- DL manuals
- Lantronix
- Server
- MSS4-D
- Installation Manual
Lantronix MSS4-D Installation Manual
Summary of MSS4-D
Page 1
Mss installation guide for mss4 device servers.
Page 2
The information in this guide may change without notice. The manufacturer assumes no responsibility for any errors which may appear in this guide. Ethernet is a trademark of xerox corporation. Unix is a registered trademark of the open group. Windows 95, windows 98, windows 2000, and windows nt are ...
Page 3: Contents
I contents 1: introduction.......................................................................... 1-1 1.1 model overview .............................................................................. 1-1 1.2 mss features................................................................................
Page 4
Ii 4: configuration ....................................................................... 4-1 4.1 rebooting the mss.......................................................................... 4-1 4.1.1 normal reboot ................................................................ 4-1 4.1.2 factory d...
Page 5
Iii 4.7 modem cards ................................................................................ 4-22 4.7.1 incoming calls............................................................... 4-23 4.7.2 outgoing calls............................................................... 4-23 5: using the mss...
Page 6: Warranty Statement
Iv c: pinouts ................................................................................ C-1 c.1 ethernet connectors ....................................................................... C-1 c.1.1 fiber link ethernet ....................................................... C-1 c.2 mss4 serial...
Page 7: 1: Introduction
1- 1 1: introduction the lantronix mss family of device servers allows you to network-enable a variety of serial devices that were not originally designed to be networked: personal computers, terminals, modems, industrial machinery, and more. This capability brings the advantages of remote managemen...
Page 8: 1.2 Mss Features
Mss features introduction 1- 2 1.2 mss features ◆ tcp/ip and unix compatibility the mss supports a variety of tcp/ip features, including telnet, rlogin, udp, dns, snmp, wins, ftp, dhcp, bootp, rarp, and http. ◆ connectivity the mss can connect serial devices directly to a 10/100base-t or 100base-fx ...
Page 9: 1.3 Tcp/ip Support
Introduction tcp/ip support 1- 3 ◆ security the mss includes several configurable security features: ❍ automatic session logouts when a port is disconnected or a device is turned off. ❍ password protection for privileges, ports, services, maintenance commands, and the remote console. ❍ an ip securit...
Page 10: 1.4 Terms
Terms introduction 1- 4 1.4 terms the following terms are used throughout this manual. Host a computer attached to the network. The term host is generally used to denote interactive computers, or computers that people can log into. Local mode the mss user interface. It is used to issue configuration...
Page 11: 2: Installation
2- 1 2: installation this chapter covers the physical installation of the mss in a wired or wireless ethernet network. If you are installing the mss for the first time, you must either attach a terminal to one of the serial ports or connect the mss to a wired ethernet network so you can configure th...
Page 12
Mss4 components installation 2- 2 2.1.1 mss4-d/dfp front panel the mss4-d and mss4-dfp front panels have four db9 serial port connectors and an rj45 ethernet connector. The mss4-dfp also has a 100base-fx fiber link ethernet connector. Figure 2-1: mss4-d/dfp front panel 2.1.2 mss4-s/sfp front panel t...
Page 13: 2.1.3 Mss4 Side Panel
Installation mss4 components 2- 3 2.1.3 mss4 side panel all models include a reset button, and two power connectors. The mss4-dfp and -sfp side panels also have two pc card slots. The following figure shows an mss side panel. Figure 2-3: mss side panel 2.1.4 mss4 leds leds are located on the front p...
Page 14
Mss4 components installation 2-4 the pcc1 and pcc2 leds, which correspond to the top and bottom pc card slot respectively, vary in meaning depending on what kind of card is currently installed. Note: although a red led during boot mode usually signals an error, red led patterns are part of the norma...
Page 15
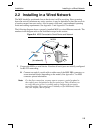
Installation installing in a wired network 2-5 2.2 installing in a wired network the mss should be positioned close to the device it will be servicing. Since powering down the unit will terminate any active sessions, it may be desirable to place the server in a location secure from user access. Also...
Page 16
Installing in a wired network installation 2- 6 when using a screw terminal block, you may have to connect from 2 to 6 wires depending upon the desired mss usage mode. Do not over-tighten the screws, but make sure the wire is secure in the block. Figure 2-5: connecting wire to screw terminal blocks ...
