- DL manuals
- Lantronix
- Server
- CoBox-FL
- User Manual
Lantronix CoBox-FL User Manual
Summary of CoBox-FL
Page 1
Cobox-fl/cobox-fl-iap user guide part number 900-285 revision e 8/03.
Page 2
Copyright and trademark © 2003, lantronix. All rights reserved. No part of the contents of this book may be transmitted or reproduced in any form or by any means without the written permission of lantronix. Printed in the united states of america. Ethernet is a trademark of xerox corporation. Unix i...
Page 3
Disclaimer and revisions operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference in which case the user, at his or her own expense, will be required to take whatever measures may be required to correct the interference. Attention: this product has been designed to comply wi...
Page 4
Declaration of conformity (according to iso/iec guide 22 and bs 7514) manufacturer’s name & address: lantronix, 15353 barranca parkway, irvine, ca 92618 usa declares that the following product: product name model: cobox-fl/cobox-fl-iap device server conforms to the following standards or other norma...
Page 5
Warranty lantronix warrants each lantronix product to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of one year after the date of shipment. During this period, if a customer is unable to resolve a product problem with lantronix technical support, a return material authorization (rma)...
Page 6
Sales offices the americas 15353 barranca parkway irvine, ca 92618, usa phone: (949) 450-7227 fax: (949) 450-7231 sales@lantronix.Com france 2 rue hélène boucher 78280 guyancourt france tel: +33 1 39 30 41 74 fax: +33 1 39 30 41 73 europesud@lantronix.Com germany karlstrasse 49 78054 vs-schwenningen...
Page 7: Table of Contents
Contents table of contents 1. Introduction...................................................................................................................... 1-1 1.1 cobox-fl ........................................................................................................... 1-1 1.2 cobox-...
Page 8
Contents 2.4.2 assign ip address and network class................................................2-6 2.4.3 test the ip address..............................................................................2-7 2.4.4 add the unit to the manage list ........................................................
Page 9
Contents 3.8 security settings ............................................................................................... 3-24 3.8.1 disable snmp .................................................................................. 3-24 3.8.2 snmp community name.......................................
Page 10
Contents 8.3 setup records......................................................................................................8-7 8.3.1 channel parameters.............................................................................8-8 8.3.2 interface mode .............................................
Page 11: List of Figures
Contents list of figures figure 1 – cobox-fl-iap ..................................................................................................... 1-2 figure 2 - rj-45 connector.................................................................................................... 1-7 figure 3 – cob...
Page 12: List of Tables
Contents list of tables table 1 - ethernet interface signals .......................................................................................1-7 table 2 - cobox-fl led functions.....................................................................................1-9 table 3 - technical specs.....
Page 13
Contents table 38 - disconnect mode options .................................................................................... 9-5 table 39 - flush mode options ............................................................................................. 9-7 table 40 - interface mode options.........
Page 15
Introduction 1 1 . . I i n n t t r r o o d d u u c c t t i i o o n n this manual describes the cobox-fl family of device servers, including the cobox-fl device server and the cobox-fl-iap device server with industrial automation protocols. Most of the material in this manual applies to all of the co...
Page 16
Introduction 1.2 cobox-fl-iap device server note: this section is for the cobox-fl-iap only. The lantronix industrial automation platform (iap) family of device servers allows a single network and protocol to connect multiple serial devices from many vendors. Iap provides the automation industry wit...
Page 17
Introduction a few examples of attached devices are: • plcs • ac/dc drives • cnc systems • operator panels and message displays • process controls • instrumentation • power monitoring equipment • scales and weighing systems • barcode scanners • label printers • most factory floor serial devices 1.2....
Page 18
Introduction 1.3 network protocols note: cobox-fl refers to cobox-fl and cobox-fl-iap except where noted. The cobox-fl uses tcp/ip protocols for network communication. The supported standards are: arp, udp, tcp, icmp, telnet, tftp, dhcp, autoip, and snmp. For transparent connections, tcp/ip (binary ...
Page 19
Introduction 1.4 serial interface the cobox-fl has two serial ports. Ch 1 uses a db-25f (dce) connector and supports rs- 232, rs-422/485. Ch 2 uses a db-9 connector and supports rs-232 only. It supports 10mb/s ethernet through the rj-45 (10base-t) connector or the st-fiber (10base-fl). It can be con...
