- DL manuals
- Lancom
- Switch
- GS-2310P
- User Manual
Lancom GS-2310P User Manual
Summary of GS-2310P
Page 1
Connecting your business lancom gs-2310p/gs-2326(p) user manual.
Page 2: Contents
Contents 1 introduction...............................................................................................................................................................7 1.1 overview...........................................................................................................
Page 3
3.6.1 basic configuration..................................................................................................................51 3.6.2 vlan configuration.................................................................................................................53 3.6.3 port group f...
Page 4
3.14.7 dscp-based qos..................................................................................................................112 3.14.8 dscp translation .................................................................................................................113 3.14.9 dscp classifi...
Page 5
4.6 snmp....................................................................................................................................................151 4.6.1 system...................................................................................................................................
Page 6
6.2.1 firmware upgrade.................................................................................................................196 6.2.2 firmware selection.................................................................................................................197 6.3 save / restore.....
Page 7: 1 Introduction
1 introduction 1.1 overview this user manual will not only show you how to install and connect your network system, but also how to configure and monitor the gs-2300 series step-by-step via cli (ssh, telnet), serial interface, the web or ethernet ports. Many detailed explanations of hardware and sof...
Page 8
2 operation of web-based management initial configuration this chapter instructs you how to configure and manage the gs-2300 series through the web user interface. With this facility, you can easily access and monitor through any one port of the switch all the status of the switch, including mibs st...
Page 9
5 the gs-2300 series is set to dhcp by default. If you do not have a dhcp server to provide an ip address to the switch, the default ip is 172.23.56.250 9 lancom gs-2310p/gs-2326(p) user manual 2 operation of web-based management.
Page 10: 2.2 Twisted-Pair Devices
2.1 connecting network devices the switch is designed to be connected to 10, 100 or 1000mbps network cards in pcs and servers, as well as to other switches and hubs. It may also be connected to remote devices using optional sfp transceivers. 2.2 twisted-pair devices each device requires an unshielde...
Page 11
Step 2: if the device is a network card and the switch is in the wiring closet, attach the other end of the cable segment to a modular wall outlet that is connected to the wiring closet. (see the section “network wiring connections.”) otherwise, attach the other end to an available port on the switc...
Page 12: 3 Configuration
3 configuration this chapter describes all of the basic network configuration tasks which include the ports, layer 2 network protocol (e.G. Vlans, qos, igmp, acls, and poe, etc.) and any setting of the switch. 3.1 port the section describes how to configure the port detail parameters of the switch. ...
Page 13
Parameter description: port: the logical port number for this row. Link: the current link state is displayed graphically. Green indicates the link is up and red that it is down. Current link speed: provides the current link speed of the port. Configured link speed: select any available link speed fo...
Page 14
Disabled: all power savings mechanisms disabled. Actiphy: link down power savings enabled. Perfectreach: link up power savings enabled. Enabled: both link up and link down power savings enabled. Buttons: save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previ...
Page 15
3.1.3 traffic overview this section describes the port statistics information and provides an overview of general traffic statistics for all switch ports. Web interface to display the port statistics overview in the web interface: 1. Click configuration, port, then traffic overview 2. If you want to...
Page 16
3.1.4 detailed statistics the section describes how to provide detailed traffic statistics for a specific switch port. Use the port select box to select which switch port details to display. The displayed counters are the totals for receive and transmit, the size counters for receive and transmit, a...
Page 17
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) multicast packets. Rx and tx broadcast: the number of received and transmitted (good and bad) broadcast packets. Rx and tx pause: a count of the mac control frames received or transmitted on this port that have an opcode indicating a pause operat...
Page 18
3.1.5 qos statistics the section describes that switch could display the qos detailed queuing counters for a specific switch port. For the different queues for all switch ports. Web interface to display the queuing counters in the web interface: 1. Click configuration, port, then qos statistics 2. I...
Page 19
If desired it is possible to minimize the latency for specific frames, by mapping the frames to a specific queue (done with qos), and then mark the queue as an urgent queue. When an urgent queue gets data to be transmitted, the circuits will be powered up at once and the latency will be reduced to t...
Page 20
Parameter description: connector type: display the connector type, for instance, utp, sc, st, lc and so on. Fiber type: display the fiber mode, for instance, multi-mode, single-mode. Tx central wavelength: display the fiber optical transmitting central wavelength, for instance, 850nm, 1310nm, 1550nm...
Page 21: 3.2 Acl
Show the transmit power of sfp module. Mon3(rx pwr): show the receiver power of sfp module. 3.2 acl the gs-2300 series access control list (acl) is probably the most commonly used object in the firmware. It is used for packet filtering but also for selecting types of traffic to be analyzed, forwarde...
Page 22
Port copy: select which port frames are copied on. The allowed values are disabled or a specific port number. The default value is "disabled". Mirror: specify the mirror operation of this port. The allowed values are: enabled: frames received on the port are mirrored. Disabled: frames received on th...
Page 23
Parameter description: rate limiter id: the rate limiter id for the settings contained in the same row. Rate the allowed values are: 0-3276700 in pps or 0, 100, 200, 300, ..., 1000000 in kbps. Unit: specify the rate unit. The allowed values are: pps: packets per second. Kbps: kbits per second. Butto...
Page 24
1. Click configuration, acl, then configuration 2. Click the button to add a new acl, or use the other acl modification buttons to specify the editing action (i.E., edit, delete, or moving the relative position of entry in the list) 3. Specify the parameters of the ace 4. Click apply to save the set...
Page 25
Ipv4: the ace will match all ipv4 frames. Action: indicates the forwarding action of the ace. Permit: frames matching the ace may be forwarded and learned. Deny: frames matching the ace are dropped. Rate limiter: indicates the rate limiter number of the ace. The allowed range is 1 to 16. When disabl...
Page 26
Specify the source mac filter for this ace. Any: no smac filter is specified. (smac filter status is "don't-care".) specific: if you want to filter a specific source mac address with this ace, choose this value. A field for entering an smac value appears. Smac value when "specific" is selected for t...
Page 27
Figure 3-2.4: the acl status parameter description: user: indicates the acl user. Ingress port: indicates the ingress port of the ace. Possible values are: any: the ace will match any ingress port. Policy: the ace will match ingress ports with a specific policy. Port: the ace will match a specific i...
Page 28: 3.3 Aggregation
The counter indicates the number of times the ace was hit by a frame. Conflict: indicates the hardware status of the specific ace. The specific ace is not applied to the hardware due to hardware limitations. Auto-refresh: activate the auto-refresh to refresh the information automatically. Refresh re...
Page 29
Parameter description: hash code contributors source mac address: the source mac address can be used to calculate the destination port for the frame. Check to enable the use of the source mac address, or uncheck to disable. By default, source mac address is enabled. Destination mac address: the dest...