Page 17: 2.3 Installing Pc Cards
Installation installing pc cards 2-7 ❍ the mss tries to obtain tcp/ip configuration information via dhcp, bootp, and/or rarp. This procedure takes approximately 40 seconds if no hosts answer the request, and boot messages will be sent to the console port. The ok led will blink green approximately th...
Page 18
Installing pc cards installation 2-8 the following diagram shows a properly-installed mss in a wireless ethernet network. Be sure to read your pc card manual for specific placement and distance requirements. Figure 2-6: mss connected to serial device and wireless network follow these steps to proper...
Page 19
Installation installing pc cards 2-9 ❍ if a pc card led is a solid green, the ata card in the corresponding slot is ready for use. ❍ if a pc card led blinks green, the ata card in the corresponding slot must be formatted before it can be used. Proceed to formatting an ata flash card on page 4-22 for...
Page 21: 3: Getting Started
3-1 3: getting started this chapter covers all of the steps needed to get the mss on-line and working. There are three basic methods you can use to log into the mss and begin configuration: ◆ incoming (remote) logins: ezwebcon is the preferred method for initial mss configuration. Users can also use...
Page 22: 3.1.1 Privileged Password
System passwords getting started 3-2 3.1.1 privileged password only the privileged user can change server or port settings. To become the privileged user, enter the set privileged command, followed by the privileged password. The default privileged password is system. Figure 3-1: set privileged comm...
Page 23: 3.2.1 Using Ezwebcon
Getting started ip address configuration 3-3 3.1.2.1 serial port logins to require a password for any connections to the mss from its serial ports, enable password protection with the change password protect enabled command. The command allows you to specify the serial ports for which you want to pr...
Page 24: 3.2.2 Using Arp and Ping
Ip address configuration getting started 3-4 3 enter or change the ip-related settings: a for ethernet address, enter the number that appears on the bottom label of your mss. B for ip address, enter the desired ip address to use for this mss. C for subnet mask, change the values provided only if you...
Page 25
Getting started ip address configuration 3-5 when the mss receives the ping packet, it will notice that its ip address is not set and will send out broadcasts to see if another node is using the specified address. If no duplicate is found, the server will use the ip address and will respond to the p...
Page 26: 3.3 Incoming Logins
Incoming logins getting started 3-6 if the mss encounters an ethernet network problem while booting it will send an alert message to the console and wait ten seconds to detect serial port activity before attempting to finish booting. If you press the return key when the error message is displayed, y...
Page 27: 3.3.1.3 Telnet
Getting started incoming logins 3-7 once you have connected to the mss, you will see the lantronix thinweb manager interface. Use the left-hand menu to navigate to subpages where you can configure important settings and view statistics and other server information. Figure 3-12: thinweb manager inter...
Page 28: 3.3.2 Serial Port Logins
Incoming logins getting started 3-8 3.3.2 serial port logins attach a terminal to one of the serial ports and press the return key. The local> prompt should be displayed. Proceed to the configuration chapter to configure the unit using the command line interface. If there was a problem during the bo...
Page 29: 3.4 Outbound Connections
Getting started outbound connections 3-9 3.4 outbound connections when logged into the mss, users can make basic outgoing connections using the methods described in this section. See the mss reference manual on the cd-rom for more information about incoming and outgoing connections. Note: if you tel...
Page 31: 4: Configuration
4-1 4: configuration certain parameters must be configured before the mss can function in the network. Although many users will prefer to use either ezwebcon or the web browser interface, this chapter explains how to configure more advanced mss features via the command line interface. The command li...
Page 32: 4.1.2 Factory Defaults
Tcp/ip configuration configuration 4-2 to reboot the mss, perform one of the following: ◆ at the local> prompt, enter the initialize delay 0 command. ◆ at the boot> prompt, enter the initialize 451 command. See entering commands at the boot prompt on page b-4 for more details. ◆ remove the power cor...
Page 33: 4.2.3 Gateway
Configuration tcp/ip configuration 4-3 when you configure the mss ip address for the first time, a default subnet mask will be configured automatically. This default subnet mask should work for most networks. If your network is divided into subnetworks, you will need to create a custom subnet mask. ...
Page 34: 4.2.5 Ip Security
Tcp/ip configuration configuration 4-4 the mss also allows you to set a default domain name to be appended to any host name for the purpose of name resolution. When a user types a host name, the mss will add this domain name and attempt the connection. Name checking applies to any mss commands that ...