Page 20
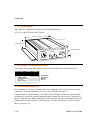
Introduction 1.4.2 channel 2 the cobox-fl channel 2 is a male db-9m supporting rs-232c dte serial interface. 5 dtra (out) txa (out) rxa(in) 1 dcda (in) gnd 9 6 ctsa (in) rtsa (out) 1.5 rj-45 ethernet interface the cobox-fl’s back panel contains a 9-30v ac/dc power plug, four leds, an st-fiber (10bas...
Page 21
Introduction 1.6 rj-45 ethernet connector the next drawing shows a typical rj-45 connector. The color is not standard but very typical patch cable. Pin 1 is located at the top of the connector (orange + white). The connector. Of an ethernet view is from the end of the orange + white orange green + w...
Page 22
Introduction 1 terface .8 serial in cable the cobox-fl can be conn l or ethernet device for setup and configuration. T rs l i -2 db-25 block con ected to a seria he serial device can be -232 or rs-485/422. The following diagram shows a typica nterface cable for the rs 32 serial interface. The uds-m-...
Page 23
Introduction 1.10 serial leds simultaneously lit red and green leds means something is wrong. If the red led is lit or n its pauses. Blink patterns the functions of the three blinking, count the number of times the green led blinks betwee indicate which fault condition exists. The following table ex...
Page 24
Introduction 1.11 dimensions the cobox-fl dimensions are shown in the following drawing. Note: for cobox-fl and cobox-fl-iap. 10 base-t 10 base-fl tx rx tx gl rx co 9-30v ac/dc 6.5 in. (16.51 cm) ) 4.46 in. (11.34 cm 1.39 in. (3.55 cm) removable guard 1.12 product information label the product infor...
Page 25
Introduction 1.14 power requirements the cobox-fl is shipped with a 12vdc, 0.8a, 100-240vac, 50-60hz power supply, but vac/dc and 30v ac/dc can be used. Any power supply between 9 10 base-t 10 base-fl rx tx tx gl 9-30v rx co ac/dc power 9-30v ac/dc cobox-fl user guide 1-11.
Page 26
Introduction 1.15 technical specifications table 3 - technical specs category description cpu, memory amd 188es cpu, 20mhz clo ck, 128kbyte ram flash, eprom 512kbyte flash prom installable serial protocols standard tunnel (cobox-f fl-iap), df1 (cobox-fl-iap) l, and cobox-fl-iap), modbus (cobox- seri...
Page 27
Getting started 2 2 . . G g e e t t t t i i n n g g s s t t a a r r t t e e d d this section describes all the procedures for configuring your unit. For a short version, see the quick start guide. Go to the lantronix web site for the latest firmware and release notes. Cobox-fl comes with standard tu...
Page 28
Getting started 2.1.3 port number every tcp connection and every udp datagram is defined by a destination ip address and a port number. For example, a telnet application commonly uses port number 23. A port number is similar to an extension on a pbx system. The unit 's serial channel (port) can be a...
Page 29
Getting started 2.3 methods of assigning the ip address the unit's ip address must be configured before a network connection is available. You have the following options for assigning an ip to your unit: method description dhcp a dhcp server automatically assigns the ip address and network settings....
Page 30
Getting started 2.3.1 dhcp the unit ships with a default ip address of 0.0.0.0, which automatically enables dhcp. Provided a dhcp server exists on the network, it will assign the unit an ip address, gateway address, and subnet mask when the unit boots up. The cobox-fl has acquired an ip address if t...
Page 31
Getting started 2.4 deviceinstaller you can manually assign the ip address using deviceinstaller software, which is found on the product cd. If you want to use a serial connection instead of an ethernet connection to configure the device, go to serial port login on page 2-12. 2.4.1 install deviceins...
Page 32
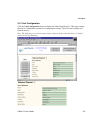
Getting started 2.4.2 assign ip address and network class click the start button on the task bar and select programs \device installer \device installer. The device installer window displays. Figure 5 - deviceinstaller window 1. Click the ip icon . T ys. He assign ip address window displa figure...
Page 33
Getting started 3. In the enter ip address to assign field, enter the unit’s ip address in s 6. At the “assign ip successful” message displays and click ok. 7. Click the back button to return to the deviceinstaller window. Xxx.Xxx.Xxx.Xxx format. 4. In the pc network class section, select the class ...
Page 34
Getting started 2.4.4 add the unit to the manage list now add the unit to the list of similar lantronix devices on the network so that you can manage and configure it. 1. Click the search the network for devices icon. T displays. He search network window ss. Class c is the default. Ic 4. Clic 5. Cli...
Page 35
Getting started 6. Click the back button to re window now lists all of the turn to the deviceinstaller window. The deviceinstaller devices in the group, including the unit you are setting up. The hardware address and firmware release number for the unit display. Ure 9 - devices in a group you can ma...