Page 30
Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values. 3.3.2 lacp ports using link aggregation control protocol (according to ieee 802.3ad specification) as their trunking method can choose their unique lacp groupid to form a logic “trunked port”. The benefit of using ...
Page 31
The key value incurred by the port, range 1-65535. The auto setting will set the key as appropriate by the physical link speed, 10mb = 1, 100mb = 2, 1gb = 3. Using the specific setting, a user-defined value can be entered. Ports with the same key value can participate in the same aggregation group, ...
Page 32
3-3.2.3 port status this section describes the lacp status which is provided when lacp is configured on the switch. Web interface to display the lacp port status in the web interface: 1. Click configuration, aggregation, lacp, port status 2. If you want to auto-refresh the information then you need ...
Page 33: 3.4 Spanning Tree
3. Click “refresh“ to refresh the lacp statistics. Figure 3-3.2.4: the lacp statistics parameter description: port: the switch port number. Lacp received: shows how many lacp frames have been received at each port. Lacp transmitted: shows how many lacp frames have been sent from each port. Discarded...
Page 34
Once a stable network topology has been established, all bridges listen for hello bpdus (bridge protocol data units) transmitted from the root bridge. If a bridge does not get a hello bpdu after a predefined interval (maximum age), the bridge assumes that the link to the root bridge is down. This br...
Page 35
Max age: the maximum age of the information transmitted by the bridge when it is the root bridge. Valid values are in the range 6 to 40 seconds, and maxage must be maximum hop count: this defines the initial value of remaining hops for msti information generated at the boundary of an msti region. It...
Page 36
Parameter description: configuration identification configuration name: the name identifying the vlan to msti mapping. Bridges must share the name and revision (see below), as well as the vlan-to-msti mapping configuration in order to share spanning trees for msti's (intra-region). The name is at mo...
Page 37
Web interface to configure the spanning tree msti priorities parameters in the web interface: 1. Click configuration, spanning tree, msti priorities 2. Scroll the priority maximum is 240. Default is 128. 3. Click "save" to save the settings. 4. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to clic...
Page 38
Figure 3-4.4: the stp cist port configuration (gs-2310p) parameter description: port: the switch port number of the logical stp port. Stp enabled: controls whether stp is enabled on this switch port. Path cost: controls the path cost incurred by the port. The auto setting will set the path cost as a...
Page 39
If enabled, causes the port not to propagate received topology change notifications and topology changes to other ports. If set it can cause temporary loss of connectivity after changes in a spanning tree's active topology as a result of persistently incorrect learned station location information. I...
Page 40
Parameter description: port: the switch port number of the corresponding stp cist (and msti) port. Path cost: controls the path cost incurred by the port. The auto setting will set the path cost as appropriate by the physical link speed, using the 802.1d recommended values. Using the specific settin...
Page 41
Figure 3-4.6: the stp bridges status parameter description: msti: the bridge instance. This is also a link to the stp detailed bridge status. Bridge id: the bridge id of this bridge instance. Root id: the bridge id of the currently elected root bridge. Root port: the switch port currently assigned t...
Page 42
Parameter description: port: the switch port number of the logical stp port. Cist role: the current stp port role of the cist port. The port role can be one of the following values: alternateport, backup port, rootport, designatedport disabled. Cist state: the current stp port state of the cist port...
Page 43: 3.5 Igmp Snooping
The number of mstp configuration bpdu's received/transmitted on the port. Rstp: the number of rstp configuration bpdu's received/transmitted on the port. Stp: the number of legacy stp configuration bpdu's received/transmitted on the port. Tcn: the number of (legacy) topology change notification bpdu...
Page 44
3. Activate which port wants to become a router port or enable/ disable the fast leave function. 4. Set the throttling parameter. 5. Click apply to save the setting 6. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the reset button. It will revert to previously saved values. Figure 3-5.1: ...
Page 45
Enable the fast leave on the port. Throttling: enable to limit the number of multicast groups to which a switch port can belong. Buttons save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values. 3.5.2 vlan configuration the section describes ...
Page 46
Rv: robustness variable. The robustness variable allows tuning for the expected packet loss on a network. The allowed range is 1 to 255; default robustness variable value is 2. Qi: query interval. The query interval is the interval between general queries sent by the querier. The allowed range is 1 ...
Page 47
5. Click apply to save the setting 6. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the reset button. It will revert to previously saved values figure 3-5.3: the igmp snooping port group filtering configuration. Parameter description: delete: check to delete the entry. It will be deleted ...
Page 48
Parameter description: vlan id: the vlan id of the entry. Querier version: working querier version currently. Host version: working host version currently. Querier status: shows the querier status is "active" or "idle". Queries transmitted: the number of transmitted queries. Queries received: the nu...
Page 49
Use the last entry of the currently displayed table as a basis for the next lookup. When the end is reached the text "no more entries" is shown in the displayed table. Web interface to display the igmp snooping group information in the web interface: 1. Click configuration, igmp snooping, group info...
Page 50
Ssm does not require group address allocation within the network, only within each source host. Different applications running on the same source host must use different ssm groups. Different applications running on different source hosts can arbitrarily reuse ssm group addresses without causing any...
Page 51: 3.6 Mld Snooping
Indicates the type. It can be either allow or deny. Auto-refresh: activate the auto-refresh to refresh the log automatically. Refresh: refresh the igmp group status manually. > go to the previous/next page or entry. 3.6 mld snooping curiously enough, a network node that acts as a source of ipv6 mult...
Page 52
Figure 3-6.1: the mld snooping basic configuration (gs-2310p) parameter description: snooping enabled: enable the global mld snooping. Unregistered ipmcv6 flooding enabled: enable unregistered ipmcv6 traffic flooding. Please note that disabling unregistered ipmcv6 traffic flooding may lead to failur...
Page 53
Save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values. 3.6.2 vlan configuration when mld snooping is enabled on a vlan, the switch acts to minimize unnecessary multicast traffic. If the switch receives multicast traffic destined for a give...
Page 54
Query response interval. The maximum response delay used to calculate the maximum response code inserted into the periodic general queries. The allowed range is 0 to 31744 in tenths of seconds; default query response interval is 100 in tenths of seconds (10 seconds). Llqi (lmqi for igmp): last liste...
Page 55
Parameter description: delete: check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save. Port: the logical port for the settings. You can enable the port to join a filtering group filtering groups the ip multicast group that will be filtered. Buttons: save – click to save changes. Reset – ...
Page 56
Working querier version currently. Host version: working host version currently. Querier status: show the querier status is "active" or "idle". Queries transmitted: the number of transmitted queries. Queries received: the number of received queries. V1 reports received: the number of received v1 rep...
