regained throttle slowly increase and hold airspeed below over speed kias mixture adjust for smooth operation caution if the over speed was significant, an engine inspection is called for upon landing. Engine operation for the balance of the flight must...
Page 37: Emergency Speed Reduction
Lose a lot of altitude in this maneuver. Emergency speed reduction the nature of this emergency must be considered before action is taken, but in general the power should be reduced to idle, nose up, speed brakes deployed, and the most critical would be the extension of the wing flaps after reaching...
Page 39: Section 5 Normal
Section 5 normal procedures table of contents horsepower table (rop)........................................................ 3 preflight inspection .............................................................. 4 starting engine...........................................................................
Page 40
After landing ............................................................................ 16 shutdown...................................................................................... 16 alternate air ............................................................................ 17 pressurization...
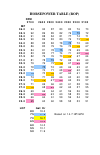
Page 41: Horsepower Table (Rop)
Horsepower table (rop) rpm 2700 2600 2500 2400 2300 2200 2100 mp 36.0 94 90 87 83 80 76 73 35.5 92 89 85 82 79 75 72 35.0 91 88 84 81 77 74 71 34.5 90 86 83 80 76 73 70 34.0 88 85 82 78 75 72 69 33.0 86 83 79 76 73 70 67 32.5 84 81 78 75 72 69 66 32.0 83 80 77 74 71 68 65 31.5 82 79 76 73 70 67 64 3...
Page 42: Preflight Inspection
Preflight inspection 1 cabin pitot tube cover remove and store control lock remove ignition switch off mixture idle cutoff circuit breakers check in master switches on (master first, then aux) pfd and mfd verfiy on, no red x annunciators verify on oil pressure low volts fuel quantity indicators chec...
Page 43: 4 Right
4 right wing wing tie-down disconnect fuel quantity check visually for desired level fuel filler cap secure aoa check for obstructions, drain if necessary hid lights check condition and cleanliness speed brakes check condition main gear and tire check for proper inflation and general condition note ...
Page 44: Warning
Warning make certain that the battery and magnetos are off and that no one is in or near the cockpit while performing this check. Hands pass through the prop arc, thus, if the prop turns, severe injury or amputation will occur. 6 left wing main gear and tire check for proper inflation and general co...
Page 45: Starting Cold Engine
7 door latched starting cold engine 1 alternate air closed 2 mixture rich 3 propeller high rpm 4 boost pump off 5 throttle closed then open one inch 6 master switches master on then aux on 7 pfd and mfd verify on, no red x 8 annunciators verify on oil pressure low volts 9 lights on as required 10 pr...
Page 46: Starting Hot Engine
Starting hot engine for several minutes (10 to 45) after stopping a hot engine, heat soaked fuel injection components, (especially the fuel injection pump) may cause vaporization of fuel in the components resulting in difficulty restarting the engine. To eliminate this difficulty, the following proc...
Page 47: Note
2 master switch off then on (pfd and mfd remain operational) 3 mfd fuel remaining initialize 4 radios set as required 5 pfd and backup altimeter set 6 flight plan load 7 altitude and heading bugs set 8 transponder set 9 speed brakes deploy and retract (pfd annunciates) 10 aoa test / checked note the...
Page 48: Before Takeoff (Runup)
Before takeoff (runup) 1 heading into wind 2 brakes set 3 propeller high rpm 4 throttle 900 – 1000 5 cabin door closed, locked and seal inflated 6 flight controls free and correct 7 trim tabs set for takeoff 8 flight instruments set and crosscheck pfd and backup flight instruments 9 radios set 10 au...
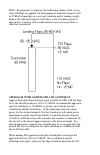
Page 49: Takeoff & Climb
27 backup ai pull to cage if required, warning flag out of view 28 oil door open takeoff & climb normal takeoff 1 lights as required 2 flaps takeoff position 3 boost pump off 4 pitot and prop heat as required 5 mixture full rich 6 propeller high rpm 7 throttle advance slowly to full power (2700 rpm)...
Page 50: Cruise
Controller 8 cabin pressurization rate control adjust as necessary 9 lights as desired climbing at or above 120 - 140 kias is preferable, particularly when climbing to higher altitudes, i.E., those that require more than 6000 feet of altitude change. A 500 fpm rate climb at cruise power provides bet...