Page 36
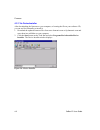
Getting started 2.4.5 opening a configuration window 1. Click the manage icon . The device management window displays. Figure 10 - device management window 2. Do one of the following: note: to assign expert settings and security settings, you must use the setup mode window in a telnet session. • to ...
Page 37
Getting started 2.5 arp and telnet the unit’s ip address must be configured before a network connection is available. You are inten n the product en hardware the ip address must be a host other than the machine on which you are working. Once there is at least llowing command to arp an ip address tel...
Page 38
Getting started 2.6 serial port login if you want to initially configure the unit through a serial connection, follow these steps: , to d down the x key at the terminal (or n. To 0. 1. Connect a console terminal or pc running a terminal emulation program to your unit's serial port. The default seria...
Page 39
Configure 3 3 . . C c o o n n f f i i g g u u r r i i n n g g t t h h e e u u n n i i t t ur • use a standard web browser to access the unit’s internal web pages and configure the unit over the network. This is the easiest and preferred method. • use a telnet connection to configure the unit over th...
Page 40
Configure 3.2 using deviceinstaller deviceinstaller is a powerful software utility for configuring device servers from a network connection. This section uses the utility to demonstrate the various methods of configuring device. The devic a e management window is a common page for gaining access to ...
Page 41
Configure 6. For telnet configuration, click the telnet to device icon. A small telnet to device window appears, showing the ip address and the port address. The main lantronix r window opens. Go to using a telnet connection on page 3-10 for a summary of the menu selections. Guration on page 3-26. I...
Page 42
Configure 3.3 web manager page note: the cobox-fl-iap may not have a web page or may use a different format web page. You can start a web browser for configuration by opening your java enabled web browser and entering the ip address or by clicking the web configuration management window. The lantron...
Page 43
Configure 3.3.1 unit configuration click the unit configuration button to display the following dialog box. This page contain the server configuration and the port configuration settings. These are static settings read from the device. Note: the following screen shots represent the web page shown wh...
Page 44
Configure 3.3.2 server properties you can change the server properties by editing any of the fields. Lingering over one of the fields w s will require you to enter the new ip ill display operator messages. Changing the ip addres address in the browser to reload the page. Fig re te net password u l m...
Page 45
Configure 3.3.3 port properties serial protocol: rs232, rs422/485 4-wire, rs485 2-wire speed: 1 , 57600, 115200 character si parity: n stop bi flow co acters to host, cts/rts (hardw 200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400 ze: 8, 7 one, even, odd t: 1,2 ntrol: none, xon/xoff, xon/xoff pass char are) udp ...
Page 46
Configure on active connection: enable, disable on passive connection: enable, disable at time of disconnect: enable, disable packing algorithm: enable, disable idle time: force transmit 12 ms, force transmit 52 ms, force transmit 250 ms, force transmit 5000 ms trailing characters: none, one, two se...
Page 47
Configure disconnect mode: with dtr drop, ignore dtr c to na p ble t et mode: enable, d le inactivity timeout: enable, disable inactivity timer: (user port password: (user selectable. Port password must be enabled) de dir ons. You can use the tech s ink dire ntronix tech support web page, the ftp-si...
Page 48
Configure 3.4 configuring via the setup mode window 3.4.1 using a telnet connection to configure the unit over the network, establish a telnet connection to port 9999. Note:if you use the telnet to device icon on the device installer device management gin to establish the connection, skip steps 1and...
Page 49
Configure *** basic parameters hardware: ethernet autodetect ip addr – 0.0.0.0/dhcp/bootp/autoip, no gateway set dhcp device name : not set ***************** snmp is snmp community telnet setup is tfpt download is port 77feh is enabled web server is enabled enhanced password is ***************** cha...
Page 50
Configure 3.4.2 using the serial port if you want to initially configure the unit through a serial connection, follow these steps: r pc running a emulation prog your unit's ttings a , 8 bits, no , 1 stop bit, no e nd back on ter power-up, nostic l nking. You have one second to minal (or up the unit....
Page 51
Configure 3.5.3 netmask: number of bits for host part host host bits to be entered, then calculates the netmask, which al-dot notation hen e s d p me are disp ed (for twork netmasks a netmask defines the number of bits taken from the ip address that are assigned for the section. Note: class a: 24 bi...
Page 52
Configure 3.5.4 change telnet configuration password s g ia a ion to po a ssword s a note: no password is required to access the setup mode window via a serial connection. Ese products. To cxxxxxx (xxxxxx is the last 6 digits of the e. You can create your own dhcp name on these products. If you are ...