Page 35: 4.2.6 Wins
Configuration tcp/ip configuration 4-5 4.2.6 wins if wins is enabled, the mss will broadcast a wins name announcement at boot time, and answer broadcast wins name queries. Other hosts can locate the mss this way. The mss will rebroadcast whenever its ip address or name changes. To enable wins, enter...
Page 36: 4.2.7.2 Configuring Snmp
Rs-485 configuration configuration 4-6 4.2.7.2 configuring snmp the mss has a single community (“public”) with read-only access. You can optionally add a single community with read-write access using the change snmpsetcomm command. See the mss reference manual for more details. Once you enable an sn...
Page 37: 4.3.1 Two-Wire Mode
Configuration rs-485 configuration 4- 7 4.3.1 two-wire mode in two-wire mode, the mss operates in half duplex: one pair of wires shares transmit and receive signals, and an optional third wire can be used for shield/ground. The main advantage of using two-wire mode is reduced cabling costs. Figure 4...
Page 38: 4.3.2 Four-Wire Mode
Rs-485 configuration configuration 4- 8 4.3.2 four-wire mode in four-wire mode, the mss operates in full duplex: one pair of wires functions as the transmit pair, another pair of wires functions as the receive pair, and there is a shield/ground wire for each pair. The mss is able to send and receive...
Page 39: 4.3.3 Termination
Configuration serial port configuration 4- 9 4.3.3 termination rs-485 connections must be terminated properly in order to work. Termination is necessary when using long cable runs, although only end nodes should be terminated. The termination option is disabled by default. Figure 4-14: enabling rs-4...
Page 40: 4.4.2 Autostart
Serial port configuration configuration 4-10 to change a serial port’s access mode, enter the change access command. The following example enables local logins to the first serial port. Figure 4-16: changing serial port access mode if an attached serial device will be continuously transmitting data,...
Page 41: 4.4.3 Serial Data
Configuration serial port configuration 4-11 4.4.2.1 saving autostart characters if the port is configured with a dedicated port host and autostart is enabled for that port, the autostart characters that start the connection can either be passed to the host as the first bytes of data or can be disca...
Page 43: 4.4.6 Flow Control
Configuration serial port configuration 4-13 4.4.6 flow control note: rts/cts flow control is not available in rs-485 mode. Both rts/cts (hardware) and xon/xoff (software) flow control methods can be used on the mss. Rts/cts controls data flow by sending serial port signals between two connected dev...
Page 44: 4.4.7.2 Signal Checking
Serial port configuration configuration 4-14 modem control implies three things: ◆ the mss will log out the port when dsr is dropped (as if dsrlogout were enabled). ◆ the mss will hold dtr low for approximately 3 seconds after the port is logged out. ◆ the mss will not autostart a new connection unt...
Page 45: 4.4.7.4 Dtrwait
Configuration serial port configuration 4-15 4.4.7.4 dtrwait note: dtrwait is not available in rs-485 mode. Spurious characters from the attached serial device may be interpreted as a login attempt, which could cause the port to be unavailable for network connections. To avoid this behavior, the mss...
Page 46: 4.4.9 Preferred Port Host
802.11 configuration configuration 4-16 4.4.9 preferred port host a default host for a port can be defined using the change preferred command. The mss attempts to use the preferred host for connections on a specified port when no host name is specified in a connection command. Figure 4-32: defining ...
Page 47: 4.5.1 802.11 Terms
Configuration 802.11 configuration 4-17 4.5.1 802.11 terms the following acronyms are used in this section: ap access point, a device that relays communications between one or more wireless devices and possibly other devices on a network. Aps are usually connected to a physical network. Note: if you...
Page 48: 4.5.3 802.11 Region
802.11 configuration configuration 4-18 4.5.2 enabling 802.11 networking the mss has 802.11 networking enabled by default. This allows the mss to check for a compatible wireless networking card at startup. If a compatible card is present, the mss will use the wireless network and ignore any wired et...
Page 49: 4.5.4 Mac Address
Configuration 802.11 configuration 4-19 4.5.4 mac address a mac address is a unique identifier that distinguishes different devices on the 802.11 network. It is the same as the unit’s hardware address. For networking purposes, the mss can be configured to use either the pc card’s mac address or its ...