Page 57
Parameter description: navigating the mld group table each page shows up to 99 entries from the mld group table, default being 20, selected through the "entries per page" input field. When first visited, the web page will show the first 20 entries from the beginning of the mld group table. The "star...
Page 58: 3.7 Mvr
4. Click “>“ to move to previous or next entry. Figure 3-6.6: the ipv6 ssm information parameter description: mldv2 information table columns vlan id: vlan id of the group. Group: group address of the group displayed. Port: switch port number. Mode: indicates the filtering mode maintained per (vlan ...
Page 59
1. Click configuration, mvr, configuration 2. Enable or disable mvr by selecting the mode. 3. Set the other parameters. 4. Click apply to save the setting 5. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the reset button. It will revert to previously saved values figure 3-7.1: the mvr con...
Page 60
3.7.2 groups information this section describes how to display the mvr groups information. Entries in the mvr group table are shown on this page. The mvr group table is sorted first by vlan id, and then by group web interface to display the mvr groups information in the web interface: 1. Click confi...
Page 61: 3.8 Lldp
Figure 3-7.3: the mvr statistics information parameter description: vlan id: the multicast vlan id. V1 reports received: the number of received v1 reports. V2 reports received: the number of received v2 reports. V3 reports received: the number of received v3 reports. V2 leaves received: the number o...
Page 62
1. Click lldp configuration 2. Modify lldp timing parameters 3. Set the required mode for transmitting or receiving lldp messages 4. Specify the information to include in the tlv field of advertised messages 5. Click apply figure 3-8.1: the lldp configuration (gs-2310p) parameter description: lldp p...
Page 63
Lldp port configuration the lldp port settings relate to the currently selected, as reflected by the page header. Port: the switch port number of the logical lldp port. Mode: select lldp mode. Rx only the switch will not send out lldp information, but lldp information from neighbor units is analyzed...
Page 64
Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values. 3.8.2 lldp neighbors this page provides a status overview for all lldp neighbors. The displayed table contains a row for each port on which an lldp neighbor is detected. The columns hold the following information: ...
Page 65
When a capability is enabled, the capability is followed by (+). If the capability is disabled, the capability is followed by (-). System description: system description is the port description advertised by the neighbor unit. Management address: management address is the neighbor unit's address tha...
Page 66
Parameter description: fast start repeat count rapid startup and emergency call service location identification discovery of endpoints is a critically important aspect of voip systems in general. In addition, it is best to advertise only those pieces of information which are specifically relevant to...
Page 67
Latitude should be normalized to within 0-90 degrees with a maximum of 4 digits. It is possible to specify the direction to either north of the equator or south of the equator. Longitude: longitude should be normalized to within 0-180 degrees with a maximum of 4 digits. It is possible to specify the...
Page 68
Trailing street suffix - example: sw. Street suffix: street suffix - example: ave, platz. House no.: house number - example: 21. House no. Suffix: house number suffix - example: a, 1/2. Landmark: landmark or vanity address - example: columbia university. Additional location info: additional location...
Page 69
Network policy discovery enables the efficient discovery and diagnosis of mismatch issues with the vlan configuration, along with the associated layer 2 and layer 3 attributes, which apply for a set of specific protocol applications on that port. Improper network policy configurations are a very sig...
Page 70
5. Softphone voice - for use by softphone applications on typical data centric devices, such as pcs or laptops. This class of endpoints frequently does not support multiple vlans, if at all, and are typically configured to use an 'untagged' vlan or a single 'tagged' data specific vlan. When a networ...
Page 71
3.8.4 lldp-med neighbors this page provides a status overview of all lldp-med neighbors. The displayed table contains a row for each port on which an lldp neighbor is detected. This function applies to voip devices which support lldp-med. The columns hold the following information: web interface to ...
Page 72
Lldp-med generic endpoint (class i): the lldp-med generic endpoint (class i) definition is applicable to all endpoint products that require the base lldp discovery services defined in tia-1057, however do not support ip media or act as an end-user communication appliance. Such devices may include (b...
Page 73
5. Softphone voice - for use by softphone applications on typical data centric devices, such as pcs or laptops. 6. Video conferencing - for use by dedicated video conferencing equipment and other similar appliances supporting real-time interactive video/audio services. 7. Streaming video - for use b...
Page 74
5 if your network without any devices which enables eee function then the table will show “no lldp eee information found”. Parameter description: local port: the port on which lldp frames are received or transmitted. Tx tw: the link partner’s maximum time that transmit path can hold off sending data...
Page 75
3.8.6 port statistics two types of counters are shown. Global counters are counters that refer to the whole switch, while local counters refer to per port counters for the currently selected switch web interface to show lldp statistics: 1. Click lldp, than click port statistics to show lldp counters...
Page 76: 3.9 Filtering Data Base
Rx errors: the number of received lldp frames containing some kind of error. Frames discarded: if an lldp frame is received on a port, and the switch's internal table has run full, the lldp frame is counted and discarded. This situation is known as "too many neighbors" in the lldp standard. Lldp fra...
Page 77
To configure mac address table in the web interface: aging configuration 1. Click configuration. 2. Specify the disable automatic aging and aging time. 3. Click apply. Mac table learning 1. Click configuration. 2. Specify the port members (auto, disable, secure). 3. Click apply. Static mac table con...
Page 78
Mac table learning if the learning mode for a given port is greyed out, another module is in control of the mode, so that it cannot be changed by the user. An example of such a module is the mac-based authentication under 802.1x. Each port can do learning based upon the following settings: auto: lea...
Page 79
Parameter description: mac table columns type: indicates whether the entry is a static or a dynamic entry. Vlan: the vlan id of the entry. Mac address: the mac address of the entry. Port members: the ports that are members of the entry. Auto-refresh: activate the auto-refresh to refresh the informat...
Page 80: 3.10 Vlan
3.10 vlan how to assign a specific vlan for management purposes the management vlan is used to establish an ip connection to the switch from a workstation connected to a port in the vlan. This connection supports a vsm, snmp, telnet, http(s) and ssh session. By default, the active management vlan is...
Page 81
Adding a new vlan: click to add a new vlan id. An empty row is added to the table, and the vlan can be configured as needed. Legal values for a vlan id are 1 through 4094. The vlan is enabled on the selected switch unit when you click on "save". The vlan is thereafter present on the other switch uni...
Page 82
Parameter description: ethertype for custom s-ports: this field specifies the ether type used for custom s-ports. This is a global setting for all the custom s-ports. Custom ethertype enables the user to change the ethertype value on a port to any value to support network devices that do not use the...
Page 83
Egress action ingress action 2. Is not 0x8100, the frame is forwarded (no additional tag added). The tpid of frame transmitted by an s-custom-port will be set to a self-customized when the port receives an untagged frame, a tag - based on the defined pvid - is added and the frame is forwarded. When ...