Page 53
Configure 3.6 channel 1 co ion (serial port parameters) nfigurat using this option, defin communications . E baudrate (960 de (4c) flow (00) no (1000 ctmode ( remote ip add remote port ( disconnmode ( mode ( nntime ( sendchar 1 ( sendchar 2 ( 3.6.1 baudrate the unit and attached se use for the seria...
Page 54
Configure the following table demonstrates how to build som table 7 - common interface mod e common interface mode settings: e settings common i/f mode setting binary hex rs-232c, 8-bit, no parity, 1 stop bit (1) 0100 1100 4c rs-232c, 7-bit, even parity, 1 stop bit (1) 0111 1000 78 rs-485 2-wire, 8-...
Page 55
Configure 3.6.5 connect mode connect mode defines how the unit makes a connection, and how it reacts to incoming connections over the network. Enter connect mode options in hexadecimal notation. Note:see table 35 - binary to hexadecimal conversion table. Table 9 - connect mode options connect mode o...
Page 56
Configure table 10 - manual connection address example command string result if remote ip is 129.1.2.3 and remote port is 1234 c121.2.4.5/1 complete override; connection is started with host 121.2.4.5, port 1 c5 connect to 129.1.2.5, port 1234 c28.10/12 connect to 129.1.28.10, port 12 autostart (aut...
Page 57
Configure table 11 - modem mode commands modem mode command function atdtx.X.X.X,pppp or atdtx.X.X.X/pppp makes a connection to an ip address (x.X.X.X) and a remote port number (pppp). Atdtx.X.X.X makes a connection to an ip address (x.X.X.X) and the remot number def e port ined within the unit. Atd...
Page 58
Configure 3.6.6 remote ip address the rem . This parameter defines the port pted. Note: t poses, use the rd port number for telnet services). Table 12 - disconnect mode options this is the destination ip address used with an outgoing connection. 3.6.7 remote port ote tcp port number must be set for ...
Page 59
Configure 3.6.9 flush mode (buffer flushing) ion nary to hexadecimal conversion table. Using this parameter, you can control line handling and network buffers with connect startup and disconnect. You can also select between two different packing algorithms. Note:see table 35 - bi table 13 - flush mo...
Page 60
Configure 3.6.10 pack control two firmware-selectable packing algorithms define how and when packets are sent to the network. The standard algorithm is optimized for applications in which the unit is used in a local environment, allowing for very small delays for single characters while keeping the ...
Page 61
Configure send characters: if 2-byte send character sequence is enabled, the unit interprets the dently. Dy in the serial buffer are included in the transmission after a "transmit" condition is found. If set, the unit sends ransmit condition (sendchar or timeout). Sent the line (for example, etx, eo...
Page 62
Configure 3.7 expert settings note:you can change these settings via telnet or serial connections only, not on the web- manager. Note: the expert settings option does not appear with cobox-fl-iap. These parameters should only be changed if you are an expert disable): (0) e in s this option allows yo...
Page 63
Configure 3.8.3 disable telnet setup this setting defaults to the n (no) option. The y (yes) option disables access to this configuration menu by telnet (port 9999). It only allows access via the web pages and the serial port of the unit. 3.8.4 disable tftp firmware upgrade this setting defaults to ...
Page 64
Configure 3.10 exit configuration mode select 8 to exit the configuration mode without saving any changes or rebooting. Select 9 to ry. On save all changes and reboot the device. All values are stored in nonvolatile memo 3.11 get configurati the device configuration information is stored in flash me...
Page 65
Configure 3.12 set configuration devic can be saved in a file and later used to set the configuration the set ion button on the device management window. The following dialog appears. E of one or several devices. To set the configuration of a device from a saved file, click configurat configuration ...
Page 67
Firmware 4 4 . . U u p p d d a a t t i i n n g g p p r r o o t t o o c c o o l l ( ( f f i i r r m m w w a a r r e e ) ) 4.1 protocol firmware you can update the unit's internal operational code to a newer revision, or change the code to s d on the software cd. Ocol firmware and release notes for th...
Page 68
Firmware 4.2.1 via deviceinstaller after downloading the firmware to your computer, or locating the file on your software cd, you can use deviceinstaller to install it. 1. Download the updated firmware files from www.Lantronix.Com or ftp.Lantronix.Com and . Ler window displays. Store them in a subfo...
Page 69
Firmware 3. Click the search the network for devices icon . The search network window displays. Fig indow 4. All active units on the local network displays. 5. 6. Roup, including the unit you are updating. Ure 15 - search network w click the start search button. A list of click the save button. A co...