Page 50: 4.5.6 Network Mode
802.11 configuration configuration 4-20 4.5.6 network mode there are two types of 802.11 networks: ad-hoc and infrastructure. In an ad-hoc network, devices communicate directly with one another on a peer-to-peer basis. In an infrastructure network (the default), several devices communicate with one ...
Page 51: 4.5.8 Wep
Configuration 802.11 configuration 4-21 4.5.8 wep some 802.11 cards can be set with a wep key, which will encrypt any data you transmit through wireless communication. To enable wep, enter the following command: figure 4-41: enabling wep 4.5.8.1 setting the wep key and index number when wep is enabl...
Page 52: 4.7 Modem Cards
Formatting an ata flash card configuration 4-22 4.6 formatting an ata flash card certain kinds of ata flash memory and disk storage cards can also be used in the pc card slots. Before you insert any kind of card into the mss, please check the lantronix web site to make sure that your card is support...
Page 53: 4.7.1 Incoming Calls
Configuration modem cards 4-23 4.7.1 incoming calls the mss will attempt to answer any incoming call that it detects. You will get a local> prompt after the modems are fully connected. 4.7.2 outgoing calls to make a call from the mss modem port, you must connect to the modem card via telnet or a loc...
Page 55: 5: Using The Mss
5-1 5: using the mss this chapter explains how to use the mss once it is running. Users can make host-initiated (incoming) connections and use the host applications and code examples included on the mss distribution cd-rom. Users can also use the mss interactively to make outgoing connections, manip...
Page 56: 5.1.2 Host Applications
Incoming connections using the mss 5-2 there are some important points to remember when making a socket connection: ◆ port access must be set to either dynamic or remote to allow network connection requests. Local access does not allow a port to receive connection requests from the network. To chang...
Page 57: 5.2.1.1 Telnet
Using the mss interactive connections 5-3 5.2 interactive connections interactive mode refers to entering commands at the local> prompt. Users can enter commands to configure the mss, connect to remote services, manipulate a connection, or receive feedback. Interactive use requires an input device, ...
Page 58: 5.2.1.2 Rlogin
Interactive connections using the mss 5-4 5.2.1.2 rlogin rlogin allows a user to log into a remote host as if he or she were a local user. In the example below, shark is the remote host and lola is the username. Unless the username is password protected, the user will be logged in normally. Figure 5...
Page 59
Using the mss interactive connections 5-5 5.2.2.2 backward, forward, and switches the backward and forward commands, when entered at the local> prompt, allow users to navigate through current sessions. You can think of a user’s open sessions as a list from the earliest to the most recently created. ...
Page 60: 5.2.2.4 Session Limits
Interactive connections using the mss 5-6 5.2.2.4 session limits the number of active sessions a user can have on the mss is limited by three factors: available server memory resources, a server-wide limit, and a port-specific limit. The absolute maximum number of sessions for the mss is eight. To r...
Page 61: 5.2.3.9 Show Session
Using the mss disk management 5-7 5.2.3.6 show server bootparams show server bootparams displays mss identification and boot procedure information. The first lines display the mss version, hardware address, network name and node number, identification string, and how long the mss has been running. Y...
Page 62: 5.3.1 Flash Disk
Disk management using the mss 5-8 5.3.1 flash disk the mss contains a flash disk (/flash), rewriteable memory that allows you to customize your mss. Any data that you want the mss to save after it is rebooted should be stored on the flash disk. Note: if there is a power glitch during rewrite, you ca...
Page 63: 5.3.3 Sdk
Using the mss encrypted sessions 5-9 5.3.3 sdk the lantronix software developers kit (sdk) allows you to customize the behavior of your mss in more ways than are available via the standard command set. You can write programs for the mss that handle serial and network data, and store the finished pro...
Page 64: 5.5 Serial Tunnel
Serial tunnel using the mss 5-10 5.5 serial tunnel two mss servers can be connected to emulate a direct serial connection across a lan or wan. Servers connected in this way can pass data only—they will not be able to pass status signals (dsr/dtr, rts/cts, etc.) or preserve timing between characters....
Page 65: 5.5.2 Udp Configuration
Using the mss multihost mode 5-11 5.5.2 udp configuration when the udp protocol is used, there is no connection; each mss serial port must be told explicitly which host it is allowed to accept packets from. For udp, each mss port has to be configured to both send packets to and accept packets from t...