Page 84
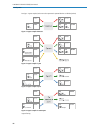
Port type – ingress samples (each arrow color represents its operate behavior to individual packet) figure 1: ingress sample: unaware figure 2: ingress sample: c-port figure 3: ingress sample: s-port figure 4: ingress sample: s-custom-port ingress filtering: 84 lancom gs-2310p/gs-2326(p) user manual...
Page 85
Enable ingress filtering on a port by checking the box. This parameter affects vlan ingress processing. If ingress filtering is enabled and the ingress port is not a member of the classified vlan of the frame, the frame is discarded. By default, ingress filtering is disabled (no checkmark). Frame ty...
Page 86
Vlan user module uses services of the vlan management functionality to configure vlan memberships and vlan port configurations such as pvid and uvid. Currently we support the following vlan user types: web/snmp: these are referred to as static. Nas: nas provides port-based authentication, which invo...
Page 87
Port: the logical port for the settings contained in the same row. Pvid: shows the vlan identifier for that port. The allowed values are 1 through 4094. The default value is 1. Port type: shows the port type. Port type can be any of unaware, c-port, s-port, custom s-port. If port type is unaware, al...
Page 88
To configure private vlan in the web interface: 1. Click add new private vlan configuration. 2. Specify the private vlan id and port members. 3. Click save. Figure 3-10.5.1: the port isolation configuration parameter description: delete: check to delete a private vlan entry. The entry will be delete...
Page 89
Parameter description: port members: a check box is provided for each port of a private vlan. When checked, port isolation is enabled on that port. When unchecked, port isolation is disabled on that port. By default, port isolation is disabled on all ports. Buttons: save – click to save changes. Res...
Page 90
Parameter description: delete: to delete a mac-based vlan entry, check this box and press save. The entry will be deleted on the selected switch. Mac address: indicates the mac address. Vlan id: indicates the vlan id. Port members: a row of check boxes for each port is displayed for each mac-based v...
Page 91
Parameter description: mac address: indicates the mac address. Vlan id: indicates the vlan id. Port members: port members of the mac-based vlan entry. Auto-refresh: activate the auto-refresh to refresh the information automatically. Refresh: refresh the mac-based vlan membership information manually...
Page 92
Parameter description: delete: to delete a protocol to group name map entry, check this box. The entry will be deleted on the switch during the next save. Frame type: frame type can have one of the following values: ethernet llc snap 5 on changing the frame type field, valid value of the following t...
Page 93
5 special character and underscore(_) are not allowed. Adding a new group to vlan mapping entry: click to add a new entry in mapping table. An empty row is added to the table; frame type, value and the group name can be configured as needed. The button can be used to undo the addition of new entry. ...
Page 94: 3.11 Voice Vlan
Vlan id: indicates the id to which group name will be mapped. A valid vlan id ranges from 1-4094. Port members: a row of check boxes for each port is displayed for each group name to vlan id mapping. To include a port in a mapping, check the box. To remove or exclude the port from the mapping, make ...
Page 95
Parameter description: mode: indicates the voice vlan mode operation. We must disable mstp feature before we enable voice vlan. It can avoid the conflict of ingress filtering. Possible modes are: enabled: enable voice vlan mode operation. Disabled: disable voice vlan mode operation. Vlan id: indicat...
Page 96
Forced: force join to voice vlan. Port security: indicates the voice vlan port security mode. When the function is enabled, all non-telephonic mac addresses in the voice vlan will be blocked for 10 seconds. Possible port modes are: enabled: enable voice vlan security mode operation. Disabled: disabl...
Page 97: 3.12 Garp
A telephony oui address is a globally unique identifier assigned to a vendor by ieee. It must be 6 characters long and the input format is "xx-xx-xx" (x is a hexadecimal digit). Description: the description of oui address. Normally, it describes which vendor telephony device it belongs to. The allow...
Page 98
Parameter description: port: the port column shows the list of ports for which you can configure garp settings. There are 2 types configuration settings which can be configured on per port bases. Timer values application attribute type garp applicant timer values: three different timers can be confi...
Page 99: 3.13 Gvrp
3.12.2 statistics this section describes the port statistics of garp for all switch ports. The port statistics relate to the currently selected unit, as reflected by the page header. Web interface to display garp port statistics in the web interface: 1. Click garp statistics. 2. Click refresh to ref...
Page 100
1. Click gvrp configure. 2. Specify gvrp configuration parameters. 3. Click apply. Figure 3-13.1: the gvrp global configuration (gs-2310p) parameter description: gvrp mode: gvrp mode is a global setting, to enable the gvrp globally select 'enable' from menu and to disable gvrp globally select 'disab...
Page 101: 3.14 Qos
Save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values. 3.13.2 statistics this section describes the basic gvrp port statistics for all switch ports. The statistics relate to the currently selected unit, as reflected by the page header. Web...
Page 102
Classification mechanism is implemented in a qos control list (qcl). The qos class assigned to a frame is used throughout the device for providing queuing, scheduling, and congestion control guarantees to the frame according to what was configured for that specific qos class. The switch supports adv...
Page 103
Dei: controls the default dei for untagged frames. Tag class.: shows the classification mode for tagged frames on this port. Disabled: use default qos class and dp level for tagged frames. Enabled: use mapped versions of pcp and dei for tagged frames. Click on the mode in order to configure the mode...
Page 104
Parameter description: port: the logical port for the settings contained in the same row. Click on the port number in order to configure the schedulers. Enabled: to activate which port you need to enable the qos ingress port policies function. Rate: to set the rate limit value for this port, the def...
Page 105
105 lancom gs-2310p/gs-2326(p) user manual 3 configuration.
Page 106
Parameter description: port: the logical port for the settings contained in the same row. Click on the port number in order to configure the schedulers. Mode: shows the scheduling mode for this port. Weight (qn): shows the weight for this queue and port. Scheduler mode: controls whether the schedule...
Page 107
Controls the weight for this queue. The default value is "17". This value is restricted to 1-100. This parameter is only shown if "scheduler mode" is set to "weighted". Queue scheduler percent: shows the weight in percent for this queue. This parameter is only shown if "scheduler mode" is set to "we...
Page 108
108 lancom gs-2310p/gs-2326(p) user manual 3 configuration.
Page 109
Parameter description: port: the logical port for the settings contained in the same row. Click on the port number in order to configure the shapers. Shapers (qn): shows "disabled" or actual queue shaper rate - e.G. "800 mbps". Shapers (port): shows "disabled" or actual port shaper rate - e.G. "800 ...