Page 70
Firmware 8. Select the desired unit and click the upgrade firmware file (.Rom) icon . The upgrade firmware window displays. Figure 17 - upgrade firmware 9. In the existing firmware list box, select the firmware t this selection must match the firmware file t will be displayed. 10. In the source fw f...
Page 71
Firmware 4. In the destination file field, enter the current al operational code or web5 for -iap, aq = standard tunnel, am = modbus, dard tunnel) field, enter the ip address of the unit being upgraded. R the file to the unit. Intern the internal web interface. (for cobox-fl ad = df1. For cobox-fl, ...
Page 72
Firmware 4.2.4 via the serial port the llo the x the software cd and on the web site. Om code to hex for application, r2h.Exe that can be used to convert the rom file to hex format. The r2h.Exe application is available at ftp://ftp.Lantronix.Com/pub. Put h ectory on a pc then open a dos window to t ...
Page 73
Devicecomm manager 5 5 . . D d e e v v i i c c e e c c o o m m m m lantronix devicecomm manager is a windows based com port redirector software utility. Its function is to redirect custo d fo the pc’s network port. Rather serial e tcp/ip protocol. Th nd ria is se he r. The en pre r om m m a a n n a ...
Page 74
Devicecomm manager 5.1 installing device manager comm the devicecomm manager software is included on the produ from the lantronix web site. Om into drive. The cd w. N button on the task bar and select run your cd drive letter, colon, backslash, devicec d:\devicecomm.Exe). Ct cd or it can be download...
Page 75
Devicecomm manager 5.1.2 setup evicecomm manager” icon 1. Open control panel. 2. Double click on the “d . Status meaning disabled unused port on your system n/a port being used by other hardware / software on your system idl an ip address and port number have been associated with the com port e co t...
Page 76
Devicecomm manager 6. Enter the port number of the target device server in the “port:” section. Click ok when ****please because this is a raw mode redirector: s and you c ets nd scs produ note: you will be re reboot your s ant to set them all up at rebo 7. Click the settings button for advanced not...
Page 77
Troubleshooting 6 6 . . T t r r o o u u b b l l e e s s h h o o o o t t i i n n g g 6.1 technical support this chapter discusses how you can diagnose and fix errors quickly without having to contact a dealer or lantronix. It helps to connect a terminal to the serial port while diagnosing an error to...
Page 78
Troubleshooting when you report a problem, please provide the following information: • your name, and y ad • lantronix model n • lantronix serial n r • software version ho 9999) • description of the problem • debug report (sta ble • status of the unit u ed (please try to include information on user ...
Page 79
Troubleshooting problem/message reason solution the ip address you are trying to confirm that your pc has an ip e assign is not on your logical subnet. Address and that it is in the sam logical subnet that you are trying to assign to the uds/cobox. The uds/cobox may not be make sure that the link le...
Page 80
Troubleshooting problem/message reason solution sequence that tells you this). If you do no the serial t get a response, use port to verify that telnet is not disabled. Wit device installer you get “wrong password” error you have chosen the incorrect setting for the existing try upgrading the firmwa...
Page 81
Monitor mode 7 7 . . M m o o n n i i t t o o r r m m o o d d e e 7.1 monitor mode mo interface used for diagnostic purposes (see table 17 - via the serial the setup mode window on page 3-10. Tor mode with network connections. Mode without network connections. Rial number 1400280 mac address 00:20:4a...
Page 82
Monitor mode table 17 - monitor mode commands command command name function dl download download firmware to the device server via the serial port in hex format sf x.X.X.X send firmware send firmware to device server with ip address x.X.X.X vs x.X.X.X version query software header record (16 bytes) ...
Page 83
Udp 8 8 . . N n e e t t w w o o r r k k c c o o n n f f i i g g u u r r a a t t i i o o n n u u s s i i n n g g u u d d p p 8.1 udp datagrams the device server can also be configured or queried over the network using udp datagrams. T udp listener set for port 30718 (77fe hex). Responses from the d e...
Page 84
Udp byte command parameters notes ip-setup (hex 49 50 2d 53 45 54 55 provides one method to of the device server if is 50). Next 2 bytes have to be set to 00. Ext 2 bytes must e serial set the ip address on the local network and the serial number is known. Remember, broadcasts are only ‘heard’ on th...
Page 85
Udp 8.2 configuring multiple devices when configuring a number of device servers identically, it is useful to create a template setup record. The setup record can then be sent to the “target” device servers from a paste” or udp (see network configuration using udp on page 8- device servers use a 120...
