Summary of Pasha 5
Page 2: Contents
2 contents general ................................................................................................................... 3 overall plan ......................................................................................................... 4 technical description .......................
Page 3: General
3 general dear mac para pilot we congratulate you on your purchase of a mac para paraglider. Extensive development work and numerous tests make the pasha 5 a high performance biplace paraglider with maximum possible safety. The pasha 5 is constructed for thermal and cross-country flying, and will en...
Page 4: Operating Limits
4 (&( operating limits the pasha 5 has been tested by dhv certification laboratory to ltf b / en-b category. The pasha 5 is certified for tandem flight. The pasha 5 has been load and shock-tested and passed with a load corresponding to 8g of the maximum weight in flight 220 kg. Its flying tests have...
Page 5: Technical Description
5 technical description construction of the canopy: the canopy of the pasha 5 consists of 54 cells over the wingspan. The wingtips are slightly pulled down and this produces a kind of stabilizer. The pasha 5 is a second rib diagonal-construction paraglider. Every second main rib is attached to the 4...
Page 6: Risers With Trim System:
6 (&( a mark on the main brake line indicates the position of the brake handle. This adjustment, on the one hand, allows sufficient brake to be applied during extreme flying situations and when landing, while on the other hand, this ensures that brakes are not permanently applied to the canopy (espe...
Page 7: Safety Equipment
7 (&( safety equipment an optimal outfit should be a matter of course for every paraglider pilot. Always wear stout footwear, a helmet, and gloves. Clothing should be warm and allow sufficient freedom of movement. A rescue-system can be life-saving in case of an irremediable disturbance of the canop...
Page 8: Riser
8 (&( riser riser lengths pasha 5 a a1 b c d trims open 460 460 465 485 510 trims closed 460 460 440 435 410 the lengths are measured from the main attachment point to the lower edge of rapid links. Color marking loop for main karabineer trims closed trims neutral trims open brake handle change of t...
Page 9: Materials
9 materials tissue (porcher sport, rue du ruisseau b.P. 710,38290 st. Quentin fallavier, france) top sail - leading edge - skytex 38 e25a - 100% nylon 6.6 , 33 dtex, 38 g/m 2 top sail - trailing edge - skytex 38 e25a - 100% nylon 6.6 , 33 dtex, 38 g/m 2 bottom sail - skytex 38 e25a - 100% nylon 6.6 ...
Page 10: Technical Specifications
10 technical specifications biplace pasha 5 pasha 5 size 39 (m) 42 (l) zoom flat [%] 95,7 100 area flat [m 2 ] 39,17 42,50 area projected [m 2 ] 35,07 38,05 span flat [m] 14,54 15,15 span projected [m] 12,21 12,72 aspect ratio flat - 5,4 5,4 root cord [m] 3,36 3,50 cells - 54 54 weight [kg] 8,65 8.7...
Page 11: Checks On A New Paraglider
11 checks on a new paraglider before delivery, as well as during production, each paraglider goes through a strict visual inspection. Additionally we recommend that you to check your new glider in accordance with the following points. We recommend that you make this check after flying extreme manoeu...
Page 12: Flying The Pasha 5
12 flying the pasha 5 the following information must not under any circumstances be taken as a manual for practising paragliding. We would like to advise you of the pasha 5's features and important information for your flying and security. Preparing for take off: as with any aircraft, a thorough pre...
Page 13: Launch
13 (&( when laying out the glider, the wind direction should be observed. The canopy should be deployed into the wind so both halves of it are loaded symmetrically. The paraglider should be arranged in a semicircle into wind. This ensures that the a-lines in the centre section of the canopy will ten...
Page 14: Flight
14 (&( the most important thing is the constancy of the pull on the a risers and not the power. Since the pasha 5 is very easy to launch, on steep take-offs or in stronger winds do not forget to brake properly to control the movement of the canopy. As already mentioned, this can be corrected by the ...
Page 15: Approach and Landing:
15 (&( in case it is impossible to control the pasha 5 with the brake lines the d-risers may be used to steer and land the canopy. Attention! Pulling brake too fast or too hard can result in the canopy entering a negative spin. Active flying (thermaling and soaring): in turbulent conditions the glid...