Page 66: 5.6.2 Adding Hosts
Multihost mode using the mss 5-12 5.6.1 enabling multihost mode to configure one of the mss serial ports for a dedicated multihost connection, use the change dedicated command with hostlist as the host name. Figure 5-13: enabling multihost mode when you enable a dedicated connection, the mss disable...
Page 67: 5.7 Modem Emulation Mode
Using the mss modem emulation mode 5-13 5.7 modem emulation mode in modem emulation mode, the mss presents a modem interface to the attached serial device: it accepts at-style modem commands and handles the modem signals correctly. The mss forms a network connection based on the atdt commands issued...
Page 68: 5.7.2 Wiring Requirements
Modem emulation mode using the mss 5-14 multiple commands can be entered on the same line (for example, ate0q1v0 will be processed the same as if each command were entered separately). However, if the mss encounters a command that it doesn’t recognize, it will ignore the whole command line. For this...
Page 69: 5.8 Com Port Redirector
Using the mss com port redirector 5-15 when using an mss serial port in modem mode: ◆ the serial device’s dtr goes out to both its own dsr in and the mss dsr in. When the device asserts its dtr, it will see its dsr asserted. That way the device thinks that the “modem” (the mss) is ready to accept co...
Page 71: A: Contact Information
A-1 a: contact information if you are experiencing an error that is not listed in appendix b or if you are unable to fix the error, contact your dealer or lantronix technical support at 800-422-7044 (us) or 949- 453-3990. Technical support is also available via internet email at support@lantronix.Co...
Page 73: B: Troubleshooting
B-1 b: troubleshooting this appendix discusses how you can diagnose and fix errors quickly without having to contact a dealer or lantronix. It will help to connect a terminal to the serial port while diagnosing an error to view any summary messages that are displayed. When troubleshooting, always en...
Page 74: B.2 Dhcp Troubleshooting
Dhcp troubleshooting troubleshooting b-2 b.2 dhcp troubleshooting if the unit is unable to get the ip address from the dhcp server, check these areas: the terminal shows a boot> prompt rather than a local> prompt. The mss is not connected properly to the ethernet. Ensure that the mss is firmly conne...
Page 75: B.3 Bootp Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting bootp troubleshooting b-3 b.3 bootp troubleshooting if the bootp request is failing and you have configured your host to respond to the request, check these areas: b.4 rarp troubleshooting if the unit is unable to get an ip address using rarp, check these areas: table b-3: bootp trou...
Page 76: Prompt
Modem configuration checklist troubleshooting b-4 b.5 modem configuration checklist most modem problems are caused by cabling mistakes or incorrect modem configuration. However, the following items should be verified after any modem configuration, and re- checked when there is modem trouble. ◆ the m...
Page 77
Troubleshooting bcp command examples b-5 a series of commands called boot configuration program (bcp) commands can be entered at the boot> prompt to configure the mss. These commands are a subset of the entire mss command set. For example, a typical tcp/ip configuration might use the following comma...
Page 78
Bcp command examples troubleshooting b-6 change dhcp {enabled, disabled} enables or disables the sending of dhcp queries during the boot sequence. It is enabled by default. Change hardware xx-xx-xx specifies the last three numbers of the server’s ethernet address. The first three numbers will be sup...
Page 79: C: Pinouts
C-1 c: pinouts in the following diagrams, unlabeled pins are not connected. C.1 ethernet connectors the mss uses a standard ethernet pinout. The figure below shows the mss rj45 ethernet connector pin connections. Figure c-1: rj45 ethernet connector c.1.1 fiber link ethernet the mss4-sfp and mss4-dfp...
Page 80
Mss4 serial connectors pinouts c-2 c.2 mss4 serial connectors the mss4 has four serial ports. The mss4-d models have db9 connectors, while the mss4-s models have screw terminal blocks. C.2.1 screw terminal block the following sections show the pin connections of the mss4 screw terminal blocks, which...
Page 81: C.2.2 Db9 Connectors
Pinouts db9 connectors c-3 c.2.2 db9 connectors the following sections show the pin connections of the mss4 db9 connectors, which provide dual rs-232/rs-485 serial ports. C.2.2.1 rs-485 db9 connectors the mss4 db9 connector provides an rs-485 serial port. Figure c-5: db9 rs-485 serial connector c.2....
Page 82: C.4 Mss4 Power Connectors
Mss4 power connectors pinouts c- 4 c.4 mss4 power connectors power is supplied to the mss using one of the connectors mentioned in this section. C.4.1 power jack the mss4 ships with a standard barrel power jack whose inner conductor is positive. Figure c-7: power jack connector c.4.2 screw block pow...