Page 51: Rpm Max
Operation, tit should be at or below 1625ºf. The following table shows maximum mp for a given rpm: rpm max mp 2300 29.5 2400 28.0 2500 27.0 descent 1 cabin pressurization controller set for field elevation 2 power as desired 3 boost pump off below 10,000 ft. 4 mixture adjust as required 5 speed brak...
Page 52
Kias. Be prepared to counteract the ballooning tendency that occurs when full flaps are applied. On final approach, maintain airspeed of 80 to 85 kias depending on crosswind condition and/or landing weight. Reduce the indicated airspeed to 80 knots as the touchdown point is approached. Landing with ...
Page 53: Balked Landing (Go Around)
Position and the aircraft slowed to 100 kts. At the faf (final approach fix), full flaps should be applied and the aircraft slowed to 90 kias. This technique will typically require a power setting in excess of 1900 rpm. Power settings resulting in approximately 1800-1850 rpm should be avoided as thi...
Page 54: Crosswind Landing
Flaps are applied. A low-power descent, from a slightly longer than normal final approach, is preferred. It provides more time to set up and establish the proper descent path. If there is an obstacle, cross over it at 78 kias. Maintain a power on approach until just prior to touchdown. Do not extend...
Page 55: Alternate Air
3 elt check not activated 4 trim tabs set to neutral 5 mixture idle cut-off after 4 or 5 minutes cooldown 6 ignition switch off 7 lights off 8 master switches aux off then master off alternate air alternate air is provided automatically from a spring-loaded door in the air filter box. This door shou...
Page 56: Pressurization Controls
Air for cabin pressurization is obtained from the engine turbocharger induction air system through four sonic ports. Bleed air is routed through a separate heat exchanger to reduce temperature for improved cabin comfort. Ambient air flows across the heat exchanger to cool the bleed air. Cabin air te...
Page 57: Note
Controls. On the center of the face is a knob that selects the altitude for cruise and the landing airport elevation during descent. The actual cabin altitude will be controlled to 1000 feet above selected altitude. This allows you to set landing field elevation and the cabin will completely de-pres...
Page 58: Cold Weather Operations
Cabin altitude and differential during the flight. Operation – cruise & descent during the cruise portion of the flight any changes in altitude or flight level assignment should be set in the cabin controller. Upon commencing descent to the destination airport, set the landing airport's altitude in ...
Page 59: Cruise Operation
Cruise operation cold weather operation may require an occasional cycle of the propeller control. This could be particularly true after long duration cruise just prior to descent where lack of governor control could cause over speeding. During descents and landing, give special attention to cylinder...
Page 61: Section 6 Weight & Balance
Section 6 weight & balance table of contents weights for 8/29/2008......................................................................... 2 measurements for 8/29/2008.............................................................. 2 empty center of gravity ..............................................
Page 62: Note
Proper cg is absolutely critical to safe flight -- no exceptions can be considered. The pilot must verify that the center of weight is in the correct position and if it is not, the center of weight must be corrected before flight. Note the allowable center of gravity range is fuselage station (fs) 9...
Page 63: Empty Center of Gravity
Empty center of gravity item weight arm moment left wheel 937 117.6875 110273.2 right wheel 911 117.6875 107213.3 nose wheel 632 35.75 22594 total 2480 96.81 240080.5 full fuel center of gravity item weight arm moment left wheel 1204 117.6875 141695.8 right wheel 1182 117.6875 139106.625 nose wheel ...
Page 64: Summary
Summary max gross weight 3600 lb empty weight 2480 lb useful load 1120 lb full fuel useful load 519 lb empty weight c.G. 96.81 in fuel arm 109.1 in pilot / copilot arm 94.95 in rear passenger 129.6 in baggage 165 in loading examples (8/29/2008) condition cg pilot (180) + empty fuel 96.7 pilot (180) ...
Page 65: Section 7 Systems
Section 7 systems descriptions table of contents airframe ......................................................................................... 3 materials .................................................................................... 3 flight controls ........................................
Page 66
Backup attitude indicator............................................... 10 angle of attack (aoa) .......................................................... 12 co guardian carbon monoxide detector ............... 13 xm weather and entertainment................................... 14 avidyne tas610 tc...
Page 67: Airframe
Airframe the aircraft is constructed of the highest quality aircraft materials. Examining the assembly manual should cover most if not all your questions concerning the various techniques and materials involved. Materials the lancair es-p is fabricated of high temperature prepreg carbon fiber skins ...