Page 110
Figure 3-14.5: the port tag remarking parameter description: port: the logical port for the settings contained in the same row. Click on the port number in order to configure tag remarking. Mode: shows the tag remarking mode for this port. Classified: use classified pcp/dei values. Default: use defa...
Page 111
3.14.6 port dscp this section shows how to configure the qos port dscp settings for all switch ports. Web interface to configure the qos port dscp parameters in the web interface: 1. Click configuration, qos, port dscp 2. Activate to enable or disable the ingress translate and scroll the classify pa...
Page 112
Port egress rewriting can be one of below parameters disable: no egress rewrite. Enable: rewrite enable without remapped. Remap: dscp from analyzer is remapped and frame is remarked with remapped dscp value. Buttons: save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and re...
Page 113
Parameter description: dscp: maximum number of support ed dscp values are 64. Trust: click to check if the dscp value is trusted. Qos class: qos class value can be any of (0-7) dpl: drop precedence level (0-3) buttons: save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and ...
Page 114
Parameter description: dscp: maximum number of supported dscp values are 64 and valid dscp value ranges from 0 to 63. Ingress: ingress side dscp can be first translated to new dscp before using the dscp for qos class and dpl map. There are two configuration parameters for dscp translation – translat...
Page 115
Remap dp1: select the dscp value from select menu to which you want to remap. Dscp value ranges form 0 to 63. There is following configurable parameter for egress side - remap: select the dscp value from select menu to which you want to remap. Dscp value ranges form 0 to 63. Buttons: save – click to...
Page 116
And dpl value buttons: save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values. 3.14.10 qos control list configuration the section shows the qos control list(qcl), which is made up of the qces. Each row describes a qce that is defined. The m...
Page 117
Any: the qce will match all frame type. Ethernet: only ethernet frames (with ether type 0x600-0xffff) are allowed. Llc: only (llc) frames are allowed. Snap: only (snap) frames are allowed ipv4: the qce will match only ipv4 frames. Ipv6: the qce will match only ipv6 frames. Smac: displays the oui fie...
Page 118
Key configuration are described as below: tag value of tag field can be 'any', 'untag' or 'tag' vid valid value of vlan id can be any value in the range 1-4094 or 'any'; user can enter either a specific value or a range of vids pcp priority code point: valid value pcp are specific(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ...
Page 119
Dscp valid dscp value can be (0-63, be, cs1-cs7, ef or af11-af43) buttons: save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values. 3.14.11 qcl status the section shows how to configure and display the qcl status each row describes the qce t...
Page 120
Indicates the classification action taken on ingress frame if parameters configured are matched with the frame's content. There are three action fields: class, dpl and dscp. Class: classified qos class; if a frame matches the qce it will be put in the queue. Dpl: drop precedence level; if a frame ma...
Page 121: 3.15 Poe
Enable or disable the storm control status for the given frame type. Rate: the rate unit is packets per second (pps). Valid values are: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1k, 2k, 4k, 8k, 16k, 32k, 64k, 128k, 256k, 512k or 1024k., 1024k, 2048k, 4096k, 8192k, 16384k or 32768k., 1024k, 2048k, 4096k...
Page 122
Maximum power: the maximum power in watts that can be delivered to a remote device. If you want the port to support ieee802.3at, the maximum allowed value is 30 w. Detection: type of detection. Select legacy, 4-point, 4-point-legacy, 2-point or 2-point-legacy. Reset: reset the specific poe port. But...
Page 123
Parameter description: port: the logical port number for this row. Delay mode: enable or disable the power delay function. Delay time: period until the poe port starts providing power to the pd. Buttons: apply – apply changes. 3.15.4 auto checking this page allows the user to specify the auto detect...
Page 124
Failure log: failure loggings counter. Failure action: the action which is taken after failed detection. Nothing: keep pinging the remote device. Reboot remote pd: turn off the power of the poe port and reboot the pd. Reboot time: the period until the poe port restores power after a reboot of the pd...
Page 125: 3.16 Sflow Agent
Select all: select all hours and weekdays. Hour: the hour for which poe should be enabled. Sunday/monday/tuesday/wednesday/thursday/friday/saturday: the day for which poe should be enabled. Buttons: apply – apply changes. 3.16 sflow agent the sflow collector configuration for the switch can be monit...
Page 126
This ip is used to monitor the sflow samples sent by sflow agent(our switch). By default, the ip is set to 0.0.0.0,and a new entry has to be added to it. Port: a port to listen to the sflow agent has to be configured for the collector. The value of the port number has to be typed into the text box. ...
Page 127: 3.17 Loop Protection
Parameter description: sflow ports: list of the port numbers on which sflow is configured. Sflow instance: configured sflow instance for the port number. Sampler type: configured sampler type on the port and could be any of the types: none, rx, tx or all. You can scroll to choice one for your sample...
Page 128
3.17.1 configuration the section describes how to configure loop protection. Web interface to configure the loop protection parameters in the web interface: 1. Click configuration, loop protection, configuration 2. Activate to select enable or disable the port loop protection. 3. Click apply to save...
Page 129
Enable: controls whether loop protection is enabled on this switch port. Action: configures the action performed when a loop is detected on a port. Valid values are shutdown port, shutdown port and log or log only. Tx mode: controls whether the port is actively generating loop protection pdu's, or w...
Page 130: 3.18 Single Ip
Loop: whether a loop is currently detected on the port. Time of last loop: the time of the last loop event detected. Auto-refresh: activate the auto-refresh to refresh the information automatically. Refresh: refresh the loop protection information manually. 3.18 single ip single ip management (sim) ...
Page 131: 3.19 Easy Port
Group name: the name of the group. The maximum length is 64 characters. Buttons: apply – apply changes. Reset – undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values. 3.18.2 information web interface to display the active slave information in the web interface: 1. Click configuration, ...
Page 132
Parameter description: port members: to activate which port wants to enable the easy port function. Role: to scroll to select what kind device you want to connect and implement with the easy port setting. Access vlan: to set the access vlan id, it means the switch port access vlan id (avid). Vlan mo...
Page 133: 3.20 Mirroring
To scroll to enable or disable the spanning tree bpdu guard function on the easy port. Buttons: save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values. 3.20 mirroring you can mirror traffic from any source port to a target port for real-tim...
Page 134: 3.21 Trap Event Severity
The logical port for the settings contained in the same row. Mode: select mirror mode. Rx only frames received on this port are mirrored on the mirror port. Frames transmitted are not mirrored. Tx only frames transmitted on this port are mirrored on the mirror port. Frames received are not mirrored....
Page 135: 3.22 Smtp Configuration
Parameter description: group name: the field describe the trap event definition. Severity level: to scroll to select the event type with “emerg, alert, crit, error, warming, notice, info and debug”. Buttons: save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to p...