Page 86
Udp to request the setup record of a properly configured device server via another device server ort enabled) on the unit that is not properly ode on page 7-1) 7 the co llowed by a carriage return, where x.X.X.X is the ip ess of the properly configured device. The properly configured device will res...
Page 87
Udp to send a setup record via monitor mode: another device server (the “target”) on the network. Ork support enabled) on the master device server (see the ip address he et, d a rria ret . To the target device server. Hyperterminal, co the tup record and select “paste to host” to he device server re...
Page 88
Udp to get and set the node configuration, 120 bytes should be exchanged at once in 32-byte a k e r th t in t e li . S ce e ch cks m is a two-digit h rese v lue from to 55. T by summin h val e d ta o the line and taking the two’s c the sum. N ng lon r t ch s e r ta a b tored at 0030, 0031, and 0032)...
Page 89
Udp 8.3 setup records a setup record consists of 120 bytes. They are transmitted at once from and to the node. Unused bytes should be initialized as 00. Table 21 - setup record construction defines the structure of a setup record: table 21 - setup record construction byte(s) function 00-03 ip addres...
Page 90
Udp 8.3.1 channel parameters use the following table to select setup record parameters for channels 1: table 22 - channel parameters byte(s) (channel 1) function 16 interface mode (see table 23 - interface mode options ) 17 line speed bits 7-5: reserved bits 4-0: baud rate (see table 25 - baud rate ...
Page 91
Udp 8.3.2 interface mode the interface (i/f) mode is a bit-coded byte entered in hexadecimal notation. Use the following table to select interface mode settings: table 23 - interface mode options i/f mode option 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 rs-232c (1) 0 0 rs-422/485 (1) 0 1 rs-485 2-wire (1) 1 1 7 bit 1 0 8 bit...
Page 92
Udp 8.3.3 baud rate the device server and attached serial device must agree on a speed or baud rate to use for o use the following table to select baud rate settings: settings the serial connecti n. Table 25 - baud rate speed (bps) hex 38400 00 19200 01 9600 02 4800 03 2400 04 1200 05 600 06 300 07 ...
Page 93
Udp 8.3.5 connect mode tion, and how it reacts to incoming connections over the network. Use the following tabl connect mode defines how the device server makes a connec e to select connect mode options: table 27 - connect mode options connect mode option 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 incoming connection never ac...
Page 94
Udp 8.3.6 disconnect mode i nect mo drop onn is red. Use the following t disconnect mode options: table 28 - discon op n discon able to select de, dtr either drops the c ection or igno nect mode tions disconnect m ode option 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 disconnect with ) dtr drop (6 1 ignore dtr 0 telnet mode an...
Page 95
Udp 8 sh mo ffer using this parame ne handling and network buffers with connection s on an ct between two different packing algorithms. Use the following table to select flush mode options: table 29 - flush ns .3.7 flu de (bu ter, you can control li c flushing) tartup and disc nect. You also sele mo...
Page 96
Udp 8.4 ip addresses each tcp/ip node on a network host has a unique ip address. This address provides the i de ard p the local ne nd ss multiple networks if n or example, address to use tcp/ip network i in th f information: the network, the subnet, and the host. 8.4.1 network por the network portio...
Page 97
Udp a router is required between all networks and all sub-networks. Generally, hosts can send network. All packets destined for other . T ort ddr ique g if 8.4.4 netw rk address a host address with all host bits set to 0 addre netw k as a whol ample, routing entries). 192.168.0.0 8 4.5 broa a host a...
Page 98
Udp table 34 - netmask examples netmask host bits 2 5.255.255. 5 252 2 255.255.255. 248 3 255.255.255. 240 4 255.255.255. 224 5 2 255. 55.255. 192 6 2 255. 8 7 55.255. 12 2 255. 8 55.255. 0 2 254. 9 55.255. 0 2 52. 0 55.255.2 0 1 2 48. 1 55.255.2 0 1 ... ... 2 .0 3 55.128.0 2 255.0.0.0 24 8.4.6 priv...
Page 99
Binary to hex 9 9 . . B b i i n n a a r r y y t t o o h h e e x x c c o o n n v v e e r r s s i i o o n n many of the device server’s configuration procedures require you to assemble a series of o as bits ommand ed byte). The resulting b e conv e h r nted as 0-9, a (for 10), b o convert binary value...
Page 100
Binary to hex table 36 - connect mode options accept incoming connections serial response upon connection active connection startup hostlist hex never none (quiet rtup n/a ) no active sta never none (quiet) any character 1 never none (quiet 2 ) active dtr never none (quiet 3 ) cr (0x0d) never none (...