Page 68: Flaps
Flaps the wing flaps are electrically operated and are actuated with the flap switch on the instrument panel. Up flaps fully retracted, suitable for cruise flight t/o flaps 10 o takeoff position land flaps 40 o landing position off flaps stop in the current position; power removed from the flap circ...
Page 69: Baggage Compartment
50 ft. Pounds of torque. Also check the rotational resistance of the wheel. If more than one free revolution of the wheel occurs upon firmly spinning the tire, the axle bolt must be tightened. Baggage compartment the baggage compartment is located aft of the pressure bulkhead behind the passenger se...
Page 70: Control Locks
Buckles and length adjustments. Belts should be adjusted to position the buckle over the inboard hip of the wearer. Lap belts may be released by lifting the upper half of the buckle. Inertia reel-type shoulder harnesses are installed on the pilot’s and front passenger seats. The inertial restraing s...
Page 71: Engine Starting
Propeller should never be rotated on the ground without assuming that the magnetos are "hot" and the off position should be checked for operation by briefly switching the magnetos to the off position while at idle rpm prior to each shutdown. Normal shutdown then is accomplished by putting the mixtur...
Page 72: Warning
Warning the airplane does not lend itself to hand starting (propping) due to its tricycle gear. This practice is very dangerous. Accessories the engine is equipped with two alternators as sources of electrical power to charge the batteries and operate various items during flight. Proper operation of...
Page 73: Propeller
Propeller this aircraft is fitted with an mt mtv-9 three blade composite propeller. Natural composite blades with fiber reinforced epoxy cover and metal leading edge protection are used to minimize weight at the highest amount of safety against fatigue fractures due to vibrations. The spinner dome i...
Page 74: Electrical System
Your brakes on downwind before landing. To do so, simply depress each pedal to verify a "firm" pedal. Your initial flights will require extra caution until you become familiar with the aircraft. Electrical system the electrical system consists of two busses, two alternators, two voltage regulators a...
Page 75: Operate.
Operate. This will normally occur only if the unit is turned off, or after the internal standby battery is exhausted. Caution the indicator may be damaged if the “pull to cage” knob is released with a “snap”. Slowly release the “pull to cage” knob avoiding a “snap” release. When the instrument switc...
Page 76: Angle of Attack (Aoa)
From the installation and maintained on a charger per current installation manual number 9015762. 2. On at least an annual basis, as well as any time there may be a question about standby battery performance (life) a full capacity test should be performed. The mid-continent web site ( www.Mcico.Com ...
Page 77: Co Guardian Carbon Monoxide
Zero lift best glide best approach high angle warning ignoring propeller effects, the transition between green and yellow on the display is l/d max , best engine out glide, best angle of climb (v x ), and maximum endurance. The top red indicator is where the critical angle of attack is reached. The ...
Page 78: Xm Weather and Entertainment
And a complete system check. Xm weather and entertainment a garmin gdl69a remote datalink receiver is rack mounted behind the instrument panel and connects to a ga-37 antenna externally mounted on top of the aircraft. The receiver delivers xm wx satellite weather tm that is displayed by the garmin g...
Page 79: Pitot Pressure System
The final heat exchanger forward of the firewall. This is the same system that provides cabin pressurization, and heat is generated by the compression of the outside air by the turbochargers (there is no muffler heat shroud). Maximum heat is provided when the cabin temp control is pulled out to the ...
Page 81: Section 8 Handling,
Section 8 handling, servicing & maintenance table of contents introduction to servicing ................................................. 3 51% rule ........................................................................................ 3 non-owner built aircraft ......................................
Page 82
Care and cleaning .................................................................. 10 exterior painted surfaces............................................... 11 engine .......................................................................................... 11 recommended servicing ................
Page 83: Introduction to Servicing
Introduction to servicing this section is designed to help you service and maintain the aircraft in a safe and efficient manner. The intended user of this handbook is the pilot, not the aircraft's mechanic. The information is intended as a guide to maintaining the aircraft and assumes any/all work a...
Page 84: Airplane Inspection Periods
Performed by the pilot. All other maintenance required must be performed by appropriately licensed personnel. In this case, it is again recommended that you secure the services of an fbo for your maintenance so that it can become familiar with the aircraft. Such personnel will undoubtedly want to fa...
Page 85: Alterations Or Repairs
Alterations or repairs if you built your aircraft and have received your "repairman" certification, you may make any modifications desired. However in the interest of safety we strongly recommend that you seek experienced consultation before making any modifications to your lancair. Any modification...