Page 136: 3.23 Upnp
Parameter description: these parameters are displayed on the smtp configuration page: mail server: specify the ip address of the server transferring your email. Username: specify the username on the mail server. Password: specify the password on the mail server. Sender: to set the mail sender name. ...
Page 137
2. Select the mode to enable or disable 3. Specify the parameters in each blank field. 4. Click apply to save the setting 5. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the reset button. It will revert to previously saved values. Figure 3-23.1: the upnp configuration parameter descripti...
Page 138: 4 System Configuration
4 system configuration this chapter describes the entire basic configuration tasks which includes the system information and any managing of the switch (e.G. Time, account, ip, syslog and snmp). 4.1 system information after you login, the switch shows you the system information. This page tells you ...
Page 139
The description of the device. In this case: “44-port 10/100/1000base-t + 4 (100/1g) sfp combo + 4 (1g/10g) sfp+ poe+ l2 plus managed switch”. Location: the physical location of the switch. User-defined. Contact: for easy managing and maintenance of the device, you may enter the name of a contact pe...
Page 140
4.1.2 configuration you can identify the system by configuring the contact information, name, and location of the switch. Web interface to configure the system information in the web interface: 1. Click system, system information, configuration. 2. Enter system contact, system name, system location....
Page 141: 4.2 Time
Parameter description: auto-refresh activate the auto-refresh to refresh the log automatically. 4.2 time this page configures the switch’s time. Local time configuration and ntp configuration is supported. 4.2.1 manual the switch provides manual and automatic ways to set the system time via ntp. Man...
Page 142
Parameter description: clock source: select which clock source is used for the gs-2300 series. You can select “use local settings” or “use ntp server” as the switchs' time clock source. Local time: shows the current time of the system. Time zone offset: provides the time zone offset relative to utc/...
Page 143: 4.3 Account
4.2.2 ntp ntp, the network time protocol is used to sync the network time based on greenwich mean time (gmt). You can use the built-in ntp time server or manually specify a user-defined ntp server as well as a time zone, the switch will sync the time shortly after pressing the button. Though it sync...
Page 144
4.3.1 users this page provides an overview of the current users. Currently the only way to login as another user on the web server is to close and reopen the browser. Web interface to configure accounts in the web interface: click system, account, users. Click add new user specify the user name para...
Page 145
4.3.2 privilege level this page provides an overview of the privilege levels. The switch provides user set privilege levels from 1 to 15 for account, aggregation, diagnostics, eee, garp, gvrp, ip, icmp snooping, lacp, lldp, lldp, med, mac table, mrp, mvr, mvrp, maintenance mirroring, poe ports, priv...
Page 146: 4.4 Ip
The name identifying the privilege group. In most cases, a privilege level group consists of a single module (e.G. Lacp, rstp or qos), but a few of them contain more than one. The following description defines the privilege level groups in details: system: contact, name, location, time zone, log. Se...
Page 147
Parameter description: dhcp client: enable the dhcp client by checking this box. If dhcp fails and the configured ip address is zero, dhcp will retry. If dhcp fails and the configured ip address is non-zero, dhcp will stop and the configured ip settings will be used. The dhcp client will announce th...
Page 148: 4.5 Syslog
The 'current' column is used to show the active ipv6 configuration. Figure 4-4.2: the ipv6 configuration parameter description: auto configuration: enable ipv6 auto-configuration by checking this box. If it fails, the configured ipv6 address is zero. The router may delay responding to a router solic...
Page 149
4. Click apply. Figure 4-5.1: the system log configuration parameter description: server mode: indicates the server mode. When the mode operation is enabled, the syslog message will be sent out to a syslog server. The syslog protocol is based on udp communication and received on udp port 514 and the...
Page 150
Parameter description: auto-refresh activate the auto-refresh to refresh the log automatically. Level level of the system log entry. The following level types are supported: information: information level of the system log. Warning: warning level of the system log. Error: error level of the system l...
Page 151: 4.6 Snmp
Parameter description: id the id (>= 1) of the system log entry. Message the detailed message of the system log entry. Refresh refresh the system log manually. Clear clear the system log manually. 4.6 snmp any network management system (nms) running the simple network management protocol (snmp) can ...
Page 152
Parameter description: these parameters are displayed on the snmp system configuration page: snmp state: enable: enable snmp operation. Disable: disable snmp operation. Default: enable. Engine id: snmpv3 engine id. Syntax: 0-9,a-f,a-f, min 5 octet, max 32 octet, fifth octet must not be 00. If the en...
Page 153
Parameter description: delete delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save. Community indicates the community access string to permit access to snmpv3 agent. The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is ascii characters from 33 to 126. The community string will be tr...
Page 154
User name a string identifying the user name that this entry should belong to. The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is ascii characters from 33 to 126. Security level indicates the security model that this entry should belong to. Possible security models are: noauth, nopriv:...
Page 155
Parameter description: delete delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save. Security model indicates the security model that this entry should belong to. Possible security models are: v1: reserved for snmpv1. V2c: reserved for snmpv2c. Usm: user-based security model (usm). Security name...
Page 156
Figure 4-6.5: the snmp views configuration parameter description: delete delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save. View name a string identifying the view name that this entry should belong to. The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is ascii characters from 33...
Page 157
5. If you want to modify or clear the setting then click reset. Figure 4-6.6: the snmp accesses configuration parameter description: delete check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save. Group name a string identifying the group name that this entry should belong to. The allowed...
Page 158
4.6.7 trap the function is used to configure snmp traps. To create a new trap account, please click on the button, and enter the trap information then click . Max group number: 6. Web interface to configure snmp traps: 1. Click snmp, trap. 2. Display the snmp trap hosts information table. 3. Choose ...
Page 159
Indicates what kind of message will send to security level. Possible modes are: info: send information, warnings and errors. Warning: send warnings and errors. Error: send errors. Security level: there are three kinds of choices. Noauth, nopriv: no authentication and no privacy. Auth, nopriv: authen...
Page 160: 5 Security
5 security this chapter describes all of the switch security configuration tasks to enhance the security of local network including ip source guard, arp inspection, dhcp snooping, aaa, etc. 5.1 ip source guard the section describes how to configure the ip source guard detail parameters of the switch...
Page 161
Parameter description: mode of ip source guard configuration: enable the global ip source guard or disable the global ip source guard. All configured aces will be lost when the mode is enabled. Port mode configuration: specify ip source guard is enabled on which ports. Only when both global mode and...
Page 162
Port: the logical port for the settings. Vlan id: the vlan id for the settings. Ip address: allowed source ip address. Ip mask: it can be used for calculating the allowed network with ip address. Mac address: allowed source mac address. Add new entry: click to add a new entry to the static ip source...