Page 101
Binary to hex accept incoming connections serial response upon connection active connection startup hostlist hex unconditionally character d5 autostart unconditionally character dc udp never none (quiet p hostlist n/a ) no active startu never none (quiet) any character hostlist 21 never none (quiet ...
Page 102
Binary to hex accept incoming connections serial response upon connection active connection startup hostlist hex unconditionally character rt h f5 autosta ostlist unconditionally character udp h n/a ostlist t nnect mo re for when you em lation: ct mode options for modem emulation he following co de ...
Page 103
Binary to hex 9.2 discon ect mode options n t ect mo able 38 - disconn de options disconnect with dtr drop (note) telnet mode and terminal type setup channel (port) password hard disconne ct state led off with connection disconnect with eot (^d) hex enable 0 enable enable 10 enable enable 20 enable ...
Page 104
Binary to hex disconnect with dtr drop (note) telnet mode and terminal type setup channel (port) password hard disconnect state led off with connection disconnect with eot (^d) hex disable 48 enable enable disable 58 enable enable disable enable 68 enable disable enable 78 enable enable disable 88 e...
Page 105
Binary to hex 9.3 flush mode (buffer flushing) options table 39 - flush mode options serial to network clear input buffer upon: network ri to se al clear output bu upon: ffer alternate packing algorithm hex none 0 active connection 10 passive connection 20 active connection nnection 30 passive co di...
Page 106
Binary to hex serial to network clear input buffer upon: network to serial clear output buffer upon: alternate packing algorithm hex active connection active connection enable 91 passive connection activ enable a1 e connection active connection passive connection tion able b1 active connec en discon...
Page 107
Binary to hex serial to network clear input buffer upon: netw a ork to seri l clea f n: r output buf er upo alternate packing algorithm hex disconnect active connection passive connection 43 active connection disconnect active connection passive connection 53 passive connection active connection pas...
Page 108
Binary to hex serial to network clear input buffer upon: network to serial clear output buffer upon: alternate packing algorithm hex active connection disconnect disconnect enable d4 passive connection disconnect disconnect enable e4 active connection passive connection disconnect disconnect enable ...
Page 109
Binary to hex serial to network clear input buffer upon: network to serial clear output buffer upon: alternate packing algorithm hex active connection passive connecti passive connection disconnect on 36 disconnect passive connection disconnect 46 active c passive connection 56 onnection disconnect ...
Page 110
Binary to hex serial to network clear input buffer upon: network to serial clear output buffer upon: alternate packing algorithm hex passive connection disconnect active connection pas 67 sive connection disconnect active connection passive connection disconnect active connectio passive conn disconn...
Page 111
Binary to hex 9.4 interface mode options table 40 - interface mode options interface bits parity stop bits hex rs-232c 7 no 1 48 rs-232c 7 no 2 c8 rs-232c 7 even 1 78 rs-232c 7 even 2 f8 rs-232c 7 odd 1 58 rs-232c 7 odd 2 d8 rs-232c 8 no 1 4c rs-232c 8 no 2 cc rs-232c 8 even 1 7c rs-232c 8 even 2 fc...
Page 112
Binary to hex 9.5 pack control options table 41 - pack control options sendcharacter defined by a: trailing characters idle time force transmit: send immediately after sendcharacter hex 1-byte sequence no 12ms 0 1-byte sequence no 52ms 1 1-byte sequence no 250ms 2 1-byte sequence no 5sec 3 1-byte se...
Page 113
Binary to hex sendcharacter defined by a: trailing characters idle time force transmit: send immediately after sendcharacter hex 2-byte sequence no 250ms yes 32 2-byte sequence no 5sec yes 33 2-byte sequence 1 12ms yes 34 2-byte sequence 1 52ms yes 35 2-byte sequence 1 250ms yes 36 2-byte sequence 1...
Page 115
Binary to hex 1 1 0 0 . . I i p p a a d d d d r r e e s s s s e e s s an ip address is a 32-bit value, divided into four octets of eight bits each. The standard al numbers (in the range of 0..255) divided by dots. Ess is divided in two parts: network and host. To support different needs, three repre...
Page 116
Binary to hex 10.4 network address the host address with all host bits set to 0 is used to address the network as a whole (in routing entries, for example). 10.5 broadcast address the address with the host part bits set to 1 is the broadcast address, meaning for every station. Roadcast addresses mus...