Page 86: Tie-Downs
Forward of the horizontal stabilizer. With the nose wheel off the ground, the aircraft can be pivoted around the main gear as required. Tie-downs built in tie-downs should be used to secure your aircraft unless it is hangared. Tie-down ropes should be left with some slack to allow for any rope shrin...
Page 87: Flyable Storage
Upholstery, instruments and avionics will suffer from excessive heat and exposure to the sun, so a cover is recommended. Elastomers such as tires also need to be protected from exposure to ultraviolet to limit their deterioration. Fuel tanks should be filled or drained completely, the control surfac...
Page 88: Oil Changes
Quantity is sufficient for the flight duration. The oil level is checked through the small door on the top of the engine cowling. A minimum of 9 quarts should be indicated before every flight. Oil changes during the initial break-in, the engine should be operated with mineral oil. The break-in is no...
Page 89: Brakes
Down on the fuselage just forward of the empennage. (2) spin the nose wheel. It should spin over one or two turns at the most. If excessive rotation occurs the axle nut must be retightened and the test conducted again until satisfactory. Verify that the bearings are properly snug; there must be no f...
Page 90: Care and Cleaning
Diodes to direct current for charging the batteries. The alternators use remotely mounted lr3c and ls1a b & c specialties voltage regulators mounted inside the cockpit on the fuselage wall in the pilot footwell. Excessively high voltage regulation will cause overcharging of the batteries and shorten...
Page 91: Exterior Painted Surfaces
Manufacturer’s instructions. Interior plastic parts should be cleaned with a damp cloth. Oil and grease can be removed with cloth dampened slightly with kerosene. Volatile solvents such as those cautioned against for the windshield are to be avoided here as well. Exterior painted surfaces caution av...
Page 92: Recommended Servicing
Recommended servicing interval item preflight check & service oil drain water trap service fuel tanks first 25 hrs service oil with ashless dispersant oil change oil filter change fuel filters check brake lines check all landing gear fairings check control surface hinges each 50 hrs change oil clean...
Page 93: Interval
Interval item propeller – nicks , within overhaul check rudder cables forcondition, security check/serivce gear fairings wheel bearings (three) – repack nose wheel and shimmy damper nose gear drag brace secure flexlines - check for chafing flap actuator – check security, wear flap to aircraft fit - ...
Page 95: Section 9 Supplements
Section 9 supplements table of contents altitude regulations ............................................................ 2 altitude reaction .................................................................. 2.
Page 96: Altitude Regulations
Altitude regulations far, 61.31 “(f) additional training required for operating high-performance airplane: (1) except as provided in paragraph (g)(3) of this section, no person may act as pilot in command of a pressurized aircraft (an aircraft that has a service ceiling or maximum operating altitude...
Page 97
10,000 fatigue, drowsiness and sharp headaches can occur with increasing quickness if flights are made without supplemental oxygen at this and higher altitudes. 18,000 this is the halfway point in the earth's atmosphere and pressure is reduced to 7.34 psi and oxygen saturation in the body is only 75...
Page 99: Section 10 Safety
Section 10 safety information table of contents introduction ............................................................................... 2 general ........................................................................................... 2 first flight..............................................
Page 100: Introduction
Introduction this is a high quality aircraft and one that will give years of service given the care a fine machine deserves. Like most other pieces of equipment, it will operate best under certain conditions, and can be dangerous in others. We have attempted to identify the latter in this manual, an...
Page 101: First Flight
First flight prior to your first flight in this aircraft, it is only prudent that you obtain some training "in type." you are encouraged to take advantage of this type of training that can be with another lancair owner in his aircraft, or thru a program offered by companies such as hpat. For informa...
Page 102: Airman'S Information Manual
Much current information is carried in the airman's information manual, advisories and notices, and other publications of u.S. Origin. Airman's information manual the aim provides pilots with basic flight information, air traffic control (atc) procedures for use in the u.S., a glossary of terms used...
Page 103: Flight Plans
60-9 induction icing—pilot's precautions and procedures 61-67 hazards associated with spins in airplanes prohibited from intentional spinning 61-84 role of preflight prepreparation 90- 23d wake turbulence 91-6a water, slush and snow on runway 1- 43 unreliable airspeed indications a similar listing o...
Page 104: Severe Weather
Landings and slower climb rates expected, though the turbocharged engine somewhat mitigates this consideration. In addition, the weather is significantly different. Winds can be extremely strong and turbulent, especially between the passes where we tend to go to improve terrain clearance. The weathe...