Page 16: Motorised Flight
16 motorised flight note!! Although, motorized flight can be a great success due to the gliders very easy take-off characteristics, stability and good handling, always use a certified combination of engine - harness and glider. If in doubt check with your federation. Contact the manufacturer or impo...
Page 17: “Cravat” / Line-Over:
17 (&( direction can be aided by a pumping out the deflation; a slow, long pumping action of the brake of the deflated side of the wing helps the canopy to re-inflate. If the pilot does not correct, the pasha 5 usually self-recovers. However, if it does not self recover and the pilot does not correc...
Page 18: Full-Stall:
18 (&( parachutal stall (deep stall): in a parachutal stall the paraglider has no forward momentum combined with a high descent rate. A parachutal stall can be caused by, among other reasons, a too slow exit from a b-line stall or severe turbulence. Porous canopies (uv influence) or canopies out of ...
Page 19: Spin (Or Negative Spin):
19 (&( spin (or negative spin): pulling brake on one side too fast or too hard can result in a negative spin. During a spin the canopy turns relatively fast around the centre section of the canopy while the inner wing flies backwards (hence the term negative). There are two usual reasons for an unin...
Page 20: Rapid Descents
20 rapid descents spiral dive: a spiral dive is the fastest way to lose altitude, however, the very high g-forces make it difficult to sustain a spiral dive for long and it can place high loads on the pilot and glider. By tensing ones abdominal muscles and a higher body tension you can to some exten...
Page 21: B-Line Stalls:
21 (&( attention! All rapid descent techniques should first be practised in calm air and with sufficient height so the pilot can use them in emergency situations! By far the best technique is to fly correctly and safely, so you never have to descend rapidly! B-line stalls: warning: although it is po...
Page 22: Storage:
22 (&( ensure that the lines are not folded tightly. It's extremely important to avoid any sharp bending of the lines, especially the main lines. Pay careful attention to the lines to avoid damaging them. Any over stretching of lines apart from the strain imposed during normal flight, should be av...
Page 23: Repairs and Checks:
23 (&( repairs and checks: tears in the canopy must be professionally sewn. Adhesive patches are only adequate for very minor damage. Repairs should only be carried out by the manufacturer, distributor or authorized workshops. Only original spare parts may be used! the lines must be checked afte...
Page 24: Treating Nature With Respect
24 aramid /poly ester a-6 843 -060 ara m id/po lyes ter a-684 3-080 v ectran 0,9 ara m id/po lyes ter a-734 3-140 v ec tra n 0, 6 arami d /poly este r a-7 343 -420 ara m id/po lyes ter a-78 50-10 0 aramid /poly ester a-7 350 -130 dyn e ma/ p olye ster a-7 850-3 6 0 ara m id/po lyes ter a-73 43 -190 ...
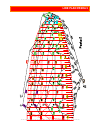
Page 25: Line Plan Pasha 5
25 line plan pasha 5.
Page 26: Full Line Lengths
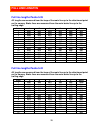
26 full line lengths full line lengths pasha 5-39 all lengths are measured from the loop of the main line up to the attachment point on the canopy. Brake lines are measured from the main brake line up to the trailing edge. Center a b c d e brakes 1 8687 8553 8634 8813 8982 9815 2 8597 8463 8545 8724...
Page 27: Components of The Check
27 manual for paraglider checks check-intervals a new mac para paraglider must be given a check every 24 months. With intensive use (> 100 flying hours per year, or excessively demanding use) an annual check is needed, after the first check. Personnel authorized to carry out checks a valid flying li...
Page 28
28 (&( line length measurement lines should be separated and each line measured under a tension of 5 kg. Measurement is made from the line karabiner to the canopy according to the method of certification. Rib numbering begins in the middle of canopy and leads to the wing tip. Measured full lengths s...
Page 29
29 (&(.
Page 30: Checks
30 checks name company date signature & stamp.
Page 31: Test Flight Certificate
31 test flight certificate paraglider type: pasha 5 – 4 2 serial number: . . . . . . . . Test flown on: ________________________________ by mac para technology confirmation by dealer: ________________________________ technical data biplace pasha 5 pasha 5 size 39 (m) 42 (l) zoom flat [%] 95,7 100 ar...
Page 32
32.