Page 164
Mode of arp inspection configuration: enable the global arp inspection or disable the global arp inspection. Port mode configuration: arp inspection is enabled on selected ports. Only when both global mode and port mode on a given port are enabled, arp inspection is enabled on this given port. Butto...
Page 165
Adding new entry: click to add a new entry to the static arp inspection table. Specify the port, vlan id, mac address, and ip address for the new entry. Click "save". Buttons: save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values. 5.2.3 dy...
Page 166: 5.3 Dhcp Snooping
5.3 dhcp snooping the section describes how to configure the dhcp snooping parameters of the switch. The dhcp snooping can prevent attackers from adding their own dhcp servers to the network. 5.3.1 configuration this section describes how to configure dhcp snooping setting including: snooping mode (...
Page 167
Untrusted: configures the port as untrusted source of the dhcp messages. Buttons: save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values. 5.3.2 statistics the section describes to show the dhcp snooping statistics information of the switch....
Page 168: 5.4 Dhcp Relay
Rx and tx lease query: the number of lease query (option 53 with value 10) packets received and transmitted. Rx and tx lease unassigned: the number of lease unassigned (option 53 with value 11) packets received and transmitted. Rx and tx lease unknown: the number of lease unknown (option 53 with val...
Page 169
Parameter description: relay mode: indicates the dhcp relay mode operation. Possible modes are: enabled: enable dhcp relay mode operation. When dhcp relay mode operation is enabled, the agent forwards and transfers dhcp messages between the clients and the server when they are not in the same subnet...
Page 170
Parameter description: transmit to server: the number of packets that are relayed from client to server. Transmit error: the number of packets that resulted in errors while being sent to clients. Receive from server: the number of packets received from server. Receive missing agent option: the numbe...
Page 171: 5.5 Nas
Drop agent option: the number of packets that were dropped which were received with relay agent information. Auto-refresh: activate the auto-refresh to refresh the information automatically. Refresh: refresh the dhcp relay statistics manually. Clear: clear the entries. 5.5 nas the section describes ...
Page 172
Parameter description: mode: indicates if nas is globally enabled or disabled on the switch. If globally disabled, all ports are allowed forwarding of frames. Reauthentication enabled: if checked, successfully authenticated supplicants/clients are reauthenticated after the interval specified by the ...
Page 173
If reauthentication is enabled and the port is in an 802.1x-based mode, this is not so critical, since supplicants that are no longer attached to the port will get removed upon the next reauthentication, which will fail. But if reauthentication is not enabled, the only way to free resources is by ag...
Page 174
Valid values are in the range [1; 255]. Allow guest vlan if eapol seen: the switch remembers if an eapol frame has been received on the port for the life-time of the port. Once the switch considers whether to enter the guest vlan, it will first check if this option is enabled or disabled. If disable...
Page 175
In port-based 802.1x authentication, once a supplicant is successfully authenticated on a port, the whole port is opened for network traffic. This allows other clients connected to the port (for instance through a hub) to piggy-back on the successfully authenticated client and get network access eve...
Page 176
Successfully authenticated. If present and valid, traffic received on the supplicant's port will be classified to the given qos class. If (re-)authentication fails or the radius access-accept packet no longer carries a qos class or it's invalid, or the supplicant is otherwise no longer present on th...
Page 177
• single 802.1x • multi 802.1x for trouble-shooting vlan assignments, use the "monitor vlans vlan membership and vlan port" pages. These pages show which modules have (temporarily) overridden the current port vlan configuration. Guest vlan operation: when a guest vlan enabled port's link comes up, t...
Page 178
5.5.2 switch status the section describes how to show the each port nas status information of the switch. The status includes admin state port state, last source, last id, qos class, and port vlan id. To show the nas switch status in the web interface: 1. Go to nas, switch port status 2. Check "auto...
Page 179
To configure a nas port status in the web interface: 1. Specify port to check. 2. Checked “auto-refresh”. Figure 5-5.3: the nas statistics parameter description: port state admin state: the port's current administrative state. Refer to nas admin state for a description of possible values. Port state...
Page 180
• multi 802.1x • mac-based auth. Last supplicant/client info: information about the last supplicant/client that attempted to authenticate. This information is available for the following administrative states: • port-based 802.1x • single 802.1x • multi 802.1x • mac-based auth. Selected counters sel...
Page 181: 5.6 Aaa
Clear all entries. 5.6 aaa this section shows you to use an aaa (authentication, authorization, accounting) server to provide access control to your network. The aaa server can be a tacacs+ or radius server to create and manage objects that contain settings for using aaa servers. 5.6.1 configuration...
Page 182
Figure 5-5.3.3: the radius configuration figure 5-5.3.4: the radius accounting configuration figure 5-5.3.4: the tacacs+ authentication configuration parameter description: timeout: the timeout, which can be set to a number between 3 and 3600 seconds, is the maximum time to wait for a reply from a s...
Page 183
Radius authentication server configuration the table has one row for each radius authentication server and a number of columns, which are: #: the radius authentication server number for which the configuration below applies. Enabled: enable the radius authentication server by checking this box. Ip a...
Page 184
Buttons: save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values. 5.6.2 radius overview this section provides an overview of the radius authentication and accounting servers status to ensure the function is working. To show the radius overvi...
Page 185
The current state of the server. This field takes one of the following values: disabled: the server is disabled. Not ready: the server is enabled, but ip communication is not yet up and running. Ready: the server is enabled, ip communication is up and running, and the radius module is ready to accep...
Page 186: 5.7 Port Security
Clear: clear all entries. 5.7 port security this section shows how to configure the port security settings of the switch. You can use the port security feature to restrict input to an interface by limiting and identifying mac addresses. 5.7.1 limit control this section shows how to configure the por...
Page 187
Parameter description: system configuration mode: indicates if limit control is globally enabled or disabled on the switch. If globally disabled, other modules may still use the underlying functionality, but limit checks and corresponding actions are disabled. Aging enabled: if checked, secured mac ...
Page 188
Controls whether limit control is enabled on this port. Both this and the global mode must be set to enabled for limit control to be in effect. Notice that other modules may still use the underlying port security features without enabling limit control on a given port. Limit: the maximum number of m...
Page 189
5.7.2 switch status this section shows the port security status. Port security is a module with no direct configuration. Configuration comes indirectly from other modules - the user modules. When a user module has enabled port security on a port, the port is set-up for software-based learning. In th...
Page 190
Ready: the port security service is in use by at least one user module, and is awaiting frames from unknown mac addresses to arrive. Limit reached: the port security service is enabled by at least the limit control user module, and that module has indicated that the limit is reached and no more mac ...
Page 191: 5.8 Access Management
Time of addition: shows the date and time when this mac address was first seen on the port. Age/hold: if at least one user module has decided to block this mac address, it will stay in the blocked state until the hold time (measured in seconds) expires. If all user modules have decided to allow this...