Page 117
Binary to hex 10.7 private ip networks and the internet if your network is not connected to the internet, and there are no plans to make such a connection, you may use any ip address you wish. Et and you have plans to connect, or you are ant to operate your cobox-fls on an intranet, use one of the r...
Page 119
Glossary of terms 1 1 1 1 . . G g l l o o s s s s a a r r y y address space a linear array of locations that a thread can access. Simple processors have only one, and these are referred to as `linear' addressing. Native to dhcp that allows hosts to automatically obtain an ip address in smaller y not...
Page 120
Glossary of terms baseband lan: g and arcnet lans use baseband transmission. Ore than one bit. Baud equals bits per second only when the signal represents a single bit. Er system es and zeros. Es the value of either 1 block variable-size piece of memory that a task can acquire. Blocks are allocated ...
Page 121
Glossary of terms broadband: a data transmission technique allowing multiple high-speed signals to share the bandwidth of a single cable via frequency division multiplexing. Twork: orks may coexist on a single cable without interfering with one another. A lan topology in which all the nodes are conn...
Page 122
Glossary of terms communication server: cut-through: e for examining incoming packets whereby an ethernet switch looks only at the first few t it also allows some bad packets to be forwarded. Carrier sense multiple access with collision detection is the ethernet media access method. All network devi...
Page 123
Glossary of terms dialback: a security feature that ensures people do not log into modems that they shouldn't have access to. When a connection is requested, the system checks the user name for validity, then "dials back" the number h that user name. A system in which each computer or node in the ne...
Page 124
Glossary of terms filtering: out any loss of incoming packets or delay in processing. Torage, e.G., some type of read-only or flash reprogrammable memory. Device to framing: data for transmission into groups of bits, and adding a header and a check sequence to form a file transfer protocol, a tcp/ip...
Page 125
Glossary of terms heartbeat: a frequency unit equal to one cycle per second. Host: etwork that can be used interactively, i.E., logged into, like a computer. Host table: a list of tcp/ip hosts on the network along with their ip addresses. Re formatted and transmitted, and what actions web servers an...
Page 126
Glossary of terms ipx: internetwork packet exchange, a netware protocol similar to ip (internet protocol). Isdn: (integrated 144k bps o services digital network): all digital service provided by telephone companies. Provides ver a single phone line (divided in two 64k bps "b" channels and one 16k bp...
Page 127
Glossary of terms layer: in networks, layers refer to software protocol levels comprising the architecture, with each layer performing functions for the layers above it. Line speed: expresse hardware d in bps, the maximum rate at which data can reliably be transmitted over a line using given . Local...
Page 128
Glossary of terms modem: a modulator-demodulator device for changing transmission signals from digital to analog for transmission over phone lines. Used in pairs, one is required at each end of the line. Communications between hosts and servers. A host. P: the ability of a dialup device to allocate ...
Page 129
Glossary of terms netbios/netbeui: microsoft's networking protocols for it's lan manager and windows nt products. Network: an interconnected system of computers that can communicate with each other and share files, da resources. Ta and k address: every node on a network has one or more addresses ass...
Page 130
Glossary of terms 11-12 cobox-fl user guide pap: (password authentication protocol) authentication scheme for ppp links. A password can be specified for both devices on a remote link. Failure to authenticate will result in a dropped connection prior to start of data transmission. Physical address: a...
Page 131
Glossary of terms cobox-fl user guide 11-13 protocol: any standard method of communicating over a network. Remote access: access to network resources not located on the same physical ethernet. (physical ethernet here refers to an entire site network topology.) remote control: form of remote access w...
Page 132
Glossary of terms 11-14 cobox-fl user guide router: device capable of filtering/forwarding packets based upon data link layer information. Whereas a bridge or switch may only read mac layer addresses to filter, routers are able to read data such as ip addresses and route accordingly. Rtel: lantronix...
Page 133
Glossary of terms cobox-fl user guide 11-15 store and forward: technique for examining incoming packets on an ethernet switch or bridge whereby the whole packet is read before forwarding or filtering takes place. Store and forward is a slightly slower process than cut-through, but it does ensure tha...
Page 134
Glossary of terms 11-16 cobox-fl user guide terminal server: a concentrator that facilitates communication between hosts and terminals. Terminator: used on both ends of a standard ethernet or thinwire ethernet segment, this special connector provides the 50 ohm termination resistance needed for the ...
Page 135
Glossary of terms cobox-fl user guide 11-17 twisted-pair cable: inexpensive, multiple-conductor cable comprised of one or more pairs of 18 to 24 gauge copper strands. The strands are twisted to improve protection against electromagnetic and radio frequency interference. The cable, which may be eithe...