Page 83: D: Updating Software
D-1 d: updating software d.1 obtaining software a current software file (mss4.Sys) is available on the distribution cd. You can obtain software updates and release notes for the mss from the lantronix world wide web site (www.Lantronix.Com), or by using anonymous ftp through the internet (ftp.Lantro...
Page 84: D.2 Reloading Software
Reloading software updating software d-2 d.2 reloading software the mss stores software in flash rom to control the initialization process, operation, and command processing. The contents of flash rom can be updated by downloading a new version of the operational software via netware, tcp/ip, or mop...
Page 85: D.2.1.2 Mop
Updating software configuring tcp/ip reload d-3 to manually configure the mss ip parameters for software reload when running operational software (not bcp mode), use the following commands. Figure d-2: configuring tcp/ip reload note: for instructions on how to log into the mss to enter these command...
Page 86
Troubleshooting flash rom updates updating software d-4 mop ensure that the ethernet circuit must has the service characteristic enabled. Ensure that the mom$load search path includes the directory containing the mss4.Sys file. Table d-1: flash rom troubleshooting protocol area to check.
Page 87: E: Specifications
E-1 e: specifications e.1 power specifications the mss4 has a screw terminal power jack and a power cube adaptor. Specifications for the adaptor varies depending on your mss4 model. E.1.1 mss4 screw terminal power the mss screw terminal power jack requires 9-30 v dc. E.1.2 mss4-d/-s adaptor the mss4...
Page 88
Environmental information specifications e-2 e.2 environmental information e.2.1 temperature limitations operating range: 5˚ to 50˚ c (41˚ to 122˚ f) storage range: -40˚ to 66˚ c (-40˚ to 151˚ f) max temp change: 20˚ c (36˚ f) per hour rapid temperature changes may affect operation. Do not operate t...
Page 89: Warranty Statement
Warranty statement lantronix warrants for a period of 5 years from the date of shipment that each mss4 device server supplied shall be free from defects in material and workmanship. During this period, if the customer experiences difficulties with a product and is unable to resolve the problem by ph...
Page 90: Declaration of Conformity
Declaration of conformity (according to iso/iec guide 22 and en 45014) manufacturer’s name: lantronix manufacturer’s address: 15353 barranca parkway, irvine, ca 92618 usa declares that the product: product name: device server model name/number: mss4 conforms to the following standards or other norma...
Page 91: Index
I index numerics 802.11 4-16–4-21, 5-6 channel 4-20 extended service set id 4-19 leds 2-4 mac address 4-19 network mode 4-20 region 4-18 wep 4-21 a access mode 4-9 access point (ap) 4-17, 4-20 altitude limitations e-2 arp entry 3-4 ata flash cards 4-22 installing 2-8 leds 2-4 using 5-8 autobaud 4-12...
Page 92
Ii f factory defaults 4-1, b-5 fiber link ethernet 2-2, 2-6 flash 5-8, d-2 troubleshooting d-3 updates b-1, d-2 flash rom 2-7, b-2 reloading b-5 flow control 4-13 flush nvr b-5 ftp d-1 g gateway 1-2, 4-3 groups 1-3 h hardware address b-3, b-6 hardware flow control 4-13 help command 1-2 host 1-4 host...
Page 93
Iii mop reloading software d-3 multihost mode 5-11 n nameserver 1-2, 4-3 network mode, wireless 4-20 node 1-4 nvram b-5 o ok led 2-6 outbound connections 3-9 p parity 4-12 passflow 4-13 password encryption 5-9 login 3-2 privileged 3-2 passwords 1-3, 3-1 pc card c-3 802.11 4-16 ata flash 4-22, 5-8 le...
Page 94
Iv rs-232 2-5, c-3 rs-422 4-9 rs-485 4-6, 5-6, c-2 four-wire mode 4-8 termination 4-9 two-wire mode 4-7 txdrive 4-8 rts/cts 4-13 s screw terminal port 2-1, 2-2, 2-6 sdk 1-3, 5-9 modem cards 2-9, 4-22 security 1-3 serial access mode 4-9 dedicated port service 4-16 device, connecting 2-5 flow control ...
Page 95
V wep 4-17, 4-21 index number 4-21 key 4-21 wins 4-5 wireless. See 802.11..