Page 105: Been Evaluated. Avoid!
Do not take the aircraft into a "full" stall. While decelerating, slowly feel out the controllability of the aircraft. As soon as an acceptably low speed is reached to allow landing at the intended airport, accept that, add about 5 kts, and land. Stall/spin characteristics of the lancair with ice ha...
Page 106
Horizon) to correct this sense the result can be vertigo. Never second guess your instruments, always believe your instruments — period. The message is be alert for vertigo. Vertigo is as insidious as hypoxia, that high altitude phenomena resulting from lack of oxygen. The regulations limit flight a...
Page 107: Engine Failure
Monoxide in the cockpit can result in similar symptoms. An open vent to increase cabin ventilation should be used even to the extent of colder than desirable temperatures. This latter should be anticipated if an exhaust heater is being used. A carbon monoxide detector in the cockpit is good insuranc...
Page 109: Section 11 Addendum
Section 11 addendum table of contents lancair es-p annual condition or 100 hour aircraft inspection report checklist ...................... 2 power plant inspection – engine .................................... 2 turbos ...................................................................................
Page 110: 100 Hour Aircraft Inspection
Lancair es-p annual condition or 100 hour aircraft inspection report checklist owner's name _____________________________________ faa registration number: ________________________ 100 hour-_______ annual-_______ date______________ tach time_____________total aircraft time_______ power plant inspecti...
Page 111
_____7. Check and clean gascolator screen and bowl check for safely. _____8. Check fuel filter clean and safety wire. _____9. Remove and inspect air filter in cowling. _____10. Check alternate air door. _____11. Inspect cylinders, fins, and baffles. _____12. Inspect fuel induction system and tighten...
Page 112: Turbos
_____25. Check engine for loose nuts, bolts, screws, studs, etc. _____26. Check engine cowling and baffles: repair when necessary. Install cowling and check security of installation. _____27. Review engine airworthiness directive notes for compliance. _____28. Check general maintenance aid notes app...
Page 113: Cabin and Cockpit Group
_____4. Inspect hub and attaching parts for defects, tightness and safety. _____5. Check propeller hub for oil leaks. _____6. Check propeller governor for security of mounting and oil leakage. _____7. Check propeller control mechanism for operation, security of installation & operation through full ...
Page 114: Wing Group
_____9. Inspect all cable attachments, cables, push pull tubes, rod ends and attachment points for controls. _____10. Inspect all safety belts and security of attachment. _____11. Inspect upholstery and rugs for attachment. _____12. Check seats for breakage, distortion and slides. _____13. Clean win...
Page 115: Empennage Group
Condition and freedom of operation. Lubricate. _____6. Check aileron and flap hinge brackets and hinge pins for looseness and condition. _____7. Inspect drain holes in flaps and ailerons. _____8. Inspect pitot mast and airspeed lines. Test pitot heat. _____9. Check all fairings and access panel scre...
Page 116: Landing Gear Group
_____3. Check tightness of battery terminals. _____4. Check electrical wiring and cables for possible chafing, security, and proper insulation. _____5. Check electrical switches for operations and fuses for abnormalities. _____6. Check strobe lights for operation and condition of flash tubes. _____7...
Page 117: Fuel System
_____7. Inspect hydraulic brake lines and hydraulic cylinders. _____8. Check oleo strut for correct inflation and height, approximately 1.5 inches compression, which will leave about 3 inches of shaft showing. _____9. Check nose gear for alignment. _____10. Inspect main gear sockets and fasteners. _...
Page 118: Radio Group (Installation)
_____5. Inspect and check condition of baggage door hinges and locks. _____6. Inspect antennas for attachment and condition. _____7. Clean off belly. Radio group (installation) _____1. Inspect radio and electronic equipment for proper installation and security of mounting. _____2. Check equipment an...
Page 119: Miscellaneous Group
Miscellaneous group _____1. Inspect any miscellaneous items of equipment installed. Inspect for proper installation security of mounting and proper operation. _____2. Compass correction card in view of pilot. Items required for flight _____1. Airworthiness certificate. _____2. Registration. _____3. ...
Page 120: Work Performed
Work performed.
Page 121: Power Plant Operational-
Power plant operational- preflight check engine make: ________________________________ model________________________________________ serial no_____________________________________ time: _________________________________________ warm up engine and check the following: generator / alternator output oi...
Page 122
Idle cut-off static rpm idle mixture check engine for oil leaks.