Page 192
Parameter description: mode: indicates the access management mode operation. Possible modes are: enabled: enable access management mode operation. Disabled: disable access management mode operation. Delete: delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save. Start ip address: indicates the st...
Page 193: 5.9 Ssh
Parameter description: interface: the interface type through which the remote host can access the switch. Received packets: number of received packets from the interface when access management mode is enabled. Allowed packets: number of allowed packets from the interface when access management mode ...
Page 194: 5.10 Https
Indicates the ssh mode operation. Possible modes are: enabled: enable ssh mode operation. Disabled: disable ssh mode operation. Buttons: save – click to save changes. Reset – click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values. 5.10 https this section shows how to use https ...
Page 195
To configure a authentication method in the web interface: 1. Specify the client (console, telnet, ssh, web) which you want to monitor. 2. Specify the authentication method (none, local, radius, tacacs+) 3. Check fallback. 4. Click apply. Figure 5-11.1: the https configuration parameter description:...
Page 196: 6 Maintenance
6 maintenance this chapter describes all of the switch maintenance configuration tasks to enhance the performance of local network including restart device, firmware upgrade, save/restore, import/export, and diagnostics. 6.1 restart device this section describes how to restart switch for any mainten...
Page 197
To upgrade the firmware via the web interface: 1. Click "browse..." to select the firmware for your device. 2. Click "upload". Figure 6-2.1: the firmware update parameter description: browse: click the “browse...” button to search the firmware url or filename. Upload: click the “upload” button start...
Page 198: 6.3 Save / Restore
Parameter description: activate alternate image: click to use the alternate image. This button may be disabled depending on system state. Cancel: cancel activating the backup image. Navigates away from this page. Image: the flash index name of the firmware image. The name of the primary (preferred) ...
Page 199
Parameter description: buttons: yes – click to reset the configuration to factory defaults. No – click to return to the port state page without resetting the configuration. 6.3.2 save start this section describes how to save the switch start configuration. Web interface to save a start configuration...
Page 200: 6.4 Export / Import
Parameter description: buttons: save – click to save current settings as backup configuration. 6.3.4 restore user this section describes how to restore users information back to the switch. Web interface to restore a user configuration in the web interface: 1. Click "restore user". 2. Click "yes". F...
Page 201
Figure 6-4.1: export configuration parameter description: save – click to store the configuration on the pc or server. 6.4.2 import config this section describes how to import the switch configuration for maintenance needs. Any current configuration file will be imported via xml format. Web interfac...
Page 202: 6.5 Diagnostics
Parameter description: browse: click to search for the configuration url and filename. Upload: click to upload the configuration from the specified location. 6.5 diagnostics this section provides a set for basic system diagnosis. It let users know that whether the system is healthy or needs to be fi...
Page 203
Parameter description: ip address: the ip address of the device to ping. Ping size: the size of the icmp packet being sent. Start: click the “start” button, the switch will start to ping the device using the set icmp packet size. Once you pressed "start", 5 icmp packets are transmitted, and the sequ...
Page 204
The destination ipv6 address ping size: the payload size of the icmp packet. Values range from 8 bytes to 1400 bytes. Start: click the “start” button, the switch will start to ping the device using the set icmpv6 packet size. Once you pressed "start", 5 icmpv6 packets are transmitted, and the sequen...
Page 205
Cable status: port: port number. Pair: the status of the cable pair. Length: the length (in meters) of the cable pair. 205 lancom gs-2310p/gs-2326(p) user manual 6 maintenance.
Page 206
A. Glossary of web-based management a ace ace is an acronym for access control entry. It describes access permission associated with a particular ace id. There are three ace frame types (ethernet type, arp, and ipv4) and two ace actions (permit and deny). The ace also contains many detailed, differe...
Page 207
Using multiple ports in parallel to increase the link speed beyond the limits of a port and to increase the redundancy for higher availability. (also port aggregation, link aggregation). Arp arp is an acronym for address resolution protocol. It is a protocol that used to convert an ip address into a...
Page 208
Dhcp used by networked computers (clients) to obtain ip addresses and other parameters such as the default gateway, subnet mask, and ip addresses of dns servers from a dhcp server. The dhcp server ensures that all ip addresses are unique, for example, no ip address is assigned to a second client whi...
Page 209
Eps eps is an abbreviation for ethernet protection switching defined in itu/t g.8031. Ethernet type ethernet type, or ethertype, is a field in the ethernet mac header, defined by the ethernet networking standard. It is used to indicate which protocol is being transported in an ethernet frame. F ftp ...
Page 210
I icmp icmp is an acronym for internet control message protocol. It is a protocol that generated the error response, diagnostic or routing purposes. Icmp messages generally contain information about routing difficulties or simple exchanges such as time-stamp or echo transactions. Ieee 802.1x ieee 80...
Page 211
Ip source guard is a secure feature used to restrict ip traffic on dhcp snooping untrusted ports by filtering traffic based on the dhcp snooping table or manually configured ip source bindings. It helps prevent ip spoofing attacks when a host tries to spoof and use the ip address of another host. L ...
Page 212
Md5 is an acronym for message-digest algorithm 5. Md5 is a message digest algorithm, used cryptographic hash function with a 128-bit hash value. It was designed by ron rivest in 1991. Md5 is officially defined in rfc 1321 - the md5 message-digest algorithm. Mirroring for debugging network problems o...
Page 213
O oam oam is an acronym for operation administration and maintenance. It is a protocol described in itu-t y.1731 used to implement carrier ethernet functionality. Mep functionality like cc and rdi is based on this optional tlvs. A lldp frame contains multiple tlvs for some tlvs it is configurable if...
Page 214
Pop3 is an acronym for post office protocol version 3. It is a protocol for email clients to retrieve email messages from a mail server. Pop3 is designed to delete mail on the server as soon as the user has downloaded it. However, some implementations allow users or an administrator to specify that ...
Page 215
R rarp rarp is an acronym for reverse address resolution protocol. It is a protocol that is used to obtain an ip address for a given hardware address, such as an ethernet address. Rarp is the complement of arp. Radius radius is an acronym for remote authentication dial in user service. It is a netwo...
Page 216
Service set identifier is a name used to identify the particular 802.11 wireless lans to which a user wants to attach. A client device will receive broadcast messages from all access points within range advertising their ssids, and can choose one to connect to based on pre-configuration, or by displ...
Page 217
Tftp is an acronym for trivial file transfer protocol. It is transfer protocol that uses the user datagram protocol (udp) and provides file writing and reading, but it does not provide directory service and security features. U udp udp is an acronym for user datagram protocol. It is a communications...